Emulating the Delivery of Sawtooth Proton Arc Therapy Plans on a Cyclotron-Based Proton Beam Therapy System
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Details of Sawtooth PAT
- F is the set of fields or ‘teeth’ within the treatment plan for IMPT and PAT, respectively, in the order corresponding with delivery;
- E is the set of all energy layers contained within the plan;
- is the set of energy layers contained within field/tooth in descending order of energy;
- S is the set of all spots contained within the plan;
- is the set of all spots contained within layer .
- = 42 cm: distance along beam axis between nozzle and isocentre when the nozzle is fully retracted;
- source-to-axis distance (SAD) = 243 cm: distance between the location of the ‘effective source’ (average steering magnet position) and isocentre along beam axis;
- source-to-surface distance (SSDf): distance along beam axis between the location of the MU effective source and patient surface at the angle corresponding to field f;
- = 10 cm: the required minimum distance along the beam axis between the nozzle and the patient surface during delivery to avoid any risk of nozzle/patient collisions;
- = 1 cms−1: experimentally measured nozzle insertion/retraction speed.
2.2. Datasets and Clinical Cases
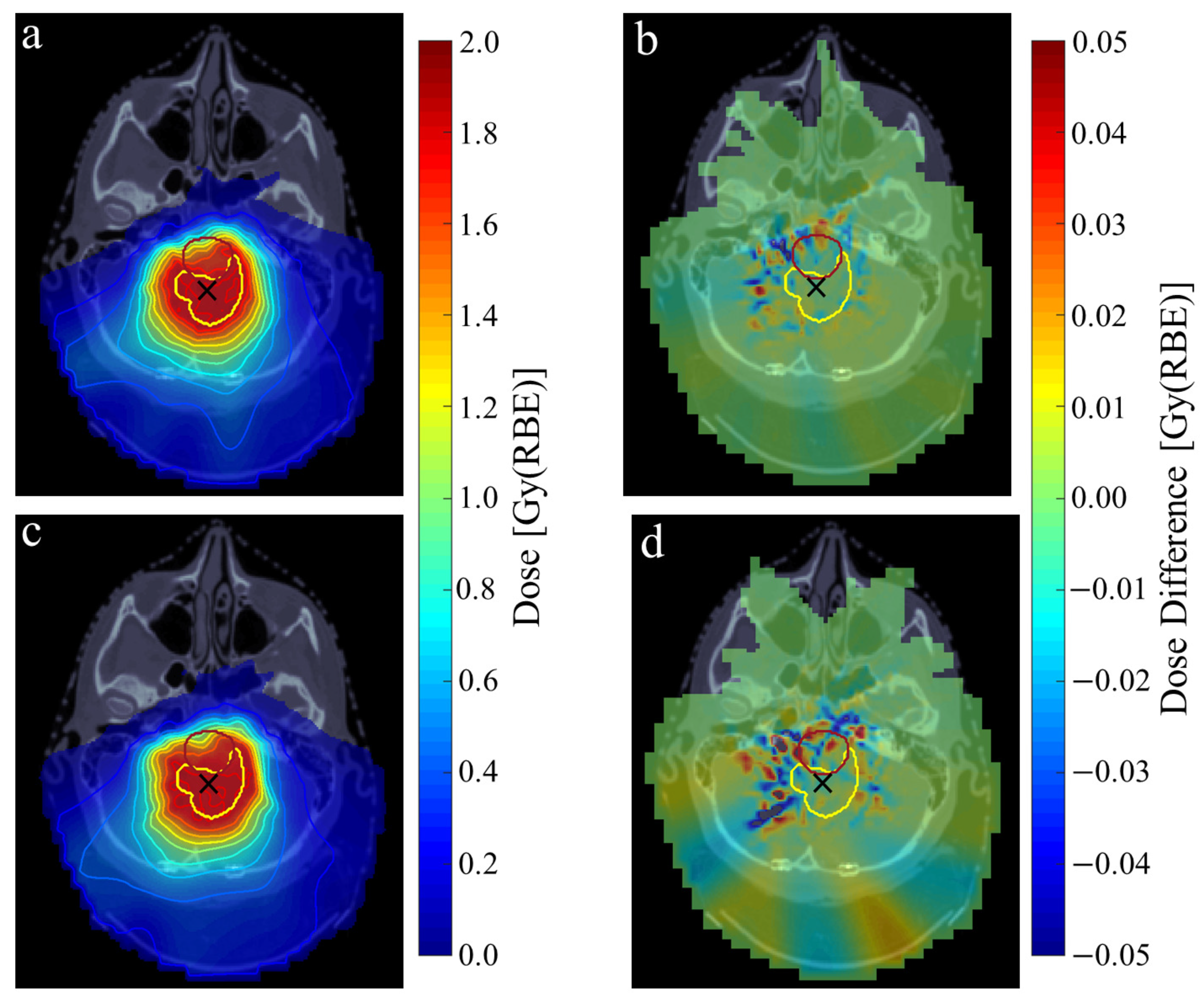
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Static IMPT and PAT Plan Parameters
| Treatment Site | Dataset | Delivery Method | # Fields/Teeth | # Spots | # ELs | Angles [°] | RS Thickness [cm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | Static IMPT | 3 | 1831 | 71 | 0, 45, 90 | 3 |
| PAT single arc | 4 | 1994 | 85 | 0 → 90 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 4 | 1975 | 88 | 0 ↔ 90 | |||
| E | 1 | Static IMPT | 3 | 1617 | 68 | 120, 180, 240 | None |
| PAT single arc | 6 | 1937 | 109 | 90 → 270 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 6 | 1751 | 118 | 90 ↔ 270 | |||
| 2 | Static IMPT | 3 | 3358 | 90 | 15, 90, 330 | 5 | |
| PAT single arc | 4 | 4822 | 116 | 330 → 90 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 4 | 4756 | 127 | 330 ↔ 90 | |||
| B | 1 | Static IMPT | 4 | 3704 | 141 | 260, 305, 55, 100 | None |
| PAT single arc | 7 | 3585 | 196 | 225 → 135 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 10 | 3427 | 231 | 225 ↔ 135 | |||
| 2 | Static IMPT | 4 | 5051 | 149 | 230, 275, 80, 130 | 2 | |
| PAT single arc | 7 | 5187 | 215 | 225 → 135 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 8 | 6502 | 186 | 225 ↔ 135 | |||
| O | 1 | Static IMPT | 5 | 7790 | 197 | 270, 315, 0, 60, 90 | 5 |
| PAT single arc | 8 | 8290 | 267 | 270 → 90 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 6 | 5220 | 163 | 270 ↔ 90 | |||
| 2 | Static IMPT | 5 | 6483 | 203 | 270, 325, 0, 45, 125 | 3 | |
| PAT single arc | 6 | 7721 | 204 | 270 → 90 | |||
| PAT dual arc | 8 | 8269 | 270 | 270 ↔ 90 |
References
