Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Number of Metastases: How Many Are Too Many?
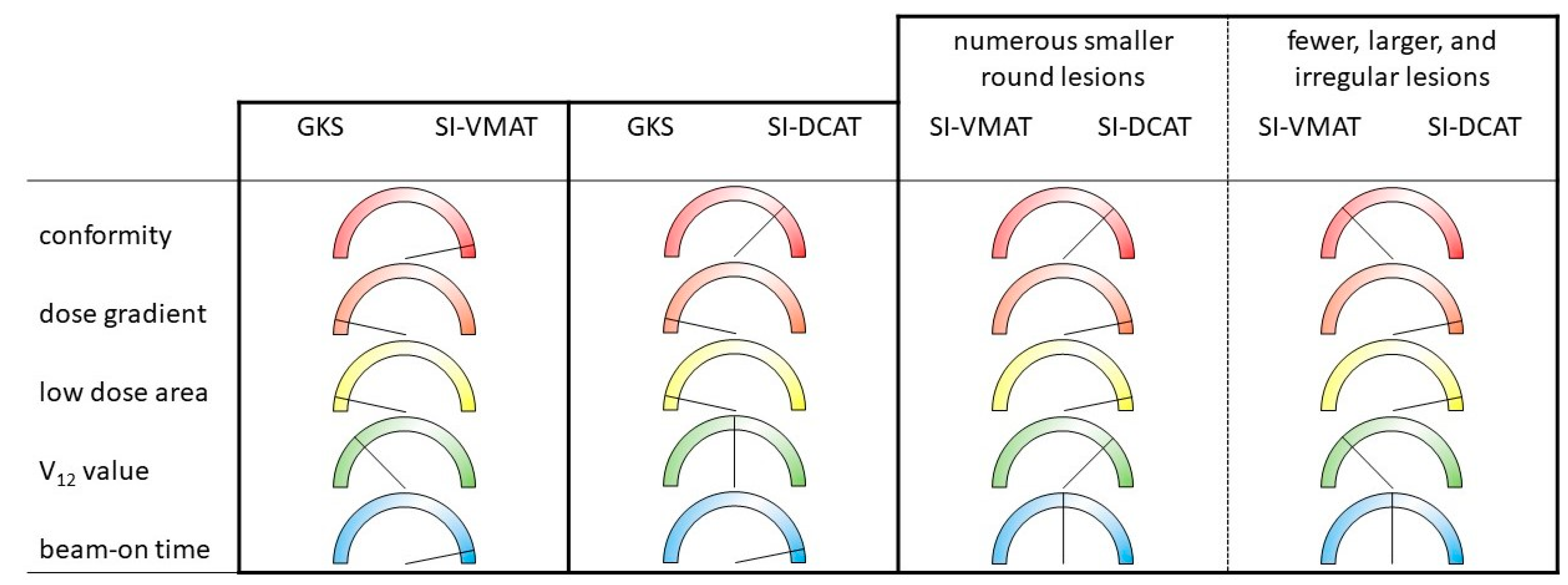
3. Planning Quality Indicators
4. Image Guidance in Single-Isocenter Techniques
5. Technical Approaches and Different Technological Solutions
| Study | Details | Gamma Knife | SI-VMAT | SI-DCAT | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [59] | 6 patients, 19 lesions. Median 3 (3–4)/patient. Median total PTV 3.6 cc (1.2–11.1). Median PTV 0.5 (1.1–10.5). GTV to PTV margin not known. | Mean CI (target) | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| Mean GI (target) | 3.7 ± 1.0 | 4.8 ± 1.5 | <0.01 | |||
| Mean V12 (cc) (target) | 3.1 ± 2.2 | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 0.58 | |||
| Mean V12 (cc) (total) | 10.9 ± 7.2 | 9.7 ± 5.1 | 0.63 | |||
| Mean V6 (cc) | 36.9 ± 16.9 | 36.3 ± 14.7 | 0.96 | |||
| Mean V4.5 (cc) | 86.7 ± 29.8 | 99 ± 27.3 | 0.15 | |||
| Mean V3 (cc) | 160.8 ± 55.7 | 224 ± 53 | 0.1 | |||
| Mean beam-on time (min) | 71.6 ± 15.9 | 6.4 ± 0.8 | <0.01 | |||
| Thomas et al. [48] | 28 patients, 113 lesions. Median 3 (2–9)/patient. Median total PTV 3.7 cc (0.2–19.6). Median PTV 0.1 cc (0.003–15.0). GTV to PTV margin not known. | Median CI (total) | 1.7 (1.3–7.4) | 1.1 (1.0–1.7) | <0.0001 | |
| Median PI (total) | 0.6 (0.3–0.8) | 0.9 (0.6–0.9) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median CI (target) | 1.9 (1.2–6.1) | 1.3 (1.0–4.3) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median PI (target) | 0.5 (0.2–0.8) | 0.8 (0.2–1.0) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median beam-on time (min) | 45.1 (17.5–121.3) | |||||
| Potrebko et al. [24] | 12 patients, 103 lesions. Median 8 (7–14)/patient. Mean GTV 1.16 cc (0.01–19.9). Prescription dose 15–21 Gy. GTV to PTV margin 0 mm. | Mean CI (target) | 2.5 ± 1.6 | 1.6 ± 0.8 (6 MV) 1.7 ± 0.9 (10 MV) | <0.001 (6 MV) <0.001 (10 MV) | |
| Mean V12 (cc) (total) | 24 ± 21 | 25 ± 17 (6 MV) 26 ± 18 (10 MV) | 0.835 (6 MV) 0.705 (10 MV) | |||
| Mean V12 (cc) (target) | 2.8 ± 6.1 | 3.0 ± 5.2 (6 MV) 3.1 ± 5.4 (10 MV) | 0.003 (6 MV) <0.001 (10 MV) | |||
| Mean V6 (cc) (total) | 81.1 ± 72.9 | 143.7 ± 81.1 (6 MV) 167.5 ± 87.5 (10 MV) | 0.09 (6 MV) 0.01 (10 MV) | |||
| Mean V3 (cc) (total) | 323.0 ± 294.8 | 880.1 ± 369.1 (6 MV) 937.9 ± 361.9 (10 MV) | 0.005 (6 MV) 0.001 (10 MV) | |||
| Median beam-on time (min) | 147.6 ± 49.3 | 10.8 ± 2.1 (6 MV) 6.4 ± 1.2 (10 MV) | 0.01 (6 MV) <0.001 (10 MV) | |||
| Chea et al. [21] | 20 patients, 95 lesions. 3–9/patient. Median GTV 0.3 cc (0.02–9.6). Prescription dose 20 Gy. GTV to PTV margin 0 mm. | Mean PI (target) | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.07 | |
| Mean GI (target) | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | <0.001 | |||
| Mean V12 (cc) (target) | 1.7 ± 2.3 | 1.9 ± 2.6 | 0.013 | |||
| Mean beam-on time (min) | 169 ± 48 | 94 ± 26 | <0.001 | |||
| Raza et al. [22] | 36 patients, 367 lesions. Median 9 (2–25)/patient. Median total GTV 1.33 cc (0.2–4.7). Median GTV 0.16 cc (0.1–2.1). Median total PTV 3.4 cc (0.6–9.4). Median PTV 0.37 (0.2–1.2). Median prescription dose 20 Gy (18–20). GTV to PTV margin 1 mm. | Median PI (target) | 0.6 (0.5–0.9) | 0.8 (0.5–0.9) | 0.005 | |
| Median GI (target) | 5.6 (3.6–8.4) | 4.5 (3.5–7.1) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V12 (cc) (total) | 18.5 (2.2–62.3) | 13.6 (1.9–45.9) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V12 (cc) (total) (1–10 lesions) | 8.2 (2.2–26.4) | 6.2 (1.87–18.1) | 0.001 | |||
| Median V12 (cc) (total) (10–25 lesions) | 38.7 (21.9–62.3) | 22.7 (12.2–45.9) | 0.001 | |||
| Median V10 (cc) (total) | 27.9 (2.9–100.6) | 17.4 (2.6–74.2) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V8 (cc) (total) | 46 (4.6–184) | 26.6 (3.7–157) | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V5 (cc) (total) | 142.3 (11.3–707.8) | 73.2 (8.18–701.8) | <0.0001 | |||
