A Review on the Preparation of Catalysts Using Red Mud Resources
Abstract
1. Introduction
| RM Source | Main Chemical Composition (wt%) | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | ||
| Stade, Lower Saxony (Germany) | 35.3 | 15.7 | 6.7 | 14.0 | 11.4 | - | [23] |
| Xi’an, China | 40.91 | 19.55 | 0.59 | 17.99 | 5.35 | 6.24 | [24] |
| Fine waste particles (<0.1 mm) of RM | 42.6 | 22.5 | - | 14 | 7 | 6.6 | [25] |
| LuBei Chemical Industry Co | 37.16 | 25.13 | 0.09 | 33.13 | 3.55 | 0.82 | [26] |
| National Aluminum Company (NALCO), India | 29.47 | 27.74 | - | 24.53 | 18.2 | - | [27] |
| Tan Rai Aluminum Factory, Lam Dong province, Vietnam | 64.2 | 12.6 | - | 3.8 | 9.4 | 4.6 | [28] |
| Shandong, China | 52.59 | 25.47 | 1.24 | 7.57 | 5.91 | 5.38 | [29] |
| Barcarena | 31.45 | 35.47 | 1.81 | 12.68 | 5.84 | - | [30] |
2. Modification Methods for RM
3. Catalytic Applications of RM in Environmental Remediation
3.1. Photocatalysis
3.2. Fenton-like Oxidation
3.3. Ozonation
3.4. Persulfate Activation
3.5. Catalytic Oxidation
3.6. Catalytic Chemical Looping Combustion
3.7. Catalytic Selective Catalytic Reduction
3.8. Long-Term Performance Comparison of RM Modification Strategies
4. Environmental Risks and Mitigation Measures for RM Catalyst Preparation
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Q.L.; Yuan, S.; Han, R.; Li, Y.J.; He, J.H.; Ning, X.B. Desulfurization, desilication, and the separation and recovery of iron from bauxite: A review. Miner. Eng. 2025, 228, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Mohanty, K. A review on advances in sustainable energy production through various catalytic processes by using catalysts derived from waste red mud. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red Mud: Fundamentals and New Avenues for Utilization. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul, M.A.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wen, G.W.; Wang, Y.S. Properties, hazards and valuable metal recovery technologies of red mud: A review. Particuology 2024, 93, 328–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Evaluation of red mud as a polymetallic source-A review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, Q.; Wang, S.F.; Wei, D.T.; Huang, Y.; Ou, X.D. Sustainable utilization of red mud and bauxite tailings: Mechanical and environmental perspectives in cemented backfill. Miner. Eng. 2025, 232, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.M.; Gondu, V.R.; Yamsani, S.K.; Varudu, R.M. Red mud stabilization using alternate industrial waste materials-mechanical and microstructural properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 391, 126511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopic, S.; Kostic, D.; Perusic, M.; Schneider, R.; Souza, I.R.; Mitrasinovic, A.; Friedrich, B. Comparative Analysis of Reduction Techniques Aiming for the Minimization of Contaminated Soil with Red Mud. Minerals 2025, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, A.; Paul, B. Unlocking the potential of red mud: Advanced strategies for economic optimization and sustainable recovery of critical minerals. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.X.; Olivetti, E.A. Strategies for industrial residue valorization through metal recovery, use in construction, or CO2 mineralization. Waste Manag. 2025, 203, 114824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Q.; Liu, C.J.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.J.; Shao, J.W.; Wang, C.X.; Su, T.; Cao, F.B.; Zhang, W.S.; Yang, Q.F.; et al. Preparation of High-Belite Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement from Industrial Solid Waste: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Golabiewska, A.; Rout, P.K. Geopolymer bricks: The next generation of construction materials for sustainable environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Wang, Y.X.; She, A.X.; Li, H.; Lei, H.