Abstract
The emission limit of non-volatile particles (i.e., particles that do not evaporate at 350 °C) with size >23 nm, in combination with the real driving emissions (RDE) regulation in 2017, resulted in the introduction of gasoline particulate filters (GPFs) in all light-duty vehicles with gasoline direct injection engines in Europe. Even though there are studies that have examined the particulate emissions at or beyond the current RDE boundary conditions, there is a lack of studies combining most or all worst cases (i.e., conditions that increase the emissions). In this study, we challenged a fresh (i.e., no accumulation of soot or ash) “advanced” prototype GPF at different temperatures (down to −9 °C), aggressive drive cycles and hard accelerations (beyond the RDE limits), high payload (up to 90%), use of all auxiliaries (air conditioning, heating of the seats and the rear window), and cold starts independently or simultaneously. Under hot engine conditions, the increase of the particulate emissions due to higher payload and lower ambient temperature was 30–90%. The cold start at low ambient temperature, however, had an effect on the emissions of up to a factor of 20 for particles >23 nm or 300 when considering particles <23 nm. We proposed that the reason for these high emissions was the incomplete combustion and the low efficiency of the three-way oxidation catalyst. This resulted in a high concentration of species that were in the gaseous phase at the high temperature of the close-coupled GPF and thus could not be filtered by the GPF. As the exhaust gas cooled down, these precursor species formed particles that could not be evaporated at 350 °C (the temperature of the particle number system). These results highlight the importance of the proper calibration of the engine out emissions at all conditions, even when a GPF is installed.
1. Introduction
Particulate matter (PM) has health and environmental effects [1]. The vehicle regulations control the PM exhaust emissions from approximately the ‘90s [2]. Ultrafine particles (i.e., particles <100 nm) might be more harmful than bigger particles (for the same mass) due to their deeper penetration in the lungs, higher deposition fraction and the possibility to translocate to other organs of the body [3]. Initially, in the European Union’s (EU) regulation, a solid particle number (SPN) limit was introduced for diesel vehicles (2011 for light-duty vehicles and 2013 for heavy-duty vehicles) (6 × 1011 #/km or #/kWh) [4]. The limit forced the use of DPFs in all diesel vehicles. DPFs are very efficient in reducing solid particles, and as recent studies confirm, they are also very efficient for the secondary aerosol reduction in combination with the rest after the treatment devices [5].
The EU plan to reduce CO2 emissions from vehicles at the end of ‘90s (Recommendation 1999/125/EC) and the introduction of mandatory CO2 standards from 2015 (Regulation (EC) 443/2009) resulted in the widespread of gasoline direct injection (GDI) vehicles due to their better fuel economy compared to the port fuel injection (PFI) ones [6]. However, GDI vehicles had initially high PM emissions, especially those running lean. A ten times higher than the diesel SPN limit was introduced in 2014 for GDI vehicles, which was reduced to the diesel one in 2017. In 2017, the real-driving emissions (RDE) regulation was also introduced, which required vehicles to fulfill the limit also on the road under a wide range of conditions [7,8]. This practically forced the use of GPFs (gasoline particulate filters) in GDI vehicles in Europe [6]. In recent years, many Asian countries have also added a SPN limit [9].
In the last years, a lot of research has been conducted for GPFs to optimize their efficiency and performance. Topics included filter structure [10], flow field [11], filter material [12], in particular for soot oxidation at absence of NOx and O2 [13,14], soot storage and oxidation [15,16], oxygen storage [17], ash loading [18], and washcoat [19]. Typically, the temperature at the GPFs is high enough to oxidize the soot when there is available oxygen (e.g., during fuel cut-offs) [20]. For this reason, the accumulation of soot over time is slow and the filtration efficiencies are relatively low. The first fresh GPFs (without soot and ash loading) had filtration efficiencies of around 60% [21]. Such low filtration efficiencies could result in high emission levels in aggressive cycles [22]. The latest technology, fresh GPFs, have filtration efficiencies closer to 90% [23]. Prototype membrane GPFs demonstrated >95% efficiency under all tested conditions [24].
The particulate emissions of GDI vehicles after the RDE regulation introduction (in 2017) are at low levels [6,25]. Nevertheless, there are still some concerns: for example, GPFs have not shown similar reduction potential against secondary organic aerosol as DPFs [26]. Due to the lower filtration of the GPFs compared to DPFs, emissions at the tailpipe of GDI vehicles are more sensitive to variation of engine-out emissions. Engine-out emissions can increase significantly due to incomplete combustion at fuel enrichment events. Studies showed that with lower lambda (from 1 to 0.85–0.875) particle number emissions increased two to three times [27,28]. Challenging cases are, for example, the cold start, low ambient temperature, aggressive driving style [29,30]. Another important factor is fuel [28,31,32,33]. Many studies have tried to correlate the particle number emissions with the fuel properties, such as aromatics content, distillation temperatures, and volatility [34,35,36]. In the last decade, various indexes have been used, with the most common being the Honda PM index [37]. The certification fuels for Europe, China, and the United States have typically PM index slightly higher than 1 (range 0.5–2.0) [38,39,40,41], but market fuel can have higher values reaching theoretically up to 3, and even higher in, e.g., Russia [42]. Many studies showed that higher PM index fuels have higher SPN emissions. For example: SPN was 15% higher with a fuel with PM index of 2.4 compared to 2.0 [39], 35% higher with a 2.2 PM index compared to 1.9 [43], 40% higher with a 2.9 PM index compared to 1.7 [38].
The majority of the studies have been carried out with SPN instruments counting from 23 nm, as prescribed in the current SPN regulation. The 10 nm SPN methodology was recently added in the GTR 15 (global technical regulation) for light-duty vehicles, and EU has the intention to apply it in the next regulatory step [9,44]. The studies with GDI vehicles measuring below 23 nm are limited and have focused on typical operating conditions. The concentration of particles between 10 and 23 nm is approximately 35% of the concentration of particles >23 nm [6,45,46,47], but higher percentages have been reported [48], in particular for cold starts and high sulfur fuels [49,50]. There are a few cases, though, that reported a very high concentration of particles below 23 nm at extreme conditions (e.g., −30 °C, or dynamic urban driving at −10 °C [51], and regeneration [21]). The current regulations cover temperatures down to −7 °C, but future regulations might cover temperatures down to −10 °C, and the research in this temperature range is lacking.
The study aims to challenge an advanced (i.e., expected filtration efficiency >99% even when fresh) prototype GPF with real-life operation worst cases. For this reason, the following conditions were included:
- The GPF was fresh/new (no soot or ash loading). Furthermore, the test protocol was designed to keep any soot and ash levels at a minimum level (high exhaust gas temperatures and availability of oxygen at decelerations and fuel cut-offs).
- Low ambient temperatures: In addition to the typical 23 °C ambient temperature, a temperature within current RDE boundary conditions (−4 °C) and a temperature lower than the current RDE boundaries (−9 °C) were included.
- At the −9 °C ambient temperature tests, the auxiliaries were on (air-conditioning (A/C), heating of the two seats, heating of the rear window).
- Most tests were conducted with almost 90% payload, the maximum allowed in current RDE regulation.
- An artificial dynamic cycle with slope (road gradient) was included.
- Hard accelerations from 0 km/h (idling) to 65 km/h or to 145 km/h were added to simulate cases such as crossing a busy road or entering the highway.
- All tests had a 95% percentile of speed times acceleration (v × a) higher than the currently allowed in the RDE regulation.
- Most tests had a distance slightly lower than the minimum distance required in RDE (16 km). The acceleration tests had much lower total distance (1 km and 4.5 km, respectively).
- Cold start tests were included.
- A fuel with a high PM index (2.2) was used, simulating an almost worst-case market fuel.
The results of this study are expected to help researchers, engine calibration engineers, and regulators to understand the severity of various parameters on the emission levels. This may help them focus on the most critical aspects.
