Changes in Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Following Green Manure–Maize Rotations in Coastal Saline Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
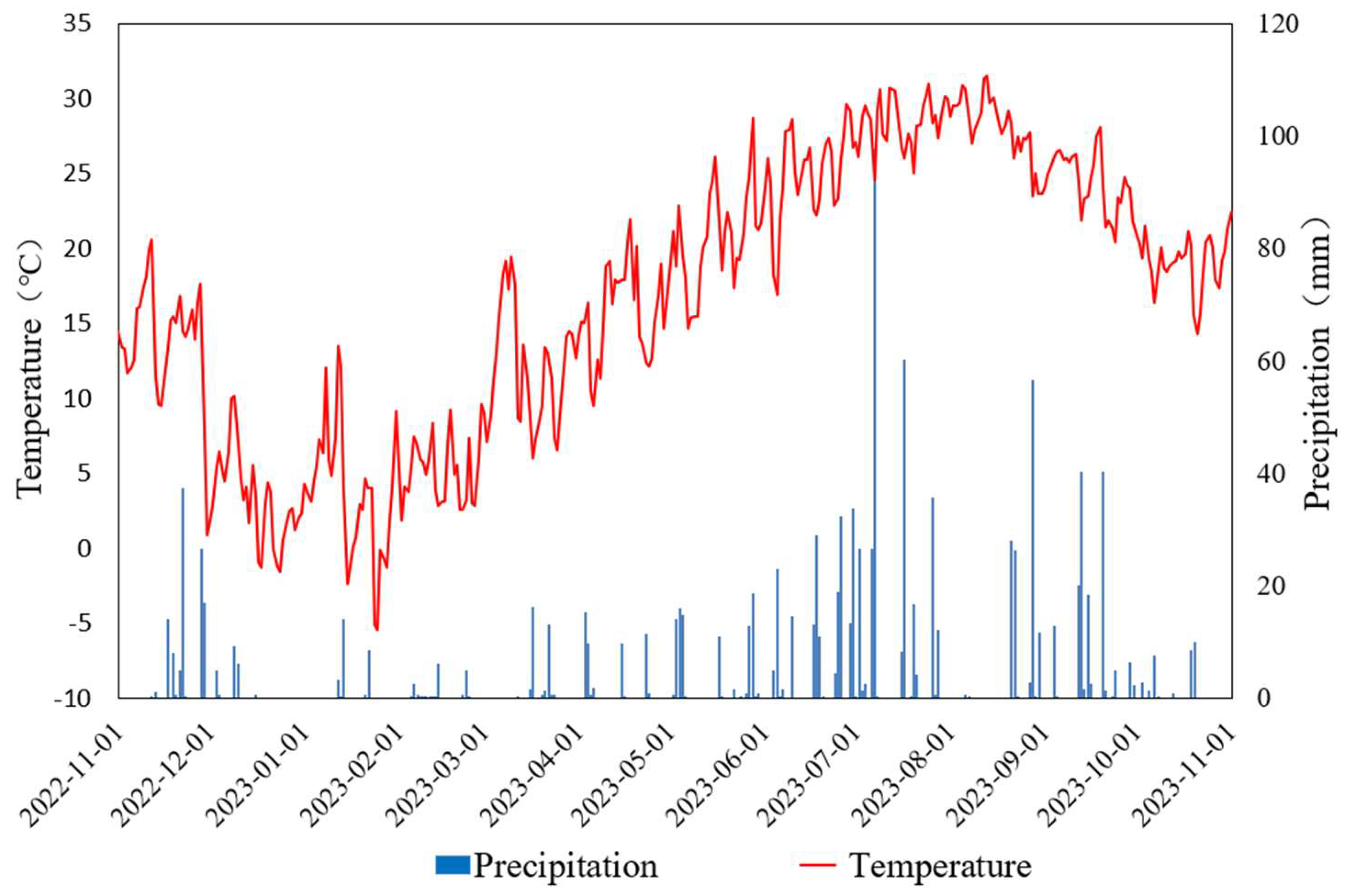
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil and Plant Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Calculations
- (1)
- Soil organic carbon
- (2)
- Analysis of content mechanical stability of soil aggregates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
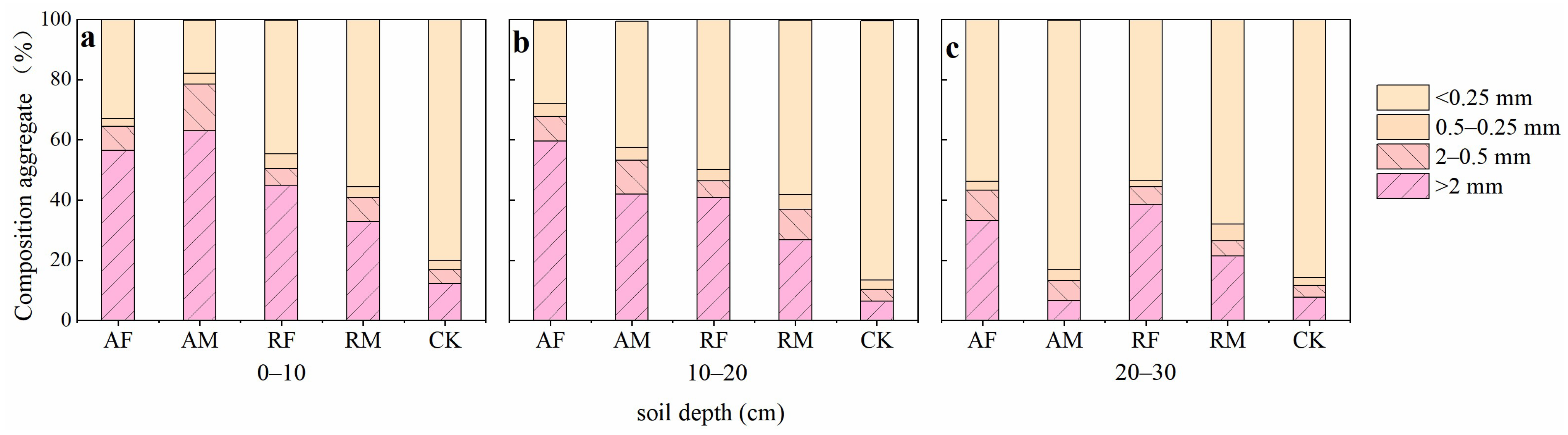
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Soil Aggregates
3.2. Stability of Soil Aggregates
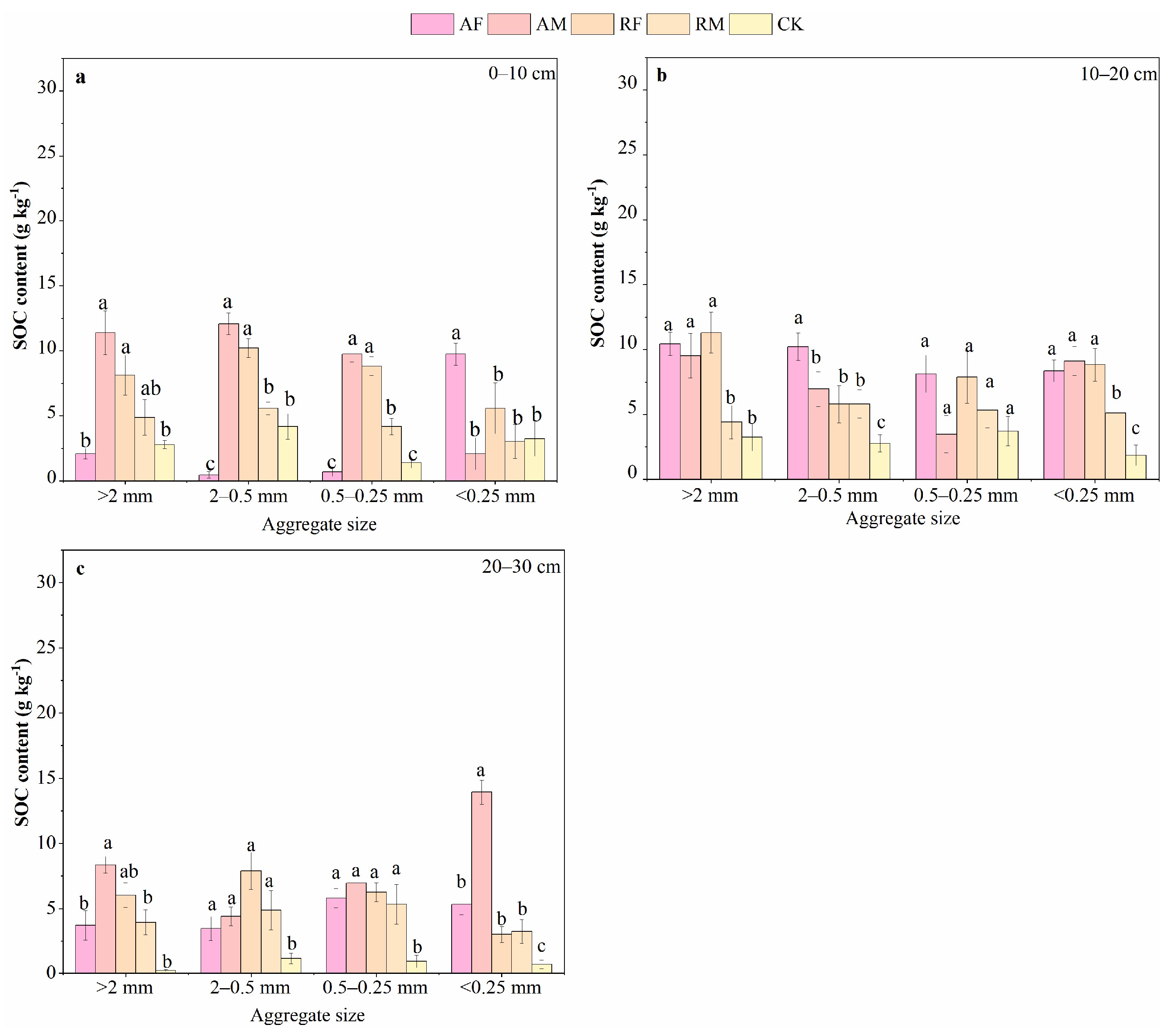
3.3. Distribution of Aggregate-Associated Carbon
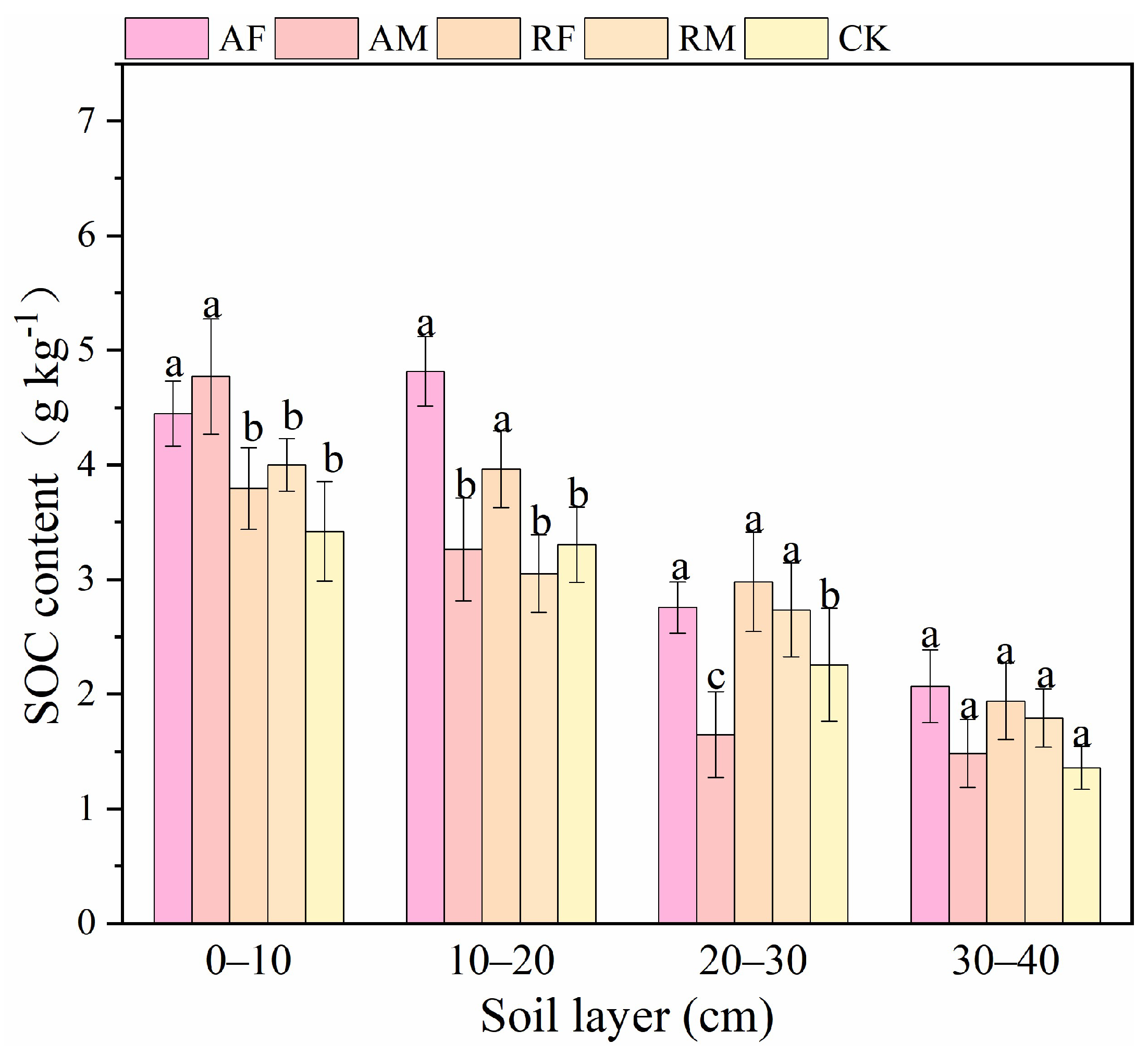
3.4. Total SOC Under Different Treatments
3.5. Contribution of Soil Aggregates to SOC
3.6. Correlation of Soil Aggregates, Erodibility, and Organic Matter Content
3.7. Effects of Green Manure–Maize Rotations on Maize Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Green Manure–Maize Rotation Enhances Soil Macroaggregate Formation and Stability
4.2. Green Manure–Maize Rotation Boosts Soil SOC Sequestration in Soil Aggregates
4.3. Green Manure–Maize Rotation Boosts Maize Productivity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhardwaj, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, A. Bibliometric review of digital transformation in agriculture: Innovations, trends and sustainable futures. J. Agribus. Dev. Emerg. Econ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Feng, B.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Shen, C.C.; Ma, D.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Zhang, J.B. Saline-alkali land reclamation boosts topsoil carbon storage by preferentially accumulating plant-derived carbon. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.J. Prevent soil salinization and increase soil productivity. Science 2021, 73, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.J. Research on Salt-affected Soils in China: History, Status Quo and Prospect. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Q.Q.; Gong, X.L.; Shi, Y.D.; Gou, F.G. Study on salinization degree and its influential factors of saline soil in coastal area of Jiangsu province. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 28, 959–965. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.M.; Yang, M.Y.; Chen, S.; Su, J.K.; Lv, H.L.; Jia, H.X.; Liu, Z.P. Saline-alkali land management in China: Current situation, problems and prospects. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2025, 48, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Liang, L.N.; Song, N.N.; Liu, D.S.; Wang, J.C. Effects of straw returning on the stability of soil organic carbon in wheat-maize rotation systems. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Xu, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Sun, N.; Wang, B.R.; Cai, Z.J.; Saeed, Q.; Naveed, M.; Mehmood, K.; et al. Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.R.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, C.H.; Xia, Z.T.; Cheng, W.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, J.X.; Fan, M.P. Effects of Continuous Annual Crop Rotation and Fallow on Soil Aggregate Stability and Organic Carbon. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yin, Z.Y.; Li, X.K.; Lu, J.W. Effects of organic carbon and iron oxides on soil aggregate stability under different tillage systems in a rice-rape cropping system. Catena 2019, 177, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, K.A.; Huang, L.; Xue, B.; Li, X.K.; Lu, J.W. Straw management stabilizes the chemical composition of Soil Organic Carbon (SOC): The relationship with aggregate-associated C in a rice-rape cropping system. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hao, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Su, D.R. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Saline-Alkali Land Improvement and Utilization on Soil Organic Carbon. Life 2022, 12, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Wang, R. Organic Amendments promote saline-alkali soil desalinization and enhance maize growth. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1177209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E. Insights into soil and biochar variations and their contribution to soil aggregate status—A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.D. Polyacrylamide and biopolymer effects on flocculation, aggregate stability, and water seepage in a silt loam. Geoderma 2015, 241–242, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhuo, Y.Q.; Chen, H.X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.Z.; Sun, Z.T. Extensive reclamation of saline-sodic soils with flue gas desulfurization gypsum on the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Geoderma 2018, 321, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, G.C.; Yang, L.J.; Liang, Z.J.; Yu, B.Y.; Zhang, T.; Si, T.; Yu, X.N.; Zhang, X.J.; Zou, X.X. Effects of different peanut rotations modes on carbon fractions in soil aggregates. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 46, 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.B.; Yao, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Yao, P.W.; Zhao, N.; He, W.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhai, B.N.; Wang, Z.H. Improving soil aggregation, aggregate-associated C and N, and enzyme activities by green manure crops in the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.P.; Luo, Z.Z.; Li, L.L.; Cai, L.Q.; Zhang, R.Z.; Niu, Y.L. Effects of lucerne-crop rotation patterns on soil aggregate stability and soil organic carbon. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.P.; Deng, X.H.; Jiang, Z.M.; Zheng, H.B.; Zhang, Z.W.; Tan, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhang, M.F. Dynamic Changes of Main Nutrients in Tobacco-planting Soil Under Different Green Manure Application. Crop Res. 2015, 29, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.N.; Zhao, R. Soil Texture Classification and Its Application in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Soil Agro-Chemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.X.; Yu, Y.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, R.L.; Shen, S.G.; Wu, D.N. Determination of Organic Carbon in Rice Soil by Potassium Dichromate Titration Method. Chem. Reag. 2023, 45, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Physical and Chemical Analysis of Soils; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1978; pp. 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, W.C.; Simanton, J.R.; Wu, J.Q.; Hagen, L.Y. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); USDA Agriculture Research Service Handbook; US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 703, pp. 1–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate stability and size distribution. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.P. Effects of soil aggregate stability on soil N following land use changes under erodible environment. Agric. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhu, B.; Yin, R.; Wang, M.W.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.Z.; Li, D.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Kardol, P.; Liu, M.Q. Organic fertilization promotes crop productivity through changes in soil aggregation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhao, X.R.; Lin, Q.M.; Li, G.T. Biochar altered native soil organic carbon by changing soil aggregate size distribution and native SOC in aggregates based on an 8-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Xiao, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, B.H. Effects of farmland conversion on the stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil aggregates on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2019, 351, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.G. Green manure improves humification and aggregate stability in paddy soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 206, 109796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. SoilTillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ding, W.; Luo, J.; Geng, R.L.; Cai, Z.C. Long-term application of organic manure and mineral fertilizers on aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon in a sandy loam soil. SoilTillage Res. 2012, 124, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T.; Coleman, D.C. Let the soil work for us. Ecol. Bull. 1988, 39, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, M.; Huang, L.; Nie, J.; Geng, M.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhou, F.L.; Xu, Y.H. Effect of reduced mineral fertilization (NPK) combined with green manure on aggregate stability and soil organic carbon fractions in a fluvo-aquic paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 211, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MHalder, S.; Liu, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.C.; Guo, Z.C.; Peng, X.H. Effects of residue stoichiometric, biochemical and C functional features on soil aggregation during decomposition of eleven organic residues. Catena 2021, 202, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, X.X.; Dong, W.X.; Liu, X.P.; Pei, L.; Zhang, H. Effects of tillage and straw returning method on the distribution of carbon and nitrogen in soil aggregates. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.W.; Wu, J.; Li, W.L.; Ren, Z.C.; Cai, L.Q.; Luo, Z.Z. Effects of Different Land Use Patterns on the Stability of Soil Aggregates in the Loess Plateau of Eastern Gansu. Crop Res. 2022, 36, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.H.; Wen, X.L.; Li, S.H.; Cheng, F.H.; Zhao, S.L.; Wang, Q.T.; Liu, X.F. Impact of returning green manure on soil aggregation, soil erodibility, and organic matter content. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Le, Z.; Lin, Z.J.; Dang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. The competitive effects of crop straw return and nitrogen fertilization on soil acidification. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 388, 109638. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Z.Q.; Chen, Q.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, S.C.; Gou, Y.X.; Sun, Z.X.; Huang, Y.F.; Shi, Z. Soil organic carbon storage, distribution, and influencing factors at different depths in the dryland farming regions of Northeast and North China. Catena 2022, 210, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Sainju, U.M.; Zhang, S.H.; Tan, G.Y.; Wen, M.M.; Dou, Y.; Yang, R.J.; Chen, J.F.; Zhao, F.Z.; Wang, J. Cover cropping promotes soil carbon sequestration by enhancing microaggregate-protected and mineral-associated carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kama, R.; He, J.X.; Nabi, F.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, C.S. Crop rotation and green manure type enhance organic carbon fractions and reduce soil arsenic content Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Steffens, M.; Mueller, C.W.; Koelbl, A.; Reszkowska, A.; Peth, S.; Horn, R.; Koegel-Knabner, I. Aggregate stability and physical protection of soil organic carbon in semi-arid steppe soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.L.; Jastrow, J.D. Physical and chemical protection in hierarchical soil aggregates regulates soil carbon and nitrogen recovery in restored perennial grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Arter, C.; Liu, X.; Horton, R.