Effects of Y Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCr1.7Ni Medium-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CoCr1.7NiYx MEAs
2.2. Composition and Structure Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Property Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
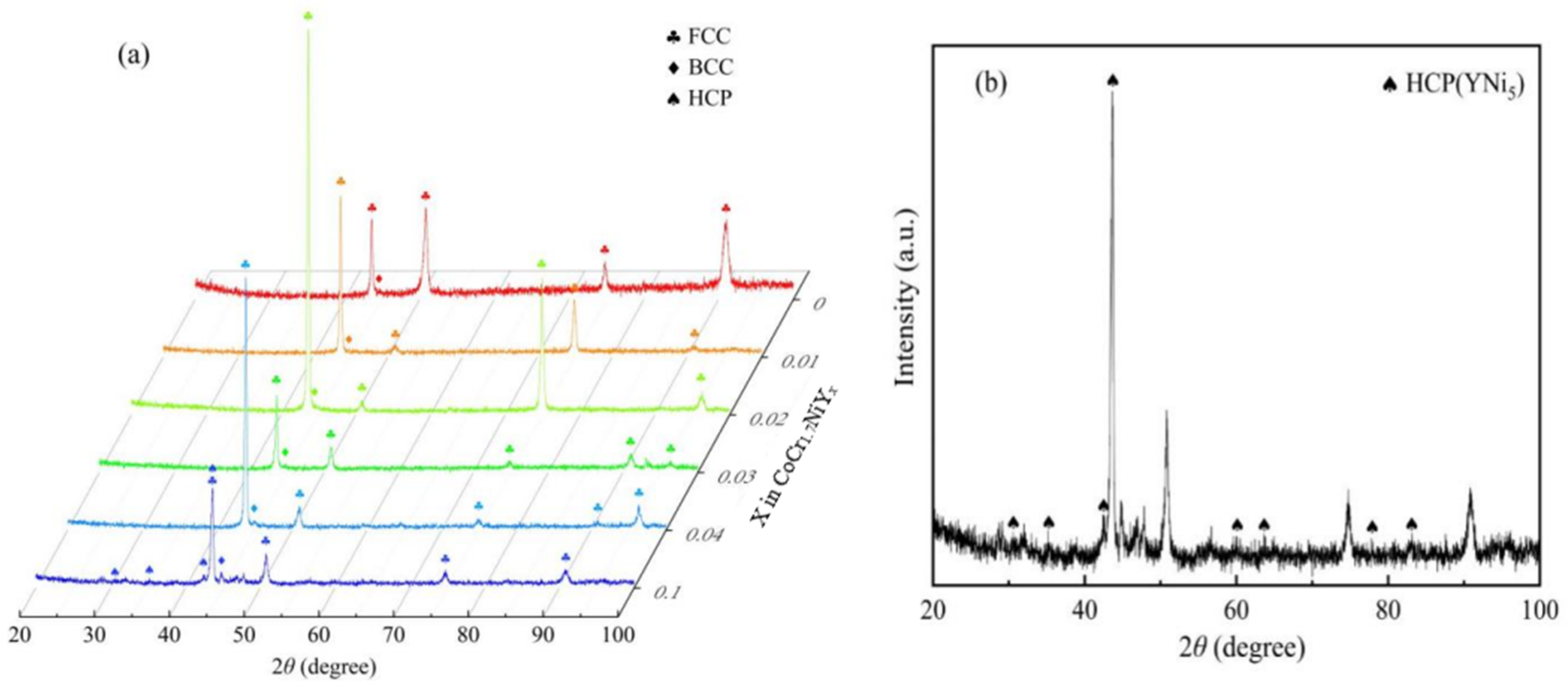
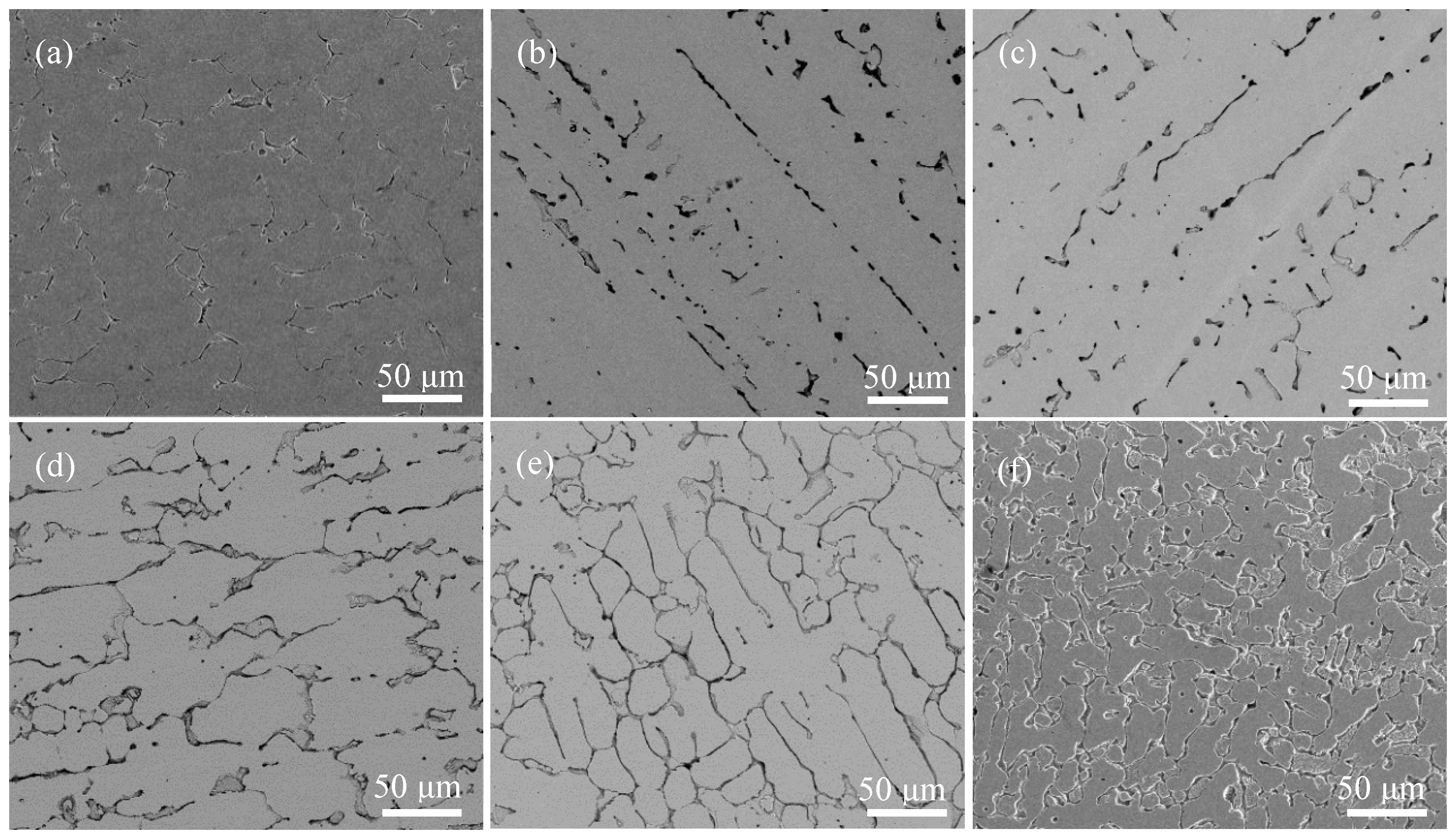