2. Results
2.1. Type Approval Cycle
Table 1 summarizes the available info regarding the WLTC (worldwide harmonized light vehicles test cycle) following the type approval procedures, with the exceptions described below. Note that the declared values at the CoC (certificate of conformity) are from a vehicle from the same family that could be even a different model. Nevertheless, they give an estimation of the expected emissions. The tests with the OEM’s (original equipment manufacturer’s) GPF removed were conducted at another laboratory. The tests with the new “advanced” GPF were conducted without any pre-conditioning of the vehicle, so they could be overestimating the emissions. Furthermore, the fuel with a high PM index was used (see Materials and Methods). It should also be emphasized that, even though the advanced GPF was of similar characteristics with the OEM’s GPF, it cannot be excluded that has influenced the engine-out emissions. The results demonstrate the extremely high efficiency of the advanced GPF even when fresh (almost 100%).

Table 1.
Results of the WLTC at 23 °C following the type approval procedures, except for the advanced GPF case where “bad” market fuel was used and no pre-conditioning was done.
2.2. Gaseous Emissions
Figure 1a plots the CO2 emissions for the various tests. Solid symbols are cold start tests, while open symbols are hot start tests. Lighter colors indicate tests with lower payload (mass). The ratio of the specific test CO2 to the type approval WLTC CO2 value is also given on the right axis. Even though the CO2 is not relevant for the particulate emissions, it shows the severity of the tests. Any CO2 “baseline” value could be used; the CoC value was used for simplicity reasons. Very demanding tests were the hard accelerations and the urban cold starts dynamic test (ratios 2.5–3). The cold start US06 tests had a ratio of 1.5–1.9, while the hot start US06 was slightly less (1.3–1.6) with the higher values at the −9 °C tests. It should be added that the CO2 ratio of the US06 at −9 °C for the first 2 km was 2.75, a value close to the hard acceleration CO2 ratios. Note that the CO2 of the first 2 km of the WLTC would be 26% higher, meaning that the CO2 ratios for short cycles (e.g., hard accelerations) would be 26% lower if the CO2 value of the first 2 km of the WLTC would be used. The high CO2 ratios were expected because cold start, dynamic driving, use of auxiliaries, higher vehicle weight are known to increase the CO2 and fuel consumption [52,53,54,55].
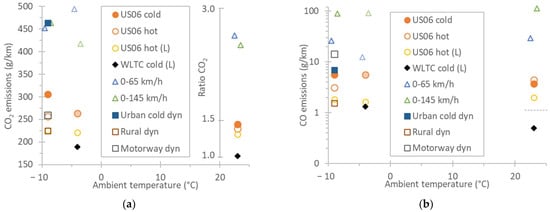
Figure 1.
Emissions for various tests at different ambient temperatures. All tests with 84% payload (1850 kg test mass), except those with “L” and the −4 °C tests where the test mass was lower (1550 kg). Auxiliaries were activated only at the −9 °C tests. Solid symbols are cold start tests, while open symbols are hot start tests. Lighter colors indicate tests with lower payload (mass). (a) CO2. The ratio gives the CO2 emissions divided to the type approval WLTC value. (b) CO. The dotted line shows the limit for the type approval cycle WLTC.
The CO emissions are given in Figure 1b. CO is a proxy for fuel enrichment strategies that impact SPN emissions. Except for the WLTC test at 23 °C, all tests exceeded the 1 g/km limit (applicable to the WLTC) and reached up to 100 g/km during hard accelerations (distances only 1–2 km). Even though such events do not take place often (e.g., only when entering a highway), and they last for a few km only (1–2 km), according to our results, one such acceleration can emit the same CO (in g) as 15 WLTCs at 23 °C (each is 22.3 km long).
The HC emissions can be used as a proxy of the TWC efficiency (Figure 2a). The HCs (and NMHCs) exceeded the WLTC limit of 100 mg/km (and 68 mg/km) at some of the accelerations and the low-temperature cold start tests, reaching 550 mg/km (and 450 mg/km) at the cold start US06 at −9 °C. The hot start tests were at low levels (10–20 mg/km) even at low ambient temperatures.
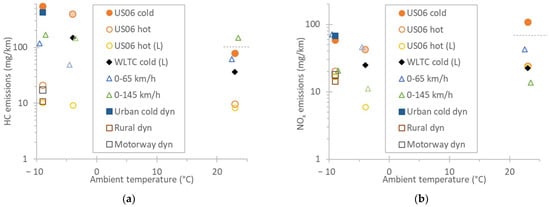
Figure 2.
Emissions for various tests at different ambient temperatures. All tests with 84% payload (1850 kg test mass), except those with “L” and the −4 °C tests where the test mass was lower (1550 kg). Auxiliaries were activated only at the −9 °C tests. Solid symbols are cold start tests, while open symbols are hot start tests. Lighter colors indicate tests with lower payload (mass). The dotted line shows the limit for the type approval cycle WLTC. (a) HC. (b) NOx.
The NOx emissions (Figure 2b) were below the WLTC limit of 60 mg/km at most tests, slightly (15%) exceeding the limit at the −9 °C cold start US06 and the 0–65 km/h accelerations, and reaching 109 mg/km at the cold start US06 at 23 °C. The high value of 109 mg/km was due to the high cold start emissions during the first minute. The hot start cycles had emissions <20 mg/km, even at the −9 °C ambient temperature.
2.3. SPN Emissions
Figure 3a plots the SPN23,ET emissions. At 23 °C, they were below 1 × 1011 #/km, and at low ambient temperatures below 2 × 1011 #/km, with the exception of the low-temperature cold start tests. The two cold start tests at −9 °C (a temperature outside the RDE boundaries) were above the limit of 6 × 1011 #/km. Nevertheless, the exceedance was less than by a factor of two. The emissions applying the RDE corrections can be found in Figure A1a in the Appendix A.
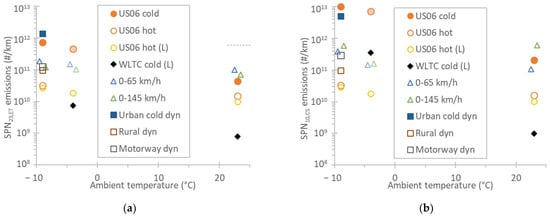
Figure 3.
Emissions for various tests at different ambient temperatures. All tests with 84% payload (1850 kg test mass), except those with “L” and the −4 °C tests where the test mass was lower (1550 kg). Solid symbols are cold start tests, while open symbols are hot start tests. Lighter colors indicate tests with lower payload (mass). Auxiliaries were activated only at the −9 °C tests. (a) Solid particle number >23 nm with the evaporation tube (SPN23,ET). The dotted line shows the limit for the type approval cycle WLTC. (b) Solid particle number >10 nm with the catalytic stripper (SPN10,CS).
Figure 3b plots the SPN10,CS emissions. For the hot start US06 cycles, the emissions were quite close to the SPN23,ET values (only 10% higher). For the accelerations and the dynamic cycles, the SPN10,CS emissions were up to 5 times higher than the SPN23,ET; and for the cold start cycles at negative ambient temperatures, the differences were more than one order of magnitude higher. The cold start emissions at low temperatures almost reached 1 × 1013 #/km, while the hot emissions were <3 × 1011 #/km. The emissions applying the RDE corrections are summarized in Figure A1b in the Appendix A.
Table 2 summarizes the increase of the emissions for various changes in the conditions. For example, the CO2 of the hot start US06 test at −4 °C was 2% higher (ratio 1.02) than the test at 23 °C (keeping the rest conditions the same) (see the third row). For CO2, the lower ambient temperature had a small effect (2%) for the hot start tests. The higher payload had a 10% effect and the cold start had 4–19% effect. For CO the effect was up to 95%, with the most influencing factors the payload and the cold start at low ambient temperature. The lower than unity values (up to −18%) show that the CO variability was quite high, and differences of at least 20% were due to the driver’s variability. For HCs the payload had a 60% effect, while the lower temperatures only 10%. However, the cold start had an effect of 8–25 times. For particles, the effect was 30–90% for hot cycles: the increase of the payload (from 28% to 84%) increased the emissions 30–40%, the lower temperature from 23 °C to −4 °C had a 80–90% effect, a further decrease to −9 °C and the use of auxiliaries had another 50–60% effect. However, the biggest effect had the cold start, which increased the emissions by a factor 3–23 (SPN23,ET) or 13–307 (SPN10,CS), with the higher values at the −9 °C. The SPN and HC ratios were more in agreement than the rest pollutants.

