Influence of Bulk Temperature on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Polycarbonate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
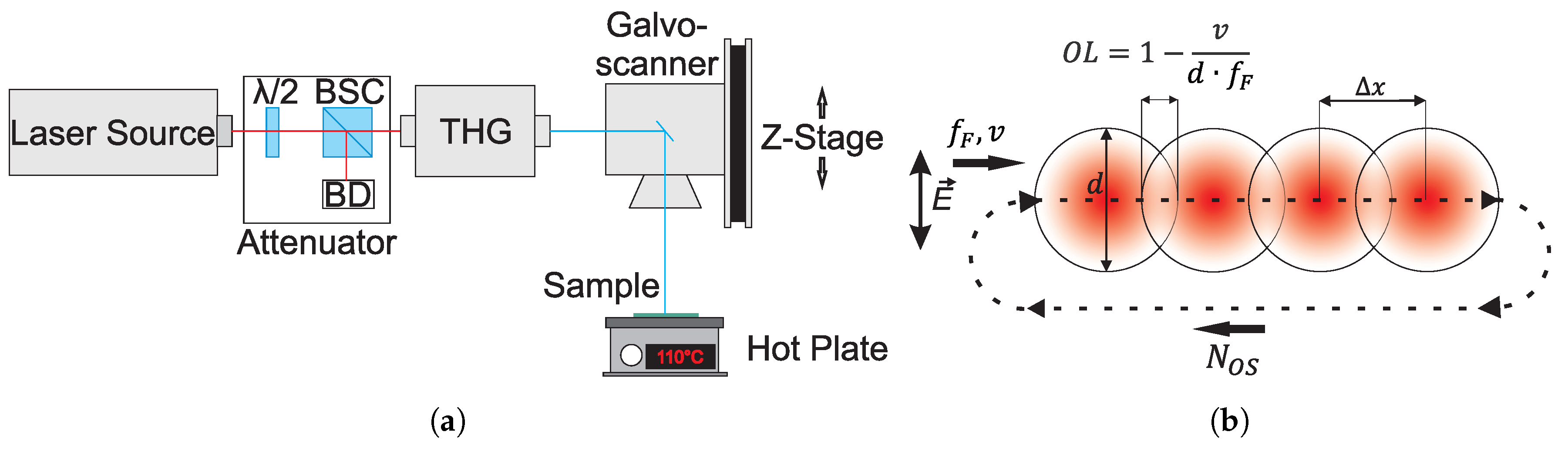
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
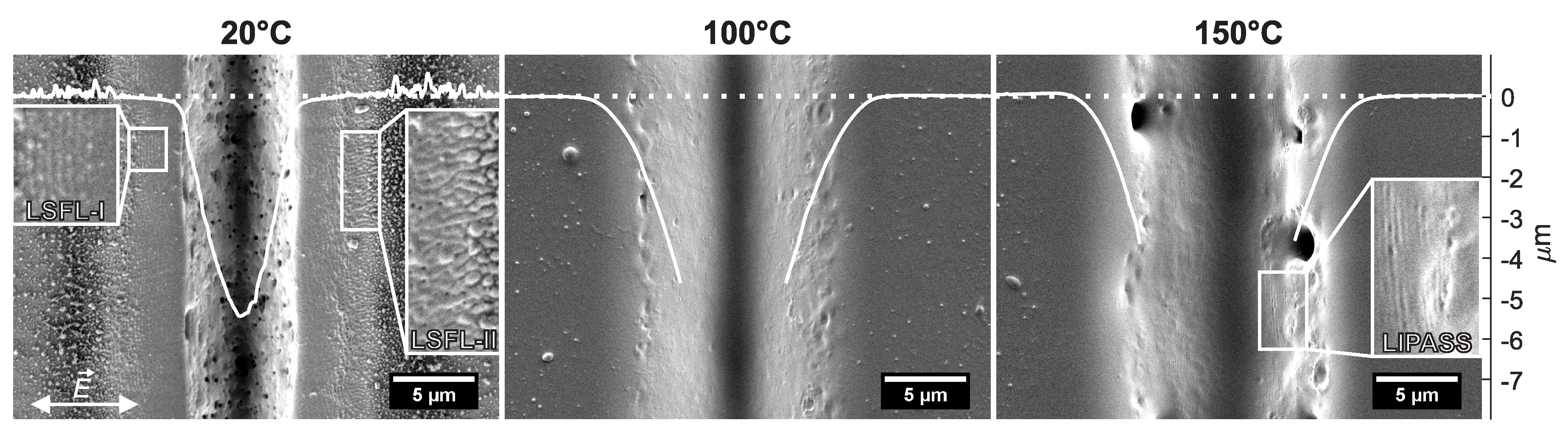
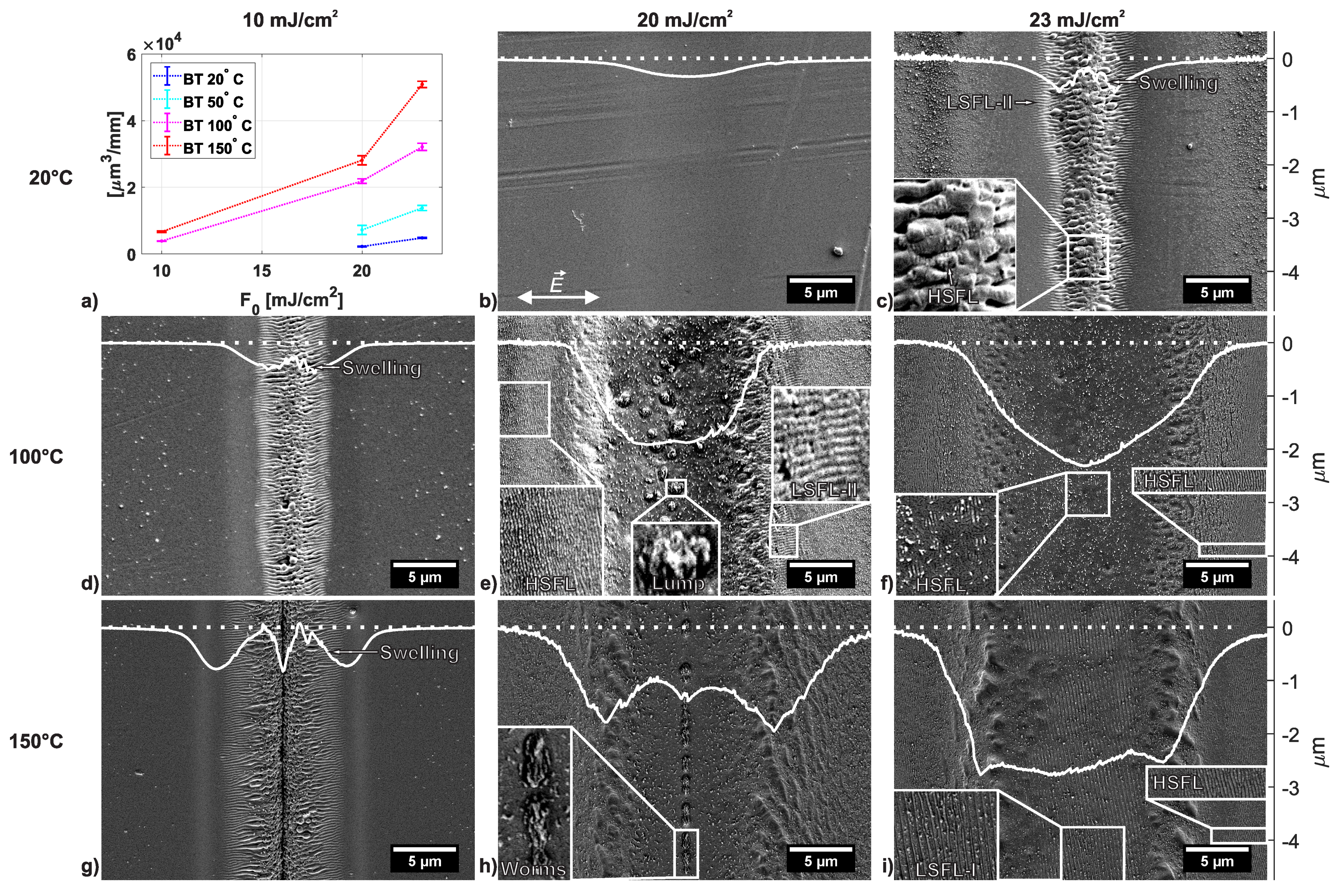
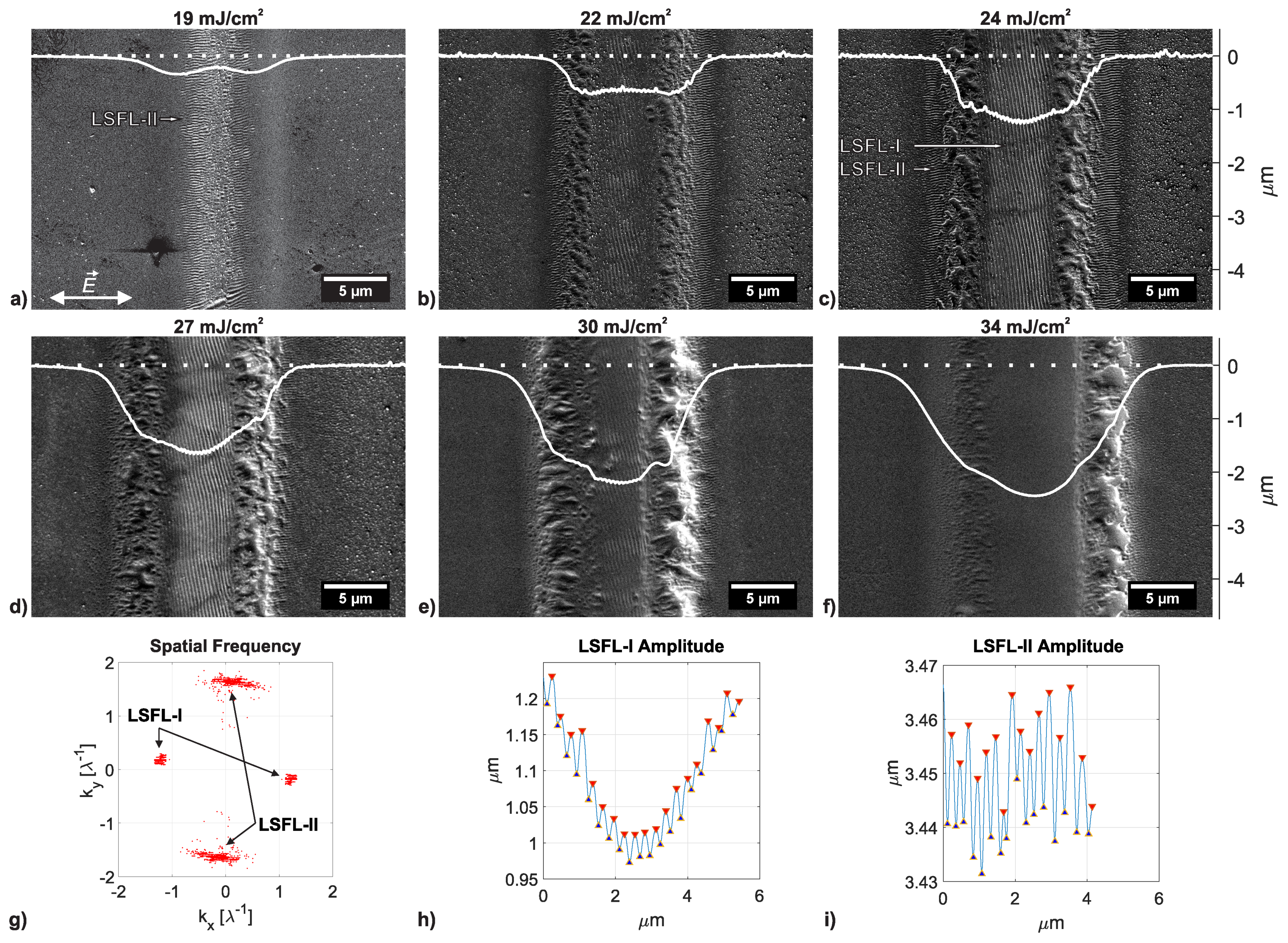
3.1. Surface Modifications for 250 and 500 Overscans
3.2. Surface Modifications for 1000 to 5000 Overscans
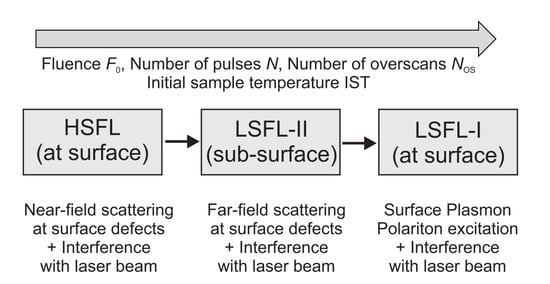
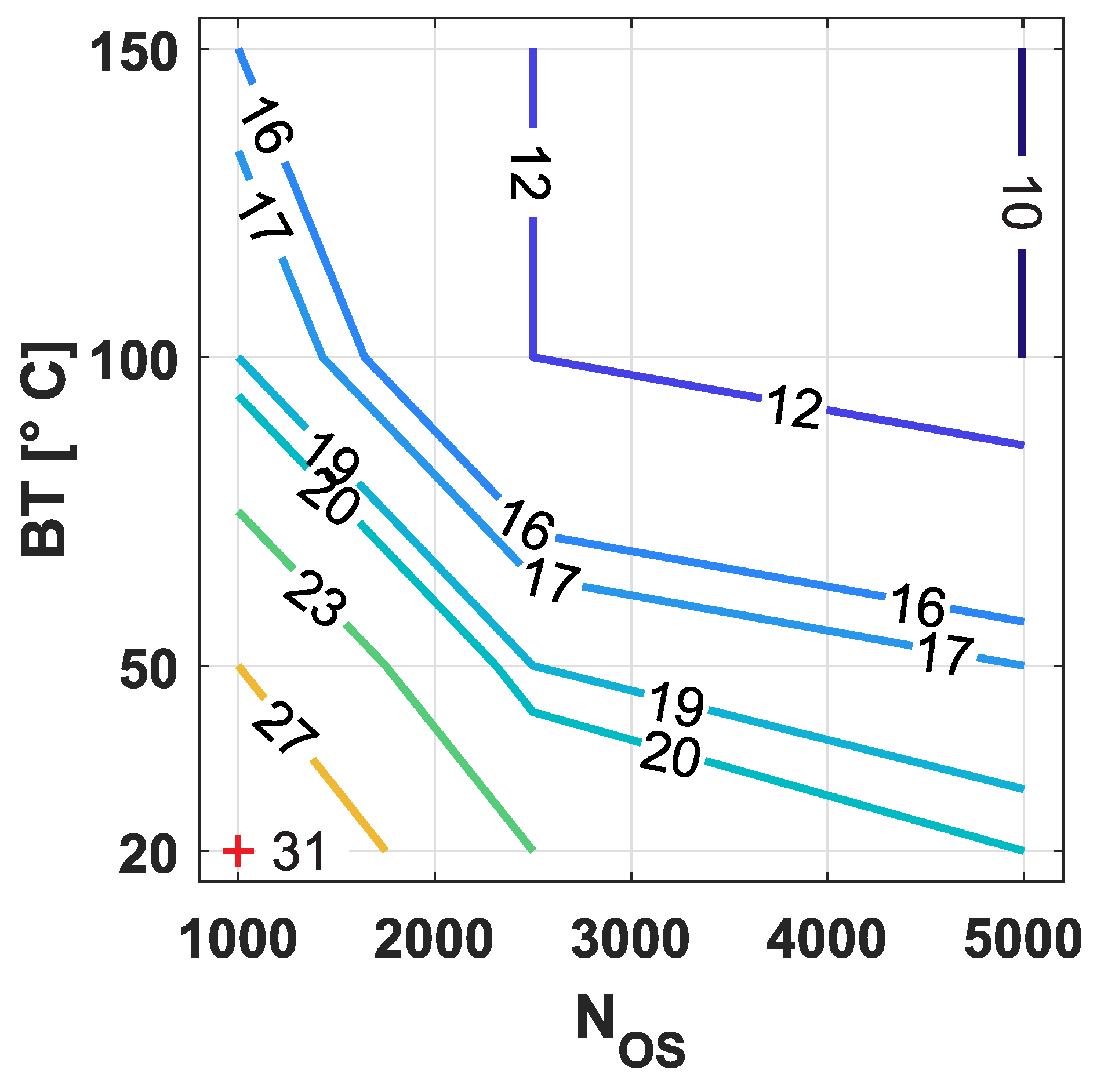
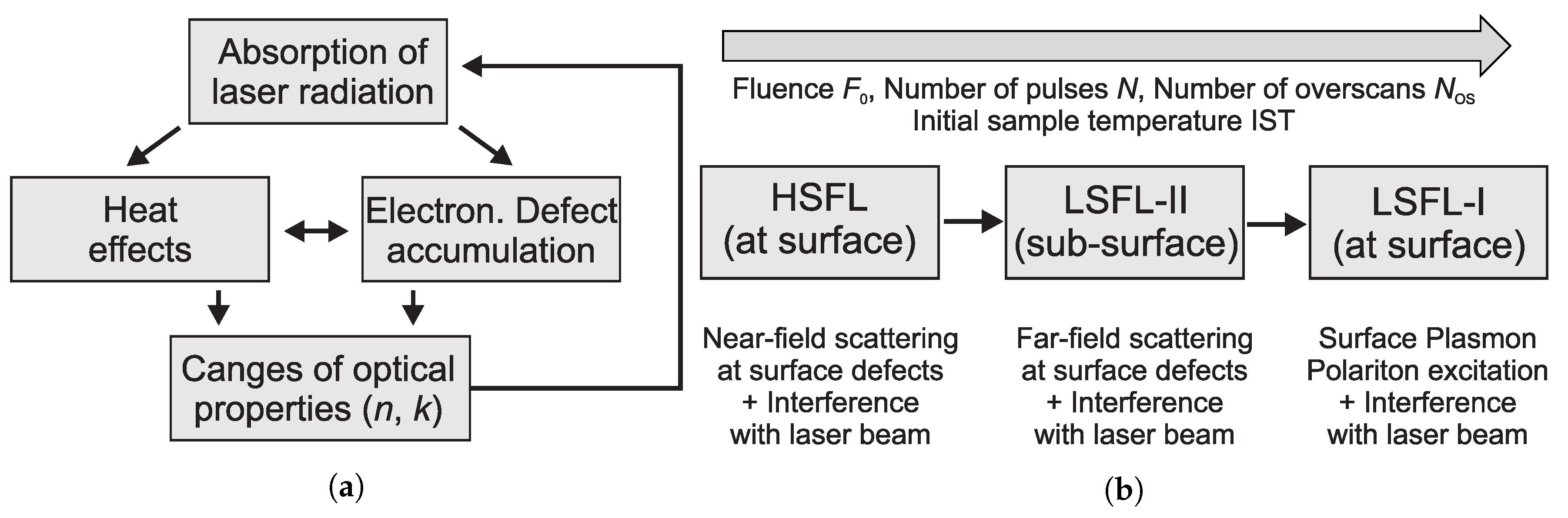
3.3. Evolution of Different LIPSS on Polycarbonate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| BT | bulk temperature |
| HSFL | High spatial frequency LIPSS |
| LIPASS | Laser-induced angular periodic surface structures |
| LIPSS | Laser-induced periodic surface structures |
| LSFL | Low spatial frequency LIPSS |
| number of overscans | |
| geometrical pulse-to-pulse overlap | |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SPP | Surface Plasmon Polariton |
| glass transition temperature | |
| melt temperature |
References
- Van Driel, H.M.; Sipe, J.E.; Young, J.F. Laser-induced periodic surface structure on solids: A universal phenomenon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezera, M.; van Drongelen, M.; Römer, G.R.B.E. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS) on polymers processed with picosecond laser pulses. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2018, 13, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Jee, Y.; Becker, M.F.; Walser, R.M. Laser-induced damage on single-crystal metal surfaces. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1988, 5, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudach, S.; Bonse, J.; Kautek, W. Ablation experiments on polyimide with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1999, 69, S395–S398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejo, M.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Martín, M.; Oujja, M.; Pérez, S.; Rebollar, E. Laser nanostructuring of polymers: Ripples and applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1464, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Rebollar, E.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Martín-Fabiani, I.; Hernández, M.; Rueda, D.R.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Domingo, C.; Moreno, P.; Castillejo, M. Assessment of femtosecond laser induced periodic surface structures on polymer films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11287–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Michalowski, A.; Kiedrowski, T.; Nolte, S. Heat accumulation in ultra-short pulsed scanning laser ablation of metals. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, S.; Bielke, U.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Prediction of the surface structures resulting from heat accumulation during processing with picosecond laser pulses at the average power of 420 W. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2018, 124, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan Mehr, M.; Van Driel, W.D.; Jansen, K.M.; Deeben, P.; Boutelje, M.; Zhang, G.Q. Photodegradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate under blue light radiation and its effect on optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepens, M.; Gijsman, P. Photodegradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migahed, M.D.; Zidan, H.M. Influence of UV-irradiation on the structure and optical properties of polycarbonate films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.R.; Garton, A. Surface modification of bisphenol-A-polycarbonate by far-UV radiation. Part I: In vacuum. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1993, 41, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaton, A.; Sallet, D.; Lemaire, J. The photochemistry of bisphenol-A polycarbonate reconsidered. Polym. Photochem. 1983, 3, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissinger, D. Complex refractive index of polycarbonate over the UV-Vis-IR region from 0.2 to 3 μm. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Kirner, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced Periodic Surface Structures—A Scientific Evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 9000615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, A.; Colombier, J.P.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J.; Itina, T.E. Spontaneous periodic ordering on the surface and in the bulk of dielectrics irradiated by ultrafast laser: A shared electromagnetic origin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Origin of laser-induced near- subwavelength ripples: Interference between surface plasmons and incident Laser. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.J.Y.; Itina, T.E.; Torres, R.; Sarnet, T.; Sentis, M. Possible surface plasmon polariton excitation under femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 083104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.J.; Koter, R.