Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedlings and Their Effects on Growth and the Antioxidant Defense System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
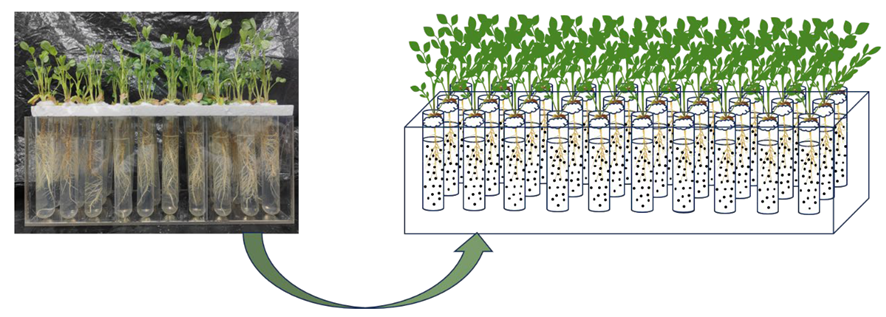
2.1. Plant and Microplastic Materials
2.2. Experimental Treatments
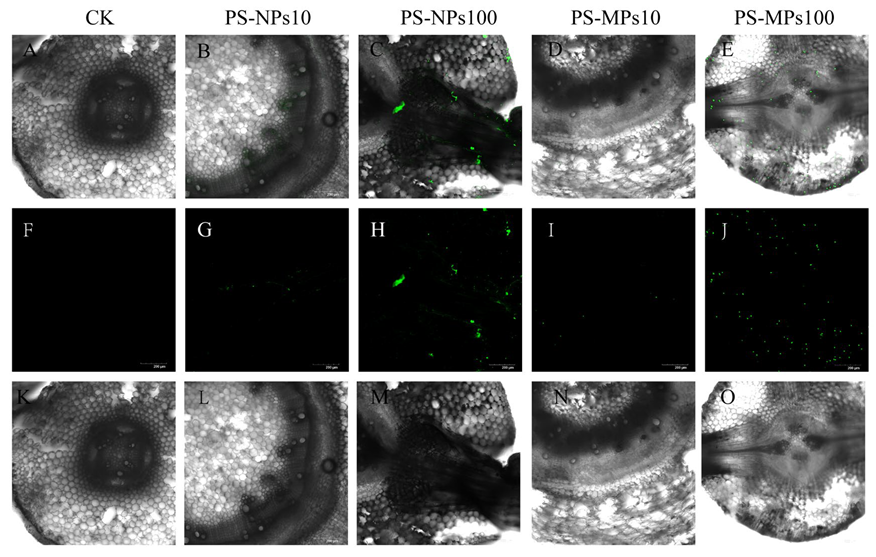
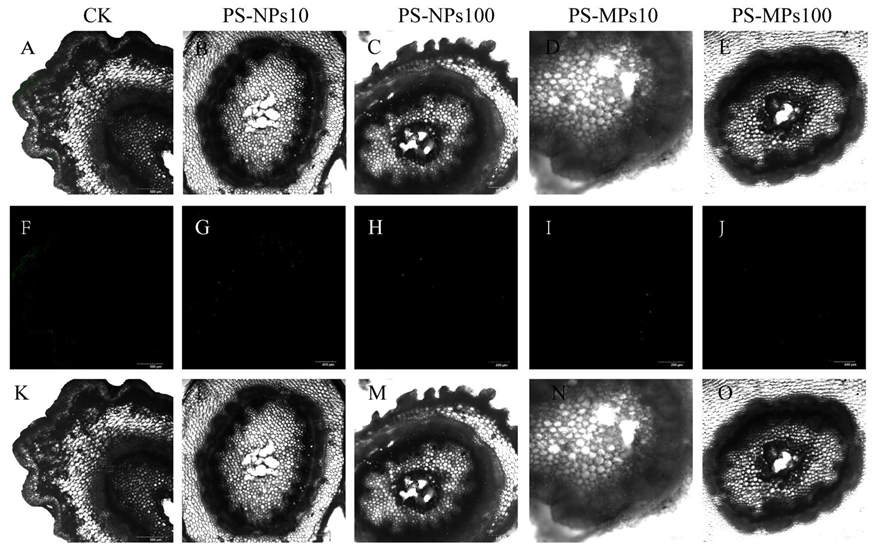
2.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Observation
2.4. Measurement of Peanut Biomass
2.5. SPAD Value and Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Leaves
2.6. Peanut Physiological Indicators
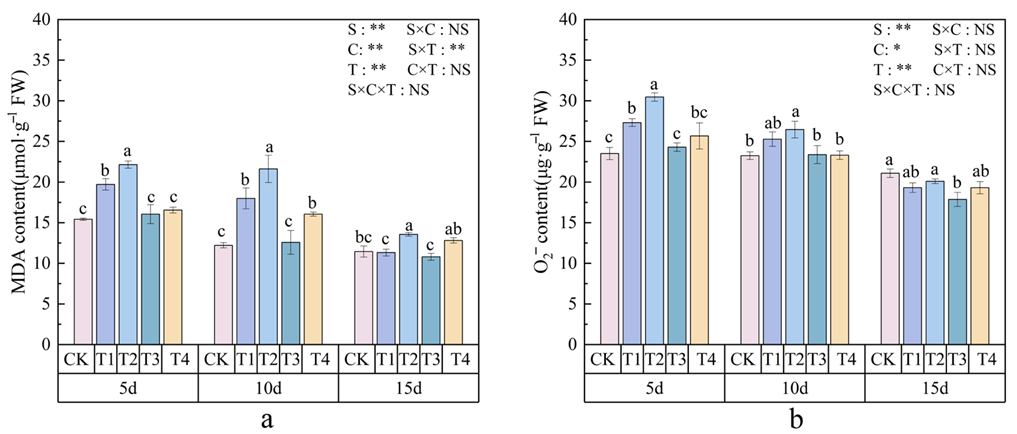
2.6.1. Measurement of MDA and O2− Content
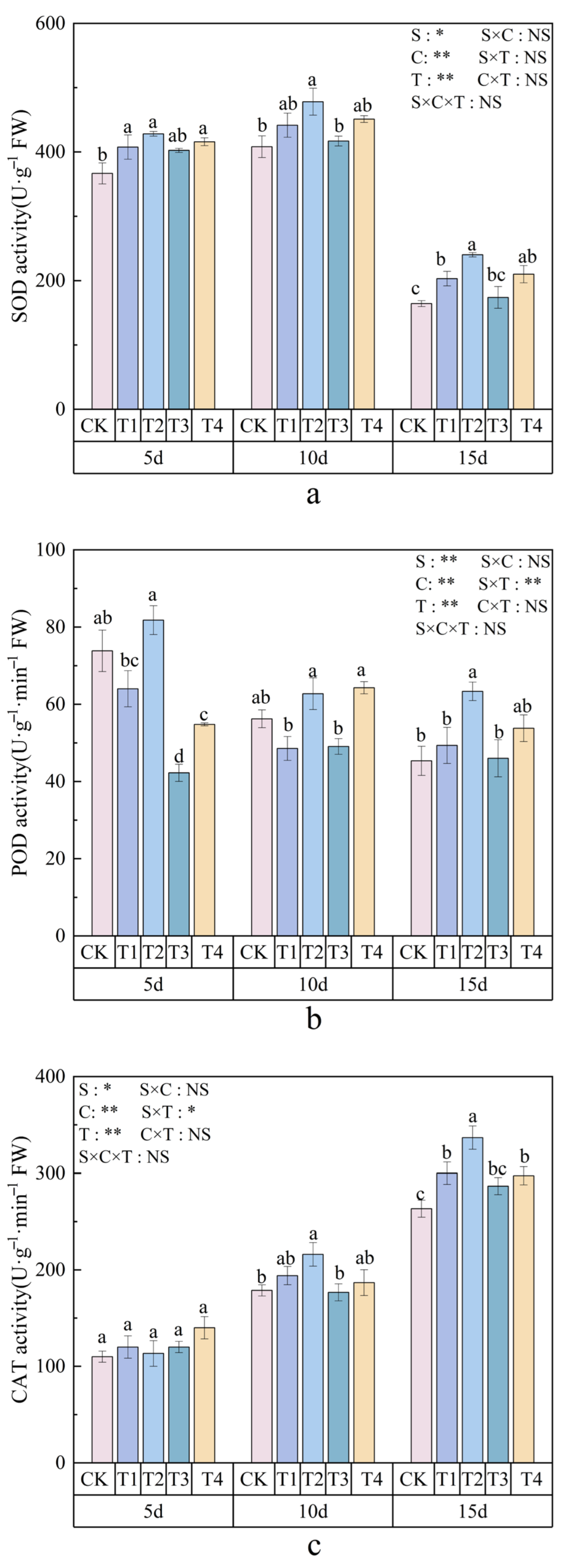
2.6.2. Measurement of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.6.3. Measurement of Antioxidant Content
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
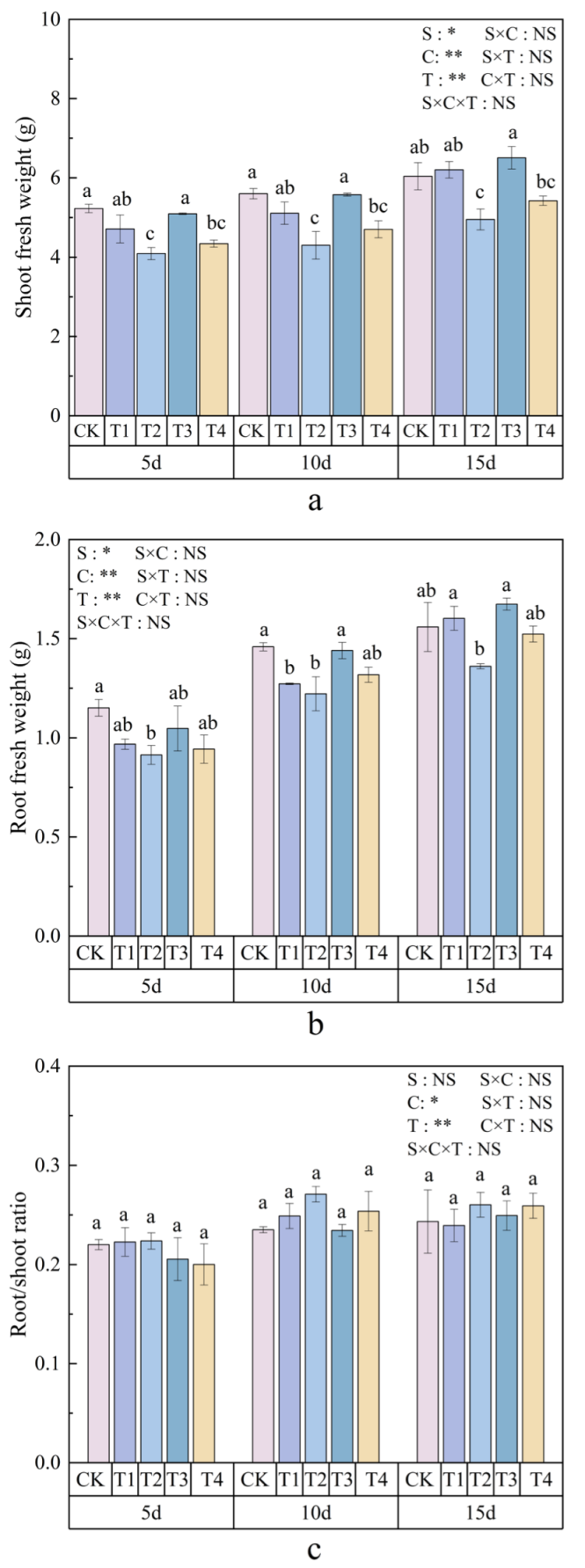
3.1. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Fresh Weight of Peanut
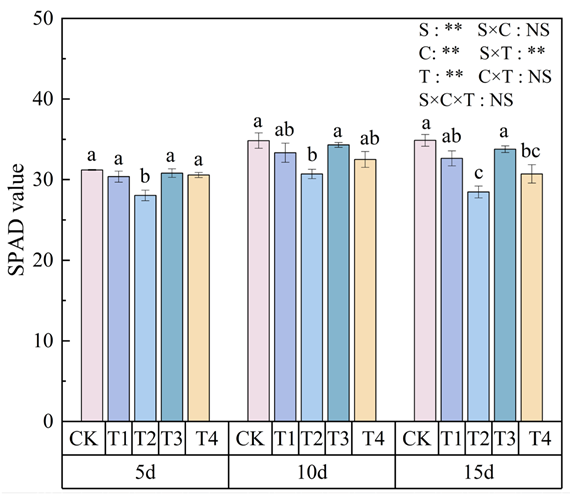
3.2. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on SPAD Value of Peanut
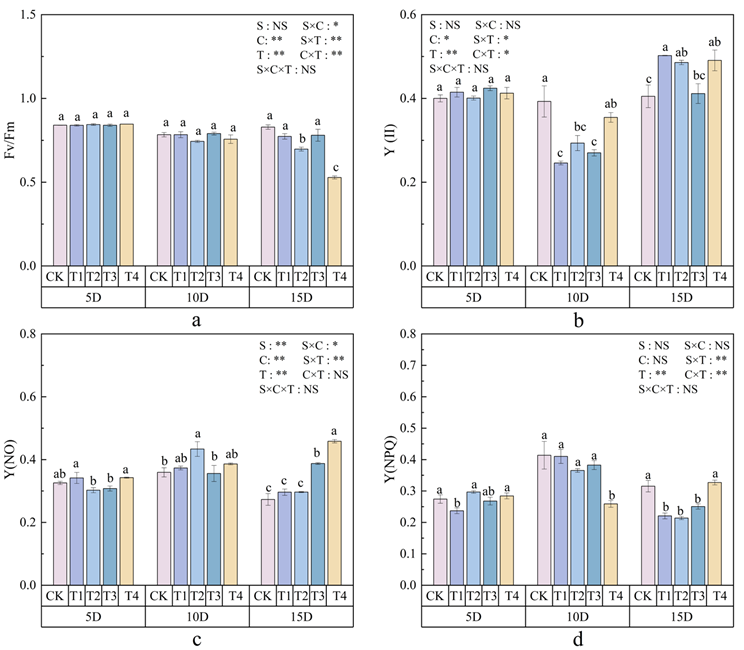
3.3. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Peanut
3.4. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on MDA and O2− Content of Peanut
3.5. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Peanut
3.6. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on the Antioxidant Content of Peanut
3.7. Correlation Analysis
3.8. Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedings
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Peanut Growth
4.2. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Photosynthetic Efficiency of Peanut
4.3. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics on Antioxidant System of Peanut
4.4. Absorb and Transport of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann, T.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N.; Adamowski, J.F.; Bayen, S.; Chen, Q.; Demokritou, P.; Flury, M.; Hüffer, T.; Ivleva, N.P.; et al. Plastics Can Be Used More Sustainably in Agriculture. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, P.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Corradini, F.; Geissen, V. Sewage Sludge Application as a Vehicle for Microplastics in Eastern Spanish Agricultural Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the Environment and Human Health: Current Consensus and Future Trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T. Things We Know and Don’t Know about Nanoplastic in the Environment. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Choi, M.-J.; Kweon, H.-S.; An, Y.