Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Prostate Patients and Structure Delineations
2.2. Treatment Plans and LETd Optimization
2.3. RBE Models
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Evaluation
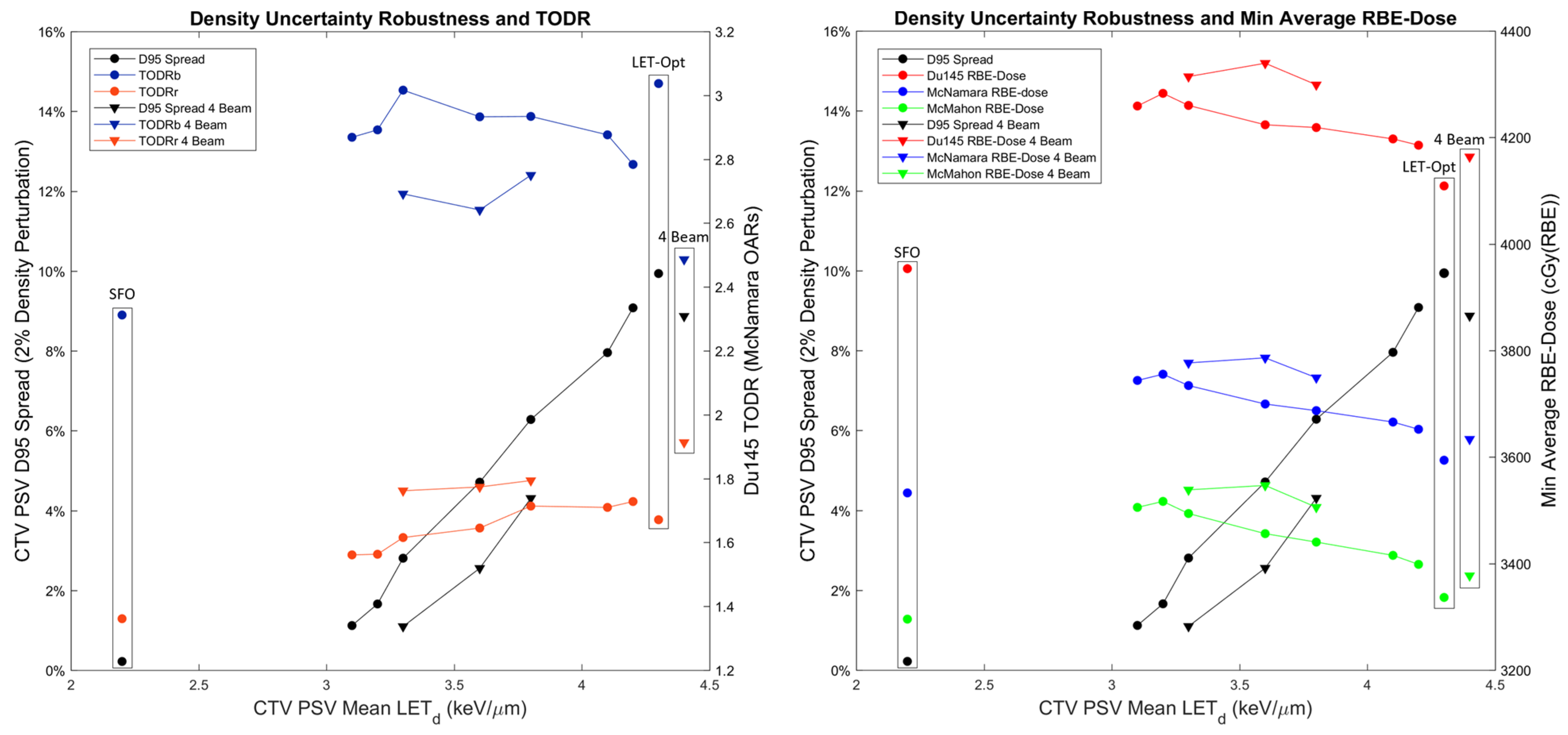
2.5. Robust Evaluation
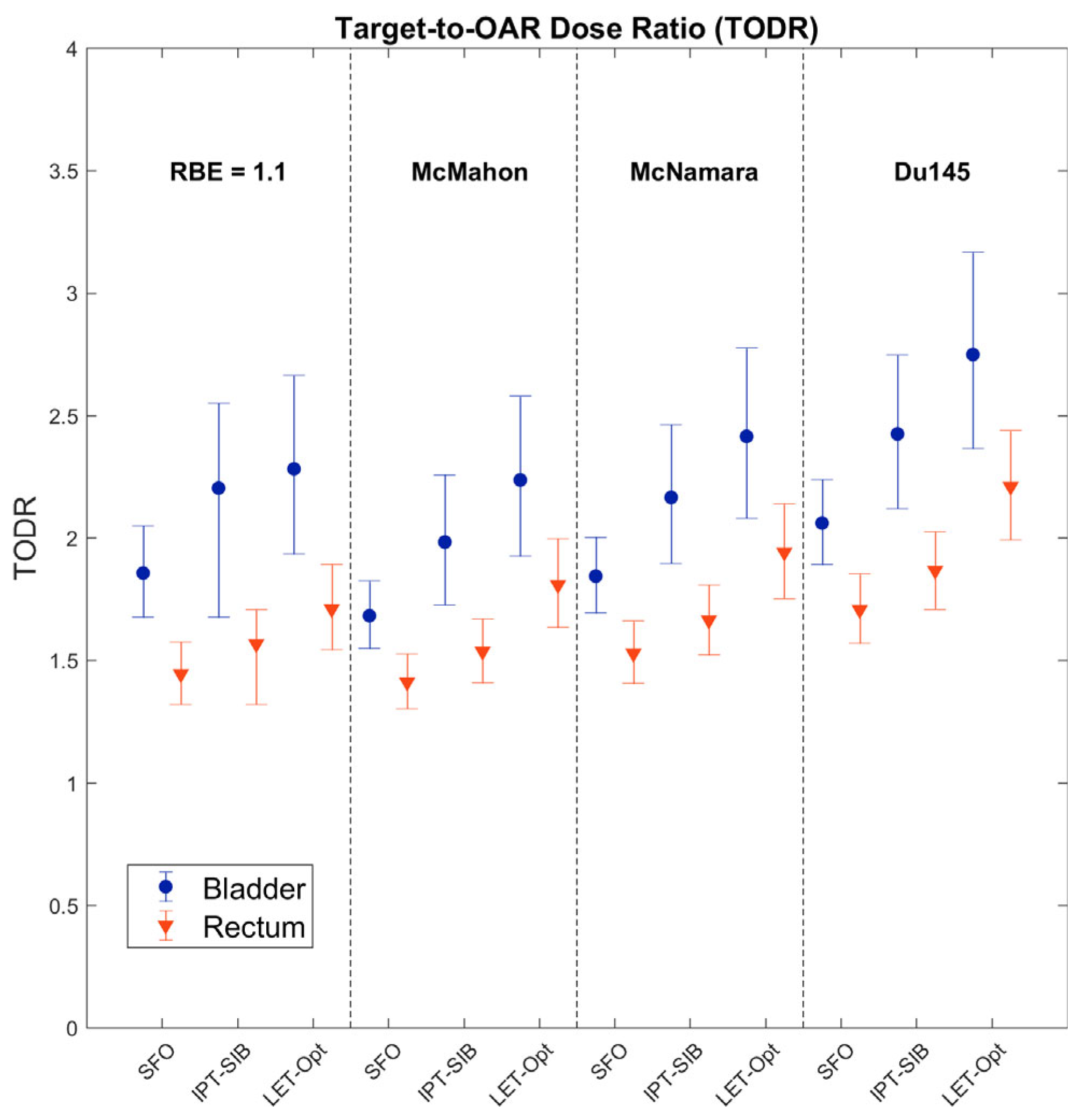
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Dosimetric Improvements and Clinical Potential
4.2. Treatment Planning Considerations for LETd Optimization
4.3. RBE Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dearnaley, D.P.; Sydes, M.R.; Graham, J.D.; Aird, E.G.; Bottomley, D.; Cowan, R.A.; Huddart, R.A.; Jose, C.C.; Matthews, J.H.; Millar, J.; et al. Escalated-Dose versus Standard-Dose Conformal Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer: First Results from the MRC RT01 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.; Tyldesley, S.; Morris, W.J.; Keyes, M.; Halperin, R.; Pai, H.; McKenzie, M.; Duncan, G.; Morton, G.; Hamm, J.; et al. ASCENDE-RT: An Analysis of Treatment-Related Morbidity for a Randomized Trial Comparing a Low-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Boost with a Dose-Escalated External Beam Boost for High- and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelefsky, M.J.; Pei, X.; Chou, J.F.; Schechter, M.; Kollmeier, M.; Cox, B.; Yamada, Y.; Fidaleo, A.; Sperling, D.; Happersett, L.; et al. Dose Escalation for Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy: Predictors of Long-Term Biochemical Tumor Control and Distant Metastases-Free Survival Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkmeijer, L.G.W.; Groen, V.H.; Pos, F.J.; Haustermans, K.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Smeenk, R.J.; Kunze-Busch, M.; de Boer, J.C.J.; van der Voort van Zijp, J.; van Vulpen, M.; et al. Focal Boost to the Intraprostatic Tumor in External Beam Radiotherapy for Patients With Localized Prostate Cancer: Results From the FLAME Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonteyne, V.; Villeirs, G.; Speleers, B.; De Neve, W.; De Wagter, C.; Lumen, N.; De Meerleer, G. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy as Primary Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Report on Acute Toxicity After Dose Escalation With Simultaneous Integrated Boost to Intraprostatic Lesion. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrayeh, E.; Westphalen, A.C.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Roach, M.; Jung, A.J.; Carroll, P.R.; Coakley, F.V. Does Local Recurrence of Prostate Cancer after Radiation Therapy Occur at the Site of Primary Tumor? Results of a Longitudinal MRI and MRSI Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, e787–e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, N.; Morganti, A.G.; Mattiucci, G.C.; Valentini, V.; Leone, M.; Luzi, S.; Manfredi, R.; Dinapoli, N.; Digesu, C.; Smaniotto, D. Analysis of Intraprostatic Failures in Patients Treated with Hormonal Therapy and Radiotherapy: Implications for Conformal Therapy Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Carver, E.; Feldman, A.; Pantelic, M.V.; Elshaikh, M.; Wen, N. Volumetric and Voxel-Wise Analysis of Dominant Intraprostatic Lesions on Multiparametric MRI. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorny, M.R.; De Rooij, M.; Duncan, E.; Schröder, F.H.; Parkinson, R.; Barentsz, J.O.; Thompson, L.C. Prospective Study of Diagnostic Accuracy Comparing Prostate Cancer Detection by Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy versus Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging with Subsequent Mr-Guided Biopsy in Men without Previous Prostate Biopsies. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feutren, T.; Herrera, F.G. Prostate Irradiation with Focal Dose Escalation to the Intraprostatic Dominant Nodule: A Systematic Review. Prostate Int. 2018, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, C.; Fryer, A.; Mahajan, C.; Indelicato, D.; Horne, D.; Chellini, A.; McKenzie, C.; Lawlor, P.; Henderson, R.; Li, Z.; et al. Dose-Volume Comparison of Proton Therapy and Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chera, B.S.; Vargas, C.; Morris, C.G.; Louis, D.; Flampouri, S.; Yeung, D.; Duvvuri, S.; Li, Z.; Mendenhall, N.P. Dosimetric Study of Pelvic Proton Radiotherapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 75, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietman, A.L.; DeSilvio, M.L.; Slater, J.D.; Rossi, C.J., Jr.; Miller, D.W.; Adams, J.A.; Shipley, W.U. Comparison of Conventional-Dose vs High-Dose Conformal Radiation Therapy in Clinically Localized Adenocarcima of the Prostate. A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 294, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.; Smith, T.L.; Henderson, R.H.; Hoppe, B.S.