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Bonse, J. Plasmonic formation mechanism of periodic 100-nm-structures upon femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon in water. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 074902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrelie, F.; Colombier, J.P.; Pigeon, F.; Tonchev, S.; Faure, N.; Reynaud, S.; Parriaux, O. Evidence of surface plasmon resonance in ultrafast laser-induced ripples. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9035–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.E.; Van Driel, H.M.; Young, J.F. Surface Electrodynamics: Radiation Fields, Surface Polaritons, and Radiation Remnants. Can. J. Phys. 1985, 63, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar, E.; Frischauf, I.; Olbrich, M.; Peterbauer, T.; Hering, S.; Preiner, J.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Romanin, C.; Heitz, J. Proliferation of aligned mammalian cells on laser-nanostructured polystyrene. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar, E.; Pérez, S.; Hernández, M.; Domingo, C.; Martín, M.; Ezquerra, T.A.; García-Ruiz, J.P.; Castillejo, M. Physicochemical modifications accompanying UV laser induced surface structures on poly(ethylene terephthalate) and their effect on adhesion of mesenchymal cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 17551–17559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollar, E.; Castillejo, M.; Ezquerra, T.A. Laser induced periodic surface structures on polymer films: From fundamentals to applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepička, P.; Siegel, J.; Lyutakov, O.; Slepičková Kasálková, N.; Kolská, Z.; Bačáková, L.; Švorčík, V. Polymer nanostructures for bioapplications induced by laser treatment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks, Inc. MATLAB® R2015b; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mezera, M.; Römer, G.R.B.E. Model based optimization of process parameters to produce large homogeneous areas of laser-induced periodic surface structures. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 6012–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezera, M.; Römer, G. Upscaling laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) manufacturing by defocused laser processing. SPIE Conf. Proc. 2019, 10906, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cariou, J.M.; Dugas, J.; Martin, L.; Michel, P. Refractive-index variations with temperature of PMMA and polycarbonate. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaton, A.; Sallet, D.; Lemaire, J. The photo-chemistry of bisphenol-A polycarbonate reconsidered: Part 3-Influence of water on polycarbonate photo-chemistry. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1986, 14, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.; Kautek, W.; Faure, N.; Audouard, E.; Stoian, R. Periodic nanoscale structures on polyimide surfaces generated by temporally tailored femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4155–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Brelet, Y.; He, Z.; Yu, L.; Forestier, B.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Houard, A. Laser-induced periodic annular surface structures on fused silica surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 251103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudach, S.; Krüger, J.; Kautek, W. Femtosecond Laser Processing of Soft Materials. Laser Rev. 2001, 29, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bityurin, N. Model for laser swelling of a polymer film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9851–9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyshev, A.Y.; Bityurin, N.M. Laser swelling model for polymers irradiated by nanosecond pulses. Quantum Electron. 2005, 35, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Rebollar, E.; Soccio, M.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Rueda, D.R.; Garcia-Ramos, J.V.; Castillejo, M.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.C. Laser-induced periodic surface structures on conjugated polymers: Poly(3-hexylthiophene). Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4024–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csete, M.; Marti, O.; Bor, Z. Laser-induced periodic surface structures on different poly-carbonate. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2001, 526, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.; Rebollar, E.; Oujja, M.; Martín, M.; Castillejo, M. Laser-induced periodic surface structuring of biopolymers. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2013, 110, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Nogales, A.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Rebollar, E. Influence of substrate and film thickness on polymer LIPSS formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebewele, R. Polymer Science and Technology, 1st ed.; CRC Press LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Marand, H. On the multiple melting behavior of bisphenol-A polycarbonate. Polymer 2000, 41, 8879–8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufft, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Das, S.K.; Grunwald, R.; Bonse, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures revisited: A comparative study on ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 034908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Values | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Temperature | 20, 50, 100, 150 | [°C] |
| Number of Overscans | 250, 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 | |
| Laser Peak Fluence | 10, 13, 16, 19…68 |
| 1000 | 2500 | 5000 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT [°C] | ||||
| 20 | 31 | 23 | 20 | |
| 50 | 27 | 19 | 17 | |
| 100 | 19 | 12 | 10 | |
| 150 | 16 | 12 | 10 | |
| LIPSS Type | Spatial Frequency | Amplitude |
|---|---|---|
| LSFL-I | 280 ± 8 nm () | 53 ± 23 nm |
| LSFL-II | 208 ± 5 nm () | 21 ± 7 nm |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mezera, M.; Bonse, J.; Römer, G.-w.R.B.E. Influence of Bulk Temperature on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Polycarbonate. Polymers 2019, 11, 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121947
Mezera M, Bonse J, Römer G-wRBE. Influence of Bulk Temperature on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Polycarbonate. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121947
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezera, Marek, Jörn Bonse, and Gert-willem R. B. E. Römer. 2019. "Influence of Bulk Temperature on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Polycarbonate" Polymers 11, no. 12: 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121947
APA StyleMezera, M., Bonse, J., & Römer, G.-w. R. B. E. (2019). Influence of Bulk Temperature on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Polycarbonate. Polymers, 11(12), 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121947