Biochar and Chlorella Synergistically Enhance Grain Yield in Saline Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Descriptions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Content and Methods
2.3.1. Measurement of Soil Chemical Indicators
2.3.2. Measurement of Root Growth Indicators
2.3.3. Yield and Component Measurement
2.3.4. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
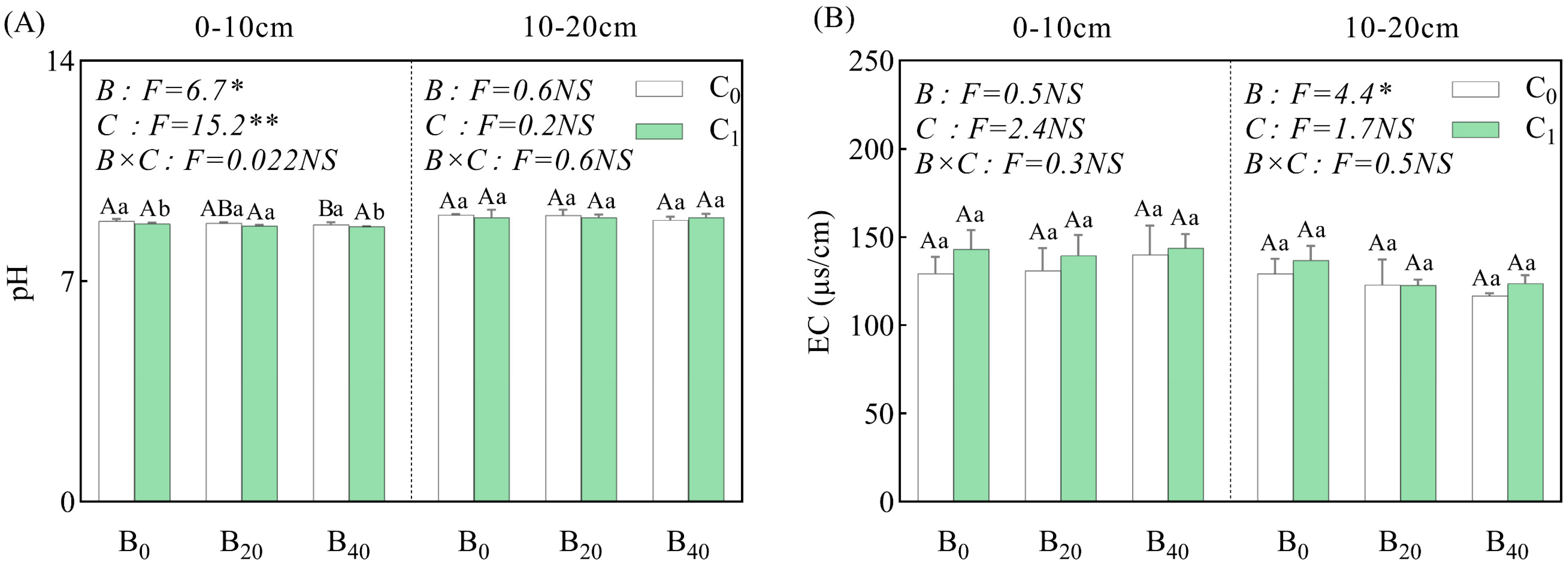
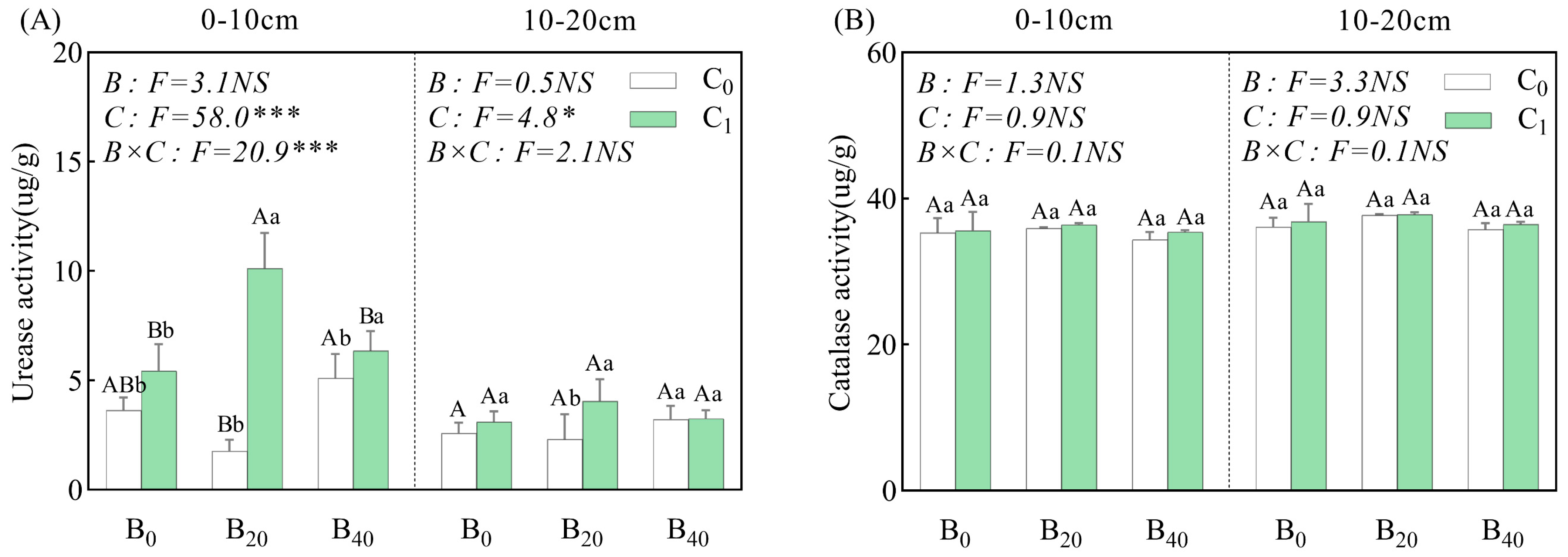
3.1. Soil Properties
3.2. Root System Indices
3.3. Yield Indices
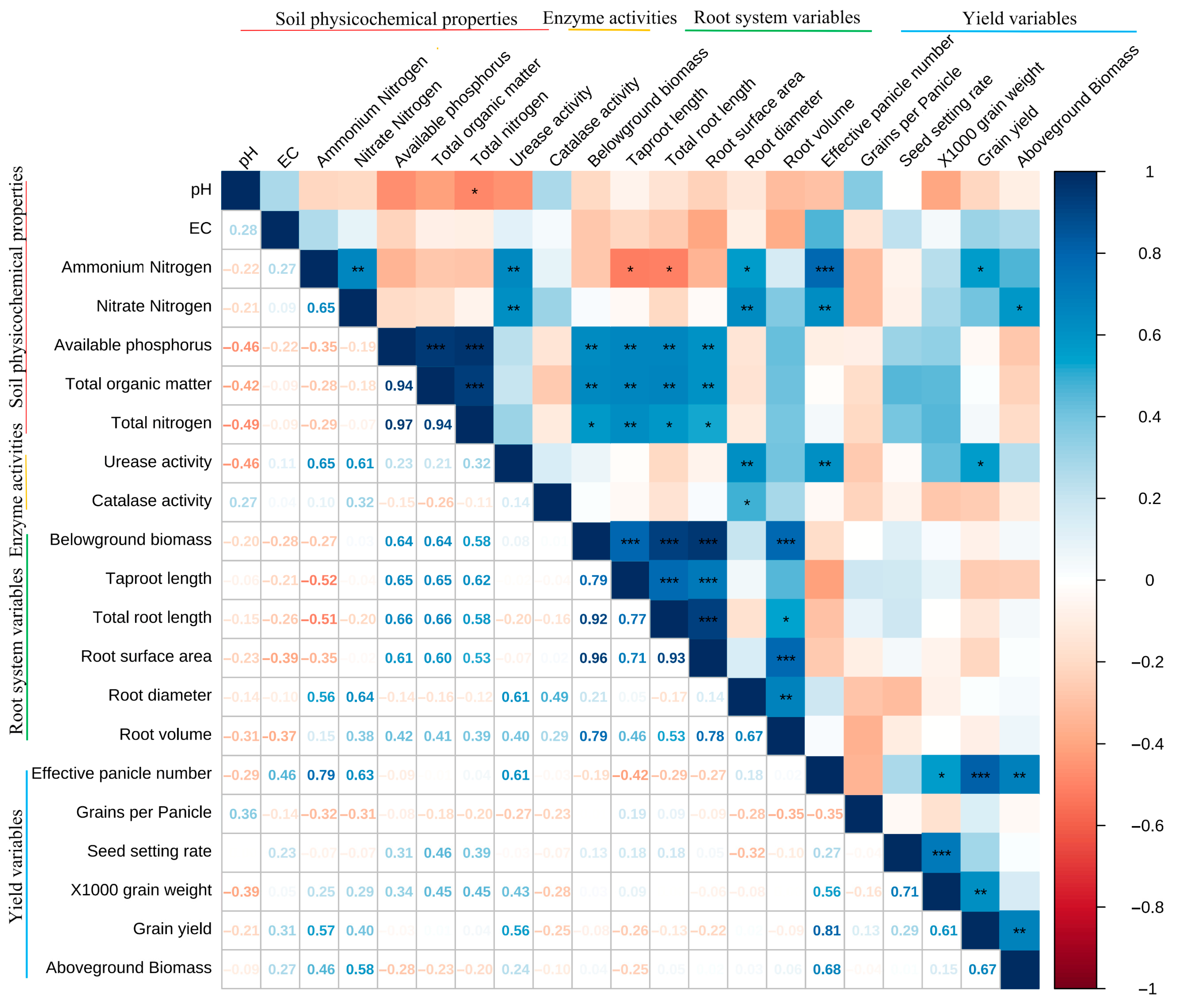
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Guo, X. Effects of Shallow Buried Straw Interlayer on Water-Salt Transport and Tomato Growth in Coastal Saline Soil. J. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 42, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil Salinization in Agriculture: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies Combining Nature-Based Solutions and Bioengineering. iScience 2024, 27, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Wang, S. Analysis and Exploration of Saline-Alkali Land Management Trends in China. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2020, 59, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yan, X.; Yin, F. Current Status and Prospects of Improvement and Comprehensive Utilization of Coastal Tidal Flat Saline-Alkali Soils in China. Chin. J. Grassl. 2024, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Niu, Y.; Dong, S. Different Straw Lengths and Burial Modes Affect the Salt Distribution in Coastal Saline Soil and the Regulation of Salt Stress Resistance in Tomato. Plant Soil 2025, 512, 1175–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Cheng, M.; Ma, J. Research Progress on Soil Improvement and Resource Utilization of Coastal Saline-Alkali Land in China. World For. Res. 2020, 33, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shao, T.; Lv, Z.; Yue, Y.; Liu, A.; Long, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, X.; Rengel, Z. The Mechanisms of Improving Coastal Saline Soils by Planting Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Wang, Y.; Ning, S.; Mao, J.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, P. Assessment of the Effects of Biochar on the Physicochemical Properties of Saline–Alkali Soil Based on Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Rasool, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, T. Biochar and Chlorella Increase Rice Yield by Improving Saline-Alkali Soil Physicochemical Properties and Regulating Bacteria under Aquaculture Wastewater Irrigation. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Kang, J.; Chen, G. Advances in Research on Wastewater Treatment Using Microalgae. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2022, 54, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lu, H.; Fu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Duan, J. A Comprehensive Benefit Evaluation of the Model of Salt-Tolerant Crops Irrigated by Mariculture Wastewater Based on a Field Plot Experiment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Mao, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhu, C. Current Situation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution and Its Control. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Liang, Z. Advances in the Application of Biochar for Saline-Alkali Soil Amelioration. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.; Chen, G. Research Progress on the Effects of Biochar in Ameliorating Saline-Alkali Soils and Its Impact on Plant Growth. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 55, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R. Abiotic and Microbial Oxidation of Laboratory-Produced Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar Effects on Soil Biota—A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, E.C.; Forstreuter, M.; Rillig, M.C.; Kohler, J. Biochar Increases Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Plant Growth Enhancement and Ameliorates Salinity Stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, W. Effects of Biochar on the Physicochemical Properties, Soil Biomass, and Maize Seedling Growth of Saline-Alkali Soil. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.L.; Weyers, S.L.; Goemann, H.M.; Peyton, B.M.; Gardner, R.D. Microalgae, Soil and Plants: A Critical Review of Microalgae as Renewable Resources for Agriculture. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Romanowska-Duda, Z.B. Ability of Cyanobacteria and Green Algae to Improve Metabolic Activity and Development of Willow Plants. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbib, Z.; Ruiz, J.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Perales, J.A. Capability of Different Microalgae Species for Phytoremediation Processes: Wastewater Tertiary Treatment, CO2 Bio-Fixation and Low Cost Biofuels Production. Water Res. 2014, 49, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Ho, S.-H. Converting Nitrogen and Phosphorus Wastewater into Bioenergy Using Microalgae-Bacteria Consortia: A Critical Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Duan, H.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Xu, T.; Guo, B. Improved Effects of Combined Application of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Azotobacter Beijerinckii and Microalgae Chlorella Pyrenoidosa on Wheat Growth and Saline-Alkali Soil Quality. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, M.; Merghoub, N.; EL Arroussi, H. Microalgae Polysaccharides: The New Sustainable Bioactive Products for the Development of Plant Bio-Stimulants? World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Meng, X.; Luo, G.; Wang, Z. Advances in the Agricultural Application of Microalgae-Based Biofertilizers. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zong, X.; Qiang, X.; Li, Q.; Shaghaleh, H.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y.; Guo, X. Response of Duckweed to Different Irrigation Modes under Different Fertilizer Types and Rice Varieties: Unlocking the Potential of Duckweed (Lemna Minor L.) in Rice Cultivation as “Fertilizer Capacitors”. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 292, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Yan, J.; Zhu, J. Effect of a Reduced Fertilizer Rate on the Water Quality of Paddy Fields and Rice Yields under Fishpond Effluent Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Shen, G.; Chen, Q. Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Effects of Rhizosphere Dissolved Oxygen Content and Nitrogen Form on Root Traits and Nitrogen Accumulation in Rice. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Soriano, M.C.; Kerré, B.; Kopittke, P.M.; Horemans, B.; Smolders, E. Biochar Affects Carbon Composition and Stability in Soil: A Combined Spectroscopy-Microscopy Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wan, S.; Kang, Y.; Feng, H. Urease Activity and Its Relationships to Soil Physiochemical Properties in a Highly Saline-Sodic Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.; Lorenzo, H. The Nutritional Control of Root Development. Plant Soil 2001, 232, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiba, T.; Krapp, A. Plant Nitrogen Acquisition Under Low Availability: Regulation of Uptake and Root Architecture. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, R.G.M.; Saeed, W.; Seguin, P.; Smith, D.L. Root Traits and Nitrogen Fertilizer Recovery Efficiency of Corn Grown in Biochar-Amended Soil under Greenhouse Conditions. Plant Soil 2017, 415, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, K.; Zhang, L.; Ji, S.; Qiao, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Meng, J.; Lan, Y. Effects of Biochar Application on Aggregate Composition and Organic Carbon Distribution in Red Soils of Yunnan Tobacco-Growing Areas. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, X.; Ge, Y.; Sun, L.; Miu, Y.; Tao, Z. A Review on the Formation of Coastal Saline-Alkali Lands and Ion Adsorption Patterns. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 48, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yi, K.; Li, M.; Feng, R.; Ma, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. Effects of Biochar on Root Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Quinoa in Saline-Alkali Soil. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2020, 52, 24–29+38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-P.; Long, X.-H.; Shao, H.-B.; Liu, Z.-P.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Q.-S.; Zong, J.-Q. Ameliorants Improve Saline–Alkaline Soils on a Large Scale in Northern Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Yan, A.; Han, R.; Yao, Y.; Chang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Meng, T. Preliminary Study on the Improvement of Newly Reclaimed Tidal Flat Saline Soil Using Microbial Amelioration Substrates. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ahmed, W.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Dai, Z.; Khan, K.A.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z. Exploring the Effect of Different Application Rates of Biochar on the Accumulation of Nutrients and Growth of Flue-Cured Tobacco (Nicotiana Tabacum). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1225031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Chen, W. Effects of Straw and Biochar Addition on Soil Nitrogen, Carbon, and Super Rice Yield in Cold Waterlogged Paddy Soils of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partey, S.T.; Preziosi, R.F.; Robson, G.D. Short-Term Interactive Effects of Biochar, Green Manure, and Inorganic Fertilizer on Soil Properties and Agronomic Characteristics of Maize. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Soil Physical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kätterer, T.; Roobroeck, D.; Andrén, O.; Kimutai, G.; Karltun, E.; Kirchmann, H.; Nyberg, G.; Vanlauwe, B.; Röing de Nowina, K. Biochar Addition Persistently Increased Soil Fertility and Yields in Maize-Soybean Rotations over 10 Years in Sub-Humid Regions of Kenya. Field Crops Res. 2019, 235, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Duan, H.; Guo, Y. Effects of Biochar Application on Root Traits: A Meta-Analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Benemann, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Qin, S. Microalgal Industry in China: Challenges and Prospects. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Kumar, R.; Neha, Y.; Srivatsan, V. Microalgae as next Generation Plant Growth Additives: Functions, Applications, Challenges and Circular Bioeconomy Based Solutions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1073546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Irrigation Mode | Control Index | Greening Stage | Tillering Stage | Jointing-Booting Stage | Heading-Flowering Stage | Milk Ripe Stage | Yellow Ripe Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flood Irrigation | Irrigation Upper Limit/mm | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| Irrigation Lower Limit/mm | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 70% |
| Treatment | Chlorella | Biochar Application Rate |
|---|---|---|
| B0C0 | No Chlorella | 0 g/kg |
| B0C1 | Apply Chlorella | 0 g/kg |
| B20C0 | No Chlorella | 0.98 g/kg |
| B20C1 | Apply Chlorella | 0.98 g/kg |
| B40C0 | No Chlorella | 1.97 g/kg |
| B40C1 | Apply Chlorella | 1.97 g/kg |
| Treatment | Effective Panicles Number (No./Hill) | Grains per Panicle (No.) | Seed Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Grain Yield (g/Hill) | Aboveground Biomass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0C0 | 6.7 ± 0.6 Ab | 109.3 ± 17.9 Aa | 91.85 ± 1.52 Aa | 23.90 ± 0.64 ABa | 17.51 ± 4.27 ABb | 31.70 ± 2.89 Bb |
| B0C1 | 10.3 ± 1.2 Aa | 102.3 ± 11.0 Aa | 92.18 ± 1.51 Aa | 24.36 ± 1.09 Aa | 25.58 ± 2.27 Aa | 46.80 ± 1.30 Aa |
| B20C0 | 5.7 ± 0.6 Ab | 108.0 ± 5.6 Aa | 91.73 ± 1.00 Aa | 22.51 ± 1.35 Bb | 13.67 ± 0.84 Bb | 32.85 ± 2.40 Bb |
| B20C1 | 9.3 ± 0.6 ABa | 98.3 ± 3.2 Aa | 91.95 ± 1.37 Aa | 24.84 ± 0.47 Aa | 22.78 ± 0.77 Aa | 38.15 ± 1.82 Ba |
| B40C0 | 8.0 ± 0.0 Ba | 106.0 ± 15.9 Aa | 93.06 ± 0.99 Aa | 25.39 ± 1.14 Aa | 21.57 ± 3.87 Aa | 40.12 ± 4.51 Aa |
| B40C1 | 8.3 ± 0.6 Ba | 101.7 ± 5.7 Aa | 93.36 ± 0.35 Aa | 25.58 ± 0.32 Aa | 21.77 ± 1.80 Aa | 29.40 ± 3.43 Cb |
| Biochar | NS | NS | NS | * | NS | * |
| Chlorella | *** | NS | NS | * | *** | * |
| Biochar × Chlorella | ** | NS | NS | NS | * | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X. Biochar and Chlorella Synergistically Enhance Grain Yield in Saline Soil. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112508
Liu B, Zhang S, Zhang J, Yang X, Zhang W, Guo X. Biochar and Chlorella Synergistically Enhance Grain Yield in Saline Soil. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112508
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bingxiao, Shuxuan Zhang, Jinhua Zhang, Xing Yang, Wenye Zhang, and Xiangping Guo. 2025. "Biochar and Chlorella Synergistically Enhance Grain Yield in Saline Soil" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112508
APA StyleLiu, B., Zhang, S., Zhang, J., Yang, X., Zhang, W., & Guo, X. (2025). Biochar and Chlorella Synergistically Enhance Grain Yield in Saline Soil. Agronomy, 15(11), 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112508







