Solochrome Dark Blue Azo Dye Removal by Sonophotocatalysis Using Mn2+ Doped ZnS Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
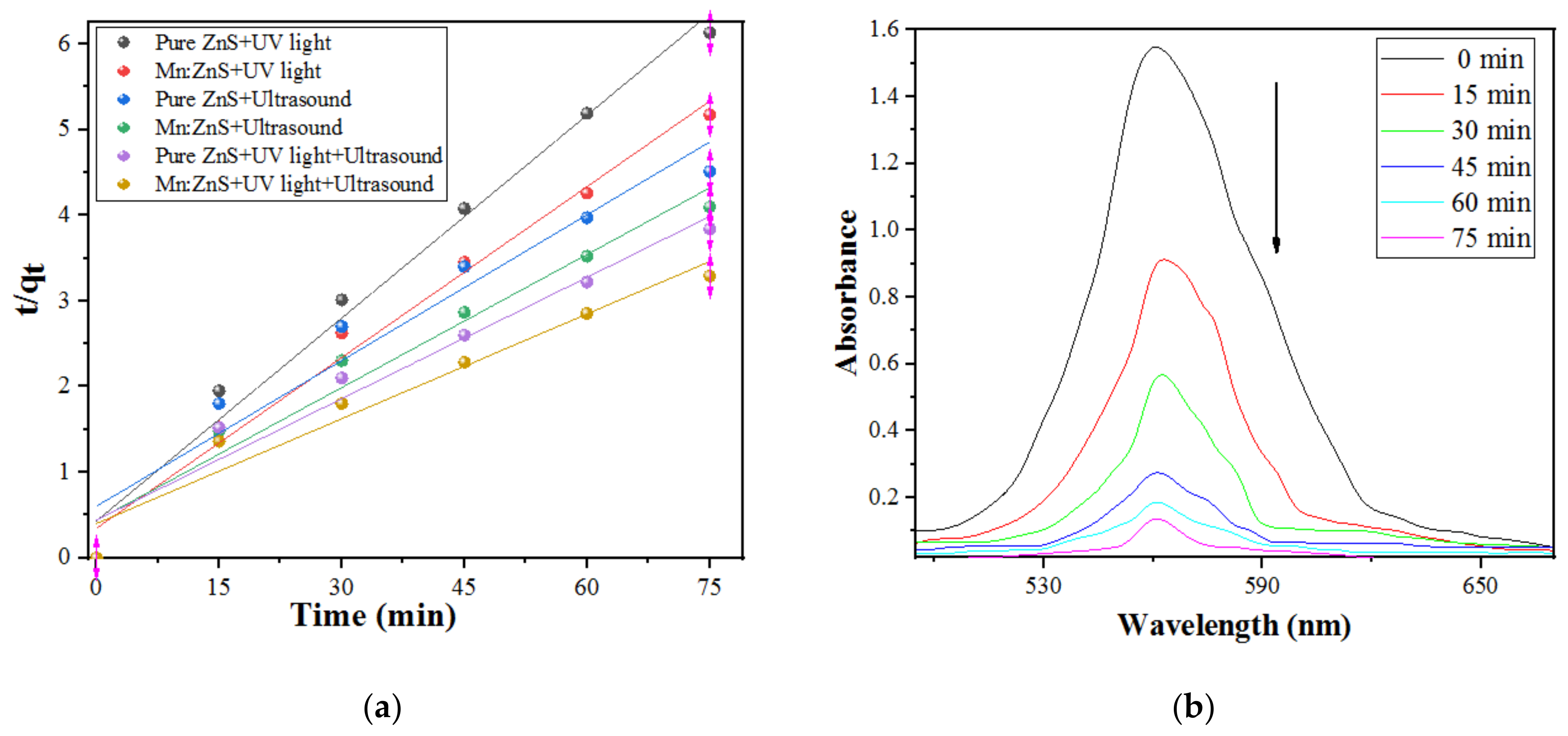
2.2. Efficiencies of Various Methods for SDB Degradation
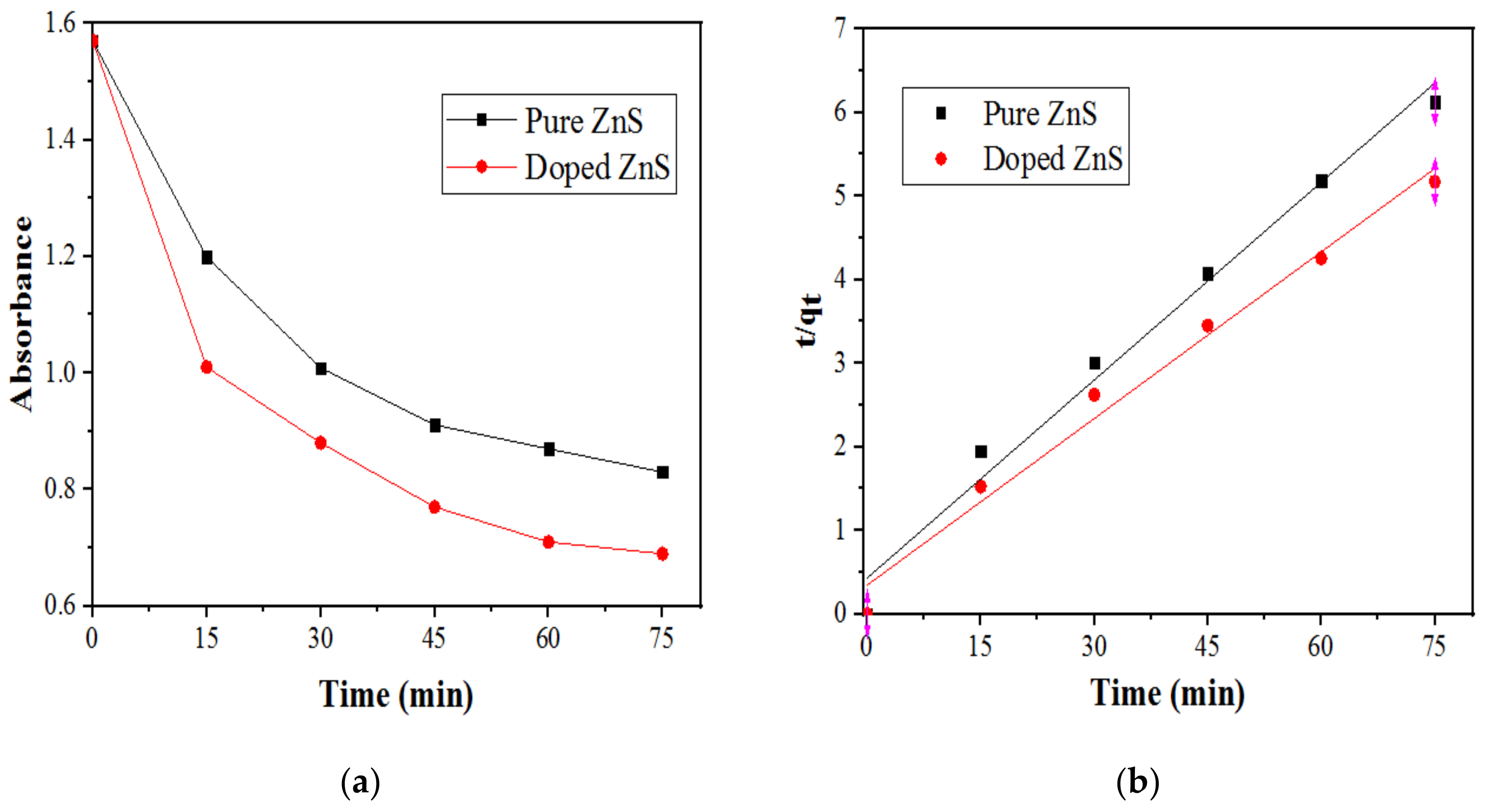
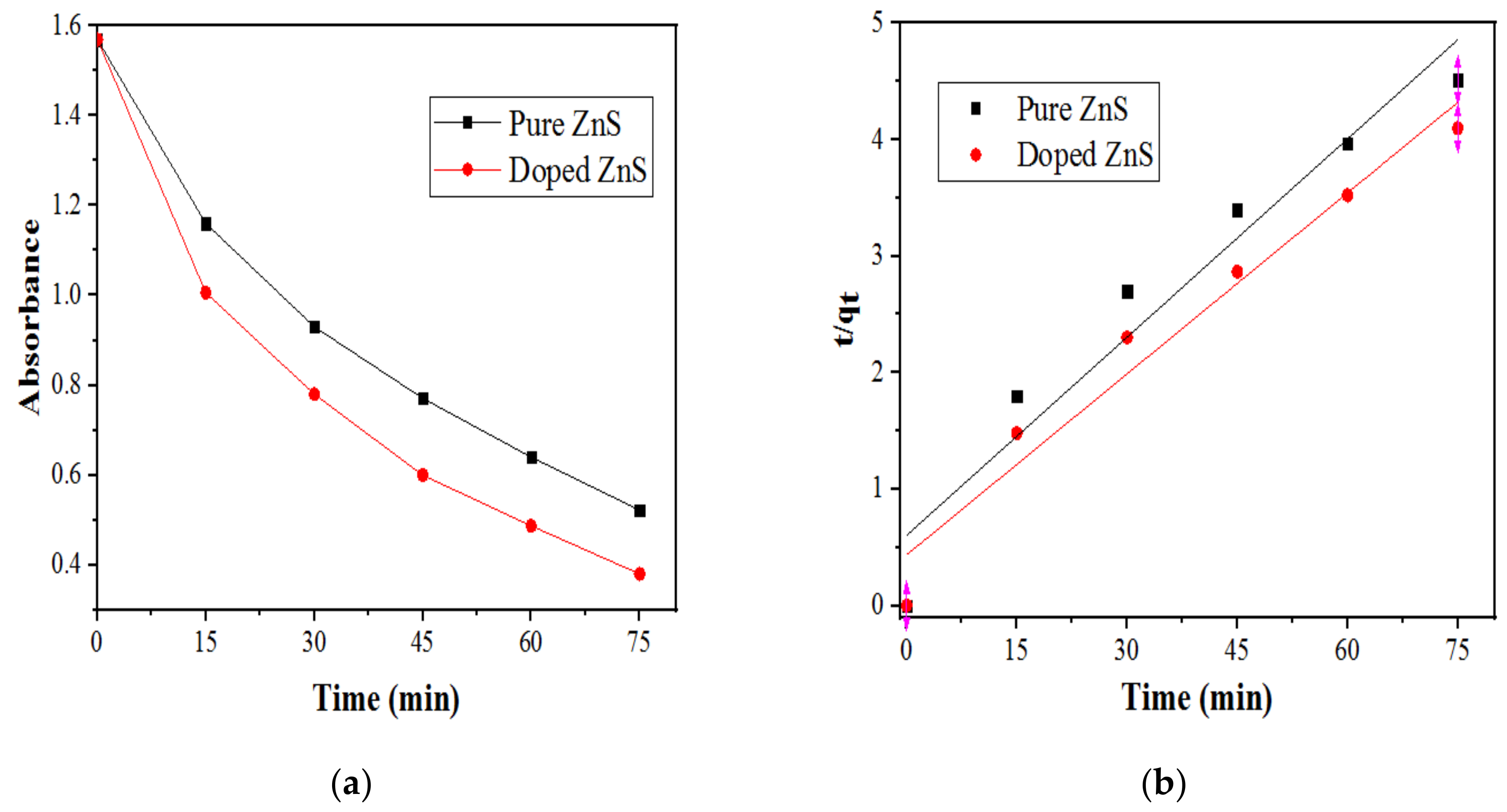
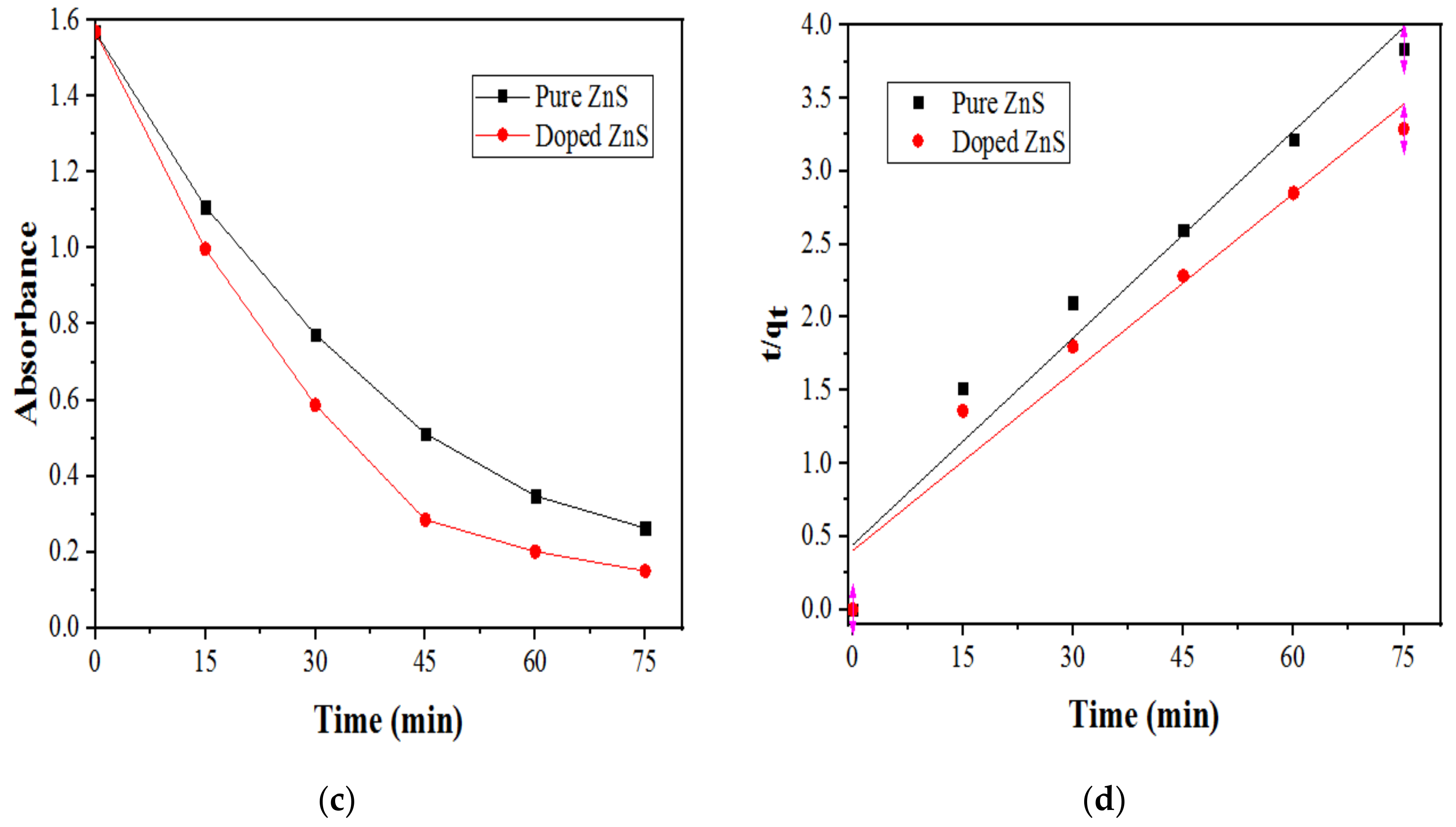
2.2.1. Kinetic Study
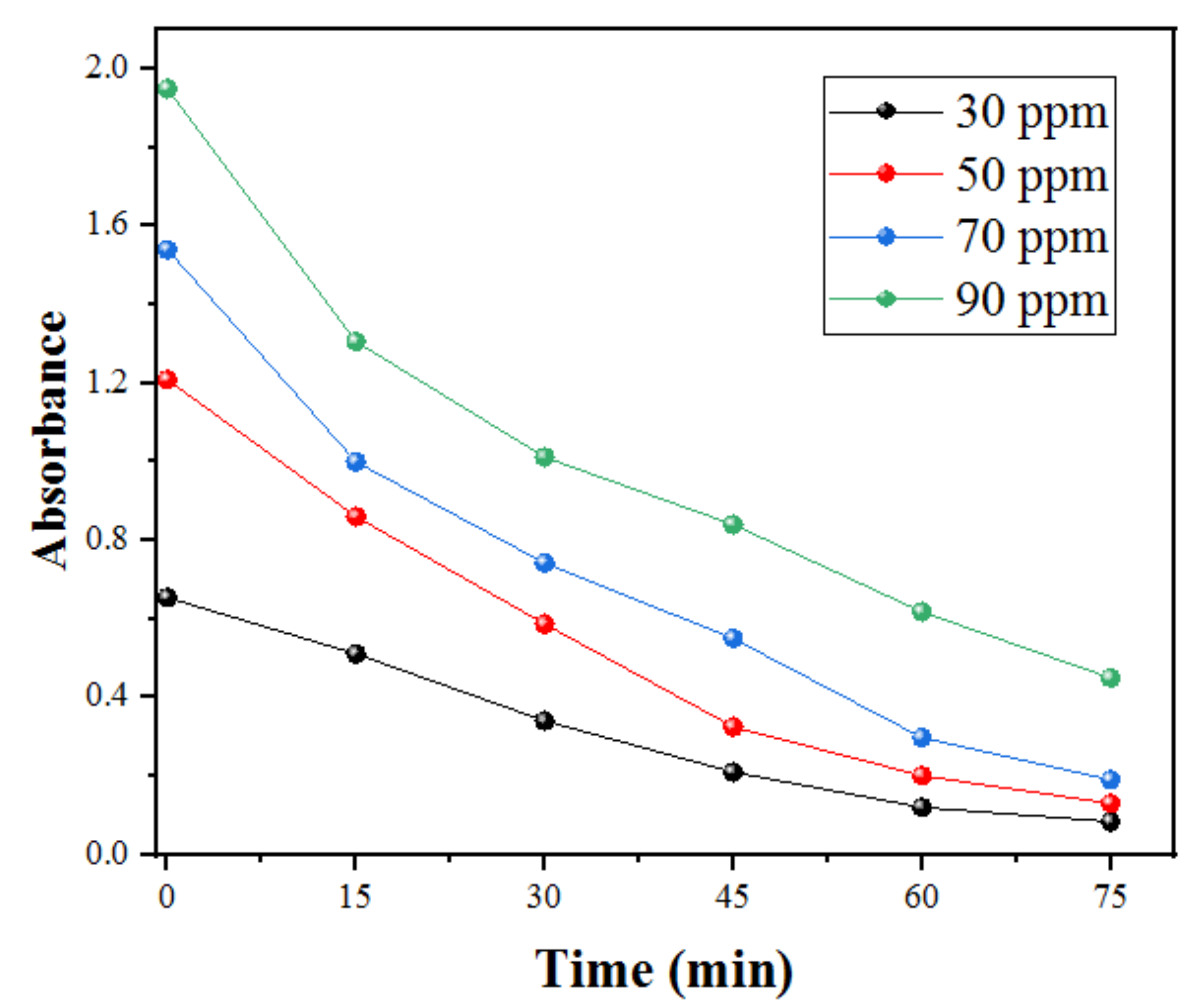
2.2.2. Effect of the Initial SDB Concentration
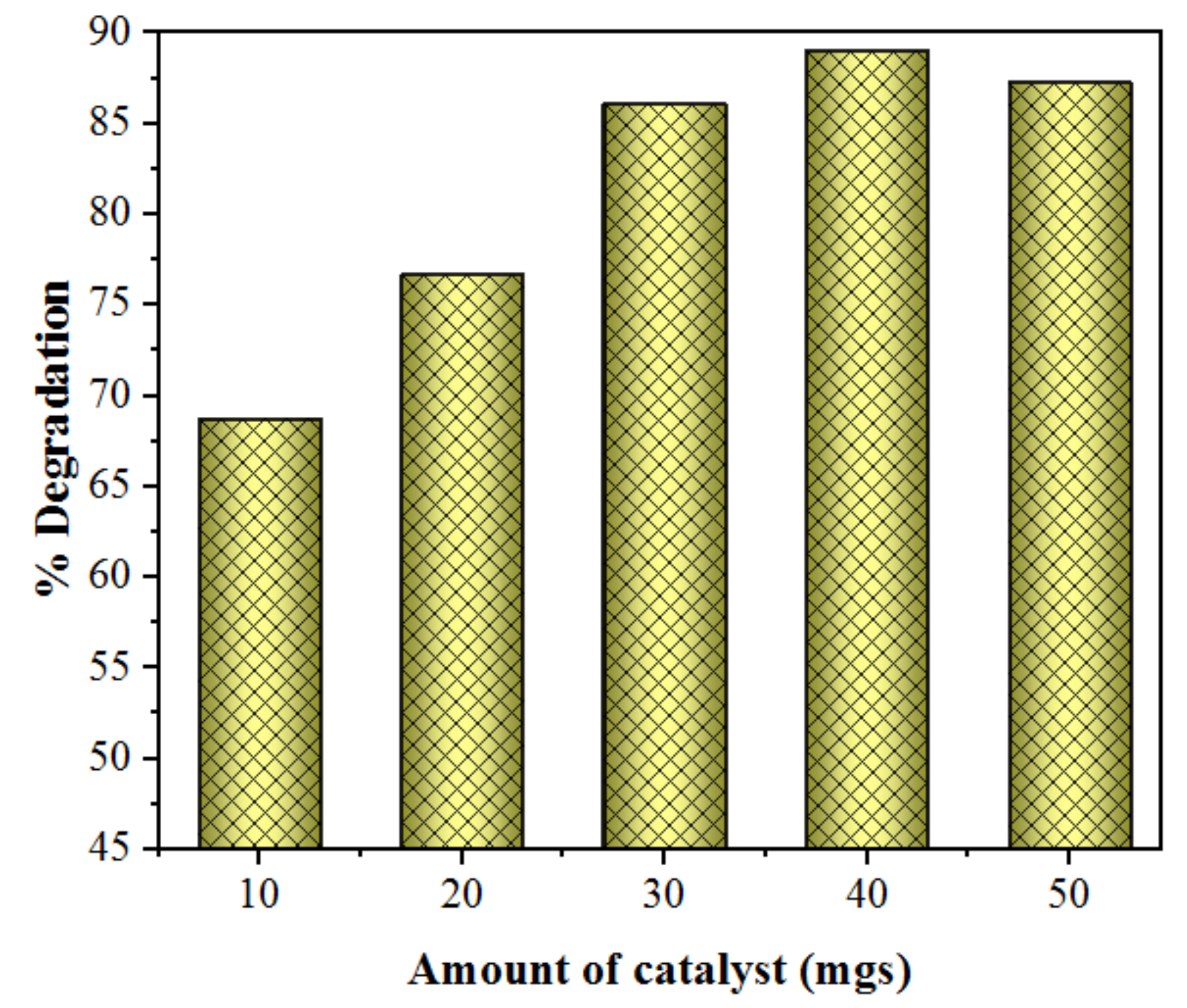
2.2.3. Effect of Catalyst Loading
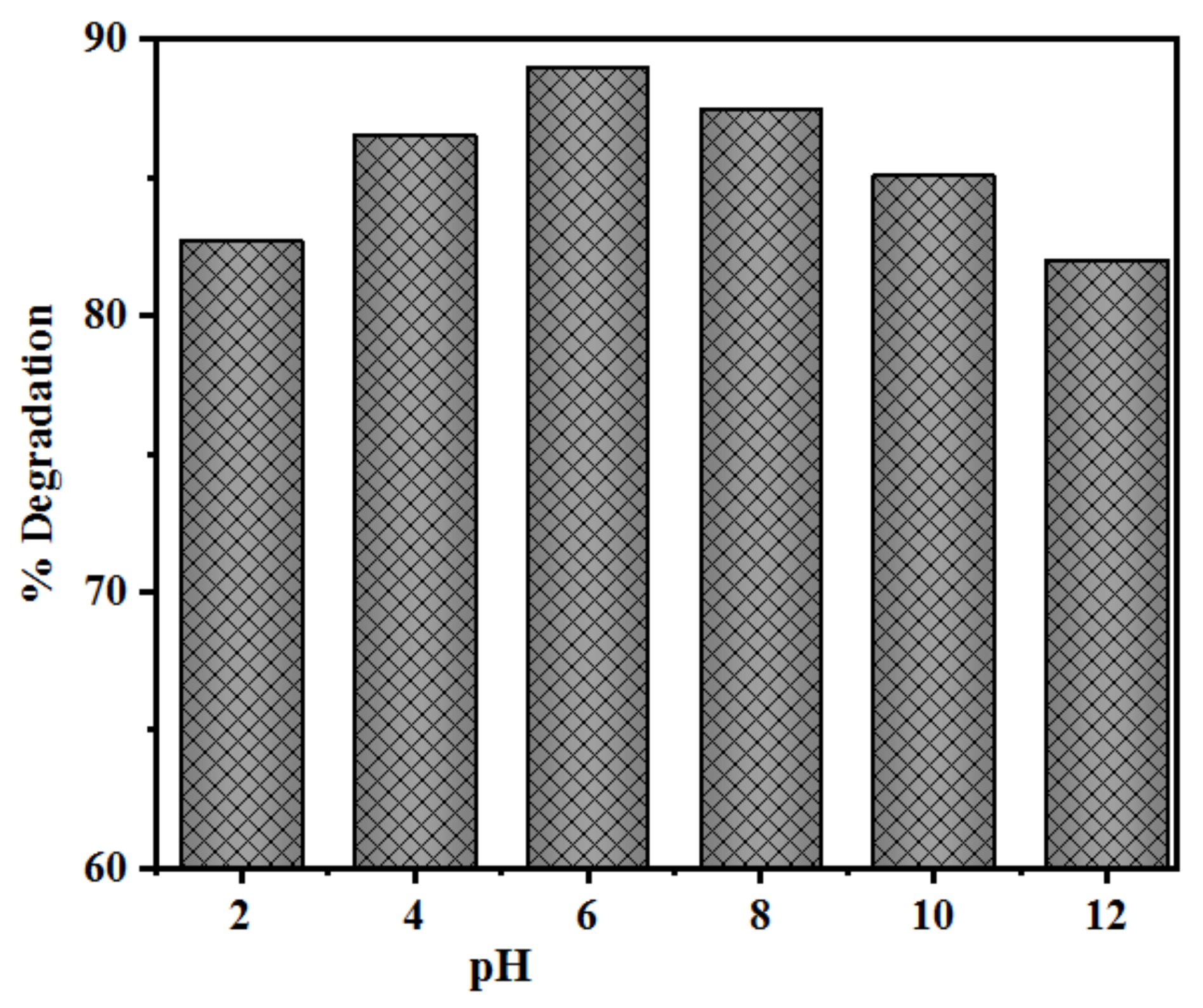
2.2.4. Effect of Initial pH
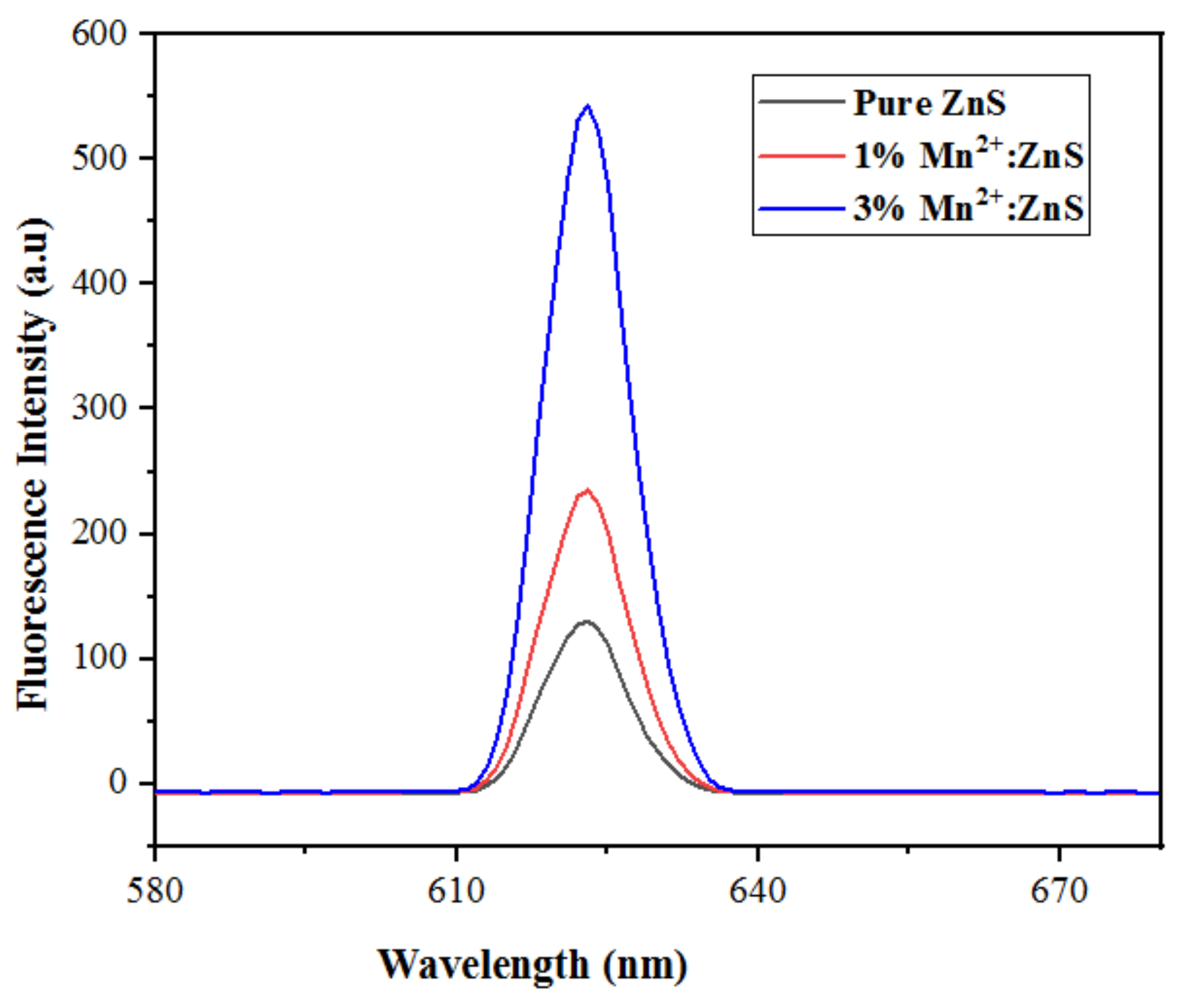
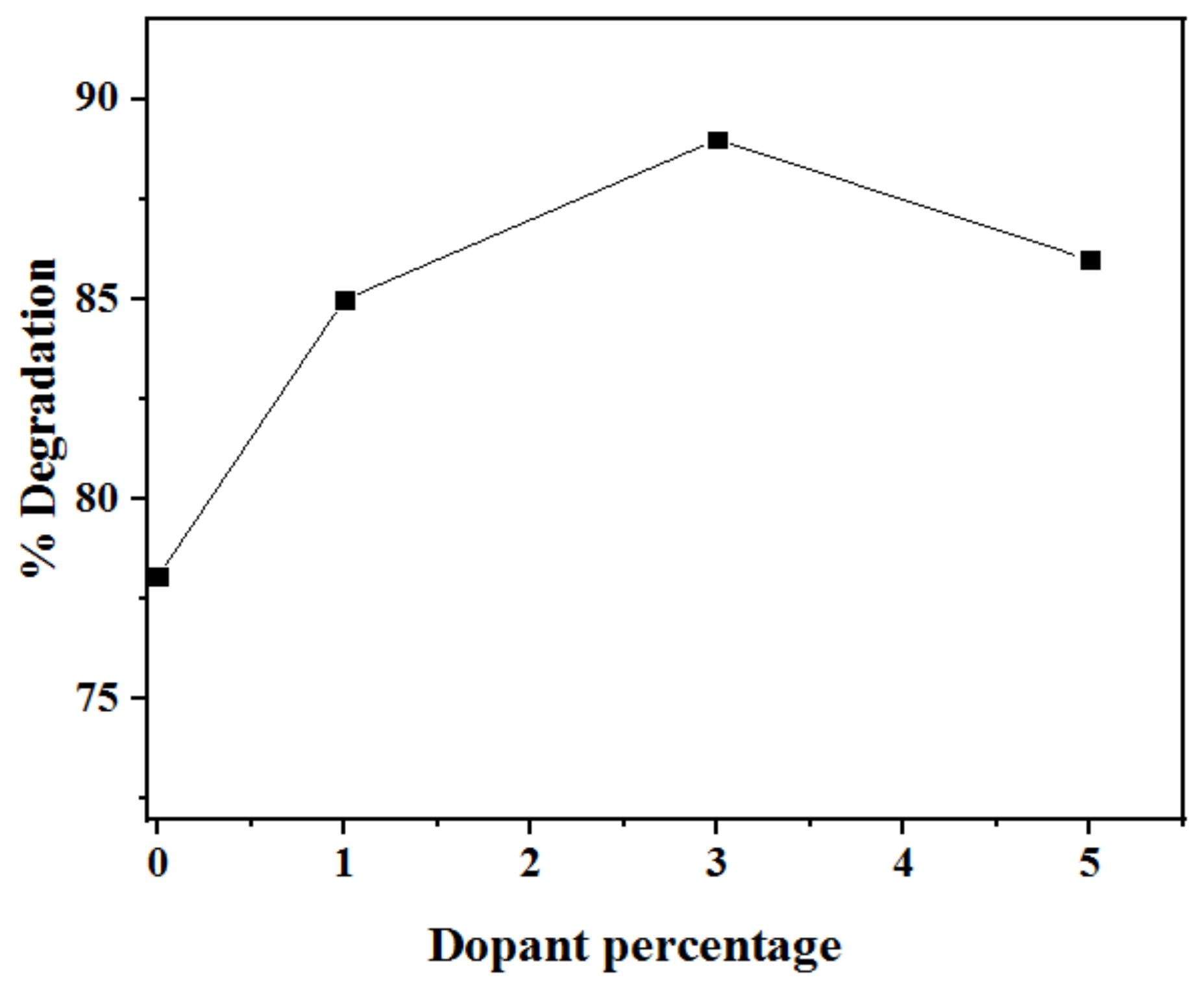
2.2.5. Effect of Mn2+ Dopant Concentration
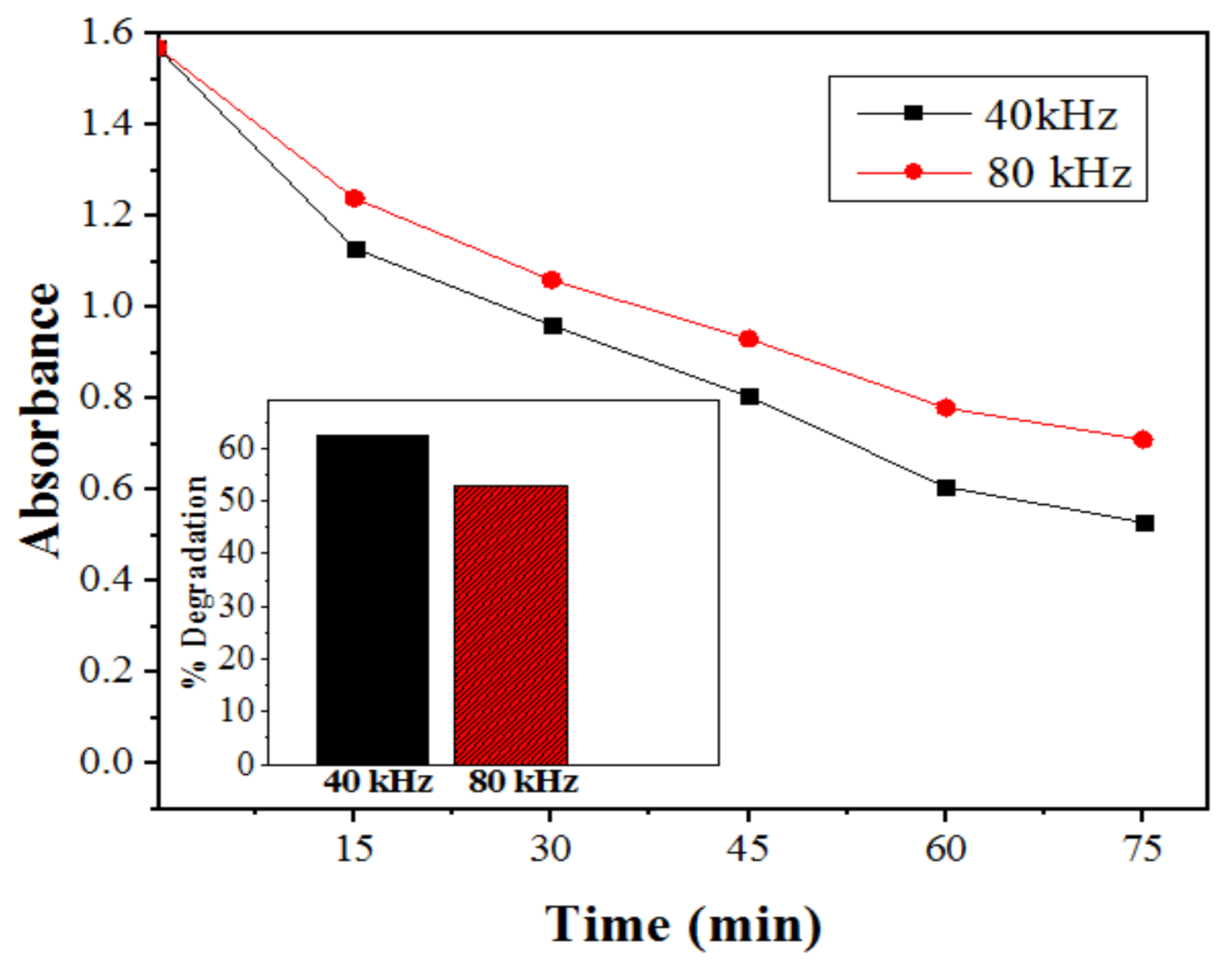
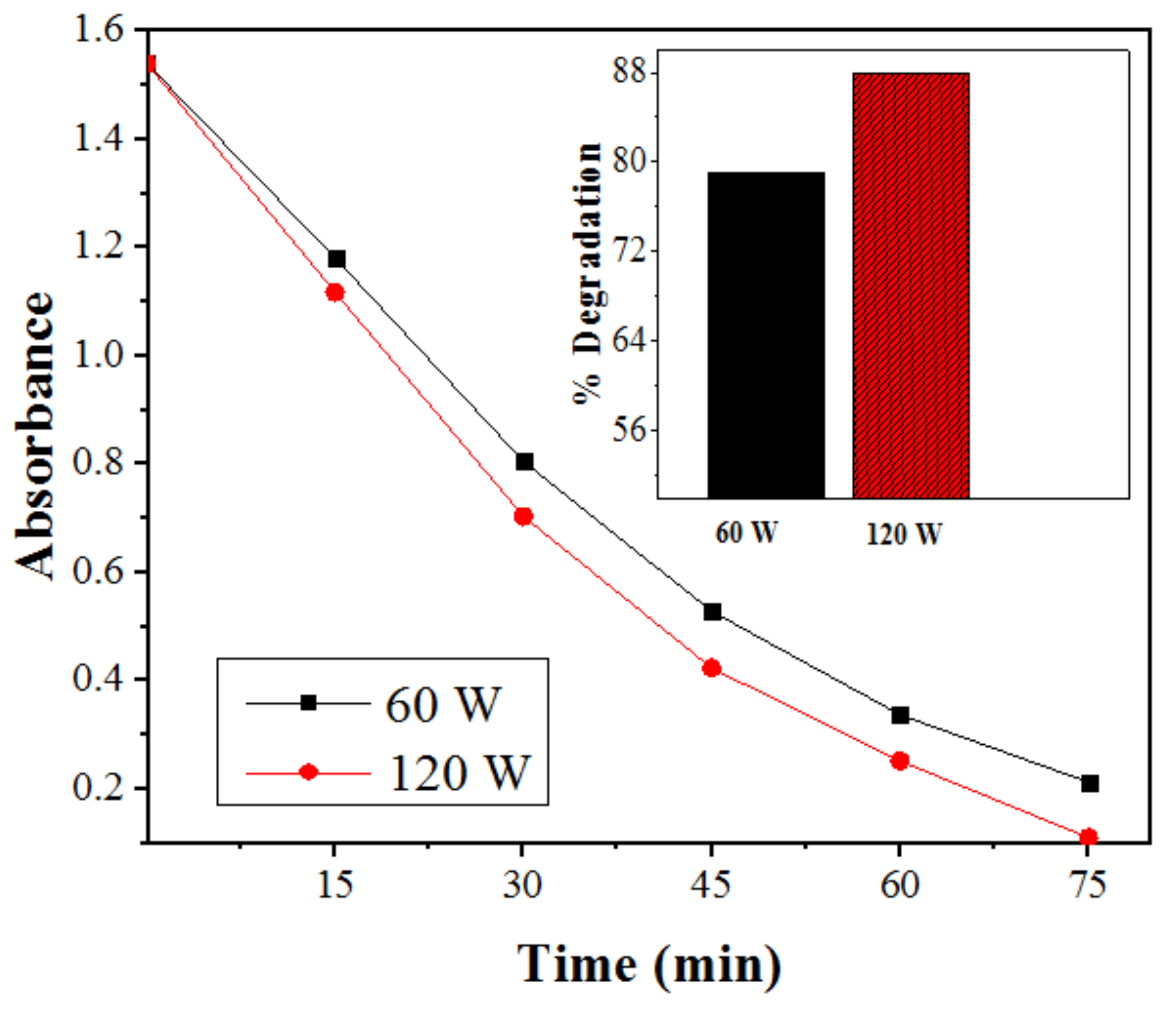
2.2.6. Effect of Ultrasonic Power on Degradation of SDB
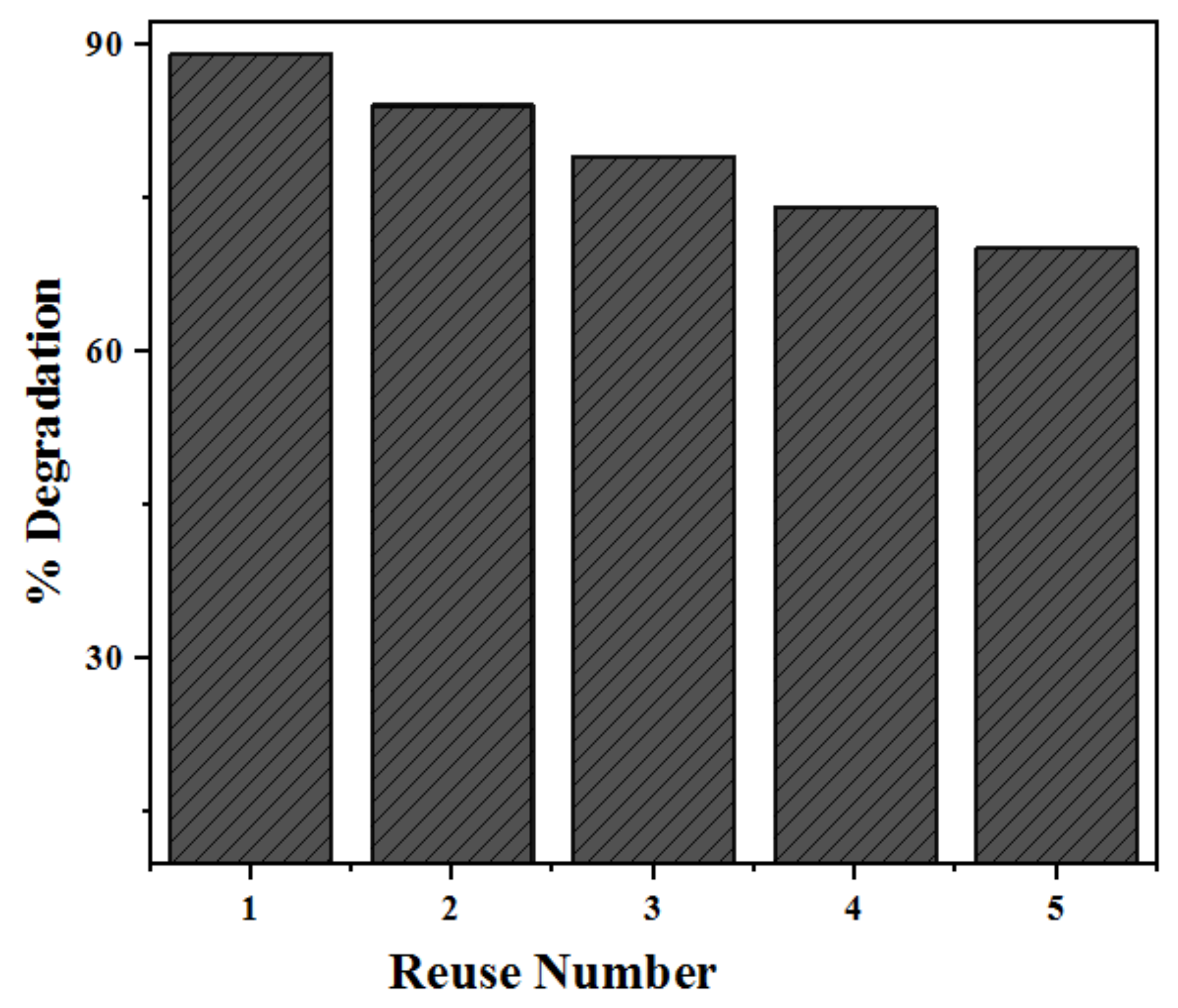
2.3. Re-Usability and Stability of Photocatalysts
2.4. Mechanism of the Sonophotocatalytic Degradation
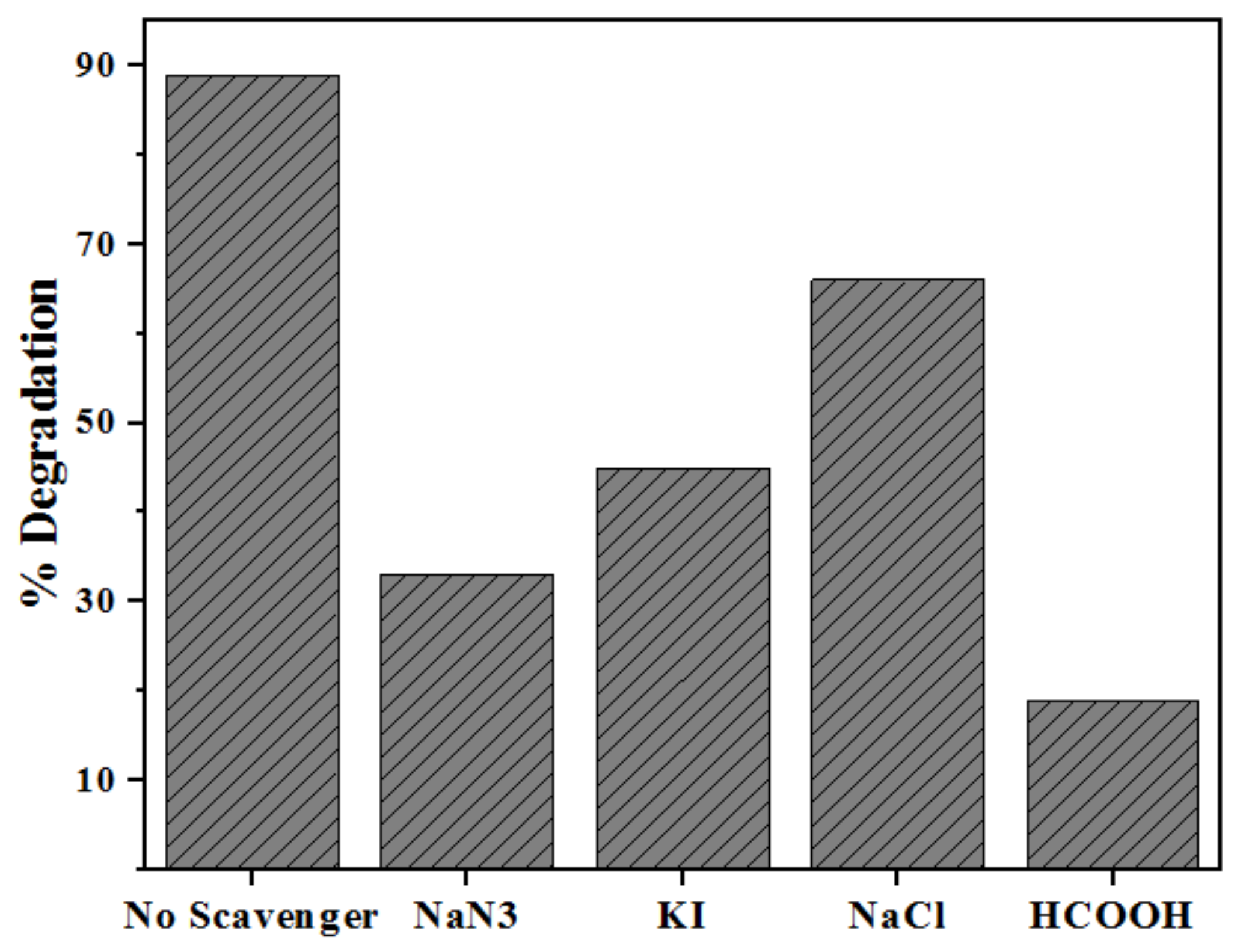
2.5. Role of Radical Trapping Agents
2.6. Degradation Products of Mn2+:ZnS Assisted Photodegradation of SDB
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Preparation of Quantum Dots
3.4. Quantum Dot Based Catalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugumar, S.; Thangam, B. BiodEnz: A database of biodegrading enzymes. Biomed. Inform. 2012, 8, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Munter, R. Advanced oxidation processes—Current status and prospects. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Chen, X. Luminescent perovskite quantum dots: Synthesis, microstructures, optical properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kumari, A.; Singh, R.R. Tunable narrow emission in ZnS/CdS/ZnS quantum well structures prepared by aqueous route. Opt. Mater. 2017, 69, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Singh, A.K.; Carabineiro, S. Carabineiro, Assessing the photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolone norfloxacin by Mn:ZnS quantum dots: Kinetic study, degradation pathway and influencing factors. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.R.; Balkus, K.J. Mesoporous molecular sieve derived TiO2 Nanofibers doped with SnO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Takeuchi, M.; Cuong, T.M.; Zhang, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Anpo, M. Recent advances in visible light responsive Titanium Oxide-based photocatalysis. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2010, 36, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.G.; Chao, C.C.; Kuo, F.T. Enhancement of the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 catalysts via transition metal modification. Catal. Today 2004, 97, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Manickam, S. Recent advancements in the sonophotocatalysis (SPC) and doped-sonophotocatalysis (DSPC) for the treatment of recalcitrant hazardous organic water pollutants. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppolian, B.; Park, J.S.; Choi, H. Effect of fenton-like oxidation on enhanced oxidative degradation of para-chlorobenzoic acid by ultrasonic Irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, C.; Theron, P.; Pichat, P.; Petrier, C. Evaluation of 1-Octanol degradation by photocatalysis and ultrasound using SPME. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics; New York Oxford Univ. Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Suslick, K.S.; Flannigan, D.J. Inside a collapsing bubble: Sonoluminescence and the conditions during cavitation. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciawi, E.; Rae, J.; Kumar, M.A.; Grieser, F. Determination of temperatures within acoustically generated bubbles in aqueous solutions at different ultrasound frequencies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 13656–13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, M.; Grieser, F.; Kumar, M.A. Sonophotocatalytic degradation of Paracetamol using TiO2 and Fe3+. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selli, E.; Bianchi, C.L.; Pirola, C.; Bertelli, M. Degradation of Methyl tert-butyl ether in water: Effects of the combined use of sonolysis and photocatalysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Rozas, O.; Vergara, C.; Mansilla, H.D.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A.; Anandan, S. Sonophotocatalytic mineralization of norflurazon in aqueous environment. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babu, S.G.; Vinoth, R.; Neppoliana, B.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kumar, M.A. Diffused sunlight driven highly synergistic pathway for complete mineralization of organic contaminants using reduced graphene oxide supported photocatalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 291, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.G.; Karthik, P.; John, M.C.; Lakhera, S.K.; Kumar, M.A.; Khim, J. Neppolian, synergistic effect of sono-photocatalytic process for the degradation of organic pollutants using CuO-TiO2/rGO. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 50, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Rozas, O.; Mansilla, H.D.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A.; Anandan, S. Low frequency ultrasound (42 kHz) assisted degradation of Acid Blue 113 in the presence of visible light driven rare earth nanoclusters loaded TiO2 nanophotocatalysts. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, V. Visible light induced sonophotocatalytic degradation of reactive red dye 198 using dye sensitized TiO2. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppolian, B.; Doronila, A.; Grieser, F.; Kumar, M.A. Simple and efficient sonochemical method for the oxidation of Arsenic (III) to Arsenic (V). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6793–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, O.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Zaki, Z.I.; Mohamed, R.M. Zinc oxide thin films prepared by thermal evaporation deposition and its photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, M.R.; Akshatha, G.; Srikantaswamy, S. Photocatalytic dye degradation and biological activities of Fe2O3/Cu2O nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8557–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samadi, M.; Zirak, M.; Naseri, A.; Kheirabadi, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Design and tailoring of one-dimensional ZnO nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes: A review. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2019, 45, 2197–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Rajabi, H.R. Study of photocatalytic activity of ZnS quantum dots as efficient nanoparticles for removal of methyl violet: Effect of ferric ion doping. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.R.; Farsi, M. Effect of transition metal ion doping on the photocatalytic activity of ZnS quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization and application for dye decolorization. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 399, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, M.; Fu, X. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes by ZnIn2S4 microspheres under visible light irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4433–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Ma, Q.; Su, X. Aqueous synthesis of mercaptopropionic acid capped Mn2+-doped ZnSe quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shen, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, F.; Han, H.; Li, C. CompositeSr2TiO4/SrTiO3(La,Cr) heterojunction based photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7905–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, R.N.; Gallagher, D.; Hong, X.; Nurmikko, A. Optical properties of manganese-doped nanocrystals of ZnS. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, V.L.; Schlamp, M.C.; Alivisatos, A.P. Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature 1994, 370, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, V.I.; Ivanov, S.A.; Nanda, J.; Achermann, M.; Bezel, I.; McGuire, J.A. Piryatinski, single-exciton optical gain in semiconductor nanocrystals. Nature 2007, 447, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, P.V.; Gamelin, D.R. High-temperature ferromagnetism in Ni2+-doped ZnO aggregates prepared from colloidal diluted magnetic semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 1572021–1572024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanif, K.M.; Meulenberg, R.W.; Strouse, G.F. Magnetic ordering in doped Cd (1−x) Co(x)Se diluted magnetic quantum dots. J. Am. Chem.Soc. 2002, 124, 11495–11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenham, N.C.; Peng, X.; Alivisatos, A.P. Charge separation and transport in conjugated-polymer/semiconductor-nanocrystal composites studied by photoluminescence quenching and photoconductivity. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1996, 54, 17628–17637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Durga, I.K.; Varma, C.V.T.; Punnoose, D.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.J. Enhance the performance of quantum dot-sensitized solar cell by manganese-doped ZnS films as a passivation layer. Org. Electron. 2015, 26, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Wu, H.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. A highly sensitive fluorescent turn-on biosensor for glycoproteins based on boronic acid functional polymer capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 995, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diestra, D.D.; Huarac, J.B.; Rincon, D.P.; Gonzalez-Feliciano, J.A.; Gonzalez, C.I.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Biocompatible ZnS:Mn quantum dots for reactive oxygen generation and detection in aqueous media. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 46101–46114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.C.; Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive non isotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, J.; Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Paul, L.J. Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots–an effective nanoscale sensor. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Guo, M.; Tan, J.; Huang, S.; Tang, Y.; Tan, L.; Liang, Y. The fabrication of highly ordered fluorescent molecularly imprinted mesoporous microspheres for the selective sensing of sparfloxacinin biological samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Goorskey, D.; Thessing, J.; Peng, X.G. An alternative of CdSe nanocrystal emitters: Pure and tunable impurity emissions in ZnSe nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17586–17587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, G.; Ekanayaka, T.K.; Yost, A.J.; Paudel, T.R. Absorption enhancement by transition metal doping in ZnS. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, V.; Praba, K.; Murugadoss, G. Synthesis and study of optical properties of transition metals doped ZnS nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 96, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, D.; Rajendran, K.V. Enhanced photoluminescence of ZnS nanoparticles doped with transition and rare earth metallic ions. Chalcogenide Lett. 2010, 7, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Shi, D.; Qi, J. Comparative studies on the magnetic properties of ZnS nanowires doped with transition metal atoms. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 084338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, D.; Qi, J.; Wang, B. First-principles study on the magnetic properties of transition-metal atoms doped (ZnS)12 cluster. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Malik, M.A.; Alghamdi, Y.G.; Ahmad, K.S.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Chemical bath deposition of Fe-doped ZnS thin films: Investigations of their ferromagnetic and half-metallic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 39, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, J.; Bazzi, H.S.; Cuie, Y.; Fortin, G.R.A.; Winnik, F.M. Maysinger, differences in subcellular distribution and toxicity of green and red emitting CdTe quantum dots. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 83, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, C.; Liedl, T.; Kudera, S.; Pellegrino, T.; Javier, A.M.; Gaub, H.E.; Stolzle, S.; Fertig, N.; Parak, W.J. Cytotoxicity of colloidal CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobara, H.M.; Elsalamony, R.A.; Hassan, S.A. Sonophotocatalytic degradation of eriochrome black-T dye in water using Ti grafted SBA-15. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Kshirsagar, A.; Biswas, R.; Banerjee, S.; Khanna, P.K. Photodegradation of organic dyes based on anatase and rutile TiO2 nano-particles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 2746–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamba, G.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Mishra, A.K. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation of eriochrome black T and eosin blue shade in water using tridoped titania decorated on SWCNTs and MWCNTs: Effect of the type of carbon nanotube incorporated. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149–150, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, V.; Shanker, U.; Kaith, B.S.; Shankar, S. Green synthesis of potassium zinc hexacyanoferrate nanocubes and their potential application in photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26141–26149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Sharma, M.K. Photocatalytic degradation of eriochrome black t using ammonium phosphomolybdate semiconductor. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2010, 8, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Kazeminezhad, I.; Sadollahkhani, A. Photocatalytic degradation of Eriochrome black-T dye using ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.A.; Ferrer, M.M.; Santana, Y.V.B.; Raubach, C.W.; Longo, V.M.; Sambrano, J.R.; Longo, E.; Andres, J.; Li, M.S.; Varela, J.A. Synthesis of wurtzite ZnS nanoparticles using the microwave assisted solvothermal method. J. Alloys. Compds. 2013, 556, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Qi, Y. Greener synthesis and optimization of highly photoluminescence Mn2+-Doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Lumin. 2015, 158, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.P.; Ou, S.L.; Yao, P.C.; Wu, B.R.; Wu, D.S. Structural, surface morphology and optical properties of ZnS Films by chemical bath deposition at various Zn/S molar ratios. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 594952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.R.; Farsi, M. Quantum dot based photocatalytic decolorization as an efficient and green strategy for the removal of anionic dye. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.I.; Li, W.; Huang, C.P.; Jung, O.; Ni, C. Study of Nd3+, Pd2+, Pt4+, and Fe3+ dopant effect on photoreactivity of TiO2 nanoparticle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6482–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tauc, J. Optical Properties of Solids; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Pouretedal, H.R.; Keshavarz, M.H.; Yosefi, M.H.; Shokrollahi, A.; Zali, A. Photodegradation of HMX and RDX in the presence of nanocatalyst of zinc sulfide doped with copper. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2009, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mall, M.; Kumar, L. Optical studies of Cd2+ and Mn2+ Co-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, P.E.; Lannoo, M. Calculation of the band gap for small CdS and ZnS crystallites. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 10935–10942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brus, L. Electronic wave functions in semiconductor clusters: Experiment and theory. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Cao, L.; Sua, G.; Liu, W. Synthesis and characterization of Mn doped ZnS d-dots with controllable dual-color emissions. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2012, 367, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Fan, Z. Melamine modulated mercaptopropionic acid capped manganese doped zinc sulphide quantum dots as a room-temperature phosphorescence sensor for detecting clenbuterol in biological fluids. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 202, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Fan, J. Simple and greener synthesis of highly photoluminescence Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots and its surface passivation mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, M.; Sharma, J.K.; Jeon, H.C.; Kang, T.W.; Kumar, S. Effect of pyridine capping on morphological and optical properties of Zns:Mn2+ core–shell quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, M.; Sharma, J.K.; Kumar, S. Morphological and optical behaviour of pyridine capped bio-compatible ZnS quantum dots. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2012, 4, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.D. The infrared spectrum of nicotinic acid. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 4064–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.K.; Branton, A.; Trivedi, D.; Nayak, G.; Bairwa, K.; Jana, S. Spectroscopic characterization of disulfiram and nicotinic acid after biofield treatment. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2015, 6, 1000265. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.J.; Khidhirbrahmendra, V.; Madhavi, J.; Thampy, U.U.; Reddy, C.V.; Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N. Structural, optical, magnetic and thermal investigations on Cr3+ ions doped ZnS nanocrystals by co-precipitation method. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.J.; Khidhirbrahmendra, V.; Avinash, M.; Reddy, N.B.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N. Structural, magnetic and thermal propertiesof Mn2+ doped ZnS nanocrystals for device applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2063, 040006. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, N.; Cholan, S.; Viruthagiri, G.; Gobi, R.; Kannadasan, N. Synthesis and characterization of Ce3+-doped flowerlike ZnS nanorods. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, B.; Das, S.; Saikia, J.; Das, G. Preferential and enhanced adsorption of different dyes on iron oxide nanoparticles: A comparative study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8024–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, S.K.; Sood, S.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K. Photocatalytic degradation of Eriochrome Black T dye using well-crystalline anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 581, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, P.; Sharma, M.; Singh, K.; Pandey, O.P. Synthesis and characterization of Zinc doped nano TiO2 for efficient photocatalytic degradation of Eriochrome Black T. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1536, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Derazkola, S.M.; Ajabshir, S.Z.; Niasari, M.S. Facile hydrothermal and novel preparation of nanostructured Ho2O3 for photodegradation of eriochrome black T dye as water pollutant. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajabshir, S.Z.; Derazkola, S.M.; Niasari, M.S. Schiff-base hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Nd2O3 nanostructures for effective photocatalytic degradation of eriochrome black T dye as water contaminant. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17849–17859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Singhal, S. Highly robust light driven ZnO catalyst for the degradation of eriochrome black T at room temperature. Superlattice Microst. 2015, 83, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritha, B.; Chockalingam, M.P. Photodegradation of eriochrome black-t dye from aqueous medium by photocatalysis. IJPAMS 2017, 116, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Preethi, M.E.L.; Priya, A.; Thiriveni, S. Solar light driven degradation of Eriochrome Black T by photocatalysis. IOSR-JAC 2015, 8, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Siddhi, I.; Disha, D. Bioremediation of azo dye: Eriochrome black t by the novel organism Bacillus lentus. Bio. Disc. 2017, 8, 771. [Google Scholar]
