High-Pressure Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses via Needle-Free Injection Preserves Therapeutic Activity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
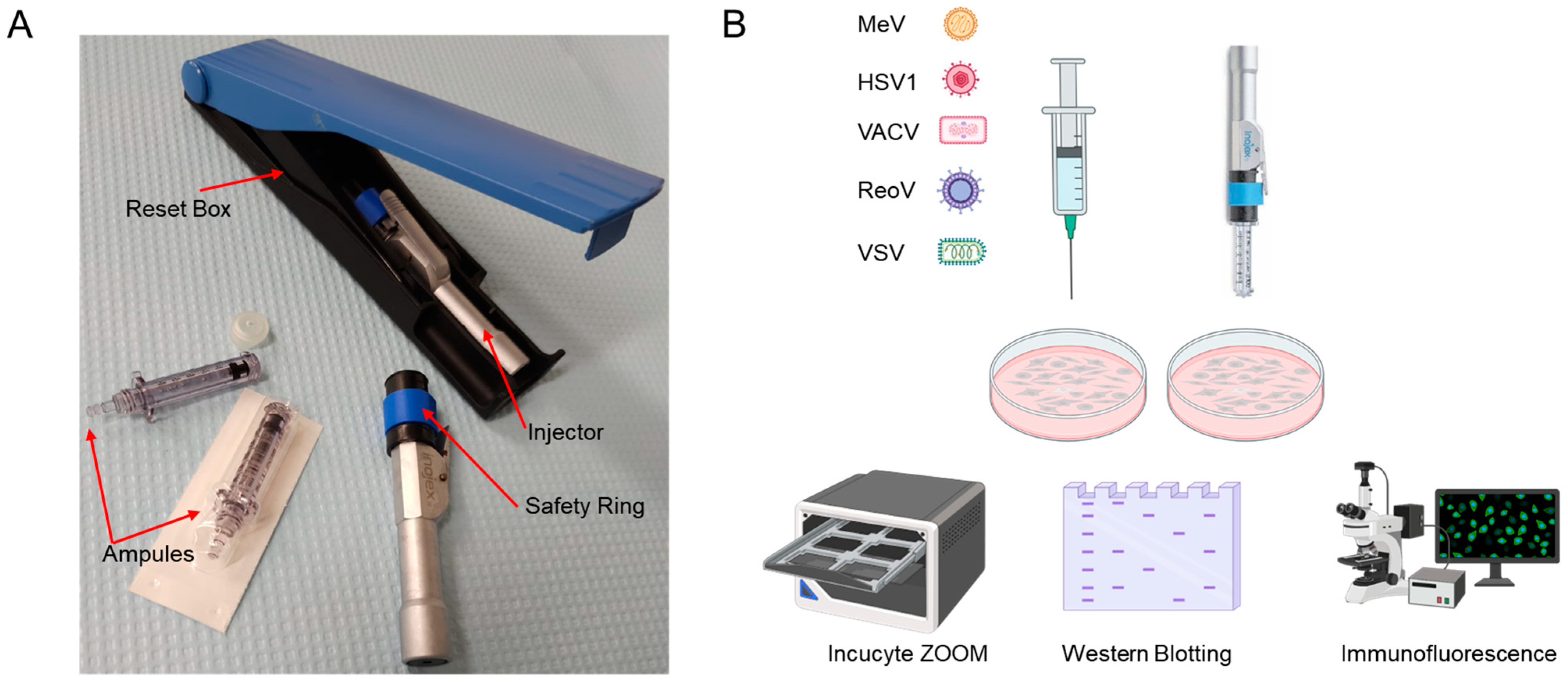
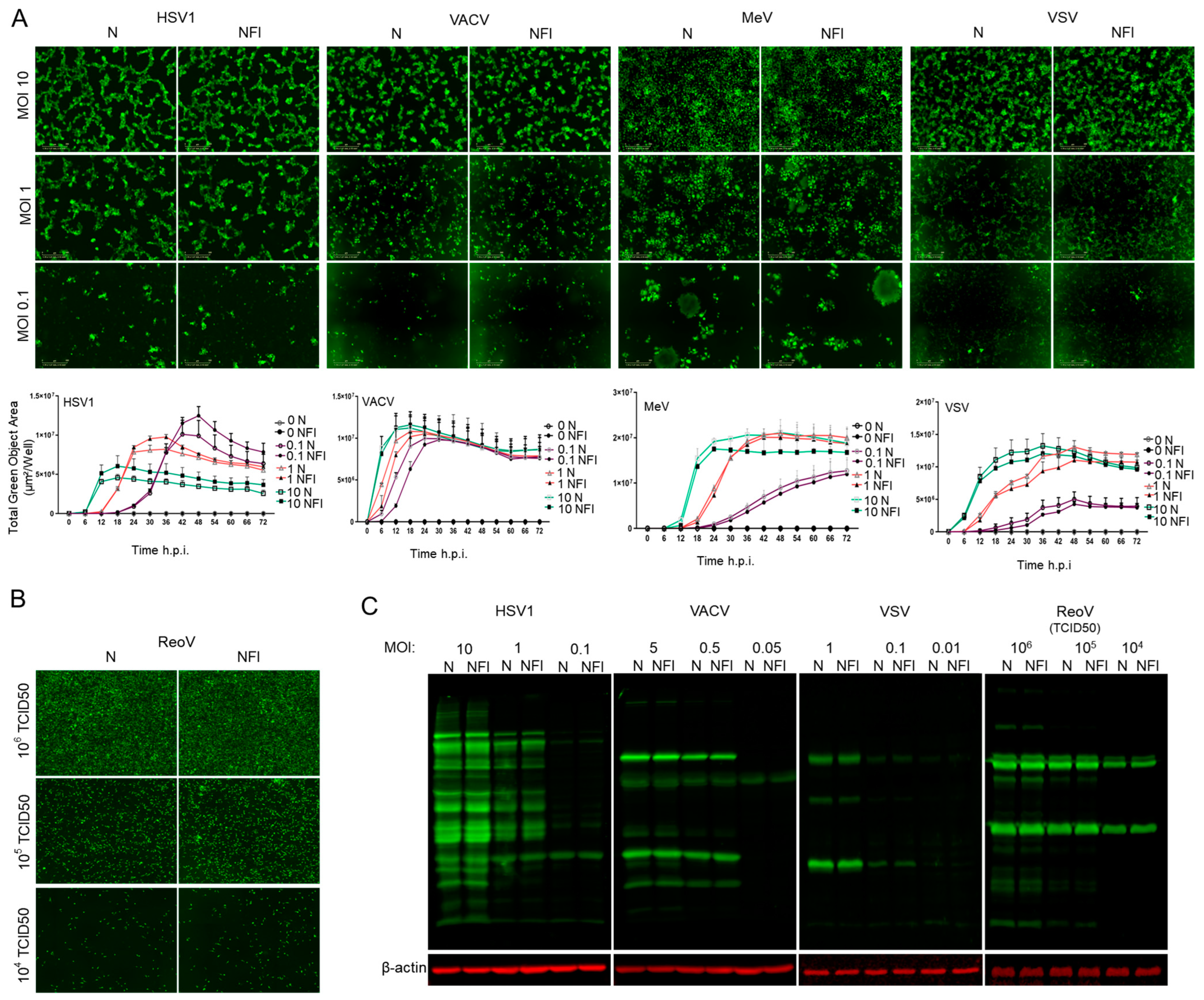
2.1. Cell Culture and Viruses
2.2. Western Blotting
2.3. First Generation Needle-Free Device
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Bromophenol Blue Injection and Detection Experiment
2.6. Live Cell Monitoring of Virus Infection
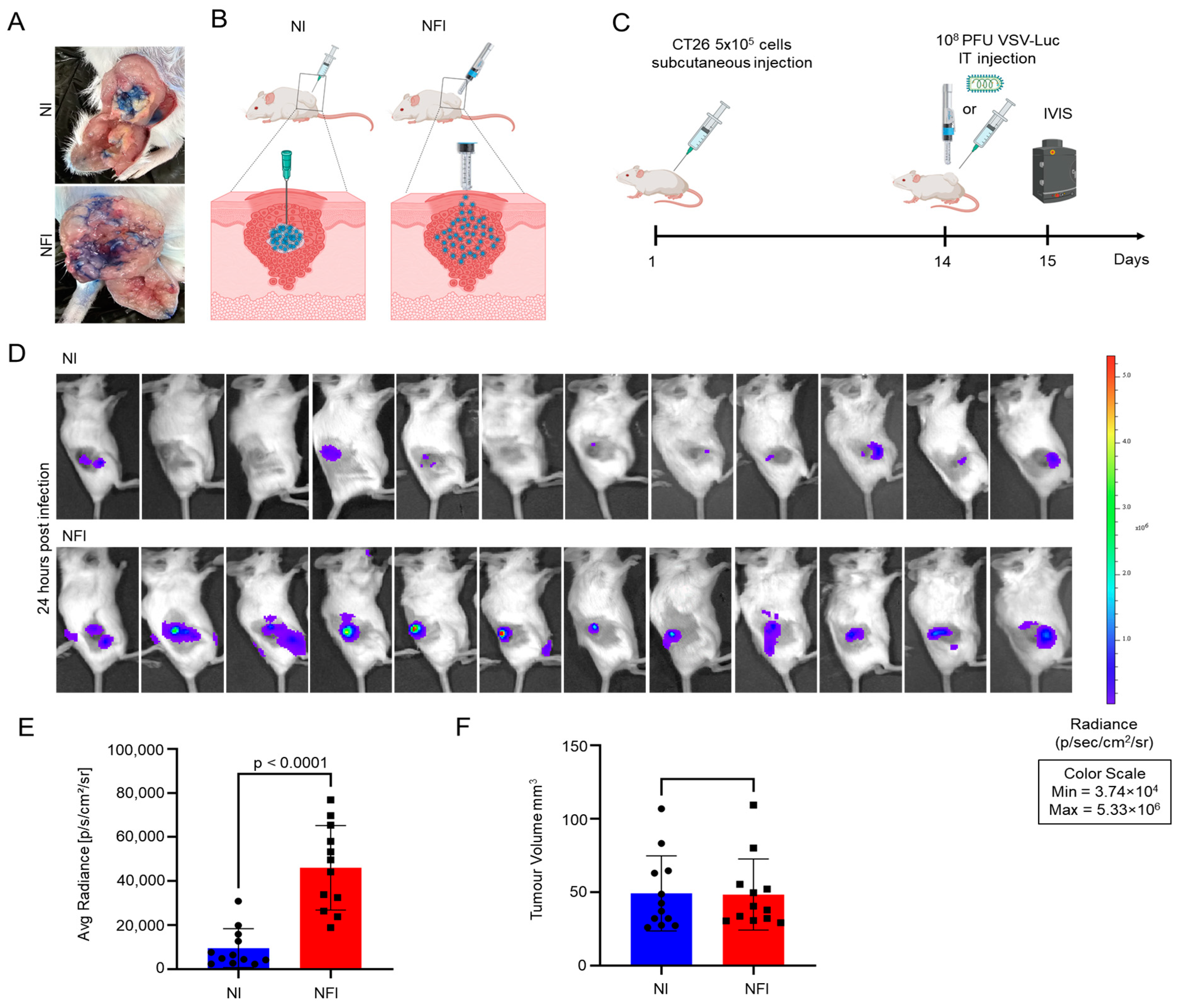
2.7. CT26 Subcutaneous Tumour Model for In Vivo Imaging System (IVIS)
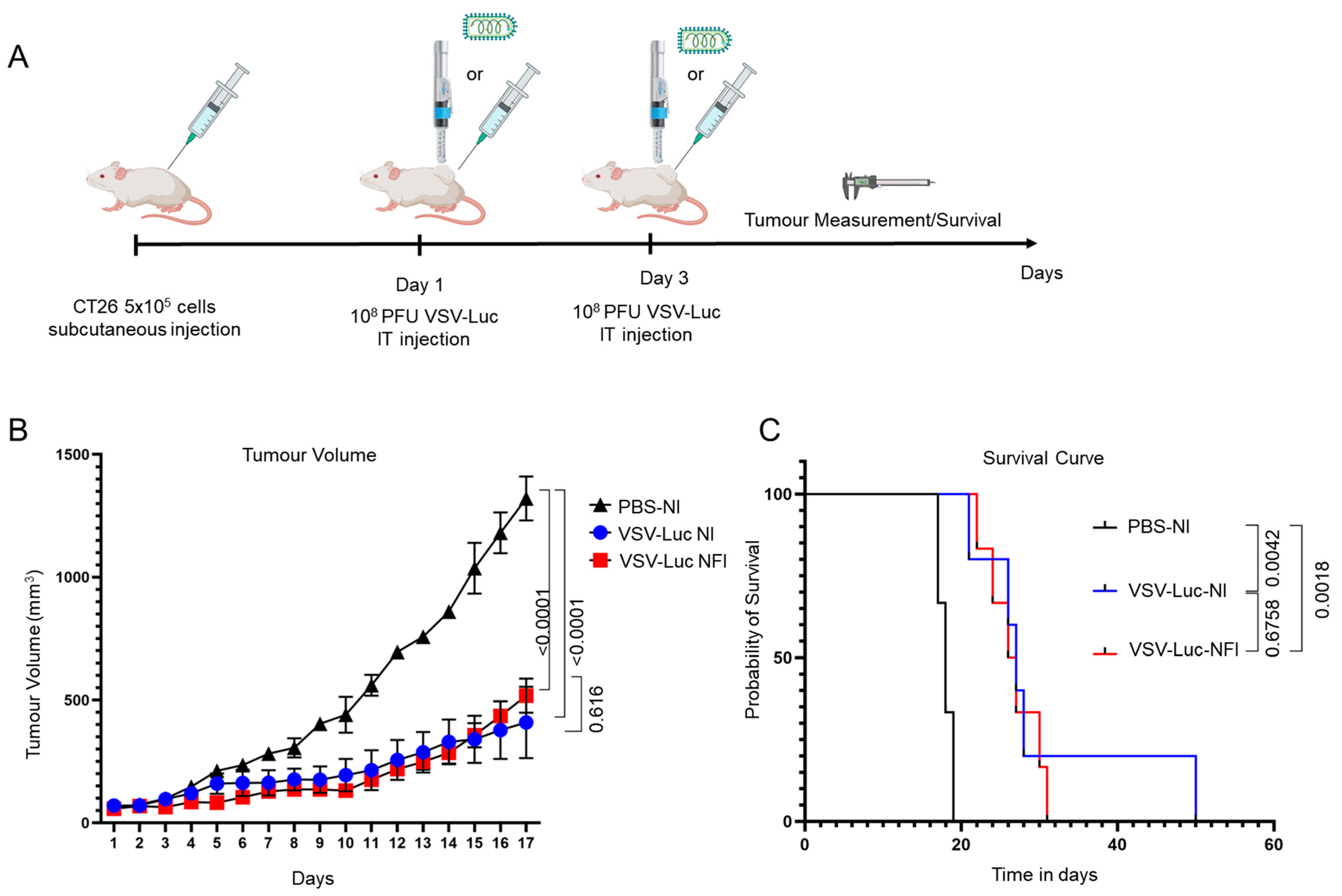
2.8. CT26 Subcutaneous Tumour Model
3. Results
3.1. High-Pressure Needle-Free Injection Does Not Affect Stability and Replication Competence of RNA and DNA OVs
3.2. Intratumoural Delivery and Spread of VSVΔ51-Luc via Needle-Free Jet Injector
3.3. Therapeutic Efficacy of VSVΔ51-Luc Administered via Needle-Free Jet Injector
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.K.; Doley, J.; Kumar, G.R.; Sahoo, A.P.; Tiwari, A.K. Oncolytic Viruses & Their Specific Targeting to Tumour Cells. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 136, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marelli, G.; Howells, A.; Lemoine, N.R.; Wang, Y. Oncolytic Viral Therapy and the Immune System: A Double-Edged Sword Against Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos de Matos, A.; Franco, L.S.; McFadden, G. Oncolytic Viruses and the Immune System: The Dynamic Duo. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichty, B.D.; Breitbach, C.J.; Stojdl, D.F.; Bell, J.C. Going Viral with Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Huang, J.; Tong, A.; Yang, H. Oncolytic Viruses for Cancer Therapy: Barriers and Recent Advances. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 15, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.; Han, D.; Tang, B.; Ma, J. Delivery and Biosafety of Oncolytic Virotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Q.; Shen, Y. The Dilemma of HSV-1 Oncolytic Virus Delivery: The Method Choice and Hurdles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, I.; van Rensburg, R.; Lieber, A. Overcoming Physical Barriers in Cancer Therapy. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e23647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradel, N.H.; Baker, A.T.; Arashkia, A.; Ebrahimi, N.; Ghorghanlu, S.; Negahdari, B. Oncolytic Virotherapy: Challenges and Solutions. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2021, 45, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vähä-Koskela, M.; Hinkkanen, A. Tumor Restrictions to Oncolytic Virus. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeh, H.J.; Downs-Canner, S.; McCart, J.A.; Guo, Z.S.; Rao, U.N.M.; Ramalingam, L.; Thorne, S.H.; Jones, H.L.; Kalinski, P.; Wieckowski, E.; et al. First-in-Man Study of Western Reserve Strain Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus: Safety, Systemic Spread, and Antitumor Activity. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaguti, P.; Melloni, E.; Cavalletti, E. Acute Intravenous Toxicity of Dimethyl Sulfoxide, Polyethylene Glycol 400, Dimethylformamide, Absolute Ethanol, and Benzyl Alcohol in Inbred Mouse Strains. Arzneimittelforschung 1994, 44, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eto, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Mukai, Y.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Development of PEGylated Adenovirus Vector with Targeting Ligand. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristi, F.; Gutiérrez, T.; Hitt, M.M.; Shmulevitz, M. Genetic Modifications That Expand Oncolytic Virus Potency. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 831091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedan, S.; Rojas, J.J.; Gros, A.; Mercade, E.; Cascallo, M.; Alemany, R. Hyaluronidase Expression by an Oncolytic Adenovirus Enhances Its Intratumoral Spread and Suppresses Tumor Growth. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva, N.; Yu, L.; Viapiano, M.; Cripe, T.P.; Chiocca, E.A.; Glorioso, J.C.; Kaur, B. Chondroitinase ABC I-Mediated Enhancement of Oncolytic Virus Spread and Antitumor Efficacy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, T.D.; Grandi, P.; Mok, W.; Alexandrakis, G.; Insin, N.; Zimmer, J.P.; Bawendi, M.G.; Boucher, Y.; Breakefield, X.O.; Jain, R.K. Degradation of Fibrillar Collagen in a Human Melanoma Xenograft Improves the Efficacy of an Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Vector. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2509–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, A.D.; Sadhna, D.; Nagpaal, D.; Chawla, L. Needle Free Injection Technology: A Complete Insight. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Long, L.; Peng, J.; Cao, Y.; Mao, J.Z.; Qi, X.; Xin, Q.; San, G.; et al. A Highly Efficient Needle-Free-Injection Delivery System for mRNA-LNP Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Nano Today 2023, 48, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Cores, J.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Dinh, P.-U.; Cheng, K. Needle-Free Injection of Exosomes Derived from Human Dermal Fibroblast Spheroids Ameliorates Skin Photoaging. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11273–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, E.L.; Campbell, J.D. Needle-Free Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Chapman, R.; Hooper, J.W.; Elma, K.; Zehrung, D.; Brennan, M.B.; Spiegel, E.K. Improved DNA Vaccine Delivery with Needle-Free Injection Systems. Vaccines 2023, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, J.-S.