Functional Characterization of Dual-Initiation Codon-Derived V2 Proteins in Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids and Constructs
2.2. Virus Genome Sequence Analysis
2.3. Agroinfiltration and Virus Inoculation
2.4. DNA Extraction, qPCR, and Southern Blot
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
3. Results
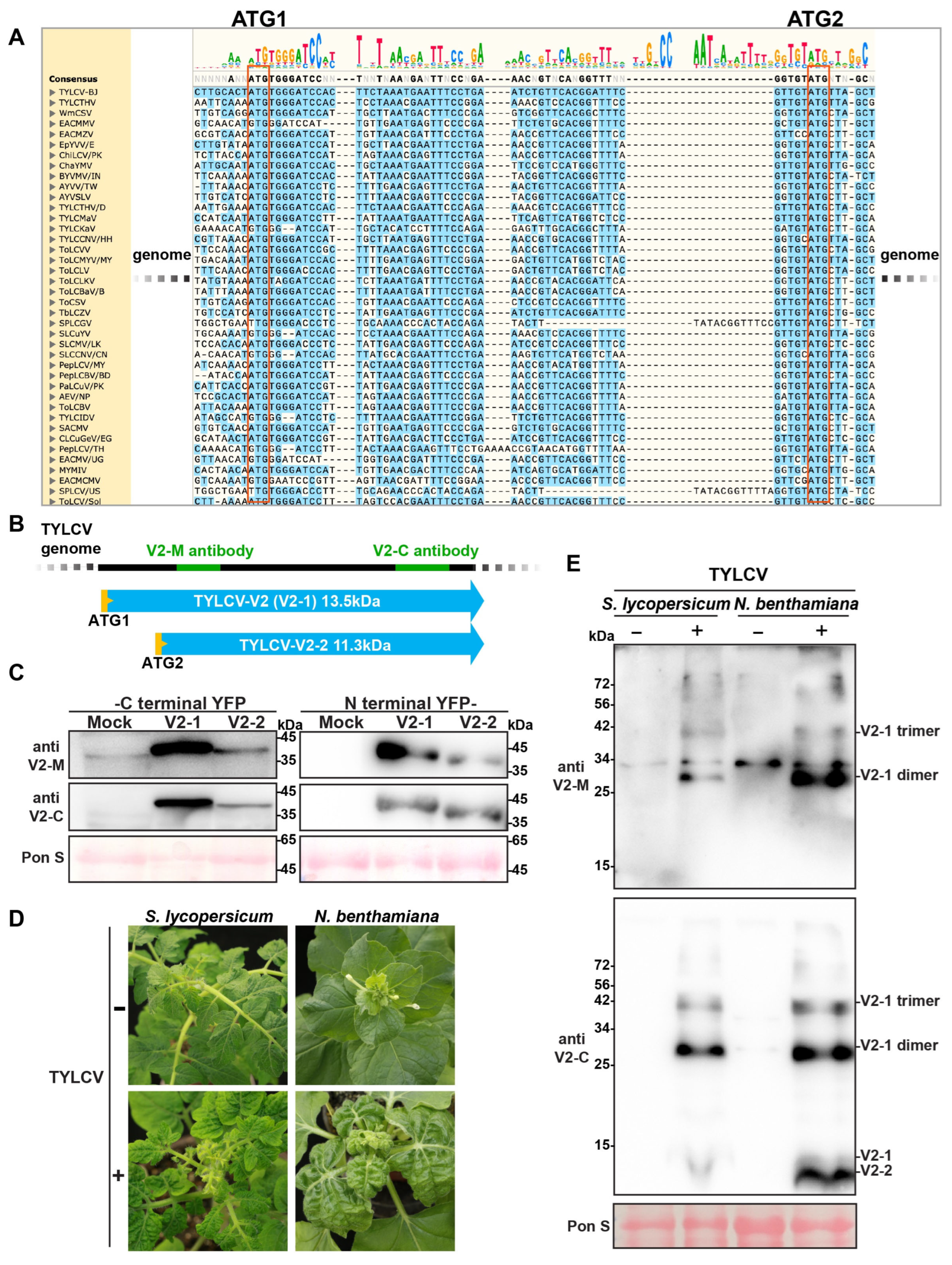
3.1. TYLCV Encodes Two Distinct V2 Protein Variants
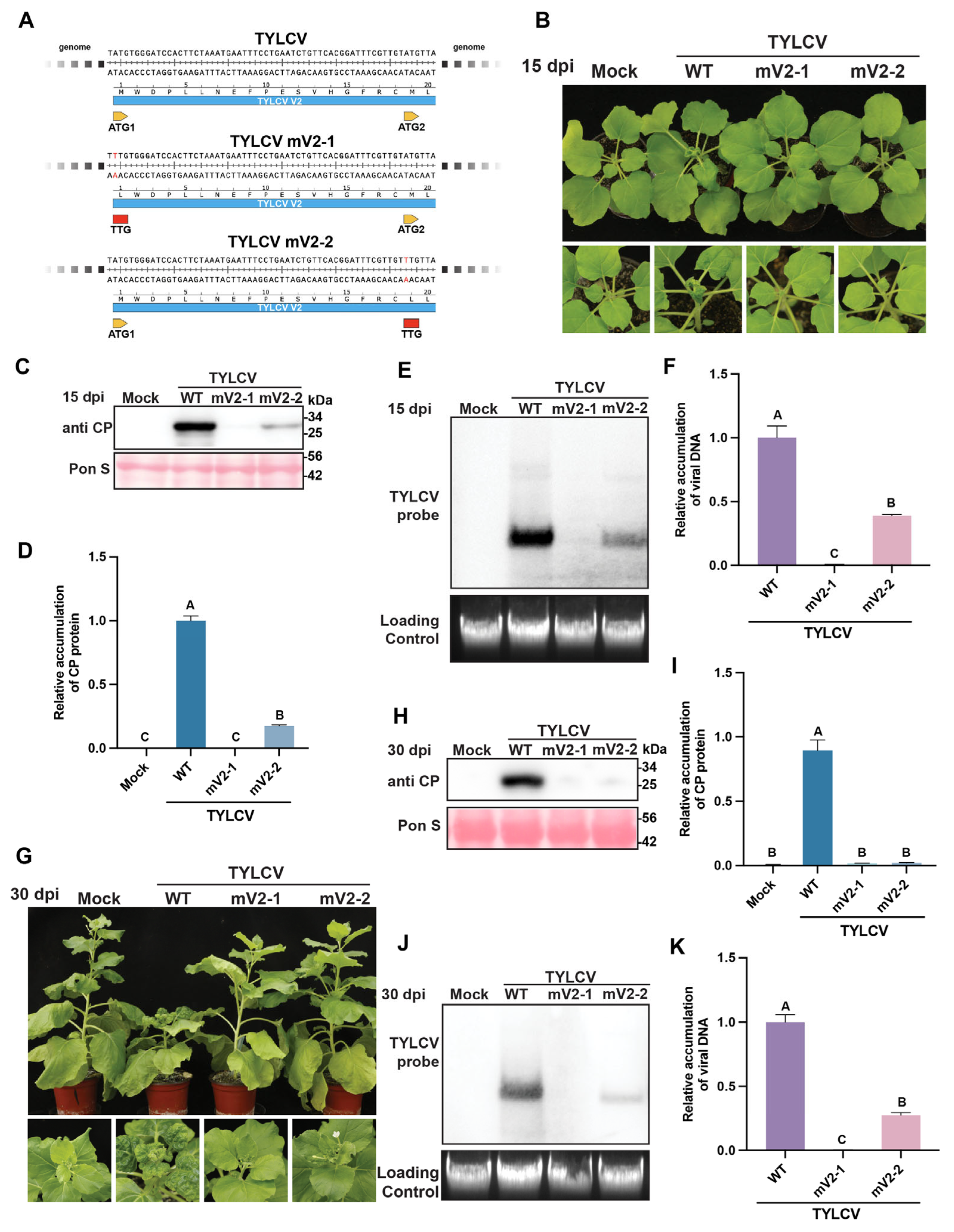
3.2. Mutations in Both ATG Codons of the V2 Protein Impair TYLCV Infectivity in N. benthamiana
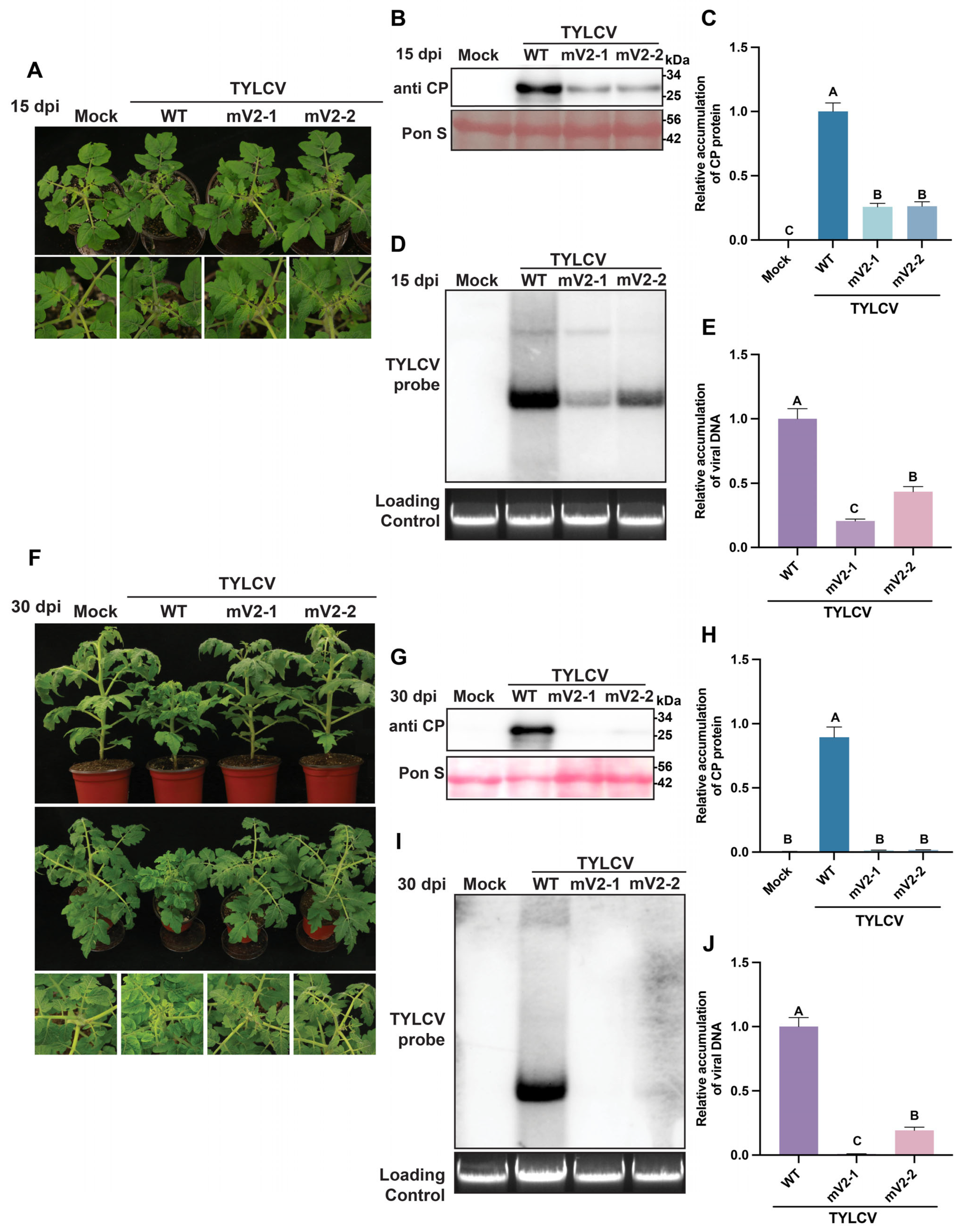
3.3. Mutations in Both ATG Codons of the V2 Protein Impair TYLCV Infectivity in S. lycopersicum
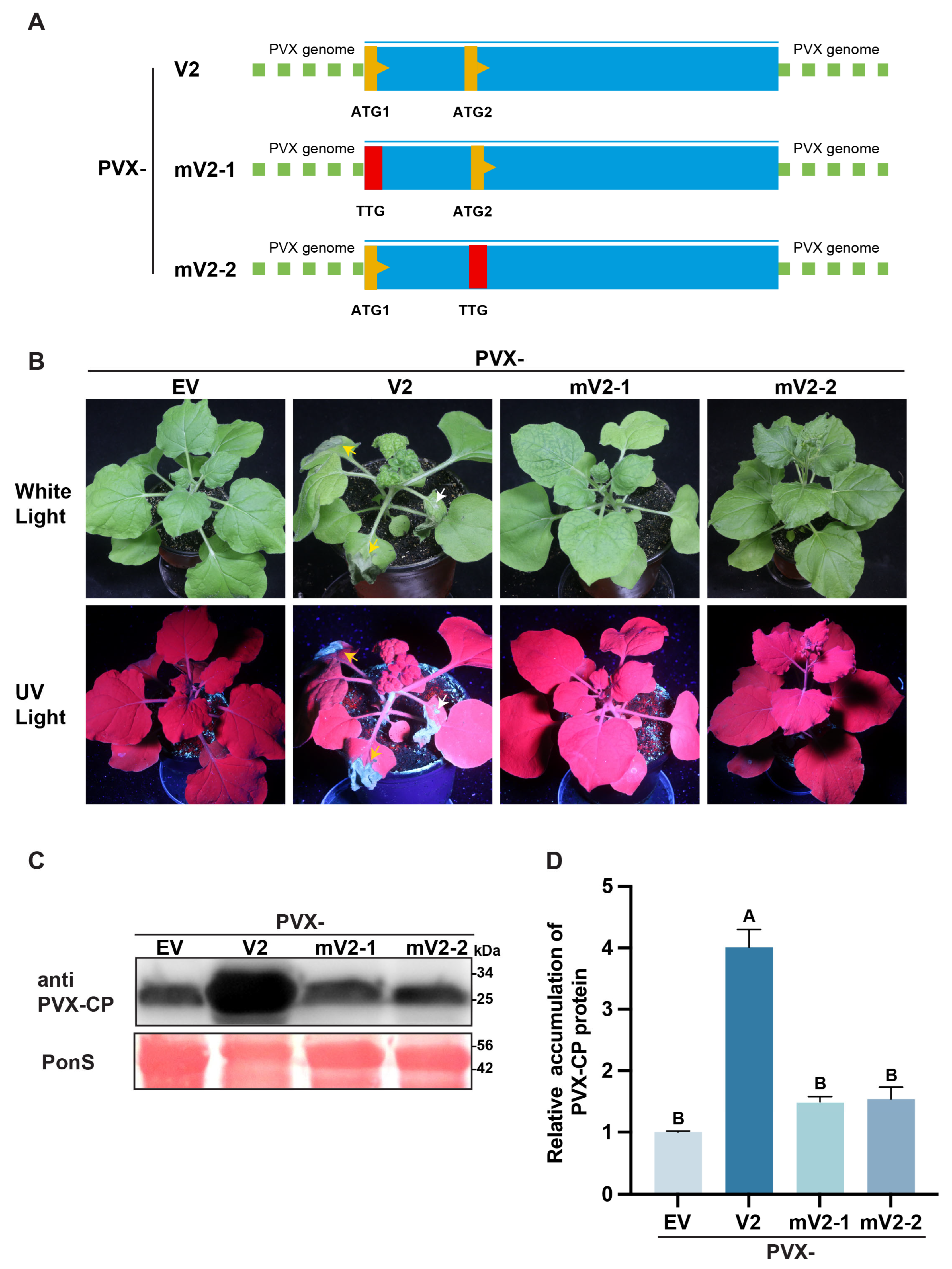
3.4. Dual ATG Mutations in the V2 Protein Compromise Its Ability to Potentiate Potato Virus X (PVX) Infection
3.5. Mutations at Both ATG Sites of the V2 Protein Attenuate Its Gene Silencing Suppression Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TYLCV | Tomato yellow leaf curl virus |
| ATG | Initiation codon |
| TGS | Transcriptional gene silencing |
| PTGS | Post-transcriptional gene silencing |
| CP | Coat protein |
| Rep | Replication-associated protein |
| TrAP | Transcription activator protein |
| REn | Replication enhancer protein |
| NSP | Nuclear shuttle protein |
| MP | Movement protein |
| MYMIV | mungbean yellow mosaic India virus |
| ALCScV | ageratum leaf curl Sichuan virus |
| TYLCCNB | tomato yellow leaf curl China betasatellite |
| RaLCB | radish leaf curl betasatellite |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| RSV | Rice streak virus |
| TSS | Transcription start site |
| PD | Plasmodesmata |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| TYLCTHV | Tomato yellow leaf curl Thailand virus |
| VSR | Viral suppressor of RNA silencing |
| SGS3 | Suppressor of gene silencing 3 |
| RDR6 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 6 |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| HDAs | Histone deacetylases |
| AGO4 | Argonaute 4 |
| ToLCCNV | Tomato leaf curl China virus |
| TIS | Translation initiation site |
| MCS | Multiple cloning site |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| TAE | Tris-acetate-EDTA buffer |
| SSC | Saline-sodium citrate buffer |
| DIG | Digoxigenin |
| dpi | Days post-inoculation |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| Y2H | Yeast two-hybrid |
| BiFC | Bimolecular fluorescence complementation |
| V2-1 | Full-length V2 isoform (initiated from ATG1) |
| V2-2 | Truncated V2 isoform (initiated from ATG2) |
| WT | Wild-type |
| mV2-1 | V2-1 isoform knockout mutant |
| mV2-2 | V2-2 isoform knockout mutant |
| PVX | Potato virus X |
| ssDNA | Single-stranded DNA |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded DNA |
| EB | Ethidium bromide |
| RbcL | Rubisco large subunit |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| A. tumefaciens | Agrobacterium tumefaciens |