Table 2.
Pollutants ratios for various conditions.
3. Discussion
In this study, a very high filtration efficiency prototype GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter) was tested under various worst-case scenarios, including low ambient temperatures, dynamic driving, hard accelerations, and cold starts. All tests were conducted with an ad hoc fuel with a high PM index, representing a bad quality market fuel. Based on the WLTC (worldwide harmonized light vehicles test cycle), the filtration efficiency was >99.9%.
While the 23-nm solid particle number (SPN23) measurements were satisfactory fulfilling the current limit in the regulation, the 10 nm solid particle number (SPN10) measurements, compared to the >23 nm results, were higher by a factor of up to 5 for dynamic tests and >10 for cold start tests at negative ambient temperatures. The final 10 nm emissions exceeded the current limit at the cold start tests at low ambient temperatures. Different conditions (e.g., higher payload, testing at lower temperatures) increased the emissions by 30–90% when the engine was hot. The CO and HC increase was on the same order for the hot tests. However, the cold start inclusion increased the emissions by a factor of 3 (SPN23) to 12.8 (SPN10) at 23 °C and 23 (SPN23) to 307 (SPN10) at −9 °C. This increase was by far higher than the CO increase (up to 79%), and more in agreement with the HCs increase (increase by a factor of 8 and 26 at 23 °C and −9 °C, respectively).
The SPN23 emissions at 23 °C were low (109–1010 #/km, reaching 1011 for the cold start US06), and are comparable with those in the literature [6,22,25,30,56]. What was rather surprising was that the vehicle was emitting a very high amount of sub-23 nm particles, exceeding the current limit for GDIs and reaching up to 1013 #/km, even though a high filtration efficiency GPF was used. A previous study reported very high emissions of solid particles (around 1013 #/km) at −18 °C even with a catalyzed GPF installed during a cold start cycle [57]. A study from the same authors reported high concentrations of sub-23 nm particles, and they were attributed to the passive regeneration of the catalyzed GPF [21]. Soot fragmentation and incomplete combustion of the deposited soot were suggested as possible reasons by the authors for particles >23 nm, but desorbed material from the transfer lines for particles <23 nm. A recent study with a Euro 6d-Temp vehicle could fulfill the RDE limit (9 × 1010 #/km) under all conditions examined, including low ambient temperature −30 °C, dynamic driving, and high payload [51]. However, the CO emissions of that vehicle were much lower (<2.5 g/km vs. up to 100 g/km in our case at −10 °C), the HC emissions were comparable (400 mg/km vs. 550 mg/km) and the position of the GPF was underfloor (vs. close-coupled in our case).
To better understand the results of our study, Figure 4 plots the cold start US06 test at −4 °C. Figure 4a plots the speed profile, the exhaust gas temperature at the GPF outlet and at the tailpipe, along with the lambda values (from OBD) at the engine outlet and the GPF outlet (“tailpipe” in Figure 4a). During the first minute, the lambda value from approximately 0.8 gradually increased to unity, and then it remained relatively constant. High values were registered during decelerations (fuel cut-offs) due to oxygen abundance, while lower values were during some accelerations (rich combustion). The engine out and post-GPF lambda values were not identical due to the oxygen storage and usage at the TWC [58]. The GPF outlet temperature reached 700 °C after one minute and remained high for the rest of the cycle. The tailpipe exhaust gas temperature hardly reached 300 °C.
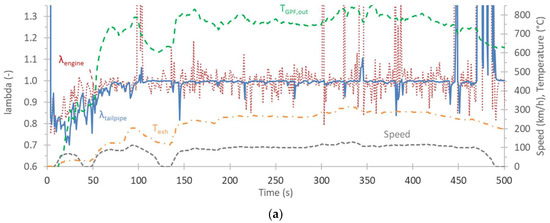
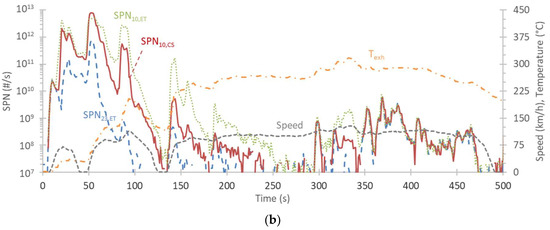
Figure 4.
Cold start US06 at −4 °C: (a) lambda values at the engine out (engine) and downstream of the GPF (tailpipe). The speed profile and the exhaust gas temperature at the GPF (gasoline particulate filter) outlet and tailpipe (exh) are also given; (b) solid particle number emissions >23 nm (SPN23) and 10 nm (SPN10), downstream of an evaporation tube (ET) or a catalytic stripper (CS). The speed profile and the exhaust gas temperature at the tailpipe outlet are also given.
Figure 4b plots again the speed profile, the exhaust gas temperature at the tailpipe outlet, along with the SPN emissions. There is a huge SPN concentration at the beginning of the cycle, reaching almost 1 × 1013 #/s. These particles appear with a small delay of a few seconds due to the delay at the tube between the vehicle and the dilution tunnel. The 10 nm CPCs (condensation particle counters) read 30,000 p/cm3 (with dilution 1000) which was higher than their maximum calibrated value of 10,000 p/cm3. Thus, the cold start concentrations might be underestimated. There was a huge difference between 23 nm and 10 nm measurements indicating that the majority of the particles were <23 nm in size. There was also big difference between the two 10 nm CPCs; the one downstream of the evaporation tube being higher. Two points need to be explained: the higher emissions at the beginning of the cycle and the differences between the instruments.
High particle concentrations during cold start and low ambient temperatures have been reported before, in particular for non-GPF equipped vehicles [6,57,59,60]. Nucleation mode peaking at 10 nm to 20 nm is sometimes reported [61]. In a study, high concentrations with a peak around 20 nm were measured at −15 °C [62]. As the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, there is limited time available for fuel and air mixing, resulting in localized rich combustion [63]. Additionally, a small amount of fuel may impinge on the piston and make direct contact with the cold cylinder walls, resulting in soot formation. In particular, for our study, due to the low fuel volatility of the fuel we used, it is possible that many fuel-rich regions were formed, resulting in very high particle number emissions, compared to previous studies [43].
The lower filtration efficiency at cold start has been discussed in detail elsewhere [51]. In short, the filtration efficiency can be lower due to the lower flow rates, cracks at the filter, leaks between the canister and the mat, and/or fragmentation of deposited soot. However, none of these reasons can adequately explain our results: the cycle was a high-speed cycle with a high flow rate from the beginning, the filter was fresh (new), and the deposited soot should be minimal due to the test cycles and protocol that supported passive regeneration of the filter. In the 23 nm to 50 nm range, high filtration efficiencies are expected [64]. At the sub-23 nm range, in many cases the filtration efficiency can be higher, but not always [64]. During cold start, the temperature at the three-way catalyst (TWC) and the GPF was also relatively low (it reached 700 °C after the first minute). Our assumption is that the particles that we measured were in the gaseous phase (volatile) at the high-temperature conditions of the GPF and thus, they passed unfiltered. As the exhaust gas cooled down, they formed “non-volatile” particles that could not evaporate in the particle number system (i.e., at 350 °C). This may be the reason why the advanced GPF of our study could not trap them.
Solid particles at the temperature conditions of the GPF (e.g., metal and carbonaceous particles) would be trapped. If this assumption is true, then: (i) improved efficiency of the TWC at low temperatures and cold start and (ii) an underfloor position of the GPF might be advantageous. The lower light-off temperature and the faster achievement of the appropriate temperatures will ensure lower concentrations of unburned particle precursors [65,66,67]. The GPF at the underfloor position might show better filtration efficiency as some species will be at the particulate phase due to the lower exhaust gas temperature, in addition to other reasons reported in the literature: due to the lower temperatures the flow velocity is lower and the filtration efficiency is higher [68] and due to the higher filtration efficiency a bigger soot cake is formed resulting in even higher filtration efficiencies [69].