- Gillin, M.T.; Sahoo, N.; Bues, M.; Ciangaru, G.; Sawakuchi, G.; Poenisch, F.; Arjomandy, B.; Martin, C.; Titt, U.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Commissioning of the discrete spot scanning proton beam delivery system at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Proton Therapy Center, Houston. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshito, T.; Omachi, C.; Kibe, Y.; Sugai, H.; Hayashi, K.; Shibata, H.; Yasui, K.; Tanaka, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Yoshida, A.; et al. A proton therapy system in Nagoya Proton Therapy Center. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2016, 39, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, A.J.; Böhringer, T.; Bolsi, A.; Coray, D.; Emert, F.; Goitein, G.; Jermann, M.; Lin, S.; Pedroni, E.; Rutz, H.; et al. Treatment planning and verification of proton therapy using spot scanning: Initial experiences. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.E.; Jäkel, O.; Haberer, T.; Debus, J. Particle therapy at the Heidelberg Ion Therapy Center (HIT)–integrated research-driven university-hospital-based radiation oncology service in Heidelberg, Germany. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 95, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.M.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Stevens, C.; Yan, D. Spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy: The first robust and delivery-efficient spot-scanning proton arc therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, W.; Qin, A.; Zhang, S.; Stevens, C.; Yan, D.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Ding, X. A novel energy sequence optimization algorithm for efficient spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) treatment delivery. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, W.; Yan, D.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Deraniyagala, R.; Stevens, C.; Grills, I.; et al. Introduce a rotational robust optimization framework for spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 68, 01NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zheng, W.; Yan, D.; Zhang, S.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Ding, X. Improve the dosimetric outcome in bilateral head and neck cancer (HNC) treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy: A feasibility study. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Krauss, D.; Kabolizadeh, P. Have we reached proton beam therapy dosimetric limitations?—A novel robust, delivery-efficient and continuous spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy is to improve the dosimetric outcome in treating prostate cancer. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; et al. Is proton beam therapy ready for single fraction spine SBRS?—A feasibility study to use spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy to improve the robustness and dosimetric plan quality. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, L.; Dilworth, J.T.; Zheng, W.; Jawad, S.; Yan, D.; Chen, P.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; et al. Feasibility study: Spot-scanning proton arc therapy (SPArc) for left-sided whole breast radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Blas, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Qin, A.; Chinnaiyan, P.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; et al. Improving dosimetric outcome for hippocampus and cochlea sparing whole brain radiotherapy using spot-scanning proton arc therapy. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Yan, D.