-J. Evidence of Parental Transfer of Nanoplastics in Pea (Pisum sativum) Plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and Release of Chemicals from Plastics to the Environment and to Wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A. Microplastics Could Be a Threat to Plants in Terrestrial Systems Directly or Indirectly. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingraffia, R.; Amato, G.; Iovino, M.; Rillig, M.C.; Giambalvo, D.; Frenda, A.S. Polyester Microplastic Fibers in Soil Increase Nitrogen Loss via Leaching and Decrease Plant Biomass Production and N Uptake. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 054012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yin, N.; Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective Uptake of Submicrometre Plastics by Crop Plants via a Crack-Entry Mode. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Uptake of Microplastics by Carrots in Presence of as (III): Combined Toxic Effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Ding, L.; Zhang, G.; Bai, B.; Han, Y.; Xiao, L.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, S.; et al. Microplastics Reduce Nitrogen Uptake in Peanut Plants by Damaging Root Cells and Impairing Soil Nitrogen Cycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, S.; Xiao, K.; Xiong, Q.; Bian, S.; Liang, S.; Hou, H.; Hu, J.; Yang, J. Metabolomics Revealing the Response of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Exposed to Polystyrene Microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosker, T.; Bouwman, L.J.; Brun, N.R.; Behrens, P.; Vijver, M.G. Microplastics Accumulate on Pores in Seed Capsule and Delay Germination and Root Growth of the Terrestrial Vascular Plant Lepidium Sativum. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, N.; Feng, L. Toxic Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Plants: A Global Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Liu, W.; Lian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zeb, A.; Tang, J. Phytotoxicity of Polystyrene, Polyethylene and Polypropylene Microplastics on Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 317, 115441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Cai, K.; Liu, T.; Wang, X. Effects of Microplastics on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.E.; Pearce, C.I.; Sanguinet, K.A.; Hu, D.; Chrisler, W.B.; Kim, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.; Flury, M. Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastic Accumulation at Arabidopsis and Wheat Root Cap Cells, but No Evidence for Uptake into Roots. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2020, 7, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambalvo, D.; Amato, G.; Ingraffia, R.; Antonella Lo Porto; Mirabile, G.; Ruisi, P.; Livio Torta; Frenda, A.S. Nitrogen Fertilization and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Do Not Mitigate the Adverse Effects of Soil Contamination with Polypropylene Microfibers on Maize Growth. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Yue, L.; White, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Nano- and Microplastics Increase the Occurrence of Bacterial Wilt in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). ACS Nano 2024, 18, 18071–18084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Men, S.; Wu, J.; Zeb, A.; Yang, T.; Ma, L.Q.; Zhou, Q. Nanotoxicological Effects and Transcriptome Mechanisms of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under Stress of Polystyrene Nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Wu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zeb, A.; Yang, T.; Su, X.; Su, L.; Liu, W. Impact of Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PSNPs) on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, U.; Chaithra Radharamanan; Venkatesan, K.; Perumal, S. Inhibition of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Growth, Development, and Promotion of Root Nodulation Including Plant Nitrogen Uptake Triggered by Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 18668–18681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Yordanov, I.; Edreva, A. Oxidative Stress and Some Antioxidant Systems in Acid Rain-Treated Bean Plants. Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozeid, A.; Ying, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Ethylene Improves Root System Development under Cadmium Stress by Modulating Superoxide Anion Concentration in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Pandey, V. Antioxidant Enzyme Responses to NaCl Stress in Cassia Angustifolia. Biol. Plant. 2004, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, H.; Erdal, S.; Genisel, M.; Atici, O.; Demir, Y.; Yanmis, D. The Regulatory Effect of Melatonin on Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Parameters in Cold-Stressed Wheat Seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 74, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachadyn-Król, M.; Materska, M.; Chilczuk, B.; Karaś, M.; Jakubczyk, A.; Perucka, I.; Jackowska, I. Ozone-Induced Changes in the Content of Bioactive Compounds and Enzyme Activity during Storage of Pepper Fruits. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, E.A.; Batool Keramat; Sorbo, S.; Maresca, V.; Zahra Asrar; Hossein Mozafari; Basile, A. Interaction of Triacontanol and Arsenic on the Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle and Their Effects on the Ultrastructure in Coriandrum sativum L. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 141, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hadi, F.; Rongliang, Q. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Antioxidants, Chlorophyll Contents, and Proline in Persicaria hydropiper L. And Its Potential for Pb Phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34697–34713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Kloas, W.; Bergmann, J.; Bachelier, J.B.; Faltin, E.; Becker, R.; Görlich, A.S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-D.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Jia, Y.; Feng, L.-J.; Zhu, F.-P.; Dong, S.-S.; Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Tian, H.; Duan, J.-L.; et al. Differentially Charged Nanoplastics Demonstrate Distinct Accumulation in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lu, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, P.; He, C.; Bian, H.; Wang, J. Interactions between Phenanthrene and Polystyrene Micro/Nano Plastics: Implications for Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. A New Perspective on the Nanoplastics Disrupting the Reproduction of an Endangered Fern in Artificial Freshwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12715–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T. Absorption, Accumulation, and Growth Response of Maize to Polystyrene Plastics Particles; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Photosynthetic Impairment in Navicula Sp. At Physiological and Transcriptomic Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tang, S.; Yuan, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, T.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B. Impacts of Polystyrene Microplastics on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Typical Crops. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 31, 2382–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, N.; Gedik, K. Particle Size-Dependent Biomolecular Footprints of Interactive Microplastics in Maize. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Ju, P.; Zheng, L. The Interactions between Microplastic Polyvinyl Chloride and Marine Diatoms: Physiological, Morphological, and Growth Effects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 111000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, J.; Wu, N.; Ahmad, B.; van Nocker, S.; Wu, J.; Abudureheman, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Control of Ovule Development in Vitis Vinifera by VvMADS28 and Interacting Genes. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, D.; Lv, M.; Liao, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, L. Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PSNPs) on the Physiology of Allium sativum L.: Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Enzymes, Phytohormones, and Nutritional Quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 259, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Song, Z.; Qiu, W. Microplastic Particles Increase Arsenic Toxicity to Rice Seedlings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. The Distribution and Impact of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Cucumber Plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 16042–16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Cai, L.; Xu, N.; Zhang, C.; Yadav, V.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Zhong, H. Visual Observation of Polystyrene Nano-Plastics in Grape Seedlings of Thompson Seedless and Assessing Their Effects via Transcriptomics and Metabolomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Du, X.; Zhou, R.; Lian, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Tang, Z. Effects of Polyethylene and Biodegradable Microplastics on the Physiology and Metabolic Profiles of Dandelion. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-Q.; Lu, C.-H.; Mai, L.; Bao, L.-J.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Response of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Roots to Nanoplastic Treatment at Seedling Stage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, T.; Huang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; White, J.C.; Fang, L. Micro/Nanoplastics Pollution Poses a Potential Threat to Soil Health. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Niazi, A.K.; Akhtar, J.; Saifullah; Farooq, M.; Souri, Z.; Karimi, N.; Rengel, Z. Acquiring Control: The Evolution of ROS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Redox Signaling Pathways in Plant Stress Responses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Geng, J.; Jiang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, C. Lead-Contaminated Soil Induced Oxidative Stress, Defense Response and Its Indicative Biomarkers in Roots of Vicia Faba Seedlings. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Rivero, R.M.