Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Peritoneal Metastasis: A Review of Current Management
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Surgical Management
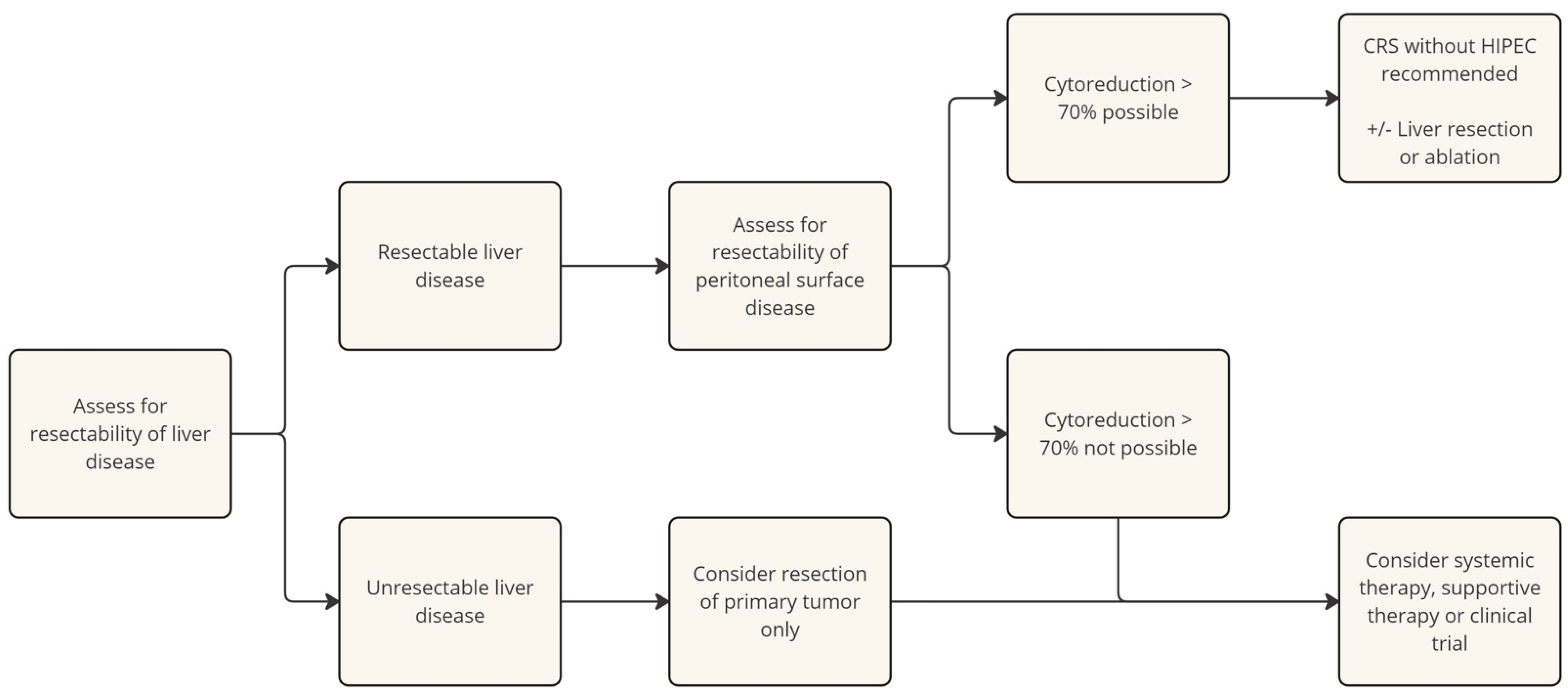
2.1. Cytoreductive Surgery (CRS)
2.2. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
3. Systemic Therapy
3.1. Somatostatin Analogs
3.2. Interferon-Alpha
3.3. Everolimus and Sunitinib
3.4. Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
3.5. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kianmanesh, R.; Ruszniewski, P.; Rindi, G.; Kwekkeboom, D.; Pape, U.F.; Kulke, M.; Sevilla Garcia, I.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Nilsson, O.; Fazio, N.; et al. ENETS consensus guidelines for the management of peritoneal carcinomatosis from neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2010, 91, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoli, M.; Wilson, H.; Armonis, P.; Kamieniarz, L.; Thuringer, J.; Mirnezami, R.; Caplin, M.; Kaltsas, G.; Toumpanakis, C. Peritoneal metastases in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms: A challenging site of metastases with clinical and prognostic implications. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Fazio, N.; Singh, S.; Buzzoni, R.; Carnaghi, C.; Wolin, E.; Tomasek, J.; Raderer, M.; Lahner, H.; Voi, M.; et al. Everolimus for the treatment of advanced, non-functional neuroendocrine tumours of the lung or gastrointestinal tract (RADIANT-4): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassetti, P.; Campana, D.; Piscitelli, L.; Casadei, R.; Nori, F.; Brocchi, E.; Santini, D.; Pezzilli, R.; Corinaldesi, R. Endocrine tumors of the ileum: Factors correlated with survival. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, E.; Falconi, M.; Grana, C.; Botteri, E.; Chiappa, A.; Misitano, P.; Spada, F.; Ravizza, D.; Bazolli, B.; Fazio, N. Small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors with liver metastases and resection of the primary: Prognostic factors for decision making. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 20, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.F.; Cates, J.; Gonzalez, R.S.; Das, S.; Berlin, J.D.; Shi, C. Impact of Peritoneal Metastasis on Survival of Patients With Small Intestinal Neuroendocrine Tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEntee, G.P.; Nagorney, D.M.; Kvols, L.K.; Moertel, C.G.; Grant, C.S. Cytoreductive hepatic surgery for neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 1990, 108, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, A.J.; Pasieka, J.L.; Dixon, E.; Rorstad, O. The palliative benefit of aggressive surgical intervention for both hepatic and mesenteric metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 2006, 144, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltering, E.A.; Voros, B.A.; Beyer, D.T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Thiagarajan, R.; Ryan, P.; Wright, A.; Ramirez, R.A.; Ricks, M.J.; Boudreaux, J.P. Aggressive Surgical Approach to the Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Report of 1,000 Surgical Cytoreductions by a Single Institution. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.E.; Sherman, S.K.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Bellizzi, A.M.; Howe, J.R. Liver-directed surgery of neuroendocrine metastases: What is the optimal strategy? Surgery 2016, 159, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, J.F.; Chivukula, S.V.; Wang, X.; Pappas, S.G.; Schadde, E.; Hertl, M.; Poirier, J.; Keutgen, X.M. Resection of primary tumor may prolong survival in metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 2019, 165, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.; Raoof, M.; Ituarte, P.H.G.; Williams, J.; Melstrom, L.; Li, D.; Lee, B.; Singh, G. Resection of the Primary Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumor Improves Survival With or Without Liver Treatment. Ann. Surg. 2019, 270, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Stein, R.M.; Aalbers, A.G.J.; Sonke, G.S.; van Driel, W.J. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Ovarian and Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenet, F.; Elias, D.; Roca, L.; Goere, D.; Ghouti, L.; Pocard, M.; Facy, O.; Arvieux, C.; Lorimier, G.; Pezet, D.; et al. Cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy versus cytoreductive surgery alone for colorectal peritoneal metastases (PRODIGE 7): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Qin, X. Comment on Granieri et al. Prognostic impact of cytoreductive surgery (CRS) with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1862–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granieri, S.; Bonomi, A.; Frassini, S.; Chierici, A.P.; Bruno, F.; Paleino, S.; Kusamura, S.; Germini, A.; Facciorusso, A.; Deraco, M.; et al. Prognostic impact of cytoreductive surgery (CRS) with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallows, M.; Samant, A.; Wilson, H.; Mirnezami, R. A Systematic Review of Surgical Management Strategies in the Treatment of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Neuroendocrine Origin. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 6316–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, D.; David, A.; Sourrouille, I.; Honore, C.; Goere, D.; Dumont, F.; Stoclin, A.; Baudin, E. Neuroendocrine carcinomas: Optimal surgery of peritoneal metastases (and associated intra-abdominal metastases). Surgery 2014, 155, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, A.; Zielinski, C.B.; Raue, W.; Pratschke, J.; Rau, B. Peritoneal metastases of rare carcinomas treated with cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC—A single center case series. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 22, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goere, D.; Passot, G.; Gelli, M.; Levine, E.A.; Bartlett, D.L.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Glehen, O. Complete cytoreductive surgery plus HIPEC for peritoneal metastases from unusual cancer sites of origin: Results from a worldwide analysis issue of the Peritoneal Surface Oncology Group International (PSOGI). Int. J. Hyperthermia 2017, 33, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, R.; Mercier, F.; Passot, G.; Pasquer, A.; Gelli, M.; Levine, E.A.; Villeneuve, L.; Poncet, G.; Walter, T.; Glehen, O. Cytoreductive surgery with or without hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for small bowel neuroendocrine tumors with peritoneal metastasis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1626–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicago Consensus Working Group. The Chicago Consensus on Peritoneal Surface Malignancies: Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.N.; Saltz, L.B. Failure to confirm major objective antitumor activity for streptozocin and doxorubicin in the treatment of patients with advanced islet cell carcinoma. Cancer 1999, 86, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, A.D.; Kulke, M.H.; Ryan, D.P.; Clark, J.W.; Shulman, L.N.; Mayer, R.J.; Bartel, S.; Fuchs, C.S. Lack of efficacy of streptozocin and doxorubicin in patients with advanced pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 27, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; O’Toole, D.; Costa, F.; Capdevila, J.; Gross, D.; Kianmanesh, R.; Krenning, E.; Knigge, U.; Salazar, R.; Pape, U.F.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for the Management of Distant Metastatic Disease of Intestinal, Pancreatic, Bronchial Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (NEN) and NEN of Unknown Primary Site. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvols, L.K. Metastatic carcinoid tumors and the malignant carcinoid syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 733, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvols, L.K.; E Oberg, K.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Mohideen, P.; de Herder, W.W.; Arnold, R.