The exact nature of these particles was not evaluated in our study. Unburned hydrocarbons that were not oxidized at the TWC during the cold start are a possibility. Many studies have measured PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) from GDIs [70,71], in particular during cold start [72]. The boiling point of PAHs is <600 °C [73]. Thus, they could be in the gaseous phase at the temperature conditions of the GPF. PAHs with four rings will also not evaporate at 350 °C (the temperature of the particle number system) [73]. Combustion models have shown the formation of particles at around 10 nm [74] supporting our assumption. The model study can also explain the high difference between 23 nm and 10 nm measurements: most of the PAHs remain below 23 nm [74]. The differences between the 10 nm measurements (evaporation tube vs. catalytic stripper) have to do with the fate of hydrocarbons downstream of the two systems. The catalytic stripper oxidizes the hydrocarbons, while downstream of the evaporation tube the evaporated hydrocarbons condense on the existing particles making them grow. At the cut-off size of the systems (around 10 nm), the larger particles at the evaporation tube system were detected with higher counting efficiency than the smaller particles at the catalytic stripper system. Artifacts at the evaporation tube system (i.e., formation of nucleation mode particles downstream of the evaporation tube) cannot be excluded [75].
Figure 5 plots three hard accelerations from 0 to 65 km/h, three from 0 to 145 km/h, and one smooth acceleration up to 145 km/h, where the speed was kept for one minute. The tests were done with a hot engine at the beginning of the test to minimize any cold start effects (i.e., formation of many small particles). In particular, the tests were conducted immediately after the cold start US06 test of Figure 4. The ambient temperature was −4 °C. Note that the scales of the Figure 4 and Figure 5 are identical, in order to put the concentration levels at the right context.
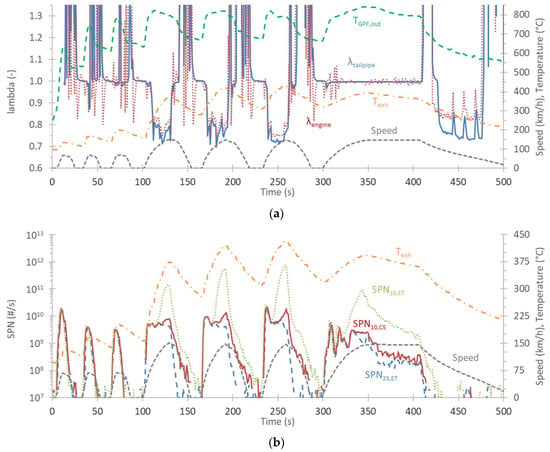
Figure 5.
Acceleration tests at −4 °C: (a) lambda values at the engine out (engine) and downstream of the GPF (tailpipe). The speed profile and the exhaust gas temperature at the GPF (gasoline particulate filter) outlet and tailpipe (exh) are also given; (b) Solid particle number emissions >23 nm (SPN23) and 10 nm (SPN10), downstream of an evaporation tube (ET) or a catalytic stripper (CS). The speed profile and the exhaust gas temperature at the tailpipe outlet are also given.
Figure 5a shows that during the 0–65 km/h accelerations the lambda values were around unity, similarly for the smooth acceleration to 145 km/h. But during the hard accelerations to 145 km/h the lambda values were around 0.75. During decelerations the values were much higher than unity due to the fuel cut-offs, as discussed in Figure 4. After the first acceleration, the temperature at the GPF outlet was >550 °C. The tailpipe temperature exceeded 300 °C at the 0–145 km/h accelerations.
At the three accelerations of 0–65 km/h, the three particle systems were measuring similar concentrations; thus the size of particles was >23 nm (Figure 5b). Similarly, during the acceleration parts of the 0–145 km/h tests the systems were in agreement. This can be explained by a study that found larger particles with lower lambda compared to the stoichiometric combustion [76]. A small deviation was noticed for the 10 nm CPC downstream of the catalytic stripper during the deceleration part. These particles could be lube oil particles, often observed during braking [77]. The deviation was very high for the 10 nm CPC downstream of the evaporation tube. This deviation remained, even when the speed was kept for one minute. A closer look at the exhaust gas temperatures revealed that the deviation of the two 10 nm CPC started when the exhaust gas temperature was around 350 °C, which is the temperature of the evaporation tube (and the catalytic stripper). This indicates that there were “semi/volatiles” that were evaporated at the evaporation tube and downstream of the evaporation tube, they were (i) growing any pre-existing particles to sizes >10 nm or (ii) they were re-nucleating forming new particles, as discussed in detail elsewhere [78,79]. In contrast, the catalytic stripper could efficiently oxidize them and remove them. The origin of the location of these particles (deposited at the vehicle tailpipe or at the sampling lines after the vehicle) remains uncertain. Other studies also found many particles <30 nm at high exhaust gas temperature conditions, and our assumption (i.e., desorbed material in combination with evaporation tube instead of catalytic stripper) could explain those results as well [21,69,80].
The discussion of the previous two examples is summarized schematically in Figure 6. The upper panel plots the emissions during a cold start at low ambient temperature. The engine-out emissions consist of carbonaceous and metal particles (grey parallelograms), heavy molecular species that are in gaseous phase at temperatures >350 °C (green asterisks), and other species that are in the gaseous phase at >50 °C (orange crosses). The high engine-out emissions are plotted as three symbols for each category.
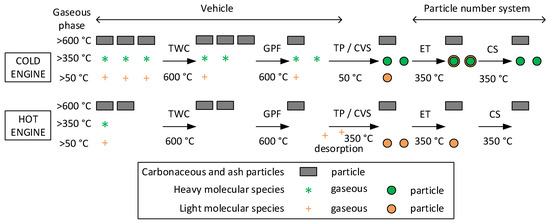
Figure 6.
Schematic explanation of the results. CS = catalytic stripper; CVS = constant volume sampling (dilution tunnel); ET = evaporation tube; GPF = gasoline particulate filter; TP = tailpipe; TWC = three-way catalyst.
At the three-way catalyst (TWC) the carbonaceous and metal particles are not affected, while the concentration of the other species in gaseous phase is reduced. As the catalyst has not reached the appropriate temperature and the lambda is less than one, the efficiency for the gaseous compounds is not 100%. The (uncoated) close-coupled GPF reduces the concentration of the carbonaceous and metal particles, but does not affect the species in the gaseous phase. Soot fragmentation or soot oxidation can take place depending on the oxygen availability and the deposited soot, which could influence the >23 nm soot concentration [20,21,81]. However, in this example, the focus is on the sub-23 nm particles, which had very high concentrations compared to the >23 nm particle concentrations.
At the conditions of the tailpipe (or dilution tunnel), where the exhaust gas temperature is low, the species that were in the gaseous phase form particles (solid or liquid) (depicted as green or orange circles, respectively). The evaporation tube of the particle number system (set at 350 °C) evaporates the particles that were formed from species that are in the gaseous phase at >50 °C. The other species (gaseous at >350 °C) remain in the solid phase because the temperature is not high enough to evaporate them. At the next step, the catalytic stripper at 375 °C (actual temperature 350 °C) cannot remove the remaining particles (because they need temperatures of >350 °C), but re-evaporates any species that had condensed on the particles downstream of the evaporation tube. Thus, the size of particles at the exit of the catalytic stripper is smaller than at the evaporation tube. For this example, the condensation on the carbonaceous particles, which have a diameter >23 nm, is assumed to be negligible and not important for the result of the particle number system measuring particles >23 nm. Indeed, studies have shown an increase of the diameter of only 1 nm due to the condensed material [82]. In contrast, the size of the formed “non-volatile” particles, which is assumed to be around 10 nm in this example, is very important for the particle number measurement system, and a few nanometers can have a big impact on the final measured concentration. For example, commercial particle number systems have an efficiency of around 35–40% at 10 nm, but 54–63% at 15 nm [83]. Since the differences were larger than by a factor of two in many cases, artifacts at the evaporation tube system cannot be excluded: the evaporated species in the evaporation tube have such a high concentration that re-nucleate during cooling downstream of the evaporation tube and form nucleation mode particles that erroneously are counted as solids [46,75].
