Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Contrasting Rapeseed Cultivars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Biomass and Estimation of Plant Major and Micro Mineral
2.2. The Analysis of the Fast Chlorophyll Fluorescence Rise Curve Through Its O, J, I, and P Steps (OJIP) and Gas Exchange Parameter Measurements
2.3. Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis and RT-qPCR Analysis
2.3.1. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.3.2. Read Processing, Alignment, and Quantification
2.3.3. Differential Expression Analysis
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Metabolomics Data Analysis and Processing of Rapeseed Plants
2.5.1. Metabolite Extraction
2.5.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5.3. Data Processing and Metabolite Identification
2.5.4. Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cr Induced Reduction in Plants Growth and Cr Content
3.2. Gas Exchange Parameters, Chlorophyll Fluorescence and PSII Efficiency Under Cr Stress
3.3. Mineral Nutrient Profile
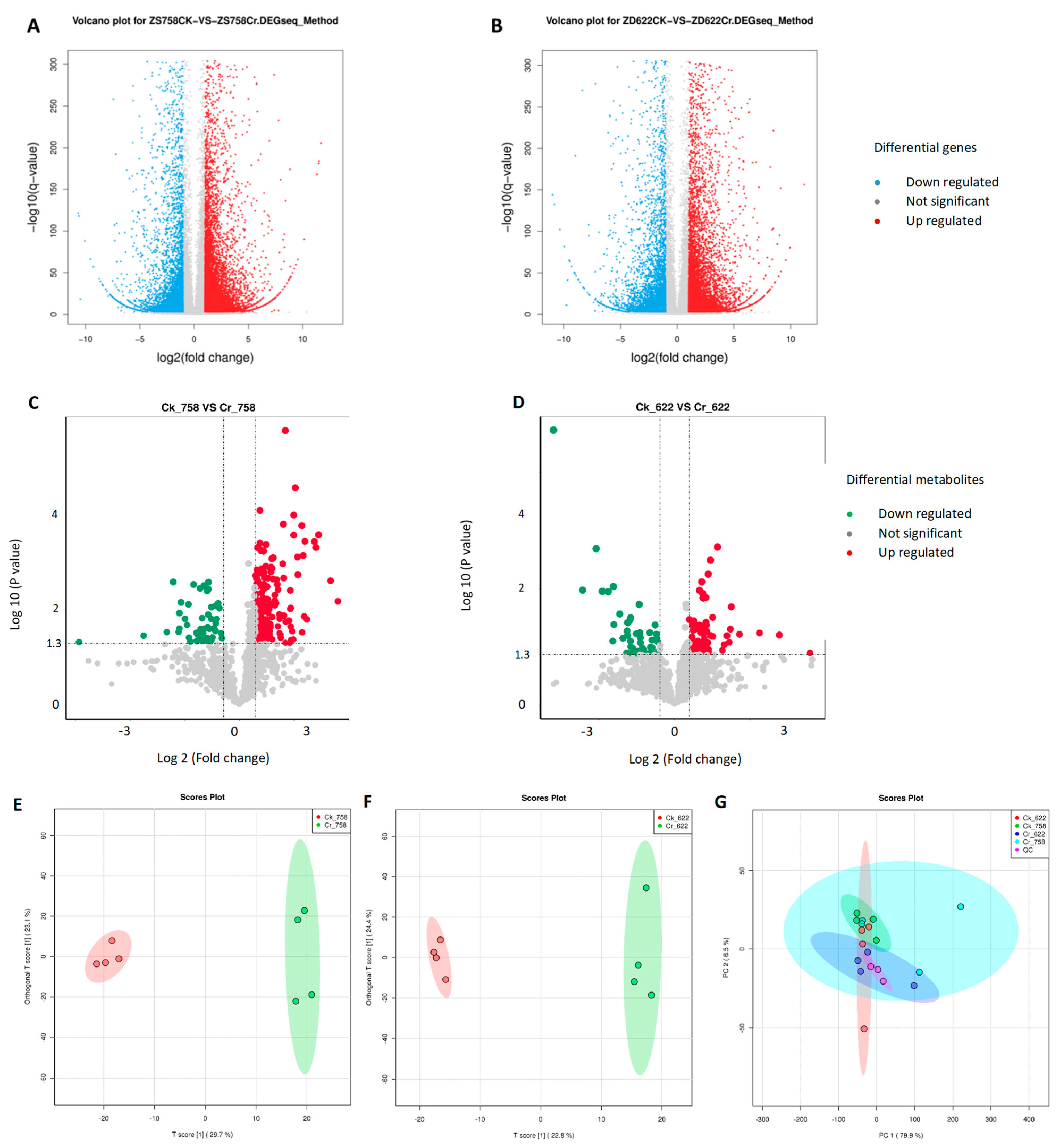
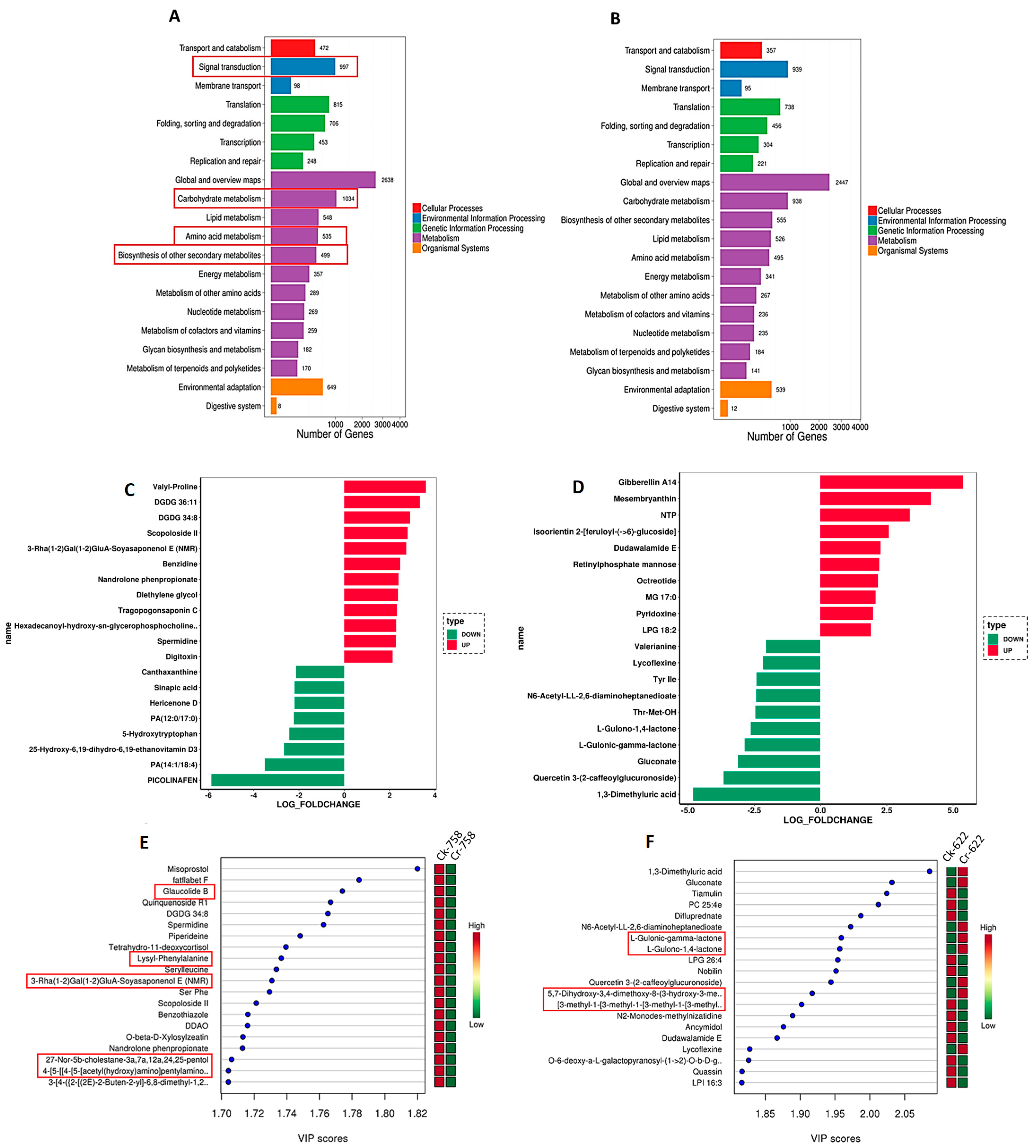
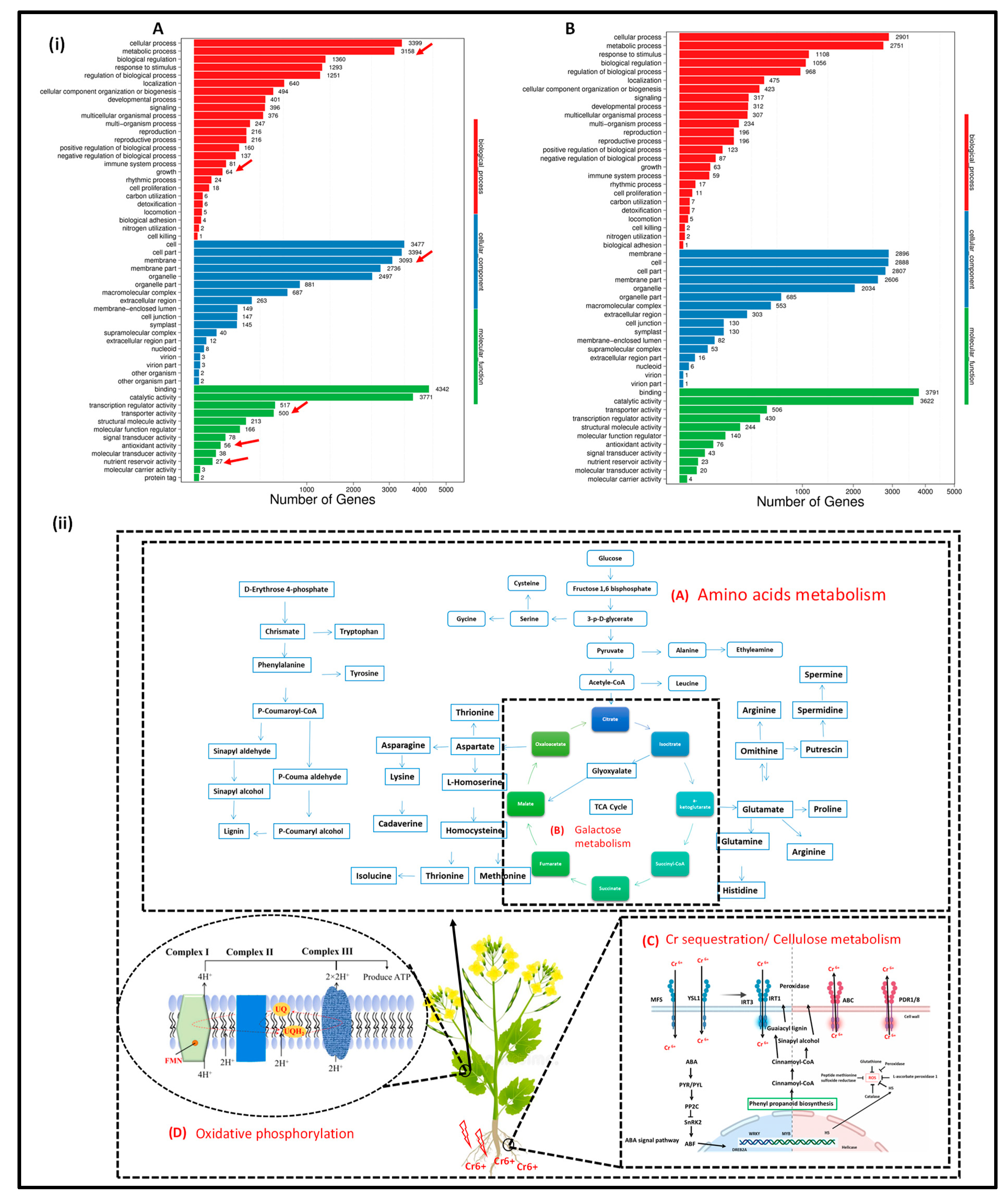
3.4. Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis and DEGs Identification and Metabolomics Profile
3.4.1. Assembly of Transcriptome Data
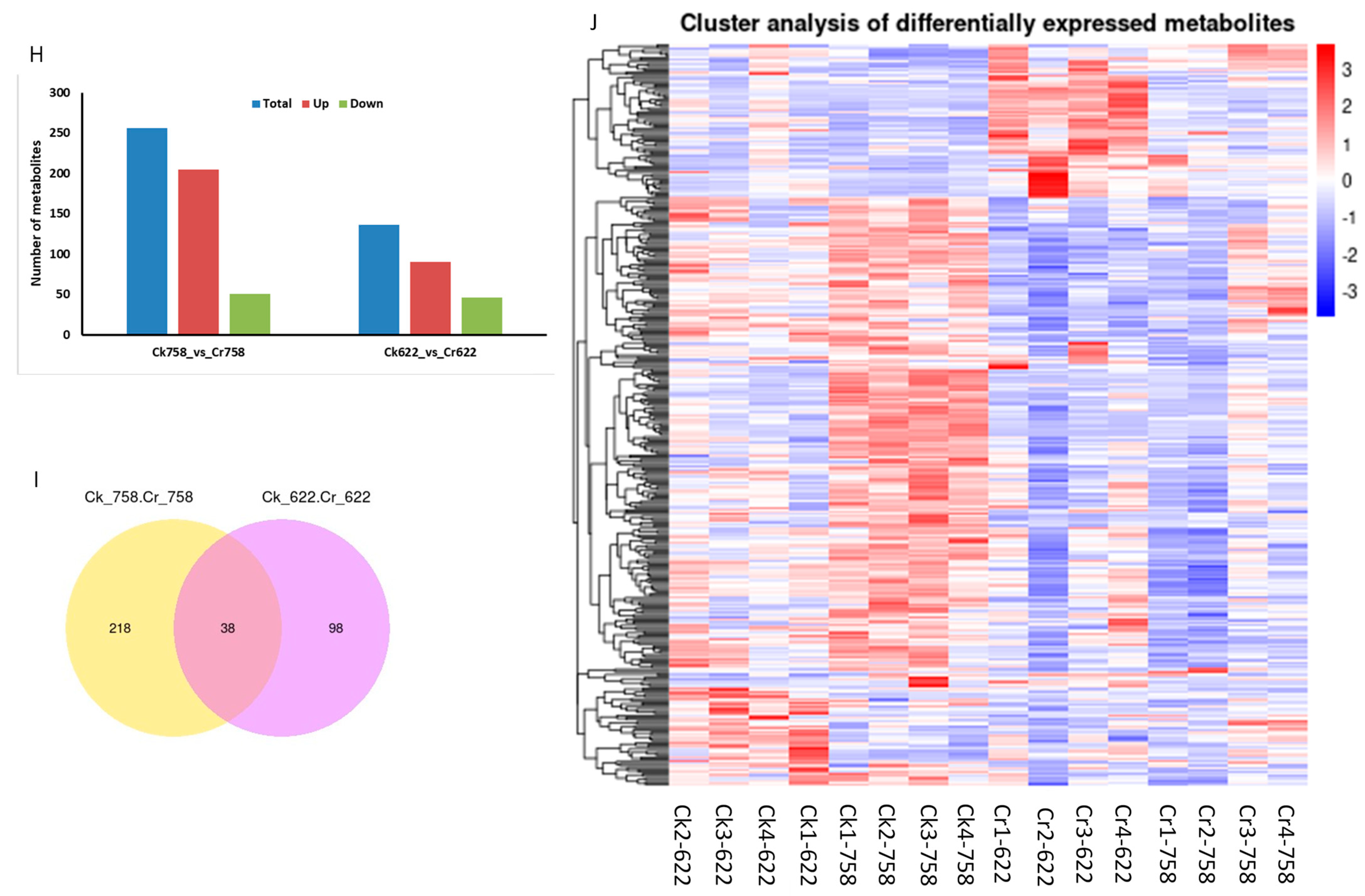
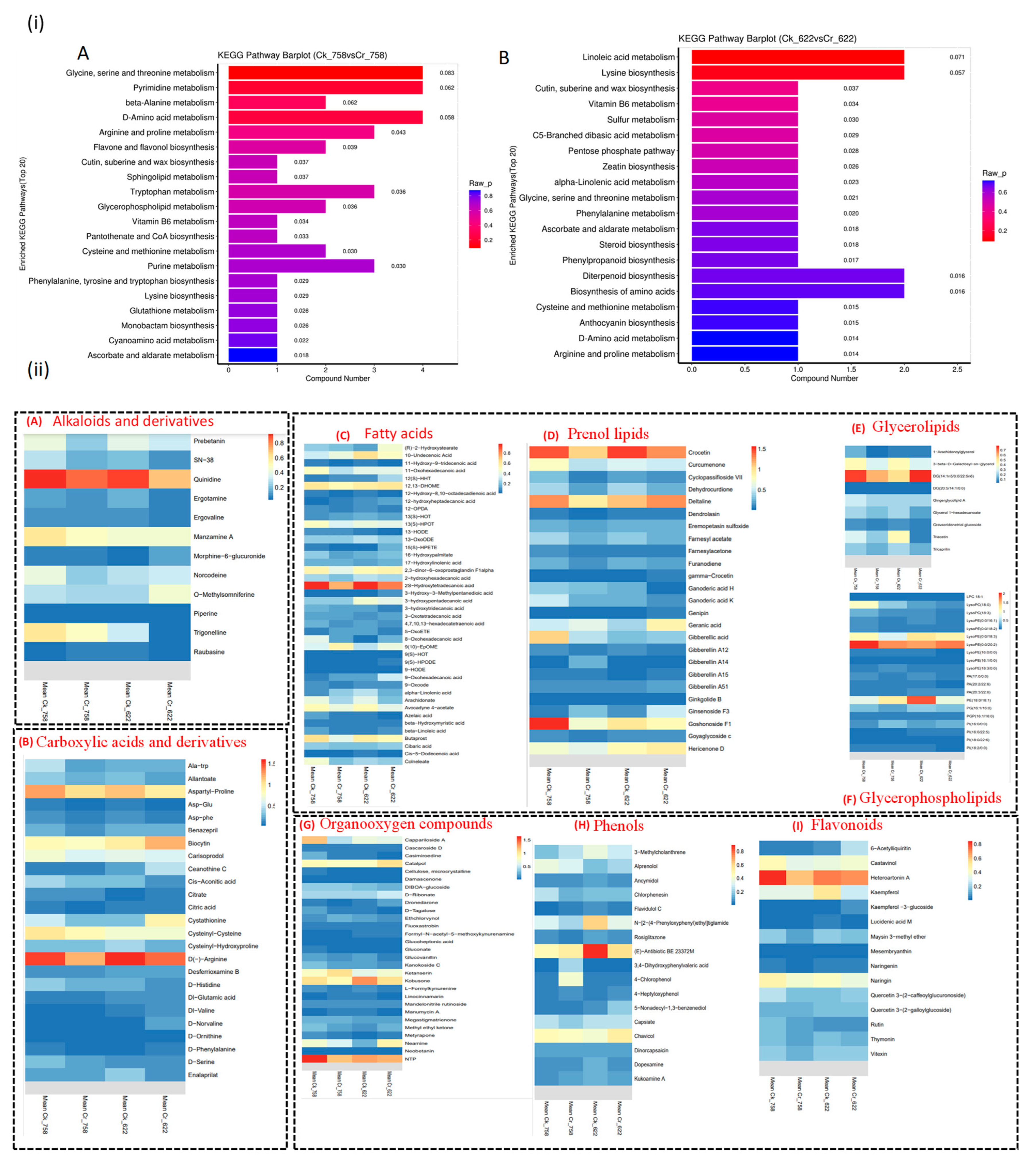
3.4.2. Metabolomics Profile Analysis
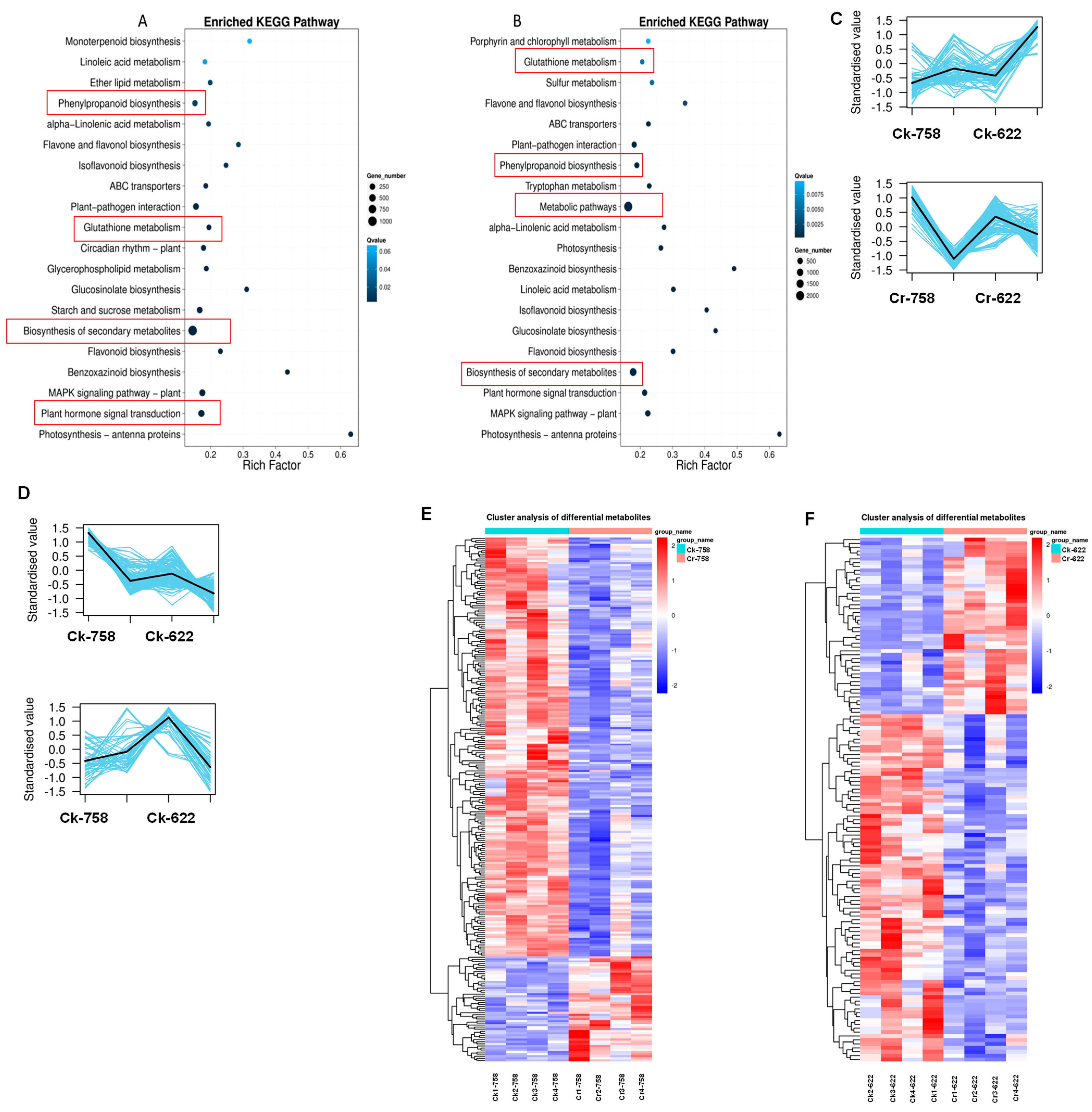
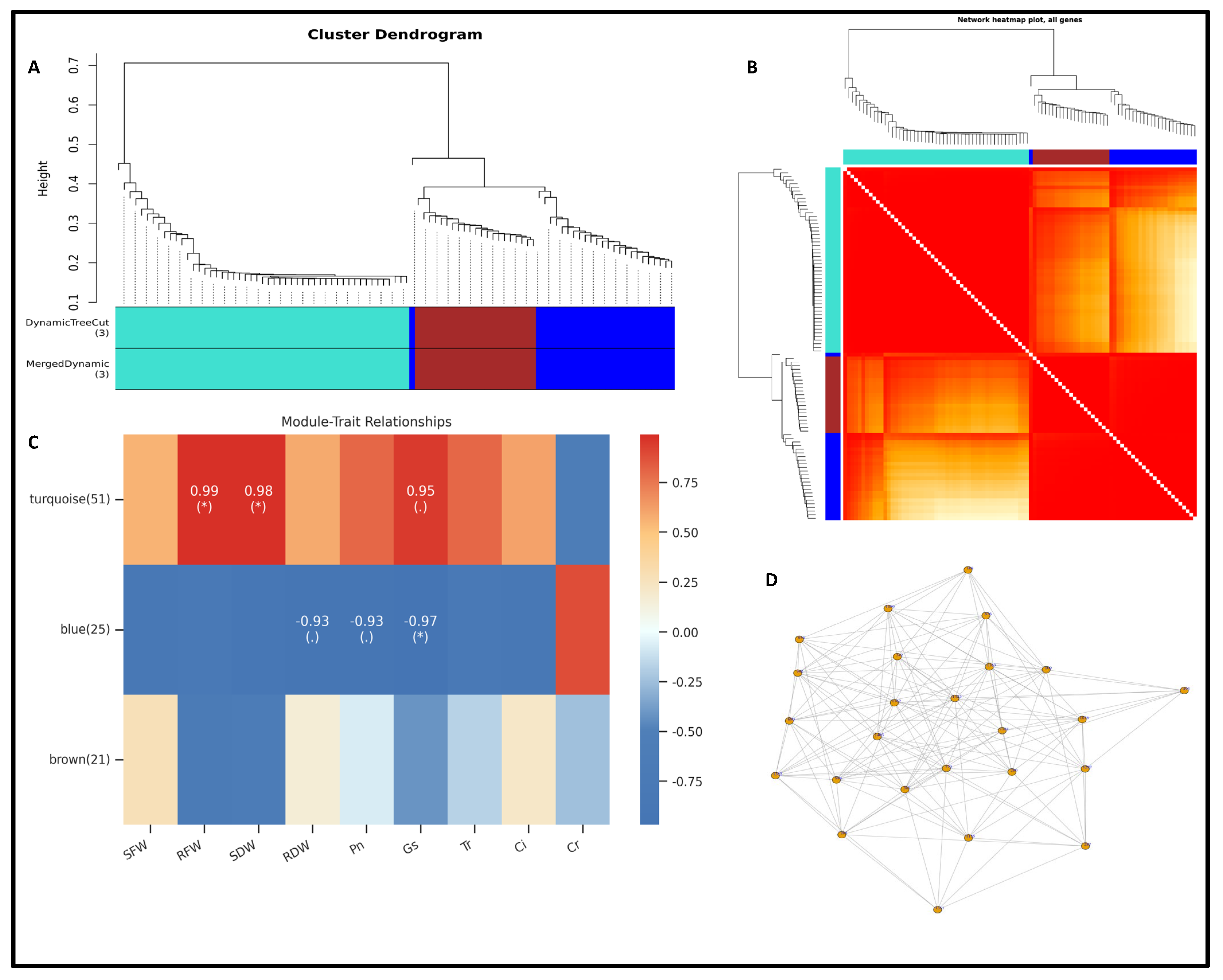
3.5. Hierarchical Clustering of DEMs and Weighted Co-Expression Network Model
3.6. Integration of Key Genes and Metabolites in Rapeseed
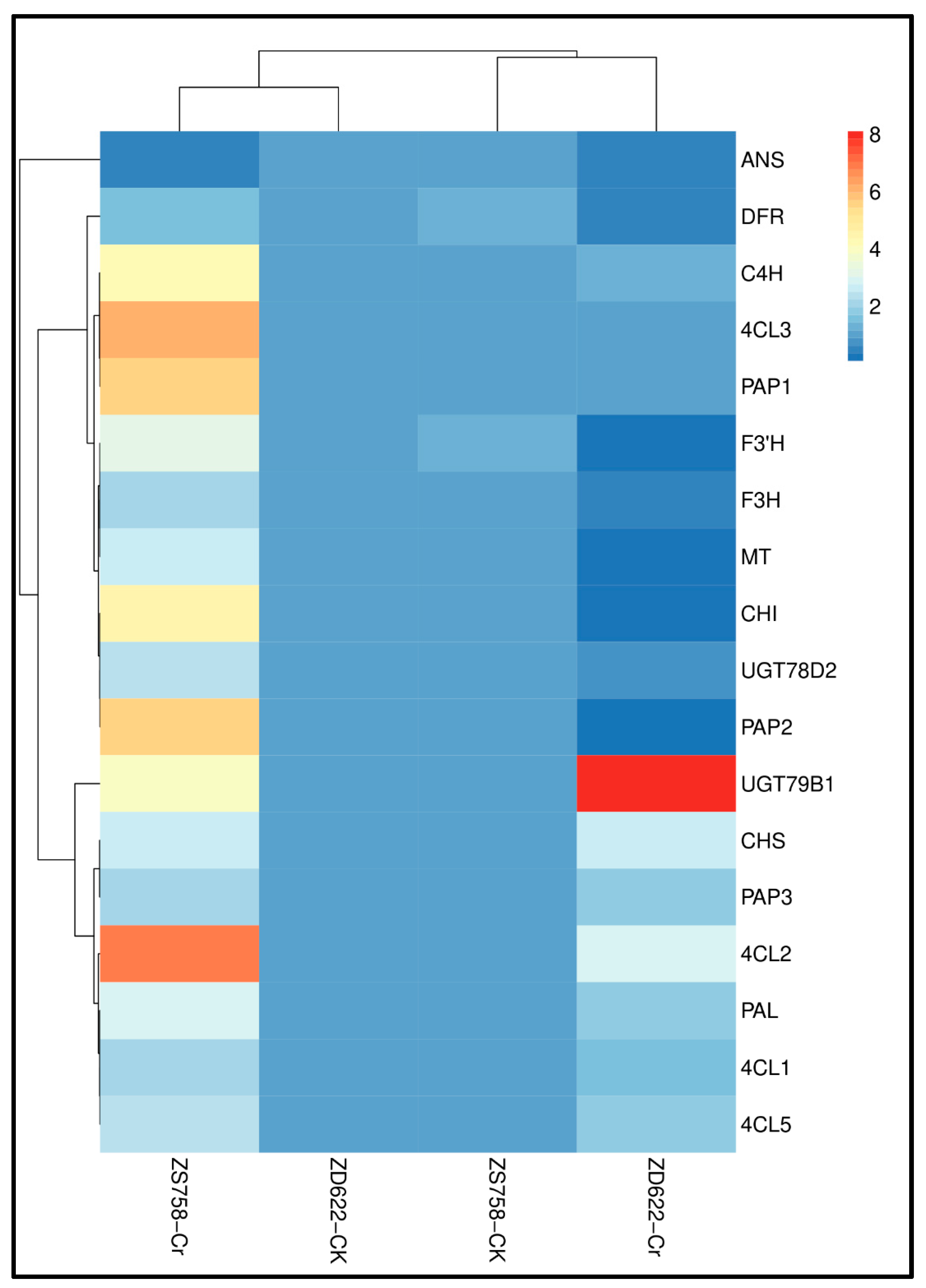
3.7. Gene Expression Analysis of Phenylpropanoid and Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathways
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Owens, G.; Kim, K.R. Distribution and extent of heavy metal(loid) contamination in agricultural soils as affected by industrial activity. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, L.; Fang, J.; Jin, M.; Fiati Kenston, S.S.; Song, X.; Shi, H. Epidemiological study on metal pollution of Ningbo in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, E.; Fratino, U.; Petrella, A.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C. Ailanthus altissima and Phragmites australis for chromium removal from contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15983–15989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Report on the National General Survey of Soil Contamination; Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Qi, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Hong, L. Analysis of heavy metal pollution in real estate stem vegetables in haishu district, Ningbo City. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2021, 31, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.; Zhang, H.; Mao, K.; Shafeeque, M.; Aslam, M.W.; Yang, X.; Zhong, L.; Feng, X.; Podgorski, J. Chromium contamination in paddy soil-rice systems and associated human health risks in Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Liao, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Feng, Y. Chromium contamination and health risk assessment of soil and agricultural products in a rural area in southern China. Toxics 2022, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khan, E. Trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in food chains/webs Concepts and implications for wildlife and human health. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M. Enhancing phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, C.; Vasile, G.G.; Buleandra, M.; Popa, D.E.; Gheorghe, S.; Ungureanu, E.M. Translocation and accumulation of heavy metals in Ocimum basilicum L. plants grown in a mining-contaminated soil. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, I.; Ayyaz, A.; Zhang, K.; Hannan, F.; Sun, Y.; Qin, T.; Athar, H.R.; Naeem, M.S.; Farooq, M.A.; Zhou, W. Transcriptome and Physiological Analyses Unravel Chromium Stress Tolerance Mechanism in Brassica napus L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2025, 44, 4022–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Global rapeseed production and breeding strategies for climate resilience. Crop Sci. 2022, 62, 345–362. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, G.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Liu, A.; Wang, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Y. RNA sequencing reveals the molecular mechanisms of chromium tolerance in Brassica napus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125687. [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff, P.; Weber, A.P.M. The role of metabolomics in informing strategies for improving photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 1696–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Rai, S.; Farag, M.A.; Maurya, S.R.; Yerasu, S.R.; Bisen, M.S.; Prabha, R.; Shukla, R.; Behera, T.K. Metabolic diversity, biosynthetic pathways, and metabolite biomarkers analysed via untargeted metabolomics and the antioxidant potential reveal for high temperature tolerance in tomato hybrid. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhan, C.; Yang, C.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. Metabolomics-centered mining of plant metabolic diversity and function: Past decade and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhongbing, C.; Xiuqin, Y.; Luying, S.; Huan, M.; Sixi, Z. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal key metabolic pathway responses in Pistia stratiotes under Cd stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Feng, G.; Liu, D. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis reveals key regulatory network that response to cold stress in common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis to characterize alkali stress responses in canola (Brassica napus L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Guo, B.; Lv, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Xu, R. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal molecular insights into waterlogging tolerance in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, I.; Ayyaz, A.; Zhang, K.; Hannan, F.; Qin, T.; Zafar, Z.U.; Farooq, M.A.; Zhou, W. Chromium uptake and its impact on antioxidant level, photosynthetic machinery, and related gene expression in Brassica napus cultivars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 59363–59381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Long, M.; Islam, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Wang, J.; Mwamba, T.M.; Shou, J.; Zhou, W. Synergistic effects of chromium and copper on photosynthetic inhibition, subcellular distribution, and related gene expression in Brassica napus cultivars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11827–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoh, E.J.J.; Zhou, W.J.; Kristiansson, B. Variation in the development of secondary dormancy in oilseed rape cultivars under conditions of stress. Weed Res. 2002, 42, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, V.P.; Kumar, D.; Chauhan, D.K. Impact of exogenous silicon addition on chromium uptake, growth, mineral elements, oxidative stress, antioxidant capacity, and leaf and root structures in rice seedlings exposed to hexavalent chromium. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, R.J.; Srivastava, A.; Tsimilli-Michael, M. The fluorescence transient as a tool to characterize and screen photosynthetic samples. In Probing Photosynthesis: Mechanisms, Regulation and Adaptation; Taylor and Francis: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 445–483. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.A.; Ali, B.; Islam, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Gill, M.B.; Mwamba, T.M.; Zhou, W. Physiological and molecular analyses of black and yellow seeded Brassica napus regulated by 5-aminolivulinic acid under chromium stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.A.; Zang, L.; Ali, B.; Farooq, M.A.; Cui, P.; Yang, S.; Ali, S.; Zhou, W. Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Parveen, A.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, I.; Rasheed, R. Investigating the role of different maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars by studying morpho-physiological attributes in chromium-stressed environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 72886–72897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.L.; Sharma, C.K.; Singh, C.K.; Sarkar, S.K.; Singh, I.; Dotaniya, M.L. Effect of chromium (VI) toxicity on morpho-physiological characteristics, yield, and yield components of two chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) varieties. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Dey, S.S.; Raychaudhuri, S.S. Chromium (VI) induced stress response in the plant Plantago ovata Forsk in vitro. Genes Environ. 2018, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Yadav, N.; Manasa, L.; Kumar, A.; Patnaik, A.; Panigrahy, M.; Biswal, D.P.; Rout, G.R.; Panigrahi, K.C. Chromium stress influences several parameters of leaf dynamics and morphology in Oryza sativa L. cultivars. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Gao, Y.J.; Cao, Z.X.; Tian, Z.Q.; Bai, Y.F.; Tang, Z.X.; Ali, A.; Zhao, F.J.; Wang, P. Ecotoxicity of hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)] in soil presents predominate threats to agricultural production with the increase of soil Cr contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 135091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, P.; Xia, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Remusat, L.; Rumpel, C.; Bloem, E.; Krasny, B.B.; Schnug, E. Speciation and distribution of chromium (III) in rice root tip and mature zone: The significant impact of root exudation and iron plaque on chromium bioavailability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Kanwal, S.; Ali, Q.; Ibrahim, M.; Gill, R.A.; Khan, M.D. Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10601–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomali, S.; Das, S.; Sarraf, M.; Johnson, R.; Janeeshma, E.; Kumar, V.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Puthur, J.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Modulation of plant photosynthetic processes during metal and metalloid stress, and strategies for manipulating photosynthesis-related traits. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 194, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Zeb, S.; Khan, M.N.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, Z. Enhancement of sweetpotato tolerance to chromium stress through melatonin and glutathione: Insights into photosynthetic efficiency, oxidative defense, and growth parameters. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 208, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. Copper stress-induced phytotoxicity associated with photosynthetic characteristics and lignin metabolism in wheat seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, R.J.; Tsimilli-Michael, M.; Srivastava, A. Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. In Chlorophyll a Fluorescence: A Signature of Photosynthesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 321–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaji, H.M.; Schansker, G.; Ladle, R.J.; Goltsev, V.; Bosa, K.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Strasser, R.J. Frequently asked questions about chlorophyll fluorescence, the sequel. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 122, 121–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Naeem, A.; Nawaz, R.; Ali, S.; Murtaza, G.; Maqsood, M.A.; Azhar, M.; Khalid, H.; Rizwan, M. Photosynthesis and growth response of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids exposed to cadmium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5521–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Singh Sidhu, G.P.; Bali, A.S.; Handa, N.; Kapoor, D.; Yadav, P.; Khanna, K. Photosynthetic response of plants under different abiotic stresses: A review. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Kalaji, H.M.; Jajoo, A. Investigation of deleterious effects of chromium phytotoxicity and photosynthesis in wheat plant. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsiros, O.; Nagy, G.; Patai, R.; Solymosi, K.; Gasser, U.; Polgár, T.F.; Garab, G.; Kovács, L.; Hörcsik, Z.T. Similarities and differences in the effects of toxic concentrations of cadmium and chromium on the structure and functions of thylakoid membranes in Chlorella variabilis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, S.; Nian, H.; He, G.; Xu, N. Effects of cadmium stress on photosynthetic apparatus of tobacco. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalariya, N.; Goswami, N.; Mehta, D.; Singh, A.; Saran, P. Chlorophyll fluorescence: A physiological mechanism and a physical tool in plant eco-physiological studies. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2019, 24, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Todorenko, D.A.; Timofeev, N.; Kovalenko, I.B.; Kukarskikh, G.P.; Matorin, D.N.; Antal, T.K. Chromium effects on photosynthetic electron transport in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 2020, 252, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, H.; Yıldız, M. Interactive effects of sulfur and chromium on antioxidative defense systems and BnMP1 gene expression in canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars differing in Cr (VI) tolerance. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akila, V. Effect of copper on growth and yield and macro and micro nutrient concentration of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in typic haplustalf. J. Curr. Crop Sci. Technol. 2023, 110, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, F.; Ruiz, K.B.; Castiglione, S.; Cicatelli, A.; Biondi, S. The combined effect of Cr (III) and NaCl determines changes in metal uptake, nutrient content, and gene expression in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Jan, A.U.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Ditta, A.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H. Sources, impacts, factors affecting Cr uptake in plants, and mechanisms behind phytoremediation of Cr-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 165726. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, W.; Khattak, W.A.; Ihtisham, M.; Ilyas, M.; Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, H.; Khan, K.A.; Ni, D.; Zhao, H. Assessing the health risks of heavy metals and seasonal minerals fluctuations in Camellia sinensis cultivars during their growth seasons. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 187, 114586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhao, W.; Sheng, L.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, Z. Integrated transcriptome and metabolomics analyses revealed key functional genes in Canna indica under Cr stress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Metabolic responses of rice seedlings to cadmium stress revealed by LC-MS based metabolomics. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Wu, H.; Lu, B.; Luo, X.; Gong, C.; Bai, J. Low concentrations of glycine inhibit photorespiration and enhance the net rate of photosynthesis in Caragana korshinskii. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, Z.; Chen, W.; Yu, C.; Song, L.; Wu, J. Identification of key genes contributing to amino acid biosynthesis in Torreya grandis using transcriptome and metabolome analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Guo, R.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, M.; Shi, L. Integration of the transcriptome and metabolome reveals the mechanism of resistance to low phosphorus in wild soybean seedling leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 194, 406–417. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Copper detoxification mechanisms in Celosia argentea revealed by metabolomic analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Zinc toxicity effects on cell membrane and chloroplast structures in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Bernardo, L.; Kane, D.; Trevisan, M.; Lucini, L. Zinc excess triggered polyamines accumulation in lettuce root metabolome, as compared to osmotic stress under high salinity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba, P.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Mahato, S.K.; Bhutia, K.D.; Mondal, T.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Zinc stress induces physiological, ultra-structural and biochemical changes in Mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata) seedlings. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2014, 20, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, H.; Song, L.; Jia, S.; Ma, D. Zinc stress affects ionome and metabolome in tea plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighanimine, J.A.; Nabuco Leva Ferreira Freitas, N.; Nemazanyy, I.; Bankolé, A.; Benarroch-Popivker, D.; Brodesser, S.; Doré, G.; Robinson, L.; Benit, P.; Ladraa, S. A homoeostatic switch causing glycerol-3-phosphate and phosphoethanolamine accumulation triggers senescence by rewiring lipid metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.K.; Chang, Y.K.; Kang, N.K. Enhancing lipid productivity in Nannochloropsis salina by overexpression of endogenous glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Leng, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, C. Lipid remodeling plays an important role in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) defense against stripe rust. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch, R.G. Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization, and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouairi, I.; Ammar, W.B.; Youssef, N.B.; Daoud, D.B.; Ghorbal, M.H.; Zarrouk, M. Comparative study of cadmium effects on membrane lipid composition of Brassica juncea and Brassica napus leaves. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanova, V.; Pavlik, M.; Pavlikova, D. Fatty acid accumulation in the model hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens under cadmium stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Reig, M.; Jaumot, J.; Pina, B.; Tauler, R. Metabolomic analysis of the effects of cadmium and copper contamination in rice crops. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, H.; Du, Z.; Hu, L.; Fu, J. Phytochelatin-mediated cadmium detoxification mechanisms in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pidatala, V.R.; Li, K.; Sarkar, D.; Wusirika, R.; Datta, R. Comparative metabolic profiling of vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides) and maize (Zea mays) under lead stress. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Shen, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R.; Sun, X.; Liu, L. Metabolomic analysis with GC-MS to reveal potential metabolites and biological pathways involved in Pb & Cd stress response of radish roots. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; Pang, Q.; Feng, J. Toxicological effects of environmentally relevant lead and zinc in halophyte Suaeda salsa by NMR-based metabolomics. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.V.; Araújo, T.O.; Arcanjo-Silva, S.; Freitas-Silva, L.; Azevedo, A.A.; Nunes-Nesi, A. Arsenic hyperaccumulation induces metabolic reprogramming in Pityrogramma calomelanos to reduce oxidative stress. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 157, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Misra, P.; Dwivedi, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Bag, S.K.; Mantri, S.; Asif, M.H.; Rai, A.; Kumar, S.; Shri, M.; et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic shifts in rice roots in response to Cr (VI) stress. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Ibarra, A.A.; Wrobel, K.; Yanez Barrientos, E.; Corrales Escobosa, A.R.; Gutierrez Corona, J.F.; Enciso Donis, I.; Wrobel, K. Impact of Cr(VI) on the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in Helianthus annuus roots studied by metabolomic tools. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Y.; Paglia, K.; Vaniya, A.; Wancewicz, B.; Keller, A.A. Metabolomics reveals the molecular mechanisms of copper induced cucumber leaf (Cucumis sativus) senescence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7092–7100. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlawat, M.; Singh, M.; Manorama, K.; Lakra, N.; Zaid, A.; Zulfiqar, F. Plant phenolics: Neglected secondary metabolites in plant stress tolerance. Braz. J. Bot. 2023, 46, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivars | Treatments | Shoot Fresh Weight (g−1 Plant) | Root Fresh Weight (g−1 Plant) | Shoot Dry Weight (g−1 Plant) | Root Dry Weight (g−1 Plant) | Pn (µmol CO2 m−2 s−1) | Gs (mol H2O m−2 s−1) | Tr (mmol H2O m−2 s−1) | Ci (µmol CO2 mol−1) | Cr (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZS758 | Control | 14.08 ± 0.33 a | 2.61 ± 0.12 a | 2.90 ± 0.15 a | 1.02 ± 0.025 ab | 16.48 ± 0.45 a | 0.84 ± 0.045 a | 11.23 ± 0.18 a | 380 ± 1.20 a | 0.004 ± 0.0001 b |
| 50 µM Cr | 10.67 ± 0.21 b | 2.04 ± 0.1 a | 2.68 ± 0.11 ab | 0.96 ± 0.01 b | 12.71 ± 0.32 b | 0.69 ± 0.038 b | 4.27 ± 0.2 c | 320 ± 2.02 c | 0.13 ± 0.001 a | |
| ZD622 | Control | 14.00 ± 0.31 a | 1.39 ± 0.04 b | 2.04 ± 0.07 bc | 1.07 ± 0.016 a | 14.08 ± 0.33 a | 0.53 ± 0.025 c | 6.04 ± 0.19 b | 368 ± 2.65 b | 0.005 ± 0.0004 b |
| 50 µM Cr | 8.00 ± 0.18 b | 1.29 ± 0.036 b | 1.71 ± 0.054 c | 0.61 ± 0.03 c | 9.73 ± 0.22 b | 0.21 ± 0.018 d | 2.74 ± 0.09 d | 285 ± 1.95 d | 0.26 ± 0.002 a |
| Parameters | Control ZS758 | Cr ZS758 | Control ZD622 | Cr ZD622 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fo | 5456.4 ± 183 a | 6941.8 ± 184 b | 5337.4 ± 452 bc | 6545 ± 327 bc |
| Fm | 27,559.2 ± 1251 b | 36,599 ± 779 a | 25,566 ± 788 c | 21,488 ± 5234 cd |
| Fj | 14,380.6 ± 345 a | 21,5935 ± 827 c | 13,702.4 ± 1274 c | 16,550 ± 1549 b |
| Fi | 25,831.2 ± 1128 a | 24,262.6 ± 740 ab | 26,727.2 ± 1004 ab | 18,860.2 ± 3604 b |
| Fv | 27,842.6 ± 863 a | 32,527.4 ± 1620 b | 22,628.6 ± 725 bc | 27,360.2 ± 711 c |
| Vj | 0.3898 ± 0.06 b | 0.3524 ± 0.03 b | 0.4532 ± 0.03 c | 0.3254 ± 0.09 b |
| Vi | 0.678 ± 0.03 ab | 0.7158 ± 0.01 c | 0.4786 ± 0.02 c | 0.6252 ± 0.03 bc |
| Fm/Fo | 5.783 ± 0.34 a | 5.3448 ± 0.32 b | 5.238 ± 0.31 ab | 3.4432 ± 0.88 b |
| Fv/Fo | 4.473 ± 0.21 a | 4.3568 ± 0.32 c | 4.3138 ± 0.31 ab | 2.6432 ± 0.88 cd |
| Fv/Fm | 0.7086 ± 0.04 a | 0.6544 ± 0.11 ab | 0.7556 ± 0.01 bc | 0.5914 ± 0.01 bc |