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Hong, Y.; Guerrero, T.; Grills, I.; Stevens, C.; Ding, X. Improve dosimetric outcome in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Ruan, D.; Lyu, Q.; Zou, W.; Dong, L.; Sheng, K. A novel energy layer optimization framework for spot-scanning proton arc therapy. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 2072–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engwall, E.; Battinelli, C.; Wase, V.; Marthin, O.; Glimelius, L.; Bokrantz, R.; Andersson, B.; Fredriksson, A. Fast robust optimization of proton PBS arc therapy plans using early energy layer selection and spot assignment. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, B.A.; Battinelli, C.; Free, J.; Wagenaar, D.; Engwall, E.; Janssens, G.; Langendijk, J.A.; Korevaar, E.W.; Both, S. Spot scanning proton arc therapy reduces toxicity in oropharyngeal cancer patients. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Parcerisa, D.; Kirk, M.; Fager, M.; Burgdorf, B.; Stowe, M.; Solberg, T.; Carabe, A. Range optimization for mono-and bi-energetic proton modulated arc therapy with pencil beam scanning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyckens, S.; Zhao, L.; Saint-Guillain, M.; Janssens, G.; Sterpin, E.; Souris, K.; Ding, X.; Lee, J.A. Bi-criteria Pareto optimization to balance irradiation time and dosimetric objectives in proton arc therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 245017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolet, A.; Carabe, A. Proton monoenergetic arc therapy (PMAT) to enhance LETd within the target. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 165006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H.; Bortfeld, T. Proton therapy. In New Technologies in Radiation Oncology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 345–363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Zheng, W.; Qin, A.; Yan, D.; Li, X.; Ding, X. Developing an accurate model of spot-scanning treatment delivery time and sequence for a compact superconducting synchrocyclotron proton therapy system. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, W.; Shen, J.; Lee, A.; Yan, D.; Deraniyagala, R.; Stevens, C.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Building a precise machine-specific time structure of the spot and energy delivery model for a cyclotron-based proton therapy system. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 01NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiler, T.; Bäumer, C.; Engwall, E.; Geismar, D.; Spaan, B.; Timmermann, B. Experimental validation of a 4D dose calculation routine for pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Z. Med. Phys. 2018, 28, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Fan, Q.; Dao, R.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, K.; Quan, H.; Tu, B.; Ding, X.; et al. A novel planning framework for efficient spot-scanning proton arc therapy via particle swarm optimization (SPArc-particle swarm). Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 69, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Yan, D.; Deraniyagala, R.; Stevens, C.; Li, X.; Ding, X. Development of a standalone delivery sequence model for proton arc therapy. Med. Phys. 2023, 51, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beebe, D.S.; Belani, K.G. Anesthesia for proton beam therapy. In Anaesthesia for Uncommon and Emerging Procedures; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, G.; Janssens, G.; De Wilde, O.; Bossier, V.; Lerot, X.; Pouppez, A.