The Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Welded Ni-Based Hastelloy X Superalloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Laser Welding
2.3. Tensile Testing
2.4. Microstructure Characterization
3. Results
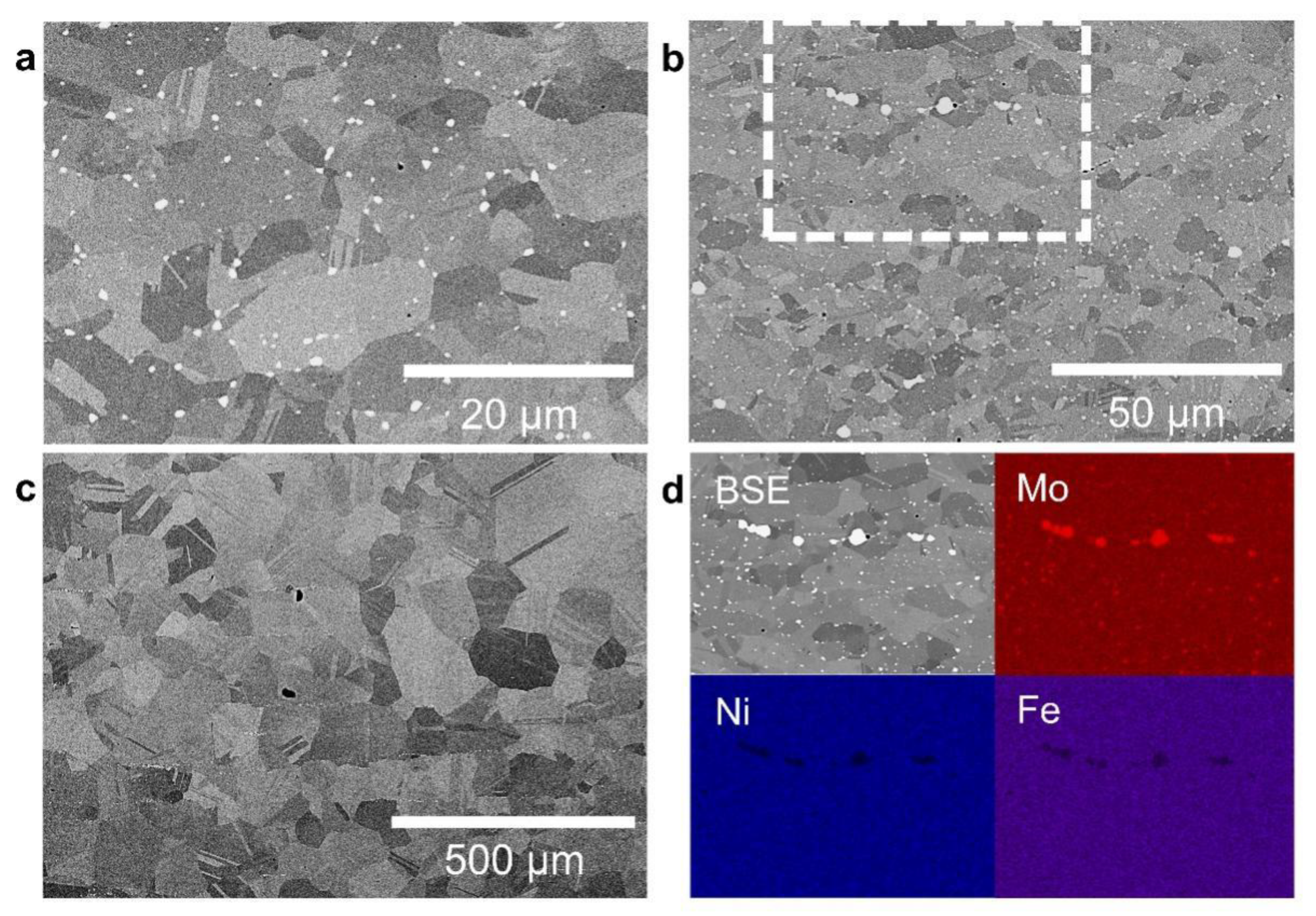
3.1. The Initial Microstructures of Base Metal
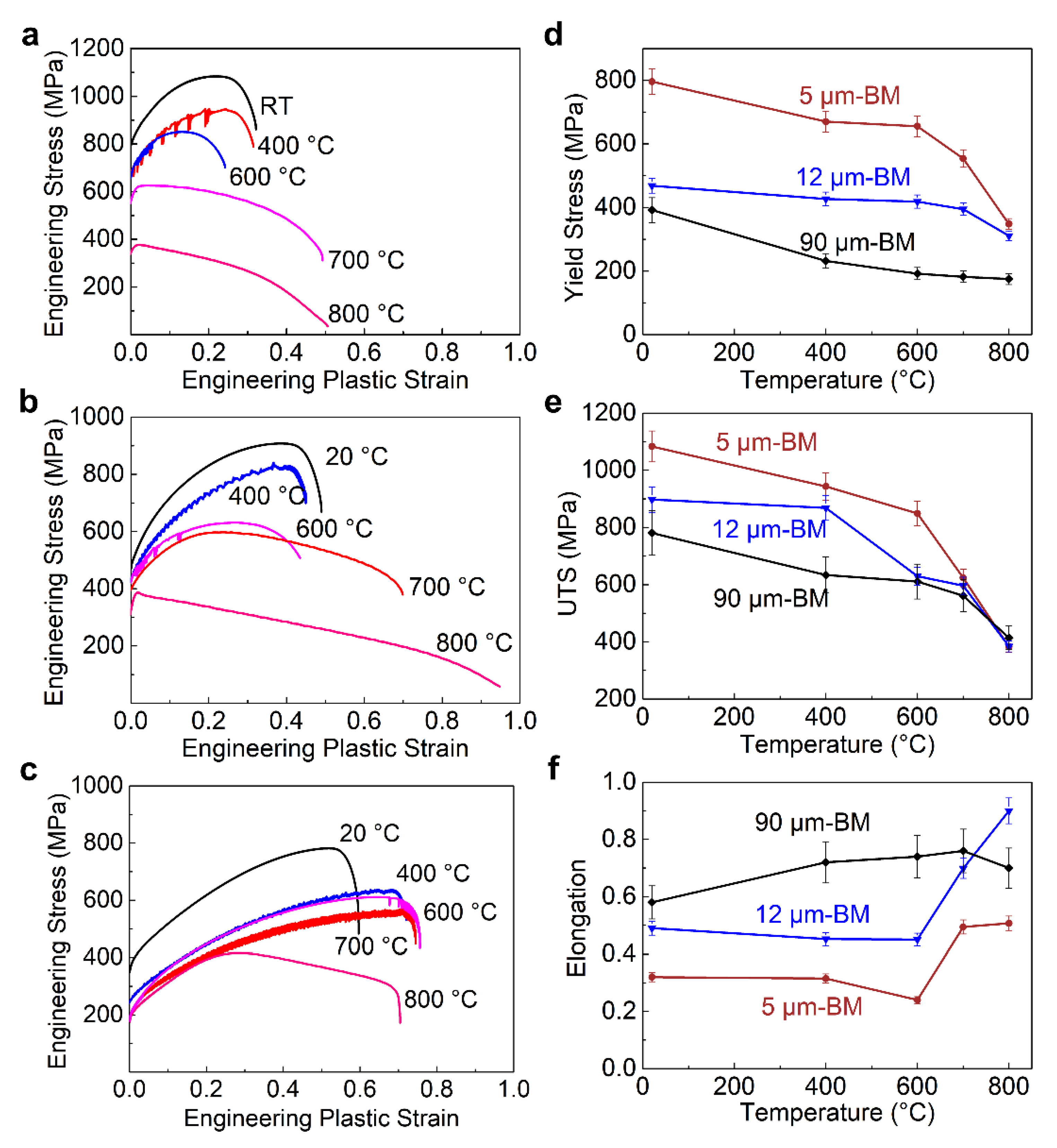
3.2. The Tensile Properties of the Hastelloy X Base Metals
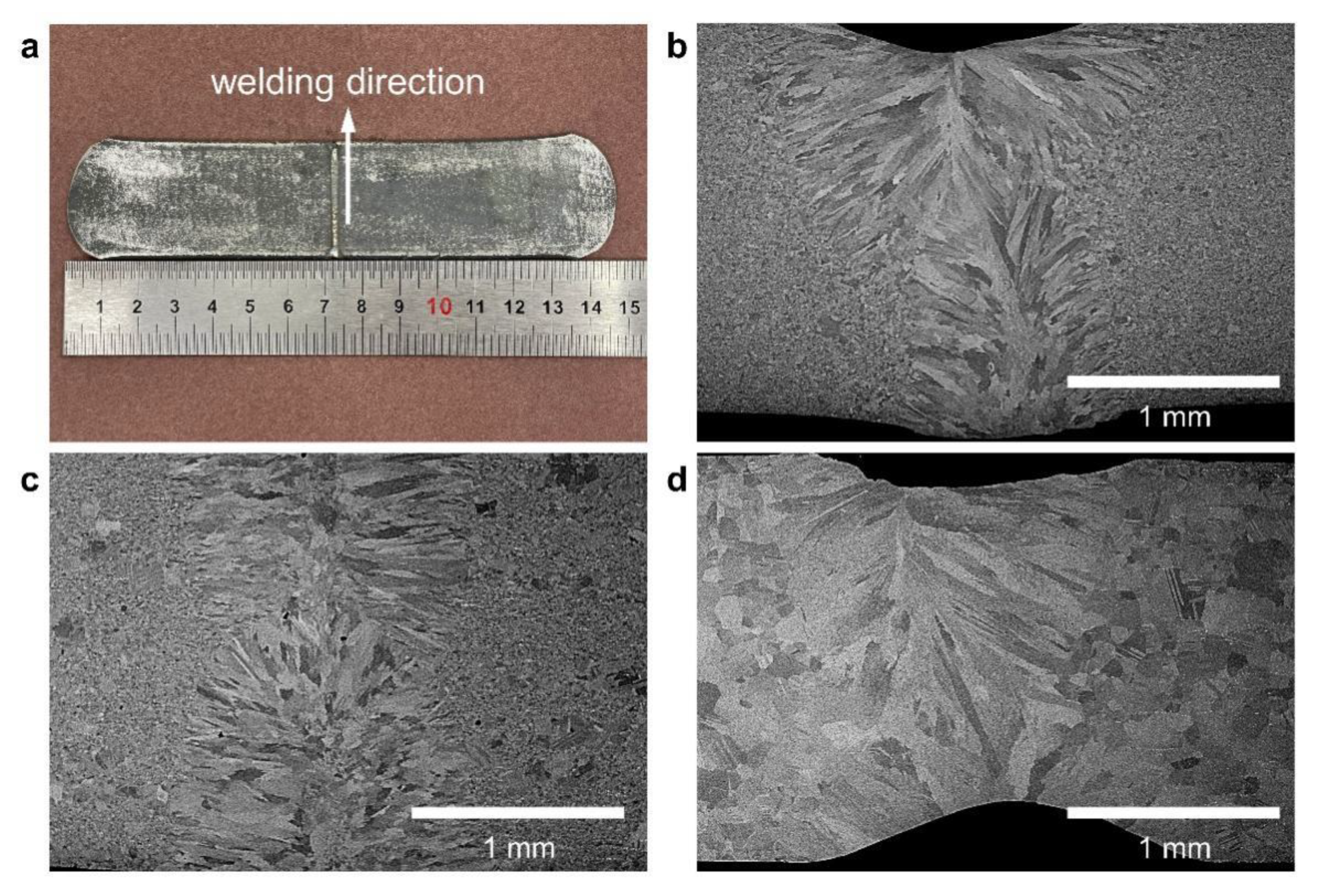
