Exploring the Effects of Biochar and Compost on Ameliorating Coastal Saline Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analyses of Experimental Samples
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
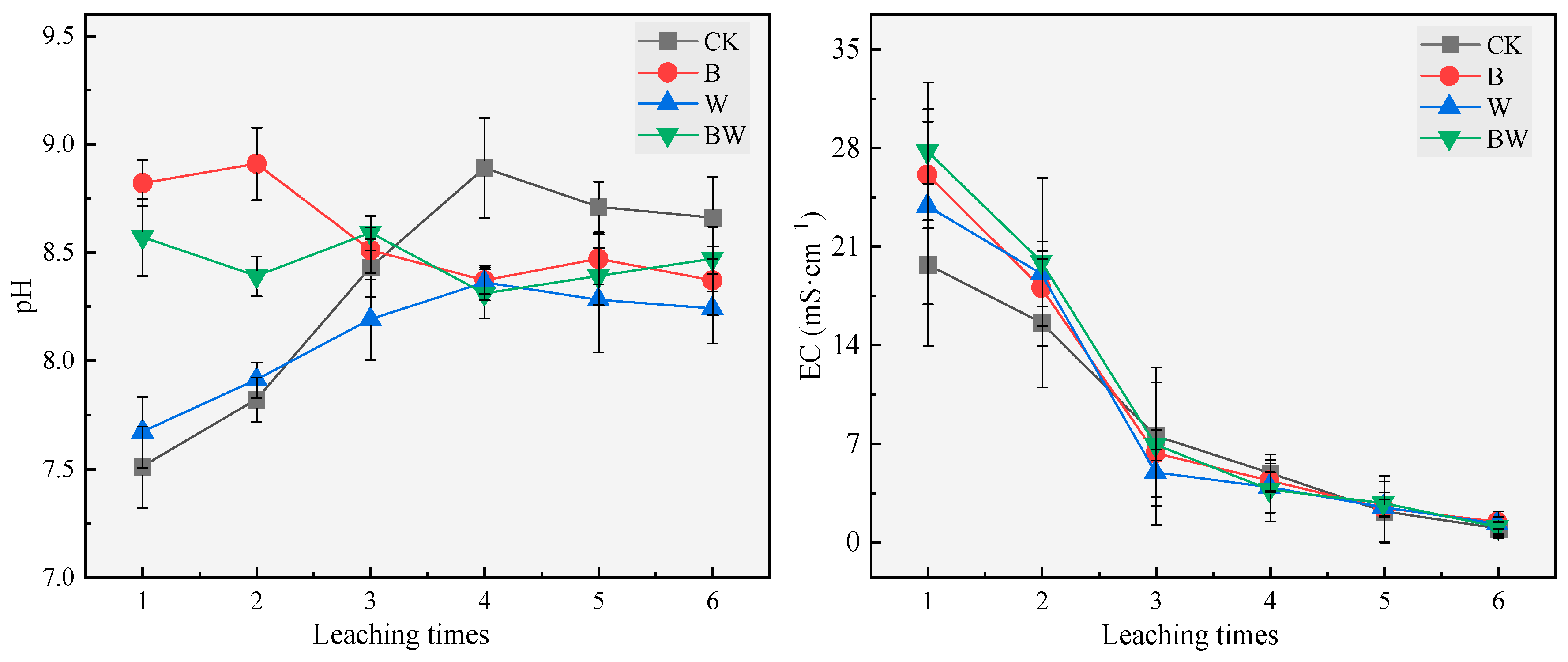
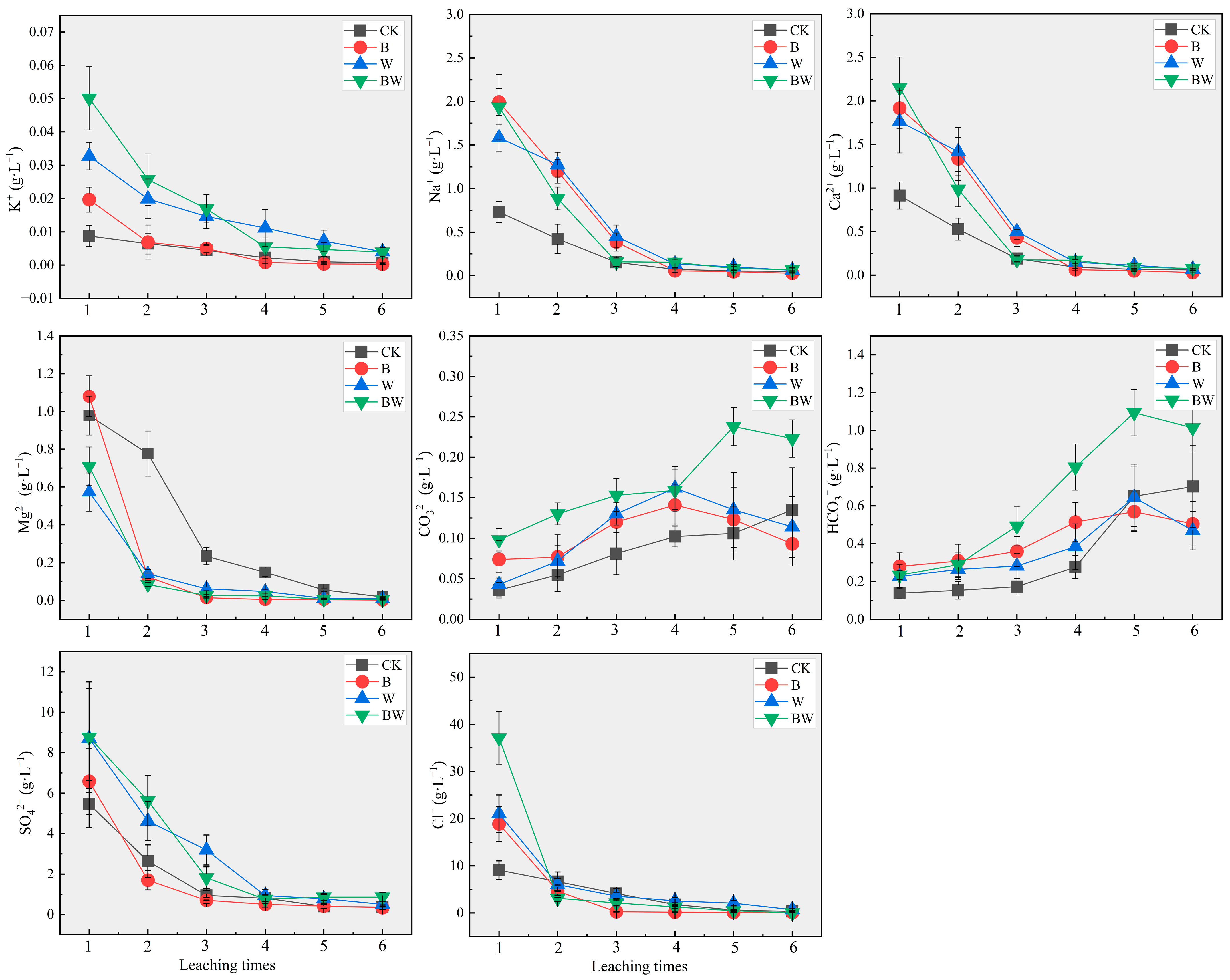
3.1. Effects of Biochar and Compost on Salt Leaching from Coastal Saline Soils
3.1.1. Properties of the Leaching Solution
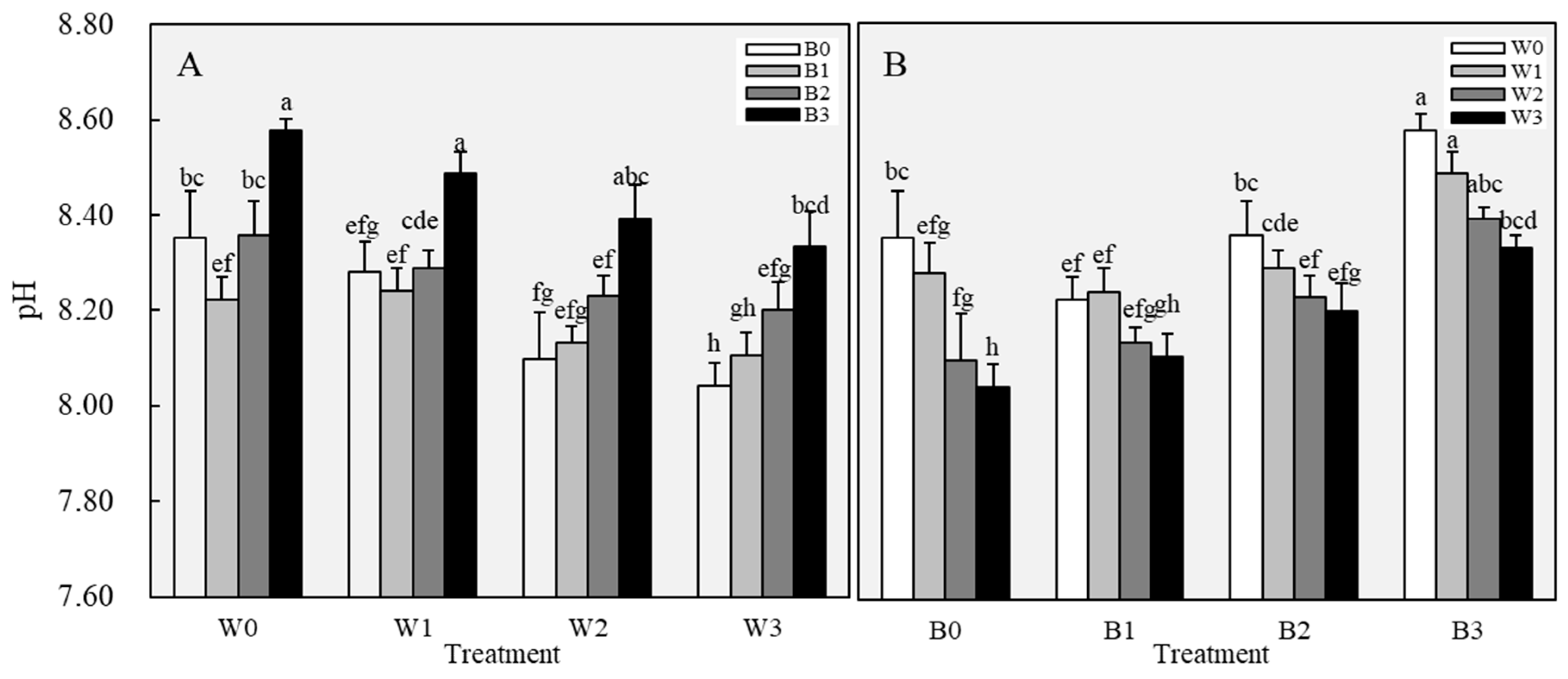
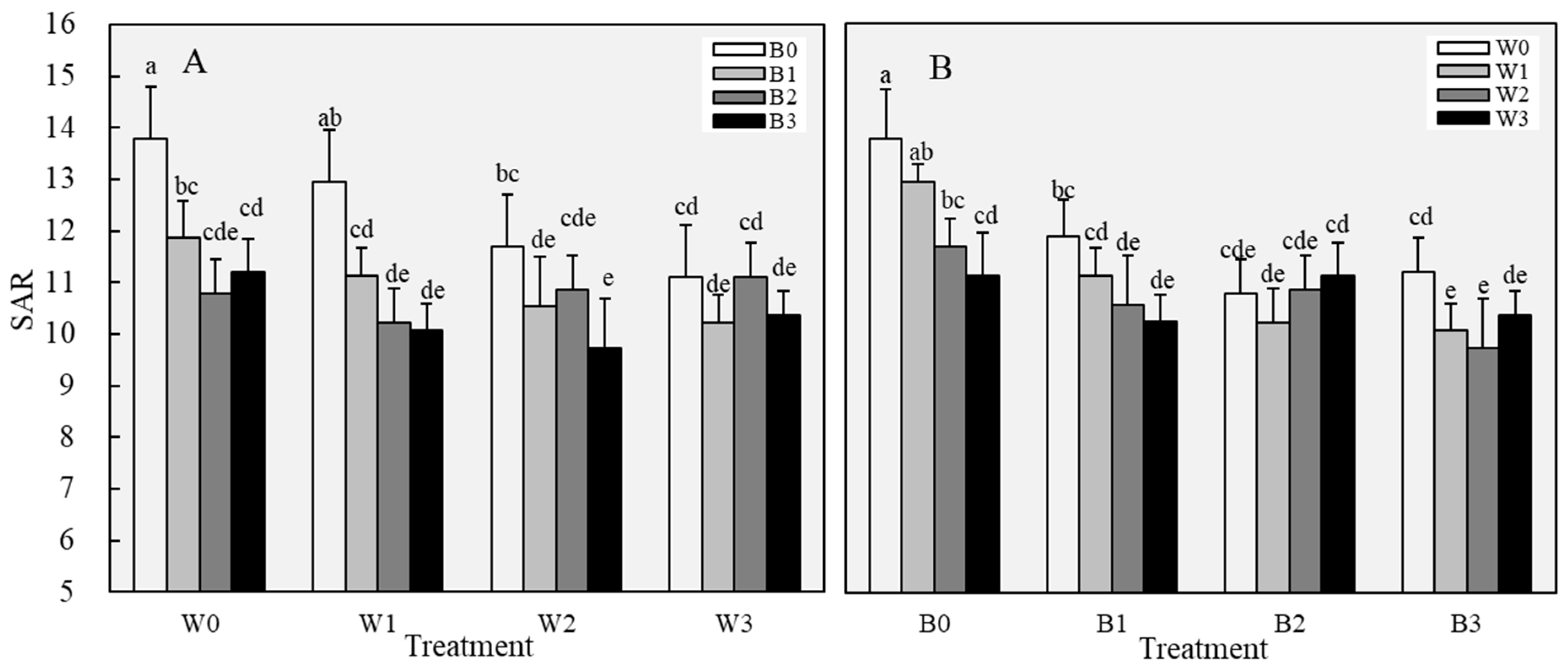
3.1.2. Soil Properties After Leaching
3.2. Effects of Biochar and Compost on Coastal Saline Soil Properties
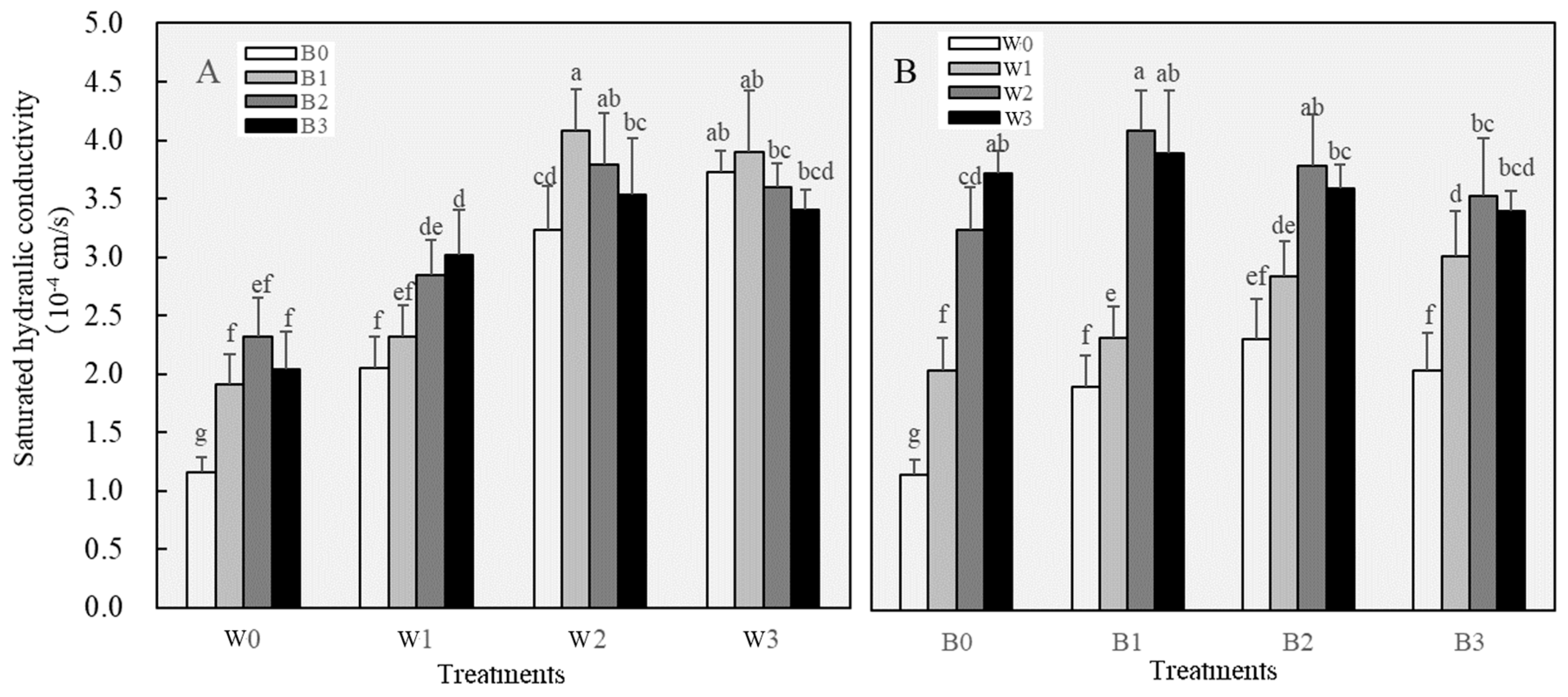
3.2.1. Changes in Soil Physical Properties
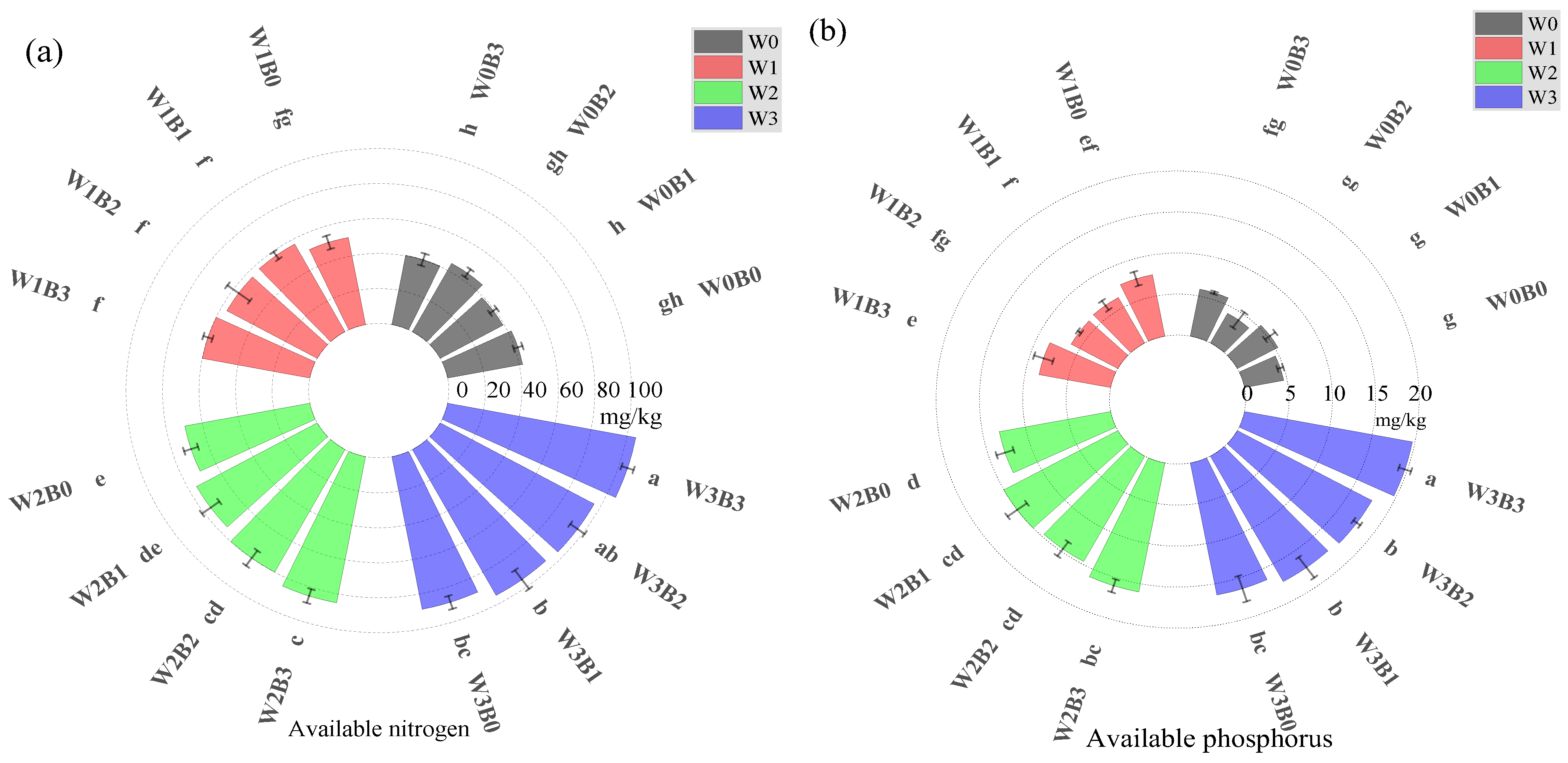
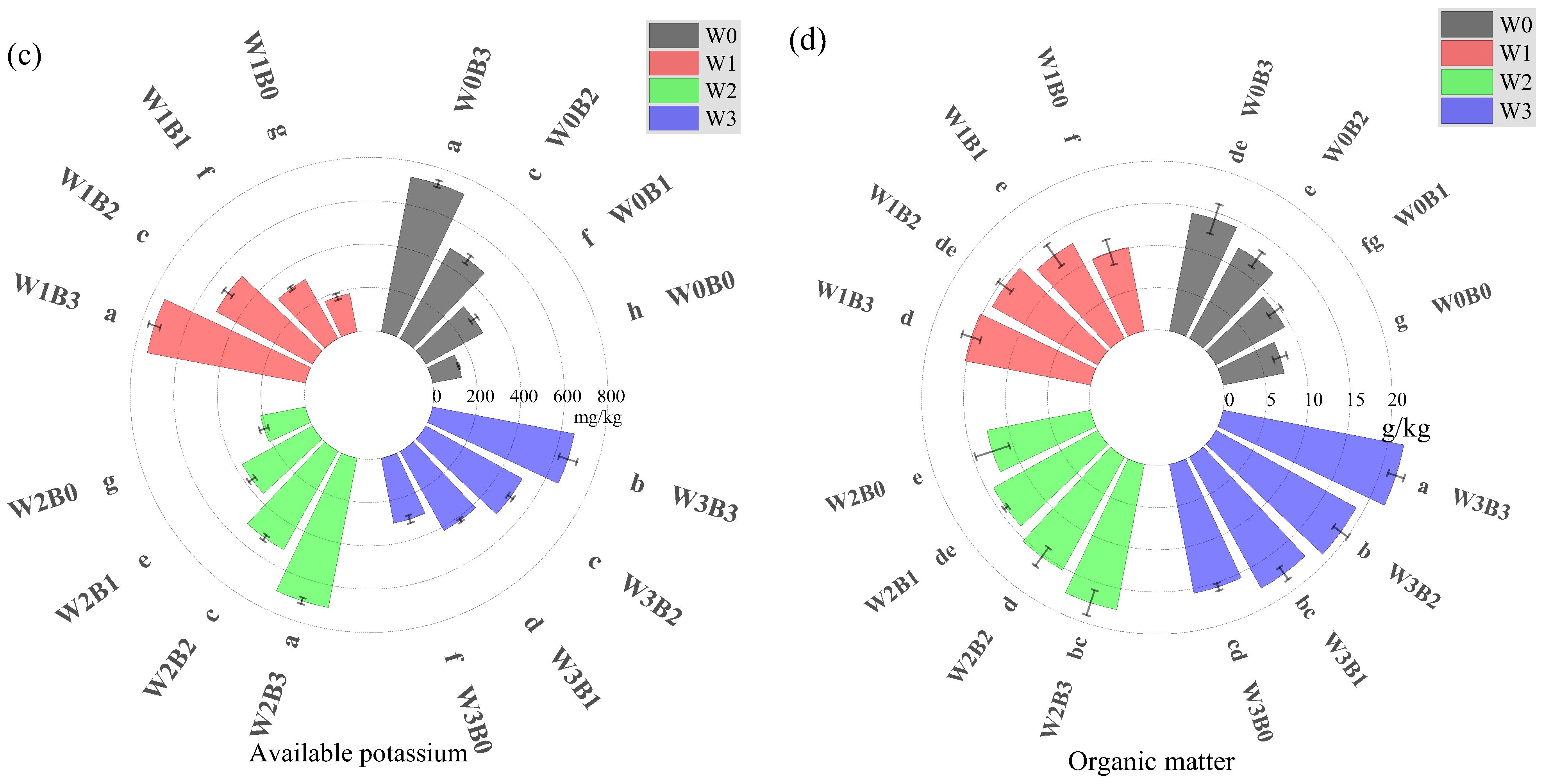
3.2.2. Changes in Soil Nutrients and Enzyme Activities
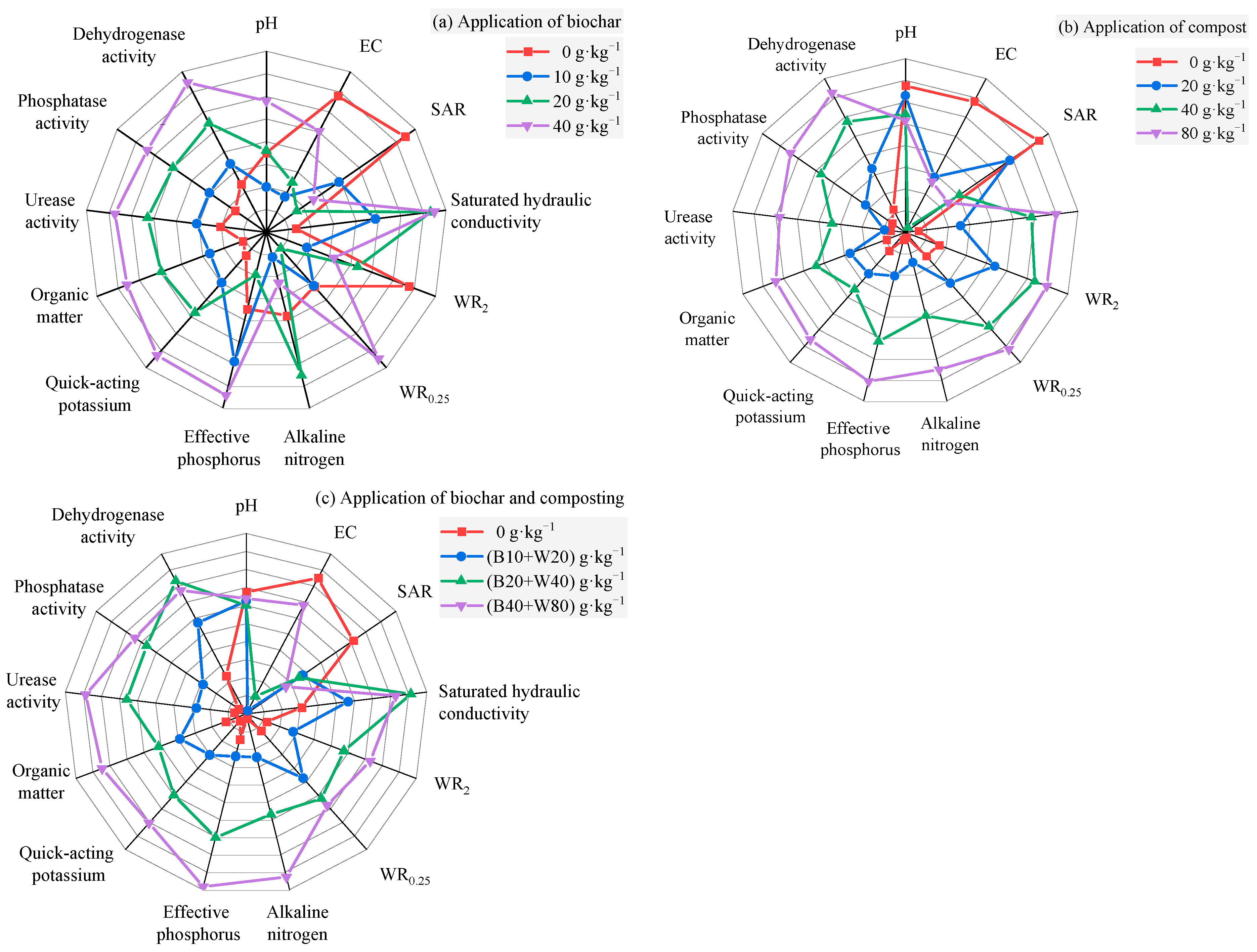
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Hu, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T. Soil salinity management with drip irrigation and its effects on soil hydraulic properties in north China coastal saline soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Kempen, B.; de Sousa, L. Global mapping of soil salinity change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities to long-term reclamation of coastal saline soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.R. Abiotic and Microbial Oxidation of Laboratory-Produced Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, M.F.; Ashraf, I.; Abid, M.; Steffens, D. Effect of biochar, lime, and compost application on phosphorus adsorption in a Ferralsol. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, H.; Zheng, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, L.; Xing, B. Reduced nitrification and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in acidic soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Gartzia-Bengoetxea, N.; Arostegi, J.; Moragues, L.; Arias-González, A. Storage and stability of biochar-derived carbon and total organic carbon in relation to minerals in an acid forest soil of the Spanish Atlantic area. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M. Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline–sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailegnaw, N.S.; Mercl, F.; Pračke, K.; Száková, J.; Tlustoš, P. Mutual relationships of biochar and soil pH, CEC, and exchangeable base cations in a model laboratory experiment. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, Z. The effects of biochar on germination and growth of wheat in different saline-alkali soil. Asian Agric. Res. 2013, 5, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Tan, J.; Ge, X.; Nan, Q. Biochar addition reduces salinity in salt-affected soils with no impact on soil pH: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guan, T.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, X. Long-term effects of biochar amount on the content and composition of organic matter in soil aggregates under field conditions. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1481–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z. Effects of modified biochar on water and salt distribution and water-stable macro-aggregates in saline-alkaline soil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Si, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhu, L.-X.; Shen, Y.-F.; Li, S.-Q. Sensitivity of soil water retention and availability to biochar addition in rainfed semi-arid farmland during a three-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Niu, W.Q.; Zhang, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Lyu, W.; Li, K.Y.; Zou, X.; Liang, B.H. Effect of biochar addition on soil evaporation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Xing, B. Enhanced growth of halophyte plants in biochar-amended coastal soil: Roles of nutrient availability and rhizosphere microbial modulation. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 41, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Hao, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of Compost Application of Green Waste on Soil Properties: A Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Tian, Y.; Gong, X. Effects of brown sugar and calcium superphosphate on the secondary fermentation of green waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, P.P.; Li, S.