The lower panel of Figure 6 depicts the acceleration cases (hot engine). In this case, the absolute emissions are lower (only one or two parts of each species are plotted). At the exit of the GPF, only carbonaceous and metal particles are found because the TWC can efficiently remove the species at the gaseous phase because it is already at the appropriate temperature. Due to the high exhaust gas temperature, the release of species from the tailpipe tubing is taking place. Thus, at the dilution tunnel nucleation mode, particles can be found. The evaporation tube of the particle number system removes some of them, but re-nucleation downstream of the evaporation tube takes also place resulting in appearance of some particles (artifact particles) [84]. The catalytic stripper efficiently removes them by oxidation.
There is a fundamental difference between the emissions of Figure 4 (cold start) and Figure 5 (hard accelerations 0–145 km/h). Even though in both cases, the lambda was low (around 0.8), the cold start emissions were much higher than the hard accelerations (1012 #/s vs. 1010 #/s). At rich combustion, the higher fuel injection rate results in wall and piston wetting and soot generation [85] and the effect is more important when the piston and walls are cold. Furthermore, at the cold start, the TWC has not reached its light-off temperature (plus the lambda is not stoichiometric), and the removal efficiency of hydrocarbons is low. We assume that the cold start particles were PAHs or other heavy molecular species (size around 10 nm) that were in the gaseous phase at the GPF temperature conditions and consequently passed the GPF unfiltered. These reasons explain the high concentrations at cold start, and why the concentration of particles <23 nm was much higher than of particles >23 nm.
During hard accelerations (with hot engine) the sub-23 nm concentration was low (when measured with a catalytic stripper). With a hot engine, a high sub-23 nm concentration was seen only with the evaporation tube system and when the exhaust gas temperature exceeded 350 °C. Without a catalytic stripper, desorbed material from the sampling lines at temperatures >350 °C could grow them to the measurement size of the instruments (>10 nm) or re-nucleate and form “artifact” particles. The existence of high concentrations of sub-23 nm non-volatile particles supports the intention of lowering the cut-off size of 23 nm to 10 nm in the next regulatory step but also highlights the importance of using a catalytic stripper.
4. Materials and Methods
The tests were conducted at the vehicle emissions laboratory (VELA 8) of the Joint Research Centre (JRC) (Ispra, Italy) of the European Commission (Figure 7). The vehicle was fixed on a chassis dynamometer. A 4-m-long heated line (80 °C) connected the tailpipe of the vehicle to the full dilution tunnel with constant volume sampling (CVS). AMA i60 gas analyzers were measured in real time from the dilution tunnel. An AVL particle counter (APC 489) (Graz, Austria) [86], compliant with the light-duty regulation requirements, was also connected to the dilution tunnel. After a hot dilution at 150 °C, an evaporation tube (ET) at 350 °C removed semi-volatile particles. A secondary dilution cooled down the diluted exhaust to the measurement range of the counters that followed. A PCRF (particle concentration reduction factor) of 1000 (100 × 10) was used. The PCRF is a combination of dilution and particle losses at 30 nm, 50 nm, and 100 nm defined in the regulation. Two condensation particle counters (CPCs) were measured in parallel: one with 50% counting efficiency at 23 nm (model 3790, TSI, Shoreview, MN, USA), and another one with 65% efficiency at 10 nm (model 3792E, TSI, Shoreview, MN, USA). In addition, in parallel, a catalytic stripper (CS) (Catalytic Instruments, Germany) at 375 °C followed by a 10 nm CPC (model 3772 TSI, Shoreview, MN, USA) were connected. The temperature of 375 °C was selected in order to have the same gas temperature as with the evaporation tube (350 °C). The models 3792E and 3772 are practically identical (the 3792E does not have a screen). A correction of 1.4 was applied to the counter downstream of the catalytic stripper to take into account the catalytic stripper particle losses in the 30 nm to 100 nm range. The solid particle number (SPN) emissions determined from the three CPCs will be abbreviated as SPN23,ET, SPN10,ET, SPN10,CS, respectively. It should be emphasized that the term “solid” refers to particles that do not evaporate at 350 °C, and the term “non-volatile” particles might be more accurate; nevertheless, the term “solid” will be used by convention in this paper. Standard OBD (on-board diagnostics) channels were acquired through the OBD portal of the vehicle (including GPF temperatures, lambda values, engine load and accelerator pedal position).
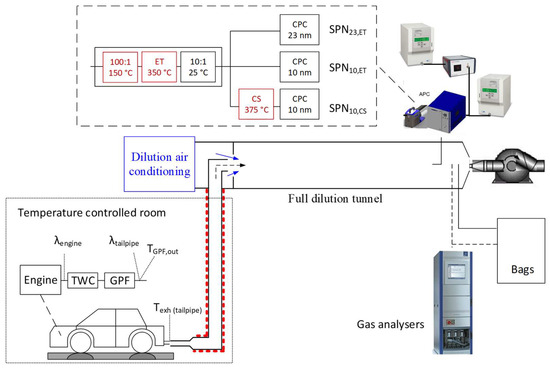
Figure 7.
Schematic setup. CPC = condensation particle counter; CS = catalytic stripper; ET = evaporation tube; GPF = gasoline particulate filter; TWC = three-way catalyst.
The vehicle was registered in 2019 as Euro 6d-Temp. It had a 1.2 L gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine (96 kW), a three-way catalyst and a close-coupled uncoated gasoline particulate filter (GPF). It had an automatic transmission. The original GPF was removed for one test (WLTC) and then replaced with an “advanced” uncoated GPF also in the close-coupled position, with which all tests of this study were conducted. The advanced GPF (high-efficiency prototype, 55% porosity, and 200/8 design) was provided by Corning and had similar dimensions to the original GPF. However, it had a modified inlet channel microstructure based on a novel approach to create a hierarchical pore structure, specially designed to have very high filtration efficiencies even without any soot or ash accumulation, with minimal increase in pressure drop [87]. Much higher efficiencies (>99%) than the commercial Dura Trap GC 2.0 are expected (>90%) [23]. We do not expect a significant effect on the engine-out emissions, but we cannot exclude different behavior of the engine due to the newly installed GPF.
The fuel, which was selected ad hoc, represented a “bad” quality market fuel, but its properties were still within the market fuel requirements in the European norm EN 228. It was an E5 (5% ethanol content) fuel specifically designed for this (and other) campaigns, where “bad” market fuel was needed. Various indexes are used to assess the sooting tendency of the fuel on the particulate emissions. The most common index is the Honda PM index which is calculated based on the evaporative performance and the unsaturated bonds of the fuel components [88]. The calculation of this index needs properties of the fuel not found in the typical fuel certificate. The PM index of our fuel, which was provided by the test fuel supplier, was 2.2. The reduced PM index, which is calculated from T90 and T70 distillation temperatures, was 2.28 [43]. The simplified Moriya index is simpler to calculate as it needs only the percentage of fuel evaporated at 150 °C. The simplified Moriya index was 1.57. Compared to other market fuels in the literature, our fuel had one of the highest PM index and Moriya values [40,41]. Studies with higher values (2.5–2.9) are limited [38,89]. Very high values (e.g., PM index of 3.2) have been tested at studies evaluating various indexes; these fuels were specifically blended for the specific studies [43]. Due to the lack of detailed fuel chemical analysis, it was not possible to calculate other indexes (e.g., MW [42]), which may correlate better with particle number emissions.
Table 3 summarizes the tests conducted and the statistics of the cycles. In short, the type approval WLTC (worldwide harmonized light vehicles test cycle) and the highway US06 cycles were tested at different ambient temperatures (23 °C, −4 °C, −9 °C) and payloads (28% and 84%). The US06 cycles were tested with engine cold (i.e., oil temperature equal to the ambient temperature) or hot (oil temperature >70 °C), while the WLTCs with a cold engine. Furthermore, hard acceleration 0–65 km/h and 0–145 km/h were added (engine hot).

Table 3.
Test cycles and conditions. “Aux on” means that air-conditioning was on, heating at the two front seats and heating of the rear windows (windshield). (L) corresponds to tests with 28% payload and 1550 kg mass. (H) corresponds to tests with 84% payload and 1850 kg mass (the dyno friction coefficient was also adjusted). “Limit” gives the maximum allowed 95th v × a value for the specific trip (mean speed). D = Distance; vm = mean speed.