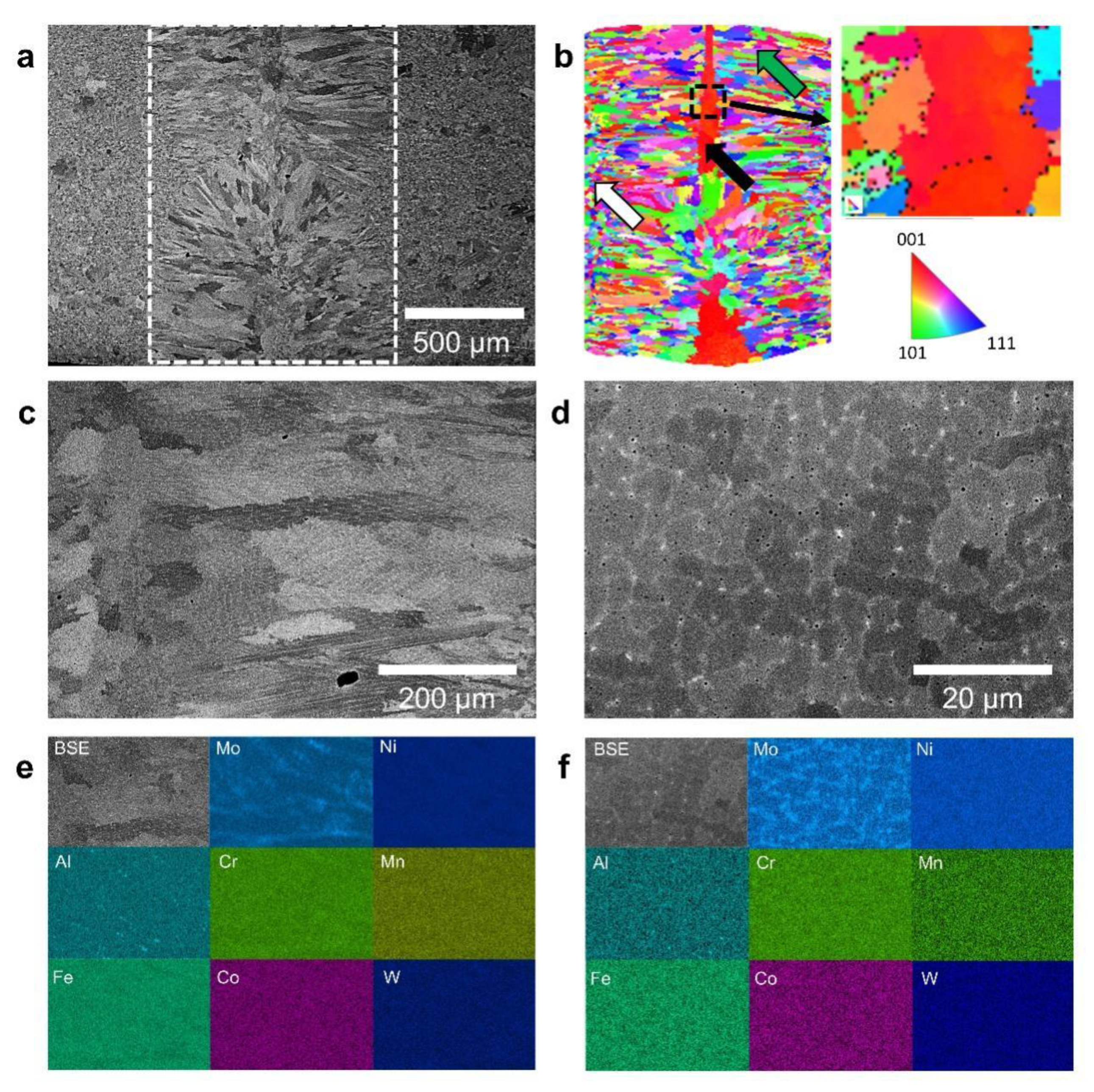
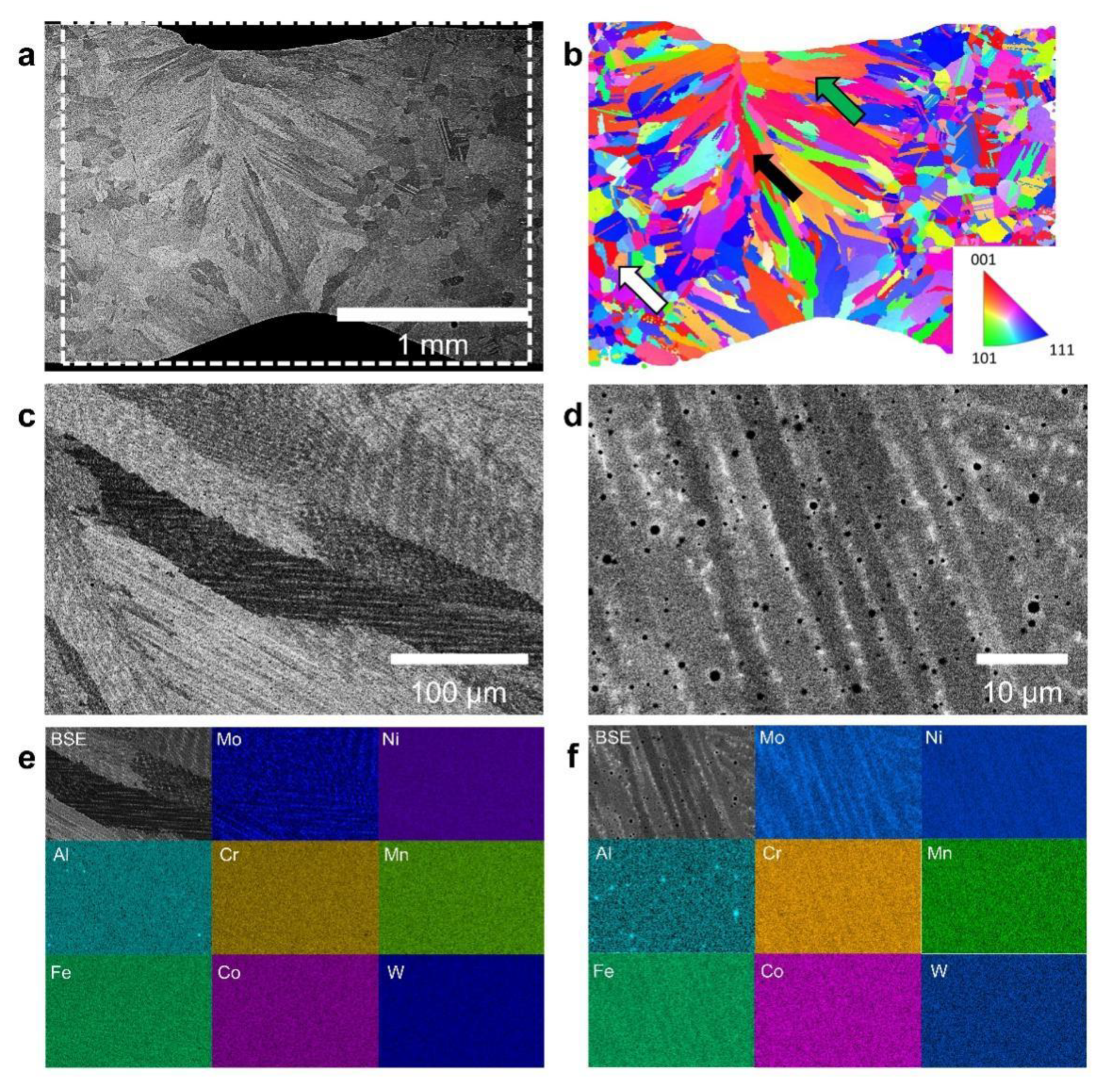
3.3. Microstructures of the Welded Hastelloy X Alloy
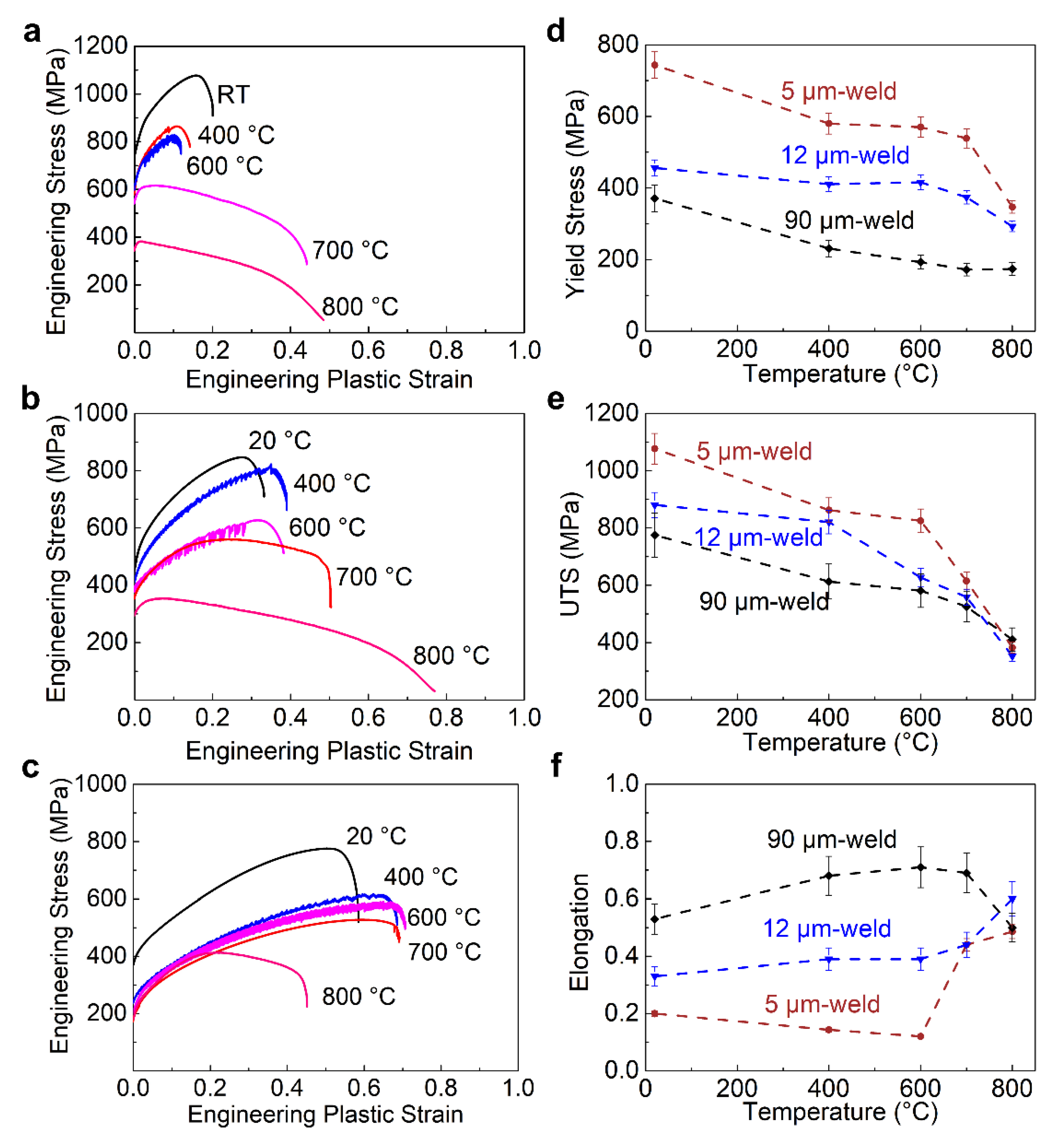
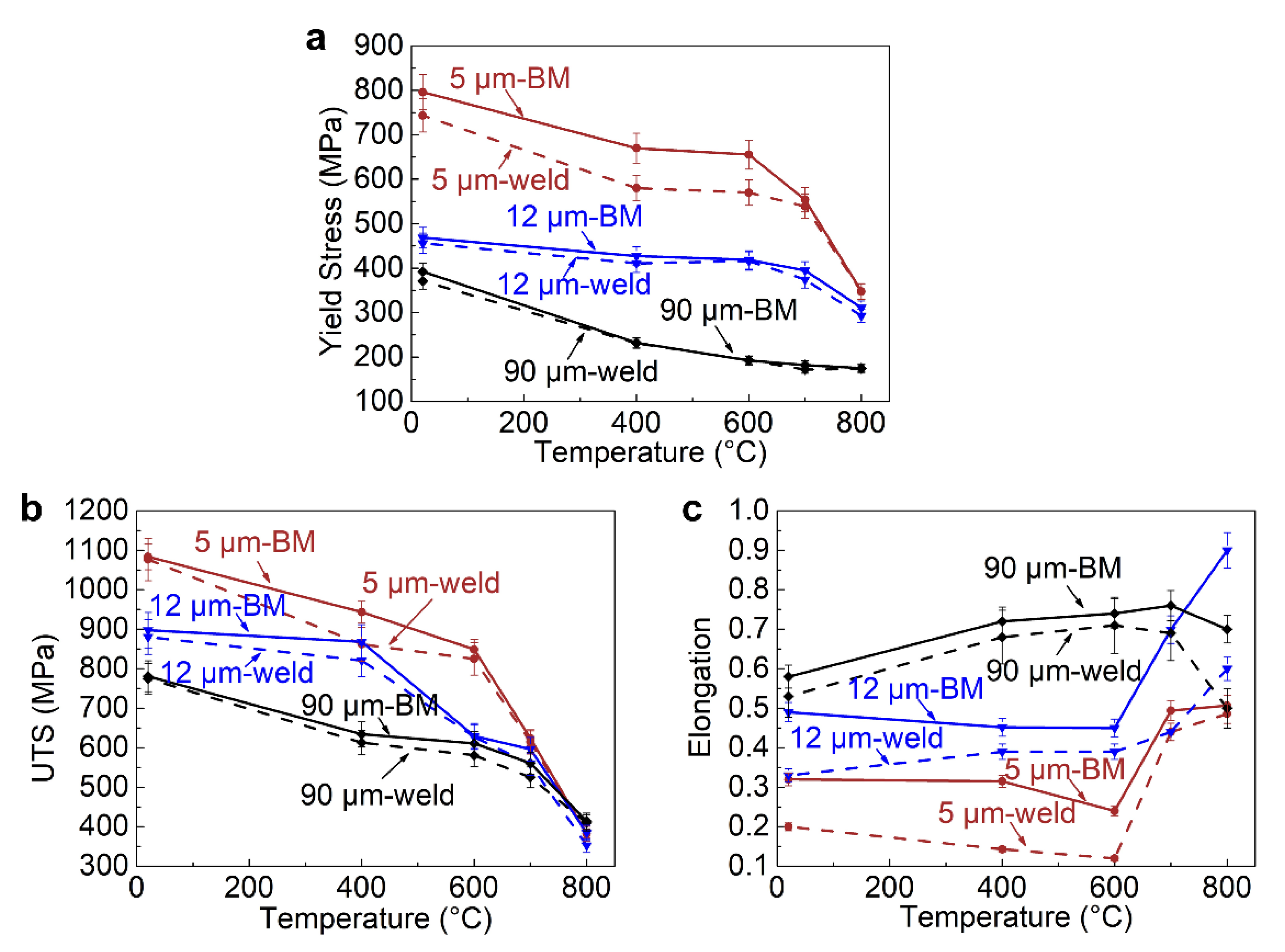
