The Positive Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizers on the Quality of Lemon Fruits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Testing Index and Method
2.4. Methodological Evaluation
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on the Single Fruit Weight of Lemon
3.2. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on the Shape Index of Lemon Fruit
3.3. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on the Edible Rate of Lemon Fruit
3.4. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on Juice Yield of Lemon Fruit
3.5. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on Vitamin C Content of Lemon Fruit
3.6. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on Total Acid Content of Lemon Fruit
3.7. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on Total Sugar Content of Lemon Fruit
3.8. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on Total Soluble Solid Content of Lemon Fruit
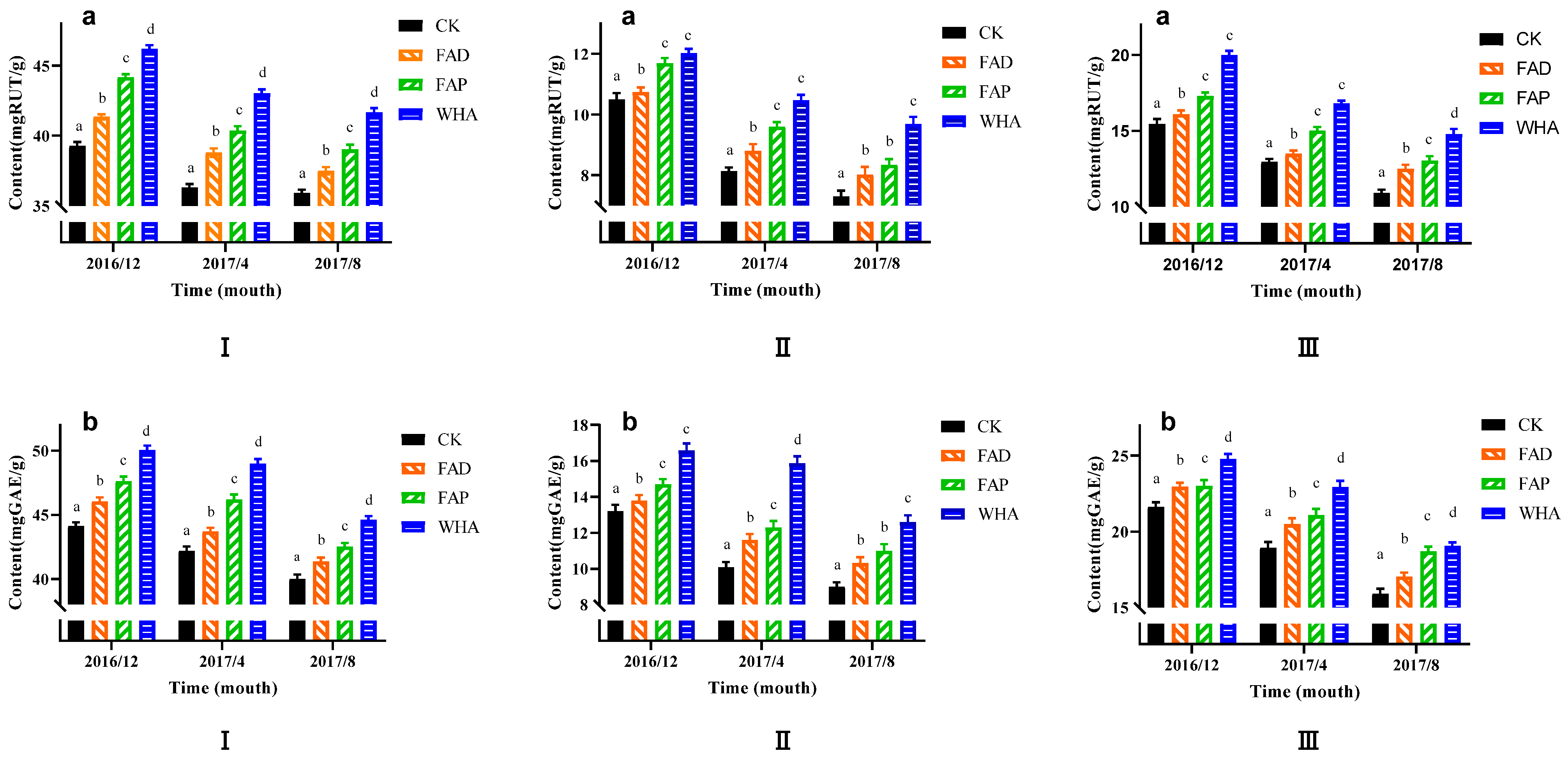
3.9. Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizer on the Contents of Total Flavonoids and Total Phenols of Lemon Fruit
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schellekens, J.; Buurman, P.; Kalbitz, K.; Zomeren, A.V.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Cerli, C.; Comans, R.N.J. Molecular features of humic acids and fulvic acids from contrasting environments. Environm. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Dosločil, L.; Burdíková-Szewieczková, J.; Enev, V.; Kalina, L.; Wasserbauer, J. Spectral characterization and comparison of humic acids isolated from some European lignites. Fuel 2018, 213, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.F.; Xiang, C.; Li, B.C. GC-MS Analysis of membrane-graded fulvic acid and its activity on promoting wheat seed germination. Molecules 2016, 21, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xue, S.; Sun, Z. Effect of humic acid (HA) compound fertilizer on the nutrient absorption and yield of grape. Soil Fertil. 2005, 6, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, J.; Ji, J.; Niu, J. Effects of application humic acid on yield, nitrogen absorption and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 4, 794–802. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.G.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, K.; Alva, A.K.; Paramasivam, S. Optimal combination of chemical compound fertilizer and humic acid to improve soil and leaf properties, yield and quality of apple (Malus Domestica). Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar]