The chassis dynamometer was set to all-wheel road simulation mode. The road coefficients and the test mass were taken from the CoC (Certificate of Conformity) of the vehicle. A 43 kg rotating mass was considered. The test mass was 1550 kg (corresponding to a payload of 28%) or 1850 kg corresponding to a payload of 84%. For the high payload tests, in addition to the test mass increase, the dyno friction coefficient was adjusted accordingly. The coefficients were not adjusted for the low-temperature tests (+10% resistance as prescribed by the legislation).
It should be highlighted that, except for the type approval cycle (WLTC), no other cycle was fulfilling the RDE boundary conditions, and thus any comparison with limits is only for putting the results into context. For example, except for WLTC, all cycles exceeded the 95th percentile of positive speed times acceleration (v × a), many cycles had a distance <16 km, and the −9 °C tests were below the minimum RDE allowed ambient temperature. The CO2 ratio of the trip to the type approval value is defining the “normality” (or severity) of the on-road tests at the RDE regulation. It should be added that the results of on-road tests, according to the RDE regulation, are corrected by the inverse of the CO2 ratio (for ratios >1.5), but no correction is applied if the ratio is <1.3. Between these values, a linear correction applies. For the specific vehicle, which was type-approved before January 2020, the respective ratios would be 1.25 (instead of 1.5) and 1.2 (instead of 1.3), respectively. The RDE regulation also applies a temperature correction (1.6) when the temperature is <0 °C or >35 °C. The results that will be presented have not been corrected with these factors, unless otherwise specified (e.g., in Appendix A).
5. Conclusions
An advanced GPF with high filtration efficiency was assessed at various extreme conditions using a “bad” quality fuel (PM index 2.2) at low ambient temperature (−9 °C and −4 °C), high payload (84% of max), with the auxiliaries on, driving dynamically and with hard accelerations (0–65 km/h or 0–145 km/h). The tests were not compliant with the RDE (real-driving emissions) boundary conditions of the regulation, and consequently, the solid particle number (SPN) emissions limit was not applicable. Nevertheless, the SPN emissions of particles >23 nm of all tests were below the current limit of 6 × 1011 #/km, with the exception of the cold start tests at −9 °C. Applying the corrections of the current real-driving emissions (RDE) regulation (CO2 ratio, 1.6 for temperatures below 0 °C), and normalizing to 16 km (the minimum RDE distance) all emissions were <3 × 1011 #/km. When considering particles <23 nm the emissions exceeded up to 17 times the limit (4.5 times the corrected). The contribution of sub-23 nm particles was small for cycles with a hot engine, up to 5 times at hard acceleration tests, and more than ten times higher for cold start tests at low temperatures. The “corrected” hot engine emissions were <2 × 1011 #/km, but the cold start tests at low ambient temperature ten times higher, indicating that the reduction of the 23 nm to 10 nm lower size is important for the next regulatory step.
Our assumption was that the sub-23 nm particles were heavy molecular species (e.g., polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons—PAHs) which were in the gaseous phase at the temperature conditions of the closed-coupled GPF and formed “non-volatile” particles as the temperature dropped along the tailpipe tube. For this reason, the GPF could not trap them efficiently. An underfloor position might be more beneficial. However, this needs to be tested in the future. The most important solution is the optimization of the engine for the cold start under challenging conditions in order to keep the cold start emissions under control.
Finally, a comparison of the concentrations measured with an evaporation tube and a catalytic stripper revealed that there can be huge differences for such systems when particles peaking around 10 nm exist. One reason is that the evaporation tube system measures larger particles since the evaporated species re-condense on the particles, compared to the catalytic stripper system, which removes all volatiles and any pre-existing non-volatile particles remain at a small size. This size difference leads to significant differences when the particle size is around the cut-off size (10 nm) of the systems. Another reason for the systems’ differences is that at high exhaust gas temperature (>350 °C) at the tailpipe, outgassed species from the lines result in re-nucleation or growth of the pre-existing particles downstream of the evaporation tube system resulting in artificially high concentrations. Thus, our findings support the current proposal of having a catalytic stripper obligatory in the 10 nm measurement systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.G.; formal analysis, B.G., V.V.; writing—original draft preparation, B.G.; writing—review and editing, A.M., V.V., M.O., G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the VELA 8 staff for the execution of the tests. Special acknowledgements to D. Rose, A. Joshi and T. Boger (Corning GmbH) that provided the prototype GPF.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and should in no way be considered to represent an official opinion of the European Commission. Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation by the European Commission or the authors.
Appendix A
Emissions after RDE regulation relevant corrections (Figure A1). Accelerator pedal position (Figure A2) and engine load (Figure A3) for the US06 test at −4 °C and the acceleration tests.
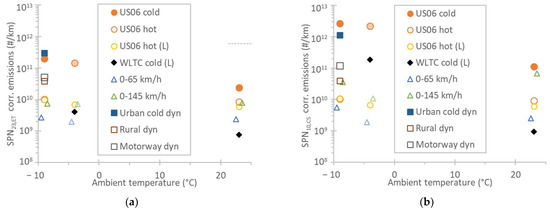
Figure A1.
Emissions for various tests at different ambient temperatures applying the following corrections: CO2 ratio, 1.6 for temperatures <0 °C, normalization to 16 km for cycles with shorter distance. All tests with 84% payload (1850 kg test mass), except those with “L” and the −4 °C tests where the test mass was lower (1550 kg). Solid symbols are cold start tests, while open symbols are hot start tests. Lighter colors indicate tests with lower payload (mass). Auxiliaries were activated only at the −9 °C tests. (a) Solid particle number >23 nm with the evaporation tube (SPN23,ET). The dotted line shows the limit for the type approval cycle WLTC. (b) Solid particle number >10 nm with the catalytic stripper (SPN10,CS).
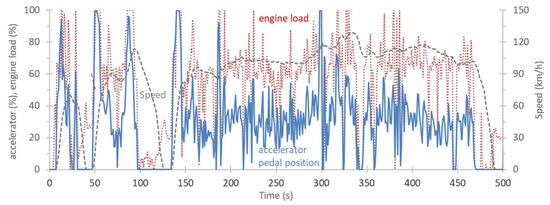
Figure A2.
Accelerator pedal position and engine load for the US06 test at −4 °C.
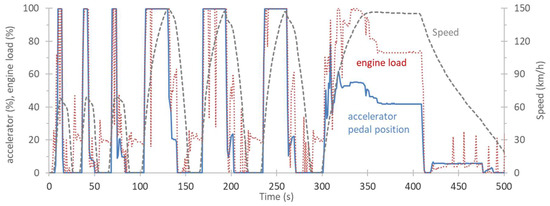
Figure A3.
Accelerator pedal position and engine load for the acceleration tests at −4 °C.