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Welded Hastelloy X Alloys
4. Discussion
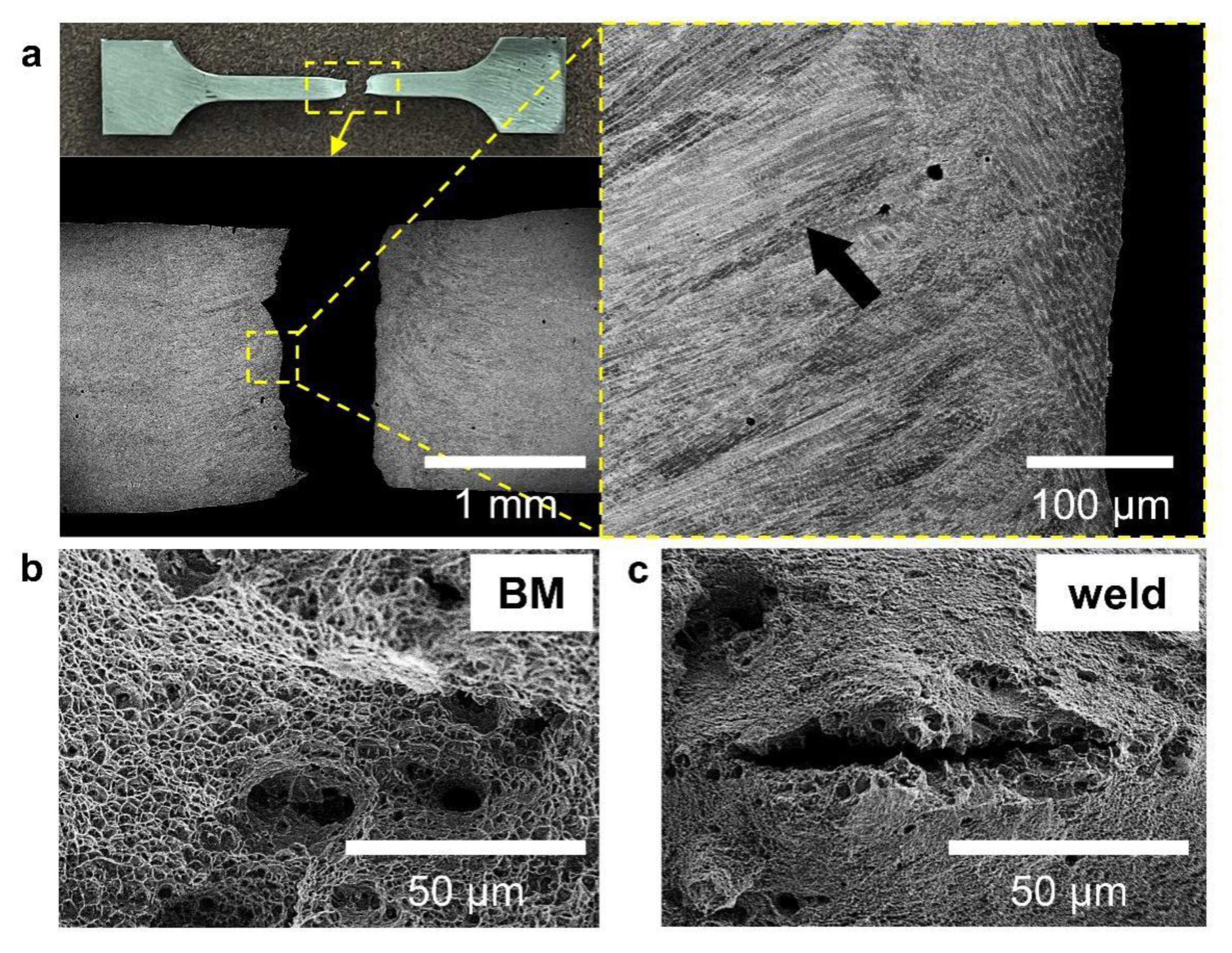
4.1. Fracture Analysis
4.2. Mechanical Behavior
5. Summary and Conclusions
- (1)
- After laser welding, there is no cracking in any welded alloys. The microstructures in the weld consist of columnar grains, which grow in the direction from the fusion line to the centerline.
- (2)
- The sizes of the columnar grains in the weld are almost the same when the grain size of the Hastelloy X base metal increases from ~5 μm to ~90 μm. There is Mo-rich segregation in the fusion zone during welding, but this segregation is not a laves phase.
- (3)
- The fractures of both base metals and welded alloys are ductile. The fractures tend to take place at the weld center due to the larger grain sizes of columnar grains at this area.
