Predictors of High-Burden Residual Axillary Disease After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Axillary Surgery and Pathological Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Axillary Surgical Approaches and Nodal Staging Post-Neoadjuvant Therapy
3.3. Predictors of Residual High-Burden Axillary Disease
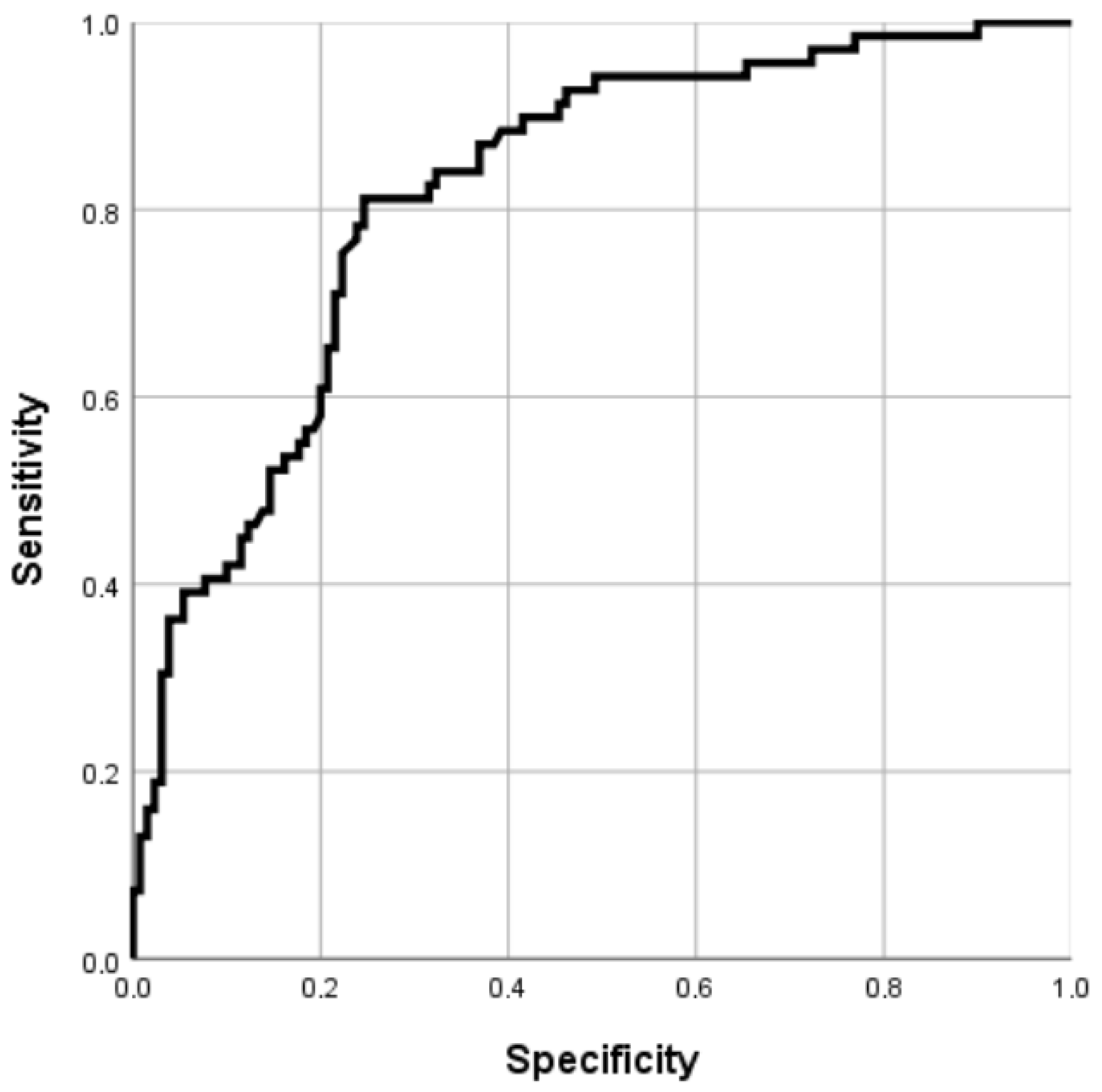
3.4. Predictive Performance of the Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Predictors of Residual High-Burden Disease and Comparative Evidence from Predictive Models and Nomograms
4.2. Validation of the Predictive Role of HR+/HER2− Tumors
4.3. The Role and Limitations of Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
4.4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teshome, M.; Hunt, K.K. Neoadjuvant Therapy in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 23, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacampa, G.; Navarro, V.; Matikas, A.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Schettini, F.; Tolosa, P.; Martínez-Sáez, O.; Sánchez-Bayona, R.; Ferrero-Cafiero, J.M.; Salvador, F.; et al. Neoadjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Plus Chemotherapy in Early Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantini, L.; Trapani, D.; Guidi, L.; Boscolo Bielo, L.; Scafetta, R.; Koziej, M.; Vidal, L.; Saini, K.S.; Curigliano, G. Neoadjuvant Therapy in Hormone Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 123, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Nomogram-Derived Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response (PCR) in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NCT). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y. Optimizing Treatment Sequence for Inoperable Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Long-Term Outcomes of Surgery First versus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in a Real-World Setting. Int. J. Cancer 2025, 156, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van la Parra, R.F.D.; Clough, K.B.; Thygesen, H.H.; Levy, E.; Poulet, B.; Sarfati, I.; Nos, C. Oncological Safety of Oncoplastic Level II Mammoplasties After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Large Breast Cancers: A Matched-Cohort Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5920–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, K.B.; Acosta-Marín, V.; Nos, C.; Alran, S.; Rouanet, P.; Garbay, J.R.; Giard, S.; Verhaeghe, J.L.; Houvenaeghel, G.; Flipo, B.; et al. Rates of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Oncoplastic Surgery for Breast Cancer Surgery: A French National Survey. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, L.; Pienkowski, T.; Im, Y.-H.; Tseng, L.-M.; Liu, M.-C.; Lluch, A.; Starosławska, E.; de la Haba-Rodriguez, J.; Im, S.-A.; Pedrini, J.L.; et al. 5-Year Analysis of Neoadjuvant Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab in Patients with Locally Advanced, Inflammatory, or Early-Stage HER2-Positive Breast Cancer (NeoSphere): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Cortés, J.; Dent, R.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Im, S.-A.; Ahn, J.-H.; et al. Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy Followed by Pembrolizumab in Patients With Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2342107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshan, M.; Cirrincione, C.T.; Sikov, W.M.; Berry, D.A.; Jasinski, S.; Weisberg, T.F.; Somlo, G.; Hudis, C.; Winer, E.; Ollila, D.W. Impact of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage II-III Triple Negative Breast Cancer on Eligibility for Breast-Conserving Surgery and Breast Conservation Rates: Surgical Results from CALGB 40603 (Alliance). Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vugts, G.; Maaskant-Braat, A.J.G.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Roumen, R.M.H.; Luiten, E.J.T.; Voogd, A.C. Patterns of Care in the Administration of Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. A Population-Based Study. Breast J. 2016, 22, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinterri, C.; Barbieri, E.; Sagona, A.; Bottini, A.; Canavese, G.; Gentile, D. De-Escalation Surgery in CT3-4 Breast Cancer Patients after Neoadjuvant Therapy: Predictors of Breast Conservation and Comparison of Long-Term Oncological Outcomes with Mastectomy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinterri, C.; Sagona, A.; Barbieri, E.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; Caraceni, G.; Ambrogi, G.; Jacobs, F.; Biondi, E.; Scardina, L.; Gentile, D. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Clinical Experience with Node-Negative and Node-Positive Disease Prior to Systemic Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahler-Ribeiro-Fontana, S.; Pagan, E.; Magnoni, F.; Vicini, E.; Morigi, C.; Corso, G.; Intra, M.; Canegallo, F.; Ratini, S.; Leonardi, M.C.; et al. Long-Term Standard Sentinel Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Treatment in Breast Cancer: A Single Institution Ten-Year Follow-Up. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughey, J.C.; Suman, V.J.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Ahrendt, G.M.; Wilke, L.G.; Taback, B.; Leitch, A.M.; Kuerer, H.M.; Bowling, M.; Flippo-Morton, T.S.; et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer: The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Clinical Trial. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, T.; Bauerfeind, I.; Fehm, T.; Fleige, B.; Hausschild, M.; Helms, G.; Lebeau, A.; Liedtke, C.; von Minckwitz, G.; Nekljudova, V.; et al. Sentinel-Lymph-Node Biopsy in Patients with Breast Cancer before and after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (SENTINA): A Prospective, Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, J.F.; Poirier, B.; Basik, M.; Holloway, C.M.B.; Gaboury, L.; Sideris, L.; Meterissian, S.; Arnaout, A.; Brackstone, M.; McCready, D.R.; et al. Sentinel Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Biopsy-Proven Node-Positive Breast Cancer: The SN FNAC Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, R.; Zuber, V.; Fiacco, E.; Carriero, F.; Gattuso, M.I.; Nazzaro, L.; Panizza, P.; Gianolli, L.; Canevari, C.; Di Muzio, N.; et al. Sentinel Node Biopsy after Primary Systemic Therapy in Node Positive Breast Cancer Patients: Time Trend, Imaging Staging Power and Nodal Downstaging According to Molecular Subtype. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, A.V.; Montagna, G.; Mamtani, A.; Sevilimedu, V.; Edelweiss, M.; Capko, D.; Cody, H.S.; El-Tamer, M.; Gemignani, M.L.; Heerdt, A.; et al. Nodal Recurrence in Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer Treated with Sentinel Node Biopsy Alone after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy—A Rare Event. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhar, C.G.; Borštnar, S.; Gazić, B.; Matos, E. Complete Response in the Axilla and the Non-Triple Negative Subtype Are Favourable Prognostic Factors for Survival Outcomes in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Breast 2023, 69, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoodi, M. Factors Affecting Pathological Complete Response in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Cases Receiving Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Eur. J. Breast Health 2024, 20, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samiei, S.; Simons, J.M.; Engelen, S.M.E.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Classe, J.-M.; Smidt, M.L. EUBREAST Group Axillary Pathologic Complete Response After Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy by Breast Cancer Subtype in Patients With Initially Clinically Node-Positive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, e210891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Abramson, V.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Anderson, B.; Bailey, J.; Burstein, H.J.; et al. Breast Cancer, Version 3.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterlund, L.; Celebioglu, F.; Hatschek, T.; Frisell, J.; de Boniface, J. Long-Term Prognosis in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Residual Disease after Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy but Not with Initial Nodal Status. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinterri, C.; Barbieri, E.; Sagona, A.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; Gentile, D. De-Escalation of Axillary Surgery in Clinically Node-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy: Comparative Long-Term Outcomes of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy versus Axillary Lymph Node Dissection. Cancers 2024, 16, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dux, J.; Habibi, M.; Malik, H.; Jacobs, L.; Wright, P.A.; Lange, J.; Camp, M.; O’Donnell, M.; Sun, B.; Tran, H.-T.; et al. Impact of Axillary Surgery on Outcome of Clinically Node Positive Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 202, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological Complete Response and Long-Term Clinical Benefit in Breast Cancer: The CTNeoBC Pooled Analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.; Canzian, J.; Barbieri, E.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; De Sanctis, R.; Tinterri, C. Superior Survival and Lower Recurrence Outcomes with Breast-Conserving Surgery Compared to Mastectomy Following Neoadjuvant Therapy in 607 Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2025, 17, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.; Sagona, A.; De Carlo, C.; Fernandes, B.; Barbieri, E.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; Jacobs, F.; Vatteroni, G.; Scardina, L.; Biondi, E.; et al. Pathologic Response and Residual Tumor Cellularity after Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy Predict Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients. Breast 2023, 69, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.H.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Dowsett, M.; McKernin, S.E.; Carey, L.A.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hayes, D.F.; Lakhani, S.R.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO/CAP Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1346–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Chen, S.; Shao, Z.-M.; Di, G.