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, F.; Li, Y. Soil aggregate stability and sizeselective sediment transport with surface runoff as affected by organic residue amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.W. Effects of Milk Vetch and Rapeseed Returned to the Field on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon Sequestration. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Nie, J.; Liao, Y.L.; Xie, J. Effects of long-term winter planted green manure on distribution and storage of organic carbon and nitrogen in water-stable aggregates of reddish paddy soil under a double-rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Fu, X.; Muhammad, I.; Liu, W.Q.; Wang, J. Effects of Straw and Plastic Film Mulching on Nitrogen Composition of Soil Aggregates in Dryland Wheat Field on the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 236–241+248. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.Z.; Cheng, J.H.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Regulation of plant height by gibberellins biosynthesis and signal transduction. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.L.; Chai, Q.; Cao, W.D.; Yu, A.Z.; Zhao, C.; Xie, J.H.; Yin, W.; Hu, F.L. Ecosystem service function of green manure and its application in dryland agriculture of China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, H.; Martens, J.R.T.; Bamford, K.; Entz, M.H. Late-season catch crops reduce nitrate leaching risk after grazed green manures but release N slower than wheat demand. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablimit, R.; Li, W.K.; Zhang, J.D.; Gao, H.N.; Zhao, Y.M.; Cheng, M.M.; Meng, X.Q.; An, L.Z.; Chen, Y. Altering microbial community for improving soil properties and agricultural sustainability during a 10-year maize-green manure intercropping in Northwest China. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jia, L.; Chen, Q.Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Deng, J.J.; Lu, J.Y.; Xu, L.; Li, H.X.; Hu, F.; Jiao, J.G. Adaptive evaluation for agricultural sustainability of different fertilizer management options for a green manure-maize rotation system: Impacts on crop yield, soil biochemical properties and organic carbon fractions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.K.; Yin, L.N.; Ju, W.X.; Li, X.K.; Liu, X.X.; Deng, X.P.; Wang, S.W. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 266, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, G.M.; Wang, L.; Zou, H.T.; Gao, Y. Effects of partial replacement of chemical nitrogen fertilizers with green manure on soil physical properties and maize (Zea mays L.) yield. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2025, 34, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.P.; Yu, A.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, F.M. Effects of green manure application methods on dry matter accumulation, distribution, and yield of maize in oasis irrigation area. Acta Agron. Sin. 2024, 50, 686–694. [Google Scholar]
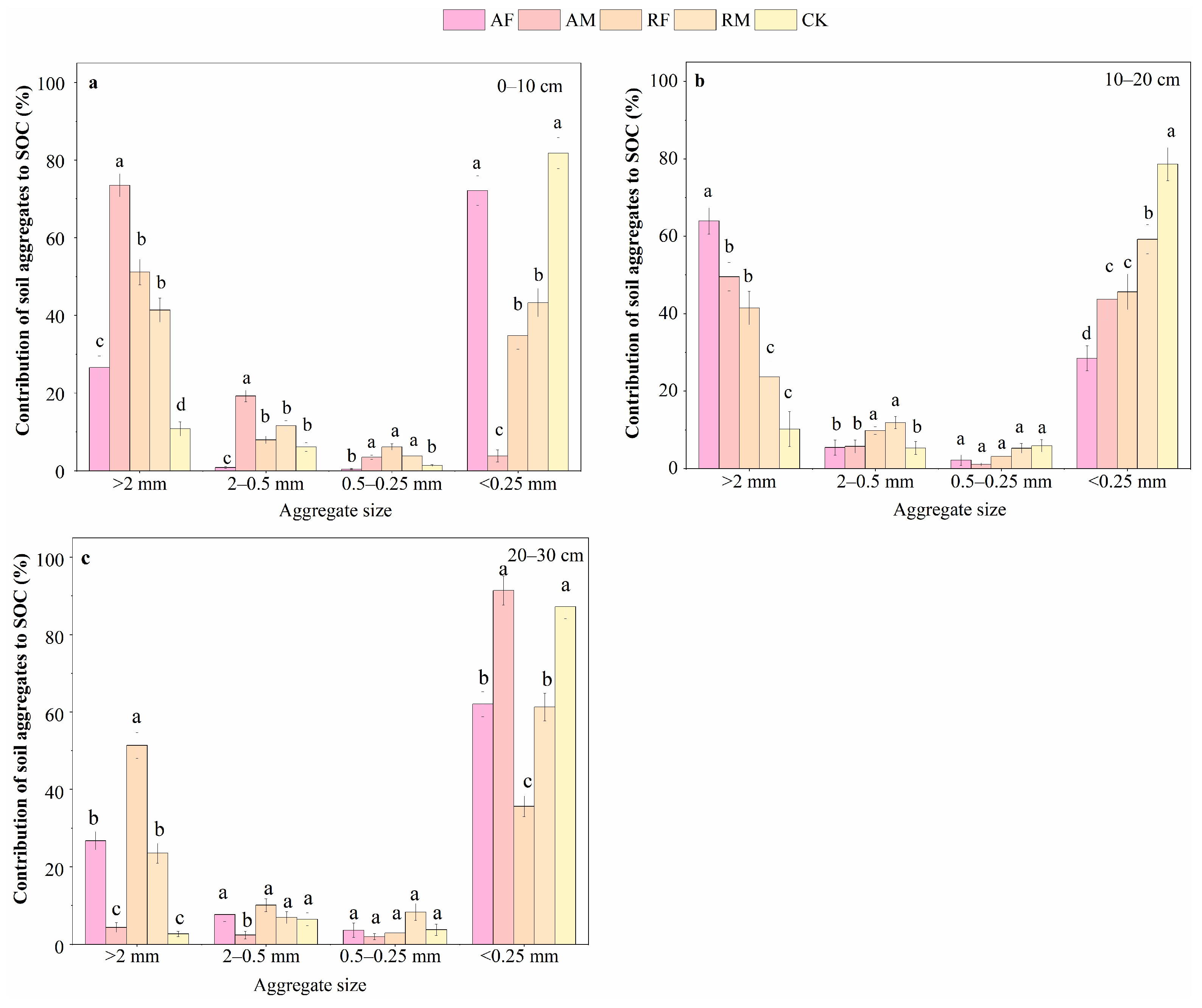
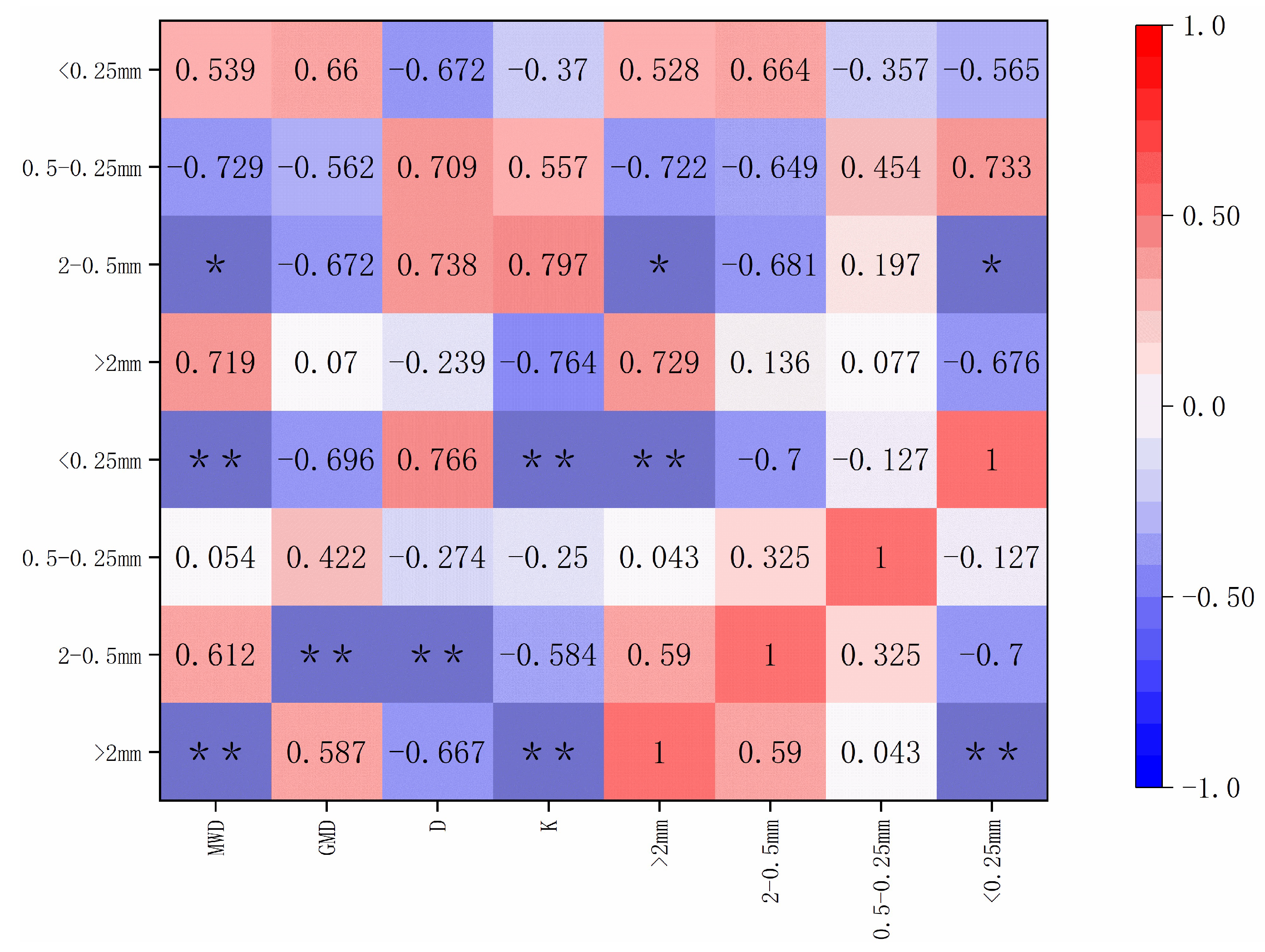
| Soil Depth (cm) | Treatment | R>0.25 mm | MWD | GWD | D | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (mm) | (mm) | ||||
| 0–10 cm | AF | 67.09 ± 2.45 a | 3.54 ± 0.10 a | 1.38 ± 0.12 a | 2.86 ± 0.08 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 d |
| AM | 82.05 ± 12.32 a | 4.01 ± 0.68 a | 2.14 ± 0.70 a | 2.64 ± 0.06 d | 0.02 ± 0.01 d | |
| RF | 55.29 ± 2.75 b | 2.83 ± 0.13 b | 0.86 ± 0.09 b | 2.9 ± 0.02 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 c | |
| RM | 44.34 ± 1.27 b | 2.15 ± 0.21 b | 0.56 ± 0.05 b | 2.85 ± 0.03 c | 0.06 ± 0.02 b | |
| CK | 19.92 ± 3.27 c | 0.90 ± 0.20 c | 0.23 ± 0.03 b | 2.96 ± 0.02 a | 0.14 ± 0.04 a | |
| 10–20 cm | AF | 71.95 ± 2.43 a | 3.72 ± 1.12 a | 1.60 ± 0.15 a | 2.82 ± 0.07 d | 0.06 ± 0.01 bc |
| AM | 57.44 ± 12.31 b | 2.73 ± 0.61 b | 0.87 ± 0.68 b | 2.85 ± 0.09 d | 0.04 ± 0.01 c | |
| RF | 50.14 ± 2.78 b | 2.59 ± 0.12 b | 0.72 ± 0.07 b | 2.92 ± 0.03 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 bc | |
| RM | 41.83 ± 1.26 b | 1.82 ± 0.15 b | 0.47 ± 0.04 b | 2.89 ± 0.04 c | 0.07 ± 0.02 b | |