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; et al. The first prototype of spot-scanning proton arc treatment delivery. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Therapy Co-Operative Group. Particle Therapy Facilities in Clinical Operation. 2023. Available online: https://www.ptcog.site/index.php/facilities-in-operation-public (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Burnet, N.G.; Mackay, R.I.; Smith, E.; Chadwick, A.L.; Whitfield, G.A.; Thomson, D.J.; Lowe, M.; Kirkby, N.F.; Crellin, A.M.; Kirkby, K.J. Proton beam therapy: Perspectives on the National Health Service England clinical service and research programme. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford-Eyre, S.S.; Aitkenhead, A.; Mackay, R.; Merchant, M.; Sitch, P.; Appleby, R.B. Sawtooth proton arc therapy: A simple strategy for proton arc therapy planning. 2024; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, H.P.; Cisternas, E.; Wahl, N.; Ulrich, S.; Stadler, A.; Mescher, H.; Müller, L.R.; Klinge, T.; Gabrys, H.; Burigo, L.; et al. Development of the open-source dose calculation and optimization toolkit matRad. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 2556–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitkenhead, A.H.; Sitch, P.; Richardson, J.C.; Winterhalter, C.; Patel, I.; Mackay, R.I. Automated Monte-Carlo re-calculation of proton therapy plans using GEANT4/GATE: Implementation and comparison to plan-specific quality assurance measurements. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grevillot, L.; Boersma, D.J.; Fuchs, H.; Aitkenhead, A.; Elia, I.A.; Bolsa, M.; Winterhalter, C.; Vidal, M.; Jan, S.; Pietrzyk, U.; et al. GATE-RTion: A GATE/GEANT4 release for clinical applications in scanned ion beam therapy. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalendralis, P.; Traverso, A.; Shi, Z.; Zhovannik, I.; Monshouwer, R.; Starmans, M.P.; Klein, S.; Pfaehler, E.; Boellaard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Multicenter CT phantoms public dataset for radiomics reproducibility tests. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Fan, Q.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Cong, X.; Yan, D.; Li, X.; Ding, X. First direct machine-specific parameters incorporated in Spot-scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) optimization algorithm. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 5682–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Shen, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, R.C.; Long, Y.; Gao, H. Energy layer optimization via energy matrix regularization for proton spot-scanning arc therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 5752–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dataset | Delivery Method | EL Switching [s] | Spot Scanning [s] | Spot Delivery [s] | Dead-Time [s] | Total [s] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Static IMPT | 106.5 ± 8.1 | 2.1 | 16.0 ± 1.4 | 69.9 | 194.5 ± 9.5 | |
| PAT single arc | SAS | 145.5 ± 9.6 | 2.1 | 15.5 ± 1.4 | 152.7 | 315.9 ± 11.0 | |