| Mo | 0.4676 ± 0.03 c | 0.4882 ± 0.05 a | 0.4704 ± 0.07 bc | 0.4716 ± 0.16 ab |
| Sm | 326.4922 ± 34 b | 256.7988 ± 22 b | 315.3738 ± 30 b | 623.4732 ± 192 d |
| Ss | 0.6346 ± 0.04 a | 0.7024 ± 0.01 a | 0.6232 ± 0.04 cd | 0.6284 ± 0.04 bc |
| N | 426.447 ± 37 bc | 454.4188 ± 26 b | 477.0206 ± 35 bc | 353.14 ± 340 d |
| Phi_Po | 0.6566 ± 0.04 a | 0.6114 ± 0.01 a | 0.5856 ± 0.01 b | 0.4554 ± 0.11 ab |
| Psi_o | 0.6182 ± 0.05 b | 0.5556 ± 0.03 b | 0.6068 ± 0.03 a | 0.3736 ± 0.09 bc |
| Phi_Eo | 0.7498 ± 0.06 c | 0.5134 ± 0.03 a | 0.5292 ± 0.03 ab | 0.4292 ± 0.1 ab |
| Phi_Do | 0.1674 ± 0.04 a | 0.4686 ± 0.01 ab | 0.1244 ± 0.01 ac | 0.2646 ± 0.09 b |
| Phi_Pav | 765.8364 ± 4.73 a | 783.3306 ± 3.36 b | 722.8084 ± 4.47 | 651.6812 ± 10 d |
| Pi_Abs | 3.346 ± 0.7464 b | 5.7696 ± 0.94 a | 3.1766 ± 1.22 bc | 3.0138 ± 0.11 cd |
| ABS/RC | 1.476 ± 0.05 a | 1.2974 ± 0.03 ab | 1.2768 ± 0.10 bc | 1.0682 ± 0.89 d |
| TRo/RC | 1.2634 ± 0.03 b | 1.3256 ± 0.02 a | 1.1114 ± 0.07 c | 1.0782 ± 0.09 cd |
| ETo/RC | 0.645 ± 0.02 a | 0.6654 ± 0.04 a | 0.4114 ± 0.02 ab | 0.6068 ± 0.11 bc |
| DIo/RC | 0.4328 ± 0.04 a | 0.254 ± 0.02 b | 0.315 ± 0.04 a | 1.3898 ± 0.87 d |
| Cultivars | Treatments | Ca (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) | K (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) | P (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) | Fe (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) | Cu (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) | Mn (mg kg−1 Dry Weight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZS758 | Control | 0.44 ± 0.005 a | 0.26 ± 0.001 a | 0.027 ± 0.004 c | 0.33 ± 0.005 a | 0.12 ± 0.0005 a | 0.031 ± 0.0001 ab |
| 50 µM Cr | 0.28 ± 0.001 b | 0.16 ± 0.001 b | 0.020 ± 0.002 c | 0.25 ± 0.005 a | 0.04 ± 0.0001 bc | 0.016 ± 0.0005 b | |
| ZD622 | Control | 0.33 ± 0.004 b | 0.31 ± 0.041 a | 0.31 ± 0.002 a | 0.29 ± 0.001 a | 0.067 ± 0.0005 b | 0.03 ± 0.0002 a |
| 50 µM Cr | 0.16 ± 0.002 c | 0.11 ± 0.001 b | 0.12 ± 0.011 b | 0.18 ± 0.001 b | 0.011 ± 0.0004 c | 0.011 ± 0.0004 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Ayyaz, A.; Hannan, F.; Khan, M.U.R.; Qin, T.; Song, W.; Naeem, M.S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, W.; Batool, I. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Contrasting Rapeseed Cultivars. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122892
Xu W, Ayyaz A, Hannan F, Khan MUR, Qin T, Song W, Naeem MS, Xu L, Zhou W, Batool I. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Contrasting Rapeseed Cultivars. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122892
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wan, Ahsan Ayyaz, Fakhir Hannan, Mujeeb Ur Rehman Khan, Tongjun Qin, Wenjian Song, Muhammad Shahbaz Naeem, Ling Xu, Weijun Zhou, and Iram Batool. 2025. "Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Contrasting Rapeseed Cultivars" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122892
APA StyleXu, W., Ayyaz, A., Hannan, F., Khan, M. U. R., Qin, T., Song, W., Naeem, M. S., Xu, L., Zhou, W., & Batool, I. (2025). Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Contrasting Rapeseed Cultivars. Agronomy, 15(12), 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122892