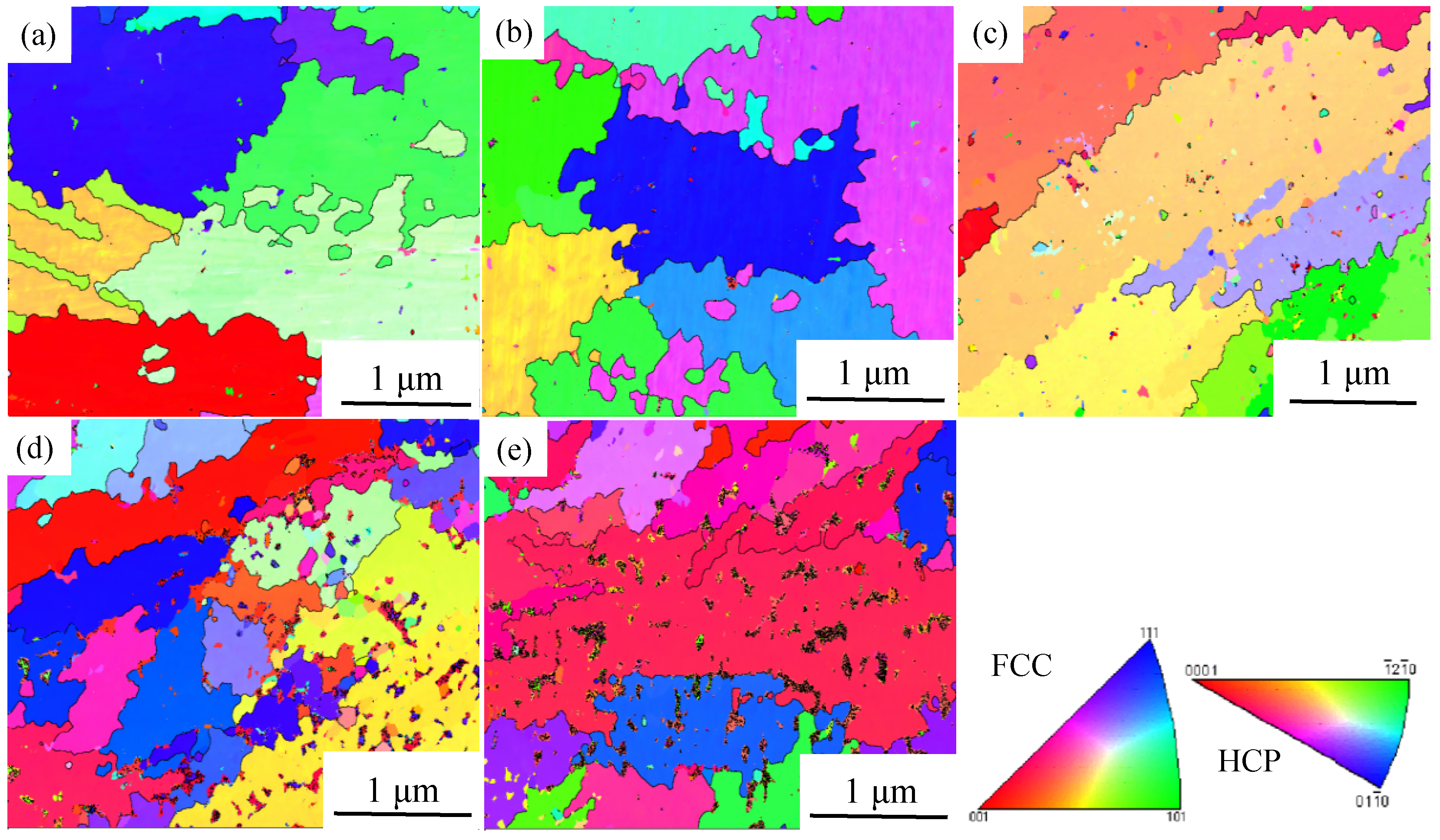
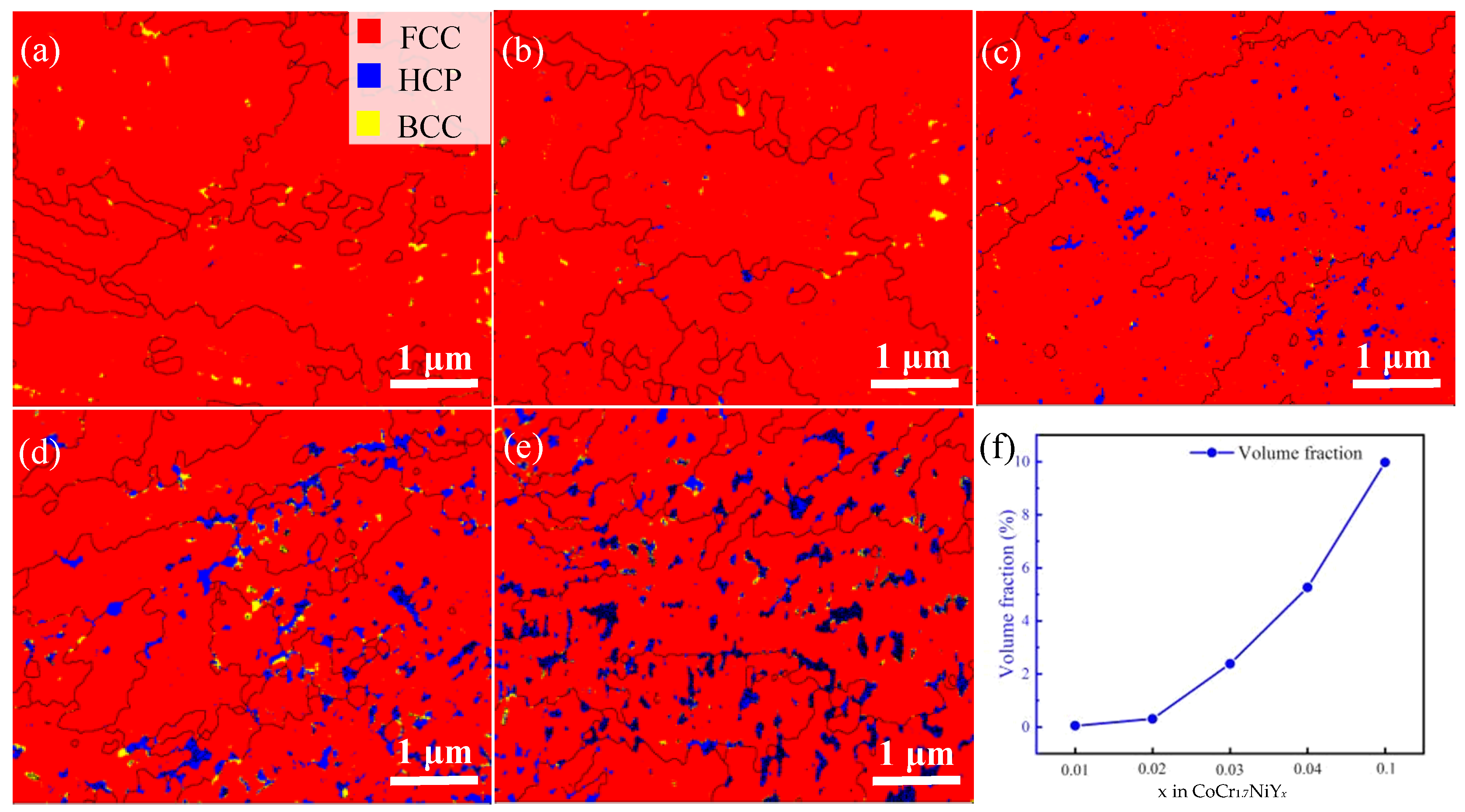
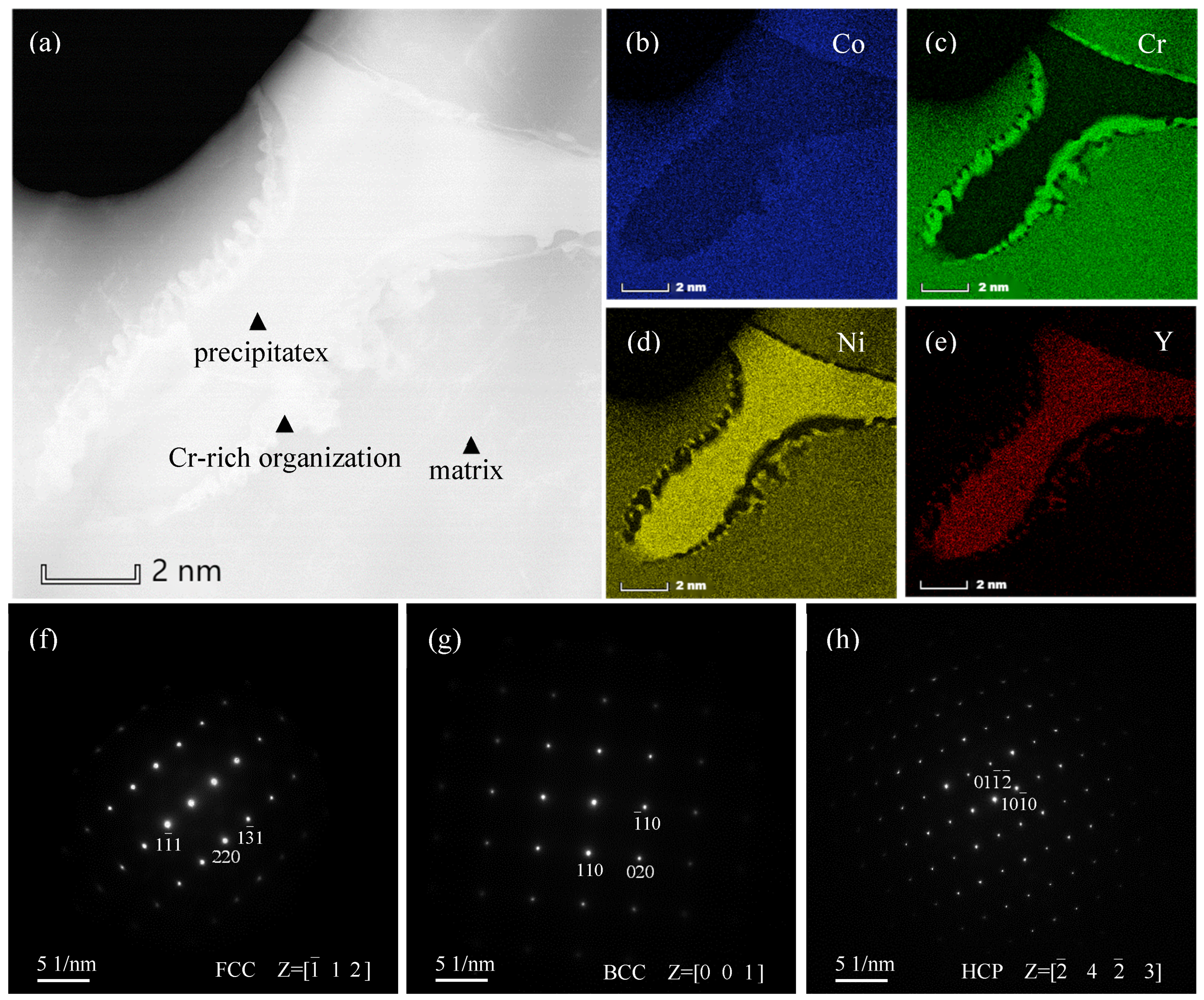
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Identification
