Technological Parameter Optimization of Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding and Its Application in Rice Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
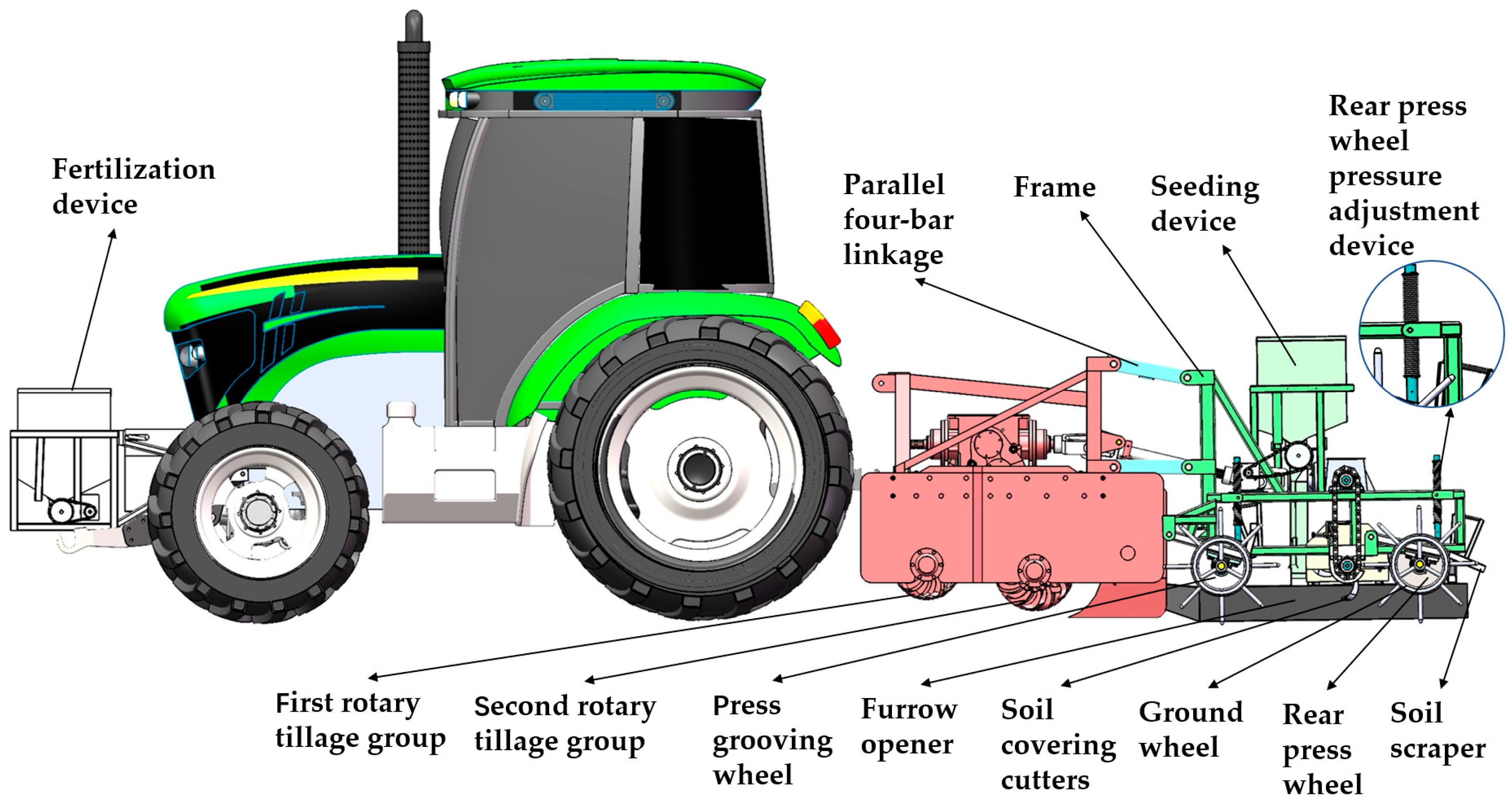
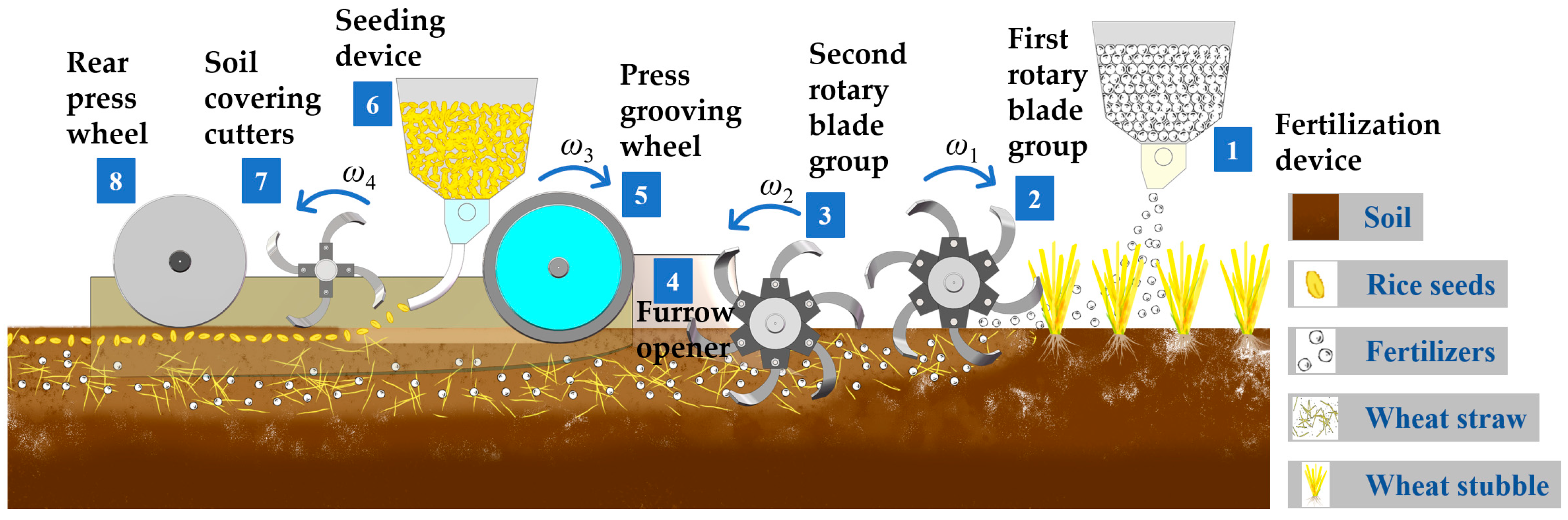
2.1. Design of the Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding Machine
2.2. Simulation Design
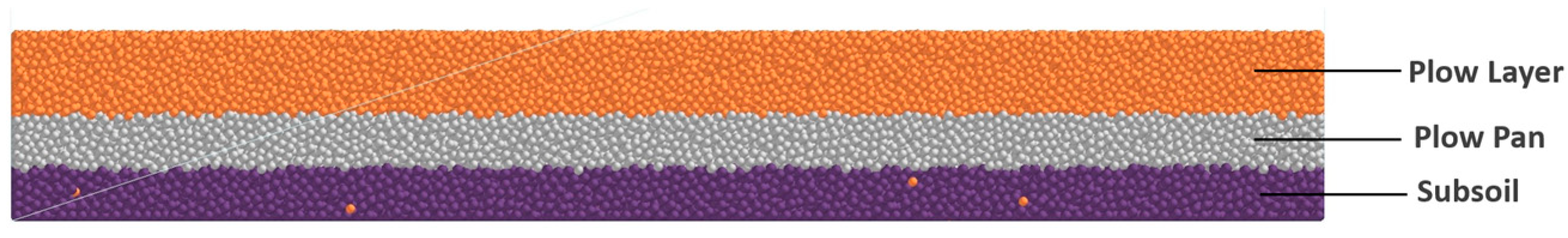