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Le Boeuf, F.; Bell, J. Propagation, Purification, and in Vivo Testing of Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Strains. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 797, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.V.T.; Schapendonk, C.M.E.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; de Swart, R.L.; Cotten, M. Complete Genome Sequences of Six Measles Virus Strains. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00184-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudier, M.; Gaudin, Y.; Knossow, M. Crystal Structure of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Matrix Protein. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Reuven, N.; Mohni, K.N.; Schumacher, A.J.; Weller, S.K. Structure of the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Genome: Manipulation of Nicks and Gaps Can Abrogate Infectivity and Alter the Cellular DNA Damage Response. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10146–10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkin, A.J.; McPherson, A.; Gershon, P.D. Structure of Intracellular Mature Vaccinia Virus Visualized by In Situ Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6332–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimzi, M.A.; Ham, Y.-B. A Needle-Free Jet Injection System for Controlled Release and Repeated Biopharmaceutical Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.D.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, K.; Jain, M.; Patil, D.R.; Maithal, K.; Mathapati, B.; Giri, S.; Mohandas, S.; Shete, A.; et al. Needle-Free Injection System Delivery of ZyCoV-D DNA Vaccine Demonstrated Improved Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy in Rhesus Macaques against SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, M.R.; Thanarajasingam, U.; Vile, R.G.; Gough, M.J. Intratumoral Immunotherapy: Using the Tumour against Itself. Immunology 2005, 114, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ramachandran, M.; Jin, C.; Quijano-Rubio, C.; Martikainen, M.; Yu, D.; Essand, M. Characterization of Virus-Mediated Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death and the Consequences for Oncolytic Virus-Based Immunotherapy of Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labani-Motlagh, A.; Ashja-Mahdavi, M.; Loskog, A. The Tumor Microenvironment: A Milieu Hindering and Obstructing Antitumor Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabelle, A.; Tselikas, L.; de Baere, T.; Houot, R. Intratumoral Immunotherapy: Using the Tumor as the Remedy. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, xii33–xii43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Orama, S.; Sheth, R.A. The Contemporary Landscape and Future Directions of Intratumoral Immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Precis. Oncol. 2023, 6, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor Microenvironment Complexity and Therapeutic Implications at a Glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, N.M.; Williams, M.; Dixon, K.; Dupuis, C.; McWatters, A.; Avritscher, R.; Manrique, S.Z.; McHugh, K.; Murthy, R.; Tam, A.; et al. Influence of Injection Technique, Drug Formulation and Tumor Microenvironment on Intratumoral Immunotherapy Delivery and Efficacy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, R.A.; Murthy, R.; Hong, D.S.; Patel, S.; Overman, M.J.; Diab, A.; Hwu, P.; Tam, A. Assessment of Image-Guided Intratumoral Delivery of Immunotherapeutics in Patients with Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e207911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheendra, D.; Léger, R.; Groppo, E.R.; Sun, D.; Durrani, A.K.; Neeman, Z.; Wood, B.J. Comparison of Three Different Needles for Percutaneous Injections. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2007, 30, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amalou, H.; Wood, B.J. Intratumoral Gene Therapy Injections with a Multi-Pronged, Multi-Side Hole Needle for Rectal Carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 561–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, L.; Hu, L.; Wang, J. Needle-Free Jet Injectors’ Geometry Design and Drug Diffusion Process Analysis. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2021, 2021, 5199278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.M.; Stockwell, K.D.; Morrison, J.B.; Mann, D.D. Effect of Injection Pressure and Fluid Volume and Density on the Jet Dispersion Pattern of Needle-Free Injection Devices. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 138, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Said, A.; Hoang, H.-D.; Earl, N.; Xiang, X.; Siddiqui, N.; Côté, M.; Alain, T. High-Pressure Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses via Needle-Free Injection Preserves Therapeutic Activity. Cancers 2023, 15, 5655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235655
Said A, Hoang H-D, Earl N, Xiang X, Siddiqui N, Côté M, Alain T. High-Pressure Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses via Needle-Free Injection Preserves Therapeutic Activity. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235655
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaid, Aida, Huy-Dung Hoang, Nathalie Earl, Xiao Xiang, Nadeem Siddiqui, Marceline Côté, and Tommy Alain. 2023. "High-Pressure Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses via Needle-Free Injection Preserves Therapeutic Activity" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235655
APA StyleSaid, A., Hoang, H.-D., Earl, N., Xiang, X., Siddiqui, N., Côté, M., & Alain, T. (2023). High-Pressure Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses via Needle-Free Injection Preserves Therapeutic Activity. Cancers, 15(23), 5655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235655







