Abstract
The soil carbon pool in saline–alkali land is a research hotspot in the field of agricultural environmental science. However, there are no systematic conclusions regarding the paddy soil carbon pool in the Yellow River Delta in China. Therefore, this study focused on the paddy soil in the Yellow River Delta; using statistical analysis methods and establishing relevant models, we explored the dynamic changes in organic carbon and its active components and their influencing factors in saline paddy fields under two planting patterns. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) content between the two planting patterns. However, the rice–wheat rotation pattern was more conducive to the accumulation of microbial biomass carbon (MBC). The soil organic carbon (SOC) and readily oxidizable organic carbon (ROC) contents increased under the two patterns and different salinization treatments. The results of the redundancy analysis and the random forest model indicated that SSA was the key environmental parameter affecting SOC and its active components under the single-season rice pattern. Under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, soil sucrase activity (SSA) was also a key environmental factor for predicting the SOC content, while electrical conductivity (EC) contributed the most to the active components of SOC. The PLS-PM model showed that the soil carbon sequestration capacity could be improved by enhancing soil enzyme activity under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, while the influence of the soil environment on SOC and its active components was not obvious under the single-season rice pattern. In general, the rice–wheat rotation pattern has agricultural advantages in terms of maintaining ecological balance and can be widely promoted in this region. The results of this study have important practical significance for promoting the green and low-carbon development of agriculture in the Yellow River Delta region and also lay a foundation for subsequent long-term positioning observations and studies on multi-factor interactions.
1. Introduction
Soil salinization significantly limits agricultural production and poses challenges globally [1,2,3]. Rice, a key crop in saline agriculture, is extensively cultivated. However, paddy fields are one of the highest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions after the industrial and transportation sectors, especially when subjected to prolonged waterlogged anaerobic conditions [4]. The mineralization and decomposition of soil organic carbon (SOC) are the primary processes driving these emissions. Consequently, enhancing soil carbon sequestration while minimizing its transformation into greenhouse gases is a critical objective for sustainable agricultural development.
SOC is crucial for both the soil carbon pool and soil fertility, directly affecting agricultural productivity [5]. Current land management strategies often target SOC regulation [6]. Straw incorporation markedly boosts SOC levels, with a strong positive correlation between straw input and SOC content [7,8]. No-tilling and rotary tillage practices not only elevate the SOC content but also significantly improve rice yields [9,10]. Unlike conventional chemical fertilizers, organic fertilizers substantially enhance the SOC content, thereby increasing the soil carbon sequestration capacity [11,12,13].
In saline soils, SOC enhances the soil environment and bolsters ecosystem functions. Studies indicate that exogenous carbon inputs elevate the proportion of macro-aggregates in saline soils, mitigating salt stress on crops [14,15]. SOC accumulation further lowers pH and salt content, optimizing the microbial community diversity [16]. SOC directly improves soil quality by enhancing physical structure and reducing salt damage while also promoting carbon sequestration by regulating microbial community dynamics.
The components of SOC are relatively complex. Based on its stability, SOC can be divided into active and inert carbon pools [17]. The active carbon pool plays an important role in improving soil fertility and is also one of the important parameters for evaluating soil quality [18]. The active components of SOC are mainly derived from plant and animal residues and mainly include dissolved organic carbon (DOC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and readily oxidizable organic carbon (ROC). DOC is very sensitive to changes in the SOC content, and the transformation status of soil nutrients can often be assessed based on its content [19]. As an important source of soil nutrients, the MBC content reflects the utilization of carbon sources by soil microorganisms and is crucial for the activities of soil microorganisms [20]. As an important energy source in the ecosystem, the ROC content can reflect the quality and availability of SOC [21]. SOC serves as the material source for DOC, MBC, and ROC. When humus in SOC decomposes, small-molecule soluble organic matter is released to form DOC. SOC provides energy and carbon sources for microorganisms, promoting their growth and reproduction, thus determining the MBC content. The highly oxidizable and decomposable part of SOC is called ROC. There is a mutual transformation between DOC and MBC. After microorganisms absorb DOC, they convert it into a part of their own biomass through metabolism, thereby increasing the MBC content. Meanwhile, when microorganisms die, decompose, or secrete molecules during metabolism, soluble organic matter is released into the soil, increasing the DOC content. DOC and MBC are considered a part of ROC because they are easily oxidized and decomposed.
Soil water and salt not only affect the decomposition and storage of organic carbon but also indirectly regulate the transformation process of organic carbon by influencing the structure and function of the microbial community. Understanding the basic laws of water and salt migration is not only crucial for the prevention and control of soil salinization but it also has far-reaching significance for maintaining the stability of agricultural production and ecosystems [22]. There is an important interrelationship between soil nutrients and organic carbon components. Increasing soil organic carbon can improve soil fertility and promote the supply and availability of nutrients. Soil enzyme activity is an important metric for assessing soil fertility and self-purification ability, which is often used as one of the metrics for measuring soil quality. Soil organic carbon provides substrates for enzyme activity and indirectly affects the production and action of enzymes through changes in microbial activity, while soil enzymes promote the mineralization and transformation of organic carbon by decomposing it.
Although the current research on SOC in paddy fields is extensive, most of it focuses on non-saline paddy fields. As an important wetland ecosystem in China, rice cultivation in the Yellow River Delta can not only increase the vegetation cover and reduce soil erosion in this area but can also serve as one of the important carbon pools in the farmland system. Some studies have shown that a wheat–maize rotation pattern can significantly increase SOC storage compared with single-season cotton planting in the Yellow River Delta [23]. However, it remains questionable whether similar conclusions can be drawn for paddy field SOC. Whether there are differences in the dynamic changes in SOC and its active components and their influencing factors under the two planting patterns and how to improve soil carbon sequestration through effective management measures for different planting patterns are urgent issues that need to be solved. This study hypothesized that there are differences in the dynamic changes in SOC and its active components and their influencing factors under two planting patterns. Random forest and redundancy analyses were used to identify the key environmental factors affecting the levels of SOC and its active components. The causal relationship between the soil environment and the levels of SOC and its active components was modeled using the PLS-PM method, with the aim of providing a theoretical basis for the sustainable development of agriculture and ecological protection in the Yellow River Delta.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
The field experiment was carried out in 2023. The experimental field was located in Dongying City (37°42′ N, 118°53′ E), Shandong Province, 2 m above sea level, belonging to the warm temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate zone. The annual average temperature was 12.4 °C, the average precipitation was 590.9 mm, the rainy season was mostly concentrated in July and August, and the annual evaporation was 1500 mm. The soils in this region are predominantly fluvo-aquic, with textures varying from sandy loam to light loam. They exhibit good permeability but moderate water and fertilizer retention. Influenced by alluviation from the Yellow River, the soil layer is deep with a relatively strong nutrient base, though the pH is slightly elevated.