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Nichols, R.C.; Morris, C.G.; Williams, C.R.; Su, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Five-Year Biochemical Results, Toxicity, and Patient-Reported Quality of Life after Delivery of Dose-Escalated Image Guided Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietman, A.L.; Bae, K.; Slater, J.D.; Shipley, W.U.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Coen, J.J.; Bush, D.A.; Lunt, M.; Spiegel, D.Y.; Skowronski, R.; et al. Randomized Trial Comparing Conventional-Dose with High-Dose Conformal Radiation Therapy in Early-Stage Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: Long-Term Results from Proton Radiation Oncology Group/American College of Radiology 95-09. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, B.S.; Michalski, J.M.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Morris, C.G.; Henderson, R.H.; Nichols, R.C.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Williams, C.R.; Regan, M.M.; Chipman, J.J.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness Study of Patient-Reported Outcomes after Proton Therapy or Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, N.P.; Li, Z.; Hoppe, B.S.; Marcus, R.B.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Nichols, R.C.; Morris, C.G.; Williams, C.R.; Costa, J.; Henderson, R. Early Outcomes from Three Prospective Trials of Image-Guided Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, N.P.; Hoppe, B.S.; Nichols, R.C.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Morris, C.G.; Li, Z.; Su, Z.; Williams, C.R.; Costa, J.; Henderson, R.H. Five-Year Outcomes from 3 Prospective Trials of Image-Guided Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, J.D.; Rossi, C.J.; Yonemoto, L.T.; Bush, D.A.; Jabola, B.R.; Levy, R.P.; Grove, R.I.; Preston, W.; Slater, J.M. Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: The Initial Loma Linda University Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Munsell, M.F.; Choi, S.