Role of MRI-Based Radiomics in Sinonasal Cancer Management: A Scoping Review
Simple Summary
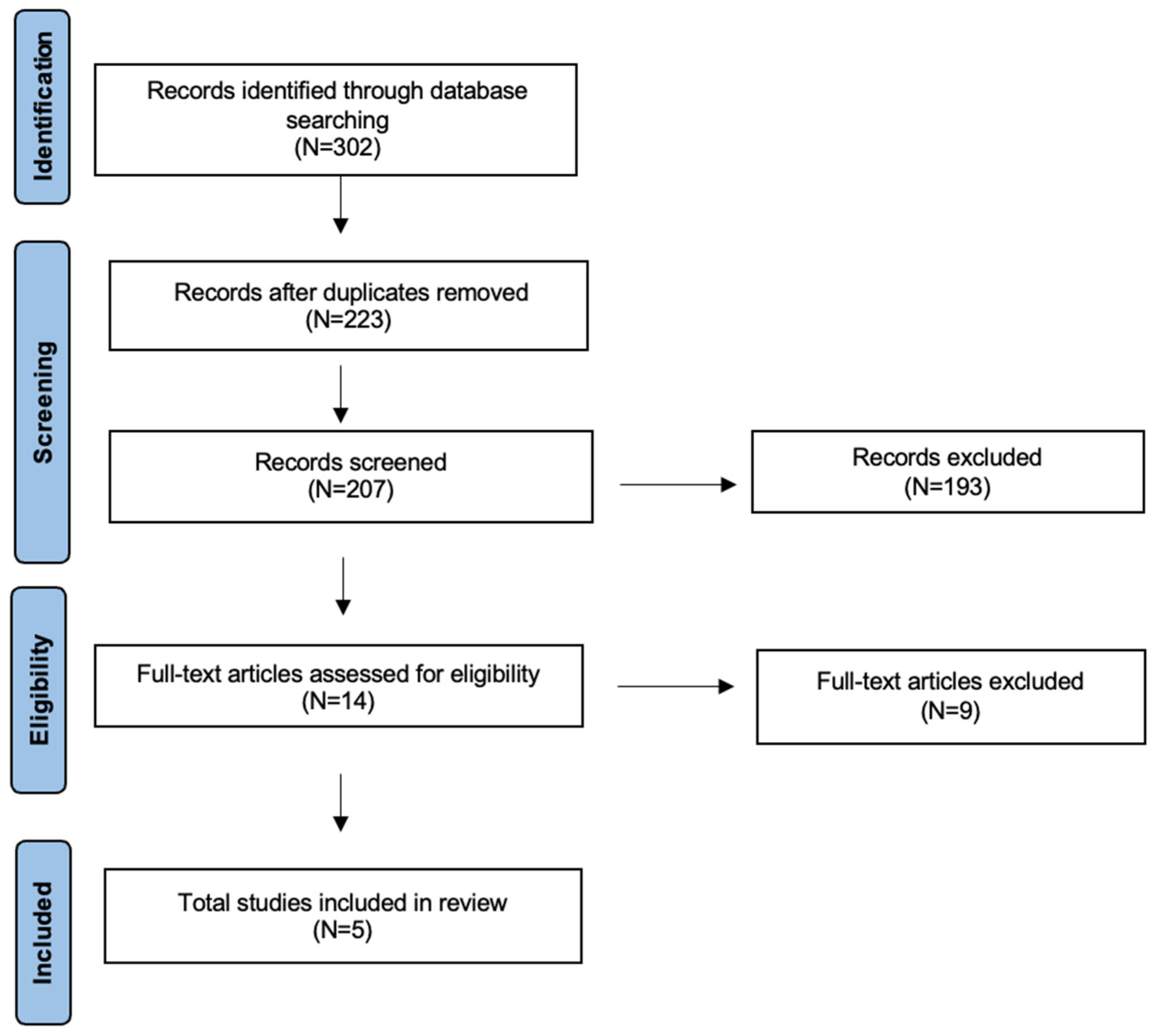
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cracchiolo, J.R.; Patel, K.; Migliacci, J.C.; Morris, L.T.; Ganly, I.; Roman, B.R.; McBride, S.M.; Tabar, V.S.; Cohen, M.A. Factors Associated with a Primary Surgical Approach for Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, R.; Dubal, P.M.; Svider, P.F.; Liu, J.K.; Baredes, S.; Eloy, J.A. Sinonasal Malignancies: A Population-Based Analysis of Site-Specific Incidence and Survival. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qurayshi, Z.; Smith, R.; Walsh, J.E. Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Presentation and Outcome: A National Perspective. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2020, 129, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youlden, D.R.; Cramb, S.M.; Peters, S.; Porceddu, S.V.; Møller, H.; Fritschi, L.; Baade, P.D. International Comparisons of the Incidence and Mortality of Sinonasal Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.F. Preoperative Chemotherapy for Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SNSCC): Time to Move Closer to a Definitive Answer. Cancer 2021, 127, 1734–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.H.; Newman, J.G.; Kennedy, D.W.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D. Clinical Outcomes of Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinomas Based on Tumor Etiology. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, M.D.; Saba, N.F. Multimodal Therapy for Sinonasal Malignancies: Updates and Review of Current Treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bonnecaze, G.; Verillaud, B.; Chaltiel, L.; Fierens, S.; Chapelier, M.; Rumeau, C.; Malard, O.; Gavid, M.; Dufour, X.; Righini, C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma: A Multicenter Study. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.Y.; Cardenas, A.D.; DeMonte, F.; Roberts, D.; Kupferman, M.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.; Kies, M. Induction Chemotherapy for Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Paranasal Sinuses. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, N. Factors Affecting Survival in Maxillary Sinus Cancer. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru Birgi, S.; Teo, M.; Dyker, K.E.; Sen, M.; Prestwich, R.J. Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Single Institutional Experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegner, E.A.; Daly, M.E.; Murphy, J.D.; Abelson, J.; Chapman, C.H.; Chung, M.; Yu, Y.; Colevas, A.D.; Kaplan, M.J.; Fischbein, N.; et al. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Tumors of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: Clinical Outcomes and Patterns of Failure. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorelli, A.; Manuelli, M.; Ciorba, A.; Stomeo, F.; Pelucchi, S.; Bianchini, C. Role of Artificial Intelligence in Human Papillomavirus Status Prediction for Oropharyngeal Cancer: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Yáñez, M.; Rameau, A.; Vaira, L.A.; Louvrier, M.; Sanchez Barrueco, A.; Alcalá-Rueda, I.; García-Curdi, F.; Mejuto-Torreiro, L.; Klein-Rodríguez, A.; Herranz-Larrañeta, J.; et al. Patient Perceptions of Artificial Intelligence in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: An International Study. Ear Nose Throat J. 2025, 1455613251351774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammaroto, G.; Migliorelli, A.; Pelucchi, S.; Meccariello, G.; De Vito, A. Social (Chats), Websites, and ChatGPT in Eagle Syndrome. In EAGLE Syndrome. In EAGLE Syndrome: The Many Faces of the Elongated Styloid Process; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Naccour, S.; Moawad, A.; Santer, M.; Dejaco, D.; Freysinger, W. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Cervical Lymph Nodes in HNSCC: A Radiomics Approach with Feature Selection Optimization. Cancers 2025, 17, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting More Information from Medical Images Using Advanced Feature Analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Gu, Y.; Basu, S.; Berglund, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Forster, K.; Aerts, H.J.; Dekker, A.; Fenstermacher, D.; et al. Radiomics: The Process and the Challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, J.; Munir, U.; Nori, A.; Williams, B. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Transforming the Practice of Medicine. Future Healthc. J. 2021, 8, e188–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.; Deshwal, A.; Cuddihy, T.O.; Jones, H.; Temperley, H.C.; Kaye-Coyle, H.; O’Sullivan, N.J.; Mac Curtain, B.M.; Kelly, M.E.; Young, O. Role of Radiomics to Predict Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravante, G.; Arosio, D.A.; Curti, N.; Biondi, R.; Berardi, L.; Gandolfi, A.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Castelnuovo, P.; Remondini, D.; Bignami, M. Artificial Intelligence and MRI in Sinonasal Tumors Discrimination: Where Do We Stand? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 282, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Man, F.; Zhang, P.; Hou, F.; Wang, H.; Hao, D. Multi-Parametric MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for Preoperative Prediction of Ki-67 Proliferation Status in Sinonasal Malignancies: A Two-Centre Study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6933–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corino, V.D.A.; Bologna, M.; Calareso, G.; Resteghini, C.; Sdao, S.; Orlandi, E.; Licitra, L.; Mainardi, L.; Bossi, P. Refining Tumor Treatment in Sinonasal Cancer Using Delta Radiomics of Multi-Parametric MRI after the First Cycle of Induction Chemotherapy. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Yu, S.; Lin, M.; Shi, Y.; Chen, W.; Xia, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Sha, Y. A Clinical-Radiomics Nomogram Based on the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) for Individualized Prediction of the Risk of Early Relapse in Advanced Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 870935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Shi, Y.; Ye, M.; Wang, L.; Sha, Y. Multiparametric MRI-Based Radiomics Approach with Deep Transfer Learning for Preoperative Prediction of Ki-67 Status in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1305836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.B.; Han, K.; Ahn, S.S.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, E.C.; Keum, K.C.; Kim, J. MRI Radiomics May Predict Early Tumor Recurrence in Patients with Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 3151–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messineo, D.; Massaro, F.; Izzo, P.; Milani, A.; Polimeni, R.; Iannella, G.; Marinozzi, S.; Consorti, F.; Cocuzza, S.; Maniaci, A.; et al. Radiomic Application for Head and Neck Squamocellular Tumor: Systematic Review. Clin. Ter. 2024, 175, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hulst, H.J.; Jansen, R.W.; Vens, C.; Bos, P.; Schats, W.; de Jong, M.C.; Martens, R.M.; Bodalal, Z.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; van den Brekel, M.W.M.; et al. The Prediction of Biological Features Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maebayashi, T.; Ishibashi, N.; Aizawa, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Saito, T.; Kawamori, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirotani, Y.; Homma, T. Roles of Ki-67 and p16 as Biomarkers for Unknown Primary Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, L.; Huang, X.; Jing, D.; Huang, D.; Fu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Shen, L. High Expression of Ki-67 Acts as a Poor Prognosis Indicator in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, G.; Mamo, C.; Bena, A.; Prudente, E.; Cavaliere, C.; Kerim, S.; Nicotra, G.; Comino, A.; Palestro, G.; Isidoro, C.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Microvessel Density and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Sinonasal Carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Qiang, J.; Qian, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z. Standard Diffusion-Weighted, Diffusion Kurtosis and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging of Sinonasal Malignancies: Correlations with Ki-67 Proliferation Status. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, J.H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Cruz, C.; Do, S.; Dreyer, K.; Brink, J. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Radiology: Opportunities, Challenges, Pitfalls, and Criteria for Success. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z. An MRI-Based Radiomics Classifier for Preoperative Prediction of Ki-67 Status in Breast Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2018, 25, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhou, X.X.; Chen, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.R.; Ge, Z.Z. Personalized CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Preoperative Predicting Ki-67 Expression in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Multicenter Development and Validation Cohort. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Patel, S.G.; Shah, J.P. Changes in the 8th Edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Staging of Head and Neck Cancer: Rationale and Implications. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author (Yrs) | Country | Histology | Modality | N° Training/N° Validation | AI Algorithm | Objective | Major Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi (2021) [23] | China | SCC 61 Other 67 | MRI | 77/51 | LASSO regression + mRMR for feature selection; LR for final model | To assess the ability of MRI-based multiparametric radiomics to predict preoperative Ki-67 status in sinonasal malignancies. | Radiomic combined model from multiparametric MRI (T1W, FS-T2WI, T1c) achieved AUC 0.852 and accuracy 86.3%. |
| Corino (2022) [24] | Italy | SCC 12 SNUC 23 Other 15 | MRI | 40/10 | SVM with features reduced via semi-supervised PCA | Delta radiomics to predict IC response in sinonasal cancer. | AUC of monomodal signatures: T1w = 0.79, T2w = 0.76, ADC = 0.93. RECIST prediction accuracy = 0.78. |
| Lin (2022) [25] | China | SCC | MRI | 106/46 | LASSO logistic regression + multivariable logistic regression for nomogram construction | Develop a nomogram integrating radiomic and clinical features to preoperatively predict early recurrence risk in advanced sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma | The nomogram demonstrated an AUC = 0.92. |
| Lin (2024) [26] | China | SCC | MRI | 185/46 | Deep transfer learning (ResNet50) for feature extraction combined with SVM, LightGBM, and ExtraTrees classifiers | Develop and validate a multiparametric MRI model combining hand-crafted and deep transfer learning features to predict Ki-67 status in squamous cell carcinoma of the nose. | RS-DL showed the best predictive ability in training and the highest AUC in testing (0.817), though not significantly better than RS-HC. |
| Park (2024) [27] | Republic of Korea | SCC | MRI | 47/21 | LASSO + RFE for feature selection; ML classifier | Assess whether MRI radiomics can predict early local failure in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. | In the test group, radiomic and combined models outperformed the clinical model (AUC 0.838 and 0.850 vs. 0.438), with no significant difference between them. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migliorelli, A.; Manuelli, M.; Ciorba, A.; Stomeo, F.; Pelucchi, S.; Bianchini, C. Role of MRI-Based Radiomics in Sinonasal Cancer Management: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203313
Migliorelli A, Manuelli M, Ciorba A, Stomeo F, Pelucchi S, Bianchini C. Role of MRI-Based Radiomics in Sinonasal Cancer Management: A Scoping Review. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigliorelli, Andrea, Marianna Manuelli, Andrea Ciorba, Francesco Stomeo, Stefano Pelucchi, and Chiara Bianchini. 2025. "Role of MRI-Based Radiomics in Sinonasal Cancer Management: A Scoping Review" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203313
APA StyleMigliorelli, A., Manuelli, M., Ciorba, A., Stomeo, F., Pelucchi, S., & Bianchini, C. (2025). Role of MRI-Based Radiomics in Sinonasal Cancer Management: A Scoping Review. Cancers, 17(20), 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203313







