Screening for Pea Germplasms Resistant to Fusarium Wilt Race 5
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pea Accessions
2.2. Pathogen Isolation and Identification
2.3. Pathogenicity and Race Tests
2.4. Resistance Evaluation of Pea Accessions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
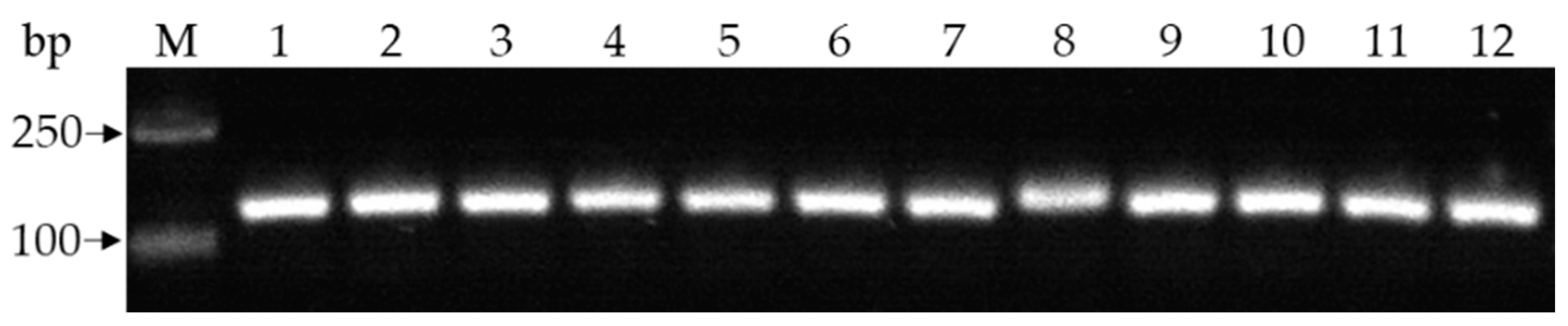
3.1. Pathogen Isolation and Identification
3.2. Pathogenicity and Race Tests
3.3. Validation of the Evaluation Criteria on Resistance
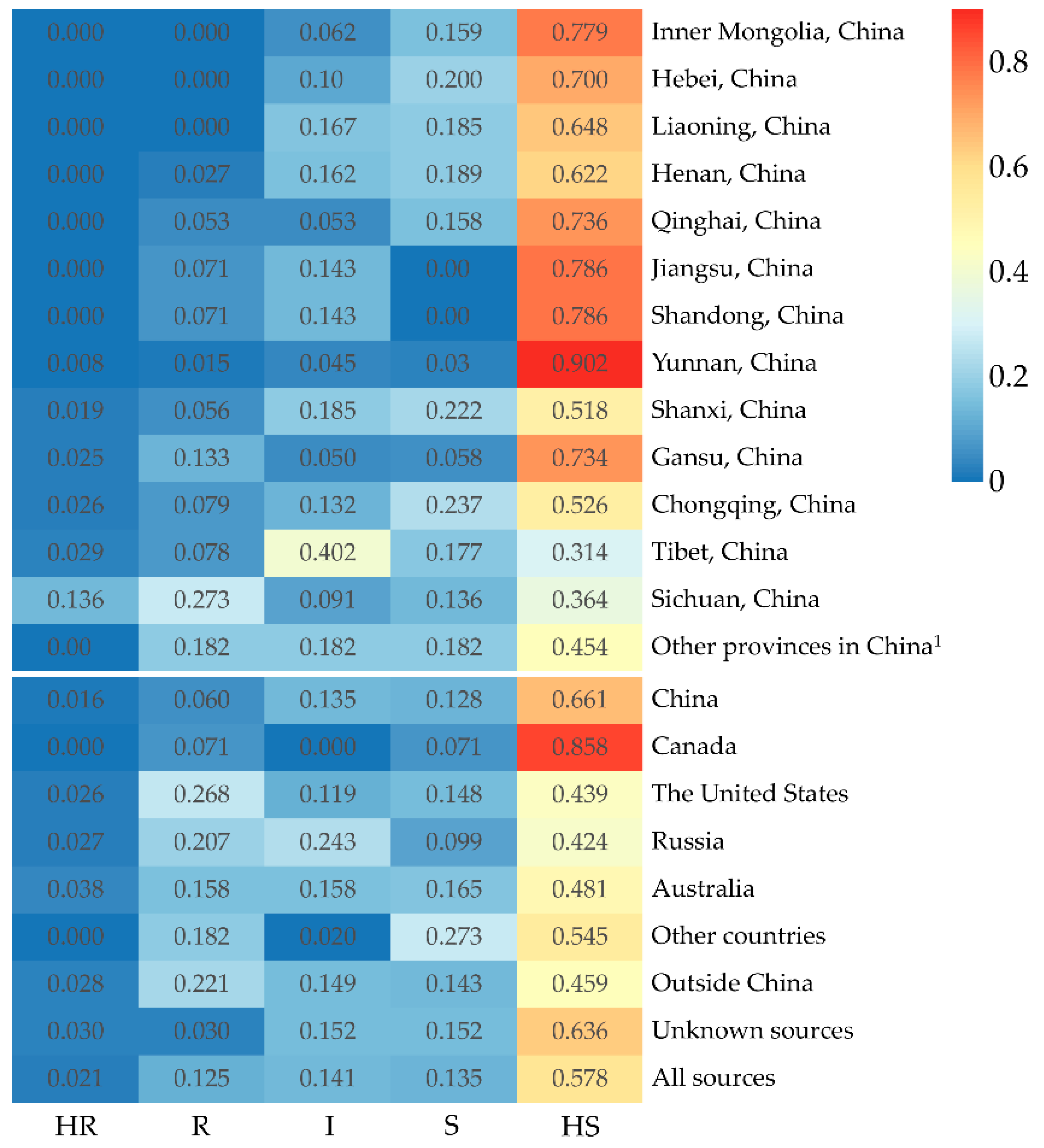
3.4. Resistance Evaluation of Pea Accessions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cousin, R. Peas (Pisum sativum L.). Field Crops Res. 1997, 53, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilorgé, E.; Kezeya, B.; Stauss, W.; Muel, F.; Mergenthaler, M. Pea and rapeseed acreage and land use for plant-based meat alternatives in the EU. OCL 2021, 28, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toklu, F.; Sen Gupta, D.; Karaköy, T.; Özkan, H. Bioactives and nutraceuticals in food legumes: Nutritional Perspective. In Breeding for Enhanced Nutrition and Bio-Active Compounds in Food Legumes; Gupta, D.S., Gupta, S., Kumar, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbek, M.C.; Lam, R.S.H.; Wang, Y.; Asavajaru, P.; Lam, A. Pea: A sustainable vegetable protein crop. In Sustainable Protein Sources; Nadathur, S.R., Wanasundara, J.P.D., Scanlin, L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, T.; Liu, R.; Redden, B.; Maalouf, F.; Zong, X. Food legume production in China. Crop J. 2017, 5, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, N.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Blair, M.W. Genetic diversity of Chinese and global pea (Pisum sativum L.) collections. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. FAOSTAT Crop Statistics. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Sharma, A.; Rathour, R.; Plaha, P.; Katoch, V.; Khalsa, G.S.; Patial, V.; Singh, Y.; Pathania, N.K. Induction of Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi) resistance in garden pea using induced mutagenesis and in vitro selection techniques. Euphytica 2010, 173, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubha, K.; Dhar, S.; Choudhary, H.; Dubey, S.C.; Sharma, R.K. Identification of resistant sources and inheritance of Fusarium wilt resistance in garden pea (Pisum sativum ssp. hortense). Indian J. Hortic. 2016, 73, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Ghazanfar, M.U.; Munir, N.; Hamid, M.I. Managing Fusarium wilt of pea by utilizing different application methods of fungicides. Pakistan J. Phytopathol. 2019, 31, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sharkawy, H.H.A.; Abbas, M.S.; Soliman, A.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; El-Nady, I.A.I. Synergistic effect of growth-promoting microorganisms on bio-control of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi, growth, yield, physiological and anatomical characteristics of pea plants. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2021, 178, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambugala, K.M.; Daranagama, D.A.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Kannangara, S.D.; Promputtha, I. Fungi vs. fungi in biocontrol: An overview of fungal antagonists applied against fungal plant pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 604923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Velandia, C.A.; Izquierdo-García, L.F.; Ongena, M.; Kloepper, J.W.; Cotes, A.M. Soil sterilization, pathogen and antagonist concentration affect biological control of Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry by Bacillus velezensis Bs006. Plant Soil 2018, 435, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sampaio, A.M.; Araújo, S.D.S.; Rubiales, D.; Vaz Patto, M.C. Fusarium wilt management in legume crops. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, U.C.; Bohra, A.; Pandey, S.; Parida, S.K. Breeding, genetics, and genomics approaches for improving Fusarium wilt resistance in major grain legumes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, J.M.; Pfleger, F.L. Compendium of Pea Diseases and Pests, 2nd ed.; American Phytopathological Society (APS Press): St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.C.; Hansen, H.N. The species concept in Fusarium. Am. J. Bot. 1940, 27, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R.; Linford, M.B. Pea Disease Survey in Wisconsin; Agricultural Experiment Station of the University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1925; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.C. A new vascular Fusarium disease of peas. Science 1933, 77, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, J.C. Een onderzoek over de Amerikaanse vaatziekte van de erwten in Nederland. Tijdschr. Over Plantenziekten 1951, 57, 175–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, A.T.; Nuttall, V.W.; Lyall, L.H. A new race of Fusarium oxysporum f. pisi. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1966, 46, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, W.A.; Kraft, J.M. Fusarium oxysporum f. pisi, race 5. Phytopathology 1970, 60, 1861–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebbeling, N. Testing for resistance to wilt and near wilt of peas caused by race 1 and 3 of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Medd Fak. Landbouw-Wet. Gent 1974, 29, 991–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Gritton, E.T.; Hubbeling, N.; Kerr, A.; Kraft, J.M.; Lawye, A.S.; Sharpe, C. Races of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi, causal agents of wilt of pea. Phytopathology 1974, 64, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, J.M.; Haglund, W.A. A reappraisal of the race classification of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Phytopathology 1978, 68, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haglund, W.A.; Kraft, J.M. Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi, race 6: Occurrence and distribution. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, A.; Kharrat, M.; Riccioni, L.; Coyne, C.J.; McPhee, K.E.; Grünwald, N.J. Screening techniques and sources of resistance to root diseases in cool season food legumes. Euphytica 2006, 147, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzoug, A.; BeLABid, L.; Youcef-BenkAdA, M.; Benfreha, F.; Bayaa, B. Pea Fusarium wilt races in western Algeria. Plant Protect. Sci. 2014, 50, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achari, S.R.; Kaur, J.; Dinh, Q.; Mann, R.; Sawbridge, T.; Summerell, B.A.; Edwards, J. Phylogenetic relationship between Australian Fusarium oxysporum isolates and resolving the species complex using the multispecies coalescent model. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.M.; Salem, K.F. Breeding Strategies of Garden Pea (Pisum sativum L.). In Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Vegetable Crops; Al-Khayri, J.M., Jain, S.M., Johnson, D.V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 331–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, K.E.; Tullu, A.; Kraft, J.M.; Muehlbauer, F.J. Resistance to Fusarium wilt race 2 in the Pisum core collection. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 124, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bani, M.; Rubiales, D.; Rispail, N. A detailed evaluation method to identify sources of quantitative resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi race 2 within a Pisum spp. germplasm collection. Plant Pathol. 2012, 61, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haglund, W.A. A rapid method for inoculating pea seedlings with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Plant Dis. 1989, 73, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.F. A preliminary list of Fusarium species in China. Chin. J. Plant Pathol. 1955, 1, 1–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D. Identification of Pathogens Causing Three Diseases on Pea. Master Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural, Beijng, China, 1 June 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, L.J.; Feng, M.Y.; Lu, W.C.; Liao, D.X. Isolation and identification of pathogen of pea Fusarium wilt in Chongqing city. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2002, 59, 84–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.G. Evaluation and utilization of pea resources resistance to disease. Inn. Mong. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2003, 1, 12–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhu, Z.D.; Duan, C.X. Identification and Control Technology of Pests and Diseases of Broad Bean and Pea; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 66–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Summerell, B.A.; Salleh, B.; Leslie, J.F. A utilitarian approach to Fusarium identification. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haegi, A.; Catalano, V.; Luongo, L.; Vitale, S.; Scotton, M.; Ficcadenti, N.; Belisario, A. A newly developed real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Fusarium oxysporum and its use in compatible and incompatible interactions with grafted melon genotypes. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, K.; Kistler, H.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R. Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: Concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Duan, C.; Zhu, Z. Confirmation of Fusarium oxysporum as a causal agent of mung bean wilt in China. Crop Prot. 2019, 117, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Sun, F.; Duan, C.; Zhu, Z. Pathotype diversity of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. mungcola causing wilt on mungbean (Vigna radiata). Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, B.L. Inheritance of Fusarium Wilt Resistance in Canning Peas; Wisc Agric Exp Stn Bull: Madison, WI, USA, 1929; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.C.; Lian, R.F.; Mo, J.P.; Wang, S.H. Research of the pea root rot and resistant breeding in Gansu province. Rain Fed Crops 2008, 28, 272–273. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Weeden, N.F.; Kumar, A.; Chittem, K.; McPhee, K. Functional codominant marker for selecting the Fw gene conferring resistance to Fusarium wilt race 1 in pea. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubara, P.A.; Inglis, D.A.; Muehlbauer, F.J.; Coyne, C.J. A novel RAPD marker linked to the Fusarium wilt race 5 resistance gene (Fwf) in Pisum sativum. Pisum Genet. 2002, 34, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Phee, K.E.; Inglis, D.A.; Gundersen, B.; Coyne, C.J. Mapping QTL for Fusarium wilt race 2 partial resistance in pea (Pisum sativum). Plant Breed. 2012, 131, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, S.T.; Malosetti, M.; Song, Q.; van Eeuwijk, F.; Rubiales, D.; Vaz Patto, M.C. Natural variation in Portuguese common bean germplasm reveals new sources of resistance against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli and resistance-associated candidate genes. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sanogo, S.; Ma, Z.; Qu, Y. Breeding, genetics, and quantitative trait locus mapping for Fusarium wilt resistance in cotton. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2435–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitwood-Brown, J.; Vallad, G.E.; Lee, T.G.; Hutton, S.F. Breeding for resistance to Fusarium wilt of tomato: A review. Genes 2021, 12, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A. The root rot-Fusarium wilt complex of peas. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1963, 16, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surv, C.P.D. Response of cultivars and breeding lines to the disease complex of Fusarium wilt and root rot of green peas in southwestern Ontario. Can. Plant Dis. Surv. 1991, 71, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.L. Brief discussion on current situation and development countermeasures of pea production in Tibet. Mod. Agric. 2018, 10, 36–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elvira-Recuenco, M.; Taylor, J.D. Resistance to bacterial blight (Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi) in Spanish pea (Pisum sativum) landraces. Euphytica 2001, 118, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiales, D.; Fondevilla, S.; Fernandez-Aparicio, M. Development of pea breeding lines with resistance to Orobanche crenata derived from pea landraces and wild Pisum spp. Agronomy 2021, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.L.; Fu, H.N.; Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, C.X.; Zong, X.X.; Zhu, Z.D. Discovery of a novel er1 allele conferring powdery mildew resistance in Chinese pea (Pisum sativum L.) Landraces. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Redden, R.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Guan, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Yan, L.; et al. Analysis of a diverse global Pisum sp. collection and comparison to a Chinese local P. sativum collection with microsatellite markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
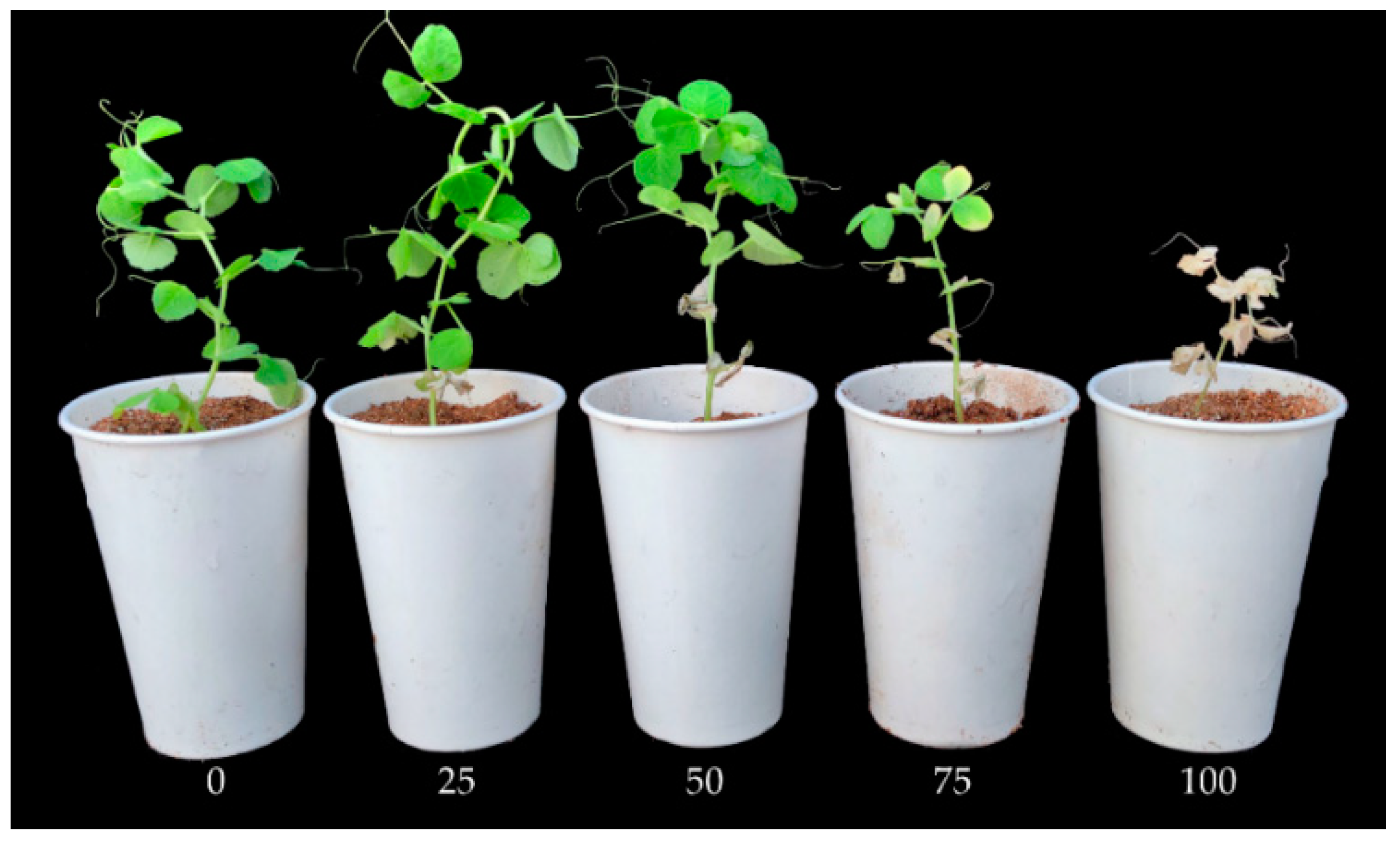
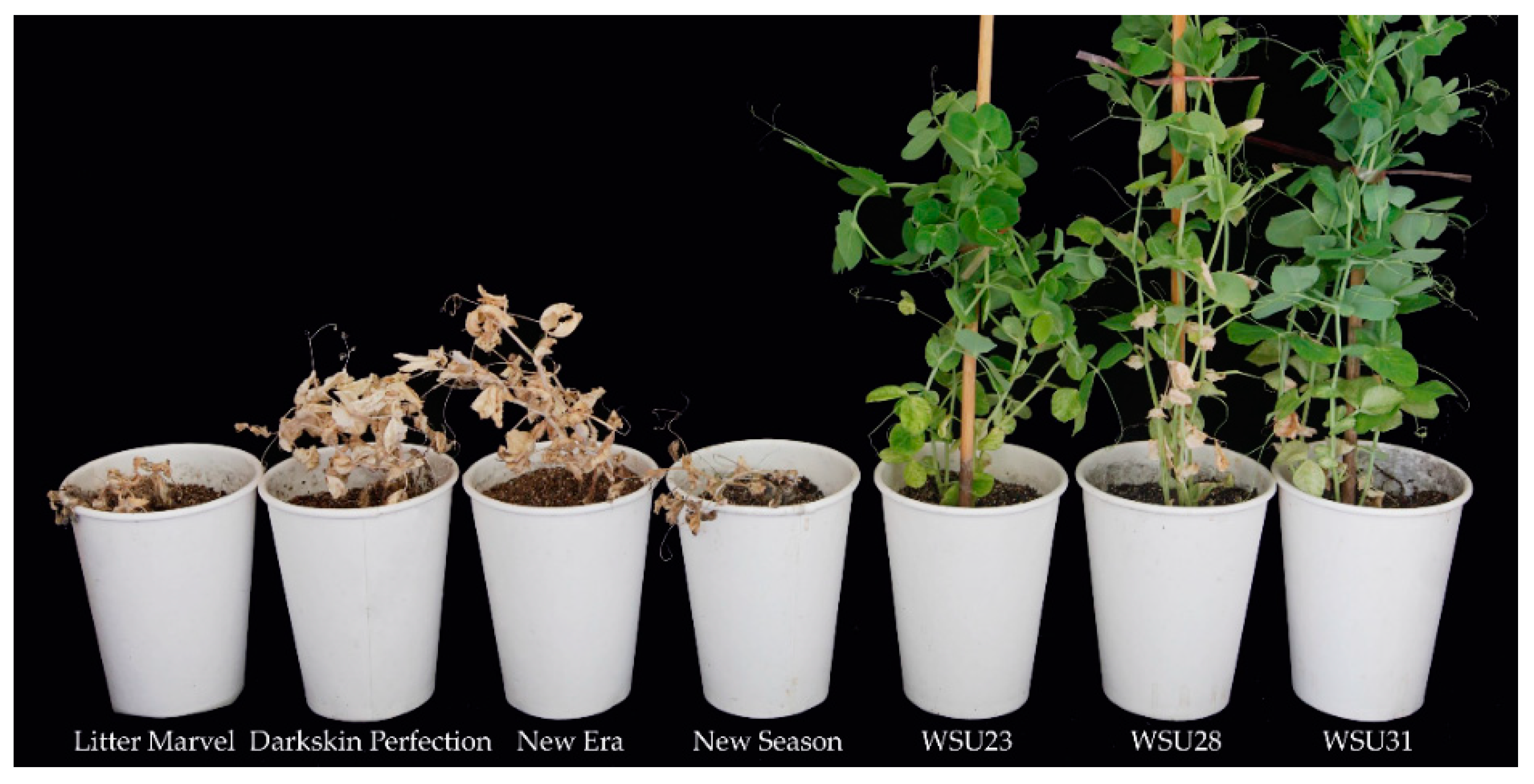


| Differential Cultivar | Resistance | Disease Ratings 1 | ||
| DR (%) | DI | PSL (%) | ||
| Little Marvel | HS | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 b |
| Darkskin Perfection | HS | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 b |
| New Era | HS | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.17 ± 3.25 b |
| New Season | HS | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 b |
| WSU23 | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 1.67 ± 2.42 a |
| WSU28 | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.00 ± 2.61 a |
| WSU31 | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.83 ± 3.43 a |
| DR | PSL | DI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR | 1.000 | ||
| PSL | 0.967 ** | 1.000 | |
| DI | 0.969 ** | 0.995 ** | 1.000 |
| Accession Number 1 | Name | Source | Resistance | Disease Ratings 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR (%) | DI | PSL (%) | ||||
| G0000005 | A053 | Henan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.50 ± 9.19 a–e |
| G0000066 | 112 | Shanxi, China | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 4.33 ± 5.57 a |
| G0000129 | 26 | Shanxi, China | R | 20.00 | 28.00 | 26.80 ± 41.82 a–g |
| G0000154 | 19 | Shanxi, China | R | 20.00 | 32.00 | 27.60 ± 41.10 a–g |
| G0000156 | 21 | Shanxi, China | R | 16.67 | 26.67 | 22.67 ± 38.72 a–g |
| G0004496 | Zhangwan 4 | Tibet, China | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 21.33 ± 38.63 a–f |
| G0004499 | Zhangwan 7 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 23.33 | 9.83 ± 10.26 a–e |
| G0004503 | Zhangwan 11 | Tibet, China | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 2.00 ± 2.83 a |
| G0004508 | Zhangwan 16 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.00 ± 0.00 a–f |
| G0004511 | Zhangwan 19 | Tibet, China | HR | 0.00 | 14.29 | 1.29 ± 1.25 a |
| G0004518 | Zhangwan 26 | Tibet, China | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 3.50 ± 4.12 a |
| G0004670 | Zhangwan 178 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 28.00 | 23.00 ± 5.87 a–g |
| G0004683 | Zhangwan 191 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.50 ± 6.36 a–f |
| G0004689 | Zhangwan 197 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 32.00 | 23.20 ± 7.69 a–g |
| G0004737 | Zhangwan 245 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 18.25 ± 4.92 a–f |
| G0004738 | Zhangwan 246 | Tibet, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 4.50 ± 0.71 a–c |
| G0005784 | 2010CQ019 | Chongqing, China | HR | 0.00 | 13.33 | 4.50 ± 4.14 a–c |
| G0005792 | 2010CQ027 | Chongqing, China | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 24.83 ± 37.20 a–g |
| G0005808 | 2010CQ043 | Chongqing, China | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 28.00 ± 36.09 a–g |
| G0005812 | 2010CQ047 | Chongqing, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 18.50 ± 2.59 a–f |
| G0006010 | L2254 | Yunnan, China | HR | 0.00 | 12.00 | 6.40 ± 6.23 a–c |
| G0006305 | Chuanwan 7 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.20 ± 3.56 a–f |
| G0006306 | Chuanwan 8 | Sichuan, China | HR | 0.00 | 12.00 | 9.40 ± 9.04 a–e |
| PEA-AC014 | 9617 | Gansu, China | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 6.33 ± 9.27 a–c |
| PEA-AC016 | 9842 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.00 ± 0.89 a–e |
| PEA-AC019 | 94-1 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.50 ± 7.82 a–f |
