Simple Summary
Established risk factors for primary malignant brain tumors include hereditary syndromes, family history of brain tumors, head trauma, smoking, alcohol consumption, radiation exposure, electromagnetic wave exposure, infections, inflammation, and exposure to toxic substances. However, the impact of acquired ocular motor cranial nerve palsies on subsequent primary malignant brain tumors remains underexplored. Our research presents an exhaustive analysis of data from the Korea National Health Insurance Service from 2010 to 2017. Correlation between ocular motor cranial nerve palsies and emergence of primary malignant brain tumors within a Korean population was investigated. Our findings emphasize an amplified risk of primary malignant brain tumors in patients diagnosed with ocular motor cranial nerve palsies, particularly among women aged below 65.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between ocular motor cranial nerve palsies (OMCNP) and the occurrence of primary malignant brain tumors in a Korean population, using the national sample cohort database from Korea National Health Insurance Service (KNHIS). KNHIS data between 2010 and 2017 were analyzed. Our sample encompassed 118,686 participants, including 19,781 from a recently diagnosed OMCNP cohort and 98,905 from a matched control cohort through a 1:5 propensity score matching based on age and gender. To counteract the issue of reverse causation, we integrated a one-year time lag in our sensitivity analysis. Study participants were followed up until 31 December 2019. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was used to compute the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for primary malignant brain tumors according to the OMCNP diagnosis. Additionally, we performed a subgroup analysis to discern effects of various factors on the association between OMCNP and primary malignant brain tumors. HR for primary malignant brain tumors was 3.272 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.294 to 4.665) in the OMCNP cohort compared to the control cohort in a fully adjusted model for age, sex, socio-economic status, smoking, drinking, regular physical exercise, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Further subgroup analysis revealed that the risk of primary malignant brain tumors was significantly increased in women with OMCNP compared to men with OMCNP (HR: 5.118 in women vs. 2.441 in men, p = 0.0440), and in those aged <65 years than in those aged ≥65 years (HR: 6.951 in age < 65 years vs. 1.899 in age ≥ 65 years, p = 0.0006). Our population-based cohort study demonstrated a significantly increased risk of subsequent primary malignant brain tumors in patients with OMCNP. Particularly, OMCNP-afflicted women aged below 65 manifested a heightened probability of developing primary malignant brain tumors compared to those devoid of OMCNP.
1. Introduction
Malignant brain tumors are fatal and crucial diseases that can be accompanied by serious neurological complications [1,2,3,4]. Given their critical nature, timely monitoring and early detection are essential for high-risk individuals. Although malignant brain tumors are composed of over 100 diverse histologically distinct subtypes [5,6], established risk factors for primary malignant brain tumors include hereditary syndromes (such as tuberous sclerosis and neurofibromatosis); family history of brain tumors; head trauma; smoking; alcohol consumption; radiation exposure; electromagnetic wave exposure; infections; inflammation; and exposure to toxic substances [7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
The ocular motor cranial nerve is composed of the third (oculomotor), fourth (trochlear), and sixth (abducens) cranial nerves. The third nerve arises from the interpeduncular fossa of the midbrain, passes along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus and through the superior orbital fissure, and innervates the levator palpebrae superioris and most extraocular muscles including the superior, medial, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles. It also has parasympathetic functions, controlling ciliary and sphincter pupillae muscles. The fourth nerve arises from the dorsal surface of the midbrain just below the inferior colliculus, surrounds the contralateral surface of the midbrain, passes along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus and through the superior orbital fissure, and innervates the superior oblique muscles. Lastly, the sixth nerve arises from the pontomedullary junction near the midline, crosses the petrous apex within Dorello’s canal, ascends to pass through the cavernous sinus near internal carotid arteries, exits through the superior orbital fissure, and innervates the lateral rectus muscle [14].