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.W. Solid waste-derived porous ceramics: Unfired foaming preparation and high-temperature thermal and sound insulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 516, 163964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.D.; Liao, B.; Jiang, J.; Chen, M.X.; Chen, F.G.; Feng, Y.P. Effect of red mud admixture on mechanical properties and failure characteristics of cold joint foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnadish, A.M.; Ramu, M.B.; Kasim, N.; Alawag, A.M.; Baarimah, A.O. A Bibliometric Analysis and Review on Applications of Industrial By-Products in Asphalt Mixtures for Sustainable Road Construction. Buildings 2024, 14, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.D.; Lv, G.Z.; Wang, S.; Li, X.F.; He, X.; Zhang, T.G. Summary of Research Progress on the Separation and Extraction of Iron from Bayer Red Mud. J. Sustain. Metall. 2025, 11, 186–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammulamadaka, H.S.; Rezaee, M.; Pisupati, S.V. Unlocking scandium from red mud: A critical review of challenges, opportunities, and recovery methods. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 236, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Deng, R.J.; Hou, B.L.; Peng, L.Y.; Ren, B.Z.; Kong, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Hursthouse, A. Sustainable Remediation: Advances in Red Mud-Based Synergistic Fabrication Techniques and Mechanistic Insights for Enhanced Heavy Metal(Loid)s Sorption in Wastewater. Processes 2025, 13, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizkardes, B.; Soyer-Uzun, S.; Uzun, A.; Kuhn, S.; Kaya-Özkiper, K.; Kurtoglu-Öztulum, S.F. A Comprehensive Review on Red Mud-Based Catalysts: Modification Methods and Applications in Thermal- and Photocatalysis. Chemcatchem 2025, 17, e202401678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.M. Red mud-based catalysts for the catalytic removal of typical air pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.S.; Zhang, J.; Wei, T.J.; Li, B. Research progress on red mud for carbon-containing air pollution control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, V.; Stopic, S.; Xakalashe, B.; Ma, Y.Q.; Ndlovu, S.; Mwewa, B.; Simate, G.S.; Friedrich, B. Effectiveness of Fly Ash and Red Mud as Strategies for Sustainable Acid Mine Drainage Management. Minerals 2020, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.X.; Chen, J.J.; Zhuang, K.; Gai, D.D.; Yu, Y.; Shen, F.H.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, S. Boosting Agroforestry Waste Valorization: Red Mud Oxygen Carriers with Tailored Oxygen Release for Enhanced Chemical Looping Gasification. Processes 2025, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.A.; Tian, X.; Zhao, H.B.; Liu, K.L.; Dong, Y.C.; Su, Z.; Zheng, C.G. Synergetic effects of cement bonded copper ore and red mud as oxygen carrier during in-situ gasification chemical looping combustion of coal char. Fuel 2021, 303, 121295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.W.; Cheng, F.; Meng, J.G.; Ge, H.J.; Lu, P.; Song, T. Ni-enhanced red mud oxygen carrier for chemical looping steam methane reforming. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 230, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, K.; Rajanikanth, B.S. Red Mud Packed Surface Discharge Reactor for NOx/THC Removal: Exploring Plasma Catalysis of Diesel Exhaust. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2021, 41, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.V.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, P.A.; Pham, T.T.P.; Mai, T.P.; Truong, Q.D.; Ha, H.K.P. Mn-Doped material synthesized from red mud and rice husk ash as a highly active catalyst for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and p-xylene. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20241–20252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.H.; Liang, C.; Chen, H.C. Modified red mud tailored to chromium contaminated soil remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.D.; Do, Q.M.; Le, V.Q. Effect of curing regime on properties of red mud based alkali activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Liu, T.J.; Kang, L.L.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, J.G.; Wang, F.P.