| PEA-AC022 | 9352-1 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.83 ± 5.23 a–d |
| PEA-AC029 | D04 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 18.20 ± 3.56 a–f |
| PEA-AC047 | GSP16-101 | Gansu, China | HR | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| PEA-AC082 | RCW1101 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.50 ± 5.47 a–e |
| PEA-AC083 | Rsw1106 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 9.00 ± 7.69 a–e |
| PEA-AC090 | S4008 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 28.67 ± 9.11 a–g |
| PEA-AC101 | Chenggong 30 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.50 ± 3.56 a–e |
| PEA-AC102 | Dinghe | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.40 ± 7.54 a–f |
| PEA-AC103 | Dingwan 5 (ma) | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.33 ± 7.58 a–f |
| PEA-AC104 | Dingwan 7 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 19.33 ± 4.93 a–f |
| PEA-AC105 | Dingwan 8 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.33 ± 5.24 a–f |
| PEA-AC108 | Dingwan 3 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 23.33 | 20.67 ± 7.74 a–f |
| PEA-AC109 | Dingwan 4 | Gansu, China | HR | 0.00 | 13.33 | 11.17 ± 11.00 a–e |
| PEA-AC110 | Dingwan 5 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.33 ± 6.15 a–f |
| PEA-AC111 | Dingwan 6 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.33 ± 6.41 a–f |
| PEA-AC127 | Xianggangdajia 618 | Gansu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.83 ± 7.78 a–f |
| PEA-AC132 | YI | Guangdong, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.75 ± 7.32 a–f |
| PEA-AC157 | Xiaobaihua | Jiangsu, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.00 ± 7.97 a–f |
| PEA-AC184 | Caoyuan 27 | Qinghai, China | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 13.83 ± 9.85 a–e |
| PEA-AC194 | GSP16–035 | Shandong, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.50 ± 6.72 a–e |
| PEA-AC203 | Chengwan 7 | Sichuan, China | HR | 0.00 | 6.67 | 3.50 ± 5.65 a |
| PEA–AC204 | Chengwan 8 | Sichuan, China | HR | 0.00 | 6.67 | 1.67 ± 2.88 a |
| PEA-AC209 | Shijiadacaiwan 1 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.67 ± 2.94 a–e |
| PEA-AC210 | Shijiadacaiwan 2 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.00 ± 3.63 a–f |
| PEA-AC211 | Shijiadacaiwan 3 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.83 ± 5.53 a–f |
| PEA-AC212 | Shijiadacaiwan 6 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 10.67 ± 7.06 a–e |
| PEA-AC214 | Shijiatiancuiwan 6 | Sichuan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.83 ± 4.96 a–d |
| PEA-AC217 | Tianshanbaiwandong | Xinjiang, China | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 6.67 ± 5.92 a–c |
| PEA-AC223 | GSP16–137 | Yunnan, China | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 3.50 ± 2.74 a |
| PEA-AC224 | L0148 | Yunnan, China | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 5.00 ± 1.87 a–c |
| Accession Number 1 | Name | Source | Resistance | Disease Ratings 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR (%) | DI | PSL (%) | ||||
| G0004475 | ATC1039 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 6.67 | 1.17 ± 2.04 a |
| G0004480 | ATC1502 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 7.00 ± 0.00 a–d |
| G0004812 | 97-027*-2 | Australia | HR | 0.00 | 13.33 | 9.00 ± 8.65 a–d |
| G0005046 | ATC1698 | Australia | R | 16.67 | 30.00 | 25.67 ± 37.22 a–g |
| G0005066 | ATC2353 | Australia | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 4.83 ± 6.52 a–c |
| G0005076 | ATC2946 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.50 ± 6.36 a–f |
| G0005078 | ATC3097 | Australia | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 2.25 ± 3.30 a |
| G0005741 | ATC3473 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 16.00 | 7.20 ± 7.05 a–d |
| G0005753 | ATC4606 | Australia | HR | 0.00 | 8.00 | 2.20 ± 3.19 a |
| G0005754 | ATC4943 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 24.00 | 17.00 ± 9.67 a–f |
| G0005758 | ATC5773 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 16.00 | 9.60 ± 6.80 a–e |
| G0005763 | A1554 | Australia | HR | 0.00 | 13.33 | 9.83 ± 10.65 a–e |