- (4)
- Compared to the base metal, the YS, UTS, and EF of the Hastelloy X alloy all reduce after laser welding. When the grain size of the Hastelloy X base metal increases, the increase in grain size for the welded alloy becomes small, and therefore the degree of reductions in YS and UTS decreases; In the meantime, the decreases of EF also become small.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.-C.; Larsen, M.; Ravikumar, V. Phase segregation and time–temperature-transformation diagram of Hastelloy X. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 293, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Long-term ageing characteristics of Hastelloy alloy X. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 2976–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-G.; Yin, S.-N.; Ryu, W.-S.; Chang, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J. Tension and creep design stresses of the “Hastelloy-X” alloy for high-temperature gas cooled reactors. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483–484, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Bei, H.; Wei, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Nano-twin-induced exceptionally superior cryogenic mechanical properties of a Ni-based GH3536 (Hastelloy X) superalloy. Mater. Today Nano 2021, 14, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Kong, W.-W.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Liu, X.; Liu, S. Effects of annealing on microstructures and properties of cold-rolled GH3536 sheet. Mater. Charact. 2021, 180, 111409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.M.; Jennings, R.; Wang, X.; Carter, L.N. Additive manufacturing of Ni-based superalloys: The outstanding issues. MRS Bull. 2016, 41, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.; Feng, Z.; Bei, H. Weldability of a high entropy CrMnFeCoNi alloy. Scr. Mater. 2016, 124, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.A.; Leonard, D.N.; Feng, Z.; Bei, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a welded CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; David, S.A. Effect of adhesive sealant on re-sistance spot welding of 301L stainless steel. J. Manuf. Processes 2020, 51, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Guo, Q.; Li, H. Effect of base metal and welding speed on fusion zone microstructure and HAZ hot-cracking of electron-beam welded Inconel 718. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Manikandan, M.; Subramani, P.; Anbarasan, N.; Jerome, S.; Arivazhagan, N. Effect of Welding Speed on Aspect Ratio of Hastelloy X Weldment by Keyhole Plasma Arc Welding (K-PAW). Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwibedi, S.; Kumar, B.; Bhoi, S.R.; Tripathy, S.R.; Pattanaik, S.; Prasad, S.; Behera, R. To investigate the influence of weld time on joint characteristics of Hastelloy X weldments fabricated by RSW process. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Kolagar, A.M.; Pouranvari, M. Microstructure-performance relationships in gas tungsten arc welded Hastelloy X nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 793, 139861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, X.; Xie, W.; Pei, R.; Yuan, L.; Zheng, M. Influence of grain size on microstructure, mechanical properties and strain hardening behavior of Mg-0.3Ca (wt.%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.N.; Gu, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.J.; Cabral, M.; Ni, S.; An, X.H.; Song, M.; Shen, L.M.; Liao, X.Z. Effects of elemental segre-gation on microstructural evolution and local mechanical properties in a dynamically deformed CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2021, 190, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Lu, F.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Hosseini, S.R.E. A comparative study on fiber laser and CO2 laser welding of Inconel 617. Mater. Des. 2015, 76, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.R.; Khamari, B.K.; Moharana, B.R. Joining of titanium and stainless steel by using different welding processes: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 66, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yan, W. Study on the micro-structure and the nano-indentation responses of laser solid formed epitaxial Ni-based superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 921, 166091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Sahu, J.K.; Payne, D.N.; Nilsson, J. Ytterbium-doped large-core fiber laser with 1.36 kW continuous-wave output power. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 6088–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Sufizadeh, A. Metallurgical investigations of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of AISI 321 and AISI 630 stainless steels. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghjari, S.; AkbariMousavi, S. Experimental investigation on dissimilar pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of AISI 420 stainless steel to kovar alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbaghzadeh, J.; Azizi, M.; Torkamany, M.J. Numerical and experimental investigation of seam welding with a pulsed laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2008, 40, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinoop, A.; Paul, C.; Kumar, J.G.; Anilkumar, V.; Singh, R.; Rao, S.; Bindra, K. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure evolution and elevated temperature mechanical properties of Hastelloy-X processed by laser directed energy deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 868, 159207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakniat, M.; Ghaini, F.M.; Torkamany, M.J. Hot cracking in laser welding of Hastelloy X with pulsed Nd:YAG and con-tinuous wave fiber lasers. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Constant Laser power (W) | 800 |
| Average Laser power (W) | 800 |
| Welding speed (mm/s) | 10 |
| Power density (W/mm2) | 603 |
| Shielding gas type | Ar |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bei, H. The Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Welded Ni-Based Hastelloy X Superalloy. Crystals 2022, 12, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12101336
Liu Y, Ding Q, Wei X, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Bei H. The Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Welded Ni-Based Hastelloy X Superalloy. Crystals. 2022; 12(10):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12101336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuan, Qingqing Ding, Xiao Wei, Yuefei Zhang, Ze Zhang, and Hongbin Bei. 2022. "The Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Welded Ni-Based Hastelloy X Superalloy" Crystals 12, no. 10: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12101336
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ding, Q., Wei, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., & Bei, H. (2022). The Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Welded Ni-Based Hastelloy X Superalloy. Crystals, 12(10), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12101336







