The Central Role of Ribosomal Proteins in p53 Regulation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The p53—Ribosome Connection
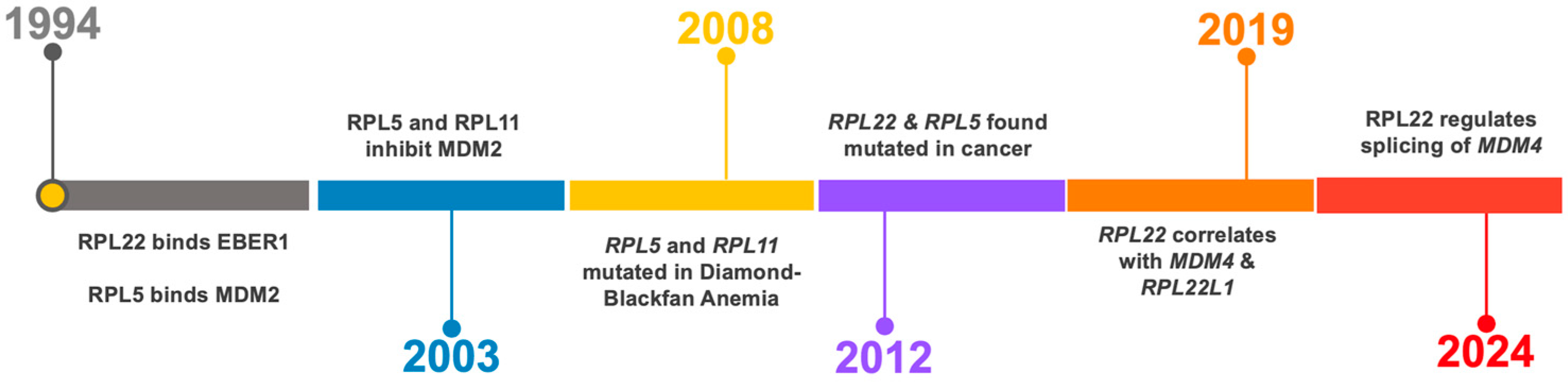
3. RPL22 and RPL22L1 Paralog Pair
4. RPL22 and RPL22L1 Alterations in Cancer
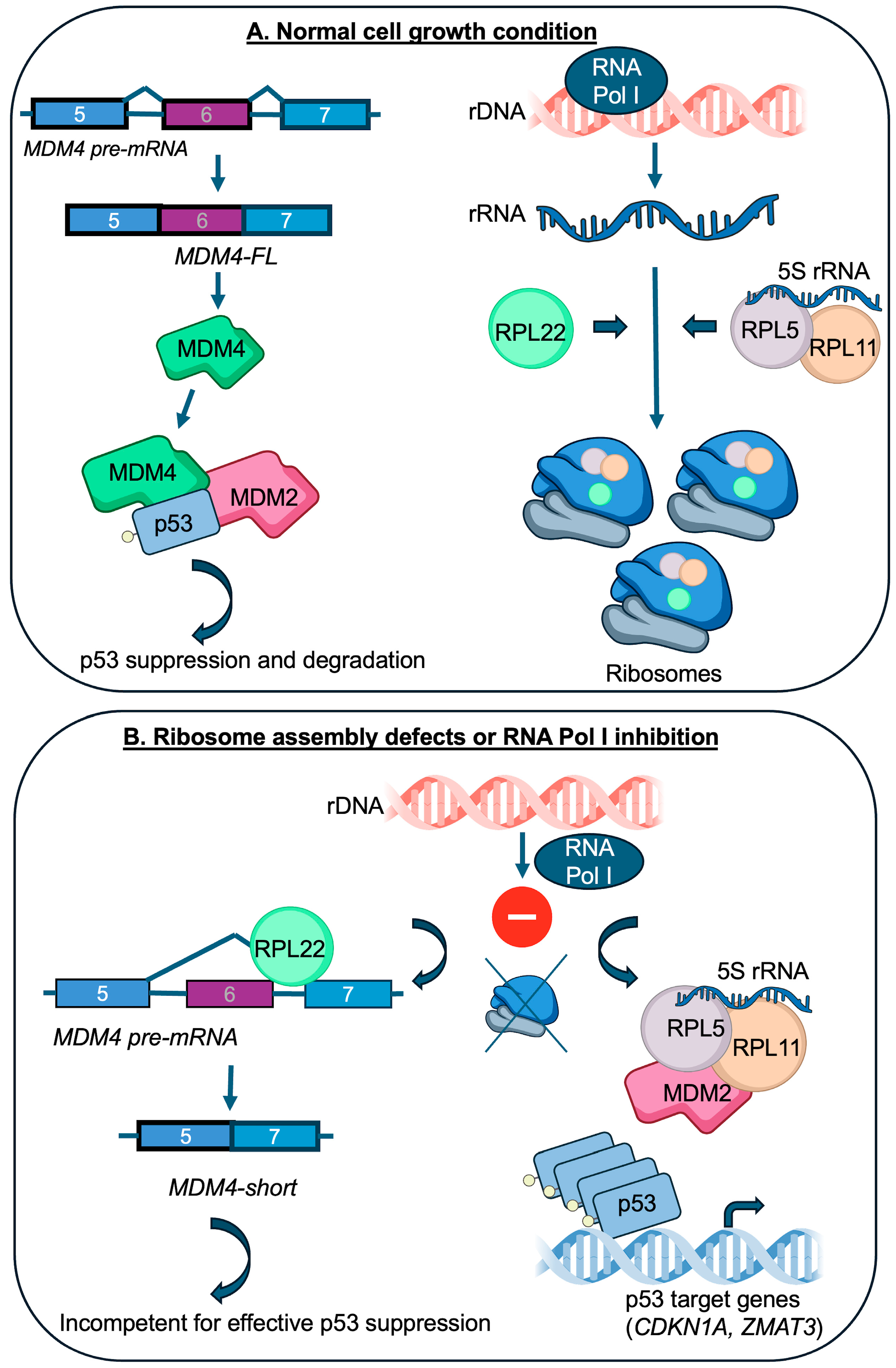
5. RPL22 Becomes Connected to MDM4 and p53
6. RPL22-MDM4 and Implications for Cancer Biology
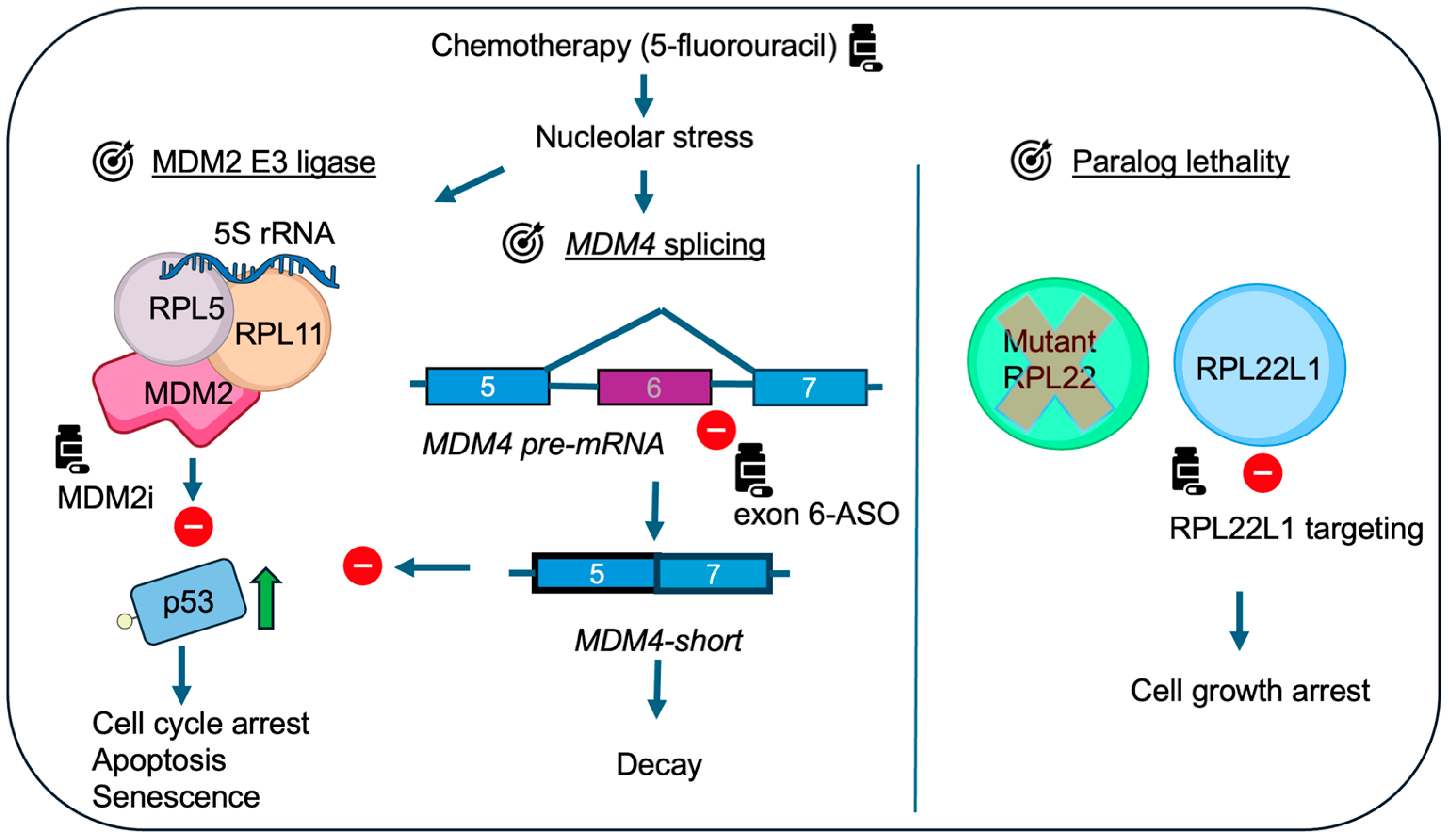
7. RPL22-MDM4 and Implications for Cancer Treatment
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warner, J.R.; McIntosh, K.B. How Common Are Extraribosomal Functions of Ribosomal Proteins? Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fancello, L.; Kampen, K.R.; Hofman, I.J.F.; Verbeeck, J.; De Keersmaecker, K. The Ribosomal Protein Gene RPL5 Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor in Multiple Cancer Types. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14462–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungström, V.; Cortese, D.; Young, E.; Pandzic, T.; Mansouri, L.; Plevova, K.; Ntoufa, S.; Baliakas, P.; Clifford, R.; Sutton, L.-A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in Relapsing Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Clinical Impact of Recurrent RPS15 Mutations. Blood 2016, 127, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, K.R.; Sulima, S.O.; Verbelen, B.; Girardi, T.; Vereecke, S.; Rinaldi, G.; Verbeeck, J.; Op de Beeck, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Meijerink, J.P.P.; et al. The Ribosomal RPL10 R98S Mutation Drives IRES-Dependent BCL-2 Translation in T-ALL. Leukemia 2019, 33, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, H.N.W.; Hu, K.; Fish, L.; Chen, Y.-A.; Allegakoen, P.; Pham, J.H.; Hui, K.S.F.; Chang, C.-H.; Tutar, M.; Benitez-Rivera, L.; et al. RPL22 Is a Tumor Suppressor in MSI-High Cancers and a Splicing Regulator of MDM4. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Tuominen, I.; van Dijk-Bos, K.; Sanjabi, B.; van der Sluis, T.; van der Zee, A.G.; Hollema, H.; Zazula, M.; Sijmons, R.H.; Aaltonen, L.A.; et al. High Frequency of RPL22 Mutations in Microsatellite-Unstable Colorectal and Endometrial Tumors. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oršolić, I.; Bursać, S.; Jurada, D.; Drmić Hofman, I.; Dembić, Z.; Bartek, J.; Mihalek, I.; Volarević, S. Cancer-Associated Mutations in the Ribosomal Protein L5 Gene Dysregulate the HDM2/P53-Mediated Ribosome Biogenesis Checkpoint. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3443–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajore, R.; Raiser, D.; McConkey, M.; Jöud, M.; Boidol, B.; Mar, B.; Saksena, G.; Weinstock, D.M.; Armstrong, S.; Ellis, S.R.; et al. Deletion of Ribosomal Protein Genes Is a Common Vulnerability in Human Cancer, Especially in Concert with TP53 Mutations. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Dolezal, J.M.; Wang, H.; Jackson, L.; Lu, J.; Frodey, B.P.; Dosunmu-Ogunbi, A.; Li, Y.; Fromherz, M.; Kang, A.; et al. Ribosomopathy-like Properties of Murine and Human Cancers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.; De Keersmaecker, K. Ribosome Specialization by Cancer-Associated Ribosomal Protein Mutations: Progress Made and Open Questions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2025, 380, 20230380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, K.E.; Bohnsack, M.T.; Watkins, N.J. The 5S RNP Couples P53 Homeostasis to Ribosome Biogenesis and Nucleolar Stress. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.; Dobbelstein, M. MDM4 Exon Skipping upon Dysfunctional Ribosome Assembly. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, S0962-8924(24)00212-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, G.C.; Wang, J.; Rose, K.L.; Jones, C.; Patel, P.; Tsui, T.; Florian, A.C.; Vlach, L.; Lorey, S.L.; Grieb, B.C.; et al. Ribosome Subunit Attrition and Activation of the P53-MDM4 Axis Dominate the Response of MLL-Rearranged Cancer Cells to WDR5 WIN Site Inhibition. eLife 2024, 12, RP90683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.; Bohnsack, K.E.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Bohnsack, M.T.; Dobbelstein, M. The Ribosomal Protein L22 Binds the MDM4 Pre-mRNA and Promotes Exon Skipping to Activate P53 upon Nucleolar Stress. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. Understanding the Complexity of P53 in a New Era of Tumor Suppression. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Kawai, H.; Nie, L.; Kitao, H.; Wiederschain, D.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Parant, J.; Lozano, G.; Yuan, Z.-M. Mutual Dependence of MDM2 and MDMX in Their Functional Inactivation of P53. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19251–19254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parant, J.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Little, N.A.; Yan, W.; Reinke, V.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Lozano, G. Rescue of Embryonic Lethality in MDM4-Null Mice by Loss of Trp53 Suggests a Nonoverlapping Pathway with MDM2 to Regulate P53. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuget, S.; Zhou, X.; Selivanova, G. Translating P53-Based Therapies for Cancer into the Clinic. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, X. MDM4 Alternative Splicing and Implication in MDM4 Targeted Cancer Therapies. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 5864–5880. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, K.M.; Soo, P.; Wong, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Hein, N.; Poh, P.; Wysoke, K.D.; Williams, T.D.; Montellese, C.; Smith, L.K.; et al. Nuclear Stabilization of P53 Requires a Functional Nucleolar Surveillance Pathway. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenroth, C.; Franklin, D.A.; Zhang, Y. The Evolution of the Ribosomal Protein-MDM2-P53 Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbi, C.P.; Milner, J. Disruption of the Nucleolus Mediates Stabilization of P53 in Response to DNA Damage and Other Stresses. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6068–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestov, D.G.; Strezoska, Z.; Lau, L.F. Evidence of P53-Dependent Cross-Talk between Ribosome Biogenesis and the Cell Cycle: Effects of Nucleolar Protein Bop1 on G(1)/S Transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 4246–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, J.A.; Berg, C.; Hendrick, J.P.; La Branche-Chabot, H.; Metspalu, A.; Rinke, J.; Yario, T. A 5S rRNA/L5 Complex Is a Precursor to Ribosome Assembly in Mammalian Cells. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Duque de Estrada, N.M.; Thoms, M.; Flemming, D.; Hammaren, H.M.; Buschauer, R.; Ameismeier, M.; Baßler, J.; Beck, M.; Beckmann, R.; Hurt, E. Structure of Nascent 5S RNPs at the Crossroad between Ribosome Assembly and MDM2-P53 Pathways. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, G.; Peddigari, S.; Mercer, C.A.; Thomas, G. 5S Ribosomal RNA Is an Essential Component of a Nascent Ribosomal Precursor Complex That Regulates the Hdm2-P53 Checkpoint. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Mercer, C.A.; Hexley, P.; Thomas, G.; Fumagalli, S. Loss of Tumor Suppressor RPL5/RPL11 Does Not Induce Cell Cycle Arrest but Impedes Proliferation Due to Reduced Ribosome Content and Translation Capacity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursać, S.; Brdovčak, M.C.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Orsolić, I.; Golomb, L.; Zhu, Y.; Katz, C.; Daftuar, L.; Grabušić, K.; Vukelić, I.; et al. Mutual Protection of Ribosomal Proteins L5 and L11 from Degradation Is Essential for P53 Activation upon Ribosomal Biogenesis Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20467–20472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagnères, S.; Santo, P.E.; Radermecker, J.; Rinaldi, D.; Froment, C.; Provost, Q.; Bongers, M.; Capeille, S.; Watkins, N.; Marcoux, J.; et al. SURF2 Is a MDM2 Antagonist in Triggering the Nucleolar Stress Response. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Fang, Z.; Liao, P.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, J.; Zeng, S.; Lu, H. Cancer-Mutated Ribosome Protein L22 (RPL22/eL22) Suppresses Cancer Cell Survival by Blocking P53-MDM2 Circuit. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 90651–90661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkovan, M.; Vadnais, C.; Ross, J.; Gigoux, M.; Suh, W.-K.; Gu, W.; Kosan, C.; Möröy, T. Miz-1 Regulates Translation of Trp53 via Ribosomal Protein L22 in Cells Undergoing V(D)J Recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5411–E5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, M.; Absalon, M.J.; McLure, K.G.; Kastan, M.B. Regulation of P53 Translation and Induction after DNA Damage by Ribosomal Protein L26 and Nucleolin. Cell 2005, 123, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.