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.W.; et al. A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, S.L.; Wang, J.T.; Yang, C.Q.; Sun, P.F.; Zhang, R.; Ling, L.C.; Jin, M.L. The Recycle of Red Mud as NH3-SCR Catalyst by Acid Pretreatment: Insight into the Interaction Between Iron and Titanium Species. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 1738–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Liu, X.; Cui, K.B.; Lyu, J.; Liu, H.Z.; Qiu, J. Hazards and Dealkalization Technology of Red Mud-A Critical Review. Minerals 2025, 15, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Z.; Yuan, W.Y.; Xie, Q.L.; Liang, X.J.; Nie, Y. Catalytic Combustion of Biodiesel Wastewater on Red Mud Catalyst. Materials 2025, 18, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.L.; Yao, H.; Cao, Y.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Huang, J.X. Assessment of one-part geopolymers incorporating optimised high-temperature calcined red mud. Structures 2025, 77, 109177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman; Tripathy, A. CO2 capture using red mud & mechanically-activated red mud and its kinetics under ambient conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.C.; Wei, G.T.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Mo, S.; Yao, Z.Q.; Yang, R.T.; Li, B.Y. Red mud-based CoFe2O4 activated by ball milling as effective peroxymonosulfate activator for the degradation of lomefloxacin hydrochloride: Preparation & activation, application and degradation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150500. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.S.; Cheng, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.; Tan, S.M.; Qiu, F.C. Continuous ultrasonic ozone coupling technology-assisted control of ceramic membrane fouling coupled enhanced multiphase mixing to treat dye wastewater and CFD flow field simulation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 104, 106839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.Q.; Cheng, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, X.H.; Zeng, G.Q.; Xu, H. Highly efficient catalytic ozonation degradation of levofloxacin by facile hydrogenation-modified red mud wastes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Ye, S.X.; Zhang, H.L.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, Z.J. Synergistic effects of zinc oxide and red mud composite material on improving the anti-aging performance of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 491, 142807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Han, L.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.J. Synergistic preparation of zeolite A from coal gasification coarse slag and red mud for the adsorptive removal of organic dyes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 149, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, G.; Selvakumar, S.; Ciotonea, C.; Giraudon, J.M.; Lamonier, J.F.; Batra, V.S. Modified Red Mud Catalyst for Volatile Organic Compounds Oxidation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, P.; Youk, J.H. A comprehensive review of carbon nitride-based catalysts for overall water splitting: Dimensional insights. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2025, 45, e01483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, M.; Birol, B.; Kutlu, O.D.; Kaya, F. Photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticle coating on porous ceramic substrates with varying porosities produced from fly ash and red mud. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 21, 1995–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.; Ma, H.R.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Li, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhou, P.; Chen, G.F. Heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of ciprofloxacin in wastewater with red mud: Characterization and performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegeni, M.; Mehri, M.; Dehdashtian, S. Photocatalytic bauxite and red mud/graphitic carbon nitride composites for Rhodamine B removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1242, 130752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.L.; Ren, H.J.; Huang, X.L.; Li, M.Y.; Tang, Y.B.; Guo, F. Low cost red mud modified graphitic carbon nitride for the removal of organic pollutants in wastewater by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.H. Utilising bauxite residue (red mud) to construct Z-type heterojunction for formaldehyde degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.J.; Ling, Y.