Canopy-Level Regulation of Within-Boll Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Under Staged Saline Water Supplemental Irrigation in Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
- Ct is the target irrigation water salinity (e.g., 3.5, 5.0 g·L−1, etc.),
- Cs is the saline water salinity (12.5 g·L−1),
- Cf is the freshwater salinity (0.3 g·L−1).
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Within-Boll Yield Components
2.3.2. Yield, Yield Components, and Fiber Quality
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cotton Yield and Yield Components
3.2. Boll Setting Rate and Shading Rate
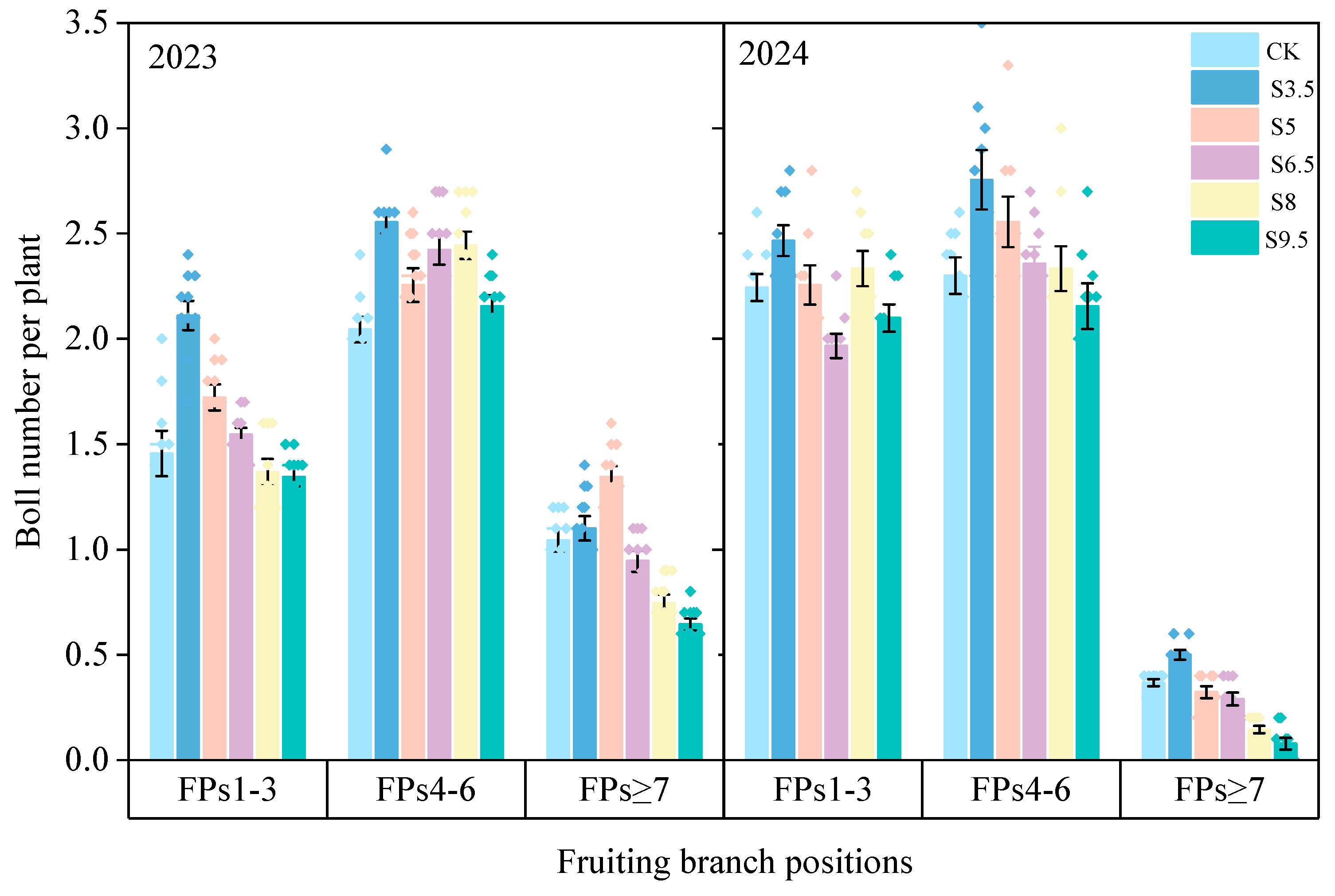
3.3. Boll Number
3.4. Within-Boll Yield Component
3.4.1. Seed Number per Boll, Seed Surface Area and Seed Index
Seed Number
Seed Surface Area
Seed Index
3.4.2. Number of Fibers per Seed, Lint Mass per Seed and Lint Mass per Unit Seed Surface Area
Fiber Number per Seed
Lint Mass per Seed
Lint Mass per Unit Seed Surface Area
3.5. Fiber Quality
3.5.1. Fiber Length
3.5.2. Uniformity
3.5.3. Fiber Strength
3.5.4. Micronaire
3.5.5. Q-Score
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Regulatory Mechanism of Staged Saline Water Supplementary Irrigation on Cotton Yield Components
4.2. Salinity Tolerance Differences in Fruit Branch Positions and Site-Specific Boll Retention Mechanisms
4.3. Salt-Driven Seed Tradeoffs Govern Boll Level Fiber Yield
4.4. Mid-Canopy Boll Fiber Traits Confer Salinity Tolerance Advantage
4.5. Site-Specific Fiber Quality Gains Under Moderate Salinity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingrao, C.; Strippoli, R.; Lagioia, G.; Huisingh, D. Water scarcity in agriculture: An overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.X.; Feng, K.S.; Sun, L.X.; Zhao, D.D.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, D.X.; Liu, Z.M.; Baiocchi, G. Rising agricultural water scarcity in China is driven by expansion of irrigated cropland in water scarce regions. One Earth 2022, 5, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Feng, S.L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, L.Y.; Zheng, Z.H.; Ai, N.J.; Guan, X.Y. The impact of temperature on cotton yield and production in Xinjiang, China. npj Sustain. Agric. 2024, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, Z.K.; Xie, J.J.; Zhao, Y.G.; Hu, J.Y. Study on the unconventional water sources: Bitter-salty water resources and its distribution characteristics in China. J. China Hydrol. 2021, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, H.Q.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, R. Effects of nitrogen application and brackish water irrigation on yield and quality of cotton. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.H.; Wang, H.D.; Fan, J.L.; Wang, X.K.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.H.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, F.C. Crop yield and water productivity under salty water irrigation: A global meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, C.M.; Grattan, S.R.; Maas, E.V. Plant salt tolerance. In ASCE Manual and Reports on Engineering Practice; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; Volume 71. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Li, F.D.; Tian, L.J.; He, X.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Ren, F.T. Soil physicochemical properties and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield under brackish water mulched drip irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.L.; Feng, D.; Li, K.J.; Ma, L.Y.; Dang, H.K.; Cao, C.Y.; Sun, J.S.; Zhang, J.P. Effects of furrow irrigation with saline water on variation of soil water-salt, cotton growth and yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yin, F.H.; Guo, L.; Wen, Y.; Song, L.B.