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Mathai, B.; Zhu, X.R.; Sahoo, N.; Gillin, M.; Johnson, J.L.; Amos, R.A.; et al. Quality of Life and Toxicity from Passively Scattered and Spot-Scanning Proton Beam Therapy for Localized Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaco, R.J.; Hoppe, B.S.; Flampouri, S.; McKibben, B.T.; Henderson, R.H.; Bryant, C.; Nichols, R.C.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Li, Z.; Su, Z.; et al. Rectal Toxicity After Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer, An Analysis of Outcomes of Prospective Studies Conducted at the University of Florida Proton Therapy Institute. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescribing, Recording, and Reporting Proton-Beam Therapy (ICRU Report 78). J. ICRU 2007, 7, 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H.; Niemierko, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Gerweck, L.E.; Goitein, M.; Loeffler, J.S.; Suit, H.D. Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Values for Proton Beam Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Values for Proton Beam Therapy. Variations as a Function of Biological Endpoint, Dose, and Linear Energy Transfer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, R419–R472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H.; Blakely, E.; Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Carlson, D.J.; Das, I.J.; Dong, L.; Grosshans, D.; Held, K.D.; Mohan, R.; Moiseenko, V.; et al. Report of the AAPM TG-256 on the Relative Biological Effectiveness of Proton Beams in Radiation Therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e53–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Proton Relative Biological Effectiveness-Uncertainties and Opportunities. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2019, 5, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassberger, C.; Trofimov, A.; Lomax, A.; Paganetti, H. Variations in Linear Energy Transfer within Clinical Proton Therapy Fields and the Potential for Biological Treatment Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkens, J.J.; Oelfke, U. Three-Dimensional LET Calculations for Treatment Planning of Proton Therapy. Z. Med. Phys. 2004, 14, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkelbach, J.; Paganetti, H. Robust Proton Treatment Planning: Physical and Biological Optimization. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fager, M.; Toma-Dasu, I.; Kirk, M.; Dolney, D.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Vapiwala, N.; Carabe, A. Linear Energy Transfer Painting with Proton Therapy: A Means of Reducing Radiation Doses with Equivalent Clinical Effectiveness. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henjum, H.; Dahle, T.J.; Fjæra, L.F.; Rørvik, E.; Pilskog, S.; Stokkevåg, C.H.; Mairani, A.; Ytre-Hauge, K.S. The Organ Sparing Potential of Different Biological Optimization Strategies in Proton Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, M.C.; Wilkens, J.J.; Huber, P.E.; Jensen, A.D.; Oelfke, U.; Taheri-Kadkhoda, Z. Application of Constant vs. Variable Relative Biological Effectiveness in Treatment Planning of Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, N.; Johansson, J.; Isacsson, U.; Medin, J.; Blomquist, E.; Grusell, E.; Glimelius, B. The Influence of RBE Variations in a Clinical Proton Treatment Plan for a Hypopharynx Cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 2765–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bradley, J.A.; Zheng, D.; Vega, R.B.M.; Beltran, C.J.; Mendenhall, N.; Liang, X. RBE-Weighted Dose and Its Impact on the Risk of Acute Coronary Event for Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Cheng, C.; Zheng, Y.; Risalvato, D.; Cersonsky, N.; Ramirez, E.; Zhao, L.; Larson, G.; Vargas, C. Proton Therapy vs. VMAT for Prostate Cancer: A Treatment Planning Study. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2014, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Cheng, C.Y.; Zhao, L.; Park, S.Y.; Larson, G.; Vargas, C.; Dunn, M.; Zheng, Y. Dosimetric and Radiobiological Impact of Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy and RapidArc Planning for High-Risk Prostate Cancer with Seminal Vesicles. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2017, 64, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, A.; Forsgren, A.; Hårdemark, B. Minimax Optimization for Handling Range and Setup Uncertainties in Proton Therapy. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RayStation 11B Reference Manual. 2021; RSL-D-RS-11B-REF-EN-1.0-2021-12-10.
