Label-Free Imaging and Histo-Optical Evaluation of Head and Neck Cancers with Multiphoton Autofluorescence Microscopy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Sample Collection
2.2. Imaging System
2.3. Histology Preparation and Pathological Evaluation of H&E
2.4. Image Feature Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Categorical Histomorphometric Analysis
2.5.2. Analysis of Nuclear CoVa
2.5.3. Multinomial Regression of Continuous and Categorical Data
3. Results
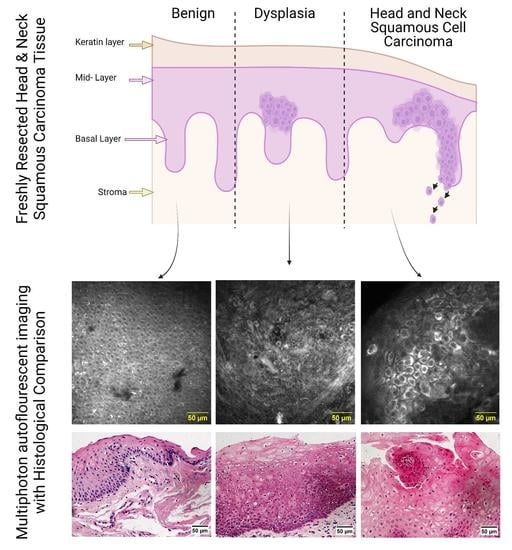
3.1. MPAM/SHG Tissue Imaging
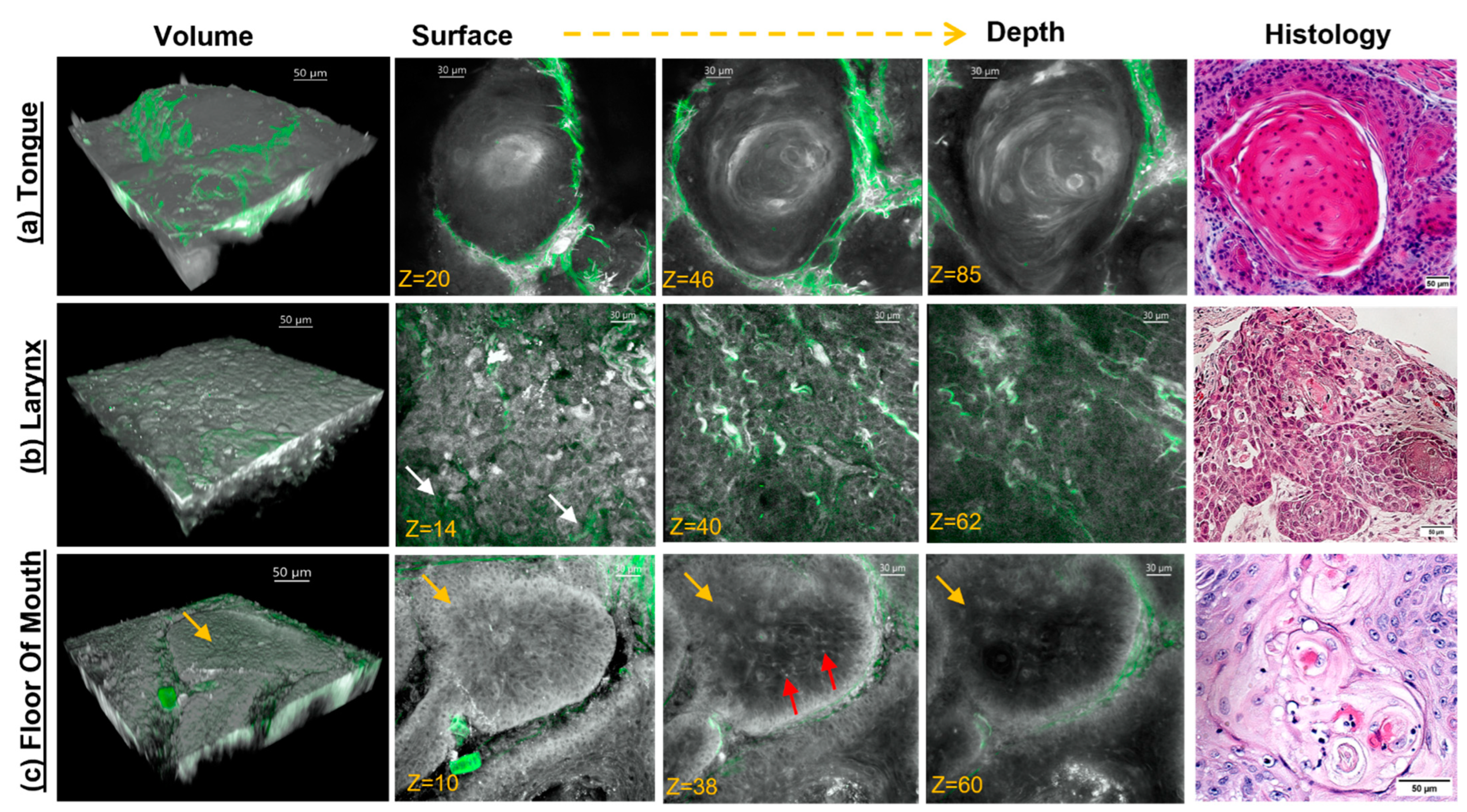
3.2. Label-Free MPAM/SHG Depth-Resolved 3D Imaging of Head and Neck SCC Tissue
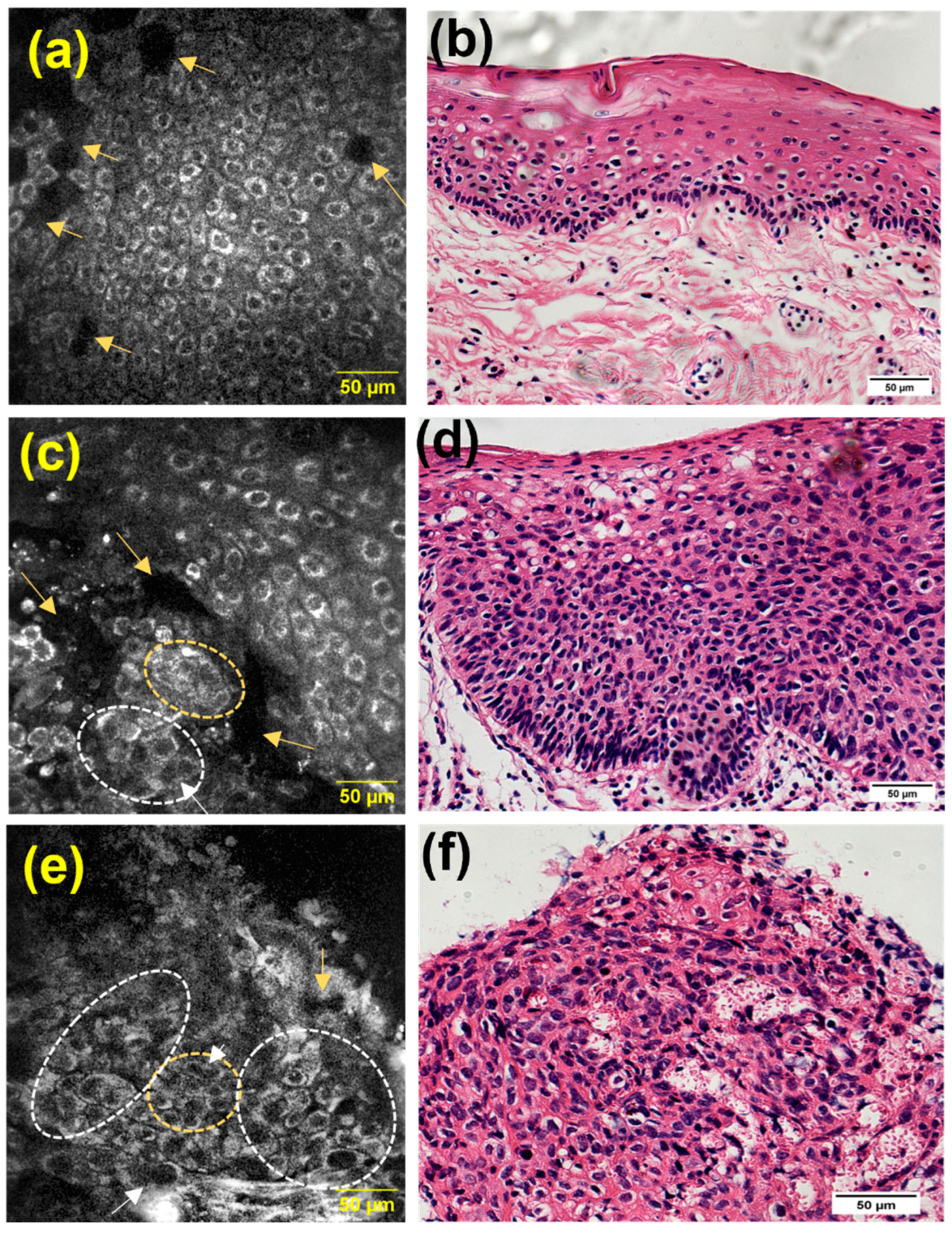
3.3. Qualitative Identification of Cellular Features Associated with Dysplasia and SCC
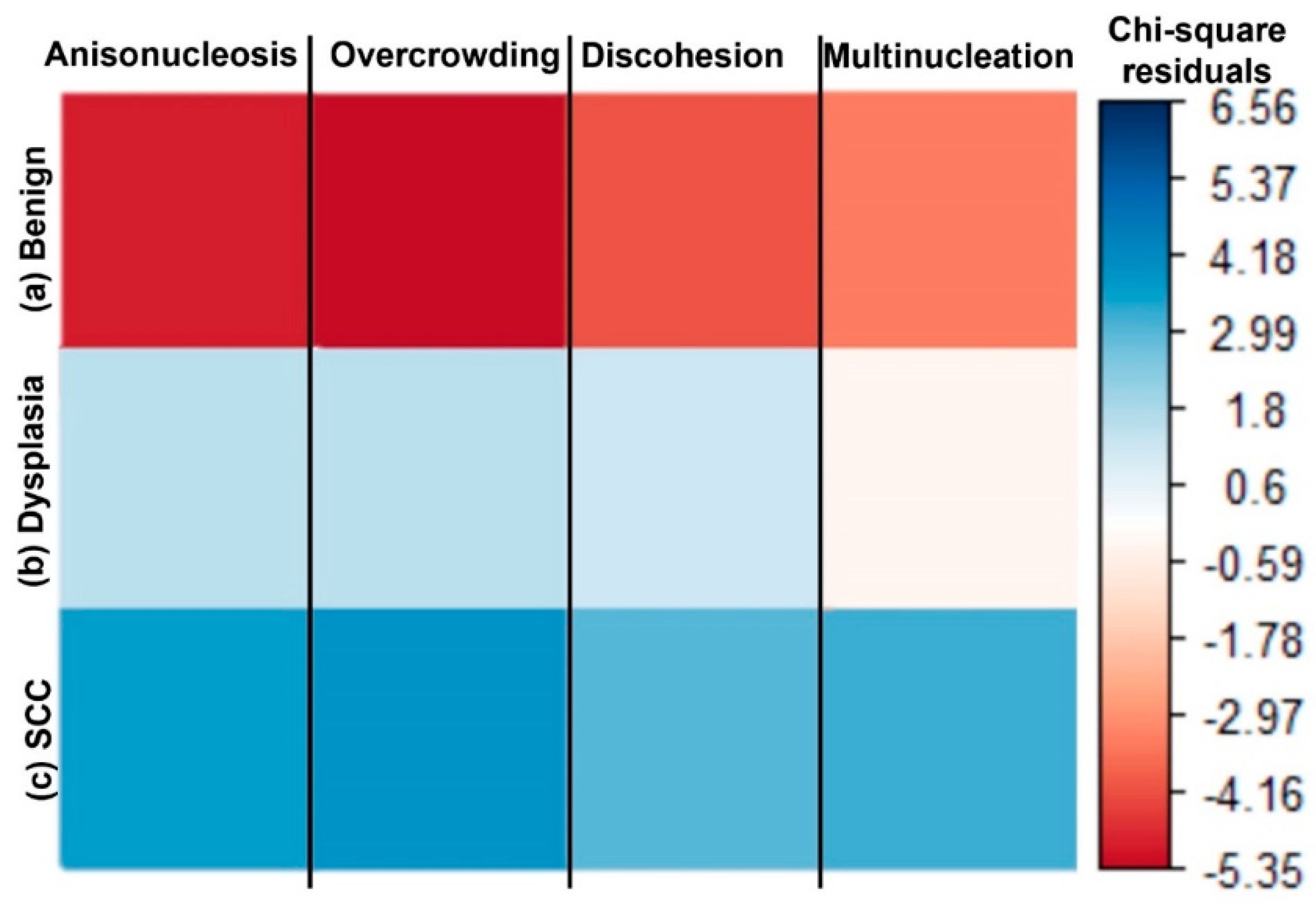
3.4. Nuclear CoVa, a Continuous Measure of Anisonucleosis, Significantly Increases in Sites of Dysplasia and SCC Relative to the Benign Sites
3.5. Transition Areas and Additional Features Identified by MPAM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maweri, S.A.; Halboub, E.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Impact of COVID-19 on the early detection of oral cancer: A special emphasis on high risk populations. Oral Oncol. 2020, 106, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, C.; Kiss, A.; Magalhaes, M.A.; Leong, I.T.; Jorden, T.; Bradley, G. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Precursor Lesions. Cancer Prev. Res. 2021, 14, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadian Cancer Society. Survival Statistics for Oral Cancer. Available online: https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/oral/prognosis-and-survival/survival-statistics (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Amirchaghmaghi, M.; Mohtasham, N.; Delavarian, Z.; Shakeri, M.T.; Hatami, M.; Mosannen Mozafari, P. The diagnostic value of the native fluorescence visualization device for early detection of premalignant/malignant lesions of the oral cavity. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 21, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Edward, K.; Ma, L.; Qiu, S.; Vargas, G. Spectroscopic characterization of oral epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma using multiphoton autofluorescence micro-spectroscopy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Shilagard, T.; Yang, J.; Villarreal, P.; Brown, T.; Qiu, S.; McCammon, S.; Resto, V.; Vargas, G. Remodeling of the Epithelial-Connective Tissue Interface in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia as Visualized by Noninvasive 3D Imaging. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4637–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Villarreal, P.; Qiu, S.; Vargas, G. In-vivo topical mucosal delivery of a fluorescent deoxy-glucose delineates neoplasia from normal in a preclinical model of oral epithelial neoplasia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Yang, J.; Ortiz, D.; Qiu, S.; Resto, V.; McCammon, S.; Vargas, G. In-vivo nonlinear optical microscopy (NLOM) of epithelial-connective tissue interface (ECTI) reveals quantitative measures of neoplasia in hamster oral mucosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingen, M.W.; Kalmar, J.R.; Karrison, T.; Speight, P.M. Critical evaluation of diagnostic aids for the detection of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolgar, J.A.; Triantafyllou, A. Pitfalls and procedures in the histopathological diagnosis of oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and a review of the role of pathology in prognosis. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Johnson, N.W.; van der Waal, I. Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 36, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.; Liu, J.L.Y.; Brocklehurst, P.; Glenny, A.-M.; Lingen, M.; Kerr, A.R.; Ogden, G.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Scully, C. Clinical assessment to screen for the detection of oral cavity cancer and potentially malignant disorders in apparently healthy adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD010173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, K.W.; Maitland, K.C.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Liu, J.T.C. In vivo microscopy as an adjunctive tool to guide detection, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 040601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitland, K.C.; Gillenwater, A.M.; Williams, M.D.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Descour, M.R.; Richards-Kortum, R.R. In vivo imaging of oral neoplasia using a miniaturized fiber optic confocal reflectance microscope. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, S.; Funabiki, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Takebayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, K.; Hara, S.; Yamashita, D.; Imai, Y.; Mizoguchi, A. Real-time imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas using confocal micro-endoscopy and applicable dye: A preliminary study. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, J.M.; Bentley, J.L.; Malik, B.H.; Nemechek, J.; Warda, J.; Cuenca, R.; Cheng, S.; Jo, J.A.; Maitland, K.C. Reflectance confocal endomicroscope with optical axial scanning for in vivo imaging of the oral mucosa. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 3781–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Jang, W.H.; Xiao, P.; Kim, B.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, E.; Kim, K.H. In vivo wide-field reflectance/fluorescence imaging and polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography of human oral cavity with a forward-viewing probe. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, P.S.-P.; Olivo, M.C.; Kho, K.-W.; Mancer, K.; Zheng, W.; Harris, M.; Soo, K.-C. Laser confocal endomicroscopy as a novel technique for fluorescence diagnostic imaging of the oral cavity. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Y.; Campagnola, P.J. Optical diagnostics of tissue pathology by multiphoton microscopy. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2010, 4, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Hu, P.S.; Ghazaryan, A.; Chen, S.J.; Tsai, T.H.; Dong, C.Y. Quantitative analysis of multiphoton excitation autofluorescence and second harmonic generation imaging for medical diagnosis. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2012, 36, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, G.; Shilagard, T.; Ho, K.H.; McCammon, S. Multiphoton autofluorescence microscopy and second harmonic generation microscopy of oral epithelial neoplasms. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 6311–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skala, M.C.; Squirrell, J.M.; Vrotsos, K.M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Gendron-Fitzpatrick, A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Ramanujam, N. Multiphoton microscopy of endogenous fluorescence differentiates normal, precancerous, and cancerous squamous epithelial tissues. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, N.D.; Andreou, S.; Hoying, J.B.; Utzinger, U. Live imaging of collagen remodeling during angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H3198–H3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Shilagard, T.; Bell, B.; Motamedi, M.; Vargas, G. In vivo multimodal nonlinear optical imaging of mucosal tissue. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.; Xie, S.; Chen, R.; Cao, N.; Zou, Q.; Xiong, S. The layered-resolved microstructure and spectroscopy of mouse oral mucosa using multiphoton microscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 4967–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amy, T.S.; Melissa, C.S. Ex vivo label-free microscopy of head and neck cancer patient tissues. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–12 February 2015; p. 93292B. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.R.; Shieh, D.B.; Lou, P.J.; Lin, C.F.; Sun, C.K. Characterization of oral squamous cell carcinoma based on higher-harmonic generation microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, E.; Rowlands, C.; So, P.T. Application of Multiphoton Microscopy in Dermatological Studies: A Mini-Review. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2014, 7, 1330010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Pérez-Cárceles, M.D.; Ardelean, L.C.; Stanciu, S.G.; Bueno, J.M. Multiphoton Microscopy of Oral Tissues: Review. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Hall, G.; Chen, D.; Liang, W.; Ning, B.; Guan, H.; Li, X. A biopsy-needle compatible varifocal multiphoton rigid probe for depth-resolved optical biopsy. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, W.; Kerr, J.N.; Nimmerjahn, A.; Helmchen, F. Miniaturized two-photon microscope based on a flexible coherent fiber bundle and a gradient-index lens objective. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2521–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Maguluri, G.; Daniel Ferguson, R.; Tu, H.; Paul, K.; Boppart, S.A.; Llano, D.A.; Iftimia, N. Two-photon microscope using a fiber-based approach for supercontinuum generation and light delivery to a small-footprint optical head. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, D.R.; Brown, C.M.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Pavlova, I.; Kobat, D.; Webb, W.W.; Xu, C. Compact and flexible raster scanning multiphoton endoscope capable of imaging unstained tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17598–17603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westra, W.H.; Lewis, J.S., Jr. Update from the 4th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumours: Oropharynx. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edward, K.; Qiu, S.; Resto, V.; McCammon, S.; Vargas, G. In vivo layer-resolved characterization of oral dysplasia via nonlinear optical micro-spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skala, M.C.; Riching, K.M.; Gendron-Fitzpatrick, A.; Eickhoff, J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; White, J.G.; Ramanujam, N. In vivo multiphoton microscopy of NADH and FAD redox states, fluorescence lifetimes, and cellular morphology in precancerous epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19494–19499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varone, A.; Xylas, J.; Quinn, K.P.; Pouli, D.; Sridharan, G.; McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Alonzo, C.; Lee, K.; Münger, K.; Georgakoudi, I. Endogenous two-photon fluorescence imaging elucidates metabolic changes related to enhanced glycolysis and glutamine consumption in precancerous epithelial tissues. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- gopinath, D.; Beena, V.T.; Stephen, M.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Choudhary, K. Basaloid Squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity:- report of two cases. Int. J. Dent. Clin. 2012, 4, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Niklander, S.E. Inflammatory Mediators in Oral Cancer: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Potential. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 642238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.V.; Aravindha, B.; Leena, S.; Balachander, N.; Malathi, L.K.; Masthan, M.K. Role of abnormal Langerhans cells in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma: A pilot study. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2015, 6, S128–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.B. Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Premalignancy. Head Neck Pathol. 2019, 13, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedeke, J.; Schreiber, P.; Seidmann, L.; Li, G.; Birkenstock, J.; Simon, F.; König, J.; Muensterer, O.J. Multiphoton microscopy in the diagnostic assessment of pediatric solid tissue in comparison to conventional histopathology: Results of the first international online interobserver trial. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3655–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muensterer, O.J.; Waldron, S.; Boo, Y.J.; Ries, C.; Sehls, L.; Simon, F.; Seidmann, L.; Birkenstock, J.; Gödeke, J. Multiphoton microscopy: A novel diagnostic method for solid tumors in a prospective pediatric oncologic cohort, an experimental study. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 48, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, K.; Breunig, H.G.; Batista, A.; Schindele, A.; Zieger, M.; Kaatz, M. Translation of two-photon microscopy to the clinic: Multimodal multiphoton CARS tomography of in vivo human skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 014515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.; Volkmer, B.; Puschmann, S.; Greinert, R.; Breitbart, E.; Kiefer, J.; Wepf, R. Assessing the risk of skin damage due to femtosecond laser irradiation. J. Biophotonics 2008, 1, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.; Volkmer, B.; Puschmann, S.; Greinert, R.; Breitbart, W.; Kiefer, J.; Wepf, R. Risk estimation of skin damage due to ultrashort pulsed, focused near-infrared laser irradiation at 800 nm. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 041320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Jarrett, J.W.; Hassan, A.M.; Dunn, A.K. Deep tissue imaging with multiphoton fluorescence microscopy. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavlokhova, V.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Sandhu, S.; Vollmer, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Engel, M.; Ristow, O.; Freudlsperger, C. Features of oral squamous cell carcinoma in ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavlokhova, V.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Sandhu, S.; Pilz, M.; Vollmer, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Engel, M.; Freudlsperger, C. Detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Sensitivity and specificity compared to histopathology. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e202000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strome, A.; Kossatz, S.; Zanoni, D.K.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Patel, S.; Reiner, T. Current Practice and Emerging Molecular Imaging Technologies in Oral Cancer Screening. Mol. Imaging 2018, 17, 1536012118808644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.; Zanoni, D.K.; Ardigo, M.; Migliacci, J.C.; Patel, S.G.; Rajadhyaksha, M. Feasibility of a Video-Mosaicking Approach to Extend the Field-of-View For Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Oral Cavity In Vivo. Lasers Surg. Med. 2019, 51, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, N.G.; Collgros, H.; Uribe, P.; Ch’ng, S.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Guitera, P. In vivo confocal microscopy for the oral cavity: Current state of the field and future potential. Oral Oncol. 2016, 54, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wei, L.; Abeytunge, S.; Peterson, G.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Liu, J. Label-free in vivo pathology of human epithelia with a high-speed handheld dual-axis confocal microscope. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 30501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, E.; Bologna-Molina, R.; Gónzalez-Gónzalez, R.; Arocena, M. The Tissue Architecture of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Visualized by Staining Patterns of Wheat Germ Agglutinin and Structural Proteins Using Confocal Microscopy. Cells 2021, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, T.J.; Roblyer, D.; Williams, M.D.; Stepanek, V.M.; Richards-Kortum, R.; Gillenwater, A.M. Noninvasive imaging of oral neoplasia with a high-resolution fiber-optic microendoscope. Head Neck 2012, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezinski, M.E. (Ed.) 13—Other Technologies. In Optical Coherence Tomography; Academic Press: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2006; pp. 353–368. [Google Scholar]