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Liu, D.; Wei, K.Z.; Sun, L.W.; Sang, Z.B. Synthesis of visible-light-driven photocatalyst of TiO2 modified waste red mud and its application in tetracycline hydrochloride removal. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 35, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Liu, X.M.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Y. One step calcination of bamboo powder enhances the adsorption and photocatalytic performance of red mud. Mater. Lett. 2021, 304, 130734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ying, W.Y.; Gou, H.L.; Li, M.H.; Huang, K.; Xu, R.Y.; Ding, G.Z.; Wang, P.Y.; Chen, S.P. A Magnetic Photocatalytic Composite Derived from Waste Rice Noodle and Red Mud. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehubijuluw, H.; Subagyo, R.; Kusumawati, Y.; Prasetyoko, D. The impregnation of ZnO onto ZSM-5 derived from red mud for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2022, 32, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Long, Q.; Wei, F.H. Heterogeneous activation of peroxide via acid-modified red mud for the degradation of phenol. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 283, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Long, Q.; Zhang, Y.T.; Yang, H.H.; Shu, J.C. Using red mud to prepare the iron-bearing catalyst for the efficient degradation of phenol in the Fenton-like process. Arabian J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Liu, M.; Zou, H.; Liu, G.S. Efficient removal of Ni-EDTA complexes utilizing 3D Ni-RM electro-fenton system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 369, 133067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.P.; Gu, J.C.; Wei, G.T.; Ba, J.S.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Pei, R.A.; Li, J.Y.; Wei, J.Q. Three-dimensional electro-Fenton degradation of ciprofloxacin catalyzed by CuO doped red mud particle electrodes: Influencing factors, possible degradation pathways and energy consumption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.Q.; Hou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.P.; Lan, H.C.; Liu, H.J.; Qu, J.H. Red mud supported on reduced graphene oxide as photo-Fenton catalysts for organic contaminant degradation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Chu, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Xue, A.; Chen, L. High removal efficiency of antibiotic and dyes by heterogeneous photo-Fenton process using red mud and waste Maotai distillers’ grains as catalyst precursors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 692, 162701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Wei, G.T.; Wang, N.; Gu, J.C.; Zhang, L.Y.; Mu, W.H. Novel S-scheme heterojunction of red mud-based Fe2O3/Co-Al-LDH for the photo-Fenton degradation of gatifloxacin under visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 369, 133160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Q.; Xie, Y.M.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.J. Preparation of Co-Ce@RM catalysts for catalytic ozonation of tetracycline. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.K.; Lu, X.; Sun, W.Q.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.J. Catalytic Ozonation for Effective Degradation of Coal Chemical Biochemical Tail Water by Mn/Ce@RM Catalyst. Water 2022, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Cheng, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Tan, S.M.; Qiu, F.C. Highly efficient catalytic O3 oxidation degradation of levofloxacin by peanut shell pyrolysis-modified red mud wastes. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Lan, M.Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, P.; Ge, C.J.; Liu, W. Immobilized N-C/Co derived from ZIF-67 as PS-AOP catalyst for effective tetracycline matrix elimination: From batch to continuous process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Long, Q.; Shu, J.C.; Wei, F.H.; Zhang, Y.T. Efficient degradation of m-cresol by MnO-doped red mud catalyst activating peroxymonosulfate process: Performance and mechanism. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2024, 28, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, W.Q.; Shah, K.J.; Sun, Y.J. Modi-Red Mud Loaded CoCatalyst Activated Persulfate Degradation of Ofloxacin. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, C.F.; Sun, Y.J.; Shah, K.J. Study on the Degradation Effect of Tetracycline Using a Co-Catalyst Loaded on Red Mud. Catalysts 2024, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.M.; Yang, M.L.; An, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ran, B.B. Efficient rhodamine B dye degradation by red mud-grapefruit peel biochar catalysts activated persulfate in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 119034–119049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; An, Q.; Deng, S.M.; Xu, B.H.; Li, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhao, B.; Ye, Z.H. Efficient activation of peroxydisulfate by modified red mud biochar derived from waste corn straw for levofloxacin degradation: Efficiencies and mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.M.; Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Liu, B.F.; Xie, G.J.; Xing, D.F. A green strategy from waste red mud to Fe0-based biochar for sulfadiazine treatment by peroxydisulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.R.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.H.; Feng, G.Q.; Pan, Z.L.; Xu, R.S.; Wang, P.C.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, G.L.; Fan, X.F.; et al. Confining manganese-based peroxymonosulfate activation in carbon nanotube membrane for phenol degradation: Combined effect of oxygen vacancy defects and nanoconfinement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, H.L.; Du, Y.S.; Zhou, X.Q.; Liao, Z.W.; Wang, H.B.; Chen, Z.Q. Red mud modified sludge biochar for the activation of peroxymonosulfate: Singlet oxygen dominated mechanism and toxicity prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.G.; Nah, J.W.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Jung, S.C.; Kim, S.C. Recycling of red mud as a catalyst for complete oxidation of benzene. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 60, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Tao, Q.Y.; Fang, H.P.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, J.; Bin, F.; Kang, R.N. Modification of red mud catalyst using oxalic acid-assisted UV treatment for toluene removal. Catal. Today 2024, 433, 114675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Lee, J.; Kannapu, H.P.R.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.; Ha, J.M.; Jung, S.C.; Park, Y.K. Acid-treated waste red mud as an efficient catalyst for catalytic fast copyrolysis of lignin and polyproylene and ozone-catalytic conversion of toluene. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.P.; Liang, W.J.; Ma, L.; Ma, C. Properties and characterization of red mud modified by hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acid for the catalytic oxidation of toluene. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xuan, Y.; Liang, Y.J.; Zhu, X.; Yun, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y. The strong Fe-Mn interaction over red mud accelerating the activation of key oxygen species for toluene oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.P.; Liang, W.J.; Ma, C.; Tao, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Effect of interaction between Pd and Fe in modified red mud on catalytic decomposition of toluene. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 77535–77550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Q.; He, H.Z.; Tang, Y.E.