Diplopia is disturbing and the most common symptom of acquired ocular motor cranial nerve palsies (OMCNP). Ptosis or mydriasis can be accompanied by third cranial nerve palsy [15,16,17,18]. The etiology of OMCNP includes microvascular ischemia, aneurysm, stroke, inflammation, infection, and trauma. Brain tumors are also well-known causes of OMCNP [15,16,17,18,19]. However, reversely, the impact of OMCNP on subsequent primary malignant brain tumors remains underexplored.
Therefore, this study aimed to ascertain the effect of OMCNP on the incidence of primary malignant brain tumors using the National Sample Cohort (NSC) database from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service (KNHIS).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
This study used nationwide population data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (KNHIS) claims database. KNHIS covers approximately 97% of Korea’s population of 50 million and gathers all health care utilization information for inpatients and outpatients using codes from the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases (KCD), 7th Revision, based on the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. KNHIS also covers a biennial national health screening program including a self-questionnaire on health behavior, past medical history, general body measurements, and laboratory tests for all beneficiaries aged ≥20 years.
We used a customized KNHIS database cohort that included 40% of the Korean population selected via stratified random sampling to ensure that the sample represented the Korean population well. We reviewed the data of both inpatient and outpatient claims, including demographics, socioeconomic status, laboratory test findings, diagnosis of disease, medical treatment, and procedure.
2.2. Study Population
This study included individuals aged ≥20 years with newly diagnosed OMCNP based on the ICD-10-CM codes between 2010 and 2017, who underwent a national health screening examination within 2 years prior to the diagnosis of OMCNP. Those with ICD-10-CM codes of H49.0 (third cranial nerve palsy), H49.1 (fourth cranial nerve palsy), and H49.2 (sixth cranial nerve palsy) were enrolled. We excluded anyone with myasthenia gravis (G70.0), dysthyroid exophthalmos (H06.2), or thyrotoxicosis (E05). Those with a history of any type of cancer at any time before enrollment were also excluded. The control cohort was selected by a 1:5 propensity score matching based on gender and age of individuals not diagnosed with OMCNP (19,781 individuals with OMCNP and 98,905 controls). The primary end point was the incidence of newly diagnosed primary malignant brain tumors. Primary malignant brain tumor was defined as a malignant neoplasm of the meninges (C70), brain (C71), spine or other central nervous systems (C72), along with a special claim for cancer (V193). We excluded benign brain tumors due to different clinical behavior and growth patterns, including mortality and morbidity between malignant and nonmalignant tumors [4,13,20]. Metastatic brain tumors were also excluded because of their different etiologies and histological variance depending on the origin of the primary tumor.
We used a 1-year time lag in sensitivity analysis to avoid the potential problem of reverse causation. Study participants were followed up until 31 December 2019.
This study was approved by the Samsung Medical Center (SMC) Institutional Review Board (IRB) (IRB no. SMC 2022-12-021). It was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The requirement for informed consent from individual patients was waived because the data used were public and anonymized under confidentiality guidelines.
2.3. Variables
When systolic blood pressure was 140 mmHg or more, diastolic blood pressure was 90 mmHg or more, or there was at least one claim per year for an antihypertensive medication prescription under ICD-10-CM codes I10-I13 or I15, hypertension was considered. When a fasting glucose level was 126 mg/dL or more, or there was at least once claim per year for a prescription of hypoglycemic agents under ICD-10-CM codes E11 to E14, diabetes mellitus (DM) was considered. When total cholesterol level was 240 mg/dL or more, or there was at least one claim per year for an antihyperlipidemic medication prescription under ICD-10 code E78, dyslipidemia was considered. When an eGFR level was less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, chronic kidney disease was considered. If a claim had an ICD-10-CM code B20 (HIV disease resulting in infectious and parasitic diseases), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection was considered. Height and weight were measured using an electronic scale at a medical facility during a health examination. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2). Based on World Health Organization recommendations for Asian populations, obesity was considered when BMI was 25 kg/m2 or more. Low income was defined as having income at the bottom 20% level of the total population.
