E2 Partner Tunes the Ubiquitylation Specificity of Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Constructs, Protein Expression and Purification
2.2. Amino acid Selective 15N Labeling and Reverse Labeling (Unlabeling)
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Titration
2.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.5. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.6. Synthesis of E2-Ub Conjugate
2.7. Oxyester Hydrolysis Assays
2.8. Ubiquitylation Assays
3. Results
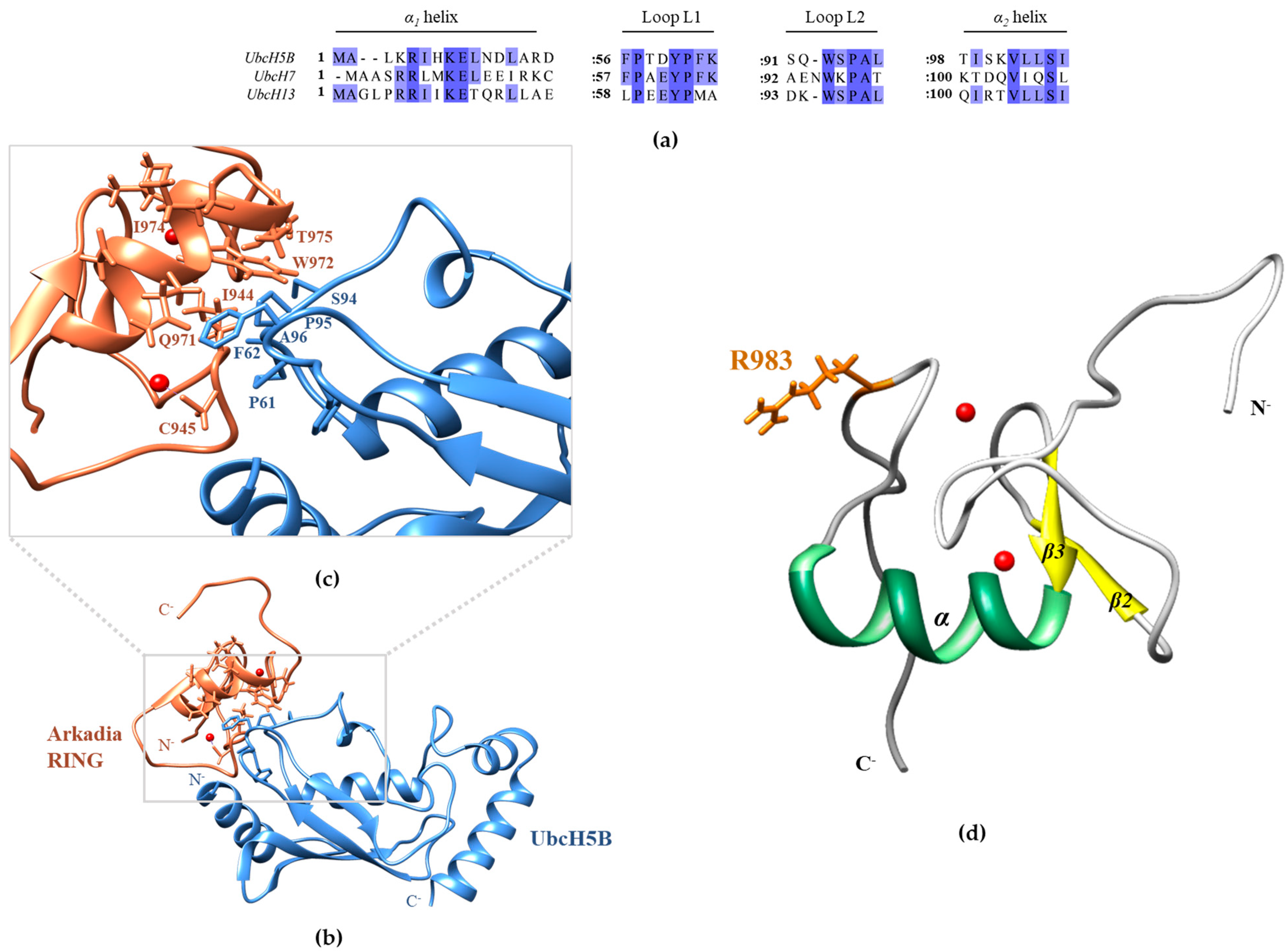
3.1. The Phe62 Residue of UbcH5B Is Critical for the Interaction with Arkadia
3.2. The SPA Motif Acts as a Specificity Determinant for the E2–Arkadia Interaction
3.3. UbB-UbcH5B Binding Enhances Ark LONG-Mediated Ub Transfer
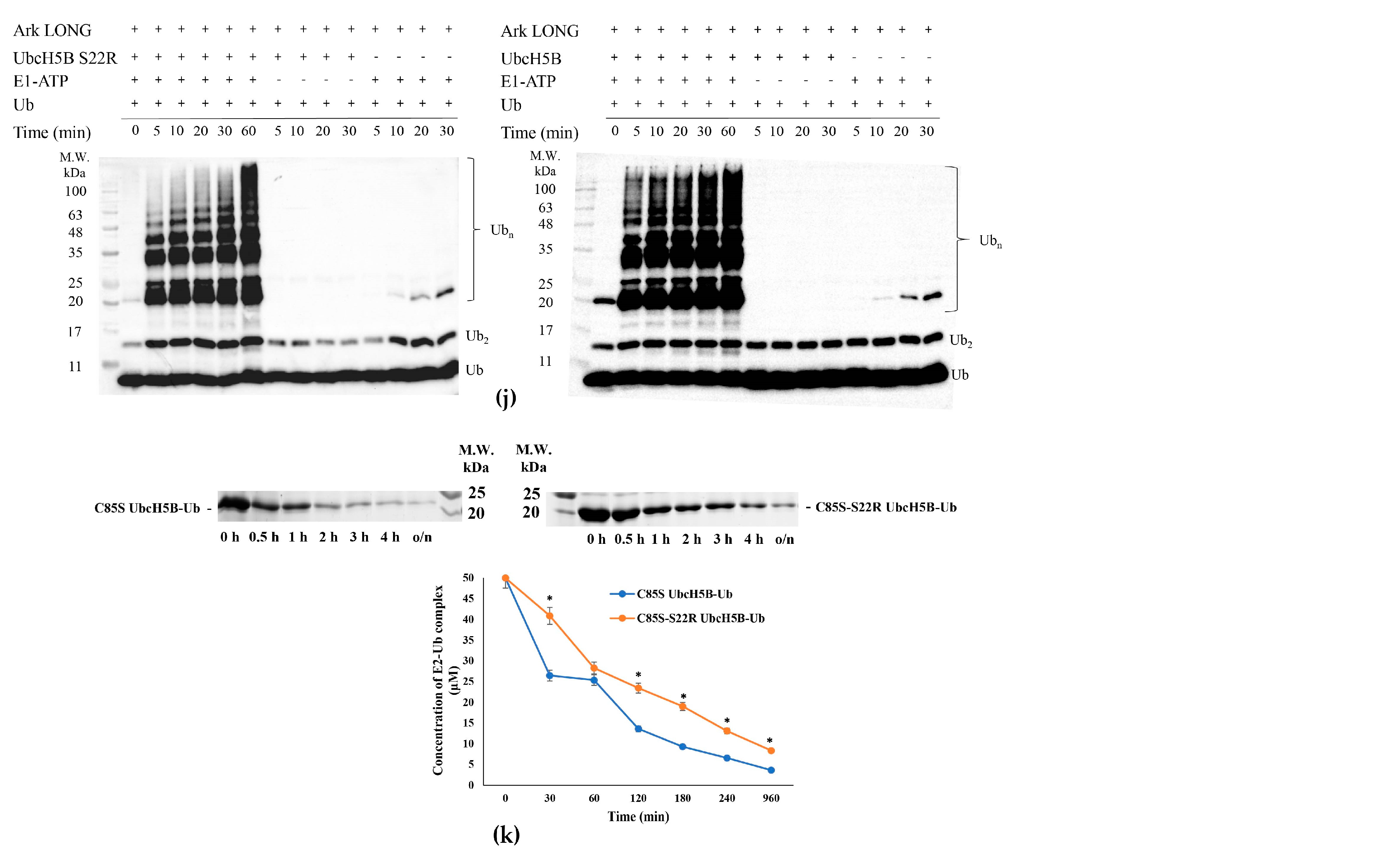
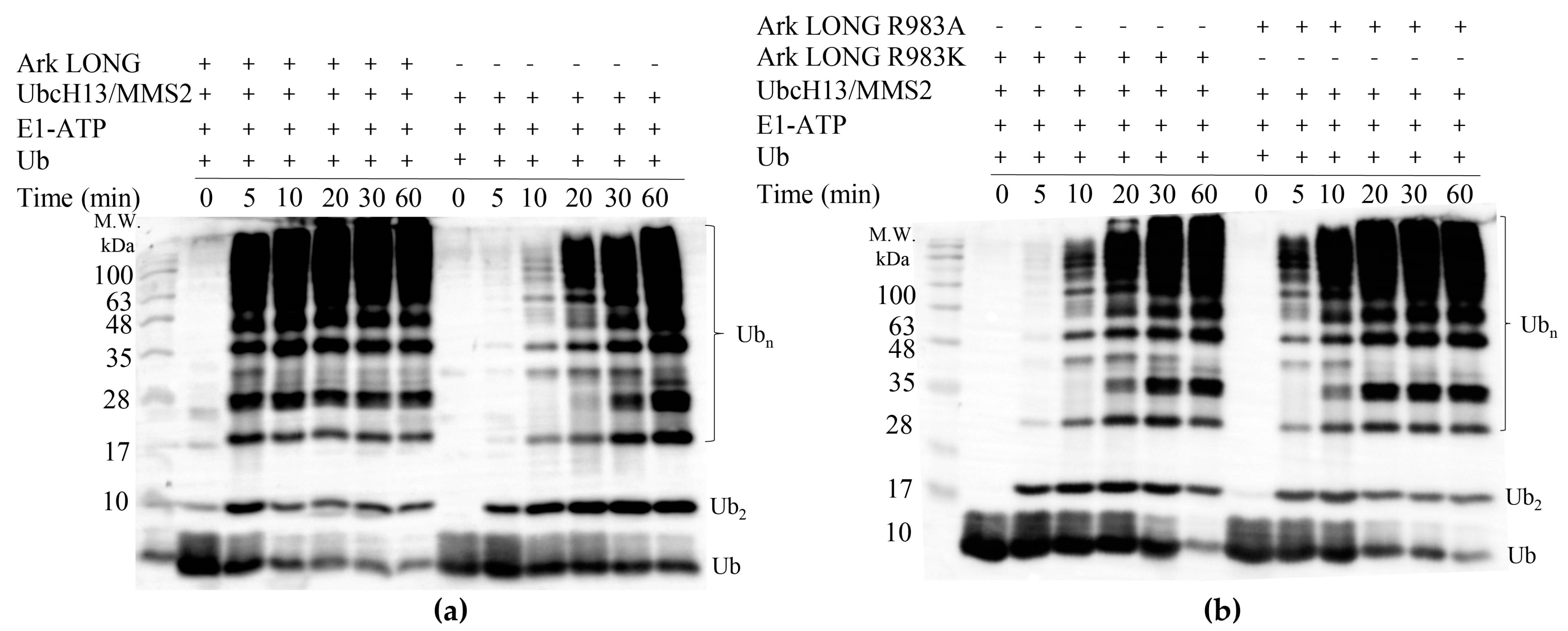
3.4. Arkadia Possesses a ‘Linchpin’ Arginine
3.5. UbcH13 Interacts with Arkadia with Weaker Affinity than UbcH5B and Leads to Its Monoubiquitylation
3.6. Ark LONG Enhances the Ability of UbcH13/MMS2 to form Free Ub Chains Using ‘Linchpin’ R983 of Arkadia
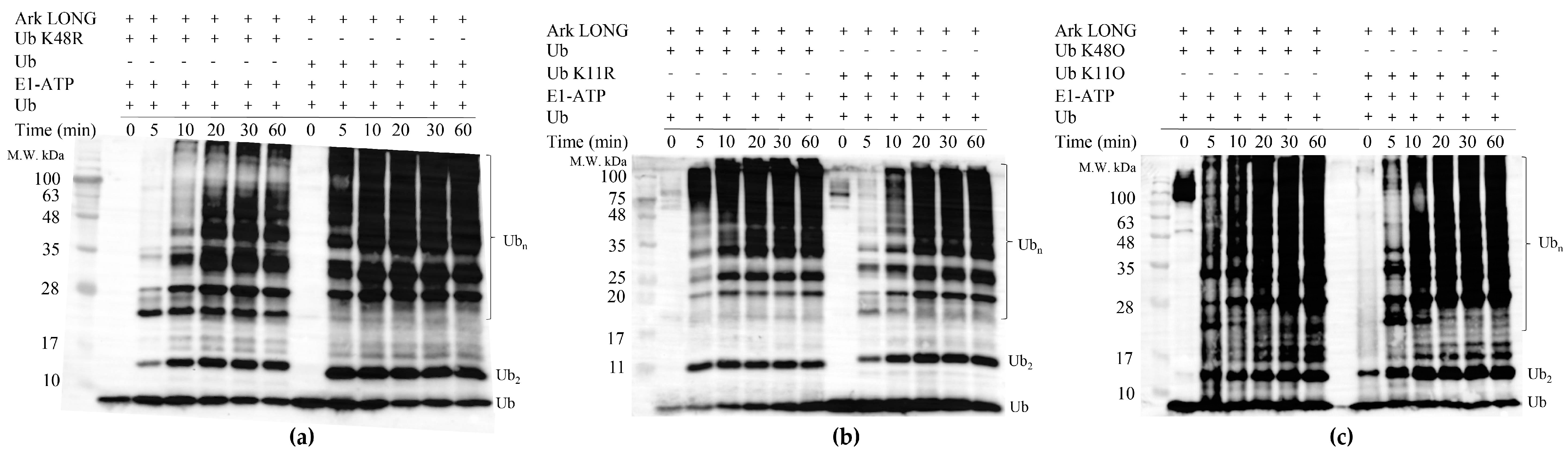
3.7. UbcH5B Promotes K48- and K11-Linked Polyubiquitylation of Arkadia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pickart, C.M. Mechanisms Underlying Ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabbe, C.; Husnjak, K.; Dikic, I. The spatial and temporal organization of ubiquitin networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei-Amponsa, V.; Walters, K.J. Proteasome substrate receptors and their therapeutic potential. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenno, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Tochio, H.; Iwai, K.; Morita, E.H.; Hayashi, H.; Murata, S.; Hiroaki, H.; Sato, M.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Structural basis for distinct roles of Lys63- and Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chains. Genes Cells 2004, 9, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangary, S.; Wang, S. Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction for Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5318–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossatz, U.; Dietrich, N.; Zender, L.; Buer, J.; Manns, M.P.; Malek, N.P. Skp2-dependent degradation of p27kip1 is essential for cell cycle progression. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2602–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, L.H.; Couch, F.J.; Erdos, M.R.; Hoskins, K.F.; Calzone, K.; Garber, J.E.; Boyd, J.; Lubin, M.B.; Deshano, M.L.; Brody, L.C.; et al. Mutations in the BRCA1 gene in families with early-onset breast and ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 1994, 8, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Shih, L.-Y.; Otsu, M.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Tamura, A.; Honda, H.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Kumano, K.; et al. Gain-of-function of mutated C-CBL tumour suppressor in myeloid neoplasms. Nature 2009, 460, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, D.F.; Tang, X.; Pelletier, B.; Orlicky, S.; Xie, W.; Plantevin, V.; Neculai, D.; Chou, Y.-C.; Ogunjimi, A.; Al-Hakim, A.; et al. An Allosteric Inhibitor of the Human Cdc34 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme. Cell 2011, 145, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M. Targeting MDM2 by the small molecule RITA: Towards the development of new multi-target drugs against cancer. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2005, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-H.; Morrow, J.K.; Li, C.-F.; Gao, Y.; Jin, G.; Moten, A.; Stagg, L.J.; Ladbury, J.E.; Cai, Z.; Xu, D.; et al. Pharmacological Inactivation of Skp2 SCF Ubiquitin Ligase Restricts Cancer Stem Cell Traits and Cancer Progression. Cell 2013, 154, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Mitsiades, C.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C. Bortezomib: Proteasome Inhibition as an Effective Anticancer Therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006, 57, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederländer, C.; Walsh, J.J.; Episkopou, V.; Jones, C.M. Arkadia enhances nodal-related signalling to induce mesendoderm. Nature 2001, 410, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinuma, D.; Shinozaki, M.; Komuro, A.; Goto, K.; Saitoh, M.; Hanyu, A.; Ebina, M.; Nukiwa, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Imamura, T.; et al. Arkadia amplifies TGF- superfamily signalling through degradation of Smad7. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6458–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Mavrakis, K.J.; Lee, K.L.; Fujii, T.; Koinuma, D.; Sase, H.; Yuki, K.; Isogaya, K.; Saitoh, M.; Imamura, T.; et al. Arkadia Induces Degradation of SnoN and c-Ski to Enhance Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20492–20501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erker, Y.; Neyret-Kahn, H.; Seeler, J.S.; Dejean, A.; Atfi, A.; Levy, L. Arkadia, a Novel SUMO-Targeted Ubiquitin Ligase Involved in PML Degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.L.; Hansen, R.K.; Wagner, S.A.; Van Cuijk, L.; van Belle, G.J.C.; Streicher, W.; Wikström, M.; Choudhary, C.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Marteijn, J.; et al. RNF111/Arkadia is a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase that facilitates the DNA damage response. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 787–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Cuijk, L.; van Belle, G.J.; Turkyilmaz, Y.; Poulsen, S.L.; Janssens, R.C.; Theil, A.F.; Sabatella, M.; Lans, H.; Mailand, N.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; et al. SUMO and ubiquitin-dependent XPC exchange drives nucleotide excision repair. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Drabsch, Y.; Dekker, T.J.A.; de Vinuesa, A.G.; Li, Y.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C.; Sheppard, K.-A.; Goumans, M.-J.; Luwor, R.B.; de Vries, C.J.; et al. Nuclear receptor NR4A1 promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis by activating TGF-β signalling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Antonacopoulou, A.G.; Tanaka, S.; Panoutsopoulos, A.A.; Bravou, V.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Episkopou, V. Enhancement of TGF-β Signaling Responses by the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Arkadia Provides Tumor Suppression in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6438–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkou, M.; Raptis, V.; Marousis, K.D.; Tsevis, A.; Bourikas, K.; Bentrop, D.; Episkopou, V.; Spyroulias, G.A. Impact of a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on the 3D Protein Structure and Ubiquitination Activity of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Arkadia. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 844129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yang, T.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Tong, X.; Yang, W.-T.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, H.-T. RNF111/Arkadia is regulated by DNA methylation and affects TGF-β/Smad signaling associated invasion in NSCLC cells. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briones-Orta, M.A.; Levy, L.; Madsen, C.D.; Das, D.; Erker, Y.; Sahai, E.; Hill, C.S. Arkadia Regulates Tumor Metastasis by Modulation of the TGF-β Pathway. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Kohli, E.; Devlin, K.I.; Bold, M.; Nix, J.C.; Misra, S. Interactions between the quality control ubiquitin ligase CHIP and ubiquitin conjugating enzymes. BMC Struct. Biol. 2008, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.E.; Brzovic, P.S.; Klevit, R.E. E2–BRCA1 RING interactions dictate synthesis of mono- or specific polyubiquitin chain linkages. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDemark, A.P.; Hofmann, R.M.; Tsui, C.; Pickart, C.M.; Wolberger, C. Molecular Insights into Polyubiquitin Chain Assembly. Cell 2001, 105, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baboshina, O.V.; Haas, A.L. Novel Multiubiquitin Chain Linkages Catalyzed by the Conjugating Enzymes E2EPF and RAD6 Are Recognized by 26 S Proteasome Subunit 5. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldeman, M.T.; Xia, G.; Kasperek, E.M.; Pickart, C.M. Structure and Function of Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme E2-25K: The Tail Is a Core-Dependent Activity Element. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 10526–10537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.-C.; Zhang, B.-X.; Ding, J.L. E2-E3 ubiquitin enzyme pairing-partnership in provoking or mitigating cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, S.; De Vries, S.J.; Kemmeren, P.; Huang, A.; Boelens, R.; Bonvin, A.M.; Timmers, H.T.M. A comprehensive framework of E2–RING E3 interactions of the human ubiquitin–proteasome system. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkou, M.; Delegkou, G.N.; Marousis, K.D.; Fragkaki, N.; Toro, T.; Episkopou, V.; Spyroulias, G.A. Unveiling the Essential Role of Arkadia’s Non-RING Elements in the Ubiquitination Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marousis, K.D.; Birkou, M.; Asimakopoulou, A.; Spyroulias, G.A. 1H, 13C, 15N backbone and side-chain resonance assignment of the native form of UbcH7 (UBE2L3) through solution NMR spectroscopy. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2020, 14, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipuria, G.; Krishnarjuna, B.; Mondal, S.; Dubey, A.; Atreya, H.S. Amino Acid Selective Labeling and Unlabeling for Protein Resonance Assignments. In Isotope Labeling in Biomolecular NMR; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marousis, K.D.; Tsika, A.C.; Birkou, M.; Matsoukas, M.-T.; Spyroulias, G.A. Lead Identification Through the Synergistic Action of Biomolecular NMR and In Silico Methodologies. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1824, pp. 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, D.S.; Seok, Y.-J.; Peterkofsky, A.; Clore, G.M.; Gronenborn, A.M. Identification by NMR of the Binding Surface for the Histidine-Containing Phosphocarrier Protein HPr on the N-Terminal Domain of Enzyme I of the Escherichia coli Phosphotransferase System. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R. The Computer Aided Resonance Assignment Tutorial; Cantina Verlag: Goldau, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 3856001123. [Google Scholar]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Kandias, N.G.; Episkopou, V.; Bentrop, D.; Spyroulias, G.A. NMR-based insights into the conformational and interaction properties of Arkadia RING-H2 E3 Ub ligase. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, D.M.; Lissounov, A.; Brzovic, P.S.; Klevit, R.E. UBCH7 reactivity profile reveals parkin and HHARI to be RING/HECT hybrids. Nature 2011, 474, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dove, K.K.; Olszewski, J.L.; Martino, L.; Duda, D.M.; Wu, X.S.; Miller, D.J.; Reiter, K.H.; Rittinger, K.; Schulman, B.A.; Klevit, R.E. Structural Studies of HHARI/UbcH7∼Ub Reveal Unique E2∼Ub Conformational Restriction by RBR RING1. Structure 2017, 25, 890–900.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buetow, L.; Gabrielsen, M.; Anthony, N.G.; Dou, H.; Patel, A.; Aitkenhead, H.; Sibbet, G.J.; Smith, B.O.; Huang, D.T. Activation of a Primed RING E3-E2–Ubiquitin Complex by Non-Covalent Ubiquitin. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Sibbet, G.J.; Huang, D.T. Structural insights into non-covalent ubiquitin activation of the cIAP1-UbcH5B∼ubiquitin complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, E.; Satoh, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yagi-Utsumi, M.; Kurimoto, E.; Tanaka, K.; Wakatsuki, S.; Kato, K. Crystal Structure of UbcH5b∼Ubiquitin Intermediate: Insight into the Formation of the Self-Assembled E2∼Ub Conjugates. Structure 2010, 18, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Mace, P.; Day, C. Secondary ubiquitin-RING docking enhances Arkadia and Ark2C E3 ligase activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruneda, J.N.; Littlefield, P.J.; Soss, S.E.; Nordquist, K.A.; Chazin, W.J.; Brzovic, P.S.; Klevit, R.E. Structure of an E3:E2∼Ub Complex Reveals an Allosteric Mechanism Shared among RING/U-box Ligases. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechanovová, A.; Jaffray, E.G.; Tatham, M.H.; Naismith, J.H.; Hay, R.T. Structure of a RING E3 ligase and ubiquitin-loaded E2 primed for catalysis. Nature 2012, 489, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandapadamanaban, M.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Csizmók, V.; Wallenhammar, A.; Espinosa, A.C.; Ahlner, A.; Round, A.R.; Trewhella, J.; Moche, M.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; et al. E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21-mediated lysine capture by UBE2E1 reveals substrate-targeting mode of a ubiquitin-conjugating E2. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11404–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, L.; Zeng, J.; Dickson, C.F.; Mallery, D.L.; Yang, J.-C.; McLaughlin, S.H.; Boland, A.; Neuhaus, D.; James, L.C. A tri-ionic anchor mechanism drives Ube2N-specific recruitment and K63-chain ubiquitination in TRIM ligases. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.D.; Duncan, E.D.; Coronado, E.; DaRosa, P.A.; Pruneda, J.N.; Brzovic, P.S.; Klevit, R.E. Tuning BRCA1 and BARD1 activity to investigate RING ubiquitin ligase mechanisms. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkou, M.; Chasapis, C.T.; Marousis, K.D.; Loutsidou, A.K.; Bentrop, D.; Lelli, M.; Herrmann, T.; Carthy, J.M.; Episkopou, V.; Spyroulias, G.A. A Residue Specific Insight into the Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity and Conformational Plasticity. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratt, D.E.; Wu, K.; Kovacev, J.; Pan, Z.-Q.; Shaw, G.S. Selective Recruitment of an E2∼Ubiquitin Complex by an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 17374–17385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooff, J.; Pastushok, L.; Hanna, M.; Fu, Y.; Xiao, W. The TRAF6 RING finger domain mediates physical interaction with Ubc13. FEBS Lett. 2004, 566, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huen, M.S.Y.; Huang, J.; Yuan, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Ashley, C.; Xiao, W.; Chen, J. Noncanonical E2 Variant-Independent Function of UBC13 in Promoting Checkpoint Protein Assembly. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6104–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soss, S.E.; Yue, Y.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Chazin, W.J. E2 Conjugating Enzyme Selectivity and Requirements for Function of the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase CHIP. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21277–21286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzovic, P.S.; Lissounov, A.; Christensen, D.E.; Hoyt, D.W.; Klevit, R.E. A UbcH5/Ubiquitin Noncovalent Complex Is Required for Processive BRCA1-Directed Ubiquitination. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paluda, A.; Middleton, A.J.; Rossig, C.; Mace, P.D.; Day, C.L. Ubiquitin and a charged loop regulate the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ark2C. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkli, M.; Lorick, K.; Weissman, A.; Jänne, O.; Palvimo, J. Transcriptional coregulator SNURF (RNF4) possesses ubiquitin E3 ligase activity. FEBS Lett. 2004, 560, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, L. Protein regulation by monoubiquitin. Nat. Rev. 2001, 2, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Gan, W.; Su, S.; Hauenstein, A.V.; Fu, T.-M.; Brasher, B.; Schwerdtfeger, C.; Liang, A.C.; Xu, M.; Wei, W. K63-linked polyubiquitin chains bind to DNA to facilitate DNA damage repair. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, aar8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