2.2. Experiment Design and Sample Treatment
The experiment type was a field trial (Supplementary Figure S1). Before conducting the experiment, we selected three farmlands with different salt contents and classified them into low salt (1–3‰), medium salt (3–5‰), and high salt (5–7‰) based on the soil salt content. The experiment included 6 treatments: (1) low salt + single cropping rice (LS), (2) low salt + rice–wheat rotation (LR), (3) medium salt + single cropping rice (MS), (4) medium salt + rice–wheat rotation (MR), (5) high salt + single cropping rice (HS), and (6) high salt + rice–wheat rotation (HR). The total planting area under each treatment was approximately 667 m2, which was evenly divided into three plots for repeated experiments. In late October 2023, winter wheat was planted in the LR, MR, and HR treatment fields (the wheat variety was “Nongda 753”, and the planting method was manual broadcasting). Field management and fertilization were carried out according to conventional treatments, and no crops were planted in the LS, MS, and HS treatment fields. In early May 2024, wheat was harvested, and rice seedlings of the variety “Yanhuangxiangjing” were cultivated simultaneously. The rice seedlings were transplanted by mechanical seeding in mid-to-late May. Field management and fertilization were carried out using conventional methods.
Soil samples were collected from each paddy field at the regreening, flowering, and maturity stages of rice. For the three experimental plots of each treatment, the topsoil samples (0–20 cm) were uniformly collected using a soil auger according to the diagonal sampling method and then mixed (Supplementary Figure S2). Then, a 40–50 g soil sample was put into an aluminum box for the determination of soil moisture content (SMC), the rest was put into a self-sealing bag, and a small part was taken back to the laboratory and stored at 4 °C for the determination of microbial biomass carbon. The rest of the soil sample was naturally dried and ground through a 20 mm sieve for the determination of other relevant indicators.
2.3. Measurement of Soil Environmental Factor Index
SMC was determined using the oven-drying method, calculated as follows [24]:
where m1 is the wet soil weight of each sample (50 g) and m2 is the dry soil weight of each sample.
SMC = (m1 − m2)/m2,
Soil salinity was measured via soil electric conductivity (EC). We added 25 mL CO2-free distilled water to 5 g air-dried soil (5:1 water-to-soil ratio), followed by 3 min of shaking, 30 min of settling, and analysis with a calibrated conductivity meter.
Available phosphorus (AP) content was assessed using the Olsen method [25]. A 2.5 g air-dried soil sample, sieved through a 2 mm mesh, was dissolved in 10 mL of 0.5 mol L−1 NaHCO3. The solution was titrated with 0.5 mol L−1 H2SO4 until the supernatant shifted from blue to yellow. Subsequently, 5 mL of a freshly prepared molybdenum–antimony–ascorbic acid color-developing agent was added, and the solution was left to stand for 30 min. Absorbance was then measured at 700 nm using a spectrophotometer (TU-1901, Beijing Puxi General Instrument Co., Ltd., China The same below).
The determination of soil available potassium (AK) content was carried out according to the industry standards (NY/T 889-2004) [26]. A 5 g air-dried soil sample, sieved through a 1 mm mesh, was mixed with 50 mL of 1 mol L-1 NH4OAc solution. The filtrate along with potassium standard solutions (0, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 50 mg L−1) prepared with the same extractant were analyzed concurrently. Potassium emission intensity was recorded at λ = 750 nm via flame photometry.
Total nitrogen (TN) content was measured using the Kjeldahl method [27]. We began by weighing 0.5 g of air-dried soil, sieved to 0.25 mm. We then added 2 g of a catalyst mixture (K2SO4:CuSO4∙5H2O:Se = 100:10:1 by mass), 5 mL of concentrated H2SO4, and 2 drops of 30% H2O2. Following digestion and cooling, the solution was transferred to a Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer. We added 40% NaOH for distillation, and the resulting ammonia was absorbed with 20 g L−1 boric acid and then titrated with 0.05 mol L−1 HCl to a pH of 4.65.
Soil sucrase, amylase, and cellulase activities (SSA, SAA, SCA) were uniformly measured using 3,5 salicylic acid colorimetry [28,29,30]. Weigh 5 g of air-dried soil sample; add 15 mL of 8% sucrose solution, 5 mL of phosphate buffer (pH = 5.5), and 5 drops of toluene; and then shake well. After incubating in a 37 °C incubator for 24 h, filter and make up the volume to obtain the SSA test solution. Weigh 5 g of air-dried soil sample; add 10 mL of 1% starch solution, 10 mL of phosphate buffer (pH = 5.6), and 5 drops of toluene; and then shake well. After incubating in a 37 °C incubator for 24 h, filter and make up the volume to obtain the SAA test solution. Weigh 10 g of air-dried soil sample; add 20 mL of 1% carboxymethyl cellulose solution, 5 mL of phosphate buffer (pH = 5.5), and 1.5 mL of toluene; and then shake well. After incubating in a 37 °C incubator for 72 h, filter and make up the volume to obtain the SCA test solution. Add DNS to the SSA test solution, heat it and make up the volume, and then measure it at λ = 508 nm with a spectrophotometer. Its activity is expressed as the number of milligrams of glucose contained in 1 g of air-dried soil after 24 h as the enzyme activity unit (mg/(g·d)). Add DNS to the SAA test solution, heat it and make up the volume, and then measure it at λ = 508 nm with a spectrophotometer. Its activity is expressed as the number of milligrams of maltose contained in 1 g of air-dried soil after 24 h as the enzyme activity unit (mg/(g·d)). Add DNS to the SCA test solution, heat it and make up the volume. After waiting for 15 min, measure it at λ = 540 nm with a spectrophotometer. Its activity is expressed as the number of milligrams of glucose contained in 1 g of air-dried soil after 24 h as the enzyme activity unit (mg/(g·d)).
2.4. Measurement of SOC and Active Components in Soil
SOC was determined using a total organic carbon (TOC) analyzer (Shimadzu TOC-Kyoto City, Japan. The same below) with the SSM-5000A solid sample measurement unit. In the sample boat of the TC reaction chamber, 50 g of air-dried soil sample acidified with phosphoric acid was added. The soil sample was heated at high temperature to generate CO2 and H2O. After separating H2O, CO2 was measured by a non-dispersive infrared detector (NDIR) and compared with the standard curve obtained from the calibration standard solution to determine the mass fraction of SOC [31].
First, weigh wet soil equivalent to 10 g of dried soil into a culture bottle. Place a small beaker filled with water in a vacuum desiccator and put two small beakers containing 30 mL of NaOH solution, one small beaker containing 50 mL of ethanol-free chloroform, and the polyethylene bottle with the soil sample into the desiccator. After sealing, use a vacuum pump to evacuate until the chloroform boils for 2 min and then place it in the dark at 25 °C for 24 h. After the fumigation is completed, use a vacuum pump to evacuate until there is no chloroform odor. Add 40 mL of 0.5 mol L−1 K2SO4 solution to the culture bottle for extraction for 30 min. Centrifuge the solution, filter it through a 0.45 μm membrane, and then measure it with a TOC analyzer [32]. The calculation formula is as follows:
where c1 is the organic carbon content of fumigated samples; c2 is the organic carbon content of unfumigated samples; and 0.45 is the conversion factor. The amount of carbon extracted by chloroform fumigation is approximately 45% of the total actual microbial biomass carbon in the soil. Therefore, it is necessary to divide by 0.45 to back-calculate the true microbial biomass carbon content.