| G0005938 | K–935 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.33 ± 6.11 a–d |
| G0005965 | Banwuyehe 1 (Bai) | - 3 | HR | 0.00 | 8.00 | 1.60 ± 2.61 a |
| G0006122 | K-6062 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 7.00 ± 1.22 a–d |
| G0006130 | K-2649 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 22.00 ± 2.16 a–f |
| G0006134 | K-5159 | Russia | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 3.25 ± 4.27 a |
| G0006173 | K–7657 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.33 ± 7.23 a–e |
| G0006182 | K-8450 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 19.50 ± 12.02 a–f |
| G0006282 | - | Japan | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.67 ± 7.23 a–f |
| G0006284 | - | Japan | R | 0.00 | 26.67 | 10.00 ± 15.62 a–e |
| G0006339 | ELS 0025-1 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.67 ± 4.04 a–f |
| G0006346 | ELS 0033 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 28.00 ± 16.27 a–g |
| G0006363 | ELS 0053 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.20 ± 7.98 a–e |
| G0006373 | ELS 0063-1 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.14 ± 7.80 a–e |
| G0006386 | ELS 0073 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.50 ± 2.65 a–e |
| G0006389 | ELS 0076 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 17.50 ± 7.33 a–f |
| G0006398 | ELS 0086 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 33.33 | 29.33 ± 34.02 a–g |
| G0006406 | ELS 0093 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 16.00 | 6.40 ± 3.78 a–c |
| G0006408 | ELS 0095 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 28.67 ± 10.91 a–g |
| G0006412 | ELS 0099 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.33 ± 7.09 a–e |
| G0006421 | ELS 0110 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 17.50 ± 4.95 a–f |
| G0006424 | ELS 0112 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 22.00 ± 0.00 a–g |
| G0006450 | ELS 0139-1 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 32.00 | 30.20 ± 8.98 a–g |
| G0006458 | ELS 0147 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 9.00 ± 0.00 a–e |
| G0006464 | ELS 0153 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.75 ± 1.71 a–d |
| G0006471 | ELS 0160 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 19.75 ± 14.75 a–f |
| G0006481 | ELS 0170 | Russia | HR | 0.00 | 5.00 | 1.25 ± 2.50 a |
| G0006490 | ELS 0180 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.33 ± 6.81 a–f |
| G0006491 | ELS 0182 | Russia | HR | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| G0006494 | ELS 0185 | Russia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.00 ± 7.07 a–f |
| G0006519 | Canstar | Canada | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.67 ± 3.21 a–e |
| G0006668 | AGG1373 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 17.50 ± 5.79 a–f |
| G0006679 | AGG4032 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.83 ± 7.47 a–e |
| G0006683 | AGG3097 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 17.33 ± 7.00 a–f |
| G0006685 | AGG3318 | Australia | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 25.33 ± 36.71 a–g |
| G0006687 | AGG4028 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 26.33 ± 13.76 a–g |
| G0006692 | AGG4037 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.20 ± 4.87 a–f |
| G0006701 | AGG107 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 18.75 ± 4.43 a–f |
| G0006828 | PI 116056 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.60 ± 8.44 a–e |
| G0006829 | PI 116844 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 24.25 ± 5.19 a–g |
| G0006832 | PI 117998 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.83 ± 4.62 a–e |
| G0006844 | PI 142775 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.67 ± 6.06 a–f |
| G0006850 | PI 162909 | The United States | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 31.33 ± 33.93c–g |
| G0006856 | PI 164779 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.33 ± 8.39 a–d |
| G0006858 | PI 164971 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.33 ± 7.81 a–e |
| G0006966 | PI 269761 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 6.50 ± 3.21 a–c |
