Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Electromagnetic Properties of Tissue
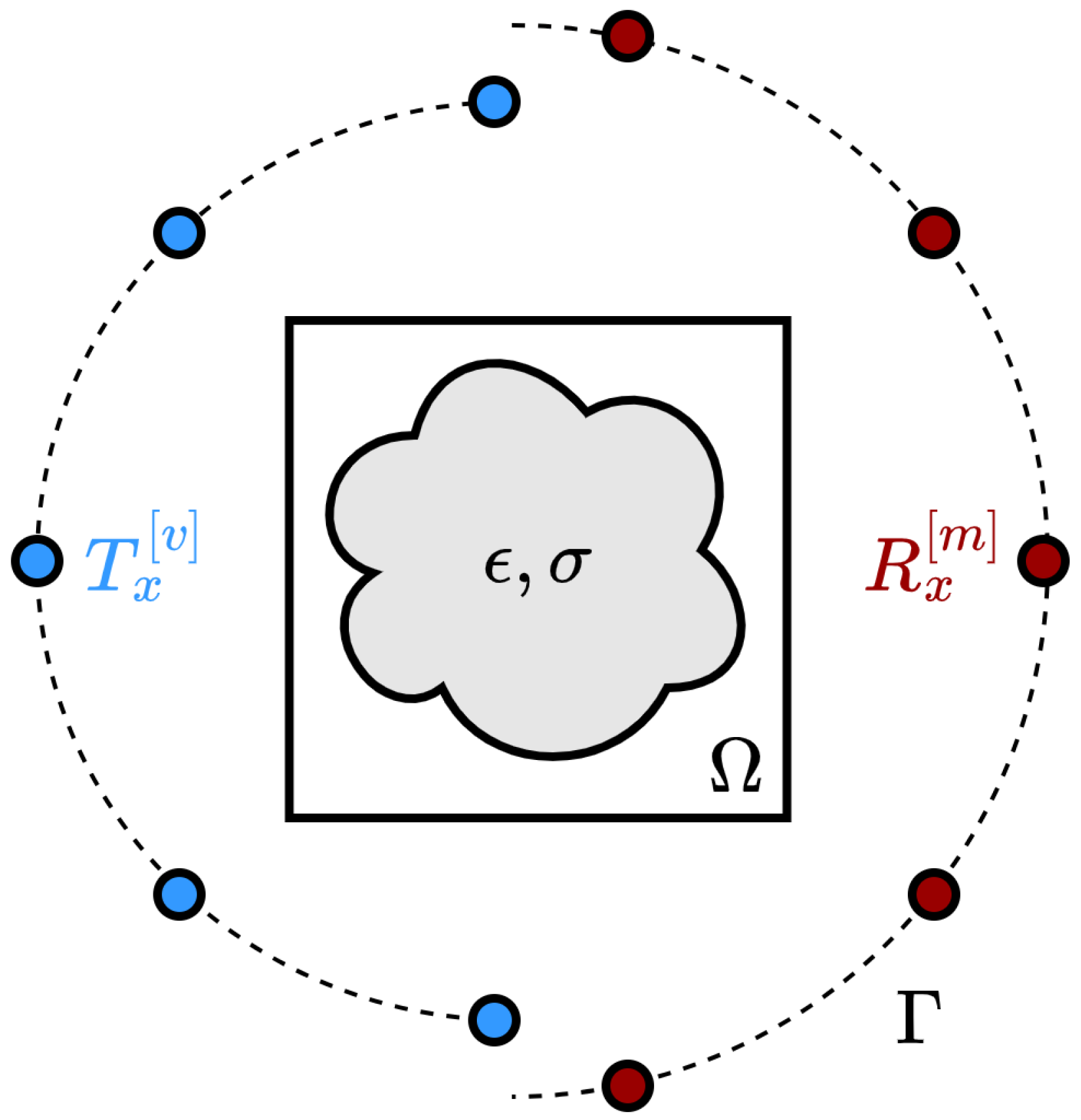
2.2. The Microwave Imaging Problem
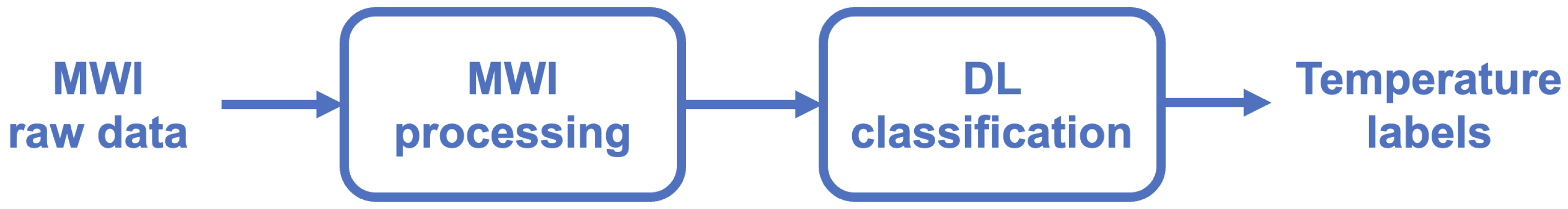
2.3. Deep Learning Microwave Imaging Framework for HT Temperature Monitoring
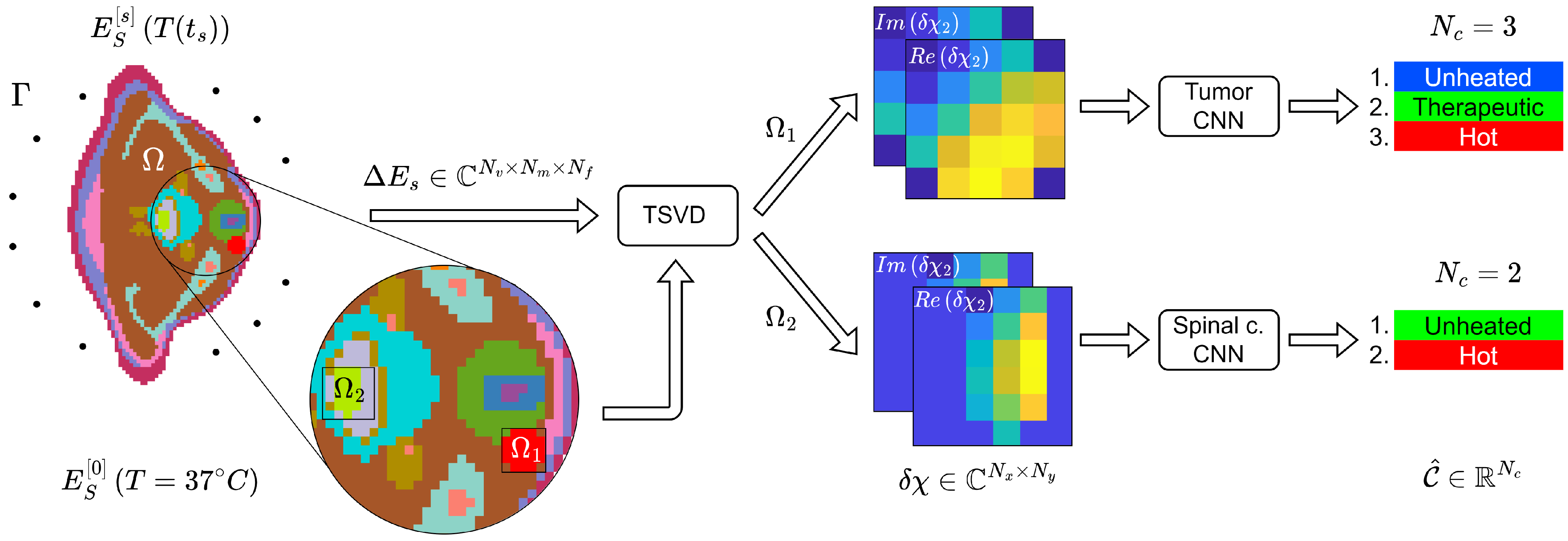
2.3.1. Microwave Imaging Processing
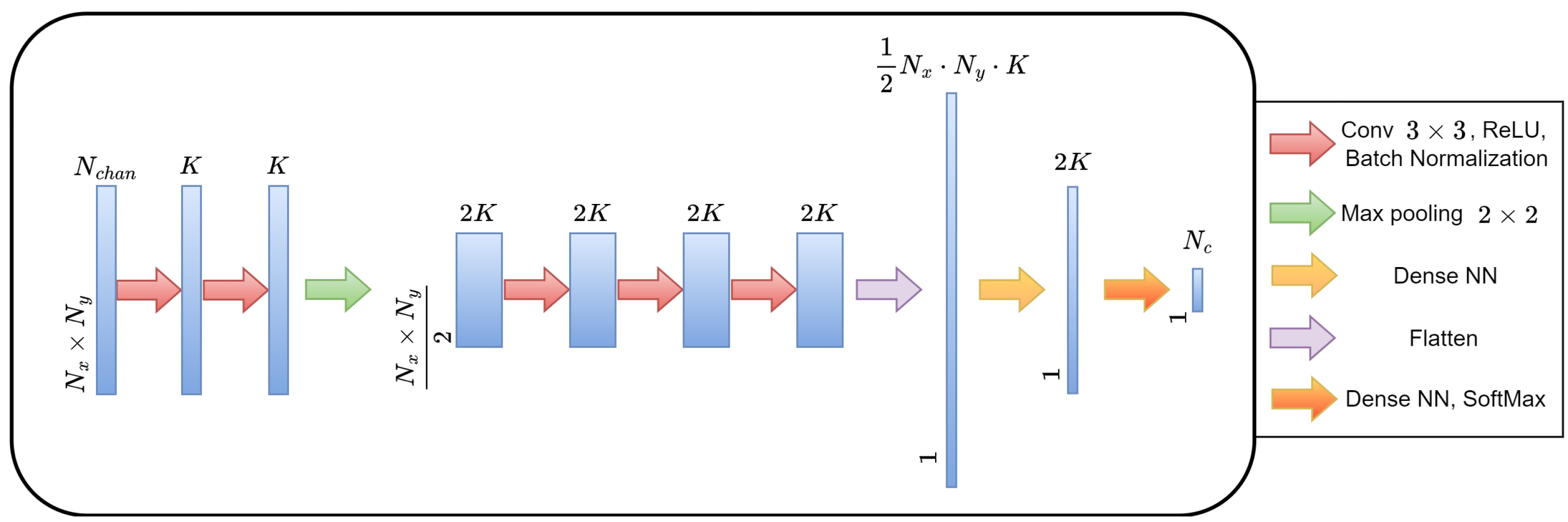
2.3.2. Deep Learning Architecture for Classification
2.4. Assessment of the DL-MWI Framework for Temperature Monitoring in Neck Tumor Hyperthermia
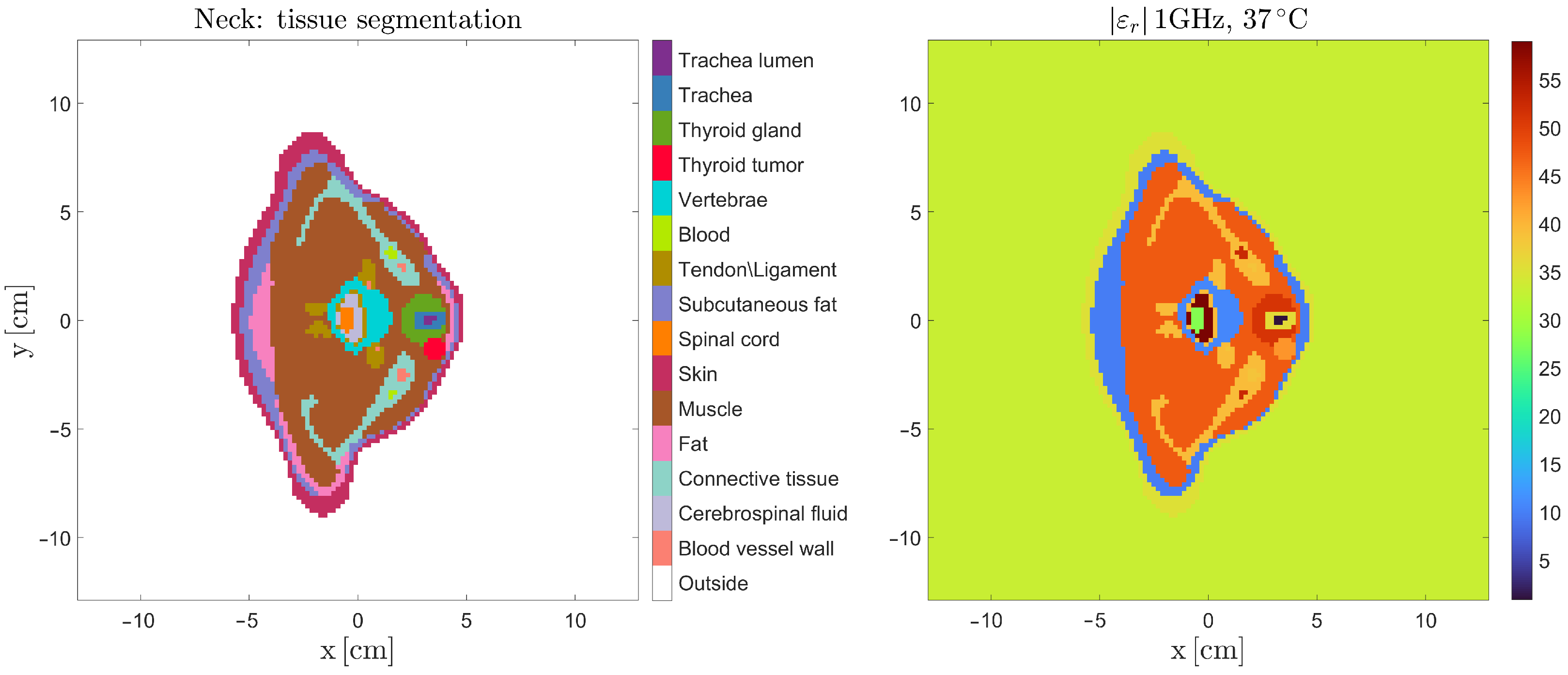
2.4.1. Anatomical Model
2.4.2. MWI Simulations
2.4.3. MWI Imaging Results
2.4.4. CNN Implementation: Categorical Labels
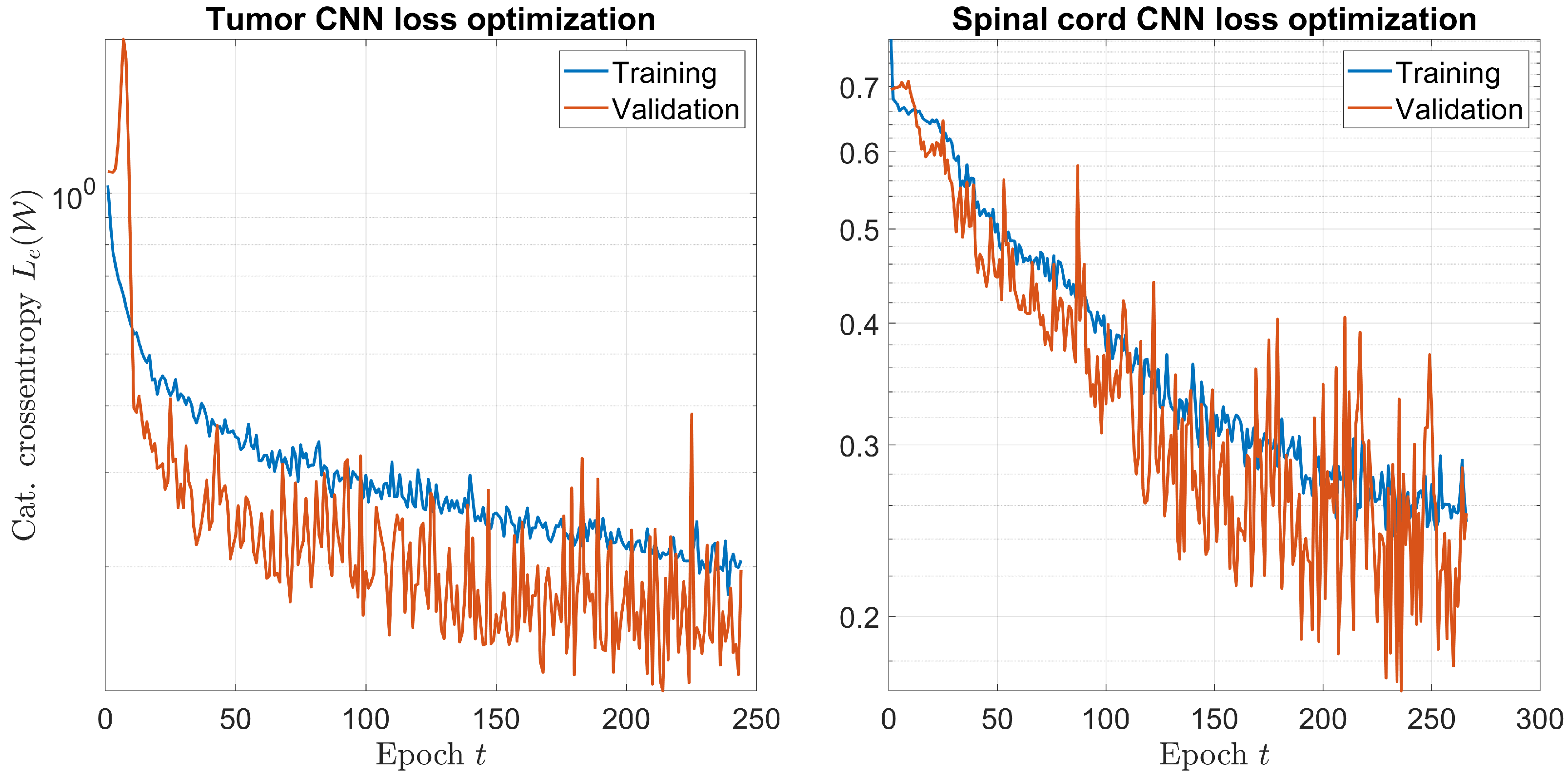
2.4.5. CNN Implementation: Training
2.4.6. Performance Assessment Metrics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, G.M. Hyperthermia and Cancer; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suit, H.D.; Gerweck, L.E. Potential for Hyperthermia and Radiation Therapy. Cancer Res. 1979, 39, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rieke, V.; Butts Pauly, K. MR thermometry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, L.; Oberacker, E.; Paul, K.; Ji, Y.; Oezerdem, C.; Ghadjar, P.; Thieme, A.; Budach, V.; Wust, P.; Niendorf, T. Magnetic resonance thermometry: Methodology, pitfalls and practical solutions. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, H.P.; Cressman, E.N.; Ceelen, W.; Brace, C.L.; Ivkov, R.; Grüll, H.; Ter Haar, G.; Wust, P.; Crezee, J. Heating technology for malignant tumors: A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 711–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, M. Microwave Imaging; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 208. [Google Scholar]
- An Introduction to Microwave Imaging for Breast Cancer Detection; Conceiç ao, R.C., Mohr, J.J., O’Halloran, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Crocco, L.; Karanasiou, I.; James, M.L.; Conceiç ao, R.C. Emerging Electromagnetic Technologies for Brain Diseases Diagnostics, Monitoring and Therapy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, S.; Schilling, S.; Fiser, O.; Vrba, J.; Sachs, J.; Helbig, M. Ultra-wideband temperature dependent dielectric spectroscopy of porcine tissue and blood in the microwave frequency range. Sensors 2019, 19, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolomey, J.; Jofre, L.; Peronnet, G. On the Possible Use of Microwave-Active Imaging for Remote Thermal Sensing. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1983, 31, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, D.L.; Kress, R.; Kress, R. Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 93. [Google Scholar]
- Meaney, P.M.; Fanning, M.W.; Paulsen, K.D.; Li, D.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Fang, Q.; Moodie, K.L. Microwave thermal imaging: Initial in vivo experience with a single heating zone. Int. J. Hyperth. 2003, 19, 617–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, O.; Helbig, M.; Sachs, J.; Ley, S.; Merunka, I.; Vrba, J. Microwave Non-Invasive Temperature Monitoring Using UWB Radar for Cancer Treatment by Hyperthermia. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2018, 162, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozerova, H.; Scapaticci, R.; Vrba, J.; Crocco, L. Monitoring regional hyperthermia via microwave imaging: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Toulouse, France, 14–17 December 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, G.; Akduman, I.; Janjic, A.; Yilmaz, T. A Novel Approach on Microwave Hyperthermia. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, M.; Rocca, P. A review of deep learning approaches for inverse scattering problems (invited review). Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2020, 167, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, T.; Chitlangia, S.; Ahuja, A.; Srinivasan, A. A review of some techniques for inclusion of domain-knowledge into deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Rueden, L.; Mayer, S.; Beckh, K.; Georgiev, B.; Giesselbach, S.; Heese, R.; Kirsch, B.; Walczak, M.; Pfrommer, J.; Pick, A.; et al. Informed Machine Learning—A Taxonomy and Survey of Integrating Prior Knowledge into Learning Systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 614–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, M. Linear Inverse and III-Posed Problems. In Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 75, pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Devaney, A.J.; Dennison, M. Inverse scattering in inhomogeneous background media. Inverse Probl. 2003, 19, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.deeplearningbook.org (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Christ, A.; Kainz, W.; Hahn, E.G.; Honegger, K.; Zefferer, M.; Neufeld, E.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J.; et al. The Virtual Family—Development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 55, N23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, A. Development and Multiphysic Analysis of a Neck Phantom for Microwave Hyperthermia. In Proceedings of the 2020 28th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 24–25 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasgall, P.; Di Gennaro, F.; Baumgartner, C.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.; Payne, D.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues, Version 4.0. IT’IS 2018. Available online: https://itis.swiss/virtual-population/tissue-properties/database/dielectric-properties/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Huang, S.; Cai, W.; Han, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Shao, G.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Cai, Z.; et al. Differences in the dielectric properties of various benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R. Origin and development of the method of moments for field computation. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1990, 32, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, J. Scattering by a dielectric cylinder of arbitrary cross section shape. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1965, 13, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catedra, M.F.; Gago, E.; Nuno, L. A numerical scheme to obtain the RCS of three-dimensional bodies of resonant size using the conjugate gradient method and the fast Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1989, 37, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachena, C.; Fedeli, A.; Fanti, A.; Lodi, M.B.; Pastorino, M.; Randazzo, A. Microwave Imaging for the Diagnosis of Cervical Diseases: A Feasibility Analysis. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2021, 5, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A. Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: Analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, B.W. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. 1975, 405, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of Tissue and Arterial Blood Temperatures in the Resting Human Forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1948, 1, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Class | DSC | MCC |
|---|---|---|
| Unheated | 0.953 | 0.928 |
| Therapeutic | 0.932 | 0.887 |
| Hot | 0.912 | 0.878 |
| Class | DSC | MCC |
|---|---|---|
| Unheated | 0.920 | 0.855 |
| Hot | 0.907 | 0.855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yago Ruiz, Á.; Cavagnaro, M.; Crocco, L. Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment. Cancers 2023, 15, 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061717
Yago Ruiz Á, Cavagnaro M, Crocco L. Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061717
Chicago/Turabian StyleYago Ruiz, Álvaro, Marta Cavagnaro, and Lorenzo Crocco. 2023. "Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061717
APA StyleYago Ruiz, Á., Cavagnaro, M., & Crocco, L. (2023). Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment. Cancers, 15(6), 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061717