MBC = (c1 − c2)/0.45
Determination of soil dissolved organic carbon: Weigh 8 g of air-dried soil sample into a centrifuge tube, add 40 mL of 0.5 mol/L K2SO4 solution, place it on a shaking table for 30 min, centrifuge for 10 min, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and measure it with a total organic carbon meter [33]. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where c0 is the test concentration of the soil sample extract, c is the concentration of K2SO4, m is the mass of the soil sample, and 40 is the conversion coefficient. The TOC analyzer directly measures the DOC concentration in 1 mL of the filtered extract. By multiplying this concentration by the total volume of the extract (40 mL), the total mass of DOC extracted from the 8 g soil sample can be obtained.
DOC = (c0 − c) × 40/m
Soil readily oxidizable organic carbon was determined by the potassium permanganate oxidation method [34]. Weigh 1 g of air-dried soil sample and place it in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 25 mL of 333 mmol L−1 K2SO4 solution, shake for 1 h, centrifuge at the speed of 4000 r min−1 for 4 min, take 0.2 mL supernatant and place it in a 50 mL volumetric flask for constant volume, colorimetrically determine the diluent at the wavelength of 565 nm of spectrophotometer, and compare it with the standard curve obtained by the calibration standard solution to calculate the content of ROC. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where V is the potassium permanganate concentration change value: 25 and 250 represent the volume (mL) of KMnO4 used and the dilution factor, respectively; 9 indicates the amount of carbon (mg) consumed corresponding to a 1 mmol L−1 change in KMnO4 concentration; and m is the mass of the soil.
ROC = V × 25 × 250 × 9/m × 1000
2.5. Data Processing and Analytics
The software SPSS 27.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to conduct ANOVA analysis on the significant differences in soil environmental factors, organic carbon, and active components among the different treatments during the same period. To ensure the correctness of the results, the Tukey HSD test was performed. The correlation between all indicators under the two planting models was then analyzed by the t-test using SPSS 27.0, and the correlation heat map was drawn using Origin 2021 software (Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA) to comprehensively analyze the linear relationships between environmental factors and the active components of SOC (MBC, DOC, and ROC). The Canoco 5 software (Biometris, The Netherlands) was used to analyze the linear relationships between the active fractions of SOC, DOC, MBC, and ROC and soil environmental factors and to quantify the explanatory degree of soil environmental factors for SOC fractions to clarify the relative importance of environmental factors to the soil organic carbon (SOC) content. The random forest model was employed to predict the significant contribution of soil environmental factors to SOC content. To comprehensively analyze the influence mechanism of the soil environment on soil organic carbon (SOC) and its active components, according to the different attributes of soil environmental factors, they were divided into different environmental components, and the PLS-PM method in the Rstudio 4.4.3 software (The University of Auckland) was used to establish a model for SOC, its active fractions, and different soil environmental components. The goodness-of-fit of the model was judged by the GOF value. R2 represents the predictive ability of the explanatory variable for the endogenous variable, and the path coefficient indicates the influencing mechanism between the two.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Environmental Parameters in Paddy Soils with Different Salinization Levels Under Two Cropping Patterns
The dynamic changes in paddy soil environmental parameters under the different treatments are shown in Figure 1. Overall, the SMC continuously decreased with the growth of the rice crop. Although the SMC under the HS and HR treatments did not change significantly during the rice turning-green and flowering stages, it decreased significantly at the maturity stage. Overall, the EC value was lowest at the rice maturity stage. Interestingly, under both low-salt and high-salt treatments, the EC value under the rice–wheat rotation pattern was significantly lower than that under the single-season rice pattern, while there was no significant difference between the two patterns under the medium-salt treatment. Overall, the AP, AK, and TN contents under both planting patterns generally showed the lowest values at the rice maturity stage. The AP content under the high-salt treatment and rice–wheat rotation pattern was significantly higher than that under the single-season rice pattern, while the opposite relationship was observed under the medium-salt treatment. At the rice turning-green stage, under the medium- and high-salt treatments, the AK content under the single-season rice pattern was significantly higher than that under the rice–wheat rotation pattern. The TN content under both treatments was the highest at the rice flowering stage. Overall, under both treatments, the SSA was the highest at the rice maturity stage. The SSA under the LS and LR treatments was significantly higher than that under the other treatments. However, the SAA was the lowest at the rice maturity stage. The SAA under the MR and HR treatments was significantly higher than that under the other treatments. The LR treatment showed the highest SCA at the rice maturity stage, while the other treatments showed the lowest values at the rice maturity stage.
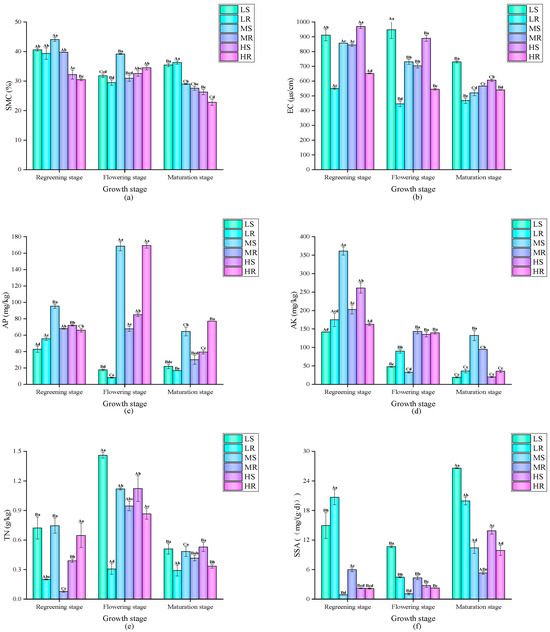
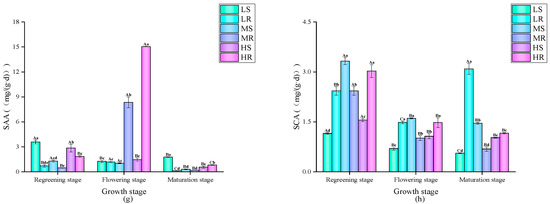
Figure 1.
Dynamic changes in soil environmental parameters under different treatments. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different time periods under the same treatment, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period (p < 0.05). This convention applies to the subsequent figures. Dynamic changes in (a) SMC; (b) EC; (c) AP content; (d) AK content; (e) TN content; (f) SSA; (g) SAA; and (h) SCA.