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhou, H.L.; Yu, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Dai, B.Q. A Review on Fe2O3-Based Catalysts for Toluene Oxidation: Catalysts Design and Optimization with the Formation of Abundant Oxygen Vacancies. Chemcatchem 2024, 16, e202400396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Ma, C.; Zhu, Y.X.; Liu, J. Performance and mechanism of modified red mud for the toluene adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Liang, H.M.; Aslam, M.; Wei, G.Q.; Qin, Y.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Du, Y.J.; Guo, Q.Z.; Wei, Y.X.; He, C. Research progress of oxygen carriers for the chemical looping process of different feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 190, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.X.; Li, K.Z.; Gu, Z.H.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y.G.; Cheng, X.M.; Wang, H. Synergy effects of combined red muds as oxygen carriers for chemical looping combustion of methane. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Zhang, C.; Song, A.G.; Xu, D.; Ma, Z. Synergistic effect of mixed red mud and pyrite cinder as oxygen carrier in CH4 chemical looping combustion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 99, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gu, Z.H.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y.G.; Long, Y.H.; Yang, K.; He, F.; Wang, H.; Li, K.Z. Synergy of red mud oxygen carrier with MgO and NiO for enhanced chemical-looping combustion. Energy 2020, 197, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.A.; Liu, K.L.; Zhao, H.B. Reduction Kinetics of Low-Cost Cu/Fe-Based Oxygen Carriers in Chemical Looping Mode. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 16716–16728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.X.; Li, K.Z.; Zhang, G.F.; Gu, Z.H.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y.G.; Wang, H. Enhanced performance of red mud-based oxygen carriers by CuO for chemical looping combustion of methane. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, C.Q.; Qing, S.; Li, K.Z. Enhanced performance of copper ore oxygen carrier by red mud modification for chemical looping combustion. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Cheng, F.; Ma, S.W.; Song, T. Synergetic promotional roles of CeO2 and Ni on red mud oxygen carrier for chemical looping steam methane reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 106, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.Y.; Cheng, H.D.; Xie, Y.M.; Liu, D.K.; Sun, H.; Chen, H.J. Recent advances in sulfur-resistant DeNOx catalysts for stationary source emissions: A state-of-the-art review. Catal. Today 2025, 459, 115434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ren, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.C.; Li, X.D.; Wang, M.M.; Yang, J. Catalysts prepared from solid wastes for efficient removal of NOx in NH3-SCR process: A review. Catal. Today 2023, 420, 114175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Lan, J.M.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, Z.M. Enhanced alkali resistance of sulfated CeO2 catalyst for the reduction of NOx from biomass fired flue gas. Catal. Commun. 2021, 149, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.K.; Gong, Z.Q.; Lu, C.M.; Niu, S.L.; Ding, K.; Xu, L.T.; Zhang, K. Preparation and Performance of Modified Red Mud-Based Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Catalysts 2018, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xuan, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, C.; Niu, S.L.; Zhao, G.J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.H.; Lu, C.M.; Crittenden, J.C. Precise regulation of acid pretreatment for red mud SCR catalyst: Targeting on optimizing the acidity and reducibility. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, Z.Q.; Shi, Q.L.; Gao, C.A.; Lu, C.M.; Crittenden, J. Acid-pretreated red mud for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Insights into inhibition mechanism of binders. Catal. Today 2021, 376, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Abubakar, A.; Li, C.M.