Interactive Effects of Foliar Application of Zinc, Iron and Nitrogen on Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
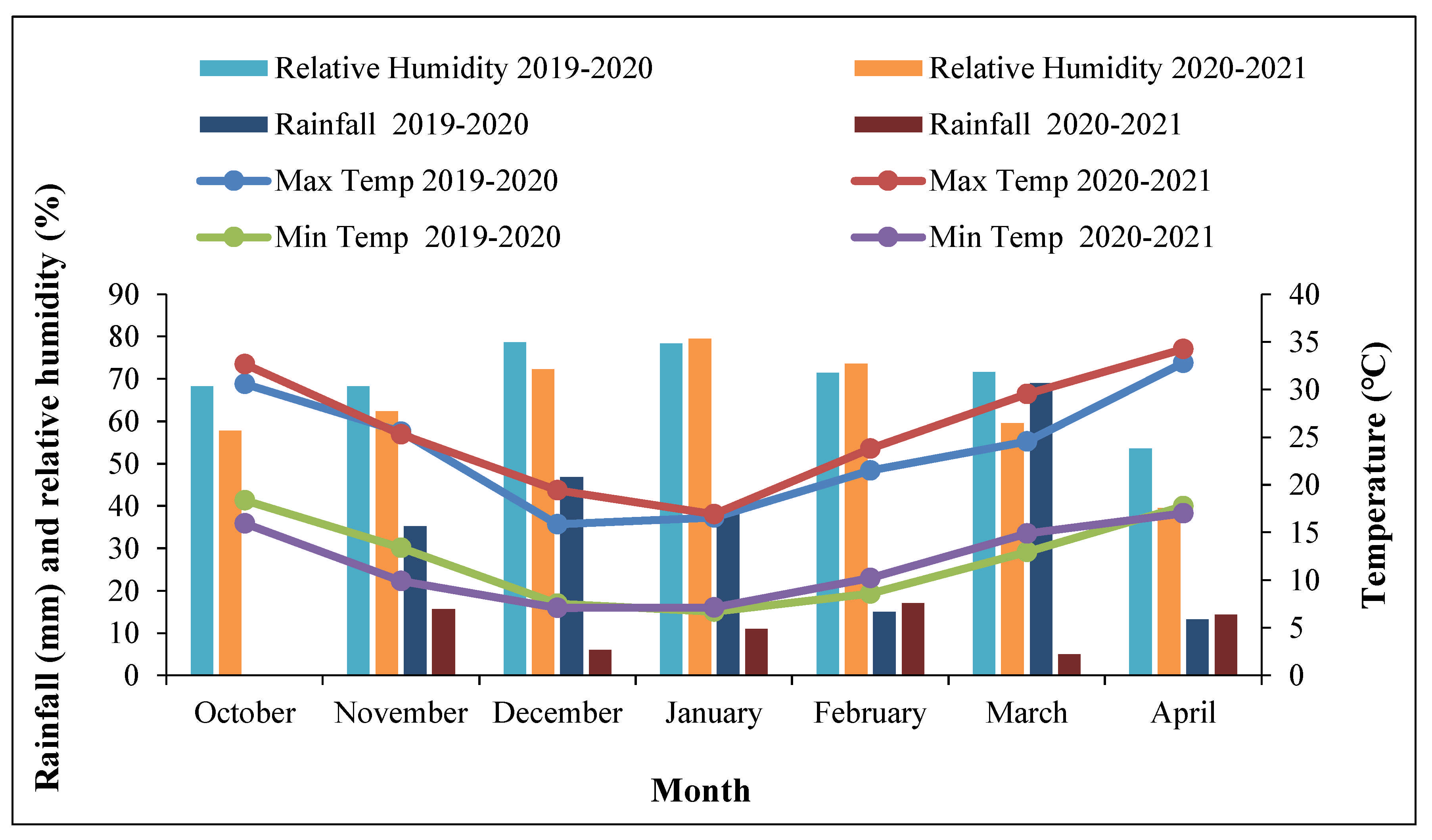
2.1. Experimental Site and Characteristics
2.2. Treatment Details
2.3. Plant Harvesting and Analysis
2.4. Zinc and Iron Use Efficiency Indices
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
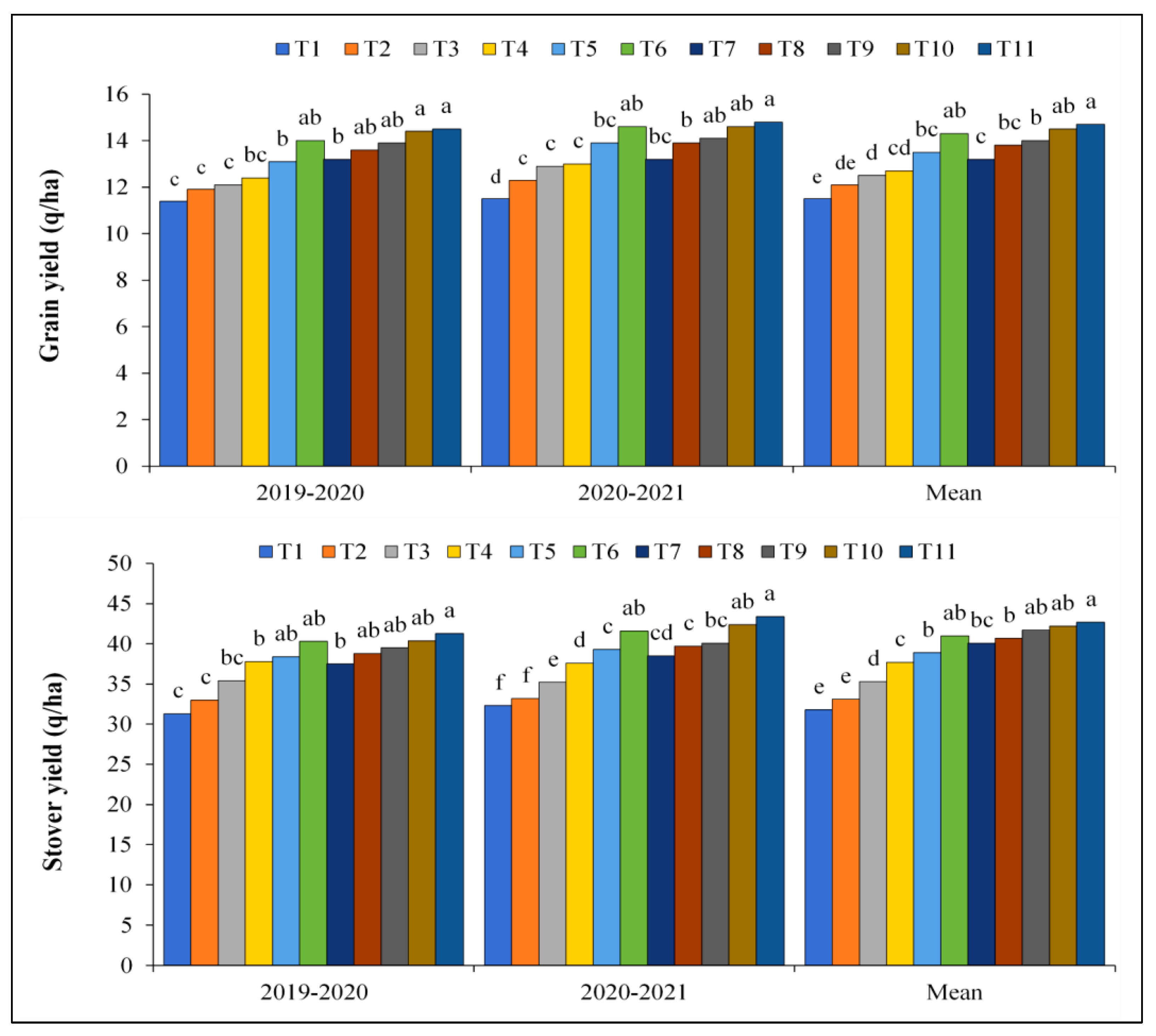
3.1. Effect of Zn, Fe and Urea Foliar Application on Grain and Stover Yield
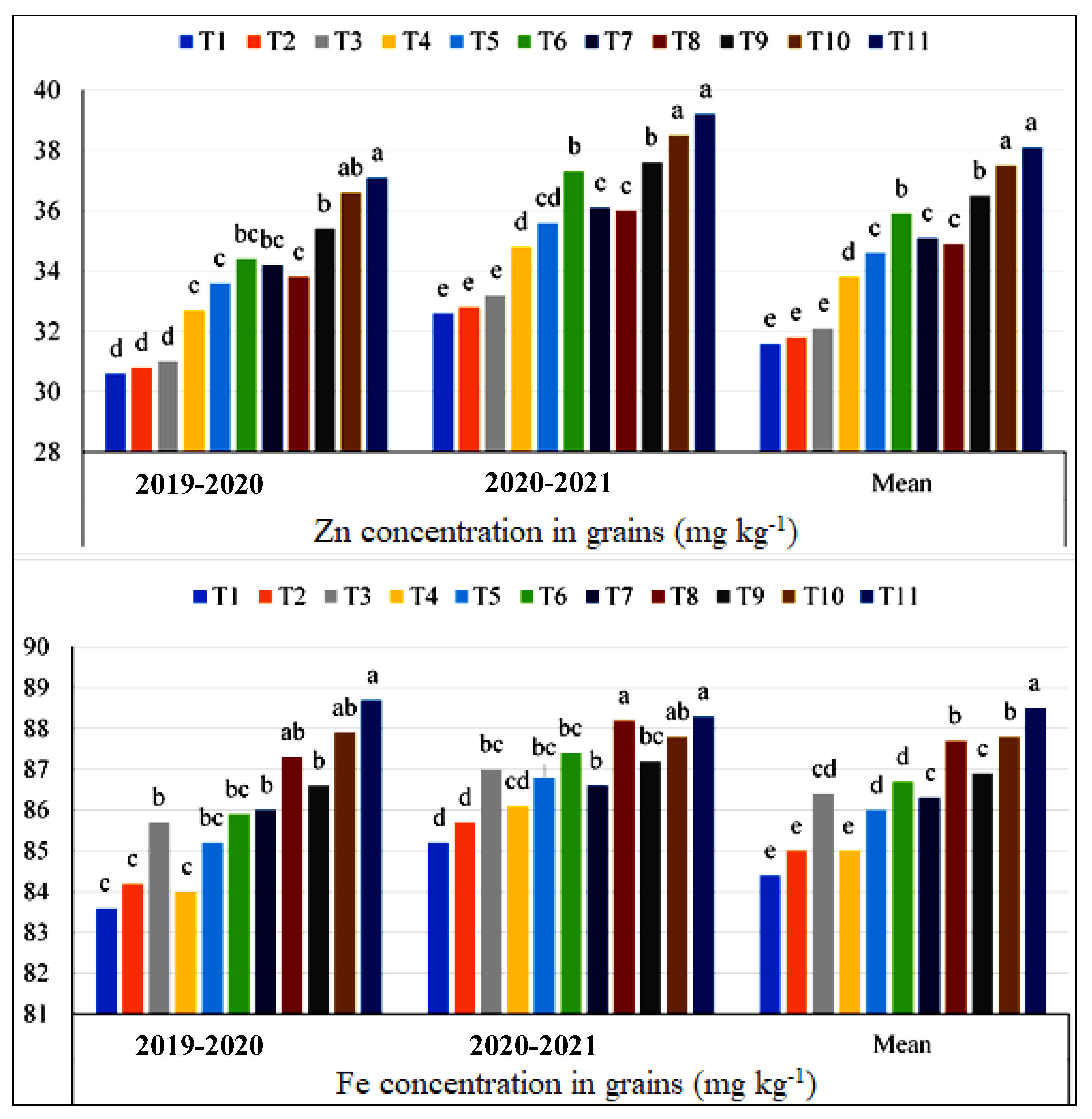
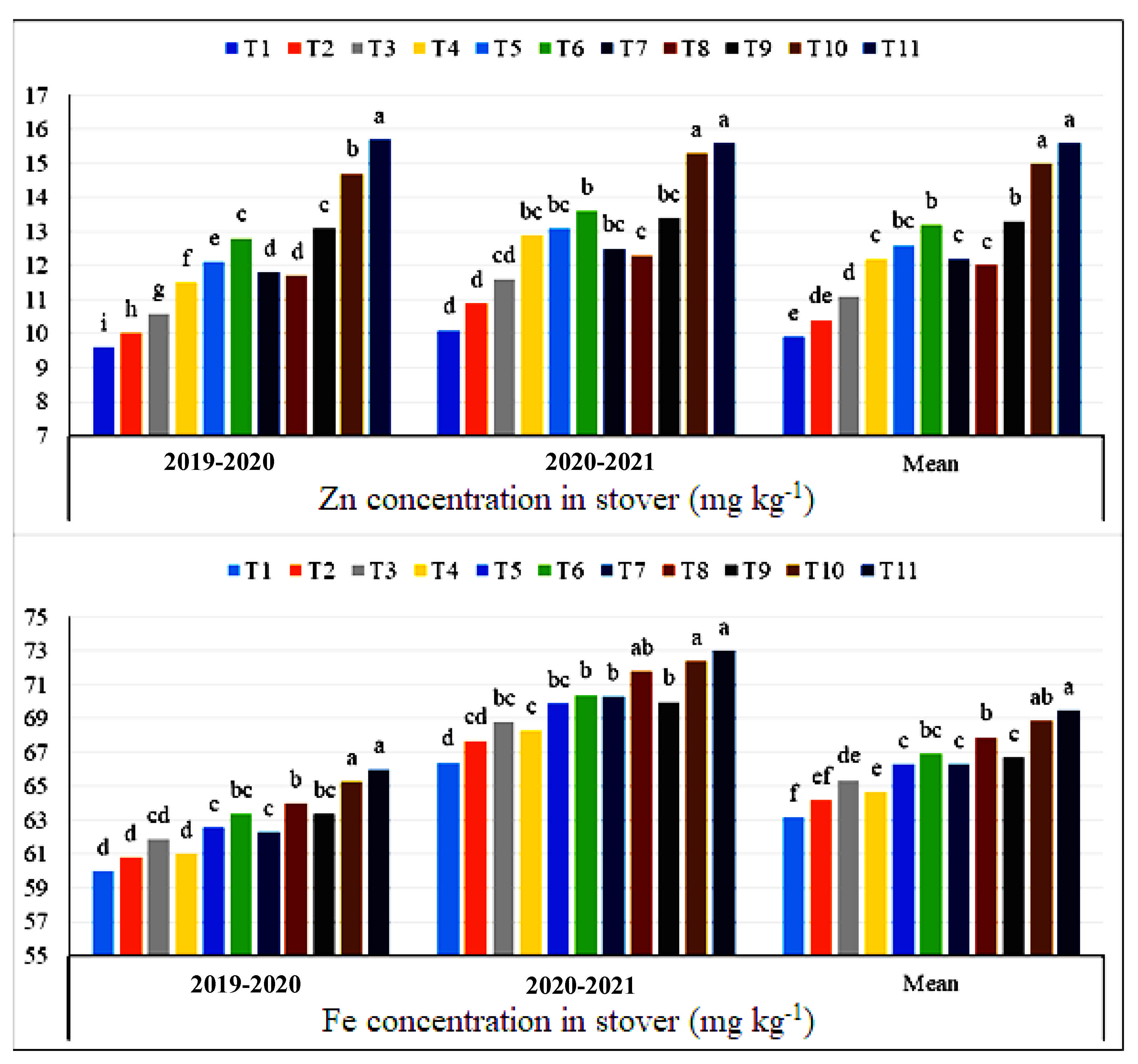
3.2. Effect of Zn, Fe and Urea Application on Zn and Fe Concentrations in Grain and Stover
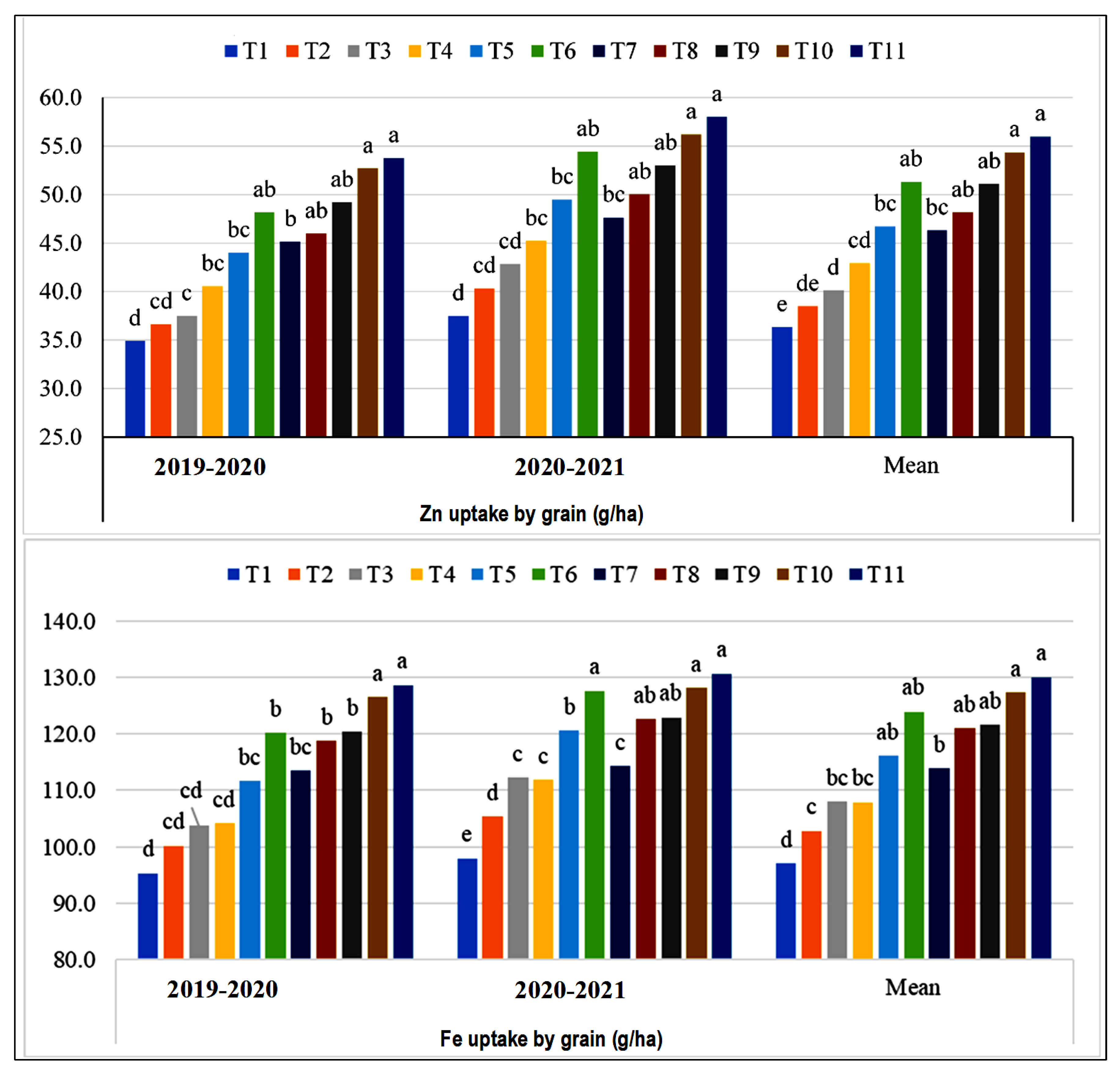
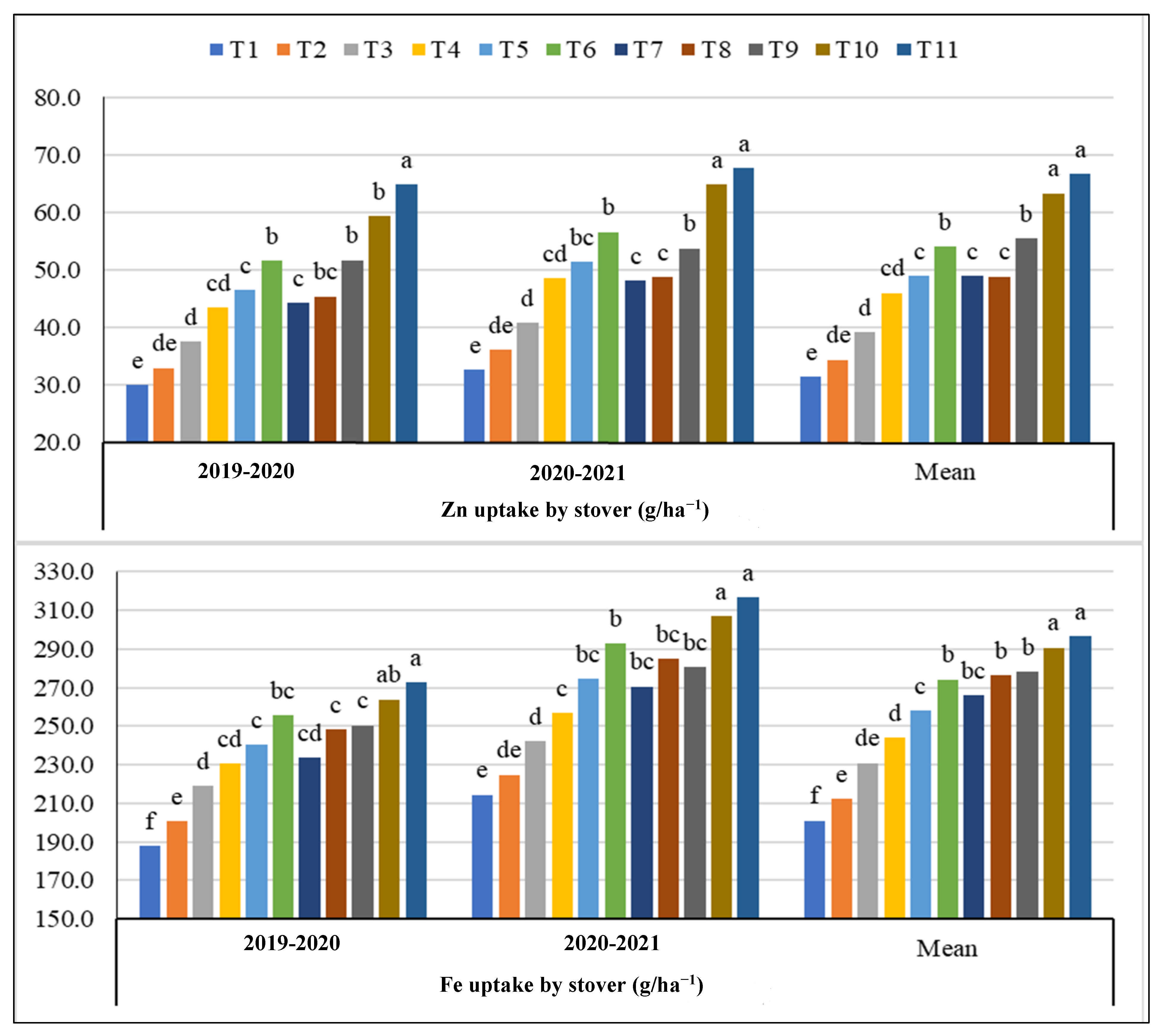
3.3. Zinc and Fe Uptake by Grains and Stover with Foliar Urea, Zn and Fe
3.4. Effect of Zn, Fe and Urea Application on Micronutrient Use Efficiencies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, M.; Khatun, A.; Liu, L.; Barkla, B.J. Brassicaceae Mustards: Traditional and agronomic uses in Australia and New Zealand. Molecules 2018, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bañuelos, G.S.; Bryla, D.R.; Cook, C.G. Vegetative production of kenaf and canola under irrigation in central California. Ind. Crop Prod. 2002, 15, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P. Effect of zinc and iron application on yield and acquisition of nutrient on mustard crop (brassica juncia L.). J. Plant Develop. Sci. 2014, 6, 413–416. