Efficacy of Radiomics in Predicting Oncologic Outcome of Liver-Directed Combined Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
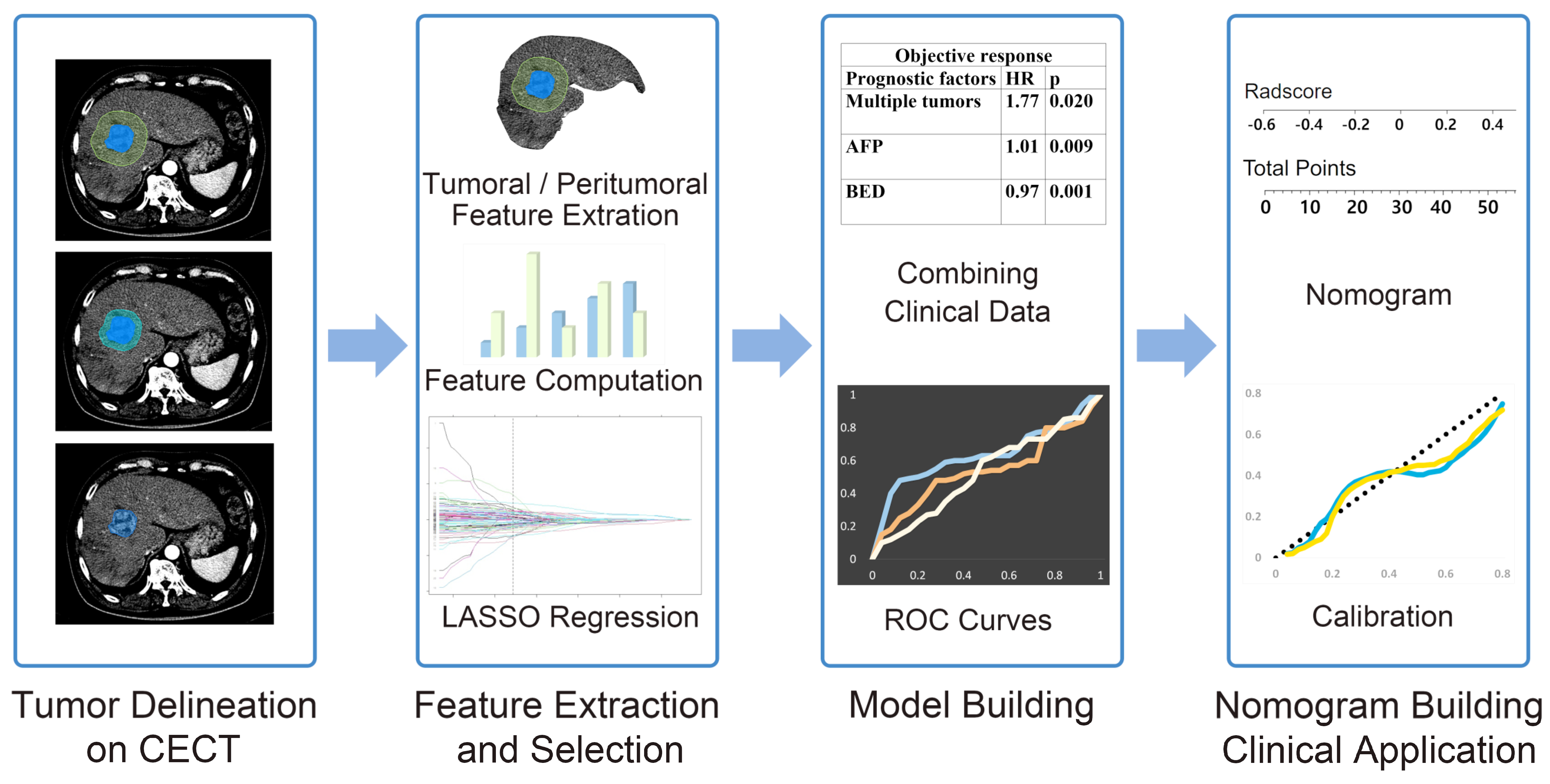
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment Protocols
2.3. CT Scan Protocols
2.4. Radiomics Feature Extraction
2.5. Feature Selection, Model Building, and Model Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors
3.3. Performance of Radiomics and Combined Clinico-Radiomics Models
3.4. Nomogram Construction and Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Schwartz, M.; Mazzaferro, V. Resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, R.; Sant, M.; Coleman, M.P.; Francisci, S.; Baili, P.; Pierannunzio, D.; Trama, A.; Visser, O.; Brenner, H.; Aradanaz, E.; et al. Cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007 by country and age: Results of EUROCARE-5—A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.Y.; Zhang, N.N.; Du, Y.W.; Wu, Y.; Song, T.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Comparison of Liver Transplantation and Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus Type I and Type II. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.E.; de Lope, C.R.; Bruix, J. Current strategy for staging and treatment: The BCLC update and future prospects. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Byun, H.K.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, G.H.; Han, D.H.; Joo, D.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Seong, J. Liver-directed combined radiotherapy as a bridge to curative surgery in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 152, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Choi, G.H.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, K.S.; Han, K.H.; Seong, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.U.; et al. Surgical resection after down-staging of locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma by localized concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.U.; Choi, G.H.; Han, D.H.; Kim, K.S.; Seong, J.; Han, K.H.; Choi, J.S. Downstaging with Localized Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Can Identify Optimal Surgical Candidates in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K. Early recognition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1986, 6, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyama, S.; Izuno, K.; Gohshi, K.; Shibata, J.; Sato, T. Clinical usefulness of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin assay in early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1991, 36, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Oguro, M.; Yanagi, M.; Mita, Y.; Suda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hata, K.; Ichii, K.; Asakura, H. Clinical significance of simultaneous determinations of alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in monitoring recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 1996, 77, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chon, Y.E.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Kang, W.; Choi, M.S.; Gwak, G.Y.; et al. Prognostic Value of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Patients Who Achieve a Complete Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, C.; Thaiss, W.M.; Kargel, R.; Grimmer, R.; Fritz, J.; Ioanoviciu, S.D.; Ketelsen, D.; Nikolaou, K.; Horger, M. Evaluation of Texture Analysis Parameter for Response Prediction in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Drug-eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) Using Biphasic Contrast-enhanced CT Image Data: Correlation with Liver Perfusion CT. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Park, S.J.; Byun, J.Y.; Choi, B.I. Prediction of Therapeutic Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Based on Pretherapeutic Dynamic CT and Textural Findings. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, W211–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, D. Texture Analysis Based on Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Conventional MRI Features for Predicting the Early Recurrence of Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatectomy. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Shui, Y.; Sun, W.; Lin, S.; Pang, H. Utility of Radiomics for Predicting Patient Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 569435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.Y.; Hu, H.T.; Feng, S.T.; Peng, Z.P.; Chen, S.L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Xie, X.Y.; Lu, M.D.; Wang, W.; et al. CT-based peritumoral radiomics signatures to predict early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative tumor resection or ablation. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.B.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.H.; Dong, Z.Y.; Xiao, L.S.; Kuang, J.J.; Zhang, X.L.; et al. Radiomics-based nomogram using CT imaging for noninvasive preoperative prediction of early recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 26, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Weng, S.; Yan, C.; Ye, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y. A Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Early Recurrence of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection or Radiofrequency Ablation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 657039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Owen, D.; Rosen, B.; Guo, X.; Cuneo, K.; Lawrence, T.S.; Ten Haken, R.; El Naqa, I. A deep survival interpretable radiomics model of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Phys. Med. 2021, 82, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Ding, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, L. A radiomics nomogram for the prediction of overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougaret, S.; Tibermacine, H.; Tardieu, M.; Sala, E. Radiomics: An Introductory Guide to What It May Foretell. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, S.S.; Aerts, H.J. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, Z.; Gu, D.; Tian, J.; Zhao, P.; Wei, J.; Yang, X.; Hao, X.; Dong, D.; He, N.; et al. Prediction early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for curative ablation using a Radiomics nomogram. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.T.; Han, J.K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging can predict early recurrence after curative resection using image features and texture analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shin, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, G.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.Y. Radiomics on Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction of Postoperative Early and Late Recurrence of Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3847–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Guo, R.P.; Lin, X.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, C.Q.; Lau, W.Y.; Li, J.Q. Partial hepatectomy with wide versus narrow resection margin for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, L.; Dinapoli, N.; Fogliata, A.; Hsu, W.C.; Reggiori, G.; Lobefalo, F.; Kirienko, M.; Sollini, M.; Franceschini, D.; Comito, T.; et al. Radiomics based analysis to predict local control and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, P.; Ye, W.; Liu, Z.; Liang, C. CT-based radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Categories (Number of Features): Features (Feature Numbers) | |