| CK | 13.46 ± 3.20 c | 0.55 ± 0.15 c | 0.18 ± 0.04 b | 2.96 ± 0.02 a | 0.17 ± 0.05 a | |
| 20–30 cm | AF | 46.18 ± 2.39 a | 2.20 ± 0.08 a | 0.59 ± 0.09 a | 2.89 ± 0.09 c | 0.06 ± 0.02 c |
| AM | 16.77 ± 4.67 b | 0.59 ± 0.18 b | 0.20 ± 0.54 a | 2.94 ± 0.10 b | 0.16 ± 0.05 a | |
| RF | 46.47 ± 2.74 a | 2.46 ± 0.15 a | 0.65 ± 0.06 a | 2.93 ± 0.03 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 c | |
| RM | 32.06 ± 1.30 a | 1.45 ± 0.11 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 a | 2.93 ± 0.05 b | 0.10 ± 0.03 b | |
| CK | 14.30 ± 3.21 b | 0.63 ± 0.18 a | 0.19 ± 0.05 a | 2.97 ± 0.03 a | 0.17 ± 0.06 a |
| Treatment | Yield and Yield Components | Aboveground Dry Matter (t hm−2) | Plant Height (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kernel Number Per Ear | 100-Grain Weight (g) | Grain Yield (t hm−2) | ||||
| AF | 528.79 b | 30.18 a | 6.52 a | 19.64 a | 216.75 a | 2.13 a |
| AM | 567.08 a | 31.94 a | 6.84 a | 18.36 a | 220.75 a | 2.18 a |
| RF | 537.07 b | 30.28 a | 6.56 a | 17.92 b | 216.42 a | 2.08 a |
| RM | 572.14 a | 32.32 a | 6.98 a | 17.45 b | 217.00 a | 1.73 a |
| CK | 529.33 b | 29.84 a | 6.25 b | 16.83 b | 215.17 a | 1.85 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhao, W.; Gao, R.; Luo, W.; Wang, T. Changes in Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Following Green Manure–Maize Rotations in Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061283
Li Y, Jia X, Zhao W, Gao R, Luo W, Wang T. Changes in Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Following Green Manure–Maize Rotations in Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061283
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yinjuan, Xuxia Jia, Weiliang Zhao, Richu Gao, Wan Luo, and Tongshun Wang. 2025. "Changes in Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Following Green Manure–Maize Rotations in Coastal Saline Soil" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061283
APA StyleLi, Y., Jia, X., Zhao, W., Gao, R., Luo, W., & Wang, T. (2025). Changes in Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Following Green Manure–Maize Rotations in Coastal Saline Soil. Agronomy, 15(6), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061283