- McMahon, S.J.; Paganetti, H.; Prise, K.M. LET-Weighted Doses Effectively Reduce Biological Variability in Proton Radiotherapy Planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 225009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Marshall, T.I.; Perozziello, F.M.; Manti, L.; Currell, F.J.; Hanton, F.; McMahon, S.J.; Kavanagh, J.N.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Romano, F.; et al. Relative Biological Effectiveness Variation along Monoenergetic and Modulated Bragg Peaks of a 62-MeV Therapeutic Proton Beam: A Preclinical Assessment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, T.I.; Chaudhary, P.; Michaelidesová, A.; Vachelová, J.; Davídková, M.; Vondráček, V.; Schettino, G.; Prise, K.M. Investigating the Implications of a Variable RBE on Proton Dose Fractionation Across a Clinical Pencil Beam Scanned Spread-Out Bragg Peak. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, A.L.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. A Phenomenological Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Model for Proton Therapy Based on All Published in Vitro Cell Survival Data. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8399–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Dale, R.G.; Jones, B. The Incorporation of the Concept of Minimum RBE (RBEmin) into the Linear-Quadratic Model and the Potential for Improved Radiobiological Analysis of High-LET Treatments. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.F. The Radiobiology of Prostate Cancer Including New Aspects of Fractionated Radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2005, 44, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J. Fractionation and Late Rectal Toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, E.; Clausen, M.; Khachonkham, S.; Deycmar, S.; Pessy, C.; Dörr, W.; Kuess, P.; Georg, D.; Gruber, S. Investigating the Impact of Alpha/Beta and LETd on Relative Biological Effectiveness in Scanned Proton Beams: An in Vitro Study Based on Human Cell Lines. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachonkham, S.; Mara, E.; Gruber, S.; Preuer, R.; Kuess, P.; Dörr, W.; Georg, D.; Clausen, M. RBE Variation in Prostate Carcinoma Cells in Active Scanning Proton Beams: In-Vitro Measurements in Comparison with Phenomenological Models. Phys. Medica 2020, 77, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efron, B.; Robert, T. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.; Park, S.H.; Lee, K.H. How to Demonstrate Similarity by Using Noninferiority and Equivalence Statistical Testing in Radiology Research. Radiology 2013, 267, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.; Flampouri, S.; Bryant, C.; Liang, X.; Mendenhall, N.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Muren, L.P. Cross-Modality Applicability of Rectal Normal Tissue Complication Probability Models from Photon- to Proton-Based Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, A.; Glimelius, L.; Bokrantz, R. The LET Trilemma: Conflicts between Robust Target Coverage, Uniform Dose, and Dose-Averaged LET in Carbon Therapy. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 7338–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poludniowski, G.; Allinson, N.M.; Evans, P.M. Proton Radiography and Tomography with Application to Proton Therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Harrison, A.P.; Zhang, L.; Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, L. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Technical Basis and Clinical Applications, 1st ed.; Xing, L., Giger, M.L., Min, J.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 265–289. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, A.; Purkayastha, S.; Padmanaban, G.P.; Krupinski, E.; Trivedi, H.; Banerjee, I.; Gichoya, J.W. Current Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Radiology and Their Best Supporting Evidence. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; Schalekamp, S.; Rutten, M.J.C.M.; van Ginneken, B.; de Rooij, M. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: 100 Commercially Available Products and Their Scientific Evidence. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
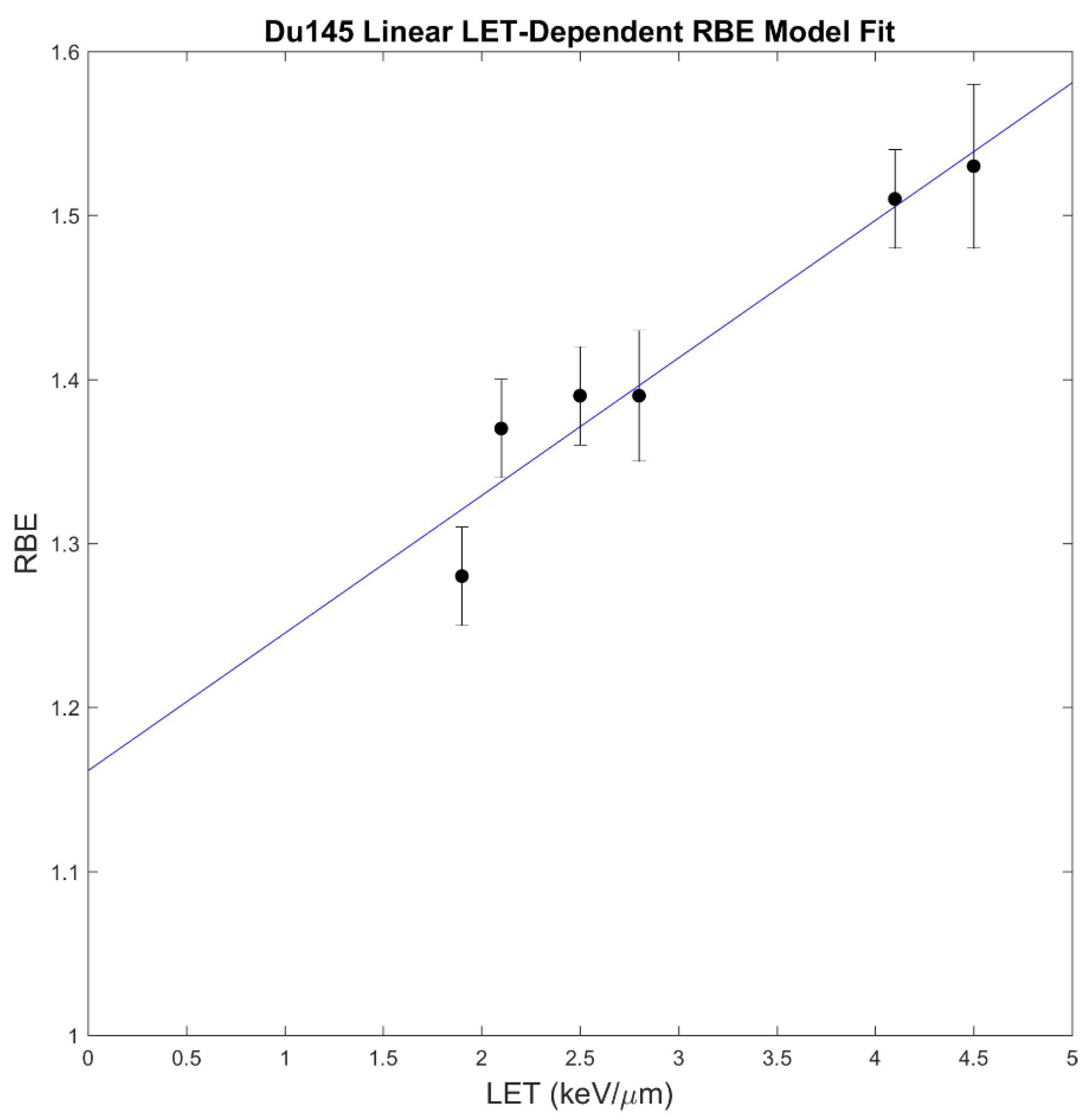
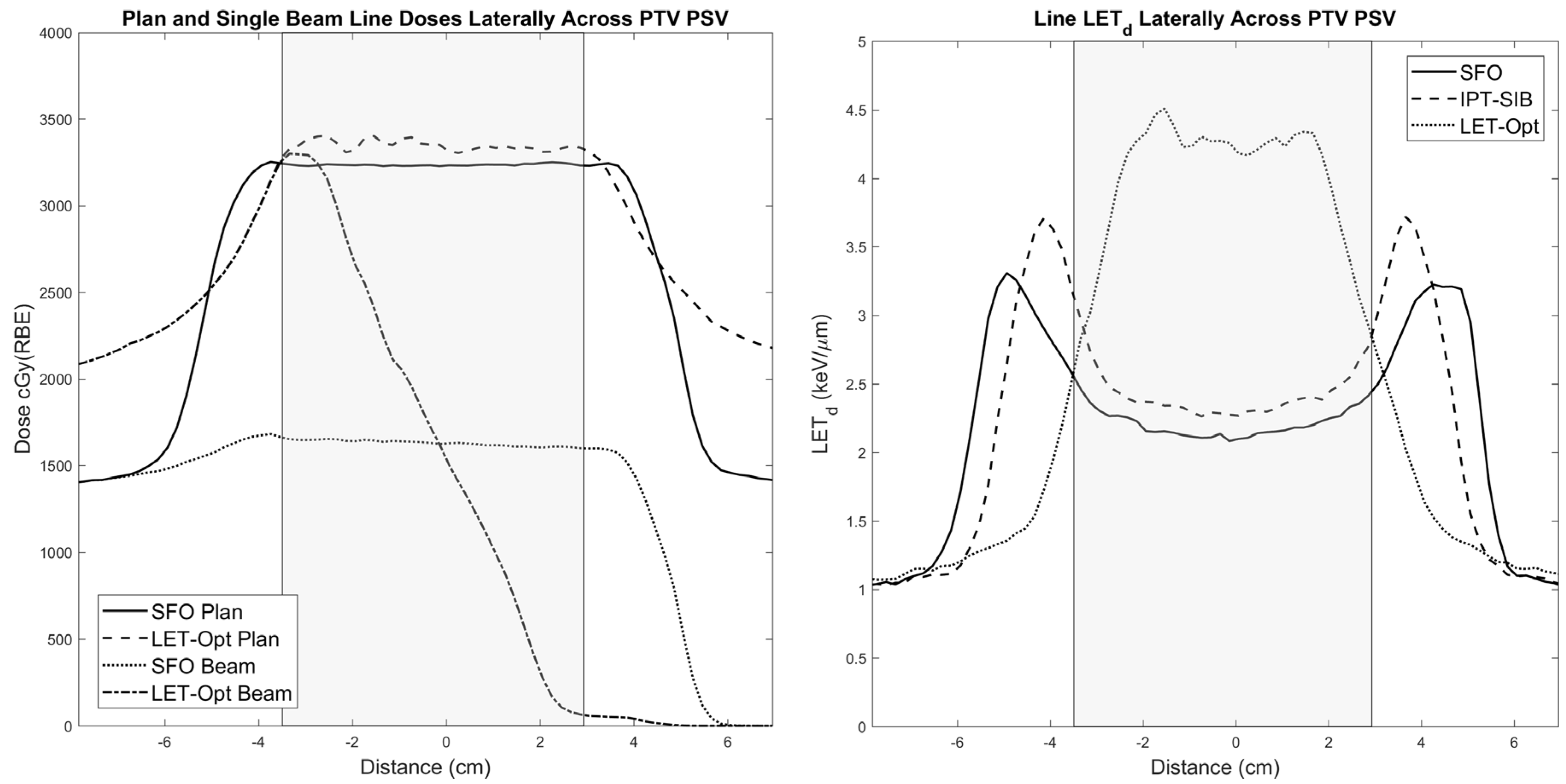
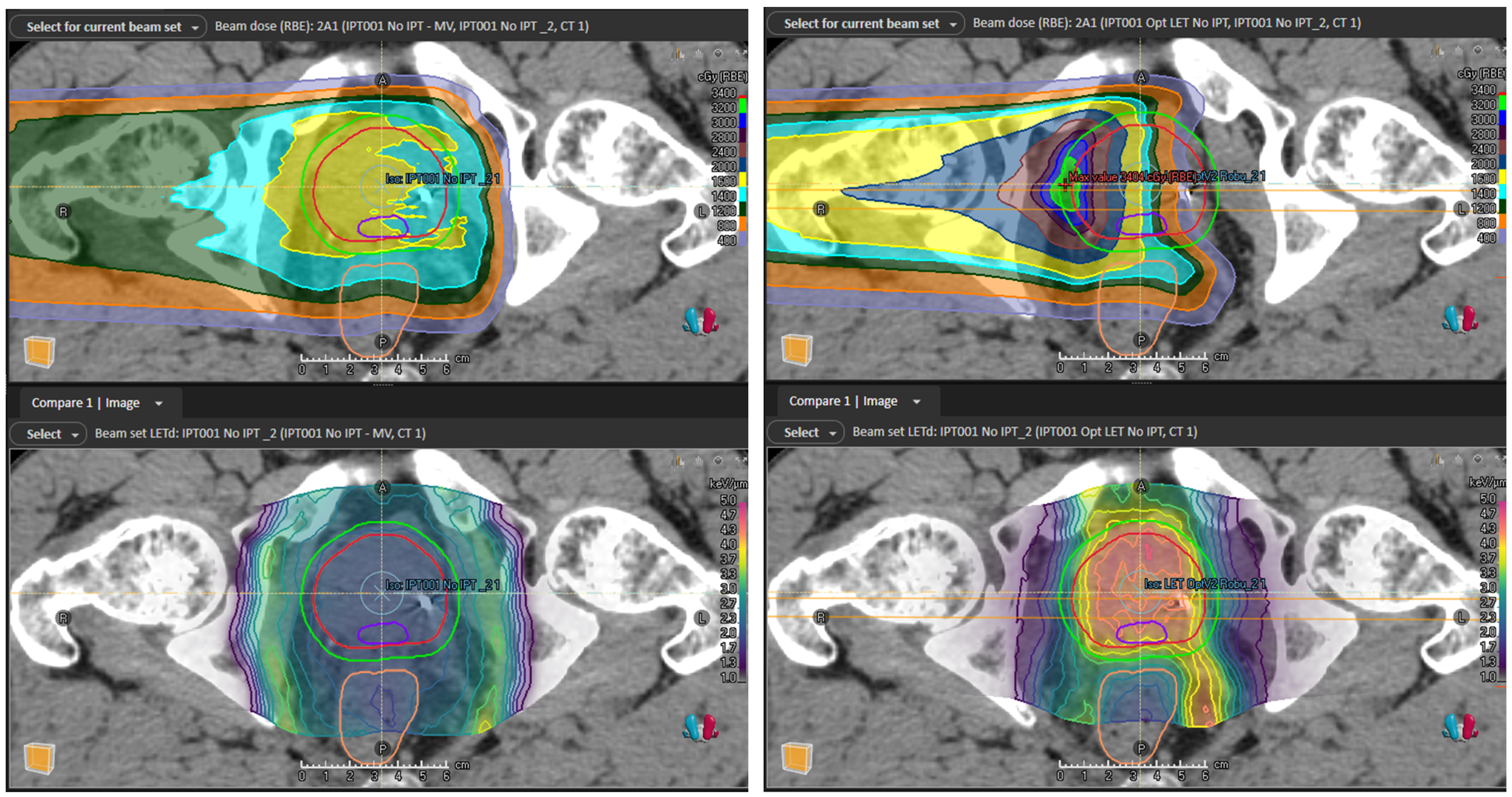
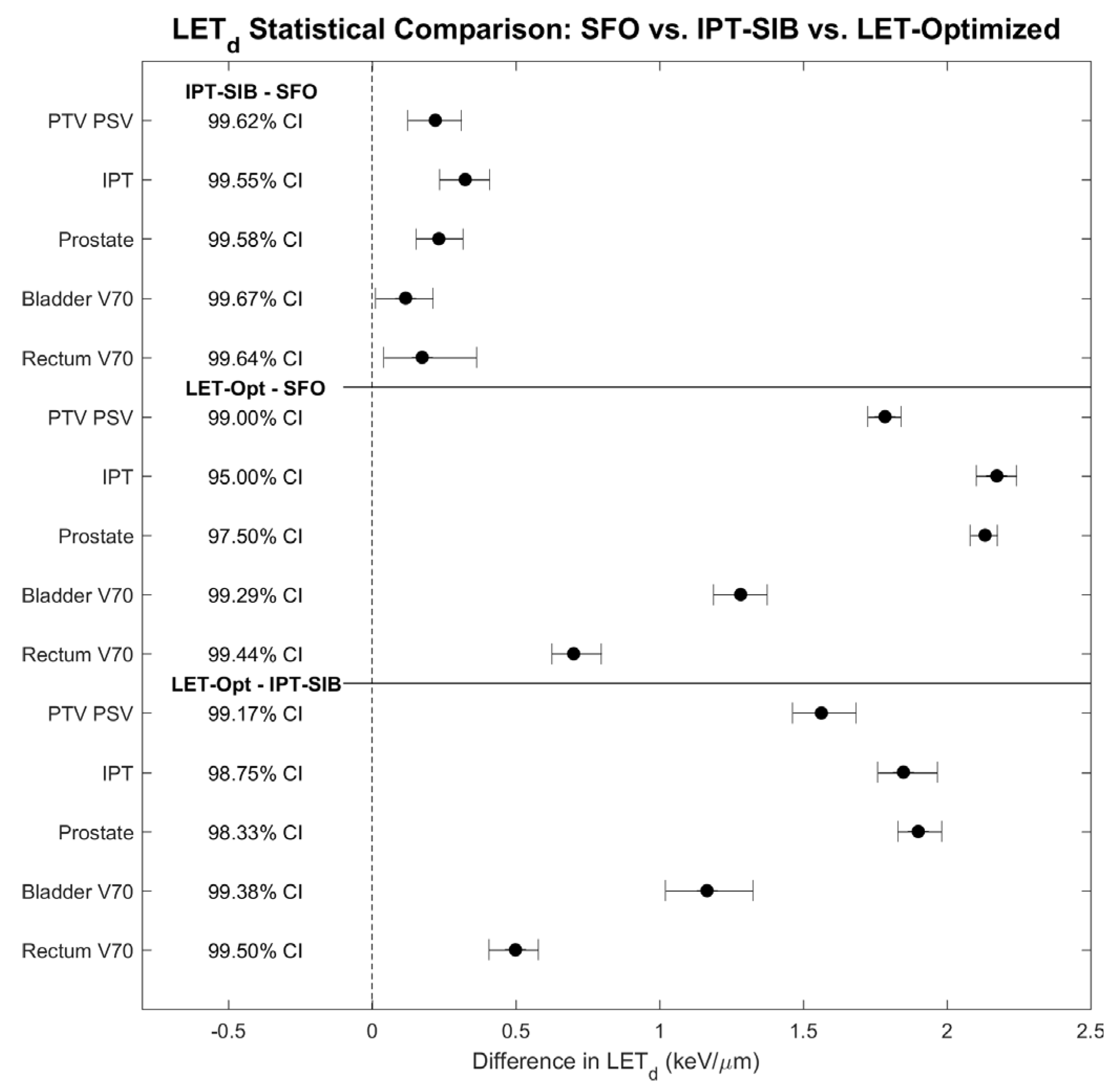
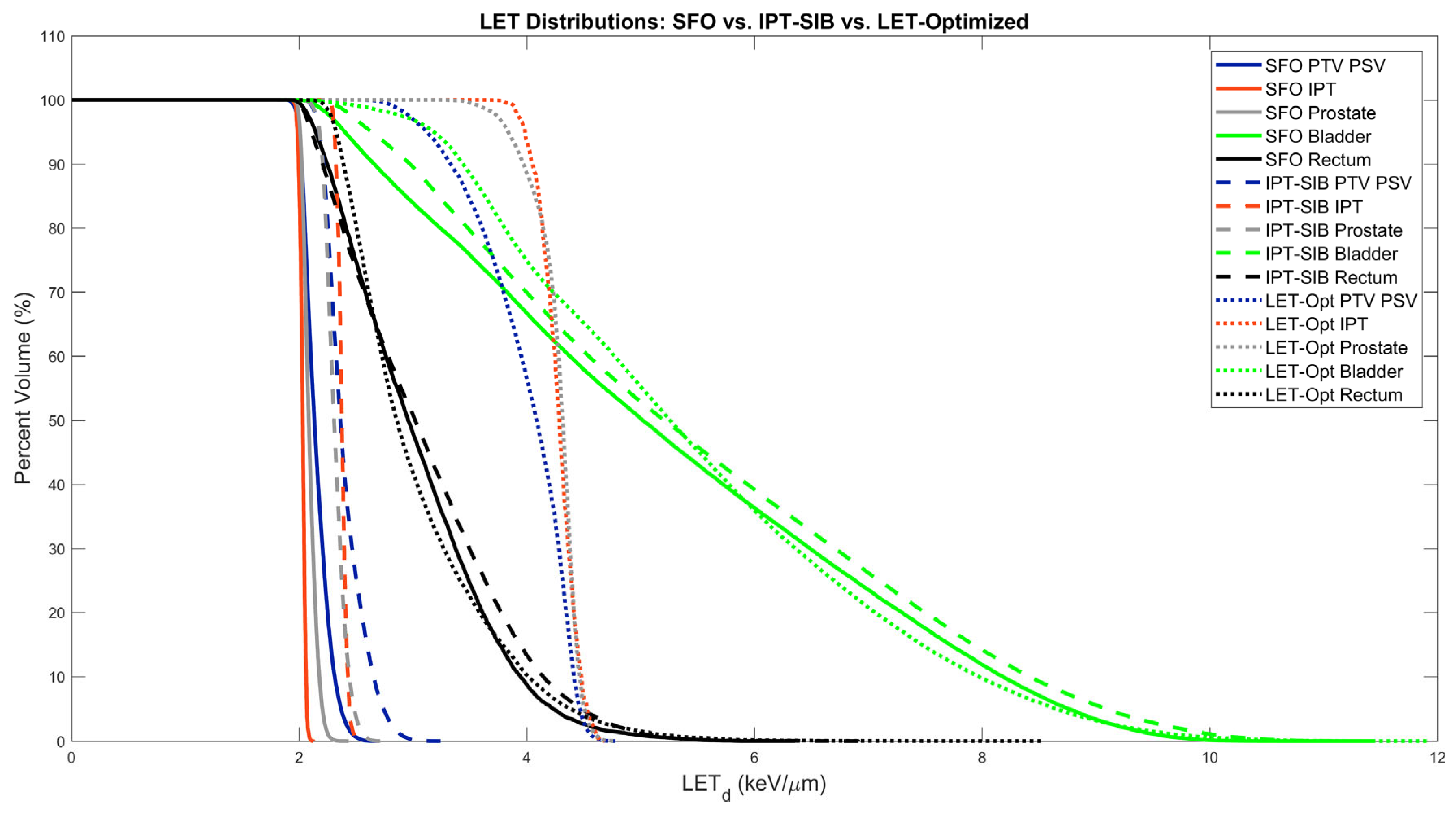
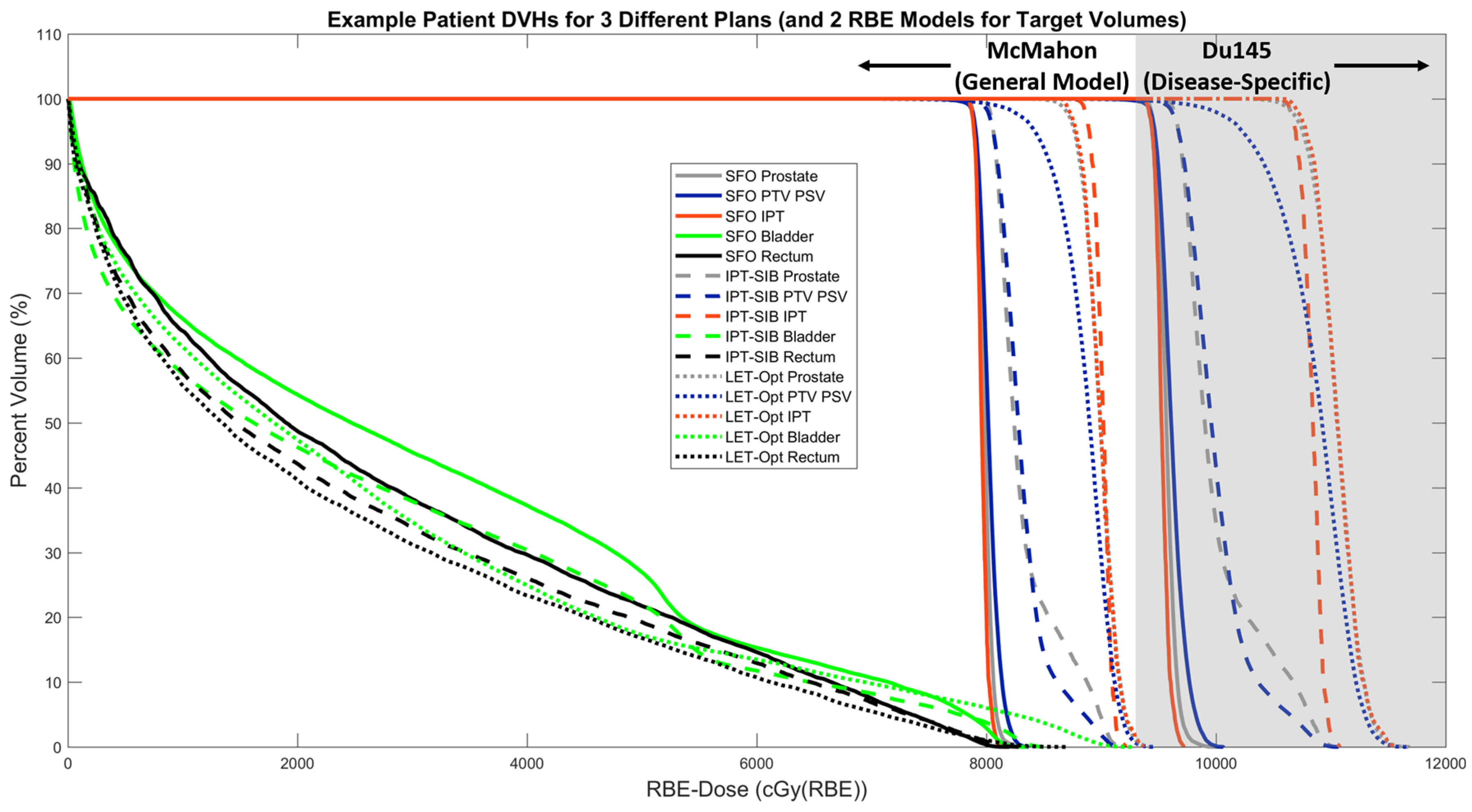
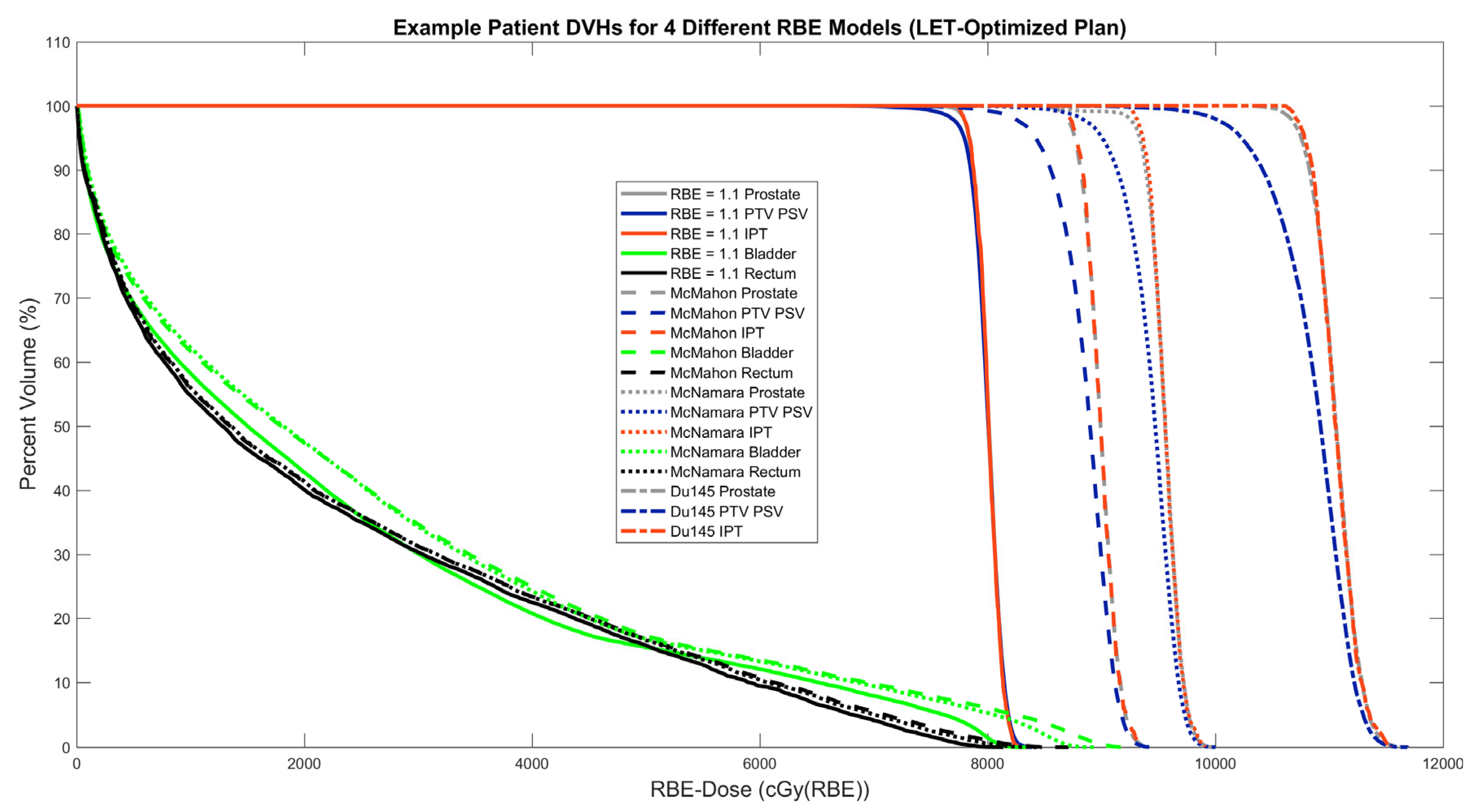
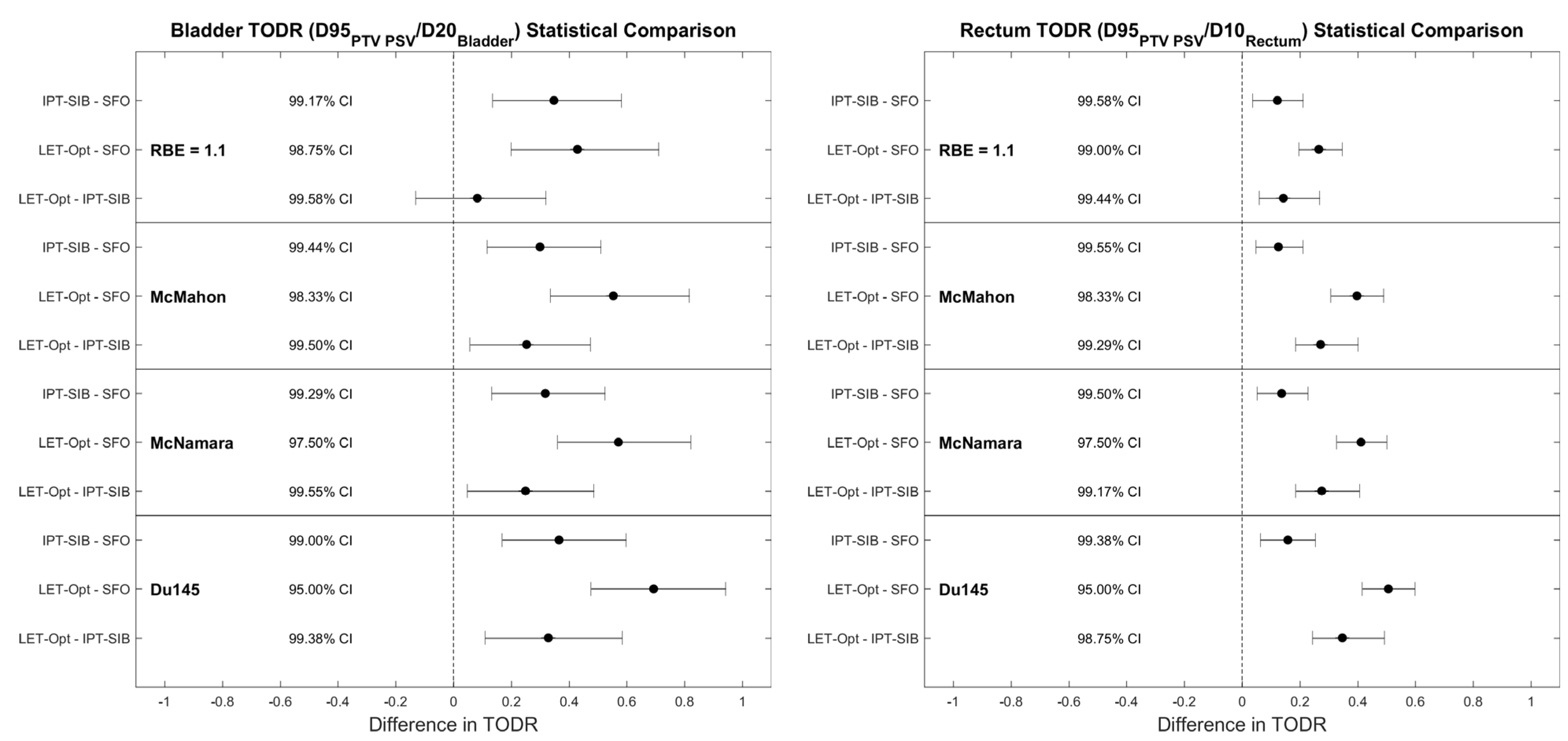