3.2. Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and Its Active Components in Paddy Soils with Different Salinization Levels Under Two Cropping Patterns
The dynamic changes in the levels of SOC and its active components in paddy fields under the different treatments are shown in Figure 2. Overall, the SOC content under the MS and LS treatments was relatively stable, while the SOC content under the other treatments reached its peak at the rice maturity stage. Throughout the whole growth period, the SOC values of the rice–wheat rotation mode under the low-salt and high-salt treatments were higher, while the SOC value of the single-season rice mode under the medium-salt treatment was higher. There were significant differences in MBC contents under the different treatments during the growth period. Under the medium-salt treatment, the MBC content of the single-season rice mode was significantly higher than that of the rice–wheat rotation mode. Interestingly, under the low-salt and high-salt treatments at the rice turning-green and flowering stages, the MBC content of the rice–wheat rotation mode was significantly higher than that of the single-season rice mode; at the rice maturity stage, it was significantly lower than that of the single-season rice mode. Overall, the DOC contents under all the treatments showed a gradually decreasing trend with the growth of the rice crop, and the DOC content of the LR treatment was particularly high at the rice turning-green stage. Throughout the whole growth period, the difference in DOC content between the two planting modes was small. There were significant and varying differences in the ROC contents of the different treatments at different growth stages. Except for the peak in the ROC contents of the MS and MR treatments at the rice turning-green stage, the change trends under the other treatments were relatively stable. Throughout the whole growth period, the ROC content of the rice–wheat rotation mode under the medium-salt treatment was higher, and the difference between the two other treatments was small.
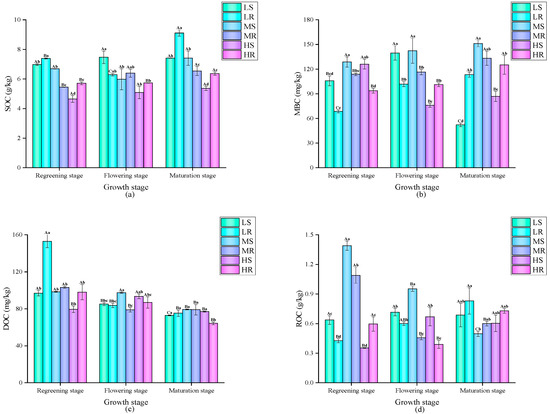
Figure 2.
Dynamic changes in the levels of SOC and its active components under different treatments: Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different time periods under the same treatment, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period (p < 0.05). (a) SOC content; (b) MBC content; (c) DOC content; (d) ROC content.
3.3. Relationship Between Soil Environmental Parameters and Soil Organic Carbon and Its Active Components
The correlation analysis between soil environmental parameters and the levels of SOC and its active components under the two planting patterns is shown in Figure 3. Under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, AP and AK were positively correlated with SOC content, while SSA was negatively correlated with SOC content. EC, AK, and SCA were all positively correlated with MBC content. EC, SMC, AK, and SAA were all negatively correlated with DOC content. TN and SAA were positively correlated with ROC content. Under the single-season rice pattern, SSA was negatively correlated with SOC content. EC and SCA were negatively correlated with MBC content, while SSA was positively correlated with MBC content. EC, SMC, AP, TN, and SCA were all negatively correlated with DOC content, and SSA was positively correlated with DOC content. EC, SMC, AP, and SCA were negatively correlated with ROC content.
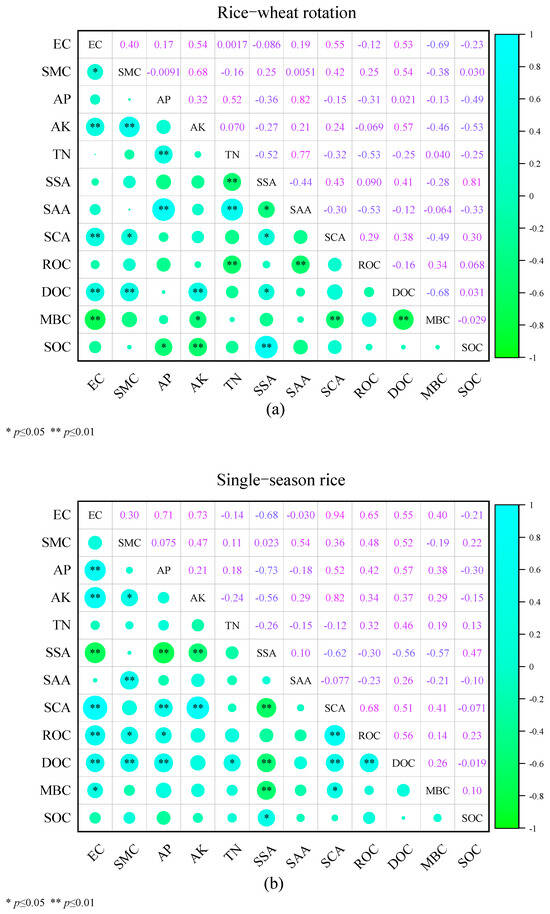
Figure 3.
Correlation analysis of soil environmental parameters and levels of SOC and its active components under the two planting patterns: (a) rice–wheat rotation; (b) single-season rice. Blue circles represent positive relationships, whereas green circles represent negative relationships. The size of the circles represents the strength of the correlation, and the numbers represent the correlation coefficients. (*) and (**) indicate a significant correlation at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.
3.4. Analysis of the Impact of Soil Environmental Parameters on Soil Organic Carbon Content
The stochastic forest model for soil environmental parameters and SOC content under the two cropping patterns is shown in Figure 4. SSA was found to be the most influential environmental parameter for SOC content under the two cropping patterns, with contribution rates of 17.72% (rice–wheat rotation) and 14.49% (single-crop rice). SAA and AP had higher impacts on SOC content under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, with contribution rates of 14.49 and 3.96%, respectively. The other environmental parameters had some impact on SOC content, but their influence was weak. EC, SMC, AP, and SCA had stronger effects on SOC content under the single-season rice mode, with contribution rates of 14.47, 13.89, 13.56, and 13.04%, respectively, while the other environmental parameters had relatively weak effects.
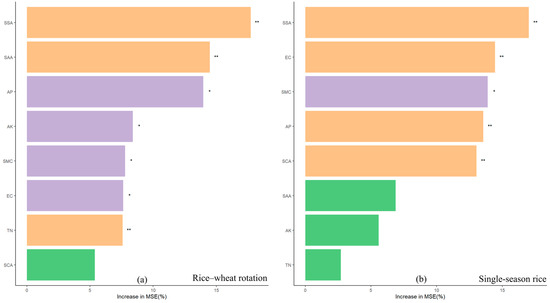
Figure 4.
Relative importance of soil environmental parameters on SOC content under two cropping patterns: (a) rice–wheat rotation; (b) single-season rice. (*) and (**) indicate a significant and highly significant correlation between SOC and the factor, respectively.
3.5. Redundancy Analysis of Soil Environmental Parameters and Active Organic Carbon Components
The redundancy analysis between soil environmental parameters and SOC active components under the two planting modes is shown in Figure 5. Under the rice–wheat rotation mode, the explanation rate of soil environmental parameters for SOC active components was 80.56%; the contribution rates of the first and second principal components were 76.76 and 3.8%. EC (43.4%, F = 13.4, p = 0.002), SSA (22.1%, F = 9.1, p = 0.004), and AK (20.5%, F = 13.3, p = 0.002) had higher contribution rates for SOC active components, while the other environmental parameters had weaker contributions. Under the single-season rice mode, soil environmental parameters explained 48.72% of the variance in SOC active components; the first and second principal components accounted for 43.94% and 4.78% of the variance, respectively. SSA (65.6%, F = 11.47, p = 0.002) and SMC (10.7%, F = 2, p = 0.174) contributed more to explaining the variance in SOC active components than the other environmental parameters.