-H. A Nomogram for Predicting the Pathological Response of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, O.; Sipsy, L.M.; Yao, K.; James, T.A. A Predictive Model for Axillary Node Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, F.; Albasini, S.; Sorrentino, L.; Armatura, G.; Carolla, C.; Chiappa, C.; Combi, F.; Curcio, A.; Della Valle, A.; Ferrari, G.; et al. Development of a Novel Nomogram-Based Online Tool to Predict Axillary Status after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in CN+ Breast Cancer: A Multicentre Study on 1950 Patients. Breast 2021, 60, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, S.B.; Hoskin, T.L.; Stafford, A.P.; Boughey, J.C. Factors Influencing Non-Sentinel Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Positive Sentinel Lymph Node(s) After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7769–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, R.-J.; de Bruijn, A.; Voogd, A.C.; Bloemen, J.G.; Van Riet, Y.E.; Vriens, B.E.P.; Smidt, M.L.; Siesling, S.; van der Sangen, M.J.C.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P. Rate and Predictors of Nodal Pathological Complete Response Following Neoadjuvant Endocrine Treatment in Clinically Biopsy-Proven Node-Positive Breast Cancer Patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 1928–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman-Eldar, O.; Ozmen, T.; El Haddi, S.J.; Goel, N.; Tjendra, Y.; Kesmodel, S.B.; Moller, M.G.; Franceschi, D.; Layton, C.; Avisar, E. Axillary Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Node-Positive, Estrogen Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Breast Cancer Patients: Predictors and Oncologic Outcomes. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Gentile, D.; Bottini, A.; Sagona, A.; Gatzemeier, W.; Losurdo, A.; Fernandes, B.; Tinterri, C. Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Luminal, Node Positive Breast Cancer: Characteristics, Treatment and Oncological Outcomes: A Single Center’s Experience. Eur. J. Breast Health 2021, 17, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Number (%)/Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age (years) | 53.1 (11.9) |
| Post-menopausal | 158 (60.3%) |
| Pre-operative staging | |
| Mammography | 180 (68.7%) |
| Breast and axillary US | 262 (100%) |
| Axillary biopsy | 102 (38.9%) |
| MRI | 105 (40.1%) |
| PET | 189 (72.1%) |
| Dimension pre-NAT (mm) | 36.3 (17.8) |
| Stage pre-NAT | |
| cT1 | 39 (14.9%) |
| cT2 | 152 (58.0%) |
| cT3 | 36 (13.7%) |
| cT4 | 35 (13.4%) |
| cN0 | 21 (8.0%) |
| cN+ | 241 (92.0%) |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | |
| NAT without anthracycline | 12 (4.6%) |
| NAT with anthracycline and taxanes | 250 (95.4%) |
| Trastuzumab | 84 (32.1%) |
| Pertuzumab | 6 (2.3%) |
| Pembrolizumab | 8 (3.0%) |
| Completed cycles | 227 (86.6%) |
| Tumor | |
| Subtype | |
| HR+/HER2− | 120 (45.8%) |
| HER2+ | 84 (32.1%) |
| Triple-negative | 58 (22.1%) |
| Histotype | |
| Ductal | 239 (91.2%) |
| Lobular | 23 (8.8%) |
| Single nodule | 190 (72.5%) |
| Pathologic response | |
| Dimension post-NAT (mm) | 19.0 (25.5) |
| Stage post-NAT | |
| ypT0 | 54 (20.6%) |
| ypTis | 13 (5.0%) |
| ypTmi | 4 (1.5%) |
| ypT1a | 18 (6.9%) |
| ypT1b | 22 (8.4%) |
| ypT1c | 60 (22.9%) |
| ypT2 | 65 (24.8%) |
| ypT3 | 4 (1.5%) |
| ypT4 | 22 (8.4%) |
| Surgical treatment | |
| BCS | 111 (42.4%) |
| Mastectomy | 151 (57.6%) |
| Post-operative treatment | |
| Taxanes | 21 (8.0%) |
| Capecitabine | 28 (10.7%) |
| Radiotherapy | 223 (85.1%) |
| Endocrine | 163 (62.2%) |
| T-DM1 | 55 (21.0%) |
| Abemaciclib | 9 (3.4%) |
| Number (%)/Median (Range) | |
|---|---|
| Type of axillary surgery | |
| SLNB followed by ALND | 87 (33.2%) |
| Direct ALND | 175 (66.8%) |
| Number of SLNs | 1 (1–6) |
| 1 | 50/87 (57.5%) |
| 2 | 19/87 (21.8%) |
| ≥3 | 18/87 (20.7%) |
