Long-Term Winter Cover Crops Alter the Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Brazilian Oxisols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Geographical Location, Climate, and Soil Description
2.2. Soil Physical Analysis
2.3. Soil Chemical Analyses
2.4. Treatments, Experimental Design and Conduction
2.5. Plant and Soil Microbial Analysis
2.5.1. Soybean Nodulation and Nitrogen Uptake
2.5.2. Soil Microbial Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Attributes
3.2. Soybean Nodulation and N Uptake
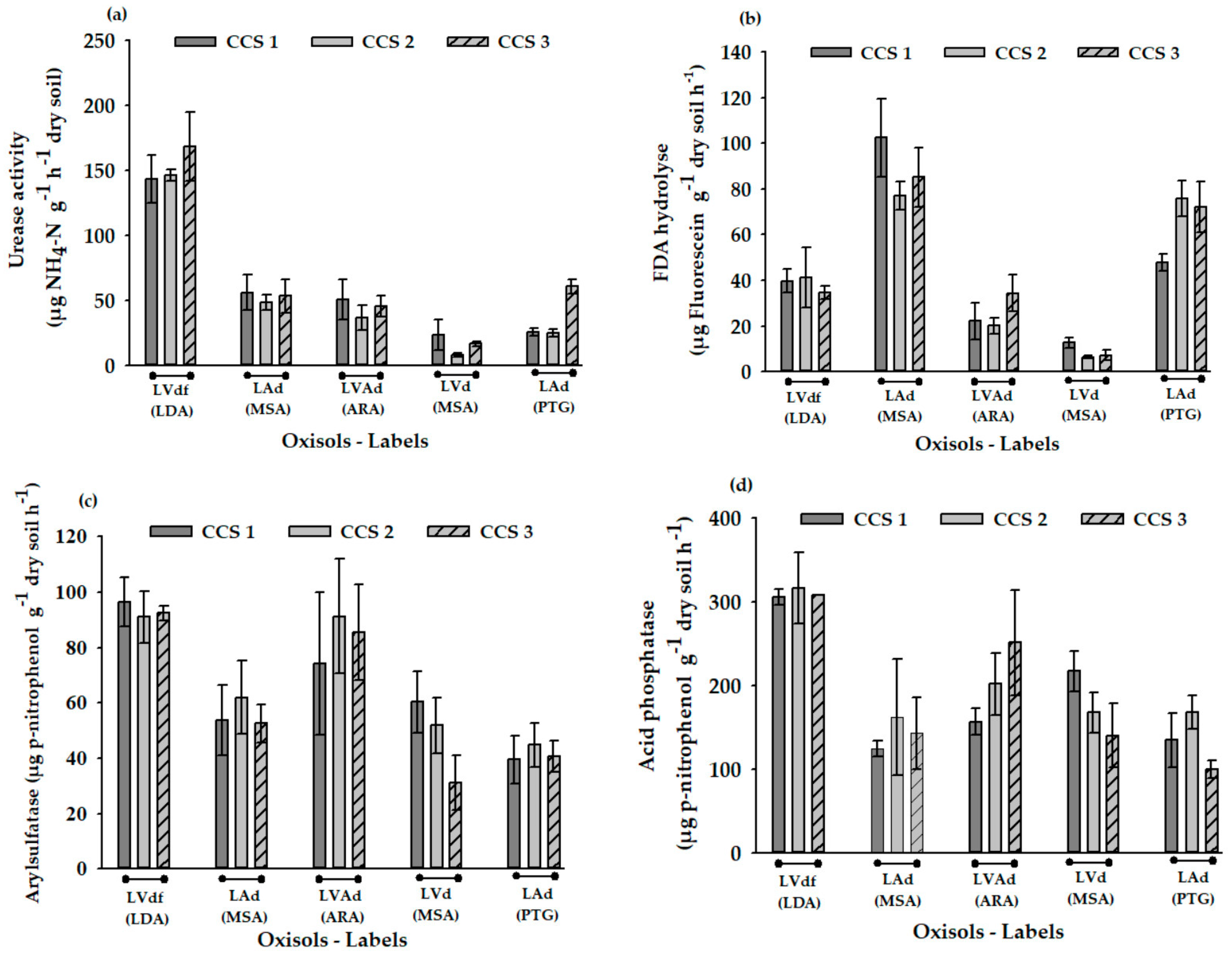
3.3. Soil Microbial Biomass, Basal Respiration and Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Attributes
4.2. Biological Nitrogen Fixation
4.3. Soil Microbial and Enzyme Activities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LVdf | LATOSSOLO VERMELHO Distroférrico |
| LAd | LATOSSOLO AMARELO Distrófico |
| LVAd | LATOSSOLO VERMELHO AMARELO Distrófico |
| LVd | LATOSSOLO VERMELHO Distrófico |
| CCS | cover crop sequences |
| LDA | Londrina |
| MSA | Mauá da Serra |
| ARP | Arapongas |
| PTG | Ponta Grossa |
| CCS 1 | canola, black-oat, white-oat, black-oat, pea |
| CCS 2 | white-oat, black-oat, white-oat, black-oat, white lupine |
| CCS 3 | crambe, black-oat, white-oat, black-oat, vetch |
| FDA | fluorescein diacetate activity |
| BIA | biochemical index activity |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
References
- Mendes, I.C.; Sousa, D.M.G.; Ozanival, D.D.; Lopes, A.A.C.; Junior, F.B.R.; Oliveira, M.I.; Chaer, G.M. Soil quality and grain yield: A win–win combination in clayey tropical oxisols. Geoderma 2021, 388, 114880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letey, J. Relationship between soil physical properties and crop production. Adv. Soil Sci. 1985, 1, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siczek, A.; Lipiec, J. Soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation in response to soil compaction and surface straw mulching. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 114, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanto, S.; Fu, B.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Zhao, W. Quantitative synthesis on the ecosystem services of cover crops. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonego, J.C.; Raphael, J.P.A.; Rigon, J.P.G.; de Oliveira Neto, L.; Rosolem, C.A. Soil compaction management and soybean yields with cover crops under no-till and occasional chiseling. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 85, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, D.P.D.; Cortez, J.W.; Tomazi, M.; Serpa, F.C.; Schwambach, D.A. A variabilidade granulométrica determina a distribuição de carbono orgânico e atributos físicos do solo em semeadura direta. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Fís. 2025, 18, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, E.L.; Araujo-Junior, C.F.; Vendrame, P.R.; de Melo, T.R. Mechanisms of aggregate breakdown in (sub) tropical soils: Effects of the hierarchical resistance. Catena 2022, 216, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Andrade, D.S.; Chueire, L.M.O.; Takemura, S.M.; Hungria, M. Tillage method and crop rotation effects on the population sizes and diversity of bradyrhizobia nodulating soybean. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzovo, A.W.S.; Silvestre, D.A.; Goes, K.; Volsi, B.; Constantino, L.V.; Bordin, I.; Telles, T.S.; Andrade, D.S. Crop rotation and inoculation increase soil bradyrhizobia population, soybean grain yields, and profitability. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 3187–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, E.L.; Filho, A.C.; Andrade, D.S.; Dick, R.P. Microbial biomass in soils under different tillage and crop rotation systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 38, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, H.F.; Sena, J.O.A.; Schwan-Estrada, K.R.F.; Balota, E.L.; Andrade, D.S. Soil chemical and microbial properties in vineyards under organic and conventional management in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2011, 35, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, E.L.; Kanashiro, M.; Colozzi Filho, A.; Andrade, D.S.; Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activities under long-term tillage crop rotation systems in subtropical agro-ecosystems. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2004, 35, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hok, L.; de Moraes Sá, J.C.; Reyes, M.; Boulakia, S.; Tivet, F.; Leng, V.; Kong, R.; Briedis, C.; da Cruz Hartman, D.; Ferreira, L.A.; et al. Enzymes and C pools as indicators of C build up in short-term conservation agriculture in a savanna ecosystem in Cambodia. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, M.; King, L.D. Seasonal fluctuations in soil microbial biomass carbon, phosphorus, and activity in no-till and reduced-chemical-input maize agroecosystems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1992, 13, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon-Debiasi, B.C.; Debiasi, H.; Rondina, A.B.L.; Moraes MTd Franchini, J.C.; Balbinot Junior, A.A.; Hungria, M.; Nogueira, M.A. Microbial attributes as structural quality index for physical health of an Oxisol under compaction levels. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wambeke, A.; Eswaran, H.; Herbillon, A.J.; Comerma, J. Oxisols. In Developments in Soil Science; Wilding, L.P., Smeck, N.E., Hall, G.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 325–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bhering, S.B.; Dos Santos, H.G.; Bognola, I.A.; Curcio, G.R.; Carvalho Junior, W.D.; Chagas, C.D.S.; Manzatto, C.V.; Aglio, M.L.D.; Silva, J.D.S. Mapa de Solos do Estado do Paraná: Legenda Atualizada; Embrapa Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.G.D.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.D.; Oliveira, V.A.D.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.D.; Araujo Filho, J.C.D.; Lima, H.N.M.; Marques, F.A.; et al. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lima RTd Araujo-Junior, C.F.; Miyazawa, M. Chemical and physical attributes of five Oxisols as predictors of shoot dry mass of white oats. Rev. Ceres 2021, 68, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E. Particle density. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Day, P.R. Particle fractionation particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Properties, Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 545–567. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Or, D. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; Soil Science Society of American: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Grohmann, F.; van Raij, B. Dispersão mecânica e prétratamento para análise granulométrica de Latossolos argilosos. R. Bras. Ci. Solo 1977, 1, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa, M.; Barbosa, G.M.d.C. Efeitos da agitação mecânica e matéria orgânica na análise granulométrica do solo. Rev. Brasil. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2011, 15, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, O.A.; Moniz, A.C.; Jorge, J.A.; Valadares, J.M.A.S. Métodos de Análise Química, Mineralógica e Física de Solos do Instituto Agronômico de Campinas. Boletim Técnico, 106; Instituto Agronômico de Campinas: Campinas, Brazil, 2009; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, L.E.; Flint, A. Porosity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 680–683. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, M.A.; Bloch, M.F.D.; Zempulski, H.C.D.; Miyazawa, M.; Zocoler, D.C. Manual de Análise Quimica de Solo e Controle de Qualidade; Instituto Agronomico do Paraná, IAPAR: Londrina, PR, Brasil, 1992; p. 51. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, D.M.G.; Lobato, E.; Rein, T.A. Uso do Gesso Agrícola Nos Solos do Cerrado; Circular Técnica Embrapa Cerrados: Brasilia, Brazil, 2005; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Quaggio, J.A.; van Raij, B. Soil acidity correction. In Fertilization and Liming Recommendation for the State of São Paulo; Van Raij, B., Cantarella, H., Quaggio, J.A., Furlani, A.M.C., Eds.; Instituto Agronômico/Fundação IAC: Campinas, Brazil, 1997; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli, S.; Rivera, L.D.; Brown, W.G.; Ochsner, T.E.; Patrignani, A. Calibration of TEROS 10 and TEROS 12 electromagnetic soil moisture sensors. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2024, 88, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.D.; Hungria, M.; Andrade, D.S. Polyphasic approach for the characterization of rhizobial symbionts effective in fixing N2 with common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Pavan, M.A.; Muraoka, T.; Carmo, C.A.F.S.D.; Melo, W.J.D. Análise química de tecido vegetal. In Manual de Análises Químicas de Solos, Plantas e Fertilizantes Tecnológica; da Silva, F.C., Ed.; Embrapa Informação: Brasília, DF, Brasil, 2009; pp. 193–233. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Horácio, E.H.; Zucareli, C.; Gavilanes, F.Z.; Yunes, J.S.; Sanzovo, A.W.d.S.; Andrade, D.S. Co-inoculation of rhizobia, azospirilla and cyanobacteria for increasing common bean production. Semin. Ciênc. Agrár. 2020, 41, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass, C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparling, G.P.; West, A.W. A direct extraction method to estimate soil microbial C: Calibration in situ using microbial respiration and 14C labelled cells. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Kragt, J.F.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: The effects of fumigation time and temperature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pell, M.; Stenström, J.; Granhall, U. Soil Respiration. In Methods for Assessing Soil Quality; Bloem, J., Hopkins, D.W., Benedetti, A., Eds.; CAB: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Balota, E.L.; Colozzi Filho, A.; Andrade, D.S.; Dick, R.P. Long-term tillage and crop rotation effects on microbial biomass and C and N mineralization in a Brazilian Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 77, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Powlson, D.S. The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil—V: A method for measuring soil biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil Enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Page, A.L., Ed.; The American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai, M.; Bremner, J. Assay of urease activity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürer, J.; Rosswall, T. Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolysis as a Measure of Total Microbial Activity in Soil and Litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, M.; Kucharski, J. Applicability of biochemical indices to quality assessment of soil polluted with heavy metals. J. Elementol. 2013, 18, 733–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzatto, D.A.; Kronka, S.N. Experimentação Agrícola; FUNDEP: Jaboticabal, Brazil, 2006; pp. 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mulumba, L.N.; Lal, R. Mulching effects on selected soil physical properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 98, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Das, T.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Ghosh, A.; Das, S.; Jha, P. Crop rotation and residue management effects on soil enzyme activities, glomalin and aggregate stability under zero tillage in the Indo-Gangetic Plains. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 184, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.J.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Allen, F.L.; Radosevich, M.; Owens, P.R. Microbial community structure is affected by cropping sequences and poultry litter under long-term no-tillage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, M.d.S.; Zanão Junior, L.A.; Ribeiro, M.R.; de Matos, M.A.; Andrade, D.S. Residual effects of agricultural gypsum on soil chemical and microbiological characteristics. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobucki, L.; Ramos, R.; Meireles, L.; Antoniolli, Z.; Jacques, R. Contribution of enzymes to soil quality and the evolution of research in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2021, 45, e0210109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xie, W.; Ding, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, L. Effects of Maize–Crop Rotation on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activities, Microbial Biomass and Microbial Community Structure in Southwest China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, M.; De Nobili, M. Relationships between soil porosity, root development and soil enzyme activity in cultivated soils. Geoderma 1993, 56, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corstanje, R.; Schulin, R.; Lark, R.M. Scale-dependent relationships between soil organic carbon and urease activity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, B.