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Reactive Oxygen Species, Abiotic Stress and Stress Combination. Plant J. 2016, 90, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yan, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Y.; Yu, R. Beneficial Effects of Abscisic Acid and Melatonin in Overcoming Drought Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Xu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Qian, K.; An, K.; Zhu, Y.; Binzeng, H.; Zhao, H.; Kuai, B. Loss-of-Function Mutations in DET2 Gene Lead to an Enhanced Resistance to Oxidative Stress in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2005, 123, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Mu, X.; Li, W.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhang, C. Invisible Threats in Soil: Microplastic Pollution and Its Effects on Soil Health and Plant Growth. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qin, M.; Li, R.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yang, L.; Liu, P.; Shi, Q. Transport Dynamics and Physiological Responses of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Pakchoi: Implications for Food Safety and Environmental Health. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 10923–10933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Liao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Klobučar, G. Ecotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics on Higher Plant Vicia Faba. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F. Uptake and Translocation of Nano/Microplastics by Rice Seedlings: Evidence from a Hydroponic Experiment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Lv, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Yan, X.; Jiao, N.; Younas, A.; et al. Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedlings and Their Effects on Growth and the Antioxidant Defense System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081895
Li Y, Huang X, Lv Q, Ma Z, Zhang M, Liu J, Fan L, Yan X, Jiao N, Younas A, et al. Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedlings and Their Effects on Growth and the Antioxidant Defense System. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081895
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuyang, Xinyi Huang, Qiang Lv, Zhanqiang Ma, Minhua Zhang, Jing Liu, Liying Fan, Xuejiao Yan, Nianyuan Jiao, Aneela Younas, and et al. 2025. "Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedlings and Their Effects on Growth and the Antioxidant Defense System" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081895
APA StyleLi, Y., Huang, X., Lv, Q., Ma, Z., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Fan, L., Yan, X., Jiao, N., Younas, A., Shaaban, M., Gao, J., Wang, Y., & Liu, L. (2025). Visual Observation of Polystyrene Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Peanut Seedlings and Their Effects on Growth and the Antioxidant Defense System. Agronomy, 15(8), 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081895