- EI-Shabrawi, H.M.; Bakry, B.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abou-EI-Lail, M. Humic and oxalic acid stimulates grain yield and induces accumulation of plastidial carbohydrate metabolism enzymes in wheat grown under sandy soil conditions. Agric. Sci. 2015, 6, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Nardi, S.; Pizzeghello, D.; Gessa, C.; Ferrarese, L.; Casadoro, G. A low molecular weight humic fraction on nitrate uptake and protein synthesis in maize seedlings. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Zandonadi, D.B.; Canellas, L.P.; Faanha, A.R. Indolacetic and humic acids induce lateral root development through a concerted plasmalemma and tonoplast H+ pumps activation. Planta 2007, 225, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, V.; Bacaicoa, E.; Zamarreño, A.M.; Aguirre, E.; Garnica, M.; Fuentes, M.; García-Mina, J.M. Action of humic acid on promotion of cucumber shoot growth involves nitrate-related changes associated with the root-to-shoot distribution of cytokinins, polyamines and mineral nutrients. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eyheraguibel, B.; Silvestre, J.; Morard, P. Effects of humic substances derived from organic waste enhancement on the growth and mineral nutrition of maize. Bioresource Technol. 2008, 99, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, X. Effects of humic substances on preventing soil from heavy metals pollution through passivating and activating approaches. Humic. Acid 2008, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi, E.; Fragoulis, G.; Ricciuti, P.; Cappa, F.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Trevisan, M.; Crecchio, C. Effects of a humic acid and its size-fractions on the bacterial community of soil rhizosphere under maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 2009, 77, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Effect of humic acid on soil restoration. Humic. Acid 2014, 4, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, M.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, H.; Lei, M. Improvement of alkaline tobacco field soil by humic acid. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2014, 6, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Lin, W.; Wu, B. Studies on effects of humic acid applied on Pomelo cv. ‘Guanximiyou’. Southeast Hortic. 2015, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S. Mechanism and Effects of HA Compound Fertilizer Improving on the Nutrition of Grape. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, B. Research progress of nutritional components and comprehensive utilization of Citrus limon. J. Neijiang Norm. Univ. 2012, 27, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, J.; Fu, X.; Zhu, C.; Yang, F.; Yue, J. Advantages and potential of Lemon industry in Yunnan province. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2017, 37, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, B.; Xie, J.M. Vc content of fruits and vegetables comparative study. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2009, 15, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yin, G.; Chen, S.; Li, R. In vitro antioxidative effect and determination of polysaccharides from Xinhui Tangerine Peel. Pharm. Today 2009, 19, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Suteerapataranon, S.; Pudta, D. Flow injection analysis-spectrophotometry for rapid determination of total polyphenols in tea extracts. J. Flow Inj. Anal. 2008, 25, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Zheng, Y.F. Bio-Medicine, DO and University, BC Comparison of antioxidant capacity and antibacterial activity of soaked fruit vinegar and fermented fruit vinegar. China Cond. 2017, 42, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kexian, L.I.; Ying, H.E.; Liu, Q.; Shen, X.; Chen, X.; Xie, H. Research on determination of total flavonoids content in water extraction of flowers of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Chin. Arch. Trad. Chin. Med. 2018, 36, 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.Q.; Ping, L.I.; Wang, R. Determination of total phenols in Zhaotong Zanthoxylum schinifolium by folin-Ciocalteu colorimetry. China Cond. 2019, 44, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Shi, H.; Liu, N.; Bai, H. Influence of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, and bacterial and fungal community structure in a brown soil of northeast China. Annal. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, M.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Fahad, S.; Li, X. Effects of fertilization on crop production and nutrient-supplying capacity under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, T. Metabolons in plant primary and secondary metabolism. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 1483–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Gamir, J.; Gravot, A.; Pétriacq, P. Chapter Three—Untangling plant immune responses through metabolomics. Adv. Bot. Res. 2021, 98, 73–105. [Google Scholar]
- Meraj, T.A.; Fu, J.; Raza, M.A. Transcription factors regulate plant stress responses through mediating secondary metabolism. Genes 2020, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, K.M.; Govindaswamy, M. Effect of fertiliser and humic acid on rhizosphere microorganisms and soil enzym. Sugarcane 2003, 5, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Su, Y. Cadmium phytoavailability and enzyme activity under humic acid treatment in fluvo-aquic soil. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 108, 042013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, A.A.M.; Shedeed, S.I.; Abdel-Aziz, N.G.; Mahgoub, M.H. Growth, flowering and chemical constituents of Chrysanthemum indicum L. plant in response to different levels of humic acid and salinity. J. App. Sci. Res. 2012, 8, 3697–3706. [Google Scholar]

| Quality Index | 26 December 2016 | 26 April 2017 | 26 August 2017 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHA | FAP | FAD | CK | WHA | FAP | FAD | CK | WHA | FAP | FAD | CK | |
| Single fruit weight (g) | 111.64 a ± 0.32 | 112.29 a ± 0.21 | 109.45 b ± 0.24 | 106.32 c ± 0.26 | 106.37 a ± 0.30 | 103.49 b ± 0.36 | 102.98 b ± 0.37 | 100.40 c ± 0.44 | 117.85 a ± 0.42 | 115.50 b ± 0.50 | 112.94 c ± 0.31 | 111.90 c ± 0.30 |