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, N.; Li, H. Soil fertility, enzyme activity, and microbial community structure diversity among different soil textures under different land use types in coastal saline soil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2240–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, N.; Mirzaei, J.; Omidipour, R.; Kooch, Y. Effects of micro-climatic conditions on soil properties along a climate gradient in oak forests, west of Iran: Emphasizing phosphatase and urease enzyme activity. Catena 2023, 224, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, E.L.; Calegari, A.; Nakatani, A.S.; Coyne, M.S. Benefits of winter cover crops and no-tillage for microbial parameters in a Brazilian Oxisol: A long-term study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovanelli, C.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Castaldini, M.; Pagliai, M.; Miclaus, N. Tillage impact on soil quality. II. Biological properties in surface soils. Ital. J. Agron. 1998, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kuht, J.; Eremeev, V.; Talgre, L.; Loit, E.; Mäeorg, E.; Margus, K.; Runno-Paurson, E.; Madsen, H.; Luik, A. Soil Microbial Activity in Different Cropping Systems under Long-Term Crop Rotation. Agriculture 2022, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
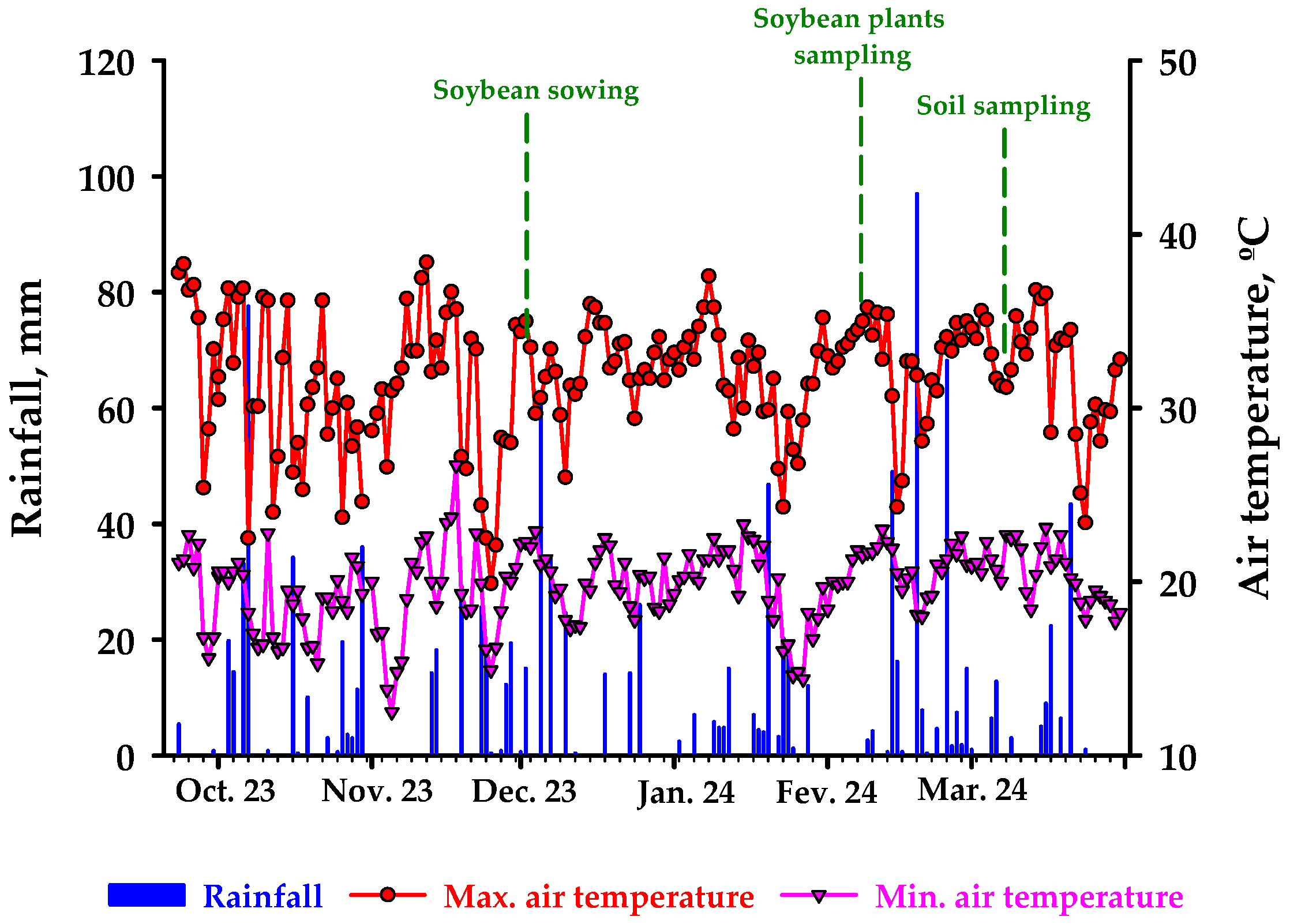





| Country | Londrina (LDA) | Mauá da Serra (MSA) | Arapongas (ARP) | Mauá da Serra (MSA) | Ponta Grossa (PTG) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Properties | ||||||
| Soil class 1 | LVdf | LAd | LVAd | LVd | LAd | |
| Soil class 2 | Rhodic Haplustox | Typic Haplustox | Typic Haplustox | Typic Haplustox | Rhodic Haplustox | |
| Geographical coordinates 3 | 23°11′19″ S 51°09′19″ W | 23°53′70″ S 51°11′30″ W | 23°22′32″ S 51°26’41″ W | 23°21′17″ S 51°11′31″ W | 25°06′70″ S 50°10′30″ W | |
| Pd, kg dm−3 | 2.99 | 2.69 | 2.68 | 2.77 | 2.61 | |
| Clay, dag kg−1 | 80 | 17 | 41 | 73 | 48 | |
| Silt, dag kg−1 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 2 | |
| Sand, dag kg−1 | 10 | 81 | 56 | 19 | 50 | |
| Texture | Very clayey | Sandy loam | Sand clay | Very clayey | Sand clay | |
| WDC, dag kg−1 | 24 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | |
| DF, % | 70 | 69 | 85 | 92 | 88 | |
| TP, dm3 dm−3 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.64 | 0.58 | |
| Bd, kg dm−3 | 1.00 | 1.51 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 1.09 | |
| DC, % | 68 | 84 | 77 | 69 | 70 | |
| Cropping Seasons | Treatments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS 1 | CCS 2 | CCS 3 | CCS 1 | CCS 2 | CCS 3 | |
| Autumn/Winter | Spring/Summer | |||||
| Cover Crop Sequences | ||||||