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hughes, G.; Anthony, L.; et al. Pasireotide (SOM230) shows efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors refractory or resistant to octreotide LAR: Results from a phase II study. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, E.M.; Jarzab, B.; Eriksson, B.; Walter, T.; Toumpanakis, C.; Morse, M.A.; Tomassetti, P.; Weber, M.M.; Fogelman, D.R.; Ramage, J.; et al. Phase III study of pasireotide long-acting release in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors and carcinoid symptoms refractory to available somatostatin analogues. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5075–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinke, A.; Müller, H.-H.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Klose, K.-J.; Barth, P.; Wied, M.; Mayer, C.; Aminossadati, B.; Pape, U.-F.; Bläker, M.; et al. Placebo-controlled, double-blind, prospective, randomized study on the effect of octreotide LAR in the control of tumor growth in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine midgut tumors: A report from the PROMID Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplin, M.E.; Pavel, M.; Cwikla, J.B.; Phan, A.T.; Raderer, M.; Sedlackova, E.; Cadiot, G.; Wolin, E.M.; Capdevila, J.; Wall, L.; et al. Lanreotide in metastatic enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jann, H.; Denecke, T.; Koch, M.; Pape, U.F.; Wiedenmann, B.; Pavel, M. Impact of octreotide long-acting release on tumour growth control as a first-line treatment in neuroendocrine tumours of pancreatic origin. Neuroendocrinology 2013, 98, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolby, L.; Persson, G.; Franzen, S.; Ahren, B. Randomized clinical trial of the effect of interferon alpha on survival in patients with disseminated midgut carcinoid tumours. Br. J. Surg. 2003, 90, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Guthrie, K.A.; Moran, C.; Strosberg, J.R.; Kulke, M.H.; Chan, J.A.; LoConte, N.; McWilliams, R.R.; Wolin, E.M.; Mattar, B.; et al. Phase III Prospective Randomized Comparison Trial of Depot Octreotide Plus Interferon Alfa-2b Versus Depot Octreotide Plus Bevacizumab in Patients With Advanced Carcinoid Tumors: SWOG S0518. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, E.; Dahan, L.; Raoul, J.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Borbath, I.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Valle, J.; Metrakos, P.; Smith, D.; Vinik, A.; et al. Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Shah, M.H.; Ito, T.; Bohas, C.L.; Wolin, E.M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Hobday, T.J.; Okusaka, T.; Capdevila, J.; de Vries, E.G.; et al. Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, R.; Tafuto, S.; Krogh, M.; Teule, A.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Klumpen, H.; Cremer, B.; Sevilla, I.; Eriksson, B.; Tabaksblat, E.; et al. LBA45 Randomized open label phase III study comparing the efficacy and safety of everolimus followed by chemotherapy (CT) with streptozotocin (STZ)-5FU upon progression or the reverse sequence, in advanced progressive panNETs: The SEQTOR Study (GETNE 1206). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulke, M.H.; Ruszniewski, P.; Van Cutsem, E.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Valle, J.W.; De Herder, W.W.; Pavel, M.; Degtyarev, E.; Brase, J.C.; Bubuteishvili-Pacaud, L.; et al. A randomized, open-label, phase 2 study of everolimus in combination with pasireotide LAR or everolimus alone in advanced, well-differentiated, progressive pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: COOPERATE-2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajetta, E.; Catena, L.; Pusceddu, S.; Spada, F.; Iannacone, C.; Sarno, I.; Di Menna, G.; Dottorini, L.; Marte, A.M. Everolimus in Combination with Octreotide Long-Acting Repeatable in a First-Line Setting for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: A 5-Year Update. Neuroendocrinology 2018, 106, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaraki, M.A.; Ajani, J.A.; Hoff, P.; Wolff, R.; Evans, D.B.; Lozano, R.; Yao, J.C. Fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and streptozocin in the treatment of patients with locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic endocrine carcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4762–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moertel, C.G.; Lefkopoulo, M.; Lipsitz, S.; Hahn, R.G.; Klaassen, D. Streptozocin-doxorubicin, streptozocin-fluorouracil or chlorozotocin in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjallskog, M.L.; Janson, E.T.; Falkmer, U.G.; Vatn, M.H.; Oberg, K.E.; Eriksson, B.K. Treatment with combined streptozotocin and liposomal doxorubicin in metastatic endocrine pancreatic tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2008, 88, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Fine, R.L.; Choi, J.; Nasir, A.; Coppola, D.; Chen, D.T.; Helm, J.; Kvols, L. First-line chemotherapy with capecitabine and temozolomide in patients with metastatic pancreatic endocrine carcinomas. Cancer 2011, 117, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, R.L.; Gulati, A.P.; Krantz, B.A.; Moss, R.A.; Schreibman, S.; Tsushima, D.A.; Mowatt, K.B.; Dinnen, R.D.; Mao, Y.; Stevens, P.D.; et al. Capecitabine and temozolomide (CAPTEM) for metastatic, well-differentiated neuroendocrine cancers: The Pancreas Center at Columbia University experience. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumarianou, A.; Kaltsas, G.; Kulke, M.H.; Oberg, K.; Strosberg, J.R.; Spada, F.; Galdy, S.; Barberis, M.; Fumagalli, C.; Berruti, A.; et al. Temozolomide in Advanced Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Pharmacological and Clinical Aspects. Neuroendocrinology 2015, 101, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitry, E.; Walter, T.; Baudin, E.; Kurtz, J.E.; Ruszniewski, P.; Dominguez-Tinajero, S.; Bengrine-Lefevre, L.; Cadiot, G.; Dromain, C.; Farace, F.; et al. Bevacizumab plus capecitabine in patients with progressive advanced well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the gastro-intestinal (GI-NETs) tract (BETTER trial)—A phase II non-randomised trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruti, A.; Fazio, N.; Ferrero, A.; Brizzi, M.P.; Volante, M.; Nobili, E.; Tozzi, L.; Bodei, L.; Torta, M.; D’Avolio, A.; et al. Bevacizumab plus octreotide and metronomic capecitabine in patients with metastatic well-to-moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: The XELBEVOCT study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moertel, C.G.; Kvols, L.K.; O’Connell, M.J.; Rubin, J. Treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas with combined etoposide and cisplatin. Evidence of major therapeutic activity in the anaplastic variants of these neoplasms. Cancer 1991, 68, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heetfeld, M.; Chougnet, C.N.; Olsen, I.H.; Rinke, A.; Borbath, I.; Crespo, G.; Barriuso, J.; Pavel, M.; O’Toole, D.; Walter, T.; et al. Characteristics and treatment of patients with G3 gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadoux, J.; Malka, D.; Planchard, D.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Caramella, C.; Guigay, J.; Boige, V.; Leboulleux, S.; Burtin, P.; Berdelou, A.; et al. Post-first-line FOLFOX chemotherapy for grade 3 neuroendocrine carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentic, O.; Hammel, P.; Couvelard, A.; Rebours, V.; Zappa, M.; Palazzo, M.; Maire, F.; Goujon, G.; Gillet, A.; Levy, P.; et al. FOLFIRI regimen: An effective second-line chemotherapy after failure of etoposide-platinum combination in patients with neuroendocrine carcinomas grade 3. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welin, S.; Sorbye, H.; Sebjornsen, S.; Knappskog, S.; Busch, C.; Oberg, K. Clinical effect of temozolomide-based chemotherapy in poorly differentiated endocrine carcinoma after progression on first-line chemotherapy. Cancer 2011, 117, 4617–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Krenning, E.P.; Lebtahi, R.; Komminoth, P.; Kos-Kudla, B.; de Herder, W.W.; Plockinger, U. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the Standards of Care in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with radiolabeled somatostatin analogs. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 90, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwekkeboom, D.J.; de Herder, W.W.; Kam, B.L.; van Eijck, C.H.; van Essen, M.; Kooij, P.P.; Feelders, R.A.; van Aken, M.O.; Krenning, E.P. Treatment with the radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177 Lu-DOTA 0,Tyr3]octreotate: Toxicity, efficacy, and survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, A.; Brunner, P.; Marincek, N.; Briel, M.; Schindler, C.; Rasch, H.; Macke, H.R.; Rochlitz, C.; Muller-Brand, J.; Walter, M.A. Response, survival, and long-term toxicity after therapy with the radiolabeled somatostatin analogue [90Y-DOTA]-TOC in metastasized neuroendocrine cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, D.L., Jr.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; O’Dorisio, M.S.; Menda, Y.; Hicks, R.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Baulieu, J.L.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Anthony, L.; Benson, A.B.; et al. 90Y-edotreotide for metastatic carcinoid refractory to octreotide. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfdanarson, T.R.; Reidy, D.L.; Vijayvergia, N.; Halperin, D.M.; Goldstein, G.; Kong, G.; Michael, M.; Leyden, S.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Sorbye, H.; et al. Pivotal phase III COMPOSE trial will compare 177Lu-eedotreotide with best standard of care for well-differentiated aggressive grade 2 and grade 3 gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. 4), TPS514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.E.; Rinke, A.; Baum, R.P. COMPETE trial: Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) with 177Lu-eedotreotide vs. everolimus in progressive GEP-NET. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 8), VIII478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Year | Patients (n): | HIPEC Agents | HIPEC Duration and Temperature | Survival Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elias et al. [18] | 2014 | 41 | IV leucovorin/5-FU Intraperitoneal oxaliplatin or oxaliplatin + Irinotecan at differing concentrations
| Time: 30 min Temperature: 43 °C | 5-year overall survival: 69% |
| Brandl et al. [19] | 2017 | 14 | Not defined | Time: 90 min for 83.3% of patients Temperature: Variable (mean 40.9 °C) | Survival at 16 month follow-up: 43% |
| Goere et al. [20] | 2017 | 127 | Cisplatin, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, oxaliplatin, or irinotecan
| Time: 25–180 min Temperature: Variable (mean 41.9 °C) | 5-year overall survival: 39.9% |
| Hajjar et al. [21] | 2022 | 67 | Not defined | Not defined | 5-year overall survival: 91.6% (CRS alone); 74.5% (CRS + HIPEC) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hounschell, C.A.; Higginbotham, S.; Al-Kasspooles, M.; Selby, L.V. Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Peritoneal Metastasis: A Review of Current Management. Cancers 2024, 16, 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203472
Hounschell CA, Higginbotham S, Al-Kasspooles M, Selby LV. Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Peritoneal Metastasis: A Review of Current Management. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203472
Chicago/Turabian StyleHounschell, Corey A., Simon Higginbotham, Mazin Al-Kasspooles, and Luke V. Selby. 2024. "Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Peritoneal Metastasis: A Review of Current Management" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203472
APA StyleHounschell, C. A., Higginbotham, S., Al-Kasspooles, M., & Selby, L. V. (2024). Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Peritoneal Metastasis: A Review of Current Management. Cancers, 16(20), 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203472