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, M.; David, A.A.; Kumar, S. Effect of different levels of NPK and zinc sulphate on yield and oil content in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) Var. Jai Kisan. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2018, 6, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.S.; Meena, V.R.; Meena, A.K. Fertilizer management studies on growth and productivity of hybrid Indian mustard Brassica juncea (L.). J. Oilseed Brassica 2013, 4, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Olama, V.; Ronaghi, A.; Karimian, N.; Yasrebi, J.; Hamidi, R.; Tavajjoh, M.; Kazemi, M.R. Seed quality and micronutrient contents and translocations in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) as affected by nitrogen and zinc fertilizers. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanisha, K.; Atwal, A.K.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Banga, S.K. Assessment of diverse sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) germplasm for mineral composition. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2013, 29, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal, S.K.; Mann, A.; Sharma, P.C.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Quality seed production, processing and certification of selected field and vegetable crops in salt affected areas. In Training Manual; ICAR, Central Soil Salinity Research Institute Kamal: Haryana, India, 2016; pp. 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Naresh, R.K.; Mandal, A.; Singh, R.; Dhaliwal, M. K Dynamics and transformations of micronutrients in agricultural soils as influenced by organic matter build-up: A review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2019, 1–2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Zinc in Soils and Crop Nutrition; International Zinc Association and International Fertilizer Industry Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasal, P.C.; Shivay, Y.S.; Pooniya, V.; Choudhary, M.; Verma, R.K. Response of wheat genotypes to zinc fertilization for improving productivity and quality. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N. Effect of micronutrients on seed oil crops. Int. J. Curr. Adv. Res. 2018, 7, 15178–15192. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Mishra, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Dubey, N.K. Micronutrients and their diverse role in agricultural crops: Advances and future prospective. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Behera, S.K.; Pakhre, A.; Chaudhari, S.K. Micronutrients in soils, plants, animals and humans. Indian J. Fertil. 2018, 14, 30–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yasari, E.; Patwardhan, A.M. Physiological analysis of the growth and devolvement of canola (Brassica napus L.). Asian J. Plant Sci. 2006, 5, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibbett, M.; Green, L.; Rate, A.; De