A standardized self-reported questionnaire was used to evaluate general health behaviors and lifestyles. Smoking status was categorized into smokers and nonsmokers/former smokers. Drinking status was classified as drinkers and nondrinkers. Regular physical activity was defined as doing high-intensity exercise for at least 20 min a day, three times a week or 30 min of moderate-intensity exercise per day, five times a week.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Baseline characteristics of the OMCNP cohort and control cohort were compared using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for continuous variables. Data were presented either as numbers with their associated percentages or as a mean with standard deviations. Incidence rates for primary malignant brain tumors were determined by dividing the number of events by 1000 person-years. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was performed to evaluate the association between OMCNP and the risk of primary malignant brain tumors with the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) calculated. To adjust for potential confounders, three models were established. Model 1 was unadjusted. Model 2 was adjusted for age and sex. Model 3 was fully adjusted for age, sex, low income, smoking, drinking, regular physical exercise, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and HIV infection. All statistical analyses were carried out using SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
Between 2010 and 2017, 60,781 individuals received a new OMCNP diagnosis. After applying exclusion criteria and selecting a control cohort through a 1:5 propensity score matching based on age and gender, a total of 118,686 participants were enrolled in this study, including 19,781 from the OMCNP cohort and 98,905 controls (Figure 1). Demographic characteristics of participants with OMCNP and the control cohort are presented in Table 1.
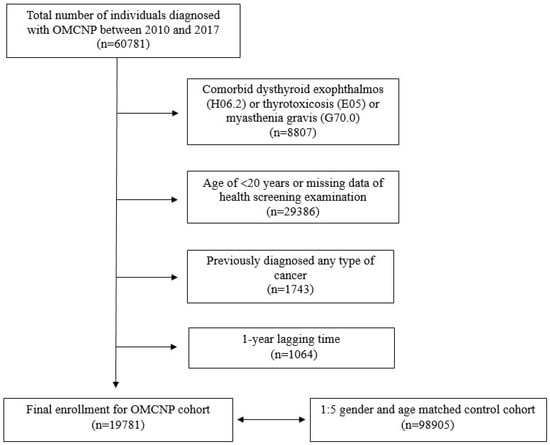
Figure 1.
Flow chart showing enrollment of current study cohort.

Table 1.
Demographics of participants with cranial nerve palsies and controls.
There were no significant differences in age, sex, smoking status, regular physical activity, or HIV infection between the two groups. However, comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, and obesity were more common in the OMCNP cohort. On the other hand, drinking and lower income rates were higher in the control cohort.
3.1. Risk of Primary Malignant Brain Tumors According to the Presence of OMCNP
Table 2 displays the incidence rate and HRs for the development of primary malignant brain tumors. The Cox proportional hazards model revealed that the HR for primary malignant brain tumors in the OMCNP cohort was significantly higher in all models. In model 1 without adjustment, patients with OMCNP had an HR of 3.239 (95% CI: 2.287–4.589) for primary malignant brain tumors compared to the control cohort. After adjusting for age and sex (model 2), HR was 3.241 (95% CI: 2.288–4.591). In a fully adjusted model (model 3, adjusted for age, sex, low-income, smoking, drinking, regular physical exercise, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, CKD, and HIV infection), the HR was 3.272 (95% CI: 2.294–4.665).

Table 2.
Hazard ratio for primary malignant brain tumors.
Cumulative incidence of primary malignant brain tumors in the OMCNP cohort and control cohort are shown in Figure 2. Primary malignant brain tumors occurred more frequently in the OMCNP cohort than in the control cohort during a follow-up period up to 9 years (log-rank p < 0.0001).