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Gao, S.Q.; Liu, Z.E.; Yu, J. Development of Red Mud Coated Catalytic Filter for NOx Removal in the High Temperature Range of 300–450 °C. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 702–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Li, W.H.; Liu, Z.M. Significantly Enhanced Catalytic Performance of Fe2(SO4)3/CeO2 Catalyst for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 15472–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Sun, Z.G.; Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.Z.; Sun, C.Z.; Gao, F.; Tang, C.J.; Dong, L. Getting insight into the effect of CuO on red mud for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.P.; Hu, L.M.; Wu, Y.J.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, B.Q.; Han, L.; Wu, B. Acid-washing-alkali-fusion pretreated red mud for fabricating Cu-based BEA zeolite for NH3-SCR. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Ahn, W.S. Co- and Mn-Coimpregnated ZSM-5 Prepared from Recycled Industrial Solid Wastes for Low-Temperature NH3-SCR. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22857–22865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yang, G.P.; Wang, D.; Gong, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.H.; Lu, C.M.; Crittenden, J. Modified red mud catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides: Impact mechanism of cerium precursors on surface physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Shen, Z.X.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhou, G.L.; Peng, Q.; Fan, H.; Liu, J. Resource utilization of red mud with biochar to prepare high-efficiency denitration catalysts. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 502, 145386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q. Potential of metallurgical iron-containing solid waste-based catalysts as activator of persulfate for organic pollutants degradation. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Geng, C.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.F.; Liu, J.G.; Chen, C. The large-scale sustainable utilization status of bauxite residue (red mud): Challenges and perspectives for China. Environ. Rev. 2025, 33, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovicevic-Klug, M.; Souza, I.R.; Springer, H.; Adam, C.; Raabe, D. Green steel from red mud through climate-neutral hydrogen plasma reduction. Nature 2024, 625, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova-Sedlackova, A.; Calderón, A.; Fernandez, A.I.; Chimenos, J.M.; Berlanga, C.; Yücel, O.; Barreneche, C.; Rodriguez, R. Mapping the research landscape of bauxite by-products (red mud): An evolutionary perspective from 1995 to 2022. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Pang, J.Y.; Berggren, S.; Tanvar, H.; Mishra, B.; Arlos, M.J. Treating Waste with Waste: Activated Bauxite Residue (ABR) as a Potential Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 45251–45262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.E.; Yue, H.Z.; Ma, L.J.; Li, Z.C.; Bai, R. Study on hydration mechanism and environmental safety of thermal activated red mud-based cementitious materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 55905–55921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y. Synergistic utilization, critical mechanisms, and environmental suitability of bauxite residue (red mud) based multi-solid wastes cementitious materials and special concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 361, 121255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.H.; Liu, J.J.; Yi, L.Y.; Luo, J.; Jiang, T. Bauxite residue (red mud) treatment: Current situation and promising solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
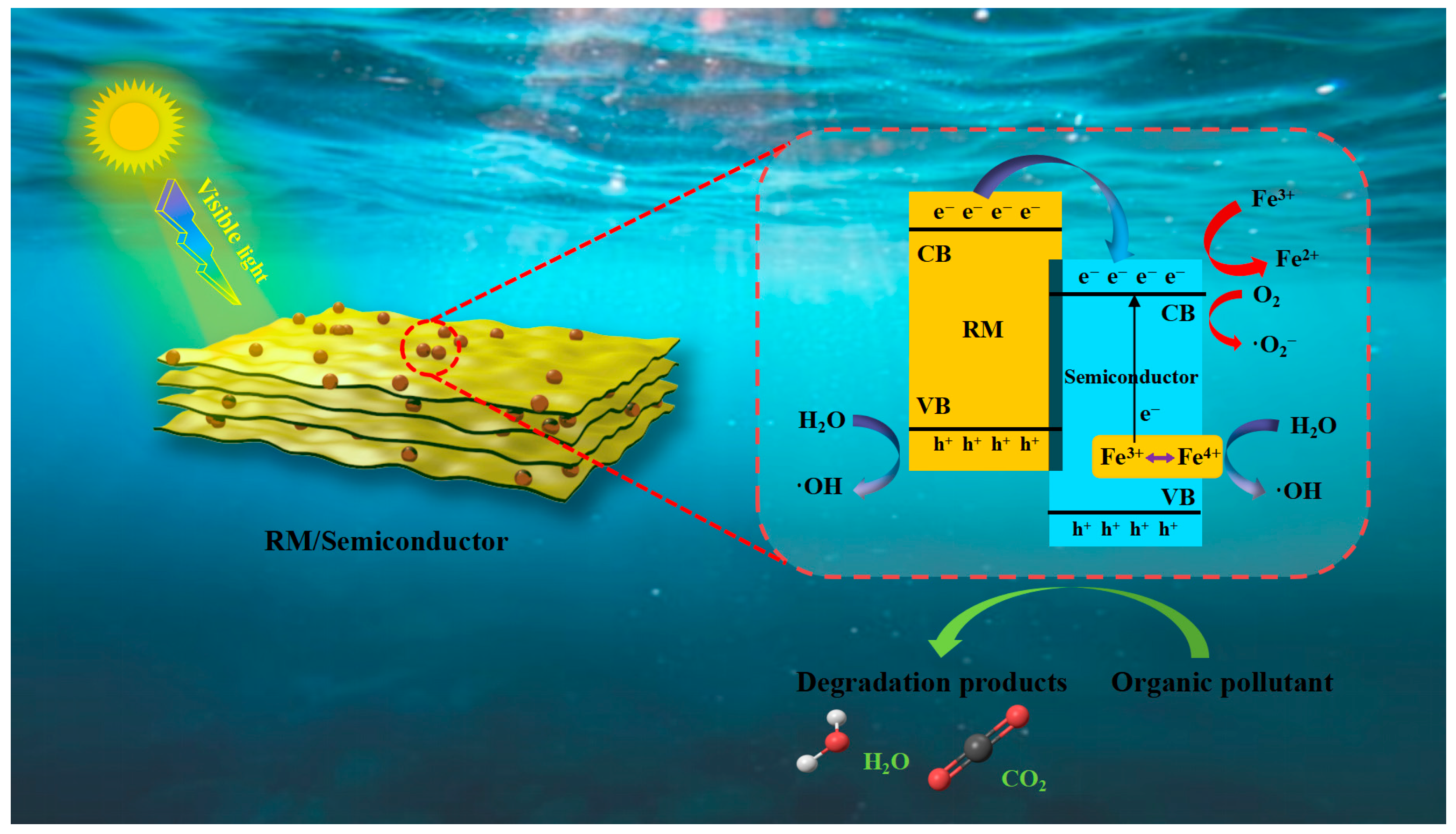

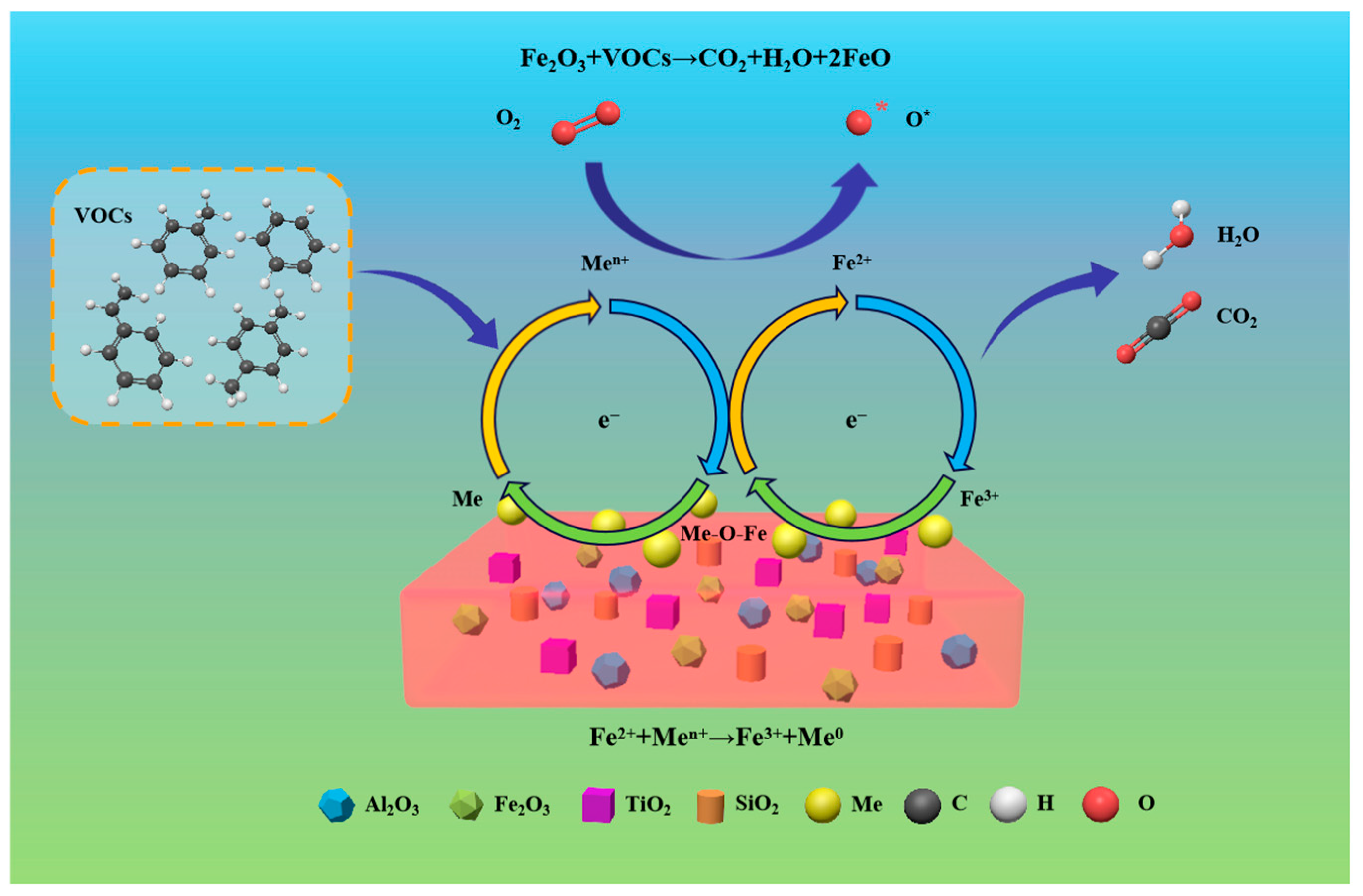
| Catalyst | Fenton Type | Pollutant and Concentration | Reaction Conditions | Removal Rate | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM4 | Traditional Fenton | Phenol; 100 mg/L | 0.02 M H2O2; 0.05 g RM4; 120 min | 96.8% | [53] |
| FRM/2%A | Traditional Fenton | Phenol; 100 mg/L | 1 g/L FRM/2%A; 5 mM H2O2; initial pH = 3–6 | 99.3% | [54] |