| G0006988 | PI 272204 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 28.00 | 26.20 ± 7.29 a–g |
| G0007103 | AGG191-1 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.50 ± 6.61 a–e |
| G0007136 | AGG4017 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 24.83 ± 15.00 a–g |
| G0007139 | AGG4029 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 9.17 ± 4.96 a–e |
| G0007141 | AGG4030 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 8.17 ± 6.24 a–d |
| G0007411 | AGG196 | Australia | R | 20.00 | 32.00 | 29.60 ± 40.00 a–g |
| G0007421 | AGG1633 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 10.83 ± 8.45 a–e |
| G0007423 | AGG1696 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.20 ± 8.73 a–f |
| G0007428 | AGG3103-1 | Australia | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 25.83 ± 7.17 a–g |
| G0007495 | 2015501235 | - | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.75 ± 7.37 a–e |
| UPH003 | PI 639977 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.67 ± 5.09 a–d |
| UPH006 | PI 639967 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.33 ± 4.68 a–f |
| UPH009 | PI 109866 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 11.00 ± 8.90 a–e |
| UPH013 | PI 117264 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.17 ± 5.53 a–e |
| UPH017 | PI 124478 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 23.86 ± 33.65 a–g |
| UPH028 | PI 156720 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.20 ± 3.56 a–e |
| UPH032 | PI 164182 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 18.33 ± 4.03 a–f |
| UPH033 | PI 164548 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 9.50 ± 6.35 a–e |
| UPH035 | PI 164779 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.00 ± 5.73 a–e |
| UPH037 | PI 164972 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 22.57 ± 34.42 a–g |
| UPH039 | PI 166084 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.57 ± 4.86 a–e |
| UPH040 | PI 166159 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.50 ± 4.72 a–f |
| UPH051 | PI 179722 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 30.00 | 24.83 ± 8.13 a–g |
| UPH054 | PI 180693 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.50 ± 8.17 a–e |
| UPH056 | PI 180699 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 26.67 | 19.17 ± 8.08 a–f |
| UPH060 | PI 181958 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.67 ± 5.57 a–e |
| UPH062 | PI 184130 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 7.33 ± 4.93 a–d |
| UPH072 | PI 197990 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.83 ± 6.97 a–f |
| UPH073 | PI 198072 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.00 ± 8.74 a–e |
| UPH078 | PI 203064 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 7.83 ± 4.12 a–d |
| UPH090 | PI 210561 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 26.67 | 20.00 ± 12.33 a–f |
| UPH092 | PI 210569 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.00 ± 4.34 a–d |
| UPH099 | PI 221697 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.00 ± 6.96 a–f |
| UPH107 | PI 242027 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 17.14 | 7.57 ± 7.89 a–d |
| UPH108 | PI 242028 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 25.71 | 15.43 ± 12.63 a–f |
| UPH109 | PI 244093 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.00 ± 5.42 a–e |
| UPH111 | PI 244150 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.71 ± 5.82 a–e |
| UPH112 | PI 244175 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 16.67 | 14.00 ± 8.00 a–f |
| UPH115 | PI 249645 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 24.71 ± 28.77 a–g |
| UPH117 | PI 250439 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 13.33 | 4.33 ± 4.04 ab |
| UPH118 | PI 250440 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 22.86 | 13.43 ± 12.61 a–e |
| UPH120 | PI 250444 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.00 ± 6.00 a–e |
| UPH128 | PI 261623 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.71 ± 5.35 a–e |
| UPH141 | PI 269761 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.57 ± 6.24 a–f |