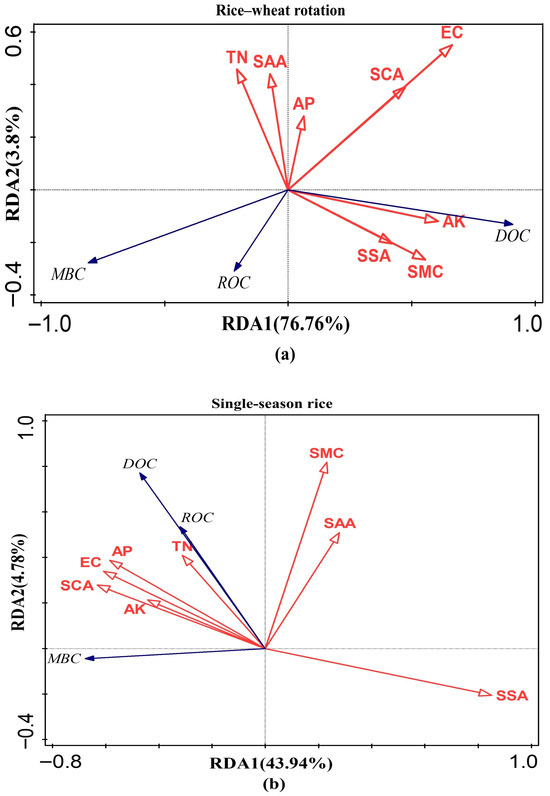
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis of soil environmental parameters and active components of SOC under two cropping patterns: (a) rice–wheat rotation; (b) single–season rice. The red lines represent soil environmental parameters, and the black lines represent active components of SOC. When the angle between two rays is greater than 90°, there is a negative correlation between the two indicators; when it is equal to 90°, there is no correlation between the two indicators; when it is less than 90°, there is a positive correlation. The length of the perpendicular line from the end of one arrow to the other ray indicates the strength of the correlation. RDA1 and RDA2 represent the interpretation rates of the first and second principal components, respectively.
3.6. Interaction Mechanism Between Soil Environment, SOC, and Active Components of SOC
The influence paths between enzyme activities and the contents of soil water, salt, nutrients, SOC, and SOC active components under the two planting patterns are shown in Figure 6. Under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, soil water and salt had a weak influence on soil nutrients and SOC, but these parameters had a significant positive influence on soil enzyme activities and SOC active components. Soil nutrients did not have a significant influence on SOC and its active components but had a negative influence on soil enzyme activities. Soil enzyme activities had a significant positive influence on SOC and its active components. SOC active components had a significant negative influence on SOC content. Under the single-season rice pattern, soil water and salt had a significant positive influence on soil nutrients, but these parameters did not have a significant influence on the other indicators. Soil nutrients had a significant negative influence on soil enzyme activities but did not have a significant influence on the other indicators. SOC active components had a significant positive influence on SOC content.
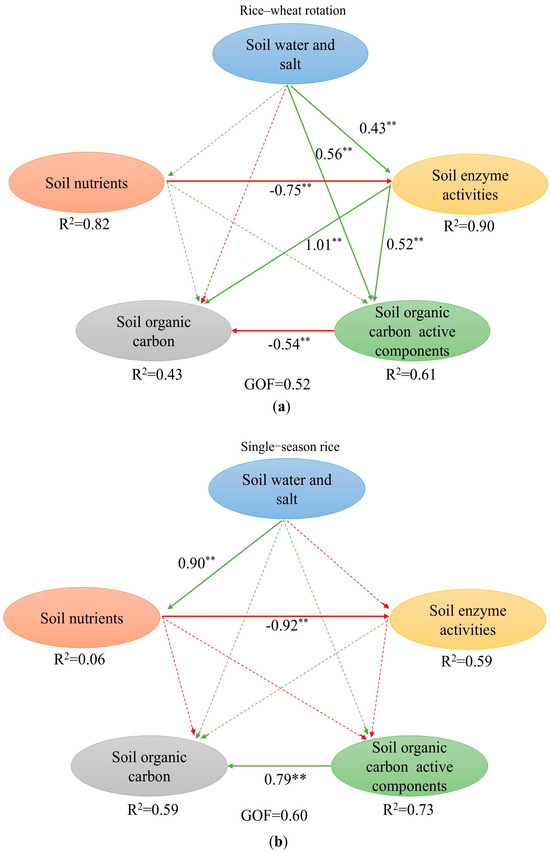
Figure 6.
Partial least squares path model (PLS-PM) for soil environment, SOC, and active components of SOC under two planting patterns: (a) rice–wheat rotation; (b) single-season rice. GOF > 0.50 indicates that the model has a good fit. R2 represents the predictive ability of the explanatory variables for the endogenous variables (the starting point of the ray is the explanatory yield, and the end point is the endogenous variable). A solid line indicates a correlation between two variables, and a dashed line indicates the absence of a correlation between two variables. Green indicates a positive correlation between two variables, red indicates a negative correlation between two variables, and the numbers represent the strength of the correlation. (**) indicates that there is a significant influence between the two.
4. Discussion
4.1. Dynamic Changes in Soil Environmental Parameters, Soil Organic Carbon (SOC), and SOC Active Components
Research has found that only when the soil moisture content is maintained within a reasonable range can the water use efficiency be balanced and the rice yield be improved [35]. The results of this study show that, under the two planting patterns, both the soil moisture content and electrical conductivity generally tended to be the lowest at the rice maturity stage. The reason for this is that the water demand of rice drops significantly at this stage, so the “field drying” treatment is usually adopted in field management. Meanwhile, the transpiration of rice plants still continuously consumes soil moisture, resulting in a significant decrease in the moisture content under both of these effects. The soil salts migrate to the deep-layer soil with water infiltration, reducing the surface salt concentration. Moreover, during the process of the rice roots absorbing nutrients, some soluble salt ions are indirectly removed, further reducing the conductivity of the soil solution. Meanwhile, this study also found that, under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, the EC values under the low-salt and high-salt treatments were significantly lower, while there was no significant difference between the two planting patterns under the medium-salt treatment. This may be because the cultivation of wheat inhibits the increase in soil salts, and the lack of a significant difference under the medium-salt treatment may be due to the relatively weak influence of this factor in the short-term experiment.
After rice enters the maturity stage, the demand for nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, by grains increases significantly, leading to an obvious downward trend in the levels of available soil nutrients [36]. This was also observed in this study. Interestingly, under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, the AP content under the high-salt treatment was higher, while the opposite occurred under the medium-salt treatment. This may be because, under the medium-salt treatment, the demand for soil AP by wheat is higher, thus reducing the soil AP content. However, under the high-salt treatment, the absorption of soil AP by wheat is restricted, resulting in a large amount of AP accumulation in the soil. At the rice turning-green stage, the roots are relatively fragile. Under the medium- and high-salt treatments, the decomposition of the residual roots of the previous wheat crop in the rice–wheat rotation field consumed part of the AK, while there was no nutrient competition from the previous crop in the single-season rice pattern, resulting in a higher AK content. This is also the reason why the AK content was higher for the single-season rice pattern under the medium- and high-salt treatments in this study. In addition, this study also found that the peak TN content under all the treatments appeared at the rice flowering stage, which may be due to the fact that the rice roots begin to age at this time, resulting in a weak ability to absorb nitrogen from the soil.