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.H.; Yao, L.Y. Amelioration effects of organic-inorganic compound amendment on coastal saline-alkali soil. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Guo, W.N.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, X.; Wu, G. Salt leaching in the saline soil relative to rate of biochar applied. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2014, 51, 914–919. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Luo, Y.; Shi, Y. Soil fractal characteristics characterized by weight distribution of particle size. Sci. Bull. 1993, 38, 1896–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Chen, B. Dual Role of Biochars as Adsorbents for Aluminum: The Effects of Oxygen-Containing Organic Components and the Scattering of Silicate Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8759–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bordoloi, S.; Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Van Zwieten, L.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Khan, B.A.; Ahmad, M.; Solaiman, Z.M.; et al. Soil acidification and the liming potential of biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.-K.; Zhao, A.-Z.; Yuan, J.-H.; Jiang, J. pH buffering capacity of acid soils from tropical and subtropical regions of China as influenced by incorporation of crop straw biochars. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, R.-K.; Wang, N.; Li, J.-Y. Amendment of acid soils with crop residues and biochars. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J. Nutrient transformation during aerobic composting of pig manure with biochar prepared at different temperatures. Environ. Technol. 2014, 36, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Cai, H.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Ali, A.; Amanullah, M. Improving pig manure composting efficiency employing Ca-bentonite. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 87, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, W.; Fu, J.; Pan, G.