- Deepa, K.P.; Panneerselvam, A.; Thajuddin, N. A Study on the waning effect of oil spill isolated miocroalga Coelastrella Sp. on a synthetic dye, eriochrome black t. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 21, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmalek, F.; Ghezzar, M.R.; Belhadj, M.; Addou, A. Bleaching and degradation of textile dyes by nonthermal plasma process at atmospheric pressure jean-louis brisset. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.N.; Kaur, S.; Khosla, E. Removal of erichrome black t by adsorption on to eucalyptus bark using green technology. Ind. J. Chem. Technol. 2011, 18, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Gu, L.; Yu, H.; Pan, M.; Huang, Y. Preparation of sludge-derived activated carbon by fenton activation and the adsorption of eriochrome black t. Materials 2019, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, J.M.F.; Oliveira, E.S.; Silva, I.N.; de Souza, S.P.M.C.; Fernandes, N.S. Adsorption of Erichrome Black T from aqueous solution onto expanded perlite modified with orthophenanthroline. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2017, 9, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Yang, H.; Xue, D.; Guo, Y.; Qi, F.; Ma, J. Sonolytic and sonophotolytic degradation of carbamazepine: Kinetic and mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Ding, M.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Z. A sono-photocatalyst for humic acid removal from water: Operational parameters, kinetics and mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 57, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Bartels, P.; Mau, U.; Witter, M.; Tumpling, W.V.; Hofmann, J.; Nietzschmann, E. Degradation of the drug diclofenac in water by sonolysisin presence of catalysts. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, N.H.; Tezcanli-Guyer, G.; Belen, R.K.; Apikyan, I.G. Ultrasound as a catalyzer of aqueous reaction systems: The state of the art and environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 29, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Susan, M.A.B.H. Cationic dye removal using novel magnetic/activated charcoal/β-cyclodextrin/alginate polymer nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, V.S. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye and chromium metal from wastewater using nanocrystalline TiO2 semiconductor. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2012, 4, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar, N.; Khataee, A.R. Removal of azo dye C.I. acid red from contaminated water using Fenton, UV/H2O2, UV/H2O2/Fe(II), UV/H2O2/Fe(III) and UV/H2O2/Fe(III)/oxalate processes: A comparative study. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2006, 41, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, C.M.; Cheng, M.Y.; Yu, J.C.; Wong, P.K. Degradation of azo dye procion red MX-5B by photocatalytic oxidation. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.R.; Karimi, F.; Kazemdehdashti, H.; Kavoshic, L. Fast sonochemically-assisted synthesis of pure and doped zinc sulfide quantum dots and their applicability in organic dye removal from aqueous media. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 181, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.R.; Khani, O.; Shamsipur, M.; Vatanpour, V. High-performance pure and Fe3+-ion Doped ZnS quantum dots as green nanophotocatalysts for the removal of malachite green under UV-light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Mao, L. Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of gaseous organic compounds on modified TiO2/AC composite photocatalyst. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Dutta, J. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.M. Heterogeneous photocatalysis: Fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daware, G.B.; Gogate, P.R. Sonochemical degradation of 3-methylpyridine (3MP) intensified using combination with various oxidants. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 67, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivkumar, M.; Pandit, A.B. Ultrasound enhanced degradation of Rhodamine B: Optimization with power density. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tao, M. Removal of organic matter and ammonia nitrogen from landfill leachate by ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, H.; Rajabi, H.R.; Kavoshi, L. Application of decorated magnetic nanophotocatalysts for efficient photodegradation of organic dye: A comparison study on photocatalytic activity of magnetic zinc sulfide and graphene quantum dots. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 397, 112534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, X.; Sun, J.; An, Q. Sonication induced amorphisation in Ag nanowires. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotronatou, A.; Mills, G.; Hoffmann, M.R. Ultrasonic irradiation of p-nitrophenol in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 3630–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Crum, L.A. Encyclopedia of Acoustics; Crocker, M.J., Ed.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Jyothi, K.P.; Yesodharan, S.; Yesodharan, E.P. Yesodharan ultrasound (US), ultraviolet light (UV) and combination (US + UV) assisted semiconductor catalysed degradation of organic pollutants in water: Oscillation in the concentration of hydrogen peroxide formed in situ. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Smirniotis, P. Enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of phenol and chlorophenols by ultrasound. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5958–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazerozohori, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Joohari, S. Photocatalytic degradation of an organic dye in some aqueous buffer solutions using nano titanium dioxide: A kinetic study. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012, 38, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Chitkara, M.; Sandhu, I.S.; Mehta, D.; Kumar, S. Photocatalytic and magnetic properties of Zn1−xCrxO nanocomposites prepared by a co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 30, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Grieser, F. Single bubble sonoluminescence- a chemist’s overview. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2004, 5, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.A.; Cozzoli, P.D. Advanced Wet-Chemical Synthetic Approaches to Inorganic Nanostructures; Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2008; pp. 107–131. [Google Scholar]
- Neppolian, B.; Ciceri, L.; Bianchi, C.L.; Grieser, F.; Kumar, M.A. Sonophotocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol using Bi2O3/TiZrO4 as a visible light responsive photocatalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Wong, K.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Hu, C.; Yu, J.C.; Chan, C.Y.; Wong, P.K. Zn:In(OH)ySz solid solution nanoplates: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7883–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Kansal, S.K. Bi2WO6 nanocuboids: An efficient visible light active photocatalyst for the degradation of levofloxacin drug in aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, N.K.V.; Dore, M. Hydroxyl radical induced decomposition of aliphatic acids in oxygenated and deoxygenated aqueous solutions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1996, 99, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical-review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen-atoms and hydroxyl radicals (•OH/•O) in aqueous-solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Sonntag, C.; Schuchmann, H.P. Peroxyl Radicals in Aqueous Solutions; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, L.; Nayak, S.; Pattnaik, S.P.; Acharya, R.; Parida, K. Resurrection of boron nitride in p-n type-II boron nitride/B-doped-g-C3N4 nanocomposite during solid-state Z-scheme charge transfer path for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Juang, R.C.; Yang, T.C.K.; Juan, J.C. Morphology-controlled synthesis of aeFe2O3 nanocrystals impregnated on g-C3N4eSO3H with ultrafast charge separation for photoreduction of Cr (VI) under visible light. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhade, A.; Tope, D.; Kushare, S. Mercenaria shell powder as a cost-effective and eco-friendly photocatalyst for the degradation of eriochrome black t dye. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2020, 44, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