| N. benthamiana | Nicotiana benthamiana |
| S. lycopersicum | Solanum lycopersicum |
Appendix A
| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| NbActin | F: AAGCTGCAGGTATCCATGAGACTA |
| R: CAATCCAGACACTGTACTTTCTCTC | |
| SlActin | F: AAAGACCAGCTCATCTGTTGAGAAG |
| R: GTGGTTTCATGAATACCAGCAGC | |
| TYLCV-DNA | F: CACGCCCGTCTCGAAG |
| R: CATAAGACTGGACTTTACATGGGC |
| Construct Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| pDonr221-TYLCV-V2-1 | F: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTAATGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTCCT |
| R: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTTGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG | |
| pDonr221-TYLCV-V2-2 | F: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTAATGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCG |
| R: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTTGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG | |
| pDonr221-TYLCVmV2-1 | F: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTATTGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTCCT |
| R: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTTGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG | |
| pDonr221-TYLCVmV2-2 | F: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTATTGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCG |
| R: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTTGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG | |
| 2 × 35S-TYLCV-V2-Flag | F: CTCAAGCTTCGAATTCCTGCAATGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: GTCCATGCCACCTCCGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTC | |
| 2 × 35S-TYLCV-mV2-1-Flag | F: CTCAAGCTTCGAATTCCTGCATTGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: GTCCATGCCACCTCCGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTC | |
| 2 × 35S-TYLCV-mV2-2-Flag | F: CTCAAGCTTCGAATTCCTGCATTGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: GTCCATGCCACCTCCGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTC | |
| PVX-TYLCV-V2 | F: GTCAGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATATGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: TAACCGTTCATCGGCGGTCGACTCAGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTG | |
| PVX-TYLCV-mV2-1 | F: GTCAGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATTTGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: TAACCGTTCATCGGCGGTCGACTCAGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTG | |
| PVX-TYLCV-mV2-2 | F: CAGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATTTGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCGTTG |
| R: TAACCGTTCATCGGCGGTCGACTCAGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTG | |
| pCambia2300-TYLCV-mV2-1 | F: CTTGCACTTTGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATT |
| R: ATCCCACAAAGTGCAAGACAAACTACTTGGGG | |