| Data on non-SLNs | |
| Number of evaluated non-SLNs | 12 (3–49) |
| Number of metastatic non-SLNs | 1 (0–34) |
| Nodal stage post-NAT | |
| ypN0 | 66 (25.2%) |
| ypNmi | 10 (3.8%) |
| ypN1 | 92 (35.1%) |
| ypN2 | 61 (23.3%) |
| ypN3 | 33 (12.6%) |
| Characteristics | ypN0-mi-1 (n = 168) | ypN2-3 (n = 94) | Univariate Analysis p-Value | Multivariate Analysis p-Value OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age [years, mean (SD)] | 52.3 (11.2) | 54.5 (13.1) | 0.149 | - |
| Menopausal status | ||||
| Pre-menopausal | 72 (42.9%) | 32 (34.0%) | 0.162 | - |
| Post-menopausal | 96 (57.1%) | 62 (66.0%) | - | |
| NAT | ||||
| NAT without anthracycline | ||||
| Yes | 6 (3.6%) | 6 (6.4%) | 0.296 | - |
| No | 162 (96.4%) | 88 (93.6%) | - | |
| Completed cycles | ||||
| Yes | 148 (88.1%) | 79 (84.0%) | 0.355 | - |
| No | 20 (11.9%) | 15 (16.0%) | - | |
| Immunotherapy | ||||
| Yes | 78 (46.4%) | 20 (21.3%) | <0.001 a | 0.401 1.837 (0.444–7.602) |
| No | 90 (53.6%) | 74 (78.7%) | - | - |
| Pre-operative staging | ||||
| Single nodule | ||||
| Yes | 122 (72.6%) | 68 (72.3%) | 0.961 | - |
| No | 46 (27.4%) | 104 (27.7%) | - | |
| Dimension pre-NAT [mm, mean (SD)] | 34.3 (17.3) | 39.9 (18.2) | 0.034 a | 0.655 1.006 (0.979–1.034) |
| Stage pre-NAT | ||||
| cT1-2 | 130 (77.4%) | 61 (64.9%) | 0.029 a | 0.507 1.466 (0.473–4.540) |
| cT3-4 | 38 (22.6%) | 33 (35.1%) | - | - |
| cN0 | 18 (10.7%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.031 a | 0.013 a 7.697 (1.537–38.550) |
| cN+ | 150 (89.3%) | 91 (96.8%) | - | - |
| Tumor | ||||
| Subtype | ||||
| HR+/HER2− | 55 (32.7%) | 65 (69.1%) | <0.001 a | 0.003 a 3.945 (1.602–9.716) |
| Non-HR+/HER2− | 113 (67.3%) | 29 (30.9%) | - | - |
| HER2+ | 72 (42.9%) | 12 (12.8%) | <0.001 a | 0.183 0.343 (0.071–1.656) |
| Non-HER2+ | 96 (57.1%) | 82 (87.2%) | - | - |
| Triple-negative | 41 (24.4%) | 17 (18.1%) | 0.237 | - |
| Non-triple-negative | 127 (75.6%) | 77 (81.9%) | - | |
| Histotype | ||||
| Ductal | 157 (93.5%) | 82 (87.2%) | 0.088 | - |
| Lobular | 11 (6.5%) | 12 (12.8%) | - | |
| Dimension post-NAT [mm, mean (SD)] | 12.9 (17.8) | 29.9 (32.7) | <0.001 a | <0.001 a 1.043 (1.021–1.066) |
| Surgery | ||||
| BCS | 73 (43.5%) | 38 (40.4%) | 0.634 | - |
| Mastectomy | 95 (56.5%) | 56 (59.6%) | - | |
| SLNB followed by ALND | 59 (35.1%) | 28 (29.8%) | 0.379 | - |
| Direct ALND | 109 (64.9%) | 66 (70.2%) | - | |
| Number of evaluated non-SLNs | ||||
| ≤12 | 71 (42.3%) | 28 (29.8%) | 0.062 | - |
| >12 | 97 (57.7%) | 66 (70.2%) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentile, D.; Canzian, J.; Barbieri, E.; Sagona, A.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; Tinterri, C. Predictors of High-Burden Residual Axillary Disease After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101596
Gentile D, Canzian J, Barbieri E, Sagona A, Di Maria Grimaldi S, Tinterri C. Predictors of High-Burden Residual Axillary Disease After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101596
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentile, Damiano, Jacopo Canzian, Erika Barbieri, Andrea Sagona, Simone Di Maria Grimaldi, and Corrado Tinterri. 2025. "Predictors of High-Burden Residual Axillary Disease After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101596
APA StyleGentile, D., Canzian, J., Barbieri, E., Sagona, A., Di Maria Grimaldi, S., & Tinterri, C. (2025). Predictors of High-Burden Residual Axillary Disease After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 17(10), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101596