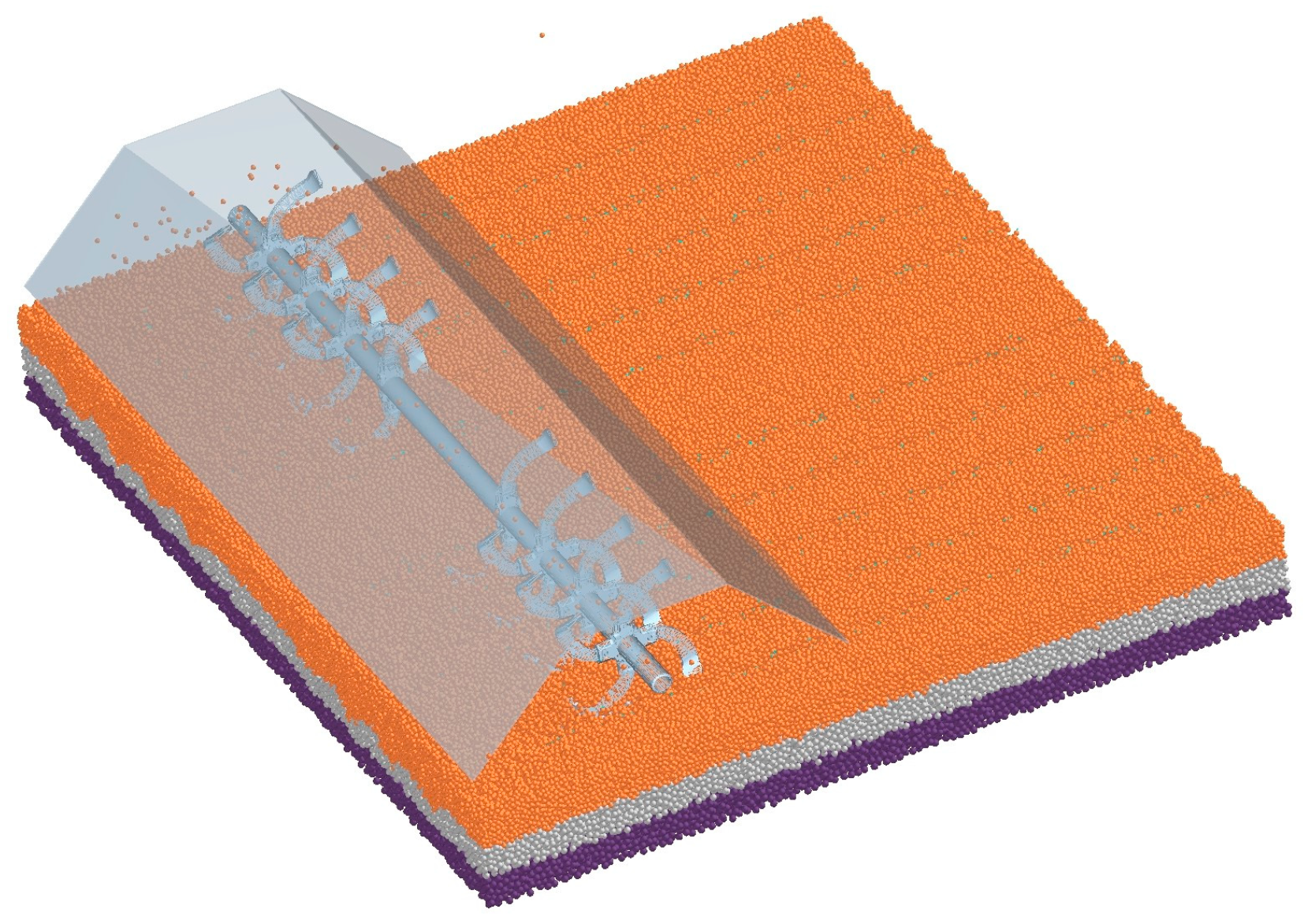
2.2.1. Simulation Model Development
2.2.2. Simulation Experiment Methodology
2.3. Field Experiment
2.3.1. Experimental Design
- (1)
- DPDS (S1): Integrated machine performing basal fertilization, dual-axis rotary tillage (20 cm depth), grooving, depth-controlled seeding (3 cm depth, 25 cm row spacing), soil covering (1.0–1.5 cm), and compaction. Seeding rate: 105 kg∙hm−2; compaction pressure: 60 kPa. Sown in early June annually; seedlings thinned to uniform density at three-leaf stage.
- (2)
- Conventional dry direct seeding (S2): Fertilization via broadcast spreader, stubble incorporation via reverse rotary tiller, seeding via 7.5 cm precision seeder (1 cm depth, 25 cm row spacing, 105 kg∙hm−2), followed by light compaction (60 kPa). Sowing and thinning timing matched S1.