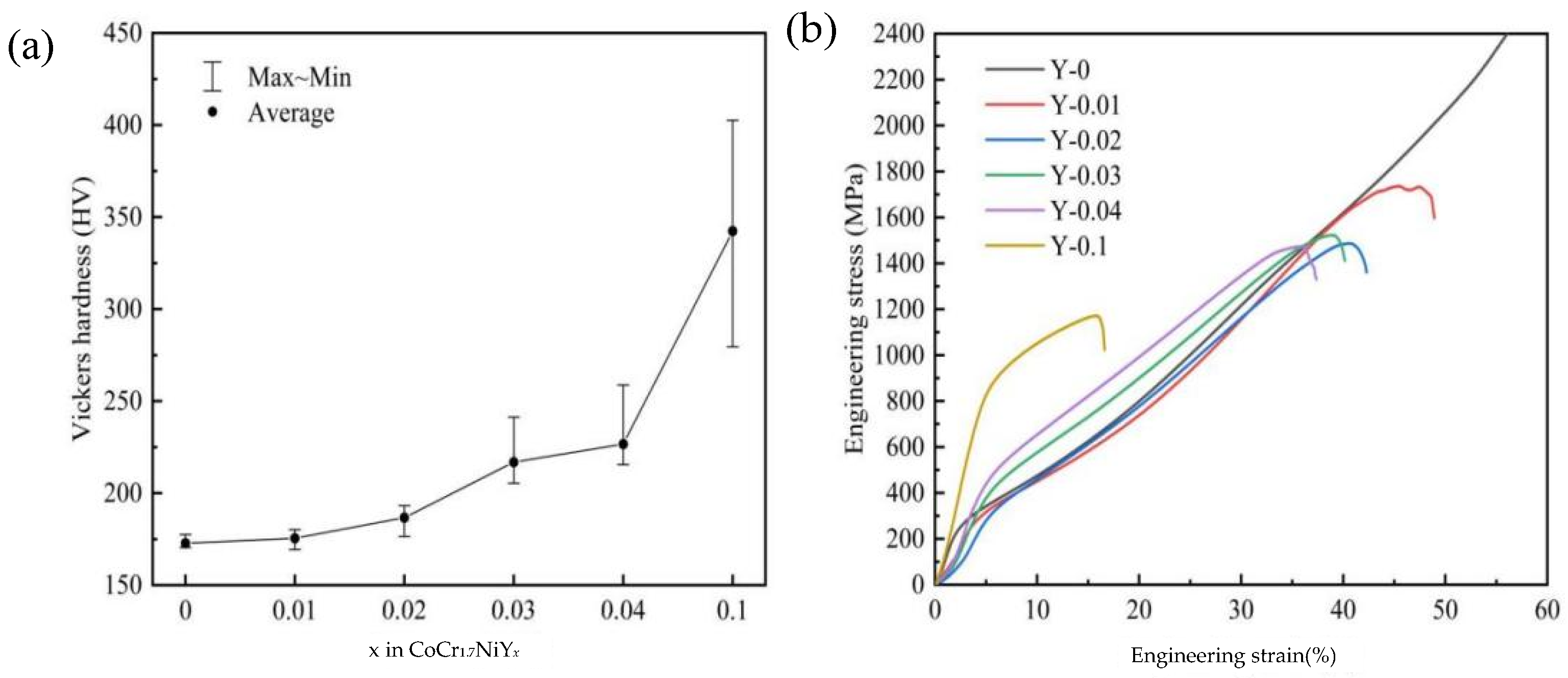
3.2. Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature
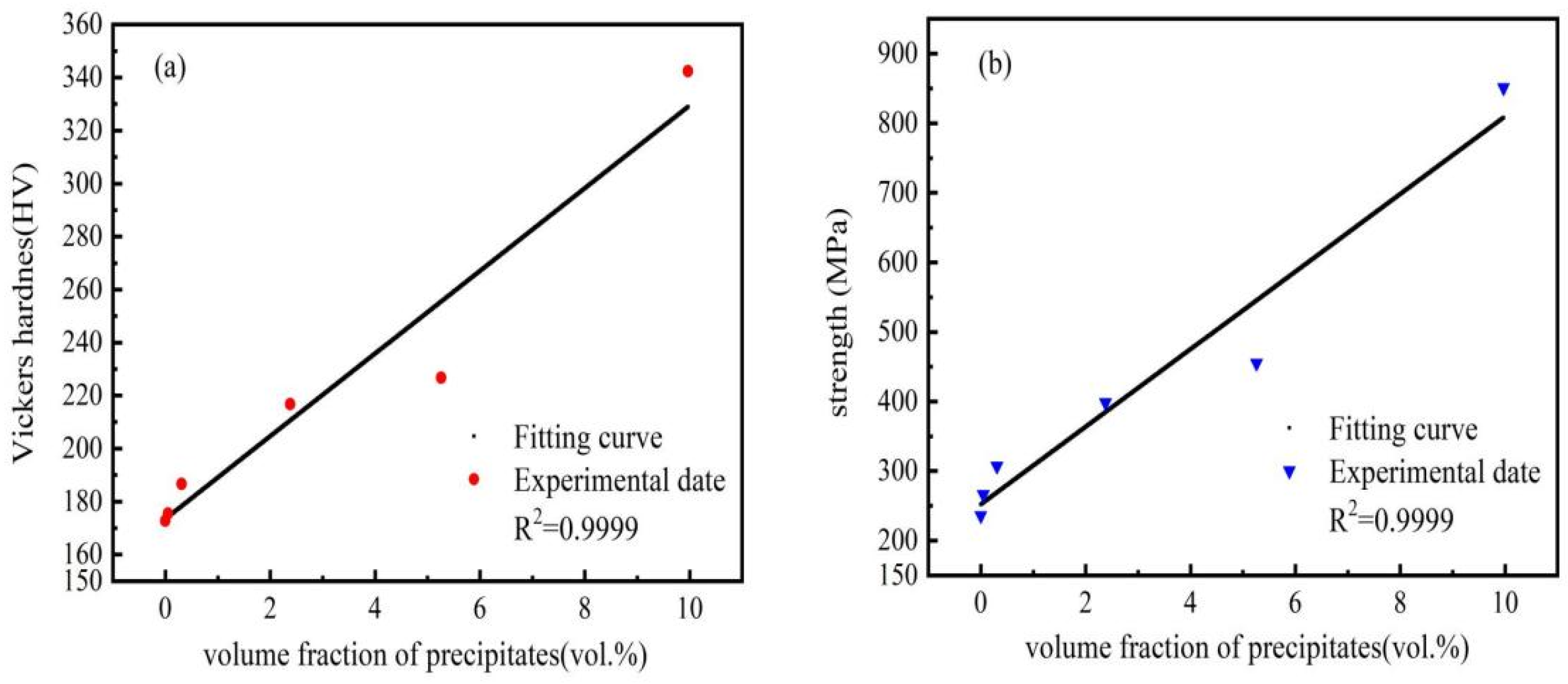
3.3. Strengthening Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- Without the addition of Y, the Y-0 alloy matrix has an FCC phase structure. The volume fraction of Cr-rich BCC precipitates was lower. The YNi5 HCP precipitate formed in Y-0.01 MEA. The volume fraction of BCC and HCP phase precipitates increased with Y content, which led to the precipitation and dispersion strengthening of CoCr1.7NiYx MEAs.