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003422-8. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, W. Legislation for the Reduction of Exhaust Gas Emissions. In Traffic and Environment; Gruden, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 3T, pp. 175–253. ISBN 978-3-540-00050-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.-S.; Ryu, M.H.; Carlsten, C. Ultrafine Particles: Unique Physicochemical Properties Relevant to Health and Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Andersson, J.; Dilara, P.; Martini, G.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of Automotive Nonvolatile Particle Number Emissions within the European Legislative Framework: A Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Simonen, P.; Ntziachristos, L.; Juuti, P.; Timonen, H.; Teinilä, K.; Saarikoski, S.; Saveljeff, H.; Lauren, M.; et al. Strategies to Diminish the Emissions of Particles and Secondary Aerosol Formation from Diesel Engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10408–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Joshi, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dilara, P. European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gis, W.; Gis, M.; Pielecha, J.; Skobiej, K. Alternative Exhaust Emission Factors from Vehicles in On-Road Driving Tests. Energies 2021, 14, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.A.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Ong, H.C.; Ashik, F.R.; Hassan, M.M.; Murshed, M.T.; Imran, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Rahman, M.A.; Hasan, M.A.M.; et al. State-of-the-Art of Establishing Test Procedures for Real Driving Gaseous Emissions from Light- and Heavy-Duty Vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Melas, A.; Martini, G.; Dilara, P. Overview of Vehicle Exhaust Particle Number Regulations. Processes 2021, 9, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Li, X.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, Y. Study on a New Gasoline Particulate Filter Structure Based on the Nested Cylinder and Diversion Channel Plug. Energies 2019, 12, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, M.; Sjöblom, J.; Sharma, N.; Ström, H.; Li, X. Experimental Study on the Flow Field of Particles Deposited on a Gasoline Particulate Filter. Energies 2019, 12, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myung, C.-L.; Kim, J.; Jang, W.; Jin, D.; Park, S.; Lee, J. Nanoparticle Filtration Characteristics of Advanced Metal Foam Media for a Spark Ignition Direct Injection Engine in Steady Engine Operating Conditions and Vehicle Test Modes. Energies 2015, 8, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matarrese, R. Catalytic Materials for Gasoline Particulate Filters Soot Oxidation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoretti, E.; Martini, F.; Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Nanostructured Equimolar Ceria-Praseodymia for Total Oxidations in Low-O2 Conditions. Catalysts 2020, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, S.; Schwanzer, P.; Hagen, G.; Haft, G.; Rabl, H.-P.; Dietrich, M.; Moos, R. Modelling the Influence of Different Soot Types on the Radio-Frequency-Based Load Detection of Gasoline Particulate Filters. Sensors 2020, 20, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses-DeBusk, M.; Storey, J.M.E.; Eibl, M.A.; Thomas, J.F.; Toops, T.J.; Finney, C.E.A.; Pihl, J.A.; Bilheux, H.Z.; Gregor, J. Nonuniform Oxidation Behavior of Loaded Gasoline Particulate Filters. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2020, 6, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, M.; Jahn, C.; Lanzerath, P.; Moos, R. Microwave-Based Oxidation State and Soot Loading Determination on Gasoline Particulate Filters with Three-Way Catalyst Coating for Homogenously Operated Gasoline Engines. Sensors 2015, 15, 21971–21988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Fang, J. Regeneration Performance and Particulate Emission Characteristics during Active Regeneration Process of GPF with Ash Loading. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 248, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, F.; Fang, N.; Yan, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. An Experimental Investigation of the Impact of Washcoat Composition on Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF) Performance. Energies 2020, 13, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolin, P.; Rose, D.; Kunath, F.; Boger, T. Modeling of the Soot Oxidation in Gasoline Particulate Filters. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Saffaripour, M.; Liu, F.; Hendren, J.; Thomson, K.A.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R.; Rideout, G. Characterization of Real-Time Particle Emissions from a Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicle Equipped with a Catalyzed Gasoline Particulate Filter during Filter Regeneration. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samaras, Z.C.; Andersson, J.; Bergmann, A.; Hausberger, S.; Toumasatos, Z.; Keskinen, J.; Haisch, C.; Kontses, A.; Ntziachristos, L.D.; Landl, L.; et al. Measuring Automotive Exhaust Particles down to 10 Nm. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2020, 3, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, T.; Glasson, T.; Rose, D.; Ingram-Ogunwumi, R.; Wu, H. Next Generation Gasoline Particulate Filters for Uncatalyzed Applications and Lowest Particulate Emissions. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2021, 3, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Zinola, S.; Leblanc, M.; Raux, S.; Boreave, A.; R’Mili, B.; Cartoixa, B. The Particulate Number Emissions from GDI Engines: Advanced Characterization and Reduction through a Gasoline Particulate Filter with Membrane Technology. Ing. De L’auto 2013, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Lähde, T.; Pavlovic, J.; Valverde, V.; Clairotte, M.; Giechaskiel, B. Laboratory and On-Road Evaluation of a GPF-Equipped Gasoline Vehicle. Catalysts 2019, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pieber, S.M.; Kumar, N.K.; Klein, F.; Comte, P.; Bhattu, D.; Dommen, J.; Bruns, E.A.; Kılıç, D.; El Haddad, I.; Keller, A.; et al. Gas-Phase Composition and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from Standard and Particle Filter-Retrofitted Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicles Investigated in a Batch and Flow Reactor. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9929–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.; Dou, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Lu, H.; Feng, J.; Feng, L. Experimental Study of the Effect of Heavy Aromatics on the Characteristics of Combustion and Ultrafine Particle in DISI Engine. Fuel 2017, 203, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, F.C.P.; Stone, R.; Richardson, D.; Lewis, A.G.J.; Akehurst, S.; Turner, J.W.G.; Shankar, V.; Chahal, J.; Cracknell, R.F.; Aradi, A. The Effect of Fuel Composition on Particulate Emissions from a Highly Boosted GDI Engine—An Evaluation of Three Particulate Indices. Fuel 2019, 252, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, D.; Hüssy, A.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Bonsack, P. Influences of Special Driving Situations on Emissions of Passenger Cars. Combust. Engines 2021, 184, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, D.; Zimmerli, Y.; Czerwinski, J.; Bonsack, P. Real Driving Emissions in Extended Driving Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Chen, L.; Leach, F.; Ding, S. A Review of Particulate Number (PN) Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engines and Their Control Techniques. Energies 2018, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karavalakis, G.; Durbin, T.D.; Yang, J.; Ventura, L.; Xu, K. Fuel Effects on PM Emissions from Different Vehicle/Engine Configurations: A Literature Review; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, T.; Olofsson, U.; Christiansen Erlandsson, A. Undiluted Measurement of the Particle Size Distribution of Different Oxygenated Biofuels in a Gasoline-Optimised DISI Engine. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Short, D.; Vu, D.; Russell, R.; Hajbabaei, M.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Durbin, T.D. Evaluating the Effects of Aromatics Content in Gasoline on Gaseous and Particulate Matter Emissions from SI-PFI and SIDI Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7021–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Zu, L. Effects of Aromatics, Olefins and Distillation Temperatures (T50 & T90) on Particle Mass and Number Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Vehicles. Energy Policy 2017, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; He, Z.; Yu, L.; Lu, X. Improvement of Combustion Performance and Emissions in a Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engine by Modulation of Fuel Volatility. Fuel 2020, 268, 117369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amara, A.; Tahtouh, T.; Ubrich, E.; Starck, L.; Moriya, H.; IIda, Y.; Koji, N. Critical Analysis of PM Index and Other Fuel Indices: Impact of Gasoline Fuel Volatility and Chemical Composition; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouraie, M.; Frommherz, M.; Mosburger, M.; Chapman, E.; Li, S.; McCormick, R.; Fioroni, G. Investigation of the Impact of Fuel Properties on Particulate Number Emission of a Modern Gasoline Direct Injection Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, S.; Ma, C. Effects of the Particulate Matter Index and Particulate Evaluation Index of the Primary Reference Fuel on Particulate Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicles. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, E.; Winston-Galant, M.; Geng, P.; Konzack, A. Global Market Gasoline Range Fuel Review Using Fuel Particulate Emission Correlation Indices; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.; Geng, P.; Konzack, A. Global Market Gasoline Quality Review: Five Year Trends in Particulate Emission Indices; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, J.-H.; Menger, L. Novel Index for Evaluation of Particle Formation Tendencies of Fuels with Different Chemical Compositions. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2017, 10, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yao, A.; Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Yao, C. A Reduced PM Index for Evaluating the Effect of Fuel Properties on the Particulate Matter Emissions from Gasoline Vehicles. Fuel 2019, 253, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahde, T.; Giechaskiel, B.; Martini, G. Development of Measurement Methodology for Sub 23 Nm Particle Number (PN) Measurements. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Prac. Mobil. 