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.H. Ultra-wide film mulching with moderate irrigation water salinity enhances cotton growth under drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. Field Crops Res. 2024, 315, 109485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.B.; Liang, C.F.; Chen, X.P.; Ye, S.T.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L.; Duan, M.L.; Wang, X.P. Magnetically-treated brackish water affects soil water-salt distribution and the growth of cotton with film mulch drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, C.; Gu, J.J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Ju, F.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Hu, W.; Zhao, W.Q.; Zhou, Z.G.; et al. Improving the soil K+/Na+ ratio under moderate salt stress synergistically increases the yield and quality of cotton fiber and cottonseed. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 213, 118441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, G.S.; Dias, A.S.; Gheyi, H.R.; dos Anjos Soares, L.A.; Nobre, R.G.; da Silva Sá, F.V.; de Paiva, E.P. Emergence, morpho-physiology and flowering of colored-fiber cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) submitted to different nitrogen levels and saline water stress irrigation. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, K.; Sun, J.; Dang, H.; Sun, C.; Rahma, A.E.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Feng, D. Effects of a 10-year irrigation with saline water on soil physico-chemical properties and cotton production. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Z.; Li, W.J.; Tang, W.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, D.M. Ffects of genotypes and plant density on yield, yield components and photosynthesis in bt transgenic cotton. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2006, 192, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, S.; Culp, T.W.; Harrell, D.C.T. The relative contributions of yield components to lint yield of upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. Euphytica 1974, 23, 399–403. Euphytica 1974, 23, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, G.G.; Smith, C.W. Combining ability for within-boll yield components in cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, J.S.; Ramey, J.H.H.; Harrell, D.C.; Culp, T.W. Ontogenetic model of cotton yield. Crop Sci. 1976, 16, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, C.W.; Nichols, R.L.; Brown, S.M. Within-boll yield components of high yielding cotton cultivars. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 2108–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Vinicius, B.B.; Cory, I.M.; Eric, H.; James, P.B.; Wayne, K.; Randy, B.; Craig, W.B. Effects of irrigation, cultivar, and plant density on cotton within-boll fiber quality. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.M.; Liu, T.J.; Ying, C.H.; Wang, G.P.; Du, W.L.; Wu, F.Q.; Li, Y.B.; Feng, L. Changes in within-boll yield components explain cotton yield and quality variation across planting dates under a double cropping system of cotton-wheat. Field Crops Res. 2023, 293, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.J.; Hao, X.Z.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, N.N.; Shi, F.