Oliveira, V.H.; Whitaker, J. The transfer of trace metals in the soil-plant-arthropod system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.B.; Warkentin, T.D. Biofortification of pulse crops: Status and future perspectives. Plants 2020, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, R.; Hossain, A.; Sharma, P. Zinc biofortification as an innovative technology to alleviate the zinc deficiency in human health: A review. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.Z.; Yaseen, M.; Abbas, T.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Yasir, H.; Saeed, Q.; Xu, M. Foliar application of micronutrients enhances crop stand, yield and the biofortification essential for human health of different wheat cultivars. J. Integrat. Agric. 2021, 18, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissuwa, M.; Ismail, A.M.; Graham, R.D. Rice grain zinc concentrations as affected by genotype native soil-zinc availability, and zinc fertilization. Plant Soil 2008, 306, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Dhaliwal, S.S. Zinc biofortification of dual purpose cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] for enhancing the productivity and nutritional quality in a semi-arid regions of India. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, C.S. Soil and Plant Analysis; Hans Publishers: Bombay, India, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa, M.K.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Toor, A.S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, M.; Verma, G. Nutrient use efficiency as a strong indicator of nutritional security and builders of soil nutrient status through integrated nutrient management technology in a rice-wheat system in northwestern India. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M. Effect of zinc and nitrogen fertilizer rates on yield and yield components of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2010, 7, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- El-Habbasha, S.F.; Abd El-Salam, M.S. Response of two canola varieties (Brassica napus L.) to nitrogen fertilizer levels and zinc foliar application. Int. J. Acad. Res. 2010, 2, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, V.; Singh, G.; Dhaliwal, S.S. A new approach in agronomic biofortification for improving zinc and iron content in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) grain with simultaneous foliar application of zinc sulphate, ferrous sulphate and urea. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Bahrani, M.J. Yield and yield components of rapeseed as influenced by water stress at different growth stages and nitrogen levels. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 755–761. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Soleymani, A.; Naranjani, L. Grain yield and forage characteristics of forage sorghum under different plant densities and nitrogen levels in second cropping after barley in Isfahan, Iran. Res. Crops 2011, 12, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, K.J.; Sokólski, M.; Szatkowski, A. The effect of autumn foliar fertilization on the yield and quality of winter oilseed rape seeds. Agronomy 2019, 9, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, V.; Singh, G.; Dhaliwal, S.S. Agronomic biofortification of chickpea with zinc and iron through application of zinc and urea. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losak, T.; Hlusek, J.; Martinec, J.; Jandak, J.; Szostkova, M.; Filipcik, R.; Manasek, J.; Prokes, K.; Peterka, J.; Varga, L.; et al. Nitrogen fertilization does not affect micronutrient uptake in grain maize (Zea mays L.). Acta. Agric. Soil Plant Sci. 2011, 61, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan, R.; Prasad, D.R.; Jain, M.C. Yield and uptake of micronutrients by rice as influenced by duration of variety and nitrogen fertilization. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2005, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafea, L.; Saffari, M. Effects of zinc (ZnSO4) and nitrogen on chemical composition of Maize grain. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Samadhiya, V.K. Response of micronutrients and urea foliar spray on yield and nutrient uptake of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) in Chhattisgarh plan. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
