Synthesis Gas Production from Co-Pyrolysis of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film and Kinetic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
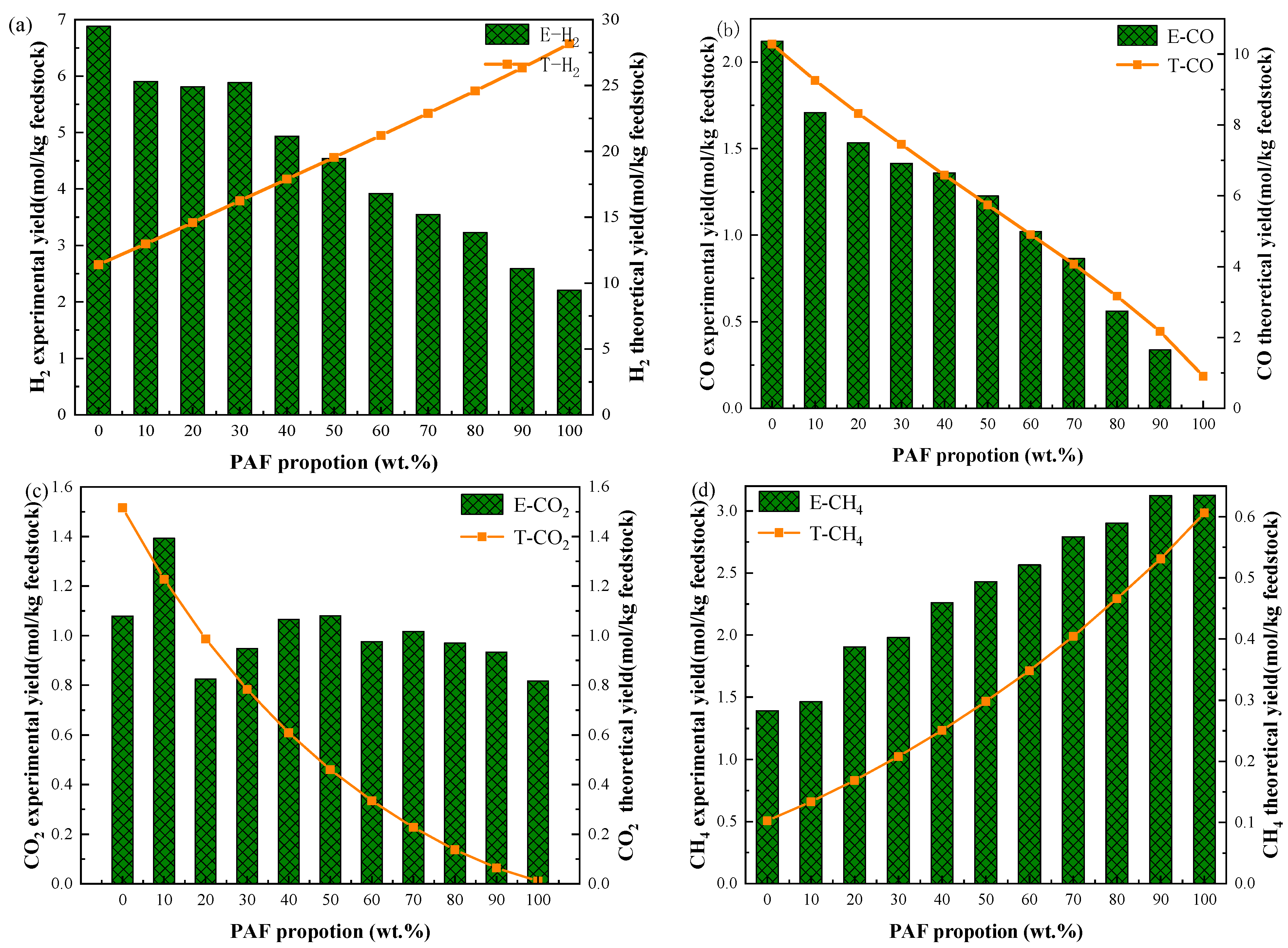
2.1. Product Distribution
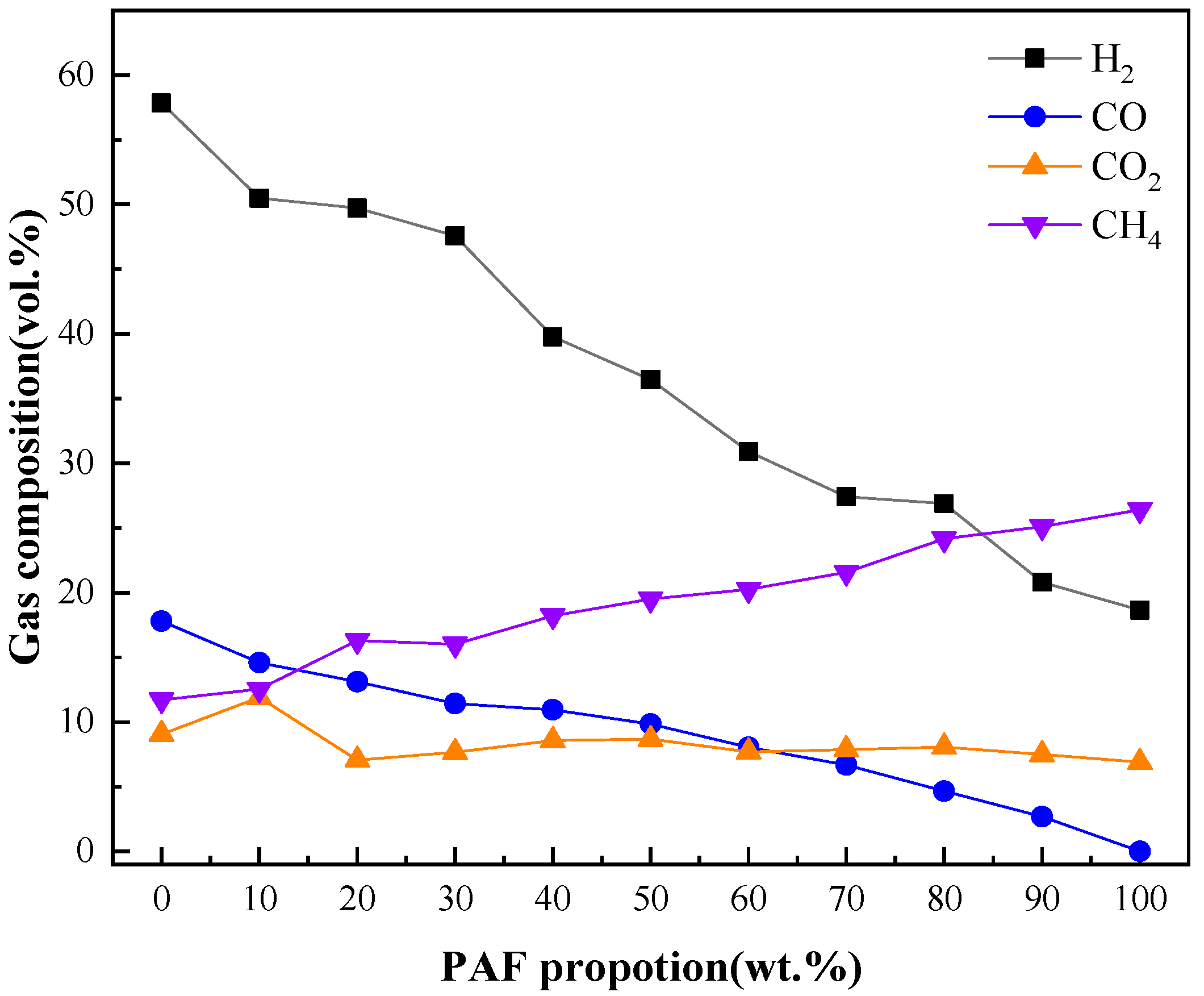
2.2. Syngas Production and Composition
2.2.1. Effect of Mixture Ratio on Syngas Production and Composition
2.2.2. Effect of Element Mass Ratio on Syngas Yield
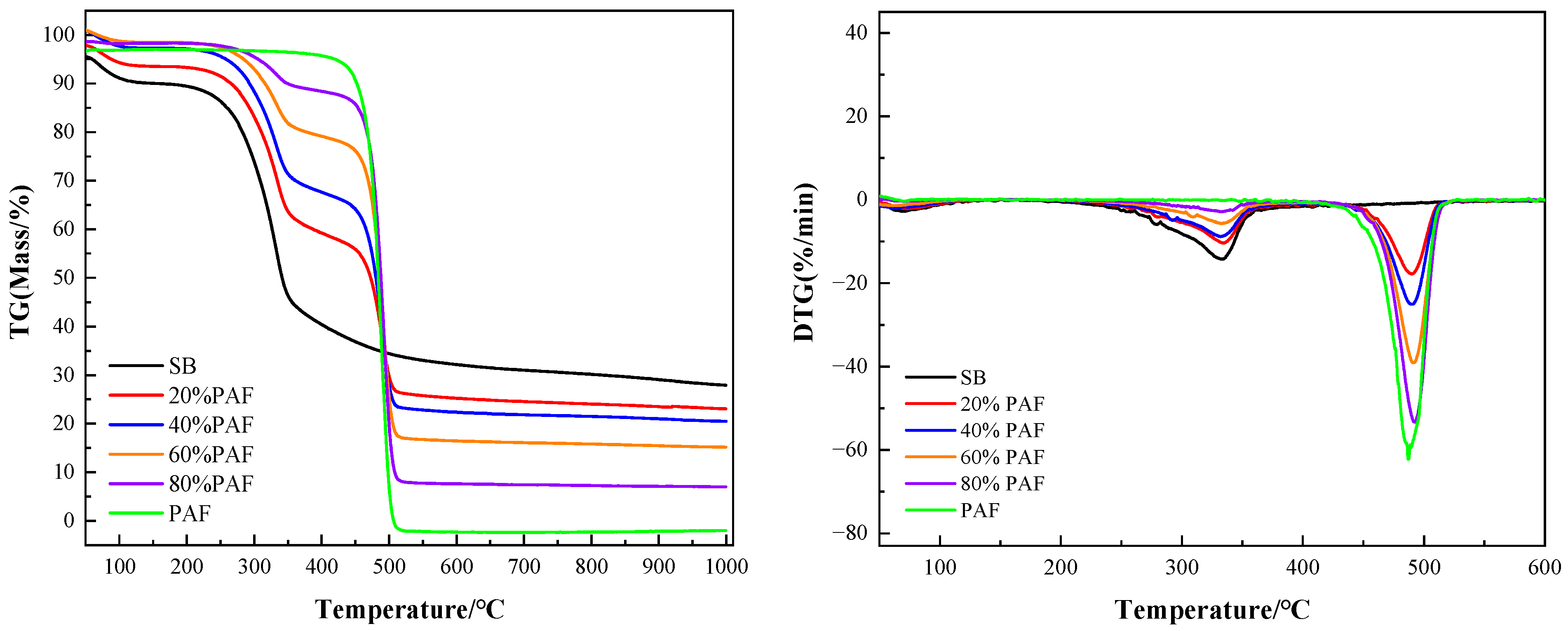
2.3. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film
2.3.1. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film with Different Mixing Ratios
2.3.2. Effect of Heating Rate on Pyrolysis Characteristics of Mixture Containing 40% Polyethylene Agricultural Film
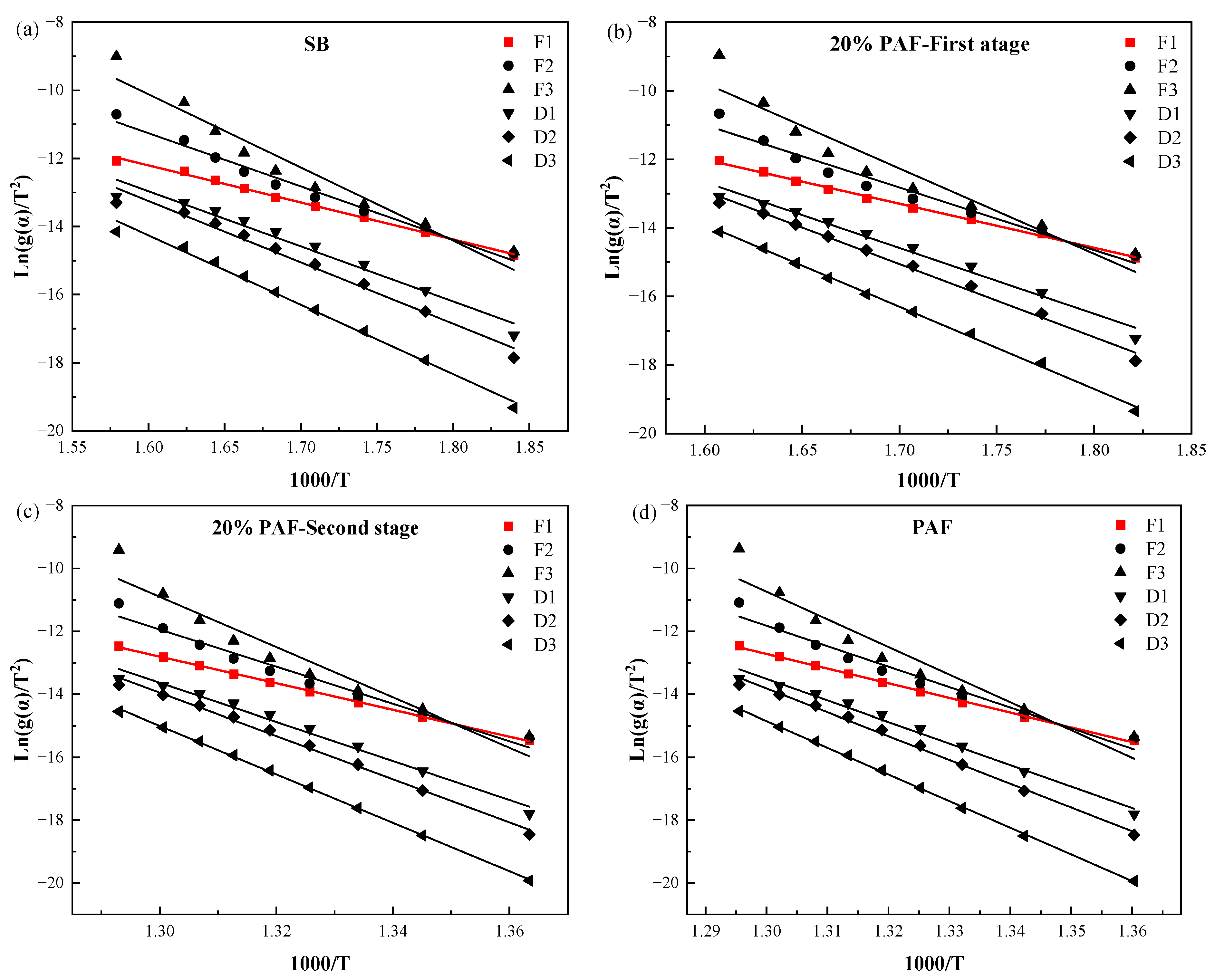
2.3.3. Pyrolysis Kinetics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
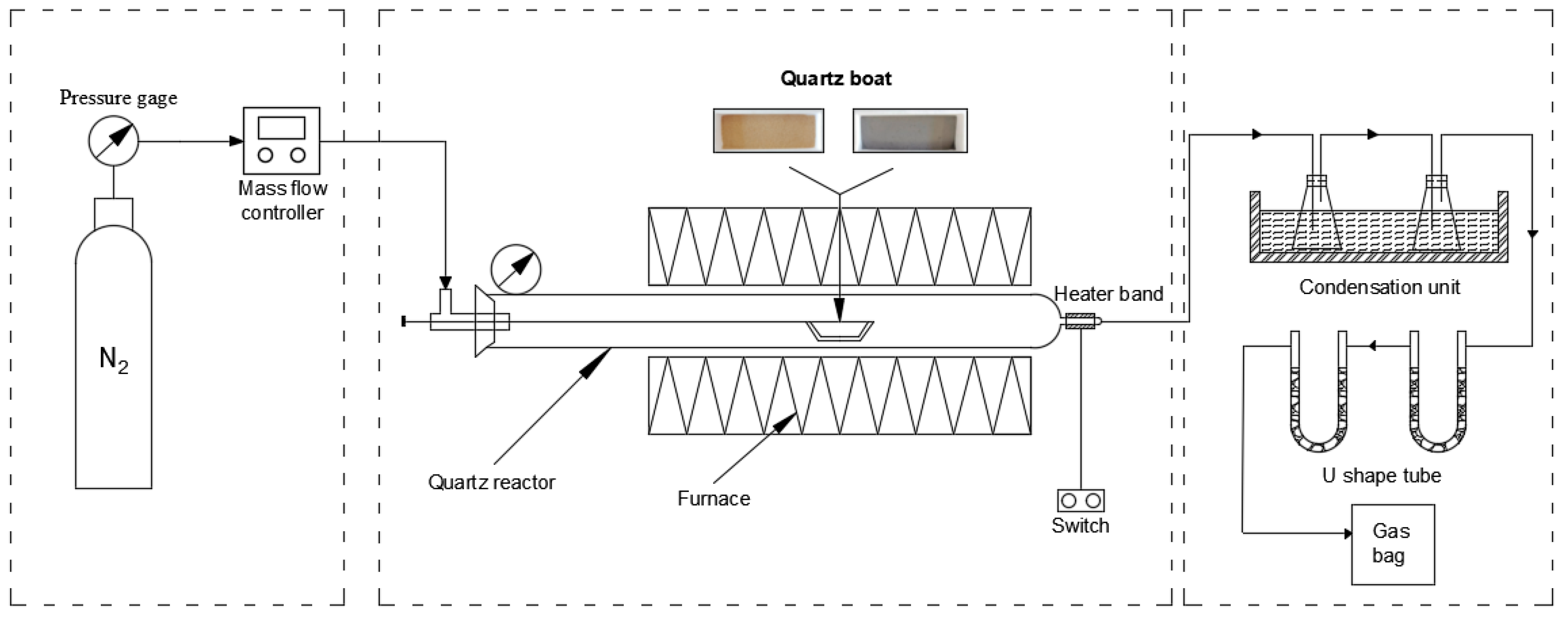
3.2. Experimental Procedure
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Kinetics Methods
3.3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3.2. Kinetics Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Dai, G.; Yang, H.; Luo, Z. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 62, 33–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Abdul Wahid, M.; Jamil, M.M.; Azli, A.A.M.; Misbah, M.F. A review on biomass-based hydrogen production for renewable energy supply. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vooradi, R.; Bertran, M.-O.; Frauzem, R.; Anne, S.B.; Gani, R. Sustainable chemical processing and energy-carbon dioxide management: Review of challenges and opportunities. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 131, 440–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.B.; Elsayed, I.; Eseyin, A. Production high yields of aromatic hydrocarbons through catalytic fast pyrolysis of torrefied wood and polystyrene. Fuel 2016, 174, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lei, T.; Chang, X.; Shi, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Zhu, J.; Yang, S. Optimization of a biomass briquette fuel system based on grey relational analysis and analytic hierarchy process: A study using cornstalks in China. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Liang, S.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Development of biochar-based nanocatalysts for tar cracking/reforming during biomass pyrolysis and gasification. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Nie, R.; Yu, Z. Syngas production from biomass gasification in China: A clean strategy for sustainable development. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.; Kwong, P.; Ahmad, E.; Nigam, K.D.P. Clean syngas from small commercial biomass gasifiers; a review of gasifier development, recent advances and performance evaluation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 21087–21111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.B.; Gaikar, V.G. Investigating production of hydrocarbon rich bio-oil from grassy biomass using vacuum pyrolysis coupled with online deoxygenation of volatile products over metallic iron. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhao, P.R.; Ahmad, E.; Pant, K.K.; Nigam, K.D.P. Environmentally friendly approach for the recovery of metallic fraction from waste printed circuit boards using pyrolysis and ultrasonication. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V. Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 38, 68–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Carlson, T.R.; Xiao, R.; Huber, G.W. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of wood and alcohol mixtures in a fluidized bed reactor. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y. The synergistic mechanism between coke depositions and gas for H2 production from co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic wastes via char supported catalyst. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, J.; Pathak, T.S.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, A.C. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of paper biomass and plastic mixtures (HDPE (high density polyethylene), PP (polypropylene) and PET (polyethylene terephthalate)) and product analysis. Energy 2016, 103, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Co-pyrolysis of xylan and high-density polyethylene: Product distribution and synergistic effects. Fuel 2020, 267, 116896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.; Erkiaga, A.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Effect of polyethylene co-feeding in the steam gasification of biomass in a conical spouted bed reactor. Fuel 2015, 153, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnisa, F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Ramalingam, S.; Azemi, M.N.B.M.; Sahu, J.N. Co-pyrolysis of palm shell and polystyrene waste mixtures to synthesis liquid fuel. Fuel 2013, 108, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, C.J.; Watkinson, A.P.; Chen, H.P.; Kim, J.R. Biomass gasification in a circulating fluidized bed. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar Sharuddin, S.D.; Abnisa, F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Aroua, M.K. A review on pyrolysis of plastic wastes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Bian, C.; Wang, G.; Bai, B.; Xie, Y.; Jin, H. Co-gasification of plastic wastes and soda lignin in supercritical water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, S.; Sun, L.; Xu, B.; He, L.; Xiang, J. Effects of inherent alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on biomass pyrolysis at different temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Mikulčić, H.; Bešenić, T.; Deng, S.; Vujanović, M.; Tan, H.; Kumfer, B.M. Synergistic effects during co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic: Gas, tar, soot, char products and thermogravimetric study. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hua, D.; Chen, Z.; Feng, W.; Yang, M.; Xie, Q. Co-pyrolysis behaviors and kinetics of plastics–biomass blends through thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yang, J.; Xing, X.; Weihrich, S.; Fan, F.; Zhang, X. Isoconversional kinetics and characteristics of combustion on hydrothermally treated biomass. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Purakayastha, S.; Ghosh, B. Thermal characterization of mustard straw and stalk in nitrogen at different heating rates. Fuel 2007, 86, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | Zone1 | Zone2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti1 | Tp1 | Tf1 | −Rp1 | Ti2 | Tp2 | Tf2 | −Rp2 | |
| SB | 232.1 | 328.8 | 410.5 | 15.4 | - | - | - | - |
| 20%PAF–80%SB | 247.8 | 335.7 | 373.7 | 11.5 | 434.7 | 490.5 | 511.5 | 18.7 |
| 40%PAF–60%SB | 254.8 | 332.9 | 372.5 | 9.7 | 433.0 | 491.9 | 512.8 | 26.2 |
| 60%PAF–40%SB | 262.0 | 333.4 | 360.5 | 8.5 | 433.1 | 489.9 | 514.9 | 41.1 |
| 80%PAF–20%SB | 282.0 | 344.5 | 353.2 | 4.6 | 435.2 | 492.0 | 518.3 | 56.6 |
| PAF | - | - | - | - | 425.9 | 483.9 | 512.0 | 80.4 |
| Samples | Zone1 | Zone2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti1 | Tp1 | Tf1 | −Rp1 | Ti2 | Tp2 | Tf2 | −Rp2 | |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-10 °C | 255 | 320 | 350 | 4.2 | 430 | 475 | 500 | 11.7 |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-20 °C | 255 | 333 | 373 | 9.7 | 433 | 492 | 513 | 26.2 |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-30 °C | 235 | 340 | 410 | 11.8 | 415 | 491.9 | 495 | 35.8 |
| Samples | Zone1 | Zone2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 KJ/mol | A1 min−1 | R12 | E2 KJ/mol | A2 min−1 | R22 | |
| SB | 91.45 | 1.08 × 108 | 0.9982 | - | - | - |
| 20%PAF-80%SB | 107.07 | 4.85 × 109 | 0.9967 | 351.55 | 6.28 × 1026 | 0.9991 |
| 40%PAF-60%SB | 113.89 | 2.48 × 1010 | 0.9979 | 360.80 | 4.0 × 1027 | 0.9994 |
| 60%PAF-40%SB | 123.55 | 2.46 × 1011 | 0.9978 | 400.03 | 4.29 × 1030 | 0.9996 |
| 80%PAF-20%SB | 162.19 | 2.11 × 1015 | 0.9948 | 424.7 | 3.52 × 1032 | 0.9998 |
| PAF | - | - | - | 387.93 | 6.19 × 1029 | 0.9979 |
| Samples | Zone1 | Zone2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 KJ/mol | A1 min−1 | R12 | E2 KJ/mol | A2 min−1 | R22 | |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-10 °C | 121.8 | 1.48 × 1011 | 0.9983 | 373.61 | 7.23 × 1025 | 0.9998 |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-20 °C | 113.89 | 2.48 × 1010 | 0.9979 | 360.80 | 4.0 × 1027 | 0.9994 |