- (3)
- Mechanical transplanting (S3): Nursery trays (60 cm × 30 cm) sown at 120 g/tray around May 25 annually. Transplanting specifications were set at 30 cm row spacing and 11 cm hill spacing, achieving a planting density of 303,000 hills per hectare with 4 seedlings retained per hill. On the 7th day after transplanting, seedling inspection and gap filling were conducted to ensure uniform seedling distribution.
2.3.2. Measurement Indicators and Methods
- (1)
- Seeding performance indicators
- (2)
- Yield and components
- (3)
- Stem and Tiller Dynamics and Spike Rate
3. Results and Discussion
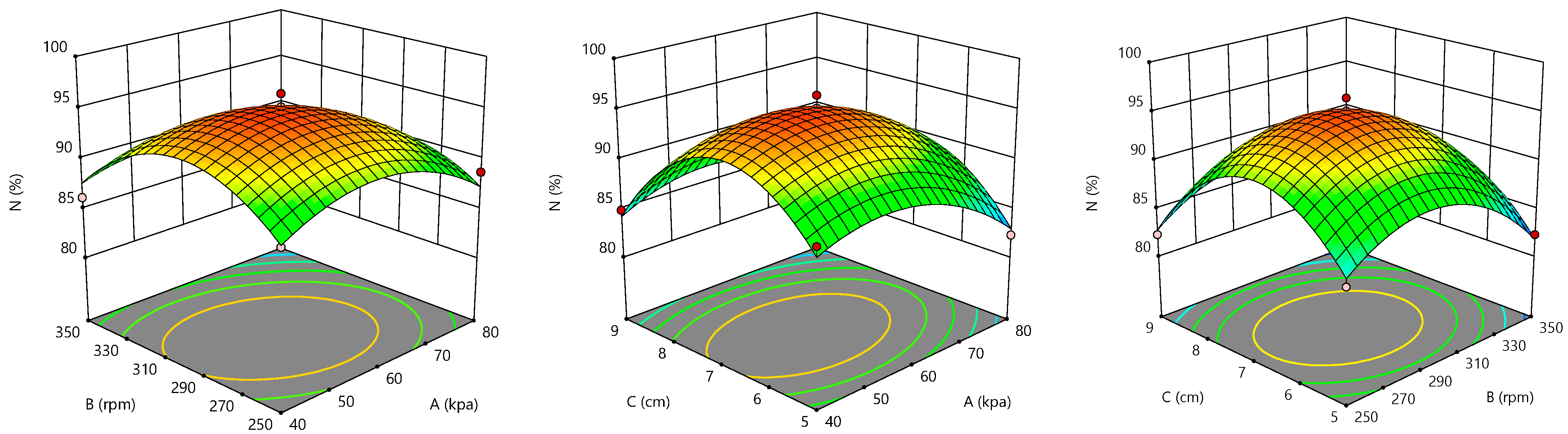
3.1. Simulation Results for Operational Parameter Optimization
3.2. Field Experiment Results
3.2.1. Seeding Performance Comparison
3.2.2. Rice Yield and Components Under Different Planting Methods
3.2.3. Tiller Dynamics and Productive Tiller Rate
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chai, X.; Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Nutritional Characteristics, Feed Utilization Status and Limiting Factors of Aged Brown Rice. Agriculture 2024, 14, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, K.; Sanjay, S.R.; Chauhan, B.S. Weed Management in Dry Direct-Seeded Rice: A Review on Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Rice Production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Kaur, R.; Das, T.K.; Raj, R.; Shivay, Y.S. Impacts of herbicides on weeds, water productivity, and nutrient-use efficiency in dry direct-seeded rice. Paddy Water Environ. 2021, 19, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Nie, L. Energy assessment of different rice–wheat rotation systems. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wu, W.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Luo, S.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, Y. The impact on Cd bioavailability and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by dry direct-seeding cultivation method in field-scale experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 172875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Y.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Design and testing of planting unit for rice dry-direct-seeding planter in cold region. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jiang, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Melatonin Alleviates Low-Temperature Stress via ABI5-Mediated Signals During Seed Germination in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abera, B.B.; Senthilkumar, K.; Cotter, M.; Asch, F. Transplanting as an option to cope with abiotic stress in high-altitude lowland rice production systems in East Africa. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 208, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Liao, P.; Wei, H.; et al. Differences in rice yield and biomass accumulation dynamics for different direct seeding methods after wheat straw return. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Design and Experimental Study on Compaction Mechanism for Dry Land Rice Direct Seeder. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, M.; Lan, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z. Design and experiments of the key components for centralized pneumatic rice dry direct seeding machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Zang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Pei, J.; He, S.; Xu, P.; Liu, S. Design and parameter optimization of rice pneumatic seeding metering device with adjustable seeding rate. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Jiang, M.; Nie, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Man, J. A preliminary study of ‘Tidy Field Technology’ to assess growth, development and weed control in direct-seeded rice. Field Crops Res. 2022, 277, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.A.; Hossain, M.I.; Gathala, M.K.; Timsina, J.; Krupnik, T.J. Optimal design and setting of rotary strip-tiller blades to intensify dry season cropping in Asian wet clay soil conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, M. A compacting device of rice dry direct-seeding planter based on DEM-MFBD coupling simulation significantly improves the seedbed uniformity and seedling emergence rate. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 246, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Suab, S.A.; Chen, X.; Singh, C.K.; Singh, D.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Korom, A.; Widyatmanti, W.; Mollah, T.H.; Minh, H.V.T.; et al. Enhancing assessment of corn growth performance using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and deep learning. Measurement 2023, 214, 112764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Ji, J. Determination of Discrete Element Modelling Parameters of a Paddy Soil with a High Moisture Content (>40%). Agriculture 2022, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Jing, H.; Zhong, X. Modeling the interaction of soil and a vibrating subsoiler using the discrete element method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, M.; Tekeste, M. Wheat straw direct shear simulation using discrete element method of fibrous bonded model. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 213, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Gu, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R. Design and experiment of no-tube seeder for wheat sowing. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Gao, W.; Gu, C.; Shi, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, R. Optimisation of no-tube seeding and its application in rice planting. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 210, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gu, F.; Hu, Z.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Luo, W. Analysis and Evaluation of Influencing Factors on Uniform Sowing of Wheat with Wide Seed Belt after Sowing and Soil Throwing Device. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torotwa, I.; Ding, Q.; Makange, N.R.; Liang, L.; He, R. Performance evaluation of a biomimetically designed disc for dense-straw mulched conservation tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7256-1:1984; Sowing Equipment—Test Methods—Part 1: Single Seed Drills (Precision Drills). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1984. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/13910.html (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Wang, W.; Du, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Effects of different mechanical direct seeding methods on grain yield and lodging resistance of early indica rice in South China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Mchugh, A.D.; Wu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Xiong, T.; Ling, D.; Tang, Q.; Liao, M.; et al. Development and performance evaluation of a wet-resistant strip-till seeder for sowing wheat following rice. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 220, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y. Seeding Unit Test Research Based on Precise Seeding Depth Control Target of Wheat After Rice. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xi, X.; Weng, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Effects of a Novel Weeding and Fertilization Scheme on Yield and Quality of Rice. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Tian, J.; Xing, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Guo, B.; et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer in whole growth duration applied in the middleand late tillering stage on yield and quality of dry direct seeding rice under “solo-stalk” cultivation mode. Acta Agron. Sin. 2021, 47, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Xing, Z.