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeelnejad, L.; Shorafa, M.; Gorji, M.; Hosseini, S.M. Impacts of Woody Biochar Particle Size on Porosity and Hydraulic Conductivity of Biochar-Soil Mixtures: An Incubation Study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, J.W.; Steiner, C.; Harris, K.; Das, K.C.; Bibens, B. Effect of Low-Temperature Pyrolysis Conditions on Biochar for Agricultural Use. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Muhlack, R.; Morton, B.J.; Dunnigan, L.; Chittleborough, D.; Kwong, C.W. Pyrolysis Temperature Effects on Biochar–Water Interactions and Application for Improved Water Holding Capacity in Vineyard Soils. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Long-term manure amendments reduced soil aggregate stability via redistribution of the glomalin-related soil protein in macroaggregates. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veum, K.S.; Goyne, K.W.; Kremer, R.; Motavalli, P.P. Relationships Among Water Stable Aggregates and Organic Matter Fractions Under Conservation Management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhao, G.; Pu, G.; Su, J.; Coyne, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; et al. Rotation and manure amendment increase soil macro-aggregates and associated carbon and nitrogen stocks in flue-cured tobacco production. Geoderma 2018, 325, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, C.R.; Jenkins, S.N.; Abbott, L.K.; Mickan, B.S. Amelioration of a saline-alkaline soil using biochar and compost: Impacts on plant growth, soil biological and chemical characteristics. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Murtaza, B.; Kahlon, U.Z.; Yaseen, M. A Comparative Study of Different Amendments on Amelioration of Saline-Sodic Soils Irrigated with Water Having Different EC: SAR Ratios. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Biochar-induced negative carbon mineralization priming effects in a coastal wetland soil: Roles of soil aggregation and microbial modulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Ye, Y.; Ji, H.; Li, L.; Kibue, G.W.; Lu, H.; Zheng, J.; Pan, G. Biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution alleviated salt stress and improved leaf bioactivity of maize in a saline soil from central China: A 2-year field experiment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 95, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-R.