| 2015/2016 | Canola | White-oat | Crambe | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| 2016/2017 | Canola | White-oat | Crambe | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| 2017/2018 | Black-oat | Black-oat | Black-oat | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| 2018/2019 | Black-oat | Black-oat | Black-oat | Dry bean | Dry bean | Dry bean |
| 2019/2020 | White-oat | White-oat | White-oat | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| 2020/2021 | Black-oat | Black-oat | Black-oat | Corn | Corn | Corn |
| 2021/2022 | Black-oat | Black-oat | Black-oat | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| 2022/2023 * | Forage Pea | White lupine | Vetch | Corn | Corn | Corn |
| 2023/2024 ** | Fallow *** | Fallow *** | Fallow *** | Soybean | Soybean | Soybean |
| Country | Londrina (LDA) | Mauá da Serra (MSA) | Arapongas (ARP) | Mauá da Serra (MSA) | Ponta Grossa (PTG) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Characterization | ||||||
| pH, CaCl2 | 6.3 (±0.12) | 6.3 (±0.36) | 6.2 (±0.41) | 6.6 (±0.13) | 6.6 (±0.15) | |
| H+ + Al3+, cmolc dm−3 | 2.75 (±0.22) | 2.01 (±0.35) | 2.63 (±0.56) | 2.62 (±0.27) | 2.51 (±0.25) | |
| Al3+, cmolc dm−3 | 0.0 (±0.0) | 0.0 (±0.0) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.0 (±0.0) | 0.0 (±0.0) | |
| TOC, g dm−3 | 15.64 (±2.9) | 12.7 (±2.15) | 20.4 (±2.09) | 21.67 (±2.17) | 16.99 (±2.39) | |
| P, mg dm−3 | 83.2 (±54.5) | 101.4 (±52.5) | 103.1 (±45.1) | 58.90 (±31.6) | 49.74 (±22.0) | |
| Ca2+, cmolc dm−3 | 7.3 (±0.86) | 3.9 (±0.85) | 6.95 (±0.70) | 7.30 (±0.80) | 5.88 (±1.02) | |
| Mg2+, cmolc dm−3 | 2.4 (±0.25) | 1.5 (±0.27) | 2.54 (±0.46) | 2.59 (±0.32) | 2.72 (±0.47) | |
| K+, cmolc dm−3 | 0.6 (±0.11) | 0.16 (±0.05) | 0.28 (±0.09) | 0.18 (±0.08) | 0.16 (±0.05) | |
| SB, cmolc dm−3 | 10.3 (±0.97) | 5.6 (±1.11) | 9.76 (±1.13) | 10.08 (±0.66) | 8.76 (±1.45) | |
| CEC, cmolc dm−3 | 13.3 (±1.06) | 7.6 (±0.94) | 12.39 (±0.70) | 12.69 (±0.63) | 11.27 (±1.35) | |
| BS, % | 78.9 (±1.7) | 73.1 (±6.7) | 78.59 (±5.41) | 79.36 (±2.28) | 77.43 (±3.61) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araujo-Junior, C.F.; Mendes, A.D.R.; Miyazawa, M.; Andrade, D.S. Long-Term Winter Cover Crops Alter the Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Brazilian Oxisols. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102323
Araujo-Junior CF, Mendes ADR, Miyazawa M, Andrade DS. Long-Term Winter Cover Crops Alter the Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Brazilian Oxisols. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102323
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraujo-Junior, Cezar Francisco, Aretusa Daniela Resende Mendes, Mario Miyazawa, and Diva Souza Andrade. 2025. "Long-Term Winter Cover Crops Alter the Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Brazilian Oxisols" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102323
APA StyleAraujo-Junior, C. F., Mendes, A. D. R., Miyazawa, M., & Andrade, D. S. (2025). Long-Term Winter Cover Crops Alter the Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Brazilian Oxisols. Agronomy, 15(10), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102323