This study found that, under the two planting patterns, SSA was the strongest at the rice maturity stage, while SAA and SCA were the weakest at this stage. This might be because the starch and cellulose substrates in the soil were largely consumed and decomposed during the early growth stage of rice, which inhibited enzyme synthesis. However, at the rice maturity stage, the plants need to transport a large amount of photosynthetic products to the grains to be converted into storage substances such as starch, and sucrose is just the main form of photosynthetic product transport, so the activity of the enzymes for these molecules significantly increased.
SOC storage in global paddy fields accounts for 14.2% of the global farmland storage [37]. The SOC content in the topsoil of Chinese paddy fields has increased significantly over the past 30 years, with the content and density increasing by 48 and 39%, respectively [37]. High-salt and high-pH environments weaken SOC stability. In the Yellow River Delta region, due to its relatively high salinity, the SOC storage is significantly lower than that in other regions [38]. The SOC content in the topsoil of paddy fields in the Huixian karst area of Guilin, China, is as high as 22.33 g/kg, while that in the paddy fields of the Songnen Plain in Heilongjiang is 15.1 g/kg [39,40]. In this study, the SOC contents in the paddy fields were all lower than 10 g/kg.
Relevant studies have shown that paddy upland rotation can improve the soil structure through periodic wet–dry alternation, which not only effectively inhibits soil salinization but also significantly increases the SOC content [41]. The results of this study found that the SOC and MBC contents of the rice–wheat rotation mode under the low-salt and high-salt treatments were higher, which is consistent with the findings of previous studies. However, under the medium-salt treatment, the single-season rice mode had higher values. This may be because extreme salinity (too high or too low) can inhibit the metabolic functions of microorganisms, while the crop diversity in rice–wheat rotation can alleviate the inhibitory effect of salt stress on the microbial community, thereby maintaining a relatively high MBC content and indirectly promoting SOC sequestration. In a medium-salt environment, the long-term waterlogging conditions in single-season rice fields can form an anaerobic micro-environment, reducing the toxic effect of salt on microorganisms. This allows microorganisms to focus more on utilizing limited carbon sources, resulting in a higher accumulation efficiency for SOC and MBC than in rice–wheat rotation systems. Meanwhile, this study also found that, under the two planting patterns, except for the higher ROC content in the rice–wheat rotation pattern under the medium-salt treatment, the differences in the DOC and ROC contents were very small. This may be because the turnover cycles of DOC and ROC are short, and they are more likely to reach a dynamic equilibrium. Under both planting modes, the active organic carbon produced by straw decomposition and root carbon exudation will be quickly utilized by microorganisms or lost through leaching. Therefore, it is difficult to maintain the difference in the total amount between the two planting patterns in the long term. In a medium-salt environment, the wet–dry alternation in rice–wheat rotation will destroy some soil aggregates, increasing the amount of ROC. Under medium-salt stress, the diversity of straw in rotation systems can maintain a more abundant microbial community, and its metabolic activities tend to accumulate ROC. Therefore, the ROC content in the rice–wheat rotation mode was only higher at this salinity level.
4.2. Influence of Soil Environment on SOC and Its Active Components
The presence of SOC results from the equilibrium between the carbon input and output, which is modulated by the soil environment through intricate regulatory mechanisms [42,43]. This study examined the impact of eight environmental parameters on SOC, focusing on soil water, salt, and nutrient contents, and enzyme activities. Soil salinity disrupts the soil aggregate structure by increasing the pH and sodium adsorption ratio, thereby reducing the stability of SOC and leading to a decrease in the contents of SOC and its active components [44]. However, in this study, there was an extremely significant positive correlation between EC and ROC, DOC, and MBC contents in the single-season rice cropping pattern. This indicates that the higher the soil salinity, the more intense the microbial activity. This result is inconsistent with the findings of previous studies, possibly because, in the single-season rice cropping pattern, the inhibitory effect of salinity on SOC transformation was overshadowed by the carbon source scarcity. Microbial activity is mainly driven by the carbon source and is less sensitive to salinity, resulting in the disappearance of the negative correlation between MBC and ROC contents and EC. Instead, a positive correlation appeared due to the synchronous change in the carbon source input and salinity. Meanwhile, in both cropping patterns, there was a significant positive correlation between EC and DOC content, which may be caused by the formation of a stable complex system between DOC and salt ions (such as Na+ and Cl−) and their retention in the plow layer soil with water. AP can increase the accumulation of SOC by promoting plant growth and microbial activity, thereby increasing plant root exudates and residues [45]. AK can also enhance the accumulation of SOC, and there was a significant positive correlation between SOC content and AK. Soils with a high SOC content usually have a high AK content [43,46]. However, in this study, AP and AK in the rice–wheat rotation pattern were negatively correlated with SOC content, indicating that the more abundant the soil nutrients, the poorer the stability of SOC. This is inconsistent with the findings of previous studies, possibly because the increase in paddy soil SOC promotes microbial activity. Under flooded conditions, soil microorganisms absorb a large amount of phosphorus and potassium from the soil for their own growth when decomposing organic matter, resulting in a decrease in the AP and AK contents. When the input of soil carbon sources is limited and the DOC or MBC content in the soil is relatively low, microorganisms are in a “carbon-limited” state. To obtain carbon, microorganisms will actively secrete more extracellular enzymes to decompose complex organic matter and release absorbable small-molecule carbon [47]. This is also the reason why there was a negative correlation between SSA and DOC and MBC contents in the single-season rice cropping pattern and a negative correlation between SCA and MBC content in the rice–wheat rotation pattern.
As the main product of soil microorganisms, an increase in the activity of SSA generally indicates an improvement in the SOC sequestration capacity. Meanwhile, a high SOC content provides an abundant energy source for soil microorganisms, creating a favorable environment for their growth and reproduction, which, in turn, promotes the secretion of sucrase [48]. This two-way feedback mechanism has been verified by field experiments. For example, in saline–alkali paddy fields, a significant positive correlation between SSA and SOC was found during the rice seedling stage (R2 = 0.97) [49]. In this study, the random forest prediction model revealed that SSA was the environmental parameter with the strongest influence under the two planting patterns. The core function of SSA is to decompose insoluble sucrose-type carbon sources in the soil into glucose and fructose, which are easily utilized by microorganisms; this process is a key step in SOC transformation. Regardless of the planting pattern, the accumulation and turnover of SOC rely on this initial decomposition step. Secondly, the SOC replenishment in both patterns depends on crop residues, and the decomposition of sucrose-type substances in the residues must be accomplished through SSA.