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; et al. Enhancing cotton yield and fiber quality via the optimization of within-boll yield components with potassium application under limited drip irrigation in arid regions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Tian, L.W.; Feng, L.; Xu, W.X.; Li, Y.B.; Xing, F.F.; Fan, Z.Y.; Xiong, S.W.; Tang, J.H.; Li, C.M.; et al. Boll characteristics and yield of cotton in relation to the canopy microclimate under varying plant densities in an arid area. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, F.E.; Bourland, F.M.; Jones, D.C. Relationships of yield component variables to yield and fiber quality parameters. J. Cotton Sci. 2016, 20, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.G.; Wang, S.; Hu, W. Novel intra-boll yield components and Q-score can further evaluate the effect of phosphorus fertilizer on cotton yield and fiber quality. Field Crops Res. 2022, 275, 108325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.A.d.A.; Fernandes, P.D.; de Lima, G.S.; Suassuna, J.F.; Brito, M.E.B.; Sá, F.V.d.S. Growth and fiber quality of colored cotton under salinity management strategies. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola E Ambient. 2018, 22, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Wang, H.; Feng, D.; Cao, C.Y.; Zheng, C.L.; Dang, H.K.; Li, K.J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, C.T. Evaluating the impacts of long-term saline water irrigation on soil salinity and cotton yield under plastic film mulching: A 15-year field study. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wen, Y.; Song, L.B.; Liang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.H. Multi-objective optimization of saline water irrigation in arid oasis regions: Integrating water-saving, salinity control, yield enhancement, and CO2 emission reduction for sustainable cotton production. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 174, Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/T0234e/T0234e00.htm (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Guo, R.S.; Lin, T.; Xu, H.J.; Cui, J.P.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Tian, L.W. Effect of saline water drip irrigation on water and salt transport features and cotton yield of oasis cotton field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.J.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.B.; Yang, A.Z.; Zhang, Z.X. Spatial distribution and simulation of soil moisture and salinity under mulched drip irrigation combined with tillage in an arid saline irrigation district, northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.T.; Yang, G.; Li, W.J.; He, X.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Tian, L.J.; Li, F.D.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, S.H. Yield-compatible salinity level for growing cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under mulched drip irrigation using saline water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, G.Y.; Liu, J.G.; An, Z.T.; Zhang, H.S.; Ai, P.F.; Wang, Y.Q. Integrated analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome reveals the molecular mechanism regulating cotton boll abscission under low light intensity. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinn, G. Water deficit and ethylene evolution by young cotton bolls. Plant Physiol. 1976, 57, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: An omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, J.L.; Collins, G.D.; Whitaker, J.; Chapman, K.D.; Horn, P. The impact of seed size and chemical composition on seedling vigor, yield, and fiber quality of cotton in five production environments. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubushar, M.; El-Hendawy, S.; Tahir, M.U.; Alotaibi, M.; Mohammed, N.; Refay, Y.; Tola, E. Assessing the Suitability of Multivariate Analysis for Stress Tolerance Indices, Biomass, and Grain Yield for Detecting Salt Tolerance in Advanced Spring Wheat Lines Irrigated with Saline Water under Field Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinn, G. Causes of Square and Boll Shedding in Cotton; US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.X. How cotton fibers elongate: A tale of linear cell-growth mode. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessarakli, M. Physiological responses of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) to salt stress. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 691–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.M.; Shakeel, A.; Haroon, M.; Manan, A.; Sahar, A.; Shoukat, A.; Mo, H.J.; Farooq, M.A.; Ren, M.Z. Effects of Salinity Stress on Some Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Germplasm. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 19, 8854–8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Shakeel, A.; Zafar, M.M.; Farooq, M.; Chattha, W.S.; Husnain, T. A study towards the development of salt tolerant upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 4115–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.T.; Majeed, S.; Rana, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Jia, Y.; Du, X.; Hinze, L.; Azhar, M.T. Impact of salinity stress on cotton and opportunities for improvement through conventional and biotechnological approaches. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Year | Soil Layer (cm) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Alkaline Nitrogen (mg·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg·kg−1) | Total Salt (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 0–20 | 7.94 | 18.59 | 16.89 | 132.83 | 0.72 |
| 20–40 | 7.19 | 19.86 | 13.63 | 147.00 | 0.68 | |
| 40–60 | 7.27 | 14.89 | 12.12 | 159.00 | 0.60 | |
| 2024 | 0–20 | 8.81 | 38.14 | 23.41 | 144.33 | 0.97 |
| 20–40 | 8.90 | 36.93 | 24.64 | 126.00 | 0.93 | |
| 40–60 | 4.78 | 15.66 | 2.80 | 170.00 | 0.84 |
| Year | Treatment | Boll Density (No./ha) | Boll Weight (g) | Lint Percentage (%) | Lint Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 95.11 d | 5.41 ab | 44.78 ab | 2304.65 c |
| S3.5 | 127.83 a | 5.67 a | 45.94 a | 3329.27 a | |
| S5 | 115.89 b | 5.42 ab | 45.14 ab | 2837.57 b | |
| S6.5 | 108.78 bc | 5.11 bc | 44.59 b | 2470.88 c | |
| S8 | 101.81 cd | 4.89 cd | 44.00 bc | 2194.92 cd | |
| S9.5 | 93.04 d | 4.73 d | 43.18 c | 1903.84 d | |
| 2024 | CK | 106.75 bc | 5.51 b | 45.53 bc | 2674.78 bc |
| S3.5 | 119.34 a | 5.71 a | 47.25 a | 3216.34 a | |
| S5 | 109.21 ab | 5.72 a | 46.31 ab | 2892.21 b | |
| S6.5 | 100.63 bc | 5.34 c | 46.27 b | 2487.21 c | |
| S8 | 97.52 bc | 5.25 c | 46.11 b | 2361.82 cd | |
| S9.5 | 93.26 c | 5.03 d | 44.69 c | 2095.10 d | |
| Source of variance | T | * | * | * | * |
| Y | ns | * | * | ns | |
| T × Y | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Year | Treatment | Seed Number per Boll (Number) | Seed Surface Area (mm2) | Seed Index (g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | ||
| 2023 | CK | 29.64 cd | 32.54 b | 28.54 b | 101.59 a | 98.17 b | 103.37 a | 9.99 a | 9.47 b | 10.26 a |