| pCambia2300-TYLCV-mV2-2 | F: CGGATTTCGTTGTTTGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCG |
| R: ACAAACAACGAAATCCGTGAACAGATTCAGGA | |
| pCAMBIA1300-N-3×HA-V2-1-YN | F: TGCCGGACTACGCGGGAATGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTC |
| R: CGCCCTTGCTCACCATACTAGTATTTAAATGGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGG | |
| pCAMBIA1300-N-3×HA-V2-2-YN | F: CATATGATGTGCCGGACTACGCGGGAATGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCGTTG |
| R: CGCCCTTGCTCACCATACTAGTATTTAAATGGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGG | |
| pCAMBIA1300-N-Flag-V2-1-YC | F: TGACAAGCTTGGAGGTGGGATGTGGGATCCACTTCTAAATGAATTTCC |
| R: GCCGTGGTTCATTCTGCAGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG | |
| pCAMBIA1300-N-Flag-V2-2-YC | F: GACAAGCTTGGAGGTGGGATGTTAGCTATTAAATATTTGCAGTCCGTTGAG |
| R: GCCGTGGTTCATTCTGCAGGGCTTCGATACATTCTGTATATTCTGGG |
Appendix B
| Virus Species | Acronym | GenBank Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| watermelon chlorotic stunt virus | WmCSV | AJ012081 |
| East African cassava mosaic Malawi virus | EACMMV | AJ006460 |
| East African cassava mosaic Zanzibar virus | EACMZV | AF422174 |
| eupatorium yellow vein virus | EpYVV/E | AB433979 |
| chilli leaf curl virus | ChiLCV/PK | AF336806 |
| chayote yellow mosaic virus | ChaYMV | AJ223191 |
| bhendi yellow vein mosaic virus | BYVMV/IN | AF241479 |
| ageratum yellow vein virus | AYVV/TW | AF307861 |
| ageratum yellow vein Sri Lanka virus | AYVSLV | AF314144 |
| tomato yellow leaf curl Thailand virus | TYLCTHV/D | AF206674 |
| tomato yellow leaf curl Malaga virus | TYLCMaV | AF271234 |
| tomato yellow leaf curl Kanchanaburi virus | TYLCKaV | AF511529; |
| tomato yellow leaf curl China virus | TYLCCNV/HH | AF311734 |
| tomato leaf curl Vietnam virus | ToLCVV | AF264063 |
| tomato leaf curl Malaysia virus | ToLCMYV/MY | AF327436 |
| tomato leaf curl Laos virus | ToLCLV | AF195782 |
| tomato leaf curl Sri Lanka virus | ToLCLKV | AF274349 |
| tomato leaf curl Bangalore virus | ToLCBaV/B | AF295401 |
| tomato curly stunt virus | ToCSV | AF261885 |
| tobacco leaf curl Zimbabwe virus | TbLCZV | AF350330 |
| sweet potato leaf curl Georgia virus | SPLCGV | AF326775 |
| squash leaf curl Yunnan virus | SLCuYV | AJ420319 |
| Sri Lankan cassava mosaic virus | SLCMV/LK | AJ314737 |
| squash leaf curl China virus | SLCCNV/CN | AF509743 |
| pepper leaf curl virus | PepLCV/MY | AF414287 |
| pepper leaf curl Bangladesh virus | PepLCBV/BD | AF314531 |
| papaya leaf curl virus | PaLCuV/PK | AJ436992 |
| fiageratum enation virus | AEV/NP | AJ437618 |
| tomato leaf curl Bangladesh virus | ToLCBV | AF188481 |
| tomato yellow leaf curl Indonesia virus | TYLCIDV | AF189018 |
| South African cassava mosaic virus | SACMV | AF155806 |
| cotton leaf curl Gezira virus | CLCuGeV/EG | AF155064 |
| pepper leaf curl virus | PepLCV/TH | AF134484 |