| Ni-RM | Electro-Fenton | Ni-EDTA; 0.1 mM | pH range: 3.3–11; current density: 10–30 mA cm−2 | 97.8% | [55] |
| CuO/URM | Electro-Fenton | CIP; 0.1 g/L | 4 g/3 LCuO/URM; pH = 7; Applied voltage: 10 V; aeration intensity: 5 L/min | 80.66% | [56] |
| RM-H/rGO | Photo-Fenton | RhB; 10–50mg/L | pH = 3.0; 10 mM H2O2; 1g/L RM-H/rGO; 20 min | 99.8% | [57] |
| RMBC | Photo-Fenton | TC, RhB, MB, AO7; - | Pyrolysis temperature of 900 °C; under visible light conditions | 91.6%, 94.5%, 77.2%, 94.2% | [58] |
| Fe/Co-Al-LDH/RM | Photo-Fenton | GAT; 20 mg/L | 120 min; 0.03 g/L Fe/Co-Al-LDH/RM; 90 mmol/L H2O2; pH = 6.5 | 94.0% | [59] |
| Catalyst | Reaction Time | Pollutant and Concentration | Reaction Conditions | Removal Rate | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnO-RM | 90 min | M-Cresol; N-50 mg/L | 2 g/LMnO-RM; 10 mM PMS; Initial pH = 3~8 | 100% | [64] |
| Co-RM | - | OFL;15 mg/L | 0.4 g/L Co-RM; 4 g/L PDS; pH = 3.0, 40 °C | 80.06% | [65] |
| Co-RM | - | TC; - | pH = 7; 0.3 g/L Co-RM; 3 g/L PDS | 89.5% | [66] |
| RMBC | - | RhB; 20 mg/L | pH = 4.6 | 89.98% | [67] |
| MRBC | 30 min | LFX; 10 mg/L | 8 mM PDS; 1.6 g/L MRBC | 88.59% | [68] |
| RM/IS | 20 min | SDZ; - | - | 99.7% | [69] |
| RSDBC | 50 min | SMX; 20 mg/L | 1.0 g/L RSDBC; pH = 2.65~10.86 | 82.5% | [71] |
| Catalysts | Calcination Environment | Dosage | Reaction Conditions | CH4 Concentration and Flow Rate | CH4 Conversion Rate | Catalytic Stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two RMs were mixed at a mass ratio of 7:3. | 900 °C; 2 h | 5 g | T = 900 °C | 5%; 100 mL/min | Average 81%; Maximum 90% | Ten cycles; 90% CO2 selectivity. | [81] |
| RM containing 15 wt% NiO and 10wt % MgO. | 900 °C; 2 h | 5 g | T = 900 °C | 5%; 200 mL/min | 65% | Twenty cycles; CH4 conversion rate:75–40%; 60% CO2 selectivity. | [83] |
| RM with 20 wt% copper oxide. | 900 °C; 2 h | 2 g | T = 800 °C | 5%; 200 mL/min | 90% | Twenty cycles; 100% CO2 selectivity; over 60% conversion rate. | [85] |
| Copper ore and RM were mixed at a mass ratio of 7:3. | 900 °C; 6 h | 2 g | T = 900 °C | 5%; 200 mL/min | 86% | Twenty cycles; CH4 conversion rate exceeds 75%, CO2 selectivity exceeds 90%. | [86] |
| RM and pyrite were mixed at a mass ratio of 1:1. | 900 °C; 2 h | 2 g | T = 900 °C | 5%; 300 mL/min | 45.82 | Twenty cycles; conversion rate: approximately 44%. | [82] |
| Catalyst | Preparation Condition | Catalytic Property and Condition | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution for Leaching | Calcination Condition | Dopants | NOx Conversion | Temperature Range | GHSV (h−1) | ||
| RM-based | HCl | 550 °C | sesbania powder (binder) | >90% | 325~450 °C | 30,000 | [93] |
| RM-based | H2SO4 | 500 °C, 5 h | - | >90% | 300~450 °C | 60,000 | [94] |
| RM-based | HNO3 | - | - | >90% | 275~475 °C | - | [92] |
| Ce0.3/RM | HNO3 | 500 °C | Ce0.3 | >80% | 275~400 °C | 30,000 | [91] |
| Ce/RM | HCl | 500 °C, 5 h | Ce | 100% | 200~400 °C | 30,000 | [99] |
| CuO/RM | HNO3 | 500 °C, 6 h | 7% CuO | >90% | 300~375 °C | 12,000 | [96] |
| Cu-BA0.5-H | NH4Cl | 600 °C, 3 h | Cu | 99% | 200~300 °C | - | [97] |
| Co-Mn/ ZSM-5 | - | 550 °C, 3 h | 5%wt Mo and 10%wt Mn | 98.8% | 150 °C | 40,000 | [98] |
| BC/RM | HNO3 | 300 °C, 2h | BC | >90% | 225~400 °C | 23,000 | [100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shah, K.J.; Sun, Y. A Review on the Preparation of Catalysts Using Red Mud Resources. Catalysts 2025, 15, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090809
Zhuang Y, Wang X, Shah KJ, Sun Y. A Review on the Preparation of Catalysts Using Red Mud Resources. Catalysts. 2025; 15(9):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090809
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Yan, Xiaotian Wang, Kinjal J. Shah, and Yongjun Sun. 2025. "A Review on the Preparation of Catalysts Using Red Mud Resources" Catalysts 15, no. 9: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090809
APA StyleZhuang, Y., Wang, X., Shah, K. J., & Sun, Y. (2025). A Review on the Preparation of Catalysts Using Red Mud Resources. Catalysts, 15(9), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090809