As the most active part of organic carbon with the fastest turnover, the active components of SOC can reflect the dynamic changes in the soil carbon pool, which is of great significance for agricultural management and ecological protection [50,51]. The results of the redundancy analysis in this study showed that, under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, EC is the environmental parameter with the highest contribution rate to variance in the active components of SOC, while under the single-season rice pattern, SSA had the highest contribution rate. Under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, the alternation of dry and wet conditions causes dynamic fluctuations in soil salinity. On the one hand, this directly affects the desorption and migration of DOC by changing the charge properties of soil colloids; on the other hand, it selects salt-tolerant microbial communities, indirectly affecting the decomposition and transformation of SOC. Therefore, salinity is the key environmental factor restricting the cycling of SOC active components under this planting pattern. Under the single-season rice pattern, SSA, as the “key initiating enzyme” for SOC decomposition, directly converts difficult-to-utilize carbon sources into easily utilizable forms, playing a key role in microbial proliferation and carbon pool changes.
In this study, the PLS-PM method was used to classify the attributes of soil environmental parameters (soil water, salt, and nutrient contents and enzyme activities), and dynamic modeling was conducted for SOC and its active components. The results showed that, under the rice–wheat rotation pattern, soil enzyme activities positively regulated the carbon pool, while the active components of SOC had a negative effect on SOC. The “alternation of wetting and drying” in the rice–wheat rotation pattern put the soil carbon cycle in a state of dynamic fluctuation. SSA, SAA, and SCA provided a continuous and easily available carbon source for SOC accumulation by efficiently decomposing insoluble carbon sources and promoting the fixation of carbon by microorganisms, thus having a direct positive impact on SOC and its active components. However, the active components, such as DOC and ROC, had a fast turnover rate, and their production rates were lower than their consumption rates, which led to the accumulation of active components and the acceleration of the mineralization and consumption of SOC, thus having a negative impact. Under the single-season rice pattern, the impact of the soil environment on SOC and its active components was not significant, and the active components positively affected SOC. This might be because, under the single-season rice pattern, the paddy fields were flooded for a long time, which made the carbon cycle enter a relatively stable accumulation stage, weakening the limiting effect of the soil environment, and the accumulation of SOC active components became the direct source for the improvement of the SOC content.
4.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
This study clarified the variations in and factors influencing SOC and its active components under different planting patterns in the saline–alkali land of the Yellow River Delta. However, there were limitations to this study. First, it is difficult for short-term experiments to fully reflect the long-term response of the carbon cycle to environmental factors. Second, only samples from the 0–20 cm tillage layer were collected, and the vertical distribution and driving mechanisms of carbon components in deep soil were not investigated. Third, the role of the microbial community was not deeply explored, and the microbial driving mechanism of the carbon cycle was not fully explained.
Future research can conduct long-term positioning experiments for more than five years to improve the reliability and generalizability of the results; perform soil sampling at multiple depths to provide a complete basis for a comprehensive assessment of the carbon sequestration potential; and combine high-throughput sequencing with microbial function verification to analyze the key microbial mechanisms and provide targeted theoretical support for optimizing saline–alkali land planting patterns and enhancing carbon sequestration capacity.
5. Conclusions
First, this study explored the dynamic changes in soil environmental parameters, SOC, and its active components under two planting patterns and different salinization treatments. The results showed that, under the two planting patterns, the soil water, salt, and nutrient contents, SAA, and SCA generally reached the lowest levels at the rice maturity stage, while soil sucrase activity (SSA) was the highest at this stage. Meanwhile, no significant difference in DOC content was found between the two planting patterns, and the rice–wheat rotation pattern produced a significantly higher MBC content. Moreover, the SOC and ROC contents under the two planting patterns varied under different salinization treatments. Second, this study elucidated the relationships between soil environmental parameters and SOC and its active components using redundancy analysis and a random forest model. The results indicated that SSA was the most influential predictor of SOC under both planting patterns. In the rice–wheat rotation pattern, EC contributed the most to explaining the variance in the SOC active components, while in the single-season rice pattern, SSA had the highest contribution. Finally, this study classified the soil environmental parameters according to their attributes and established a PLS-PM model. In the rice–wheat rotation pattern, soil enzyme activity had a positive impact on the changes in SOC and its active components, while the impact of the soil environment on SOC and its active components was not obvious in the single-season rice pattern. In conclusion, although there were differences in the contents of SOC and its active components and their influencing factors between the two planting patterns, overall, the rice–wheat rotation pattern has agricultural advantages in terms of improving the ecological balance and can be promoted in this region. Meanwhile, the soil carbon sequestration capacity under this pattern can be enhanced by increasing soil enzyme activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15112524/s1, Figure S1: Dynamic change patterns of soil environmental indicators under different treatments; Figure S2: Dynamic change patterns of soil organic carbon and active component contents under different treatments.
Author Contributions
M.L.; Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft preparation, J.D.; Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft preparation, S.G.; Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft preparation, D.Z.; Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition, C.W.; Methodology, Formal analysis, J.X.; Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition, L.Z.; Supervision, Writing—review and editing, J.W. (Jun Wang); Supervision, Project administration, H.W.; Software, Resources, J.W. (Jianlin Wang); Conceptualization, Resources, S.Z.; Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review and editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 32071954, NO. 31872882), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (NO. ZR2019PC040), Natural Science Foundation of Dongying (NO. 2023ZR05), Dongying City-University Cooperation Fund Project (NO. SXHZ-2024-02-8, NO. SXHZ-2022-02-8), Youth Science and Technology Rising Star Program Project of Binzhou City (NO. QMX2023002), and a PhD initiative project (NO. 2019Y17) from Shandong University of Aeronautics (formerly known as Binzhou University), Graduate Innovation Fund Project of Shandong University of Aeronautics (SHSYCX02).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SMC | Soil moisture content |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| AK | Available potassium |
| SSA | Soil sucrase activity |
| SAA | Soil amylase activity |
| SCA | Soil cellulase activity |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| MBC | Microbial biomass carbon |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| ROC | Readily oxidizable organic carbon |
References
- Pistocchi, C.; Ragaglini, G.; Colla, V.; Branca, T.A.; Tozzini, C.; Romaniello, L. Exchangeable Sodium Percentage Decrease in Saline Sodic Soil after Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag Application in a Lysimeter Trial. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Effects of the Interaction between Biochar and Nutrients on Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration in Soda Saline-Alkali Grassland: A Review. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e01449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The Threat of Soil Salinity: A European Scale Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. Research Advances in the Mechanism Underlying Alternating Wet and Dry Irrigation and Biochar Affect Carbon Sequestration and Methane Emissions in Paddy Field. China Rice 2024, 30, 7–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z. Research advances in soil organic carbon and its fractions under different management pattern. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 2203–2209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng-zhe, E.; Ding, N.; Li, L.; Yuan, J.; Che, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shai, L. Relationship of crop yield and soil organic carbon and nitrogen under long-term fertilization in black loessial soil region on the Loess Plateau in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 4047–4055. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Miao, Y.; Liang, A.; Liu, Q.; Hou, R. Improving Cropland Soil Water Management to Promote Soil Organic Carbon Increase through Organic Material Returning in Cold Black Soil Areas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 382, 109470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Cai, L. Effects of Different Straw Incorporation Amounts on Soil Organic Carbon, Microbial Biomass, and Enzyme Activities in Dry-Crop Farmland. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Huang, G.; Miao, J.; Liu, Y.; Shah, A.N.; Nawaz, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Hassan, M.U. Different Rotation and Double Straw Returning Significantly Increase Liable Organic Carbon Content and Yield of Double Cropping Paddy Field in Southern China. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2023, 17, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Peng, S.; Li, C.; Wen, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, H. Effects of Long-Term Soil Tillage Practices on Soil Organic C Accumulation Characteristics in Double-Cropped Rice Paddy. Land 2024, 13, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Xing, P.; Gu, Q.; Qi, J.; Tang, X. A Rapid Increase of Soil Organic Carbon in Paddy Fields after Applying Organic Fertilizer with Reduced Inorganic Fertilizer and Water-Saving Irrigation Is Linked with Alterations in the Structure and Function of Soil Bacteria. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 379, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Zheng, J. Organic Fertilizer Substitution Increased Soil Organic Carbon through the Association of Microbial Necromass C with Iron Oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Han, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y. Organic Fertilizer Enhances Soil Aggregate Stability by Altering Greenhouse Soil Content of Iron Oxide and Organic Carbon. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 24, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhong, M.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Exogenous Carbon Inputs Alleviated Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress to Cotton in Salinized Field by Improving Soil Aggregate Structure and Microbial Community. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1522534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Fu, Y.; Qiu, R.; Ning, H.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Gao, Y. Carbon Amendments Shape the Bacterial Community Structure in Salinized Farmland Soil. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Qu, X. Soil Depth Exerts a Stronger Impact on Microbial Communities and the Sulfur Biological Cycle than Salinity in Salinized Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kwadwo, A.D. Anning Dominic Kwadwo. Effects of Four Fertilization Regimes on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Carbon Pool Management Index of Potato Farmland. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 912–919. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, C.; Tang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Wen, L.; Xiao, X. Effects of long-term fertilizer management on soil labile organic carbon fractions and hydro lytic enzyme activity under a double-cropping rice system of southern China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 921–930. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Z. Effects of Long-term Fertilization on Content of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Rice Rhizosphere Soil. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 9695–9697. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, X.; Luo, Y. Effect of Different Mode of Alternating Crop-planting on Content of Organic Carbon and Microbial Biomass Carbon in the Soil Within Tobacco Root Regions in Yunnan, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 133–138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xiang, W. Research progress in effects of land use mode on soil active organic carbon. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2012, 32, 134–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; She, D.; Yi, J.; Sun, X.; Han, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H. Roles of Soil Amendments in the Water and Salt Transport of Coastal Saline Soils through Regulation of Microstructure. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2382–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gong, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, T. Continuous Crop Rotation Increases Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in River Deltas: A 40-Year Field Evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kelly, B.C. Accurate Determination of Moisture Content of Organic Soils Using the Oven Drying Method. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, I.C.R. Soil Phosphorus: Its Measurement, and Its Uptake by Plants. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 889-2004; Determination of Exchangeable Potassium and Non-Exchangeable Potassium Content in Soil. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese)
- Sáez-Plaza, P.; Michałowski, T.; Navas, M.J.; Asuero, A.G.; Wybraniec, S. An Overview of the Kjeldahl Method of Nitrogen Determination. Part I. Early History, Chemistry of the Procedure, and Titrimetric Finish. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 178–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Yi, Z.; Qian, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X. Rotations Improve the Diversity of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities, Enzyme Activities and Tomato Yield. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0270944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokač, T.; Šalić, A.; Dukarić, A.-M.; Tišma, M.; Planinić, M.; Zelić, B.; Božinović, M. Standardization of 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic Acid (DNS) Assay for Measuring Xylanase Activity: Detecting and Solving Problems. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 15, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Lei, F.; Dong, L.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L.; Xie, A.; Sun, X. Correction: Analysis of Exogenous Lactic Acid Bacteria on Growth and Development of Different Herbaceous Peony Varieties and Rhizosphere Soil Nutrients. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Study on Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition on Organic Carbon Mineralization in Saline-Alkali Farmland in Western Jilin Province, China; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2020; (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, H.; Huang, C. A Method for Measuring Microbial Biomass C in Waterlogged Soil: Chloroform Fumigation Extraction-Water Bath Method. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2006, 06, 981–988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. A Preliminary Study on the Effects of Land Use on the Contents of Soil Active Organic Carbon. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 44, 46–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.; Lefroy, R.; Lisle, L. Soil Carbon Fractions Based on Their Degree of Oxidation, and the Development of a Carbon Management Index for Agricultural Systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. The Effect of Soil Moisture on Water Consumption and Growth of Rice. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 15+36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Oliveira, J.P. Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Interactions in Upland Rice. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Song, Z.; Van Zwieten, L.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Significant Accrual of Soil Organic Carbon through Long-term Rice Cultivation in Paddy Fields in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2024, 30, e17213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Lu, T.; Guo, Y.; Ding, X. Impacts of Salinity on the Stability of Soil Organic Carbon in the Croplands of the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Xia, X.; Zong, S.; Li, B. Distribution and influencing factors of organic carbon content in paddy soil in main agricultural areas of China. Earth Sci. Front. 2011, 18, 11–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Zeng, H.; Luo, K.; Huang, J.; Lu, W.; Tang, Z. Content of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Relationship with Nutrients in Karst Cave Wetlands, Paddy Fields and Dry Farmlands in Huixian. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 485–490. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizizi, A.; Dawutijiang, A.; Yan, C.; Tu, M.; Li, J.; Ma, M.; Na, A. Paddy-upland rotation planting technology model It can effectively control the process of soil salinization. Agric. Compr. Dev. China 2025, 6, 9–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil organic carbon: Review and prospects. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 855–870. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Yang, L.; Zhu, G.; Lan, X.; Luo, H.; Yu, Z. Change Characteristics of Soil Organic Carbon and Soil Available Nutrients and Their Relationship in the Subalpine Shrub Zone of Qilian Mountains in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Hu, Q.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gan, G.Y. Response of Soil Organic Carbon and Bacterial Community to Amendments in Saline-Alkali Soils of the Yellow River Delta. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 76, e70147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Biochar Application Regulates Organic Phosphorus Fractions and the Release of Available Phosphorus in Farmland Soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, B. Response of Soil Organic Carbon to Different Mate rials Input in Northern Farmland. J. Agric. Catastrophology 2019, 9, 24–26+52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shao, X.; Liang, W.; Wu, M. Activities and Its Relationship with Active Organic Carbon Fractions in Hangzhou Bay. Wetl. Sci. Manag. 2011, 7, 54–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.H.; Yang, H.C.; Gale, W.J.; Cheng, Z.B.; Yan, J.H. Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon after Reclamation of Abandoned, Salinized Farmland. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 155, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Nan, L.; Li, B.; Cao, S. Pilot-scale Study on In-situ Reduction of Black and Odorous Sediment in River Channel by Immobilized Microorganism Technology. J. Irrig. Drain. 2018, 37, 66–71+128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of Land Consolidation on Active Fractions of Soil Organic Carbon and Carbon Sequestration Measures. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2018, 14, 6–9+19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Chen, Q.; Liao, M.; Yang, S. Effects of interplanting grass on soil organic carbon and active components of carbon pool in peach orchard. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 6002–6010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).