| CON | 60.4 | 223.6 ± 11.0 | |||||
| PAT dual arc | SAS | 148.1 ± 10.1 | 2.0 | 15.3 ± 1.4 | 241.7 | 407.2 ± 11.4 | |
| CON | 65.9 | 231.3 ± 11.4 | |||||
| E1 | Static IMPT | 105.3 ± 7.9 | 1.9 | 13.7 ± 1.2 | 0.0 | 120.9 ± 9.1 | |
| PAT single arc | SAS | 221.6 ± 13.0 | 2.2 | 9.9 ± 0.9 | 278.8 | 513.5 ± 13.5 | |
| CON | 91.2 | 325.9 ± 13.5 | |||||
| PAT dual arc | SAS | 228.2 ± 13.5 | 2.1 | 10.6 ± 0.95 | 432.8 | 673.7 ± 14.5 | |
| CON | 101.4 | 341.9 ± 14.5 | |||||
| B1 | Static IMPT | 184.6 ± 16.4 | 4.9 | 26.4 ± 2.4 | 0.0 | 215.9 ± 18.8 | |
| PAT single arc | SAS | 312.7 ± 23.0 | 3.3 | 22.6 ± 2.0 | 354.6 | 694.2 ± 25.0 | |
| CON | 149.5 | 489.1 ± 25.0 | |||||
| PAT dual arc | SAS | 427.6 ± 27.3 | 3.8 | 20.3 ± 1.8 | 595.4 | 1047.2 ± 29.1 | |
| CON | 206.7 | 658.4 ± 29.1 | |||||
| O1 | Static IMPT | 252.1 ± 22.9 | 12.9 | 148.4 ± 13.3 | 64.1 | 447.5 ± 36.2 | |
| PAT single arc | SAS | 389.6 ± 31.1 | 14.3 | 152.8 ± 13.7 | 369.3 | 924.9 ± 4.8 | |
| CON | 186.5 | 742.1 ± 44.8 | |||||
| PAT dual arc | SAS | 264.0 ± 19.8 | 9.6 | 146.3 ± 13.1 | 552.6 | 972.6 ± 32.9 | |
| CON | 118.4 | 538.3 ± 32.9 | |||||
| Dataset | Delivery Method | CP Spacing [°] | Spot Shifts | Pass Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°] | [mm] | ||||
| A1 | Single Arc | 0.8 | 0.33 ± 0.28 | 0.82 ± 2.52 | 99.3 ± 0.15 |
| Dual Arc | 1.6 | 0.65 ± 0.50 | 1.07 ± 4.03 | 97.4 ± 0.32 | |
| E1 | Single Arc | 1.1 | 0.42 ± 0.33 | 1.04 ± 1.75 | 99.3 ± 1.12 |
| Dual Arc | 2.2 | 0.86 ± 0.69 | 1.55 ± 2.03 | 96.8 ± 5.02 | |
| B1 | Single Arc | 0.7 | 0.25 ± 0.28 | 1.40 ± 2.80 | 95.8 ± 4.80 |
| Dual Arc | 1.0 | 0.29 ± 0.31 | 1.50 ± 2.84 | 94.9 ± 6.68 | |
| O1 | Single Arc | 0.6 | 0.26 ± 0.19 | 0.96 ± 2.05 | 98.8 ± 1.38 |
| Dual Arc | 1.6 | 0.81 ± 0.59 | 1.78 ± 2.44 | 87.6 ± 10.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burford-Eyre, S.; Aitkenhead, A.; Aylward, J.D.; Henthorn, N.T.; Ingram, S.P.; Mackay, R.; Manger, S.; Merchant, M.J.; Sitch, P.; Warmenhoven, J.-W.; et al. Emulating the Delivery of Sawtooth Proton Arc Therapy Plans on a Cyclotron-Based Proton Beam Therapy System. Cancers 2024, 16, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193315
Burford-Eyre S, Aitkenhead A, Aylward JD, Henthorn NT, Ingram SP, Mackay R, Manger S, Merchant MJ, Sitch P, Warmenhoven J-W, et al. Emulating the Delivery of Sawtooth Proton Arc Therapy Plans on a Cyclotron-Based Proton Beam Therapy System. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193315
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurford-Eyre, Samuel, Adam Aitkenhead, Jack D. Aylward, Nicholas T. Henthorn, Samuel P. Ingram, Ranald Mackay, Samuel Manger, Michael J. Merchant, Peter Sitch, John-William Warmenhoven, and et al. 2024. "Emulating the Delivery of Sawtooth Proton Arc Therapy Plans on a Cyclotron-Based Proton Beam Therapy System" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193315
APA StyleBurford-Eyre, S., Aitkenhead, A., Aylward, J. D., Henthorn, N. T., Ingram, S. P., Mackay, R., Manger, S., Merchant, M. J., Sitch, P., Warmenhoven, J.-W., & Appleby, R. B. (2024). Emulating the Delivery of Sawtooth Proton Arc Therapy Plans on a Cyclotron-Based Proton Beam Therapy System. Cancers, 16(19), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193315