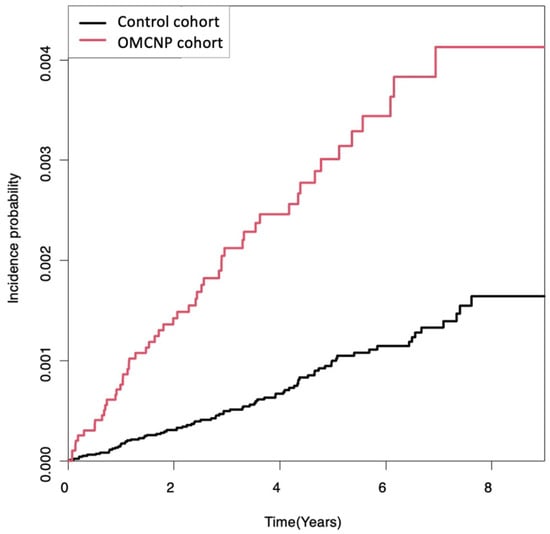
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the incidence probability of primary malignant brain tumors for up to 9 years in participants with cranial nerve palsies and controls. There was an increased risk of developing primary malignant brain tumors during the follow-up period in the OMCNP cohort compared to the control cohort (log-rank p < 0.0001). OMCNP, ocular motor cranial nerve palsies.
3.2. Hazard Ratio with a Further Time Lag
When a 3-year time lag was applied, the HR for primary malignant brain tumors in the OMCNP cohort was 2.425 (95% CI: 1.442–4.078) in model 1, and 2.425 (95% CI: 1.442–4.078) in model 2, compared to the control cohort. In the fully adjusted model, HR was 2.39 (95% CI: 1.406–4.061). When a 5-year time lag was applied, the HR was 2.041 (95% CI: 0.899–4.634) in model 1, 2.042 (95% CI: 0.900–4.637) in model 2, and 2.055 in the fully adjusted model (95% CI: 0.892–4.735) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Hazard ratio for primary malignant brain tumors with 3-year or 5-year time lag.
3.3. Locations of Primary Malignant Brain Tumors
Locations of primary malignant brain tumors in participants with OMCNP and controls are presented in Table 4. The OMCNP cohort showed a higher prevalence of primary malignant tumors in the meninges compared to the control cohort, although the brain parenchyma was the most common site in both groups (p = 0.0047).

Table 4.
Locations of primary malignant brain tumors in participants with cranial nerve palsies and controls.
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
Subgroup analysis was performed to evaluate the effects of other factors (including age, sex, smoking status, drinking status, regular physical activities, low income, and other comorbidities) on the association of OMCNP with primary malignant brain tumors. Younger than 65 years (HR: 6.951, 95% CI: 3.995–12.094 in age <65 years vs. HR: 1.899, 95% CI: 1.158–3.114 in age ≥65 years, p = 0.0006) and women (HR: 5.118, 95% CI: 2.933–8.932 in women vs. HR: 2.441, 95% CI: 1.532–3.889 in men, p = 0.0440) were significant interaction factors between OMCNP and primary malignant brain tumors (Table 5).

Table 5.
Subgroup analysis for other factors on association of ocular motor cranial nerve palsies with primary malignant brain tumors.
4. Discussion
Results of this study showed an increased risk of primary malignant brain tumors within the OMCNP cohort during a follow-up period of up to 9 years. Compared to the control cohort, the OMCNP cohort demonstrated a 3.372-fold increase in the risk of primary malignant brain tumors, even after adjusting for variables such as age, sex, socio-economic status, smoking, drinking, regular physical exercise, and other comorbidities (obesity, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney diseases, and HIV infection). In particular, the OMCNP cohort displayed a marked surge in primary malignant brain tumor risk among women compared to men (HR: 5.118 in women vs. 2.441 in men, p = 0.0440) and those aged below 65 years versus those aged 65 years or more (HR: 6.951 in age < 65 years vs. 1.899 in age ≥ 65 years, p = 0.0006). We adopted a 1-year lag post OMCNP diagnosis before the emergence of primary malignant brain tumors to exclude reverse causation, in order to analyze the effect of OMCNP on primary malignant brain tumors. In addition, further temporal analyses incorporating 3-year and 5-year lag periods were conducted to sharpen our understanding of OMCNP’s potential role in brain tumor genesis. The risk of developing a brain tumor after OMCNP decreased slightly from 3.27 with a 1-year lag to 2.39 with a 3-year lag and 2.06 with a 5-year lag. However, these risks remained significantly higher than those in the general population. While it is impossible to completely rule out the delayed diagnosis of very slowly growing brain tumors, the fact that the risk remained significantly higher (double) than the general population even with a 5-year lag, supports the increased likelihood of new brain tumor development in patients with OMCNP without a pre-existing tumor. Thus, in addition to the risk of belatedly discovering a brain tumor originally causing the OMCNP, there is a risk of new brain tumor development in patients who initially have OMCNP without an actual brain tumor.