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S.; Owens, G.; Nehls, T.; Wessolek, G.; Kim, K.-H. Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, J.A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Jackson, W.R.; Patti, A.F. Does Biochar Improve Establishment of Tree Seedlings in Saline Sodic Soils? Land. Degrad. Dev. 2015, 27, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Guo, M.; Chow, T.; Bennett, D.N.; Rajagopalan, N. Sorption properties of greenwaste biochar for two triazine pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, W.; Williams, D.; Walker, J.T.; Shi, W. Is biochar-manure co-compost a better solution for soil health improvement and N2O emissions mitigation? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching and reclamation of a biochar and compost amended saline–sodic soil with moderate SAR reclaimed water. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Shao, H.B. Furfural and its biochar improve the general properties of a saline soil. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-G.; Sun, F.-F.; Zong, Y.-T. Effect of rice husk biochar and coal fly ash on some physical properties of expansive clayey soil (Vertisol). CATENA 2014, 114, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Han, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhang, S. Effects of biochar and straw addition on agglomerate composition and organic carbon distri-bution in sandy ginger black soil. China Agric. Sci. 2015, 705–712. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aggelides, S.M.; Londra, P.A. Effects of compost produced from town wastes and sewage sludge on the physical properties of a loamy and a clay soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Pietramellara, G.; Mbagwu, J. Effects of coal derived humic substances on water retention and structural stability of Mediterranean soils. Soil Use Manag. 