| Sr No. | Treatments Details |
|---|---|
| T1 | RDF (Control) |
| T2 | RDF + 1% Urea Foliar spray 45 DAS |
| T3 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 DAS |
| T4 | RDF + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 DAS |
| T5 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 DAS |
| T6 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O + 1% Urea foliar spray 45 DAS |
| T7 | RDF + 1% Urea Foliar spray 45 and 60 DAS |
| T8 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 and 60 DAS |
| T9 | RDF + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 and 60 DAS |
| T10 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O foliar spray 45 and 60 DAS |
| T11 | RDF + 0.5% FeSO4·7H2O + 0.5% ZnSO4·7H2O + 1% Urea foliar spray 45 and 60 DAS |
| Treatments | PE (Zn) | PE (Fe) | ARE (Zn) | ARE (Fe) | ME (Zn) | ME (Fe) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.19 | 1.34 |
| T2 | 11,838.33 | 3575.887 | - | - | 3.06 | 1.32 |
| T3 | 8860.17 | 1907.025 | - | 2.16 | 2.90 | 1.32 |
| T4 | 5807.35 | 3011.892 | 0.85 | - | 2.77 | 1.31 |
| T5 | 7371.15 | 2732.967 | 1.13 | 3.06 | 2.74 | 1.30 |
| T6 | 7507.63 | 2819.979 | 1.51 | 4.02 | 2.72 | 1.30 |
| T7 | 5376.76 | 1947.357 | - | - | 2.89 | 1.30 |
| T8 | 8355.37 | 2565.779 | - | 3.60 | 2.90 | 1.29 |
| T9 | 6970.28 | 2835.754 | 1.45 | - | 2.75 | 1.30 |
| T10 | 6218.74 | 2645.546 | 1.96 | 4.60 | 2.50 | 1.28 |
| T11 | 5910.54 | 2543.284 | 2.18 | 5.06 | 2.44 | 1.27 |