| Hofmaier et al. [61] | 20 patients, 66 lesions. Median 3 (2–6). Median PTV 0.8 cc (0.1–11.9). Prescription dose 15–20 Gy. GTV to PTV margin 1 mm. | Median PI (target) | 0.73 (0.38–0.88) | 0.75 (0.58–0.89) | <0.05 | |
| Median GI (target) | 7.17 (3.35–33.0) | 5.99 (3.5–15.73) | <0.05 | |||
| Median V12 (cc) (target) | 3.1 (0.5–13.9) | 2.1 (0.1–13.1) | <0.05 | |||
| Median V10 (cc) (target) | 4.9 (1.0–19.9) | 3.2 (0.4–19.3) | <0.05 | |||
| Median V8 (cc) (total) | 26.6 (10.6–86.4) | 17.4 (6.3–52.6) | <0.05 | |||
| Median V5 (cc) (total) | 69.1 (26.0–273.6) | 33.7 (13.0–120.5) | <0.05 | |||
| Median V4 (cc) (total) | 123.1 (37.5–418.6) | 45.6 (18.5–215.9) | <0.05 | |||
| Gevaert et al. [23] | 10 patients, 40 lesions. Median 3 (1–8)/patient. Mean GTV 3.15 cc (0.1–24.6). Mean total PTV 10.60 (0.6–28.7). Prescription dose 20 Gy. GTV to PTV margin ≤ 1 mm (variable). | Mean PI (target) | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | ||
| Mean GI (target) | 7.1 ± 3.1 | 3.9 ± 1.4 | <0.05 | |||
| Mean V12 (cc) (total) | 46.3 ± 35.9 | 36.3 ± 27.1 | <0.05 | |||
| Mean V10 (cc) (total) | 67.9 ± 55.9 | 48.5 ± 35.9 | <0.05 | |||
| Mean V5 (cc) (total) | 266.7 ± 216.7 | 161.6 ± 143.6 | ||||
| Liu et al. [62] | 30 patients, 217 lesions. 7.5 (4–10)/patient. Median total PTV 7.1 cc. Median PTV 0.4 cc. Median prescription dose 18 Gy (14–24). GTV to PTV margin ≤ 1 mm (variable). | Median CI (target) | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 | |
| Median PI (target) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V12 (cc) (total) | 19.2 | 23.7 | <0.0001 | |||
| Median V8 (cc) (total) | 44.1 | 53.6 | 0.024 | |||
| Median V5 (cc) (total) | 142.8 | 141.4 | 0.009 | |||
| Dmean (Gy) | 2.8 | 2.6 | <0.0001 | |||
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, T.; Kiecker, F.; Schaefer, S.; Stege, H.; Kaehler, K.; Terheyden, P.; Gesierich, A.; Gutzmer, R.; Haferkamp, S.; Uttikal, J.; et al. Combined immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab with and without local therapy in patients with melanoma brain metastasis: A DeCOG* study in 380 patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurich, S.; Rothschild, S.I.; Hoffmann, M.; Fabri, M.; Sommer, A.; Garcia-Marquez, M.; Thelen, M.; Schill, C.; Merki, R.; Schmid, T.; et al. Local Tumor Treatment in Combination with Systemic Ipilimumab Immunotherapy Prolongs Overall Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.; Wittig, A.; Piroth, M.D.; Treuer, H.; Seegenschmiedt, H.; Ruge, M.; Grosu, A.L.; Guckenberger, M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases. A report of the DEGRO Working Group on Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2014, 190, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Baumert, B.; Combs, S.E.; Kinhult, S.; Kros, J.M.; Marosi, C.; Metellus, P.; Radbruch, A.; Villa Freixa, S.S.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases from solid tumors: Guidelines from the European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO). Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodensohn, R.; Kaempfel, A.L.; Boulesteix, A.L.; Orzelek, A.M.; Corradini, S.; Fleischmann, D.F.; Forbrig, R.; Garny, S.; Hadi, I.; Hofmaier, J.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with 4–10 brain metastases: A nonrandomized controlled trial. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2023, 186, 109744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Guckenberger, M.; Smits, M.; Dummer, R.; Bachelot, T.; Sahm, F.; Galldiks, N.; de Azambuja, E.; Berghoff, A.S.; Metellus, P.; et al. EANO-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with brain metastasis from solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1332–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Hwang, S.K.