1996, 12, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Abdrakhmanov, T.; Jabbarov, Z.; Abdullaev, S.; Azimov, A.; Mohamed, I.; AlHarbi, M.; Abu-Elsaoud, A.; Elkelish, A. Biochar improves the growth and physiological traits of alfalfa, amaranth and maize grown under salt stress. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Choudhary, R.L.; Meena, M.K.; Meena, V.D.; Singh, H.; Lakaria, B.L.; Jat, R.S.; Rai, P.K.; Kumar, K.; Doutaniya, R.K.; et al. Dynamics of major plant nutrients and enzymatic activities in soil influenced by application of biochar and organic waste. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ju, T.; Liang, K.; Li, Y. Biochar-influenced solubilization and mineralization mechanisms of phosphorus in sa-line-sodic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, P.S. Role of organic fertilizers in the management of nutrient deficiency, acidity, and toxicity in acid soils—A review. J. Glob. Agric. Ecol. 2021, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Heal, K.; Tigabu, M.; Xia, L.; Hu, H.; Yin, D.; Ma, X. Biochar addition to forest plantation soil enhances phosphorus availability and soil bacterial community diversity. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 455, 117635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Biochar drives humus formation during composting by regulating the specialized metabolic features of microbiome. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Paredes, A.; Valdés, G.; Araneda, N.; Valdebenito, E.; Hansen, F.; Nuti, M. Microbial Community in the Composting Process and Its Positive Impact on the Soil Biota in Sustainable Agriculture. Agronomy 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Responses of soil microbial community structure changes and activities to biochar addition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, B.; Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ye, H.; Qin, L.; Lai, C. Biochar-compost as a new option for soil improvement: Application in various problem soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 162024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Materials | pH | EC (mS·cm−1) | CEC (cmol·kg−1) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | ||||||||||||