| Fruit shape index | 1.36 a ± 0.05 | 1.37 a ± 0.07 | 1.39 a ± 0.04 | 1.36 a ± 0.02 | 1.36 a ± 0.03 | 1.37 a ± 0.06 | 1.38 a ± 0.09 | 1.36 a ± 0.07 | 1.37 a ± 0.04 | 1.35 a ± 0.03 | 1.35 a ± 0.08 | 1.34 a ± 0.06 |
| Edible rate (%) | 72.65 a ± 0.60 | 72.70 a ± 0.52 | 71.13 b ± 0.49 | 69.94 b ± 0.61 | 70.01 a ± 0.75 | 68.54 b ± 0.40 | 68.51 b ± 0.51 | 66.08 c ± 0.47 | 76.62 a ± 0.69 | 74.58 b ± 0.75 | 73.99 b ± 0.50 | 71.70 c ± 0.46 |
| Juice yield (%) | 55.89 b ± 0.81 | 57.21 a ± 0.60 | 54.90 b ± 0.71 | 51.32 c ± 0.79 | 53.77 a ± 0.59 | 51.03 b ± 0.72 | 50.91 b ± 0.68 | 48.95 c ± 0.60 | 59.27 a ± 0.54 | 56.20 b ± 0.89 | 55.97 b ± 0.61 | 52.46 c ± 0.70 |
| Vitamin C (mg/100 g) | 67.10 b ± 0.49 | 68.61 a ± 0.61 | 66.95 b ± 0.78 | 61.85 c ± 0.76 | 66.99 a ± 0.89 | 65.39 b ± 0.74 | 64.06 c ± 0.55 | 59.02 d ± 0.49 | 72.01 a ± 0.60 | 69.17 b ± 0.35 | 67.05 c ± 0.62 | 63.30 d ± 0.70 |
| Total acid (g/kg) | 47.51 a ± 0.44 | 47.69 a ± 0.58 | 45.05 b ± 0.65 | 43.88 c ± 0.70 | 45.97 a ± 0.51 | 44.10 b ± 0.49 | 43.96 b ± 0.78 | 42.04 c ± 0.56 | 49.56 a ± 0.48 | 49.08 a ± 0.39 | 48.79 a ± 0.60 | 45.82 b ± 0.54 |
| Total sugar (g/100g) | 1.92 b ± 0.10 | 2.00 a ± 0.08 | 1.90 b ± 0.12 | 1.70 c ± 0.06 | 2.09 a ± 0.13 | 2.05 a ± 0.09 | 1.94 b ± 0.08 | 1.81 c ± 0.14 | 1.81 b ± 0.11 | 1.97 a ± 0.10 | 1.82 b ± 0.06 | 1.65 c ± 0.05 |
| Total soluble solid (%) | 8.24 a ± 0.21 | 8.15 a ± 0.16 | 7.94 b ± 0.27 | 7.69 b ± 0.14 | 8.31 a ± 0.29 | 8.30 a ± 0.12 | 7.99 b ± 0.31 | 7.72 b ± 0.20 | 8.20 a ± 0.27 | 7.71 b ± 0.22 | 7.60 b ± 0.20 | 7.58 b ± 0.34 |
| Analyte | Part | Stability | Repeatability | Recovery | Standard | Precision (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total flavonoids | Peel | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.39 | Rutin | 0.70 |
| Pulp | 0.64 | 1.03 | 0.80 | |||
| Seed | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.41 | |||
| Total phenols | Peel | 0.92 | 0.52 | 0.76 | Gallic acid | 0.32 |
| Pulp | 0.79 | 0.42 | 0.54 | |||
| Seed | 0.85 | 0.46 | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Dai, W.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, M. The Positive Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizers on the Quality of Lemon Fruits. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081919
He X, Zhang H, Li J, Yang F, Dai W, Xiang C, Zhang M. The Positive Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizers on the Quality of Lemon Fruits. Agronomy. 2022; 12(8):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081919
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaoying, Hanqi Zhang, Jinxue Li, Fan Yang, Weifeng Dai, Cheng Xiang, and Mi Zhang. 2022. "The Positive Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizers on the Quality of Lemon Fruits" Agronomy 12, no. 8: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081919
APA StyleHe, X., Zhang, H., Li, J., Yang, F., Dai, W., Xiang, C., & Zhang, M. (2022). The Positive Effects of Humic/Fulvic Acid Fertilizers on the Quality of Lemon Fruits. Agronomy, 12(8), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081919