| Cellular Atypia Identified by MPAM in Resected Tissue | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Representative MPAM Micrographs | Histopathological Grading | |||
| Full View | Zoom-in View | Benign | Dysplasia | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
| Overcrowding: Increase of localized, cluster-like nuclei overlapping |  | 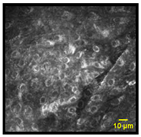 | 6% | 85% | 97% |
| Cell Discohesion: loosened intercellular connections between squamous cells | 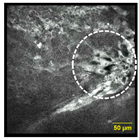 |  | 16% | 45% | 80% |
| Multinucleated Cells: Squamous cells that appear poly nuclear or have more than one nuclei per cell | 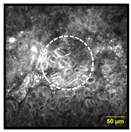 | 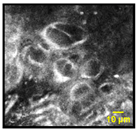 | 16% | 85% | 93% |
| Anisonucleosis/Nuclear Pleomorphism: Abnormal variation in nuclear size and shape | 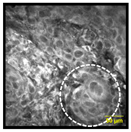 | 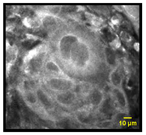 | 6% | 90% | 100% |
| Odds Ratios Increase as Histological Grade Severity Increases | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Variable | Benign | Dysplasia | SCC |
| OR * | OR CI | OR CI | |
| Anisonucleosis | 1 | 69 (17–544) | 702 (82–32,417) |
| Overcrowding | 1 | 208 (24–10,071) | 964 (110–50,236) |
| Discohesion | 1 | 3 (1.3–13) | 17 (7–51) |
| Multinucleation | 1 | 19 (6–96) | 52 (19–209) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villarreal, P.P.; Pal, R.; Qiu, S.; Coblens, O.; Villasante-Tezanos, A.; Resto, V.; McCammon, S.; Vargas, G. Label-Free Imaging and Histo-Optical Evaluation of Head and Neck Cancers with Multiphoton Autofluorescence Microscopy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041302
Villarreal PP, Pal R, Qiu S, Coblens O, Villasante-Tezanos A, Resto V, McCammon S, Vargas G. Label-Free Imaging and Histo-Optical Evaluation of Head and Neck Cancers with Multiphoton Autofluorescence Microscopy. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041302
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillarreal, Paula Patricia, Rahul Pal, Suimin Qiu, Orly Coblens, Alejandro Villasante-Tezanos, Vicente Resto, Susan McCammon, and Gracie Vargas. 2023. "Label-Free Imaging and Histo-Optical Evaluation of Head and Neck Cancers with Multiphoton Autofluorescence Microscopy" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041302
APA StyleVillarreal, P. P., Pal, R., Qiu, S., Coblens, O., Villasante-Tezanos, A., Resto, V., McCammon, S., & Vargas, G. (2023). Label-Free Imaging and Histo-Optical Evaluation of Head and Neck Cancers with Multiphoton Autofluorescence Microscopy. Cancers, 15(4), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041302