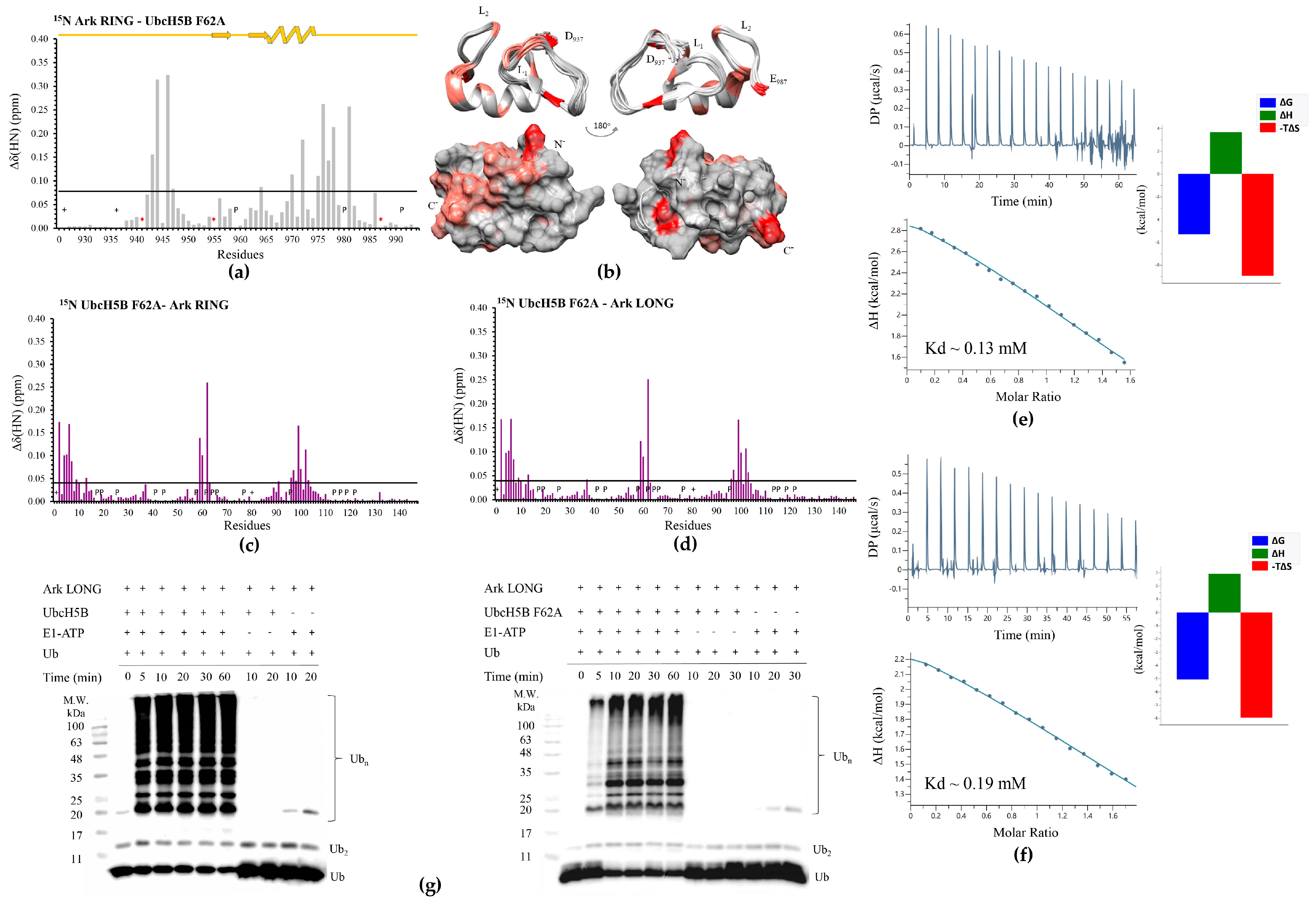

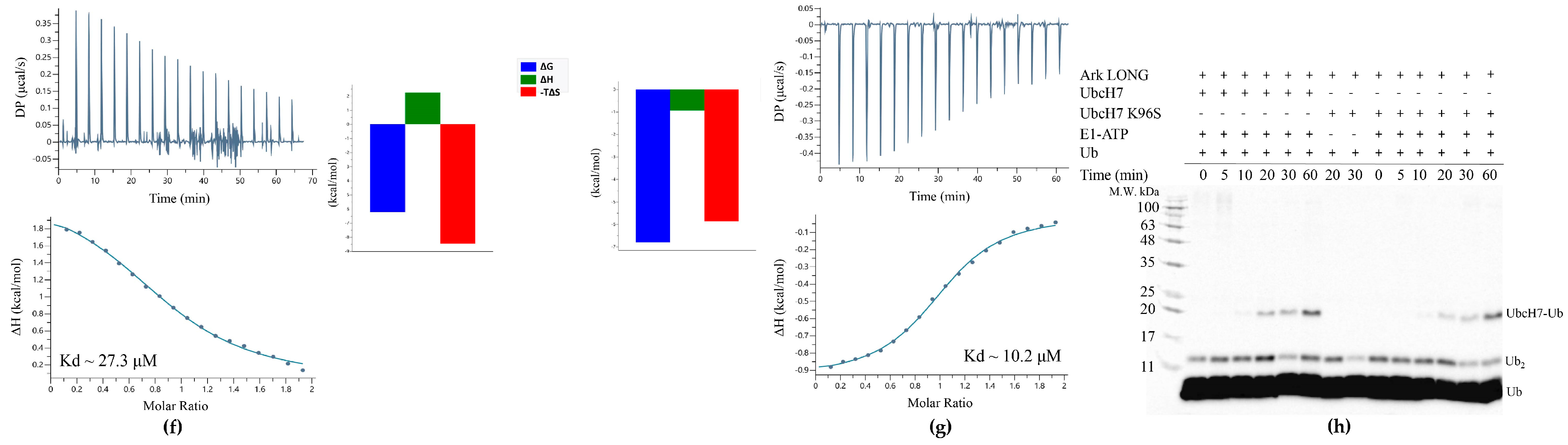
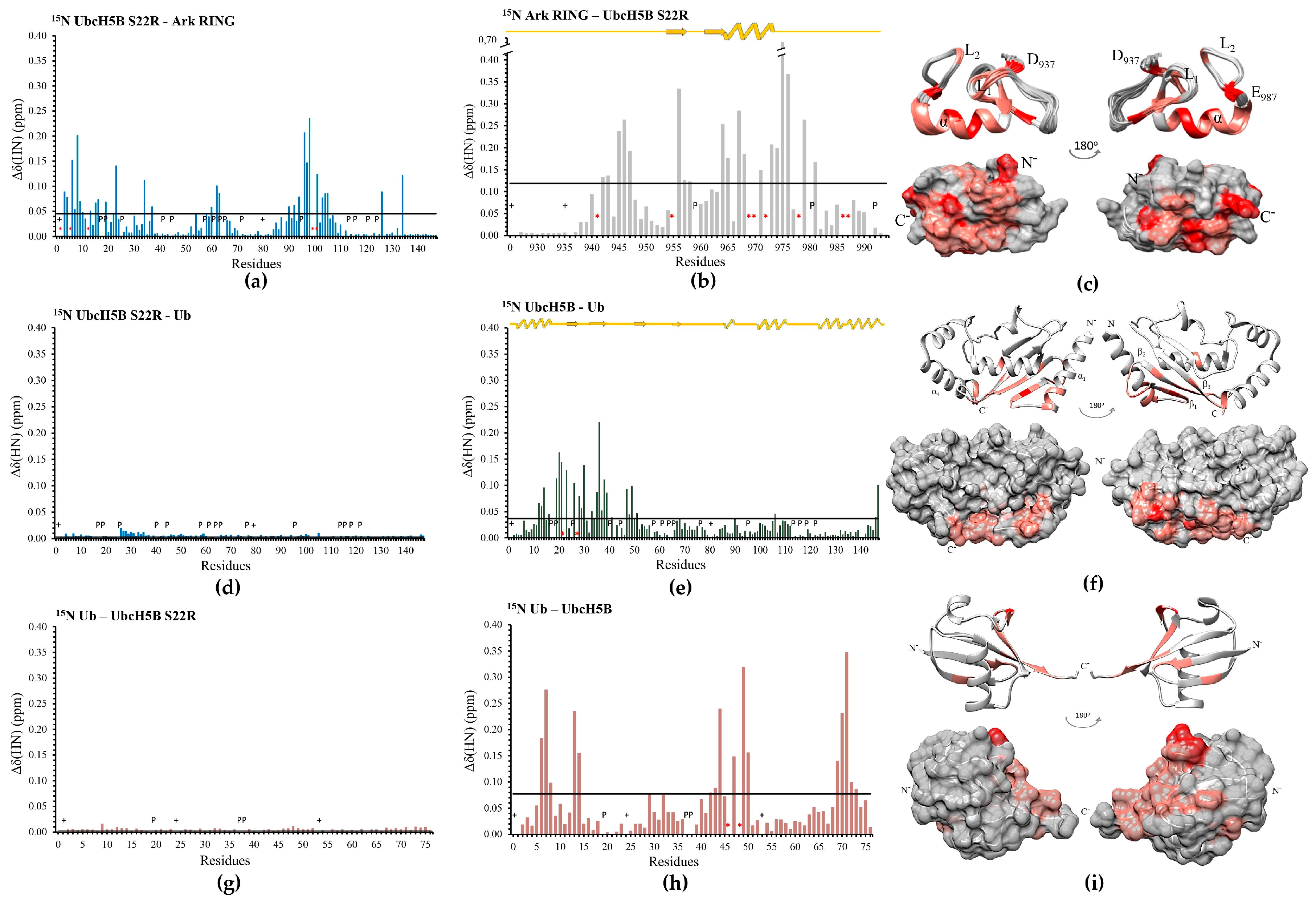


| Protein | Titrant | Kd (μM) | N | ΔG (Kcal/mol) | ΔH (Kcal/mol) | −TΔS (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ark RING | UbcH5B | 32 ± 2 | 1 | −6.1 | 3.1 | −9.3 |
| Ark LONG | UbcH5B | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 0.6 | −7.6 | −4.7 | −2.9 |
| Ark LONG R983A | UbcH5B | 8.4 ± 0.4 | 0.7 | −6.9 | −5.8 | −1.1 |
| Ark LONG R983K | UbcH5B | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 0.5 | −7.2 | −3.6 | −3.6 |
| Ark RING | UbcH5B F62A | 130 ± 17 | ND | −5.3 | 3.6 | −8.9 |
| Ark LONG | UbcH5B F62A | 194 ± 24 | ND | −5.0 | 2.9 | −7.9 |
| Ark RING | UbcH7 | 27.3 ± 2 | 0.9 | −6.2 | 2.2 | −8.4 |
| Ark LONG | UbcH7 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 0.7 | −7.3 | −0.7 | −6.5 |
| Ark RING | UbcH7 K96S | 10.2 ± 0.6 | 1 | −6.8 | −0.9 | −5.8 |
| Ark RING | UbcH13 | 264 ± 46 | 1.1 | −4.8 | 3.4 | −8.3 |
| Ark LONG | UbcH13 | 51.9 ± 5 | 0.9 | −5.8 | −2.3 | −3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delegkou, G.N.; Birkou, M.; Fragkaki, N.; Toro, T.; Marousis, K.D.; Episkopou, V.; Spyroulias, G.A. E2 Partner Tunes the Ubiquitylation Specificity of Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. Cancers 2023, 15, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041040
Delegkou GN, Birkou M, Fragkaki N, Toro T, Marousis KD, Episkopou V, Spyroulias GA. E2 Partner Tunes the Ubiquitylation Specificity of Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041040
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelegkou, Georgia N., Maria Birkou, Nefeli Fragkaki, Tamara Toro, Konstantinos D. Marousis, Vasso Episkopou, and Georgios A. Spyroulias. 2023. "E2 Partner Tunes the Ubiquitylation Specificity of Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041040
APA StyleDelegkou, G. N., Birkou, M., Fragkaki, N., Toro, T., Marousis, K. D., Episkopou, V., & Spyroulias, G. A. (2023). E2 Partner Tunes the Ubiquitylation Specificity of Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. Cancers, 15(4), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041040