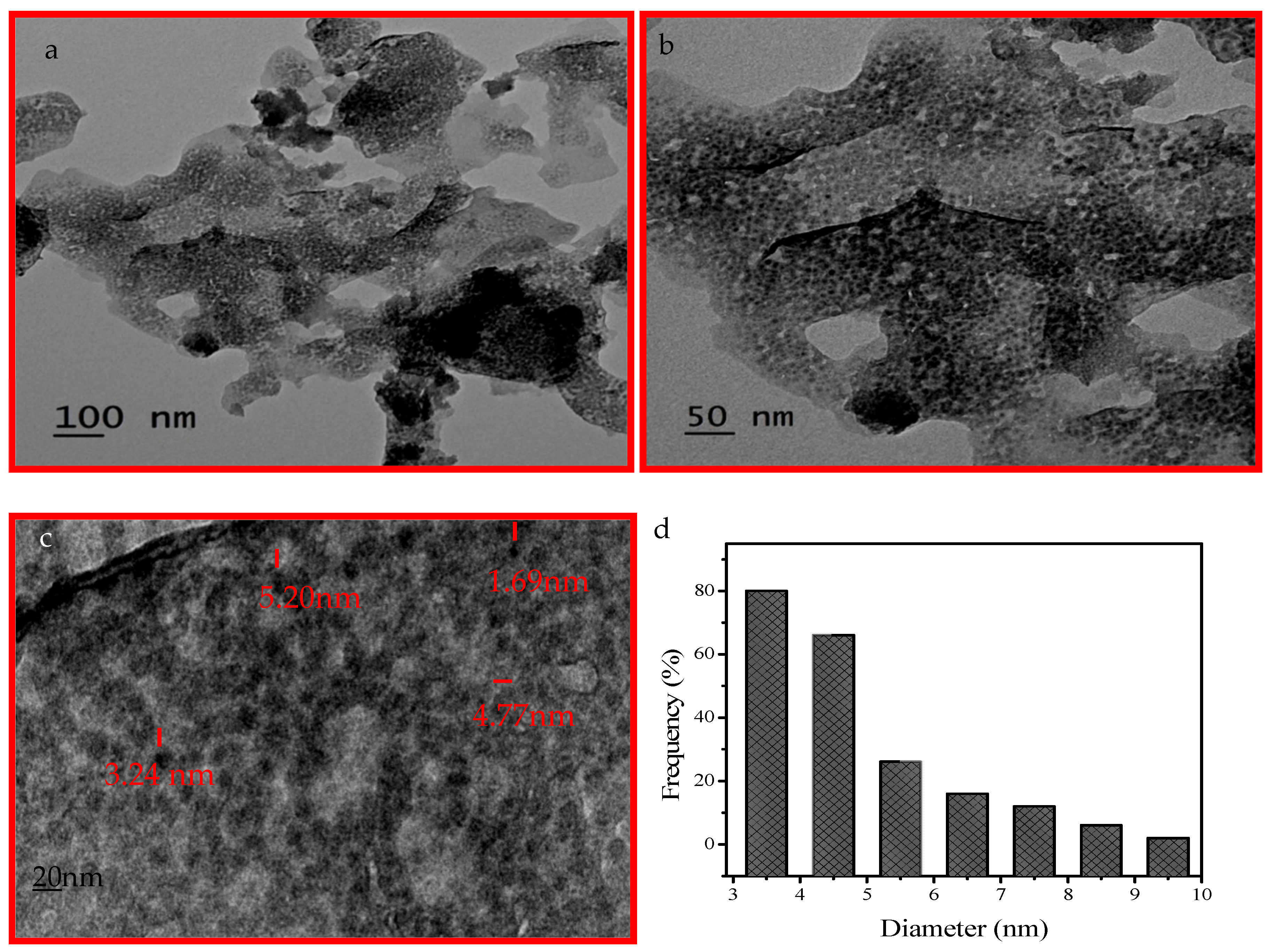
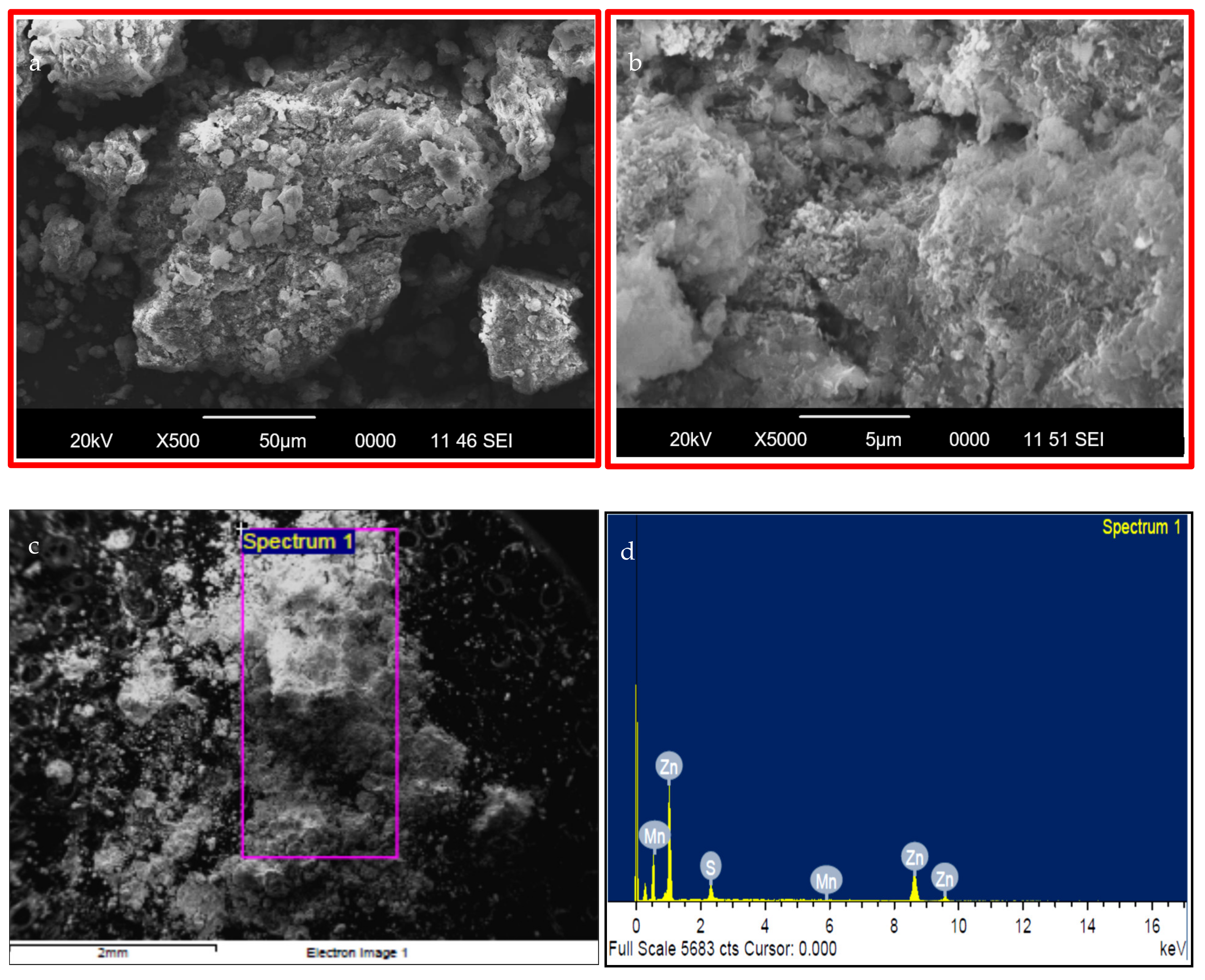

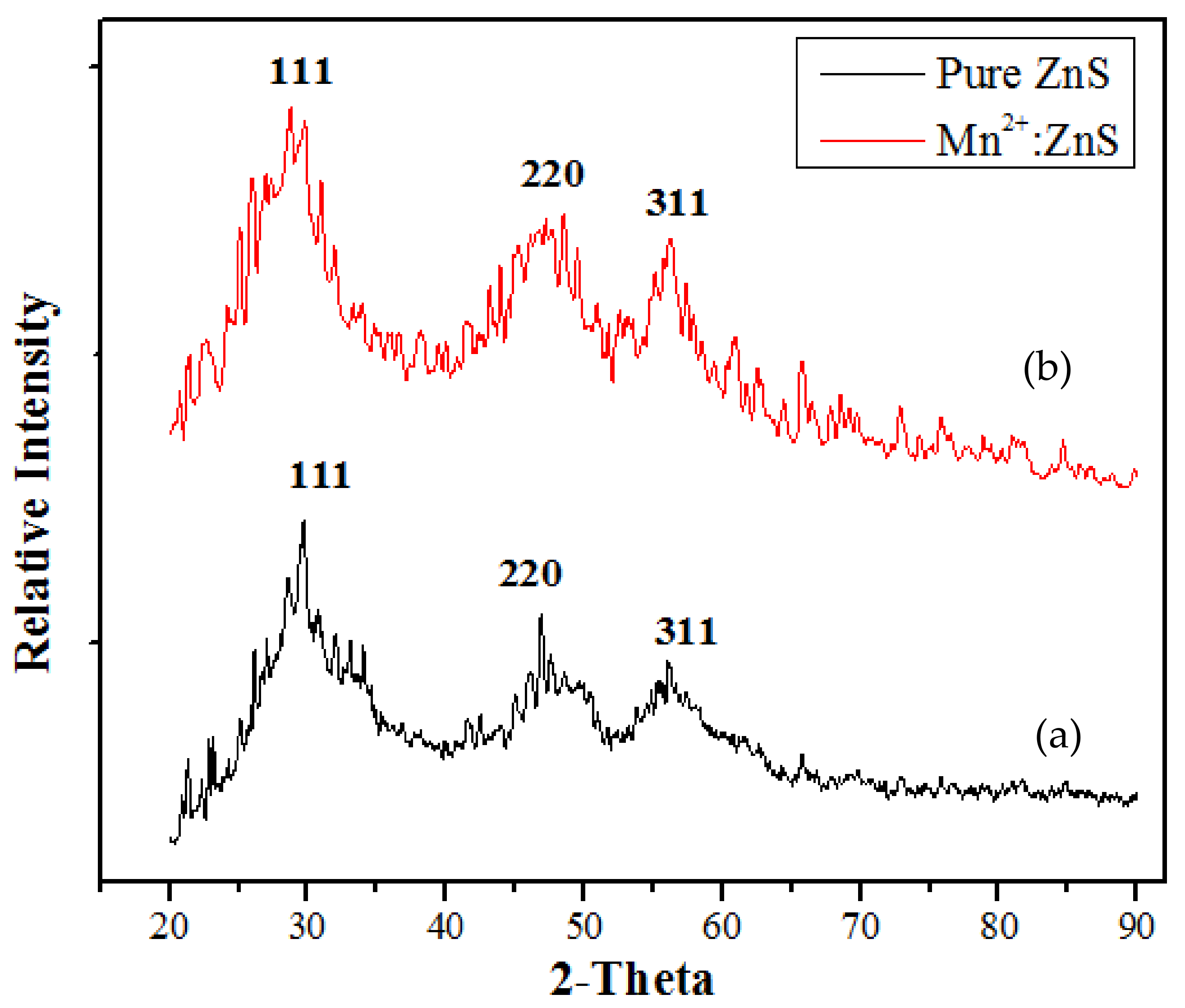

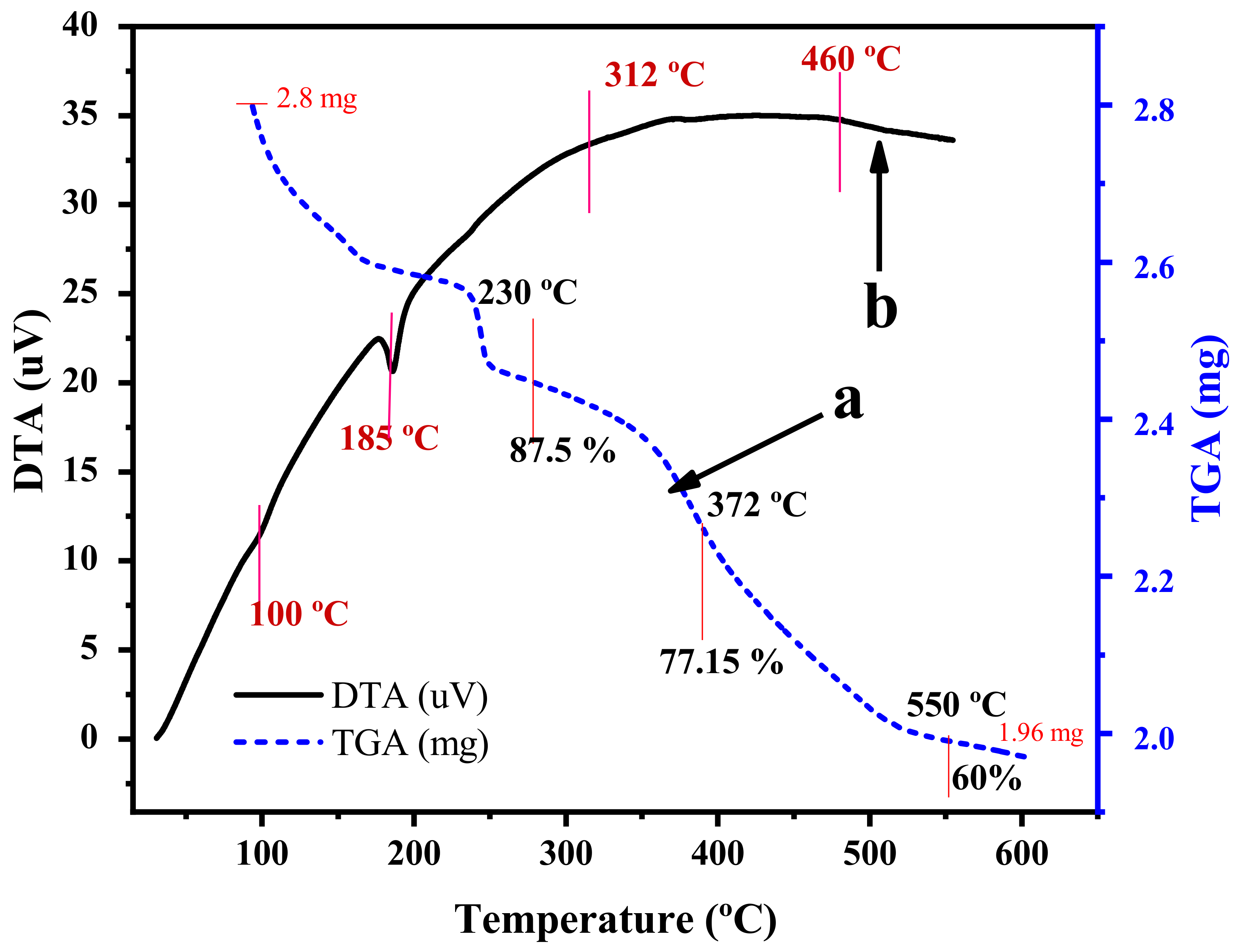


| Catalyst | % Degradation | Dye Conc., Catalyst Dose for Volume of Dye Solution | pH | Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti Grafted SBA-15 | 88.7% | Conc: 50 mg/L Catalyst: 300 mg in 300 mL | - | 70 min | [52] |
| TiO2 Nanoparticles | Anatase 65% Rutile 55.65% | Conc: 100 mg/L Catalyst: 1000 mg | - | 150 min | [53] |
| Iron Oxide Nanoparticles | 67% | Conc: 200 mg/L Catalyst: 2000 mg/L | 5.0 | 20 min | [78] |
| Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles | 82% | Conc: 25 mg/L Catalyst: 25 mg in 100 mL | - | 90 min | [79] |
| Undoped and Zn Doped Nano TiO2 Nanoparticles | Undoped 88.73% Doped 99.4% | Catalyst: 100 mg in 100 mL | - | 6 h | [80] |
| Nanostructured Ho2O3 | 80% | Conc: 2 mg Catalyst: 40 mg | - | 100 min | [81] |
| Nanostructured Nd2O3 | 79% | Conc: 2 mg Catalyst: 80 mg | - | 100 min | [82] |
| ZnO Nanoparticles | 90% | Conc: 0.08 mM Catalyst: 1000 mg/L in 100 mL | 3 | 90 min | [83] |
| TiO2 Nanoparticles | 92% | Conc: 50 mg/L Catalyst: 250 mg/L | 5 | - | [84] |
| TiO2 Nanoparticles | 100% | Conc: 10−4 M Catalyst: 300 mg in 100 mL | 7 | 240 min | [85] |
| MWCNT/Nd, N, SeTiO2, SWCNT/ Nd, N, SeTiO2 | 49.0%, 54.1% | Conc: 20 ppm Catalyst:100 mg in 100 mL | - | 4 h | [54] |
| Potassium Zinc Hexacyanoferratenanocubes | 76.13% | Conc: 5 mg/L, Catalyst: 15 mg in 10 mL | 7 | 120 min | [55] |
| Ammonium Phosphomolybdate Semiconductor | 93.9% | Conc: 10−3 M Catalyst: 300 mg in 50 mL | 11 | 240 min | [56] |
| Bacillus Lentus Bacteria SG-7 Strain | 98% | Conc: 100 mg/L | 7 | 30 h | [86] |
| Microalga Coellastrella | 85% | Conc: 10 mg/L Catalyst: 10% inoculum | 8 | 20 days | [87] |
| Non-Thermal Plasma Generated by Electric Discharges | 88.4% | - | - | 60 min | [88] |
| ZnO Nanoparticles | 75, 83, and 88% at pH 4, 8, 11 | Conc: 20 mg/L Catalyst: 50 mg in 100 mL | 4, 8, 11 | 180 min | [57] |
| Adsorption on Eucalyptus Bark | 77.33% | Conc: 250 mg/L Catalyst: 125 mg in 100 mL | 8 | 120 min | [89] |
| Sludge-Derived Activated Carbon | 90.66% | Conc: 500 mg/L, Catalyst: 50 mL in 3000 mg/L | 6 | 720 min | [90] |
| Perlite Modified with Orthophenanthroline | 63.74% | Conc: 2 × 10−4 M Catalyst: 50 mg in 20 mL | 5 | 20 min | [91] |
| Mn2+:ZnS Qds | 88% | Conc: 70 mg/L Catalyst: 40 mg in 15 mL | 6 | 75 min | This Work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, J.; Singh, A.K.; Jain, B.; Yadav, S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Susan, M.A.B.H. Solochrome Dark Blue Azo Dye Removal by Sonophotocatalysis Using Mn2+ Doped ZnS Quantum Dots. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091025
Patel J, Singh AK, Jain B, Yadav S, Carabineiro SAC, Susan MABH. Solochrome Dark Blue Azo Dye Removal by Sonophotocatalysis Using Mn2+ Doped ZnS Quantum Dots. Catalysts. 2021; 11(9):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091025
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Jyoti, Ajaya K. Singh, Bhawana Jain, Sushma Yadav, Sónia A. C. Carabineiro, and Md. Abu Bin Hasan Susan. 2021. "Solochrome Dark Blue Azo Dye Removal by Sonophotocatalysis Using Mn2+ Doped ZnS Quantum Dots" Catalysts 11, no. 9: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091025
APA StylePatel, J., Singh, A. K., Jain, B., Yadav, S., Carabineiro, S. A. C., & Susan, M. A. B. H. (2021). Solochrome Dark Blue Azo Dye Removal by Sonophotocatalysis Using Mn2+ Doped ZnS Quantum Dots. Catalysts, 11(9), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091025