-S.; Zeng, S.X.; Jin, Y.; Sun, X.-X.; David, L.; Lu, H. Ribosomal Protein L23 Activates P53 by Inhibiting MDM2 Function in Response to Ribosomal Perturbation but Not to Translation Inhibition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7654–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Russo, G. Ribosomal Proteins Control or Bypass P53 during Nucleolar Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Wang, Y.; Raje, H.; Rosby, R.; DiMario, P. Nucleolar Stress with and without P53. Nucleus 2014, 5, 402–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, I.; Novoa, E.M. Ribosomal Protein Paralogues in Ribosome Specialization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2025, 380, 20230387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, M.M.; Catala, M.; Abou Elela, S. Differential Expression of Duplicated Ribosomal Protein Genes Modifies Ribosome Composition in Response to Stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik Ghulam, M.; Catala, M.; Reulet, G.; Scott, M.S.; Abou Elela, S. Duplicated Ribosomal Protein Paralogs Promote Alternative Translation and Drug Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, S.; Dopler, A.; Faller, W.J. Ribosome Specialization in Cancer: A Spotlight on Ribosomal Proteins. NAR Cancer 2024, 6, zcae029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, P.; Pelletier, J.; Gentilella, A. Decoding Ribosome Complexity: Role of Ribosomal Proteins in Cancer and Disease. NAR Cancer 2024, 6, zcae032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.N.; Schreiber, K.H.; Zhang, Y.; Duc, A.-C.E.; Rao, S.; Hale, J.S.; Academia, E.C.; Shah, S.R.; Morton, J.F.; Holstein, C.A.; et al. The Ribosomal Protein RPL22 Controls Ribosome Composition by Directly Repressing Expression of Its Own Paralog, RPL22L1. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrhámová, K.; Nemčko, F.; Libus, J.; Převorovský, M.; Hálová, M.; Půta, F.; Folk, P. Introns Provide a Platform for Intergenic Regulatory Feedback of RPL22 Paralogs in Yeast. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabunilas, J.; Chanfreau, G. Splicing-Mediated Autoregulation Modulates RPL22p Expression in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.G.; Chen, A.S.; Ware, V.C. Expression of Ribosomal Protein L22e Family Members in Drosophila Melanogaster: RPL22-like Is Differentially Expressed and Alternatively Spliced. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2701–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; O’Leary, M.N.; Peri, S.; Wang, M.; Zha, J.; Melov, S.; Kappes, D.J.; Feng, Q.; Rhodes, J.; Amieux, P.S.; et al. Ribosomal Proteins RPL22 and RPL22L1 Control Morphogenesis by Regulating Pre-mRNA Splicing. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, T.D.; Bastola, S.; Aksinina, T.E.; Anufrieva, K.S.; Wang, J.; Shender, V.O.; Andreev, D.E.; Kovalenko, T.F.; Arapidi, G.P.; Shnaider, P.V.; et al. Alternative RNA Splicing Modulates Ribosomal Composition and Determines the Spatial Phenotype of Glioblastoma Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahl, S.P.; Sertori, R.; Zhang, Y.; Contreras, A.V.; Harris, B.; Wang, M.; Perrigoue, J.; Balachandran, S.; Kennedy, B.K.; Wiest, D.L. Loss of Ribosomal Protein Paralog RPL22-like1 Blocks Lymphoid Development without Affecting Protein Synthesis. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahl, S.P.; Harris, B.; Coffey, F.; Wiest, D.L. RPL22 Loss Impairs the Development of B Lymphocytes by Activating a P53-Dependent Checkpoint. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahl, S.P.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Duc, A.-C.E.; Wiest, D.L. Regulatory Roles of RPL22 in Hematopoiesis: An Old Dog with New Tricks. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 35, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Gutierrez, A.; Perrigoue, J.; Thapa, R.J.; Tu, Z.; Jeffers, J.R.; Rhodes, M.; Anderson, S.; Oravecz, T.; et al. Inactivation of Ribosomal Protein L22 Promotes Transformation by Induction of the Stemness Factor, Lin28B. Blood 2012, 120, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, N.; Bertrand, D.; Hillmer, A.M.; Zang, Z.J.; Yao, F.; Jacques, P.-É.; Teo, A.S.M.; Cutcutache, I.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, W.H.; et al. Whole-Genome Reconstruction and Mutational Signatures in Gastric Cancer. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novetsky, A.P.; Zighelboim, I.; Thompson, D.M.; Powell, M.A.; Mutch, D.G.; Goodfellow, P.J. Frequent Mutations in the RPL22 Gene and Its Clinical and Functional Implications. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 128, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keersmaecker, K.; Atak, Z.K.; Li, N.; Vicente, C.; Patchett, S.; Girardi, T.; Gianfelici, V.; Geerdens, E.; Clappier, E.; Porcu, M.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Mutation in CNOT3 and Ribosomal Genes RPL5 and RPL10 in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Huang, F.W.; Jané-Valbuena, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lo, C.C.; McDonald, E.R.; Barretina, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; Bielski, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Next-Generation Characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 2019, 569, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine, J.-C.; Jochemsen, A.G. MDMX (MDM4), a Promising Target for P53 Reactivation Therapy and Beyond. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieging-Rolett, K.T.; Kaiser, A.M.; Morgens, D.W.; Boutelle, A.M.; Seoane, J.A.; Van Nostrand, E.L.; Zhu, C.; Houlihan, S.L.; Mello, S.S.; Yee, B.A.; et al. Zmat3 Is a Key Splicing Regulator in the P53 Tumor Suppression Program. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 452–469.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, H.; Stachelek, G.C.; Begum, A.; Davis, C.E.; Dorado, T.E.; Ernst, G.; Reinhold, W.C.; Ozbek, B.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Ribosomal RNA Transcription Governs Splicing through Ribosomal Protein RPL22. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.08.15.608201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.P. Balanced Production of Ribosomal Proteins. Gene 2007, 401, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Buszczak, M. The Homeostatic Regulation of Ribosome Biogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 136, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregoso, O.I.; Das, S.; Akerman, M.; Krainer, A.R. Splicing-Factor Oncoprotein SRSF1 Stabilizes P53 via RPL5 and Induces Cellular Senescence. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, J. Biological Function and Molecular Mechanism of SRSF3 in Cancer and Beyond. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbelstein, M.; Shenk, T. In Vitro Selection of RNA Ligands for the Ribosomal L22 Protein Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus-Expressed RNA by Using Randomized and cDNA-Derived RNA Libraries. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 8027–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczyski, D.P.; Matera, A.G.; Ward, D.C.; Steitz, J.A. The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Small RNA EBER1 Binds and Relocalizes Ribosomal Protein L22 in EBV-Infected Human B Lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3463–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczyski, D.P.; Steitz, J.A. EAP, a Highly Conserved Cellular Protein Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus Small RNAs (EBERs). EMBO J. 1991, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, N.; Szekely, L.; Klein, G. Differential Expression and Localization of EBER-1 and EBER-2 in Epstein-Barr Virus-Carrying Cells. J. Hum. Virol. 1998, 1, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Marechal, V.; Elenbaas, B.; Piette, J.; Nicolas, J.C.; Levine, A.J. The Ribosomal L5 Protein Is Associated with Mdm-2 and Mdm-2-P53 Complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7414–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda, H.T.; Sheen, M.R.; Vlachos, A.; Choesmel, V.; O’Donohue, M.-F.; Schneider, H.; Darras, N.; Hasman, C.; Sieff, C.A.; Newburger, P.E.; et al. Ribosomal Protein L5 and L11 Mutations Are Associated with Cleft Palate and Abnormal Thumbs in Diamond-Blackfan Anemia Patients. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrum, M.A.E.; Ludwig, R.L.; Kubbutat, M.H.G.; Hanlon, M.; Vousden, K.H. Regulation of HDM2 Activity by the Ribosomal Protein L11. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wolf, G.W.; Bhat, K.; Jin, A.; Allio, T.; Burkhart, W.A.; Xiong, Y. Ribosomal Protein L11 Negatively Regulates Oncoprotein MDM2 and Mediates a P53-Dependent Ribosomal-Stress Checkpoint Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8902–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.-S.; Lu, H. Inhibition of MDM2-Mediated P53 Ubiquitination and Degradation by Ribosomal Protein L5. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44475–44482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkes, D.M.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. MDMX Regulation of P53 Response to Ribosomal Stress. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5614–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, D.A.; Liu, S.; Jin, A.; Cui, P.; Guo, Z.; Arend, K.C.; Moorman, N.J.; He, S.; Wang, G.G.; Wan, Y.Y.; et al. Ribosomal Protein RPL11 Haploinsufficiency Causes Anemia in Mice via Activation of the RP-MDM2-P53 Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Hayano, S.; Kawanabe, N.; Wang, Z.; Shimada, A.; Saito, M.K.; Asaka, I.; Kamioka, H. Investigation of the Molecular Causes Underlying Physical Abnormalities in Diamond-Blackfan Anemia Patients with RPL5 Haploinsufficiency. Pathol. Int. 2021, 71, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houmani, J.L.; Davis, C.I.; Ruf, I.K. Growth-Promoting Properties of Epstein-Barr Virus EBER-1 RNA Correlate with Ribosomal Protein L22 Binding. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9844–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Lee, N. Epstein-Barr Virus Noncoding RNA EBER1 Promotes the Expression of a Ribosomal Protein Paralog to Boost Oxidative Phosphorylation. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado-Palacin, L.; Varetti, G.; Llanos, S.; Gómez-López, G.; Martinez, D.; Serrano, M. Partial Loss of Rpl11 in Adult Mice Recapitulates Diamond-Blackfan Anemia and Promotes Lymphomagenesis. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, E.; Jin, A.; Deisenroth, C.; Bhat, K.; Mao, H.; Lindström, M.S.; Zhang, Y. An ARF-Independent c-MYC-Activated Tumor Suppression Pathway Mediated by Ribosomal Protein-Mdm2 Interaction. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, H.E.; Øbro, N.F.; Williams, N.; Tan, S.; Boukerrou, A.Z.; Davies, M.; Belmonte, M.; Mitchell, E.; Baxter, E.J.; Mende, N.; et al. Convergent Somatic Evolution Commences in Utero in a Germline Ribosomopathy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-X.; Dai, M.-S.; Lu, H. 5-Fluorouracil Activation of P53 Involves an MDM2-Ribosomal Protein Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8052–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-X.; Dai, M.-S.; Lu, H. Mycophenolic Acid Activation of P53 Requires Ribosomal Proteins L5 and L11. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12387–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, L.A.; McHugh, A.; Fernandes, K.; Boag, G.; Proby, C.M.; Leigh, I.M.; Saville, M.K. Targeting the Spliceosome for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Therapy: A Role for c-MYC and Wild-Type P53 in Determining the Degree of Tumour Selectivity. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 23029–23046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, P.; Lv, H.; Liu, S.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, S.; Ji, G.; et al. Ribosomal Protein L22-like1 (RPL22L1) Mediates Sorafenib Sensitivity via ERK in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, Y.; Guan, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, M.; et al. RPL22L1, a Novel Candidate Oncogene Promotes Temozolomide Resistance by Activating STAT3 in Glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Peri, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Cai, K.Q.; Harris, B.; Rhodes, M.; Connolly, D.C.; Testa, J.R.; Wiest, D.L. RPL22L1 Induction in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and 5-FU Resistance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.R.; de Weck, A.; Schlabach, M.R.; Billy, E.; Mavrakis, K.J.; Hoffman, G.R.; Belur, D.; Castelletti, D.; Frias, E.; Gampa, K.; et al. Project DRIVE: A Compendium of Cancer Dependencies and Synthetic Lethal Relationships Uncovered by Large-Scale, Deep RNAi Screening. Cell 2017, 170, 577–592.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Cai, K.Q.; Stadanlick, J.E.; Greenberg-Kushnir, N.; Solanki-Patel, N.; Lee, S.-Y.; Fahl, S.P.; Testa, J.R.; Wiest, D.L. Ribosomal Protein RPL22 Controls the Dissemination of T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yao, N.; Du, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, X.; Lv, C.; Lai, J. Ribosomal Protein L22 like 1: A Promising Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Li, D.; Zhao, Q. RPL22L1 Is a Novel Biomarker for Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Lung Adenocarcinoma, Promoting the Growth and Metastasis of LUAD Cells by Inhibiting the MDM2/P53 Signaling Pathway. Aging 2024, 16, 12392–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindström, M.S. The Central Role of Ribosomal Proteins in p53 Regulation. Cancers 2025, 17, 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101597
Lindström MS. The Central Role of Ribosomal Proteins in p53 Regulation. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101597
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindström, Mikael S. 2025. "The Central Role of Ribosomal Proteins in p53 Regulation" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101597
APA StyleLindström, M. S. (2025). The Central Role of Ribosomal Proteins in p53 Regulation. Cancers, 17(10), 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101597