| Mean LETd (keV/µm) | McMahon RBE | McNamara RBE | Du145 RBE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFO Plan PTV PSV IPT (2 Gy(RBE = 1.1)/fx) Prostate Bladder V70 Rectum V70 | 2.190 [2.153, 2.227] 2.103 [2.067, 2.140] 2.120 [2.088, 2.154] 2.349 [2.281, 2.409] 2.196 [2.136, 2.258] | 1.120 [1.118, 1.123] 1.116 [1.114, 1.118] 1.117 [1.115, 1.119] 1.129 [1.126, 1.133] 1.121 [1.118, 1.124] | 1.195 [1.193, 1.197] 1.190 [1.188, 1.192] 1.191 [1.189, 1.193] 1.123 [1.121, 1.125] 1.112 [1.110, 1.114] | 1.344 [1.341, 1.347] 1.337 [1.334, 1.340] 1.338 [1.335, 1.341] - - |
| IPT-SIB Plan PTV PSV IPT (2.2 Gy(RBE = 1.1)/fx) Prostate Bladder V70 Rectum V70 | 2.411 [2.324, 2.494] 2.428 [2.352, 2.500] 2.353 [2.280, 2.429] 2.466 [2.351, 2.569] 2.370 [2.233, 2.500] | 1.133 [1.128, 1.137] 1.134 [1.129, 1.138] 1.129 [1.125, 1.134] 1.136 [1.129, 1.141] 1.130 [1.123, 1.138] | 1.206 [1.202, 1.211] 1.199 [1.196, 1.203] 1.203 [1.199, 1.207] 1.127 [1.123, 1.130] 1.118 [1.113, 1.122] | 1.363 [1.355, 1.370] 1.364 [1.358, 1.370] 1.358 [1.352, 1.364] - - |
| LET-Optimized Plan PTV PSV IPT (2 Gy(RBE = 1.1)/fx) Prostate Bladder V70 Rectum V70 | 3.975 [3.945, 4.004] 4.277 [4.226, 4.327] 4.253 [4.215, 4.286] 3.631 [3.588, 3.673] 2.905 [2.847, 2.967] | 1.219 [1.217, 1.220] 1.235 [1.233, 1.238] 1.234 [1.232, 1.236] 1.200 [1.197, 1.202] 1.160 [1.157, 1.163] | 1.287 [1.286, 1.289] 1.302 [1.300, 1.305] 1.301 [1.299, 1.303] 1.167 [1.165, 1.168] 1.135 [1.133, 1.137] | 1.494 [1.491, 1.496] 1.519 [1.515, 1.524] 1.517 [1.514, 1.520] - - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieceli, M.; Park, J.; Hsi, W.C.; Saki, M.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Johnson, P.; Artz, M. Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models. Cancers 2024, 16, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040780
Vieceli M, Park J, Hsi WC, Saki M, Mendenhall NP, Johnson P, Artz M. Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040780
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieceli, Michael, Jiyeon Park, Wen Chien Hsi, Mo Saki, Nancy P. Mendenhall, Perry Johnson, and Mark Artz. 2024. "Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models" Cancers 16, no. 4: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040780
APA StyleVieceli, M., Park, J., Hsi, W. C., Saki, M., Mendenhall, N. P., Johnson, P., & Artz, M. (2024). Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models. Cancers, 16(4), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040780