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; et al. Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems. Agronomy 2023, 12, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, M.; He, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; et al. Responses of Yield and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Rice to Climate Resources under Different Crop Rotation Patterns and Planting Methods. Plants 2024, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Tian, J.; Cheng, S.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Guo, B.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Effects of mechanical dry direct seeding ways on rice yield and photosynthetic material production characteristics. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Tian, J.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, B.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H. Effects of one-time nitrogen basal application on the yield and quality of different direct-seeding rice crops by machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tan, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, Y. Effects of Different Mechanical Direct Seeding Patterns on Yield and Lodging Resistance of High-Quality Late indica Rice in South China. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2020, 34, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Category | Coefficient of Restitution | Static Friction Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Plow layer–plow layer | 0.35 | 0.29 |
| Plow pan–plow pan | 0.35 | 0.32 |
| Subsoil–subsoil | 0.40 | 0.25 |
| Inter-layer | 0.3 | 0.50 |
| Rice–tillage components | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Soil–rice | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Soil–tillage components | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Level | Test Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compaction Force (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Soil Engagement Depth (cm) | |
| 1 | 40 | 250 | 5 |
| 2 | 60 | 300 | 7 |
| 3 | 80 | 350 | 9 |
| Test No. | Factor | N (%) | M (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (kPa) | B (rpm) | C (cm) | |||
| 1 | 60 | 250 | 9 | 88.72 | 5.14 |
| 2 | 80 | 300 | 9 | 82.29 | 2.57 |
| 3 | 60 | 300 | 7 | 94.81 | 1.29 |
| 4 | 40 | 300 | 9 | 88.72 | 5.14 |
| 5 | 80 | 300 | 5 | 82.29 | 7.71 |
| 6 | 60 | 300 | 7 | 95.15 | 0 |
| 7 | 60 | 300 | 7 | 94.81 | 1.29 |
| 8 | 40 | 350 | 7 | 86.15 | 7.71 |
| 9 | 40 | 250 | 7 | 88.72 | 9.00 |
| 10 | 80 | 250 | 7 | 88.72 | 5.14 |
| 11 | 60 | 300 | 7 | 94.81 | 1.29 |
| 12 | 60 | 300 | 7 | 94.81 | 1.29 |
| 13 | 80 | 350 | 7 | 84.87 | 5.14 |
| 14 | 40 | 300 | 5 | 84.87 | 9.00 |
| 15 | 60 | 350 | 9 | 81.01 | 2.57 |
| 16 | 60 | 250 | 5 | 84.87 | 7.71 |
| 17 | 60 | 350 | 5 | 82.29 | 7.71 |
| Source | N | M | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Square | Mean Square Sum | F | p | Mean Square | Mean Square Sum | F | p | |
| Model | 500.69 | 55.63 | 36.59 | <0.0001 | 149.10 | 16.57 | 45.13 | <0.0001 |
| A | 25.03 | 25.03 | 16.46 | 0.0048 | 13.24 | 13.24 | 36.05 | 0.0005 |
| B | 20.67 | 20.67 | 13.6 | 0.0078 | 1.86 | 1.87 | 5.07 | 0.0590 |
| C | 10.1 | 10.1 | 6.64 | 0.0366 | 34.90 | 34.90 | 95.08 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 3.72 | 3.72 | 2.45 | 0.1615 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 1.13 | 0.3224 |
| AC | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.09 | 0.3320 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 1.12 | 0.3259 |
| BC | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.6144 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 4.50 | 0.0716 |
| A2 | 53.43 | 53.43 | 35.14 | 0.0006 | 38.38 | 38.38 | 104.54 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 112.53 | 112.53 | 74.01 | <0.0001 | 30.62 | 30.62 | 83.40 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 231.64 | 231.64 | 152.34 | <0.0001 | 17.76 | 17.77 | 48.39 | 0.0002 |