| Coastal saline soil | 8.41 | 3.56 | 17.28 | 7.29 | 5700 | 2890 | 180 | 120 | 5020 | 1120 | 43.38 | 5.63 | 146.15 |
| Biochar | 9.12 | 12.73 | 32.25 | - | 2.75 | 11.26 | 14.21 | 1.26 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Waste compost | 7.91 | 6.76 | 68.34 | - | 1730 | 10.45 | 1100 | 2260 | 1960 | 13,900 | - | - | - |
| Treatment | pH | EC (mS·cm−1) | SAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.66 ± 0.09 ab | 0.41 ± 0.05 a | 3.28 ± 0.71 a |
| B | 8.71 ± 0.14 a | 0.23 ± 0.07 b | 1.58 ± 0.38 bc |
| W | 8.45 ± 0.11 c | 0.27 ± 0.05 b | 2.03 ± 0.31 b |
| BW | 8.58 ± 0.07 bc | 0.20 ± 0.06 b | 1.19 ± 0.47 c |
| Index | Treatment | W0 | W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WR0.25 | B0 | 18.90 ± 1.33 hi | 22.24 ± 1.66 fg | 27.59 ± 1.08 de | 30.38 ± 1.27 c |
| B1 | 18.88 ± 1.55 hi | 22.63 ± 1.58 fg | 29.79 ± 1.75 cd | 32.95 ± 1.49 ab | |
| B2 | 17.92 ± 0.62 i | 23.96 ± 0.87 f | 29.81 ± 1.92 cd | 35.13 ± 1.84 a | |
| B3 | 20.77 ± 1.24 gh | 26.63 ± 0.99 e | 31.53 ± 0.72 bc | 33.51 ± 1.68 ab | |
| WR2 | B0 | 0.62 ± 0.18 f | 1.65 ± 0.24 e | 2.39 ± 0.31 cd | 2.61 ± 0.16 bcd |
| B1 | 0.32 ± 0.14 f | 2.36 ± 0.41 cd | 3.06 ± 0.47 ab | 3.24 ± 0.21 a | |
| B2 | 0.47 ± 0.20 f | 2.18 ± 0.55 de | 3.12 ± 0.53 ab | 3.52 ± 0.30 a | |
| B3 | 0.40 ± 0.19 f | 2.45 ± 0.53 cd | 3.07 ± 0.27 ab | 3.36 ± 0.25 a |
| Index | Treatment | W0 | W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWD | B0 | 0.23 ± 0.01 h | 0.30 ± 0.04 f | 0.36 ± 0.03 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.02 bc |
| B1 | 0.22 ± 0.03 h | 0.33 ± 0.07 def | 0.39 ± 0.03 b | 0.43 ± 0.06 a | |
| B2 | 0.22 ± 0.02 h | 0.32 ± 0.06 ef | 0.37 ± 0.03 bc | 0.43 ± 0.03 a | |
| B3 | 0.24 ± 0.02 h | 0.34 ± 0.08 cde | 0.38 ± 0.07 b | 0.42 ± 0.07 a | |
| GMD | B0 | 0.14 ± 0.02 f | 0.16 ± 0.02 ef | 0.20 ± 0.02 cd | 0.23 ± 0.03 ab |
| B1 | 0.15 ± 0.02 ef | 0.16 ± 0.01 ef | 0.21 ± 0.02 bc | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | |
| B2 | 0.14 ± 0.01 f | 0.17 ± 0.01 def | 0.21 ± 0.02 bc | 0.25 ± 0.03 a | |
| B3 | 0.14 ± 0.02 f | 0.18 ± 0.02 de | 0.21 ± 0.02 bc | 0.24 ± 0.03 a |
| Index | Treatment | W0 | W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urease activity | B0 | 10.10 ± 0.33 h | 10.92 ± 0.39 g | 18.2 ± 0.70 f | 25.48 ± 0.84 e |
| B1 | 12.74 ± 0.59 g | 16.8 ± 0.69 f | 25.48 ± 1.13 e | 28.82 ± 1.23 c | |
| B2 | 18.20 ± 0.72 f | 24.48 ± 0.93 e | 29.12 ± 1.07 c | 32.76 ± 1.28 b | |
| B3 | 21.84 ± 0.96 d | 28.12 ± 1.33 c | 32.76 ± 1.61 b | 36.4 ± 1.66 a | |
| Phosphatase activity | B0 | 19.20 ± 0.81 h | 27.52 ± 1.24 f | 41.48 ± 2.03 d | 51.13 ± 2.97 b |
| B1 | 22.64 ± 1.20 g | 34.40 ± 1.75 e | 48.16 ± 2.70 c | 60.37 ± 2.60 a | |
| B2 | 27.52 ± 1.32 f | 42.28 ± 2.54 d | 54.48 ± 2.75 b | 61.92 ± 3.65 a | |
| B3 | 30.96 ± 1.76 e | 44.72 ± 2.42 c | 55.04 ± 2.86 b | 63.47 ± 2.92 a | |
| Dehydrogenase activity | B0 | 1.90 ± 0.06 i | 3.49 ± 0.13 f | 5.32 ± 0.23 d | 6.44 ± 0.27 b |
| B1 | 2.28 ± 0.09 h | 4.56 ± 0.19 e | 6.08 ± 0.30 c | 6.74 ± 0.23 b | |
| B2 | 3.04 ± 0.11 g | 4.94 ± 0.23 d | 6.65 ± 0.25 b | 7.60 ± 0.36 a | |
| B3 | 3.80 ± 0.18 f | 5.32 ± 0.21 d | 6.84 ± 0.31 b | 6.18 ± 0.22 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Xing, S.; Wu, Y.; Zou, R.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H. Exploring the Effects of Biochar and Compost on Ameliorating Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092093
Zhou W, Xing S, Wu Y, Zou R, Li S, Sun X, Zhang H. Exploring the Effects of Biochar and Compost on Ameliorating Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092093
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wenzhi, Shuo Xing, Yaqi Wu, Rongsong Zou, Suyan Li, Xiangyang Sun, and Huaxin Zhang. 2025. "Exploring the Effects of Biochar and Compost on Ameliorating Coastal Saline Soil" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092093
APA StyleZhou, W., Xing, S., Wu, Y., Zou, R., Li, S., Sun, X., & Zhang, H. (2025). Exploring the Effects of Biochar and Compost on Ameliorating Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy, 15(9), 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092093