The association between OMCNP and primary malignant brain tumors might be due to the existence of common causal factors between the two diseases. Representatively, head trauma, brain infections, and inflammation are not only causes of OMCNP, but are also risk factors for brain tumors [10,16,17,18,19,20,21]. The causal relationship between inflammation and cancer is widely accepted [22,23,24,25]. Chronic inflammation may induce DNA damage and genetic instability that can cause malignant transformation through mutation or epigenetic pathways [23,24,25]. Head trauma may also induce malignant brain tumors through cell damage, inflammation, and repair processing [8,26,27]. A previous study has highlighted molecular mechanisms that entities such as p53, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and c-MYC play important roles in the relationship between head trauma and glioblastoma [7]. It is conceivable that these elements initially manifest as OMCNP, and pave the way for primary malignant brain tumor development over time. HIV infection is known to increase the risk of not only primary brain lymphoma, but also other types of primary brain tumors [28,29]. However, in the present study, there was no significant difference in HIV infection between the two groups. In addition, the effect of HIV infection on primary malignant brain tumors could not be proven due to a low prevalence of HIV in South Korea [30,31].
Our subgroup analysis showed that younger women (below 65 years) diagnosed with OMCNP were especially vulnerable to primary malignant brain tumors. This finding is likely attributable to OMCNP’s etiological variation across age groups. While the elderly predominantly exhibit microvascular ischemia as the primary cause of OMCNP, younger individuals lean towards trauma, inflammation, and infections [17,18]. Therefore, age-specific OMCNP etiologies might elucidate the differential brain tumor risks seen in these groups.
A limitation of this study was its retrospective design, which limited the determination of cause and effect between OMCNP and primary malignant brain tumors. Our data could only suggest a correlation between the two diseases without predicting a causative relationship between them. Secondly, we could not analyze histopathologic details of tumors, and whether recovery from OMCNP was associated with the risk of primary malignant brain tumors due to the nature of the KNHIS. Further large prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm that OMCNP is a causal risk factor for primary malignant brain tumors and to determine whether the recovery from OMCNP affects the risk of primary malignant brain tumors. Nonetheless, our research holds significance by spotlighting the heightened primary malignant brain tumor risk among OMCNP patients by leveraging a comprehensive nationwide cohort.
5. Conclusions
OMCNP is a salient predictor for subsequent primary malignant brain tumors, with women diagnosed before age 65 being especially susceptible. Therefore, consistent surveillance for primary malignant brain tumors in OMCNP patients aged below 65 years is advocated even if brain tumors are not detected on neuroimaging
during the initial evaluation.
Author Contributions
I.J.L. wrote and revised the manuscript; K.H. prepared and analyzed the data; K.-A.P. designed the study and revised the manuscript; S.Y.O. designed and supervised the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant (No. NRF-2021R1A2C1007718 to K.-A.P.) from the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT), and a grant (No. NRF-2021R1F1A1047180 to S.Y.O.) from the Basic Science Research Program through the NRF funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Republic of Korea. The sponsor or funding organization had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Samsung Medical Center (SMC) Institutional Review Board (IRB) (IRB no. SMC 2022-12-021). It was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
The requirement for informed consent from individual patients was waived because data used were public and anonymized under confidentiality guidelines.