| CD (α = 0.05) | 412.99 | NS | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Shukla, A.K.; Verma, V.; Sandhu, P.S.; Behera, S.K.; Singh, P.; Kaur, J.; Singh, H.; Abdel-Hafez, S.H.; et al. Interactive Effects of Foliar Application of Zinc, Iron and Nitrogen on Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112333
Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Shukla AK, Verma V, Sandhu PS, Behera SK, Singh P, Kaur J, Singh H, Abdel-Hafez SH, et al. Interactive Effects of Foliar Application of Zinc, Iron and Nitrogen on Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112333
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhaliwal, Salwinder Singh, Vivek Sharma, Arvind Kumar Shukla, Vibha Verma, Prabhjodh Singh Sandhu, Sanjib K. Behera, Prabhjot Singh, Janpriya Kaur, Harkirat Singh, Shams H. Abdel-Hafez, and et al. 2021. "Interactive Effects of Foliar Application of Zinc, Iron and Nitrogen on Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.)" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112333
APA StyleDhaliwal, S. S., Sharma, V., Shukla, A. K., Verma, V., Sandhu, P. S., Behera, S. K., Singh, P., Kaur, J., Singh, H., Abdel-Hafez, S. H., Gaber, A., Sayed, S., & Hossain, A. (2021). Interactive Effects of Foliar Application of Zinc, Iron and Nitrogen on Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Agronomy, 11(11), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112333