| S3.5 | 31.38 a | 33.71 a | 30.51 a | 95.44 a | 95.55 c | 107.05 ab | 9.06 ab | 9.08 c | 10.82 a | |
| S5 | 31.04 ab | 32.41 b | 28.06 b | 97.65 a | 98.35 b | 104.42 ab | 9.39 a | 9.50 b | 10.42 a | |
| S6.5 | 29.94 bc | 30.66 c | 27.45 b | 96.25 a | 100.95 a | 100.03 ab | 9.18 a | 9.90 a | 9.76 ab | |
| S8 | 28.85 cd | 30.79 c | 26.09 c | 95.26 a | 101.18 a | 99.03 ab | 9.03 ab | 9.93 a | 9.60 b | |
| S9.5 | 28.50 d | 29.56 c | 25.04 c | 94.08 a | 97.82 bc | 97.50 b | 8.85 b | 9.42 b | 9.37 b | |
| 2024 | CK | 29.95 bc | 32.03 a | 28.65 b | 105.49 a | 98.28 a | 100.04 a | 10.58 a | 9.49 ab | 9.76 a |
| S3.5 | 32.85 a | 33.25 a | 30.35 a | 96.53 b | 96.8 a | 99.06 a | 9.22 bc | 9.27 ab | 9.61 a | |
| S5 | 32.70 a | 32.85 a | 30.24 a | 99.79 b | 97.51 a | 100.24 a | 9.72 b | 9.37 ab | 9.79 a | |
| S6.5 | 30.70 b | 32.50 a | 29.30 ab | 100.59 ab | 95.48 a | 95.49 b | 9.84 b | 9.07 b | 9.07 b | |
| S8 | 29.24 cd | 30.50 b | 28.95 ab | 95.17 b | 98.67 a | 94.95 b | 9.02 c | 9.55 ab | 8.98 b | |
| S9.5 | 28.35 d | 29.25 b | 27.18 c | 100.43 ab | 100.89 a | 96.37 b | 9.82 b | 9.89 a | 9.20 b | |
| Source of variance | T | * | ns | ns | ||||||
| FPs | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| Y | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| T × FPs | * | ns | * | |||||||
| T × FPs × Y | * | ns | ns | |||||||
| Year | Treatment | Fibers per Seed (Number) | Lint Mass per Seed (mg) | Lint Mass per Unit SSA (μg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | FPs1–3 | FPs4–6 | FPs ≥ 7 | ||
| 2023 | CK | 18,142.62 ab | 19,794.17 bc | 21,996.35 a | 78.45 a | 80.42 a | 81.18 ab | 771.60 ab | 819.01 ab | 785.43 ab |
| S3.5 | 20,587.02 a | 21,968.19 a | 22,576.26 a | 77.91 a | 80.41 a | 86.95 a | 816.67 a | 841.53 a | 812.94 a | |
| S5 | 17,809.52 ab | 21,004.81 ab | 21,182.83 ab | 76.30 a | 82.05 a | 82.66 ab | 781.36 ab | 834.44 a | 791.61 ab | |
| S6.5 | 17,651.98 ab | 21,790.22 a | 20,607.42 ab | 73.73 ab | 83.86 a | 75.59 bc | 766.23 ab | 830.50 a | 753.4 bc | |
| S8 | 17,173.82 ab | 21,194.24 ab | 20,412.65 ab | 69.43 ab | 83.24 a | 74.06 bc | 726.87 bc | 822.91 a | 747.55 bc | |
| S9.5 | 15,945.860 b | 18,892.26 c | 18,529.96 b | 65.67 b | 73.79 b | 70.59 c | 695.64 c | 754.30 b | 726.22 c | |
| 2024 | CK | 20,944.48 ab | 21,412.73 a | 23,309.52 a | 81.95 a | 80.89 b | 86.27 a | 776.92 bc | 823.22 ab | 862.34 ab |
| S3.5 | 22,639.92 a | 21,716.38 a | 22,013.06 a | 82.15 a | 82.55 ab | 87.00 a | 851.15 a | 852.86 a | 878.19 a | |
| S5 | 19,417.34 bc | 22,343.59 a | 24,952.82 a | 79.2 ab | 82.27 ab | 87.78 a | 794.04 b | 843.93 a | 875.55 a | |
| S6.5 | 19,617.05 bc | 21,088.86 a | 23,255.46 a | 80.35 a | 80.31 b | 79.94 b | 798.79 b | 841.23 a | 837.14 b | |
| S8 | 17,840.47 c | 22,748.20 a | 21,618.42 a | 73.20 c | 83.42 a | 79.29 b | 769.10 bc | 845.53 a | 835.32 b | |
| S9.5 | 19,149.58 bc | 22,082.99 a | 21,092.62 a | 75.41 bc | 80.73 b | 77.31 b | 750.21 c | 801.78 b | 802.28 c | |
| Source of variance | T | * | * | * | ||||||
| FPs | * | ns | ns | |||||||
| Y | * | ns | ns | |||||||
| T × FPs | ns | * | * | |||||||
| T × FPs × Y | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| Year | Fruit Position (FPS) | Treatment | Fiber Length (mm) | Uniformity (%) | Fiber Strength (CN·Tex−1) | Micronaire | Q-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | FPs1–3 | CK | 30.10 b | 86.60 c | 28.35 a | 5.05 a | 32.14 b |
| S3.5 | 31.95 a | 88.10 a | 29.30 a | 4.10 b | 33.15 a | ||
| S5 | 31.35 a | 87.50 ab | 29.50 a | 4.80 b | 32.95 a | ||
| S6.5 | 30.00 b | 86.85 bc | 29.35 a | 4.85 b | 32.18 b | ||