- Most of the added Y elements were enriched with Ni to form HCP phase YNi5 precipitates, and the remaining Y elements were solidly soluble in the FCC phase matrix. As the relatively large atomic radius of Y element replaces the position of Co, Cr and Ni elements in the matrix, lattice distortion is caused. At the same time, the degree of lattice distortion increased with the increase in Y addition, resulting in solid solution strengthening effect on CoCr1.7NiYx MEAs.
- The addition of element Y significantly improved the strength and hardness of the CoCr1.7NiYx MEAs, and the degree of improvement increased with the increase in Y content, and the highest level of improvement is achieved when the Y content is 0.1. The microhardness and yield strength of Y-0.1 MEA reached 342 HV and 851 MPa, respectively; compared with Y-0 MEA, the increase reached 98.18% and 260.59%, respectively. However, the plasticity of CoCr1.7NiYx MEAs deteriorated due to the less slip system of the HCP phase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-sheng, T.; Wen-zhe, Z.; Qing-biao, T.; Ming-xu, W.; Shen, Q.; Guo-liang, Z.; Da, S.; Bao-de, S. A review of refractory high-entropy alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 3487–3515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Xie, Y.; Chen, B. A review on recent progress of refractory high entropy alloys: From fundamental research to engineering applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1097–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Des Mater. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Cao, R.; Zhou, W.; Shen, Z.; Li, Y. Microstructures, mechanical properties, and strengthening mechanisms of the (NbMoTa)100−xCx refractory medium-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 214, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Tan, X.; Xiao, S.; Su, C.; Guo, N.; Guo, S. AlxHfTaTi (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) refractory medium entropy alloys with excellent room-temperature tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 909, 146849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y. A novel Cu-containing TiZrNb-based medium entropy alloy with excellent mechanical properties, antibacterial activity and biocompatibility. Intermetallics 2024, 171, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Gadaud, P.; Horst, O.; Otto, F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Temperature dependencies of the elastic moduli and thermal expansion coefficient of an equiatomic. single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiping, Z.; Jingxiang, M.; Hui, J.; Hongbin, Z.; Wenqing, W.; Shengxue, Q.; Lv, T.; Jian, X. Effect of rare-earth element Y addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrFeNi2 medium entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2023, 163, 108079. [Google Scholar]
- Laplanche, G.; Kostka, A.; Reinhart, C.; Hunfeld, J.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Y.; Qiu, P.P.; Hu, L.L. Research on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrxNi Medium-Entropy Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2023, 52, 511–558. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, X.W.; Hsueh, C.H. Effects of yttrium addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2022, 140, 107405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Agustianingrum, M.P.; Park, N.; Tsuji, N. Synergistic effect by Al addition in improving mechanical performance of CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 800, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Sun, Y.N.; Wu, Y.D.; Tian, J.J.; Li, Z.R.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.Y.; Hui, X.D. High temperature strengthening via nanoscale precipitation in wrought CoCrNi-based medium-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 798, 140213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Pei, X.H.; Tang, Z.W.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.F.; Liu, W.M. Mechanical and tribological performance of CoCrNiHfx eutectic medium-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 90, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.F. Mechanical and dry sliding tribological properties of CoCrNiNbx medium-entropy alloys at room temperature. Tribol. Int. 2021, 163, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.Q.; Huang, B. Effects of Nb additions on structure and mechanical properties evolution of CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Lin, W.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, D.; Yeli, G.M.; He, F.; Zhao, S.J.; Kai, J.J. Effect of silicon addition on the microstructures. mechanical properties and helium irradiation resistance of NiCoCr-based medium-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Huang, H.; Ruan, J.M.; Ji, S.X. In-situ Mo nanoparticles strengthened CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.B.; Fang, W.; Yan, J.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Yin, F.X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrNi-Mo medium entropy alloys: Experiments and first-principle calculations. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Gu, J.; Gan, B.; Qiao, Q.; Ni, S.; Song, M. Effects of Mo-doping on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2726–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, M.D.