| Residual | 10.64 | 1.52 | 2.57 | 0.37 | ||||
| Anomalistic term | 8.67 | 2.89 | 5.86 | 0.0602 | 1.24 | 0.41 | 1.24 | 0.4054 |
| Pure error | 1.97 | 0.5 | 1.33 | 0.33 | ||||
| Performance Indicator (Mean) | DPDS Machine | Conventional Dry Seeding |
|---|---|---|
| Sowing uniformity (%) | 85.01 ± 0.25 | 79.04 ± 0.21 |
| Qualified seeding depth (%) | 94.24 ± 0. 18 | 85.32 ± 0.20 |
| Missed seeding rate (%) | 2.31 ± 0.13 | 4.56 ± 0.17 |
| Year | Method | Panicle Number (×104 hm−2) | No. of Grains per Panicle | Seed-Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | S1 | 396.18 ± 0.26 b | 113.81 ± 0.15 b | 91.80 ± 0.11 b | 25.15 ± 0.11 b | 10.02 ± 0.26 b |
| S2 | 402.39 ± 0.18 a | 103.95 ± 0.23 c | 89.80 ± 0.21 c | 24.85 ± 0.31 b | 9.25 ± 0.39 c | |
| S3 | 361.15 ± 0.34 c | 122.60 ± 0.28 a | 93.38 ± 0.28 a | 25.30 ± 0.23 a | 10.35 ± 0.21 a | |
| 2023 | S1 | 400.00 ± 0.35 b | 114.10 ± 0.11 b | 92.05 ± 0.09 b | 25.19 ± 0.27 b | 10.43 ± 0.35 b |
| S2 | 415.17 ± 0.12 a | 101.77± 0.16 c | 90.06 ± 0.16 c | 25.15 ± 0.29 b | 9.57 ± 0.47 c | |
| S3 | 363.17 ± 0.16 c | 127.41 ± 0.35 a | 93.27 ± 0.32 a | 25.41 ± 0.37 a | 10.96 ± 0.31 a | |
| 2024 | S1 | 401.40 ± 0.09 b | 109.80 ± 0.29 b | 92.80 ± 0.45 b | 24.95 ± 0.28 b | 10.25 ± 0.25 b |
| S2 | 410.44 ± 0.25 a | 101.50 ± 0.31 c | 89.11 ± 0.26 c | 25.05 ± 0.19 b | 9.39 ± 0.20 c | |
| S3 | 361.55 ± 0.27 c | 123.22± 0.09 a | 94.00 ± 0.24 a | 25.15 ± 0.13 a | 10.65 ± 0.25 a | |
| Av. | S1 | 397.82 | 112.57 | 92.22 | 25.10 | 10.11 |
| S2 | 408.15 | 102.41 | 89.99 | 25.02 | 9.33 | |
| S3 | 363.29 | 124.08 | 93.55 | 25.29 | 10.79 |
| Year | Method | No. of Stems and Tillers/(×104 hm−2) | Percentage of Productive Tillers (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jointing | Heading | Maturity | |||
| 2022 | S1 | 513.25 ± 0.31 b | 413 ± 0.26 b | 371 ± 0.37 b | 77.74 ± 0.23 b |
| S2 | 535.74 ± 0.17 a | 452 ± 0.13 a | 385 ± 0.23 a | 74.86 ± 0.26 c | |
| S3 | 455.71 ± 0.33 c | 361 ± 0.41 c | 355 ± 0.19 c | 78.94 ± 0.21 a | |
| 2023 | S1 | 553.63 ± 0.25 b | 416.04 ± 0.15 b | 397.58 ± 0.27 b | 72.58 ± 0.25 b |
| S2 | 601.36 ± 0.14 a | 432.69 ± 0.23 a | 409.24 ± 0.24 a | 69.04 ± 0.21 c | |
| S3 | 469.96 ± 0.32 c | 378.69 ± 0.10 c | 357.43 ± 0.12 c | 77.28 ± 0.19 a | |
| 2024 | S1 | 551.42 ± 0.43 b | 409.14 ± 0.29 b | 386.11 ± 0.15 b | 73.05 ± 0.28 b |
| S2 | 587.71 ± 0.38 a | 435.09 ± 0.17 a | 399.28 ± 0.08 a | 69.59 ± 0.26 c | |
| S3 | 463.31 ± 0.17 c | 375.69 ± 0.25 c | 354.28 ± 0.17 c | 77.70 ± 0.25 a | |
| Av. | S1 | 539.43 | 412.73 | 384.90 | 74.46 |
| S2 | 574.94 | 439.93 | 397.84 | 71.16 | |
| S3 | 462.99 | 371.79 | 355.57 | 77.97 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Shen, X.; Cheng, X.; Xu, J.; Hong, J.; Han, L.; Xi, X.; Zhang, R. Technological Parameter Optimization of Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding and Its Application in Rice Production. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071704
Shi Y, Shen X, Cheng X, Xu J, Hong J, Han L, Xi X, Zhang R. Technological Parameter Optimization of Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding and Its Application in Rice Production. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071704
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yangjie, Xingye Shen, Xinhui Cheng, Jintao Xu, Jiawang Hong, Lianjie Han, Xiaobo Xi, and Ruihong Zhang. 2025. "Technological Parameter Optimization of Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding and Its Application in Rice Production" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071704
APA StyleShi, Y., Shen, X., Cheng, X., Xu, J., Hong, J., Han, L., Xi, X., & Zhang, R. (2025). Technological Parameter Optimization of Double-Press Precision Depth-Control Seeding and Its Application in Rice Production. Agronomy, 15(7), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071704