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.; Hwang, J.H.; Hamm, I.S.; Park, Y.M. Gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases from lung cancer. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Lee, S.R.; Cho, J.M.; Yang, K.A.; Kim, S.H. Therapeutic effect of gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2011, 50, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Koh, E.J.; Choi, H.Y. Multiple gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple metachronous brain metastases associated with lung cancer: Survival time. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2012, 52, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. A Multi-institutional Prospective Observational Study of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients With Multiple Brain Metastases (JLGK0901 Study Update): Irradiation-related Complications and Long-term Maintenance of Mini-Mental State Examination Scores. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Kasuya, H.; Barfod, B.E. A Cohort Study of Stereotactic Radiosurgery Results for Patients With 5 to 15 Versus 2 to 4 Brain Metastatic Tumors. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Kasuya, H. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Results for Patients with 5–10 versus 11–20 Brain Metastases: A Retrospective Cohort Study Combining 2 Databases Totaling 2319 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2021, 146, e479–e491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Capone, L.; Nardiello, B.; El Gawhary, R.; Raza, G.; Scaringi, C.; Bianciardi, F.; Gentile, P.; Paolini, S. Neurological outcome and memory performance in patients with 10 or more brain metastases treated with frameless linear accelerator (LINAC)-based stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 148, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limon, D.; McSherry, F.; Herndon, J.; Sampson, J.; Fecci, P.; Adamson, J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, F.F.; Floyd, S.; Kirkpatrick, J.; et al. Single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 2, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routman, D.M.; Bian, S.X.; Diao, K.; Liu, J.L.; Yu, C.; Ye, J.; Zada, G.; Chang, E.L. The growing importance of lesion volume as a prognostic factor in patients with multiple brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodensohn, R.; Kaempfel, A.L.; Fleischmann, D.F.; Hadi, I.; Hofmaier, J.; Garny, S.; Reiner, M.; Forbrig, R.; Corradini, S.; Thon, N.; et al. Simultaneous stereotactic radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases using single-isocenter dynamic conformal arc therapy: A prospective monocentric registry trial. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2021, 197, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, M.; Fezzani, K.; Jacob, J.; Cuttat, M.; Croisé, M.; Simon, J.M.; Feuvret, L.; Valery, C.A.; Maingon, P.; Benadjaoud, M.A.; et al. Dosimetric study between a single isocenter dynamic conformal arc therapy technique and Gamma Knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases treatment: Impact of target volume geometrical characteristics. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, G.H.; Capone, L.; Tini, P.; Giraffa, M.; Gentile, P.; Minniti, G. Single-isocenter multiple-target stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: Dosimetric evaluation of two automated treatment planning systems. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, T.; Steenbeke, F.; Pellegri, L.; Engels, B.; Christian, N.; Hoornaert, M.T.; Verellen, D.; Mitine, C.; De Ridder, M. Evaluation of a dedicated brain metastases treatment planning optimization for radiosurgery: A new treatment paradigm? Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrebko, P.S.; Keller, A.; All, S.; Sejpal, S.; Pepe, J.; Saigal, K.; Kandula, S.; Sensakovic, W.F.; Shridhar, R.; Poleszczuk, J.; et al. GammaKnife versus VMAT radiosurgery plan quality for many brain metastases. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, C.Y.; Sneed, P.K.; Shu, H.K.; Lamborn, K.R.; McDermott, M.W.; Chang, S.; Nowak, P.; Petti, P.L.; Smith, V.; Verhey, L.J.; et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: Relationship of dose and pattern of enhancement to local control. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahgal, A.; Barani, I.J.; Novotny, J., Jr.; Zhang, B.; Petti, P.; Larson, D.A.; Ma, L. Prescription dose guideline based on physical criterion for multiple metastatic brain tumors treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Kline, R.; Gillin, M.; Souhami, L.; Hirschfeld, A.; Dinapoli, R.; Martin, L. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: Radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1993, 27, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddick, I. A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddick, I.; Lippitz, B. A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonigen, B.J.; Steinmetz, R.D.; Levin, L.; Lamba, M.A.; Warnick, R.E.; Breneman, J.C. Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupattelli, M.; Alì, E.; Ingrosso, G.; Saldi, S.; Fulcheri, C.; Borghesi, S.; Tarducci, R.; Aristei, C. Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases: Imaging Tools and Dosimetric Predictive Factors for Radionecrosis. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Scaringi, C.; Clarke, E.; Valeriani, M.; Osti, M.; Enrici, R.M. Frameless linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brain metastases: Analysis of patient repositioning using a mask fixation system and clinical outcomes. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, S.A.; Mancini, A.; Dal Col, A.H.; Asso, R.N.; Neves-Junior, W.F.P. Frameless Image-Guided Radiosurgery for Multiple Brain Metastasis Using VMAT: A Review and an Institutional Experience. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, J.; Chanyavanich, V.; Betzel, G.; Switchenko, J.; Dhabaan, A. Single-Isocenter Multiple-Target Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Risk of Compromised Coverage. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winey, B.; Bussiere, M. Geometric and dosimetric uncertainties in intracranial stereotatctic treatments for multiple nonisocentric lesions. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2014, 15, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhope, C.; Chang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yin, F.F.; Kim, G.; Salama, J.K.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Adamson, J. Physics considerations for single-isocenter, volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery for treatment of multiple intracranial targets. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, T.; Verellen, D.; Tournel, K.; Linthout, N.; Bral, S.; Engels, B.; Collen, C.; Depuydt, T.; Duchateau, M.; Reynders, T.; et al. Setup accuracy of the Novalis ExacTrac 6DOF system for frameless radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.U.Y.; Cheung, M.L.M.; Kan, M.W.K.; Chan, A.T.C. Shift detection discrepancy between ExacTrac Dynamic system and cone-beam computed tomography. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Mendes, V.; Reiner, M.; Huang, L.; Reitz, D.; Straub, K.; Corradini, S.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; Kurz, C.; Landry, G.; et al. ExacTrac Dynamic workflow evaluation: Combined surface optical/thermal imaging and X-ray positioning. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzell, G.A. The spatial accuracy of two frameless, linear accelerator-based systems for single-isocenter, multitarget cranial radiosurgery. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2017, 18, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrett, B.; Ukath, J.; Horgan, E.; Noble, C.; Ramachandran, P. A Framework for ExacTrac Dynamic Commissioning for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. J. Med. Phys. 2022, 47, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinnen, A.C.C.; Öllers, M.C.; Loon Ong, C.; Verhaegen, F. The potential of an optical surface tracking system in non-coplanar single isocenter treatments of multiple brain metastases. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangesius, J.; Seppi, T.; Weigel, R.; Arnold, C.R.; Vasiljevic, D.; Goebel, G.; Lukas, P.; Ganswindt, U.; Nevinny-Stickel, M. Intrafractional 6D head movement increases with time of mask fixation during stereotactic intracranial RT-sessions. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksell, L. Stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1983, 46, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leksell, L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir. Scand. 1951, 102, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.R.; Kundu, P.; Levin-Epstein, R.; Chang, E.M.; Agazaryan, N.; Hegde, J.V.; Steinberg, M.L.; Tenn, S.E.; Kaprealian, T.B. Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing Comparison of Stereotactic Radiosurgery to Multiple Brain Lesions Using Single-Isocenter Versus Multiple-Isocenter Technique. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.M.; Popple, R.A.; Wu, X.; Clark, G.M.; Markert, J.M.; Guthrie, B.L.; Yuan, Y.; Dobelbower, M.C.; Spencer, S.A.; Fiveash, J.B. Comparison of plan quality and delivery time between volumetric arc therapy (RapidArc) and Gamma Knife radiosurgery for multiple cranial metastases. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 409–417, discussion 417–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, W.; Winston, K.R.; Maleki, N. A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1988, 14, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, N.T.; Glenn, C.; Hughes, R.; Raval, R.; Chu, J.; DiCostanzo, D.; Bell, E.H.; Grecula, J.; Arnett, A.; Gondal, H.; et al. Linear accelerator-based radiosurgery is associated with lower incidence of radionecrosis compared with gamma knife for treatment of multiple brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 147, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalasova, I.; Liu, H.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Nie, K.; Shi, W.; Teo, B.K.; Yu, Y.; Yue, N.J.; et al. Multi-Institutional Dosimetric Evaluation of Modern Day Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) Treatment Options for Multiple Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Nichol, A.; Hossain, S.; Wang, B.; Petti, P.; Vellani, R.; Higby, C.; Ahmad, S.; Barani, I.; Shrieve, D.C.; et al. Variable dose interplay effects across radiosurgical apparatus in treating multiple brain metastases. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2014, 9, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Ren, L.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Wang, Z. SU-E-T-645: Treatment of Multiple Brain Metastases Using Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Single-Isocenter Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy: Comparison with Conventional Dynamic Conformal Arc and Static Beam Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chin, K.; Robbins, J.R.; Kim, J.; Li, H.; Amro, H.; Chetty, I.J.; Gordon, J.; Ryu, S. Radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases with single-isocenter dynamic conformal arcs (SIDCA). Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2014, 112, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kaneda, N.; Hagiwara, M.; Ishiguchi, T. Dosimetric Study of Automatic Brain Metastases Planning in Comparison with Conventional Multi-Isocenter Dynamic Conformal Arc Therapy and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Brain Metastases. Cureus 2016, 8, e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.M.; Popple, R.A.; Young, P.E.; Fiveash, J.B. Feasibility of single-isocenter volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery for treatment of multiple brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.; Ueda, Y.; Akino, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Masaoka, A.; Hirata, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Koizumi, M.; Teshima, T. HyperArc VMAT planning for single and multiple brain metastases stereotactic radiosurgery: A new treatment planning approach. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, B.K.; DiDomenico, J.D.; Barani, I.J.; Barranco, F.D. ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery System: A Preliminary Analysis of Clinical Applications within a Retrospective Case Series. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2022, 100, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Andrews, D.W.; Evans, J.J.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Yu, Y.; Dicker, A.P.; Shi, W. Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency for Radiosurgery to Multiple Brain Metastases: Non-Coplanar RapidArc vs. Gamma Knife. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, R.; Naccarato, S.; Mazzola, R.; Ricchetti, F.; Corradini, S.; Fiorentino, A.; Alongi, F. Linac-based VMAT radiosurgery for multiple brain lesions: Comparison between a conventional multi-isocenter approach and a new dedicated mono-isocenter technique. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmaier, J.; Bodensohn, R.; Garny, S.; Hadi, I.; Fleischmann, D.F.; Eder, M.; Dinc, Y.; Reiner, M.; Corradini, S.; Parodi, K.; et al. Single isocenter stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases: Dosimetric comparison of VMAT and a dedicated DCAT planning tool. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Thomas, E.M.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Andrews, D.; Markert, J.M.; Fiveash, J.B.; Shi, W.; Popple, R.A. Interinstitutional Plan Quality Assessment of 2 Linac-Based, Single-Isocenter, Multiple Metastasis Radiosurgery Techniques. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Schuler, J.; Takacs, I.; Peng, J.; Jenrette, J.; Vanek, K. Comparison of radiation dose spillage from the Gamma Knife Perfexion with that from volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery during treatment of multiple brain metastases in a single fraction. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemierko, A. Reporting and analyzing dose distributions: A concept of equivalent uniform dose. Med. Phys. 1997, 24, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyazi, M.; Niemierko, A.; Paganetti, H.; Söhn, M.; Schapira, E.; Goldberg, S.; Adams, J.; Kim, V.; Oh, K.S.; Hwang, W.L.; et al. Volumetric and actuarial analysis of brain necrosis in proton therapy using a novel mixture cure model. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 142, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Multiinstitutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer (JLGK0901 study-NSCLC). J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, Z.A.; Fogh, S.E.; Westcott, S.K.; Braunstein, S.; Larson, D.A.; Barani, I.J.; Nakamura, J.; Sneed, P.K. Interval From Imaging to Treatment Delivery in the Radiation Surgery Age: How Long Is Too Long? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, I.; Roengvoraphoj, O.; Bodensohn, R.; Hofmaier, J.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; Nachbichler, S.B. Stereotactic radiosurgery combined with targeted/ immunotherapy in patients with melanoma brain metastasis. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Chu, L.; Wang, S.; Tong, T.; Chu, X.; Yu, F.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, T.; et al. Overall survival benefit of osimertinib and clinical value of upfront cranial local therapy in untreated EGFR-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer with brain metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carron, R.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Amatore, F.; Padovani, L.; Malissen, N.; Balossier, A.; Loundou, A.; Bonnet, N.; Muracciole, X.; Régis, J.M.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery combined with anti-PD1 for the management of melanoma brain metastases: A retrospective study of safety and efficacy. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 135, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhaled, S.; Jullian, N.; Collen, C. Letter to the editor regarding the article “Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with 4–10 brain metastases: A non-randomized controlled trial” by Bodensohn et al. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2023; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Bodensohn, R.; Niyazi, M. Response to the letters to the editor of S. Benkhaled et al. and C.H. Rim regarding the article “Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with 4–10 brain metastases: A nonrandomized controlled trial” by Bodensohn et al. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2023, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Shoukat, S.; Oliver, D.E.; Chowdhary, M.; Rizzo, M.; Lawson, D.H.; Khosa, F.; Liu, Y.; Khan, M.K. Ipilimumab and Stereotactic Radiosurgery Versus Stereotactic Radiosurgery Alone for Newly Diagnosed Melanoma Brain Metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Anzellini, D.; Reverberi, C.; Cappellini, G.C.A.; Marchetti, L.; Bianciardi, F.; Bozzao, A.; Osti, M.; Gentile, P.C.; Esposito, V. Stereotactic radiosurgery combined with nivolumab or Ipilimumab for patients with melanoma brain metastases: Evaluation of brain control and toxicity. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Le Rhun, E. Should radiotherapy be considered for the initial treatment of brain metastases? Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Scaringi, C.; Paolini, S.; Lanzetta, G.; Romano, A.; Cicone, F.; Osti, M.; Enrici, R.M.; Esposito, V. Single-Fraction Versus Multifraction (3 × 9 Gy) Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large (>2 cm) Brain Metastases: A Comparative Analysis of Local Control and Risk of Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodensohn, R.; Maier, S.H.; Belka, C.; Minniti, G.; Niyazi, M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques. Cancers 2023, 15, 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225404
Bodensohn R, Maier SH, Belka C, Minniti G, Niyazi M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225404
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodensohn, Raphael, Sebastian H. Maier, Claus Belka, Giuseppe Minniti, and Maximilian Niyazi. 2023. "Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225404
APA StyleBodensohn, R., Maier, S. H., Belka, C., Minniti, G., & Niyazi, M. (2023). Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques. Cancers, 15(22), 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225404