| 40%PAF-60%SB-30 °C | 91.97 | 1.42 × 108 | 0.9983 | 335.49 | 2.91 × 1024 | 0.9969 |
| SB | PAF | |
|---|---|---|
| Ultimate analysis (mass%, dry ash free) | ||
| Carbon | 37.97 | 83.66 |
| Hydrogen | 5.44 | 12.71 |
| Oxygen | 39.86 | 2.59 |
| Nitrogen | 1.30 | - |
| Sulfur | 0.26 | - |
| Proximate analysis (mass%, dry basis) | ||
| Water content | 6.95 | - |
| Ash | 63.05 | - |
| Volatile | 12.55 | - |
| Fixed carbon | 17.45 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Wang, L. Synthesis Gas Production from Co-Pyrolysis of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film and Kinetic Analysis. Catalysts 2025, 15, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060517
Zhao Z, Wang L. Synthesis Gas Production from Co-Pyrolysis of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film and Kinetic Analysis. Catalysts. 2025; 15(6):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060517
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhen, and Lei Wang. 2025. "Synthesis Gas Production from Co-Pyrolysis of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film and Kinetic Analysis" Catalysts 15, no. 6: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060517
APA StyleZhao, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Synthesis Gas Production from Co-Pyrolysis of Straw Biomass and Polyethylene Agricultural Film and Kinetic Analysis. Catalysts, 15(6), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060517