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, J.T.; Cui, P.; Yu, P.F.; Jing, Q.; Ma, M.Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Li, G.; et al. Effects of rare-earth element, Y, additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 275, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhu, H.G.; Xie, Z.H. Effects of Y and Al additions on the microstructure and tensile properties of CoCr3Fe5Ni high entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2021, 299, 130110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.H.; Ding, D.Y.; Lai, L.M.; Xiao, S.M.; Guo, N.; Song, B.; Guo, S.F. Effect of Y on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of CrMoTaTi refractory high entropy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 103, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhao, X.F.; Guo, F.W.; Xiao, P. Y-Hf co-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with superior oxidation and spallation resistance at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Mao, P.; Gou, Y.F.; Chao, Y.; Xi, S.Q. Microstructure and properties of MgMoNbFeTi2Yx high entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 402, 126303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliari, F.R.; Candioto, K.C.G.; Reis, D.A.P. Effect of aging treatment on inconel 718 superalloy: Application in elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 825, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume-Rothery, W. The Engel-Brewer theories of metals and alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1968, 130, 229–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Bei, H.B.; Egami, T.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, F.X. Severe local lattice distortion in Zr-and/or Hf-containing refractory multi-principal element alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 183, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.S.; Zhao, C.C.; Zhu, W.W.; Wei, P.B.; Jiang, F.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Sun, Q.P.; Ren, F.Z. Overcoming the strength-ductility trade-off via the formation of nanoscale Cr-rich precipitates in an ultrafine-grained FCC CrFeNi medium entropy alloy matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.S.; Wei, C.X.; Ren, F.Z. Introducing Laves phase strengthening into an ultrafine-grained equiatomic CrFeNi alloy by niobium addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 806, 140611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Guo, W.; Jin, K.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Gao, Y.F.; Bei, H.B. Enhanced strength and ductility of a tungsten-doped CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Gao, Y.F.; Bei, H.B. Thermal activation mechanisms and Labusch-type strengthening analysis for a family of high-entropy and equiatomic solid-solution alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 120, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Y-0 | Y-0.01 | Y-0.02 | Y-0.03 | Y-0.04 | Y-0.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average microhardness (HV) | 172.75 | 175.47 | 186.69 | 216.76 | 226.66 | 342.35 |
| Rate of increase (%) | - | 1.57 | 8.07 | 25.47 | 31.20 | 98.17 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | UCS (MPa) | Compression (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y-0 | 236 | - | - |
| Y-0.01 | 266 | 1732 | 47.5 |
| Y-0.02 | 307 | 1485 | 40.6 |
| Y-0.03 | 398 | 1522 | 39.0 |
| Y-0.04 | 455 | 1473 | 35.9 |
| Y-0.1 | 851 | 1170 | 15.7 |
| Element (Atomic Radius (Å), Melting Point (°C), Valence Electrons) | Co | Cr | Ni | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co (1.26, 1495, 9) | - | −4 | 0 | −22 |
| Cr (1.27, 1907, 6) | - | - | −7 | 11 |
| Ni (1.24, 1453, 10) | - | - | - | −32 |
| Y (1.80, 1522, 3) | - | - | - | - |
(kJ/mol) | (J/mol·k) | /% | (K) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y-0 | −5.46 | 8.85 | 2709 | 0.98 | 7.89 | 1672.94 | −14,812 |
| Y-0.01 | −5.54 | 8.98 | 2713 | 2.43 | 7.88 | 1672.53 | −15,028 |
| Y-0.02 | −5.61 | 9.08 | 2707 | 3.28 | 7.87 | 1672.13 | −15,190 |
| Y-0.03 | −5.68 | 9.17 | 2698 | 3.95 | 7.85 | 1671.73 | −15,333 |
| Y-0.04 | −5.75 | 9.25 | 2687 | 4.50 | 7.84 | 1671.33 | −15,462 |
| Y-0.1 | −6.16 | 9.63 | 2609 | 6.87 | 7.76 | 1668.97 | −16,077 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Shu, X.; Hu, L.; Yuan, X.; Qiu, P.; Xu, X. Effects of Y Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCr1.7Ni Medium-Entropy Alloys. Crystals 2025, 15, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020172
Zhou S, Shu X, Hu L, Yuan X, Qiu P, Xu X. Effects of Y Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCr1.7Ni Medium-Entropy Alloys. Crystals. 2025; 15(2):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020172
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shaoshuai, Xiaoyong Shu, Linli Hu, Xunyu Yuan, Panpan Qiu, and Xiwen Xu. 2025. "Effects of Y Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCr1.7Ni Medium-Entropy Alloys" Crystals 15, no. 2: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020172
APA StyleZhou, S., Shu, X., Hu, L., Yuan, X., Qiu, P., & Xu, X. (2025). Effects of Y Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCr1.7Ni Medium-Entropy Alloys. Crystals, 15(2), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020172