| S8 | 29.40 b | 86.40 c | 29.25 a | 4.80 b | 31.79 b | ||
| S9.5 | 29.70 b | 86.50 c | 28.90 a | 4.90 b | 31.94 b | ||
| FPs4–6 | CK | 29.60 b | 86.50 ab | 28.60 d | 4.85 a | 31.85 b | |
| S3.5 | 31.65 a | 87.30 a | 31.65 a | 4.05 b | 33.10 a | ||
| S5 | 30.65 ab | 86.45 ab | 30.80 ab | 4.50 ab | 32.50 ab | ||
| S6.5 | 30.15 ab | 85.55 b | 30.15 bc | 4.55 ab | 32.06 b | ||
| S8 | 30.30 ab | 86.10 ab | 29.55 bcd | 4.60 a | 32.17 ab | ||
| S9.5 | 30.05 b | 85.10 b | 29.20 cd | 4.65 a | 31.87 b | ||
| FPs ≥ 7 | CK | 28.90 a | 83.95 a | 28.20 b | 4.65 ab | 31.03 ab | |
| S3.5 | 30.10 a | 85.75 a | 29.05 ab | 4.55 a | 31.96 a | ||
| S5 | 29.75 ab | 85.20 a | 28.50 a | 4.70 ab | 31.68 a | ||
| S6.5 | 28.40 b | 85.55 a | 28.65 b | 4.62 c | 31.05 ab | ||
| S8 | 28.60 ab | 84.40 a | 28.45 ab | 4.60 bc | 30.96 ab | ||
| S9.5 | 28.30 b | 82.90 a | 26.90 ab | 4.95 ab | 30.51 b | ||
| 2024 | FPs1–3 | CK | 28.35 b | 83.77 b | 29.55 a | 5.06 a | 30.96 c |
| S3.5 | 32.57 a | 85.06 a | 30.16 a | 4.00 d | 33.06 a | ||
| S5 | 31.86 a | 86.29 a | 30.26 a | 4.51 c | 33.03 a | ||
| S6.5 | 30.97 ab | 85.96 a | 30.10 a | 4.69 bc | 32.56 ab | ||
| S8 | 29.88 ab | 85.50 a | 29.63 a | 4.89 ab | 31.95 abc | ||
| S9.5 | 28.78 b | 84.49 ab | 29.64 a | 4.93 ab | 31.26 bc | ||
| FPs4–6 | CK | 28.95 c | 84.78 a | 30.65 a | 4.71 a | 31.44 c | |
| S3.5 | 32.64 a | 84.79 a | 31.16 a | 4.17 c | 33.19 a | ||
| S5 | 30.26 b | 84.60 a | 30.81 a | 4.39 bc | 32.00 b | ||
| S6.5 | 30.11 b | 84.94 a | 30.79 a | 4.53 abc | 32.01 b | ||
| S8 | 28.48 c | 83.70 ab | 30.35 a | 4.73 ab | 31.01 d | ||
| S9.5 | 27.93 c | 83.21 b | 30.38 a | 4.80 a | 30.68 d | ||
| FPs ≥ 7 | CK | 28.32 bc | 82.98 b | 28.76 b | 4.75 a | 30.67 c | |
| S3.5 | 31.12 a | 84.95 a | 30.13 a | 4.56 a | 32.45 a | ||
| S5 | 29.21 b | 83.86 ab | 29.73 a | 4.39 a | 31.25 b | ||
| S6.5 | 27.92 bc | 83.65 ab | 28.33 ab | 4.48 a | 30.46 c | ||
| S8 | 27.90 bc | 83.51 ab | 28.91 ab | 4.80 a | 30.57 c | ||
| S9.5 | 27.39 c | 80.72 c | 27.65 b | 5.06 a | 29.83 d | ||
| Source of variance | T | ns | ** | * | ns | ns | |
| FPs | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||
| Y | ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | ||
| T × FPs | * | * | ns | * | * | ||
| T × FPs × Y | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhong, P.; Wang, L.; Guo, R.; Lin, T.; Tian, L.; Cui, J. Canopy-Level Regulation of Within-Boll Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Under Staged Saline Water Supplemental Irrigation in Xinjiang. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112662
Zhang N, Yang Y, Xu W, Zhong P, Wang L, Guo R, Lin T, Tian L, Cui J. Canopy-Level Regulation of Within-Boll Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Under Staged Saline Water Supplemental Irrigation in Xinjiang. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112662
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Na, Yachen Yang, Wenxiu Xu, Penghao Zhong, Liang Wang, Rensong Guo, Tao Lin, Liwen Tian, and Jianping Cui. 2025. "Canopy-Level Regulation of Within-Boll Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Under Staged Saline Water Supplemental Irrigation in Xinjiang" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112662
APA StyleZhang, N., Yang, Y., Xu, W., Zhong, P., Wang, L., Guo, R., Lin, T., Tian, L., & Cui, J. (2025). Canopy-Level Regulation of Within-Boll Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Under Staged Saline Water Supplemental Irrigation in Xinjiang. Agronomy, 15(11), 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112662