| UPH145 | PI 269778 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.86 ± 7.99 a–e |
| UPH146 | PI 269782 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 ± 3.61 a–f |
| UPH150 | PI 269804 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.86 ± 5.52 a–e |
| UPH153 | PI 269818 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 8.40 ± 6.31 a–d |
| UPH167 | PI 272175 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.20 ± 6.65 a–e |
| UPH174 | PI 272218 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.29 ± 10.59 a–e |
| UPH181 | PI 275821 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 22.86 | 13.14 ± 12.97 a–e |
| UPH184 | PI 275826 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.67 ± 10.54 a–e |
| UPH189 | PI 280252 | The United States | R | 16.67 | 33.33 | 29.50 ± 35.33 a–g |
| UPH195 | PI 280616 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.57 ± 7.50 a–e |
| UPH202 | PI 285717 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 15.29 ± 9.11 a–f |
| UPH204 | PI 285719 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 16.33 ± 7.00 a–f |
| UPH209 | PI 285739 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 17.14 | 11.43 ± 8.08 a–e |
| UPH228 | PI 324702 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 11.86 ± 7.54 a–e |
| UPH229 | PI 324703 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 25.00 ± 34.14 a–g |
| UPH233 | PI 340128 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 25.86 ± 33.77 a–g |
| UPH238 | PI 343331 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.71 ± 4.54 a–e |
| UPH240 | PI 343824 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.43 ± 6.55 a–e |
| UPH241 | PI 343958 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 9.83 ± 6.46 a–e |
| UPH245 | PI 343987 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 17.14 | 8.57 ± 7.81 a–d |
| UPH253 | PI 347281 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 28.00 ± 32.31 a–g |
| UPH255 | PI 347457 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 17.57 ± 5.35 a–f |
| UPH257 | PI 347490 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.20 ± 4.97 a–e |
| UPH258 | PI 347496 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 9.57 ± 5.09 a–e |
| UPH262 | PI 356984 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 13.14 ± 6.54 a–e |
| UPH263 | PI 356986 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.29 ± 2.36 a–f |
| UPH272 | PI 358640 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.50 ± 6.66 a–e |
| UPH275 | PI 378157 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 2.86 | 0.43 ± 1.13 a |
| UPH280 | PI 404225 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 6.67 | 0.67 ± 1.21 a |
| UPH281 | PI 409031 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 5.00 | 0.50 ± 1.00 a |
| UPH289 | PI 413698 | The United States | R | 14.29 | 31.43 | 25.14 ± 33.33 a–g |
| UPH291 | PI 429839 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 6.67 | 1.33 ± 2.16 a |
| W617519 | WSU23 | The United States | HR | 0.00 | 10.00 | 1.67 ± 2.42 a |
| W617520 | WSU28 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 14.00 ± 2.61 a–f |
| W617521 | WSU31 | The United States | R | 0.00 | 20.00 | 10.83 ± 3.43 a–e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, D.; Sun, S.; Wu, W.; Zong, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Duan, C.; Zhu, Z. Screening for Pea Germplasms Resistant to Fusarium Wilt Race 5. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061354
Deng D, Sun S, Wu W, Zong X, Yang X, Zhang X, He Y, Duan C, Zhu Z. Screening for Pea Germplasms Resistant to Fusarium Wilt Race 5. Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061354
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Dong, Suli Sun, Wenqi Wu, Xuxiao Zong, Xiaoming Yang, Xiaoyan Zhang, Yuhua He, Canxing Duan, and Zhendong Zhu. 2022. "Screening for Pea Germplasms Resistant to Fusarium Wilt Race 5" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061354
APA StyleDeng, D., Sun, S., Wu, W., Zong, X., Yang, X., Zhang, X., He, Y., Duan, C., & Zhu, Z. (2022). Screening for Pea Germplasms Resistant to Fusarium Wilt Race 5. Agronomy, 12(6), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061354