| East African cassava mosaic virus | EACMV/UG | AF126806 |
| mungbean yellow mosaic India virus | MYMIV | AF126406 |
| East African cassava mosaic Cameroon virus | EACMCMV | AF112354 |
| sweet potato leaf curl virus | SPLCV/US | AF104036 |
| tomato leaf curl virus | ToLCV/Sol | AF084006 |
References
- Wang, Y.; Pruitt, R.N.; Nürnberger, T.; Wang, Y. Evasion of Plant Immunity by Microbial Pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Castillo, J.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Emerging Virus Diseases Transmitted by Whiteflies. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 219–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.R.; Macedo, M.A.; Maliano, M.R.; Soto-Aguilar, M.; Souza, J.O.; Briddon, R.W.; Kenyon, L.; Rivera Bustamante, R.F.; Zerbini, F.M.; Adkins, S.; et al. World Management of Geminiviruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 637–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Pan, L.-L.; Liu, S.-S.; Navas-Castillo, J. Transmission of Begomoviruses and Other Whitefly-Borne Viruses: Dependence on the Vector Species. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Zerbini, F.M.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E.; Ramos-Sobrinho, R.; Silva, J.C.F.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Briddon, R.W.; Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Idris, A.; et al. Revision of Begomovirus Taxonomy Based on Pairwise Sequence Comparisons. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1593–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, E.P. A Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Justification for Three Genera of Geminiviridae. Arch. Virol. 1994, 139, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Lett, J.-M.; Martin, D.P.; Roumagnac, P.; Varsani, A.; Zerbini, F.M.; Navas-Castillo, J. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Geminiviridae 2021: This Article Is Part of the ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profiles Collection. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooma, W.; Petty, I.T.D. Tomato Golden Mosaic Virus Open Reading Frame Al4 Is Genetically Distinct from Its C4 Analogue in Monopartite Geminiviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunter, G.; Bisaro, D.M. Transactivation in a Geminivirus: AL2 Gene Product Is Needed for Coat Protein Expression. Virology 1991, 180, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondong, V.N. Geminivirus Protein Structure and Function. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufs, J. Geminivirus Replication: Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of Rep Protein Function, a Review. Biochimie 1995, 77, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.R.; Jiang, H.; Salati, R.; Xoconostle-Cázares, B.; Sudarshana, M.R.; Lucas, W.J.; Gilbertson, R.L. Functional Analysis of Proteins Involved in Movement of the Monopartite Begomovirus, Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Virology 2001, 291, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley-Bowdoin, L.; Settlage, S.B.; Orozco, B.M.; Nagar, S.; Robertson, D. Geminiviruses: Models for Plant DNA Replication, Transcription, and Cell Cycle Regulation. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 35, 105–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarowitz, S.G.; Beachy, R.N. Viral Movement Proteins as Probes for Intracellular and Intercellular Trafficking in Plants. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. Advances in Understanding Begomovirus Satellites. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, K.; Bedford, I.D.; Yahara, T.; Stanley, J. The Earliest Recorded Plant Virus Disease. Nature 2003, 422, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, M.W.; Mao, Y.; Storz, G.; Qian, S.-B. Alternative ORFs and Small ORFs: Shedding Light on the Dark Proteome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, X.; Huang, C.; Gu, Z.; Cao, L.; Hu, T.; Ding, M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. The AC 5 Protein Encoded by Mungbean Yellow Mosaic India Virus Is a Pathogenicity Determinant That Suppresses RNA Silencing-based Antiviral Defenses. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Su, F.; Meng, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, G.; Li, M.; Qing, L. The C5 Protein Encoded by Ageratum Leaf Curl Sichuan Virus Is a Virulence Factor and Contributes to the Virus Infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Functional Analysis of a Novel βV1 Gene Identified in a Geminivirus Betasatellite. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Reddy, K.; Gnanasekaran, P.; Zhai, Y.; Chakraborty, S.; Pappu, H.R. Functional Characterization of a New ORF βV1 Encoded by Radish Leaf Curl Betasatellite. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 972386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Sharma, N.; Hari-Gowthem, G.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Prasad, M. Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus: Impact, Challenges, and Management. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Qiu, P.; Jin, J.; Liu, S.; Ul Islam, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Kormelink, R.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z. The Cap Snatching of Segmented Negative Sense RNA Viruses as a Tool to Map the Transcription Start Sites of Heterologous Co-Infecting Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Chang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus V3 Protein Traffics along Microfilaments to Plasmodesmata to Promote Virus Cell-to-Cell Movement. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Tan, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rong, J.; Fu, X.; Lozano-Durán, R.; et al. Geminiviruses Encode Additional Small Proteins with Specific Subcellular Localizations and Virulence Function. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Gong, P.; Ren, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. The Novel C5 Protein from Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus Is a Virulence Factor and Suppressor of Gene Silencing. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Gong, P.; Zhang, M.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Yan, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, F. Functional Identification of a Novel C7 Protein of Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Virology 2023, 585, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Ingolia, N.T. Ribosome Profiling as a Tool to Decipher Viral Complexity. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2015, 2, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-W.; Li, Y.-R.; Lin, C.-Y.; Yeh, H.-H.; Liu, M.-J. Translation Initiation Landscape Profiling Reveals Hidden Open-Reading Frames Required for the Pathogenesis of Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Thailand Virus. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1804–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley-Bowdoin, L.; Bejarano, E.R.; Robertson, D.; Mansoor, S. Geminiviruses: Masters at Redirecting and Reprogramming Plant Processes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima Priyadarshini, C.G.; Ambika, M.V.; Tippeswamy, R.; Savithri, H.S. Functional Characterization of Coat Protein and V2 Involved in Cell to Cell Movement of Cotton Leaf Curl Kokhran Virus-Dabawali. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, A.P.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Morilla, G.; Wang, L.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Castillo, A.G.; Bejarano, E.R. V2 from a Curtovirus Is a Suppressor of Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, E.; Zrachya, A.; Levy, Y.; Mett, A.; Gidoni, D.; Belausov, E.; Citovsky, V.; Gafni, Y. Interaction with Host SGS3 Is Required for Suppression of RNA Silencing by Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus V2 Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.-K.; Lozano-Duran, R. A Virus-Encoded Protein Suppresses Methylation of the Viral Genome through Its Interaction with AGO4 in the Cajal Body. Elife 2020, 9, e55542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus V2 Interacts with Host Histone Deacetylase 6 To Suppress Methylation-Mediated Transcriptional Gene Silencing in Plants. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00036-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Ismayil, A.; Yuan, Y.; Lian, B.; Jia, Q.; Han, M.; Deng, H.; Hong, Y.; et al. Geminiviral V2 Protein Suppresses Transcriptional Gene Silencing through Interaction with AGO4. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01675-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D.C. The Role of Viruses in Identifying and Analyzing RNA Silencing. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2022, 9, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lu, R.; Lau, N.; Lai, E.C.; Li, W.-X.; Ding, S.-W. Virus Discovery by Deep Sequencing and Assembly of Virus-Derived Small Silencing RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlotshwa, S.; Pruss, G.J.; Vance, V. Small RNAs in Viral Infection and Host Defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. SGS3 Cooperates with RDR6 in Triggering Geminivirus-Induced Gene Silencing and in Suppressing Geminivirus Infection in Nicotiana benthamiana. Viruses 2017, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Iki, T.; Tsutsui, Y.; Miyashita, K.; Poethig, R.S.; Habu, Y.; Ishikawa, M. 3′ Fragment of miR173-Programmed RISC-Cleaved RNA Is Protected from Degradation in a Complex with RISC and SGS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4117–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakura, N.; Takeda, A.; Fujioka, Y.; Motose, H.; Takano, R.; Watanabe, Y. SGS3 and RDR6 Interact and Colocalize in Cytoplasmic SGS3/RDR6-Bodies. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Gong, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Zhou, X.; Li, F. Geminivirus C5 Proteins Mediate Formation of Virus Complexes at Plasmodesmata for Viral Intercellular Movement. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Ismayil, A.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Gu, H.; Ludman, M.; Fátyol, K.; et al. A Calmodulin-Binding Transcription Factor Links Calcium Signaling to Antiviral RNAi Defense in Plants. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1393–1406.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-X.; Shang, H.-L.; Xie, Y.; Shen, Q.-T.; Zhou, X.-P. Monoclonal Antibodies against the Whitefly-Transmitted Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus and Their Application in Virus Detection. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, X. Production and application of monoclonal antibodies against Potato virus X. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2005, 31, 608–612. [Google Scholar]
- Machkovech, H.M.; Bloom, J.D.; Subramaniam, A.R. Comprehensive Profiling of Translation Initiation in Influenza Virus Infected Cells. PLOS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creixell, P.; Schoof, E.M.; Tan, C.S.H.; Linding, R. Mutational Properties of Amino Acid Residues: Implications for Evolvability of Phosphorylatable Residues. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrachya, A.; Glick, E.; Levy, Y.; Arazi, T.; Citovsky, V.; Gafni, Y. Suppressor of RNA Silencing Encoded by Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus-Israel. Virology 2007, 358, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ikegami, M. Tomato Leaf Curl Java Virus V2 Protein Is a Determinant of Virulence, Hypersensitive Response and Suppression of Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing. Virology 2010, 396, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.P.; Morilla, G.; Voinnet, O.; Bejarano, E.R. Functional Analysis of Gene-Silencing Suppressors from Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Disease Viruses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jia, M.; Wang, A. Hidden Viral Proteins: How Powerful Are They? PLOS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1011905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, A.M.; Lukhovitskaya, N.I.; Olendraite, I.; Firth, A.E. A Case for a Negative-Strand Coding Sequence in a Group of Positive-Sense RNA Viruses. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, A.E.; Brierley, I. Non-Canonical Translation in RNA Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1385–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallack, H.; Popova, K.D.; Laurie, M.T.; Sunshine, S.; DeRisi, J.L. Persistence of Ambigrammatic Narnaviruses Requires Translation of the Reverse Open Reading Frame. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhao, M.; Qi, T.; Guo, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhan, G.; Kang, Z.; Zheng, L. A Novel Ambigrammatic Mycovirus, PsV5, Works Hand in Glove with Wheat Stripe Rust Fungus to Facilitate Infection. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, X.; Li, F. Targeting of viral RNAs by nonsense-mediated decay is compromised by virus–plant interactions. New Plant Prot. 2024, 1, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Li, F.; Zhou, X.; Lozano-Durán, R. New Genes on the Block: Additional Open Reading Frames in the Genomes of Geminiviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lozano-Duran, R.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X. Identification of a Novel C6 Protein Encoded by Tomato Leaf Curl China Virus. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Gong, P.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. Functional Characterization of Dual-Initiation Codon-Derived V2 Proteins in Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071726
Wang Z, Gong P, Zhao S, Li F, Zhou X. Functional Characterization of Dual-Initiation Codon-Derived V2 Proteins in Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071726
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiyuan, Pan Gong, Siwen Zhao, Fangfang Li, and Xueping Zhou. 2025. "Functional Characterization of Dual-Initiation Codon-Derived V2 Proteins in Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071726
APA StyleWang, Z., Gong, P., Zhao, S., Li, F., & Zhou, X. (2025). Functional Characterization of Dual-Initiation Codon-Derived V2 Proteins in Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Agronomy, 15(7), 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071726