Data Availability Statement
Data that support the findings of this study are available from Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) of Republic of Korea. However, HIRA’s audited approval is mandatory to have access to these data. Thus, these data are not publicly available. However, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fernandez, P.M.; Brem, S. Malignant brain tumors in the elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 1997, 13, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcman, M. The morbidity and mortality of brain tumors. A perspective on recent advances in therapy. Neurol. Clin. 1985, 3, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeill, K.A. Epidemiology of Brain Tumors. Neurol. Clin. 2016, 34, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Meade, P.; Marenco-Hillembrand, L.; Sherman, W.J. Neuro-oncologic Emergencies. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohana, N.; Benharroch, D.; Sheinis, D.; Cohen, A. Traumatic glioblastoma: Commentary and suggested mechanism. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.S.; Sanan, A.; Morell, A.A.; Eichberg, D.G.; Shah, A.H.; Luther, E.; Lu, V.M.; Elarjani, T.; Higgins, D.M.O.; Patel, N.V.; et al. Traumatic brain injury and subsequent brain tumor development: A systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 3003–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Adel Fahmideh, M.; Cote, D.J.; Muskens, I.S.; Schraw, J.M.; Scheurer, M.E.; Bondy, M.L. Risk factors for childhood and adult primary brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrensch, M.; Minn, Y.; Chew, T.; Bondy, M.; Berger, M.S. Epidemiology of primary brain tumors: Current concepts and review of the literature. Neuro Oncol. 2002, 4, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J. The relationship between radiofrequency-electromagnetic radiation from cell phones and brain tumor: The brain tumor incidence trends in South Korea. Environ. Res. 2023, 226, 115657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vienne-Jumeau, A.; Tafani, C.; Ricard, D. Environmental risk factors of primary brain tumors: A review. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, A.; Liu, G. Primary Brain Tumors in Adults: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 93, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalaqua, M.; do Nascimento, F.B.P.; Miura, L.K.; Reis, F.; Garcia, M.R.T.; Barbosa Júnior, A.A. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cranial nerves in congenital, traumatic, and vascular diseases: A pictorial essay. Radiol. Bras. 2021, 54, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanza, J.C.; Ngweme, G.B.; Kayembe, D.L. Ocular motor nerve palsy: A clinical and etiological study. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 54, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein Hesselink, T.; Gutter, M.; Polling, J.R. Neurological Imaging in Acquired Cranial Nerve Palsy: Ophthalmologists vs. Neurologists. Strabismus 2017, 25, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.A.; Oh, S.Y.; Min, J.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, Y. Cause of acquired onset of diplopia due to isolated third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerve palsies in patients aged 20 to 50 years in Korea: A high resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 407, 116546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.D.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.H.; Yang, T.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.H.; et al. Acquired Ocular Motor Nerve Palsy in Neurology Clinics: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 15, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.T.; Volpe, N.J.; Galetta, S.L. Liu, Volpe, and Galetta’s Neuro-Ophthalmology: Diagnosis and Management, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörner, R.; Kassubek, J.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.C. The spectrum and differential diagnosis of acquired ocular motor nerve palsies: A clinical study of 502 patients. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandia, R.; Munjal, A. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2020, 119, 199–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.P.; Patil, P.B.; Thakkannavar, S.S.; Pujari, V.B. Inflammation and cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elinav, E.; Nowarski, R.; Thaiss, C.A.; Hu, B.; Jin, C.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, T.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C. The role of markers of inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wen, L. Inflammatory response following diffuse axonal injury. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandachi, D.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Chong, I.; Serpa, J.A.; Giordano, T.P.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Fowler, N.; Colen, R.R.; Morón, F.E. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in patients with and without HIV infection: A multicenter study and comparison with U.S national data. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, D.T.; Raizer, J.J.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Bilsky, M.H.; Hariharan, S.; Abrey, L.E. Primary intracranial neoplasms in patients with HIV. Neurology 1999, 52, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Ahn, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Seong, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Jun, Y.H.; et al. Cancer Incidence Among Adults With HIV in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2224897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.; Wang, J.S.; Park, S.J.; Cha, J.O.; Jung, Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Han, M.G.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kee, M.K. Characteristics of recent HIV infection among individuals newly diagnosed as HIV-positive in South Korea (2008–2015). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).