2020, 3, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Manfredi, U.; Martini, G. Engine Exhaust Solid Sub-23 Nm Particles: I. Literature Survey. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Vanhanen, J.; Väkevä, M.; Martini, G. Investigation of Vehicle Exhaust Sub-23 Nm Particle Emissions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, H.; Inomata, S.; Tanimoto, H. Particle and VOC Emissions from Stoichiometric Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicles and Correlation between Particle Number and Mass Emissions. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Song, B.; Quan, Y. Impact of Test Cycle on Mass, Number and Particle Size Distribution of Particulates Emitted from Gasoline Direct Injection Vehicles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinola, S.; Leblanc, M.; Rouleau, L.; Dunand, X.; Baltzopoulou, P.; Chasapidis, L.; Deloglou, D.; Melas, A.D.; Konstandopoulos, A.G.; Rüggeberg, T.; et al. Measurement of Sub-23 Nm Particles Emitted by Gasoline Direct Injection Engine with New Advanced Instrumentation; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler, P.; Schreiber, D.; Schröter, K. Characterization of the Emission of Particles Larger than 10 Nm in the Exhaust of Modern Gasoline and CNG Light Duty Vehicles. Fuel 2021, 291, 120074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Valverde, V.; Kontses, A.; Melas, A.; Martini, G.; Balazs, A.; Andersson, J.; Samaras, Z.; Dilara, P. Particle Number Emissions of a Euro 6d-Temp Gasoline Vehicle under Extreme Temperatures and Driving Conditions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaras, G.; Zacharof, N.-G.; Ciuffo, B. Fuel Consumption and CO2 Emissions from Passenger Cars in Europe—Laboratory versus Real-World Emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 60, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Komnos, D.; Fontaras, G. Impacts of Extreme Ambient Temperatures and Road Gradient on Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of a Euro 6d-Temp Gasoline Vehicle. Energies 2021, 14, 6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, T.; Stolten, D. The Impact of Drive Cycles and Auxiliary Power on Passenger Car Fuel Economy. Energies 2018, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K. Comparative Evaluation of the Effect of Vehicle Parameters on Fuel Consumption under NEDC and WLTP. Energies 2020, 13, 4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Xiang, G. Testing and Evaluation of Cold-Start Emissions in a Real Driving Emissions Test. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 86, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Meloche, E.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Black Carbon Emissions in Gasoline Exhaust and a Reduction Alternative with a Gasoline Particulate Filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6027–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, C.; Malashchuk, V.; Kubinski, D.; Hagen, G.; Moos, R. Catalyst State Diagnosis of Three-Way Catalytic Converters Using Different Resonance Parameters—A Microwave Cavity Perturbation Study. Sensors 2019, 19, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Astorga, C. Impact of Cold Temperature on Euro 6 Passenger Car Emissions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, H.; Kittelson, D.; Northrop, W. Particle Emissions from Light-Duty Vehicles during Cold-Cold Start. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, S. Characterizing Particulate Matter Emissions from GDI and PFI Vehicles under Transient and Cold Start Conditions. Fuel 2017, 189, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorscheidt, F.; Pischinger, S.; Claßen, J.; Sterlepper, S.; Krysmon, S.; Görgen, M.; Nijs, M.; Straszak, P.; Abdelkader, A.M. Development of a Novel Gasoline Particulate Filter Loading Method Using a Burner Bench. Energies 2021, 14, 4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piock, W.; Hoffmann, G.; Berndorfer, A.; Salemi, P.; Fusshoeller, B. Strategies towards Meeting Future Particulate Matter Emission Requirements in Homogeneous Gasoline Direct Injection Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorscheidt, F.; Sterlepper, S.; Görgen, M.; Nijs, M.; Claßen, J.; Yadla, S.K.; Maurer, R.; Pischinger, S.; Krysmon, S.; Abdelkader, A. Gasoline Particulate Filter Characterization Focusing on the Filtration Efficiency of Nano-Particulates down to 10 Nm; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tian, G.; Sorniotti, A.; Karci, A.E.; Di Palo, R. Review of Thermal Management of Catalytic Converters to Decrease Engine Emissions during Cold Start and Warm Up. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 147, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rood, S.; Eslava, S.; Manigrasso, A.; Bannister, C. Recent Advances in Gasoline Three-Way Catalyst Formulation: A Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getsoian, A.B.; Theis, J.R.; Paxton, W.A.; Lance, M.J.; Lambert, C.K. Remarkable Improvement in Low Temperature Performance of Model Three-Way Catalysts through Solution Atomic Layer Deposition. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, C.; Nakatani, T.; Miyairi, Y.; Yuuki, K.; Makino, M.; Kurachi, H.; Heuss, W.; Kuki, T.; Furuta, Y.; Kattouah, P.; et al. New Particulate Filter Concept to Reduce Particle Number Emissions; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, S. Reduction of Particle Emissions from Gasoline Vehicles with Direct Fuel Injection Systems Using a Gasoline Particulate Filter. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Cocker, D.R.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Brezny, R.; Geller, M.; Karavalakis, G. Gasoline Particulate Filters as an Effective Tool to Reduce Particulate and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Vehicles: A Case Study with Two GDI Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Haag, R.; Zeyer, K.; Mohn, J.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Heeb, N.V. Effects of Four Prototype Gasoline Particle Filters (GPFs) on Nanoparticle and Genotoxic PAH Emissions of a Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Vehicle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10709–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostenidou, E.; Martinez-Valiente, A.; R’Mili, B.; Marques, B.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Durand, A.; André, M.; Liu, Y.; Louis, C.; Vansevenant, B.; et al. Technical Note: Emission Factors, Chemical Composition, and Morphology of Particles Emitted from Euro 5 Diesel and Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles during Transient Cycles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 4779–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, C.; Andersson, J.T. Overview of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds (PAC). Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, N.; Min, K. Numerical Investigation of Soot Emission in Direct-Injection Spark-Ignition Engines Using a Detailed Soot Model Framework; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Differences between Tailpipe and Dilution Tunnel Sub-23 Nm Nonvolatile (Solid) Particle Number Measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Dong, W.; Yu, X. Effects of Coolant Temperature Coupled with Controlling Strategies on Particulate Number Emissions in GDI Engine under Idle Stage. Fuel 2018, 225, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihersaari, H.; Pirjola, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Kulmala, K.; Keskinen, J.; Rönkkö, T. Particulate Emissions of a Modern Diesel Passenger Car under Laboratory and Real-World Transient Driving Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Effect of Sampling Conditions on the Sub-23 Nm Nonvolatile Particle Emissions Measurements of a Moped. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Pham, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Durbin, T.D.; Karavalakis, G.; Kittelson, D.; Jung, H. Impacts of Exhaust Transfer System Contamination on Particulate Matter Measurements. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2020, 6, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saffaripour, M.; Chan, T.W.; Liu, F.; Thomson, K.A.; Smallwood, G.J.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Effect of Drive Cycle and Gasoline Particulate Filter on the Size and Morphology of Soot Particles Emitted from a Gasoline-Direct-Injection Vehicle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11950–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boger, T.; Rose, D.; Nicolin, P.; Gunasekaran, N.; Glasson, T. Oxidation of Soot (Printex® U) in Particulate Filters Operated on Gasoline Engines. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Chirico, R.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Clairotte, M.; Adam, T.; Martini, G.; Heringa, M.F.; Richter, R.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U. Evaluation of the Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Protocol to Remove the Vehicles’ Exhaust Aerosol Volatile Phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5106–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Melas, A.D.; Valverde, V.; Clairotte, M. Uncertainty of Laboratory and Portable Solid Particle Number Systems for Regulatory Measurements of Vehicle Emissions. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Melas, A.D.; Lähde, T.; Martini, G. Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review. Vehicles 2020, 2, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.; James, S.C.; Yoon, S.S. Experimental and Numerical Simulations of Spray Impingement and Combustion Characteristics in Gasoline Direct Injection Engines under Variable Driving Conditions. Flow Turbul. Combust 2016, 96, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Carriero, M.; Martini, G.; Bergmann, A.; Pongratz, H.; Joergl, H. Comparison of Particle Number Measurements from the Full Dilution Tunnel, the Tailpipe and Two Partial Flow Systems; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Boger, T.; Nicolin, P.; Jung, F.; Collins, T.; Ingram-Ogunwumi, R. Aftertreatment Technologies Supporting the Path towards Zero-Impact Emissions. In Proceedings of the 30th Aachen Colloquium Sustainable Mobility, Aachen, Germany, 4–6 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa, K.; Sakurai, T.; Jetter, J.J. Development of a Predictive Model for Gasoline Vehicle Particulate Matter Emissions. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Lax, D.; Gunter, G.C.; Hendren, J.; Kubsh, J.; Brezny, R. Assessment of the Fuel Composition Impact on Black Carbon Mass, Particle Number Size Distributions, Solid Particle Number, Organic Materials, and Regulated Gaseous Emissions from a Light-Duty Gasoline Direct Injection Truck and Passenger Car. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10452–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).