|---|---|
| Texture—histogram features (7): Histogram mean (1), standard deviation (2), minimum (3) and maximum (4) intensities, skewness (5), kurtosis (6), and entropy (7) | Texture—GLRLM features (22): Four direction mean and standard deviation of short run emphasis (27,28), long run emphasis (29,30), gray-level non-uniformity (31,32), run length non-uniformity (33,34), run percentage (35,36), low gray-level run emphasis (37,38), high gray-level run emphasis (39,40), short run low gray-level emphasis (41,42), short run high gray-level emphasis (43,44), long run low gray-level emphasis (45,46), long run high gray-level emphasis (47,48) |
| Texture—percentile intensities at (5): 5% (8), 25% (9), 50% (10), 75% (11), 95% (12) | |
| Texture—GLCM features (14): Four direction mean and standard deviation of angular second moment (13,14), contrast (15,16), sum average (17,18), sum variance (19,290), sum entropy (21,22), entropy (23,24), and difference entropy (25,26) | Texture—LBP features (59): 10 uniform patterns in LBP histogram (49–107) |
| Shape features (9): Area/perimeter ratio (108), convex area (109), eccentricity (110), major axis length (111), minor axis length (112), perimeter (113), solidity (114), Min curvature (115), Mean curvature (116) | |
| Characteristics | Training Set (n = 307) | Validation Set (n = 102) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56 (ranges, 33–83) | 60 (ranges, 28–85) | 0.076 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 260 (84.7) | 89 (87.3) | 0.527 |
| Female | 47 (15.3) | 13 (12.7) | |
| ECOG PS | |||
| 0, 1 | 293 (95.4) | 91 (89.2) | 0.133 |
| 2 | 14 (4.6) | 11 (10.8) | |
| Viral etiology | |||
| HBV | 254 (82.7) | 79 (77.5) | 0.166 |
| HCV | 19 (6.2) | 5 (4.9) | |
| Non-B, non-C | 34 (11.1) | 18 (17.6) | |
| Child–Pugh class | |||
| A | 252 (82.1) | 85 (83.3) | 0.775 |
| B | 55 (17.9) | 17 (16.7) | |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.5 (ranges, 2.1–4.8) | 3.7 (ranges, 2.0–4.9) | 0.187 |
| Serum bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.70 (ranges, 0.20–5.5) | 0.70 (ranges, 0.30–4.5) | 0.516 |
| INR | 1.1 (ranges, 0.80–1.7) | 1.1 (ranges, 0.80–1.6) | 0.401 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 280 (ranges, 1.70–12,000) | 500 (ranges, 1.20–12,000) | 0.441 |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 2000 (ranges, 10–75,000) | 1400 (ranges, 11–75,000) | 0.566 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 9.2 (ranges, 2.0–21) | 8.9 (ranges, 2.0–20) | 0.737 |
| Number of tumors | |||
| Solitary | 161 (52.4) | 50 (49.0) | 0.550 |
| Multiple | 146 (47.6) | 52 (51.0) | |
| PVTT | |||
| Vp0 | 92 (30.0) | 40 (39.3) | 0.096 |
| Vp1–2 | 70 (22.8) | 18 (17.6) | |
| Vp3 | 81 (26.4) | 24 (23.5) | |
| Vp4 | 64 (20.8) | 20 (19.6) | |
| Surgery after RT | 55 (17.9) | 19 (18.6) | 0.872 |
| Objective Response Rates | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prognostic Factors | HR | 95% CI | p |
| Multiple tumors | 1.77 | 1.09–2.86 | 0.020 |
| AFP | 1.01 | 0.98–1.03 | 0.009 |
| BED | 0.97 | 0.95–0.99 | 0.001 |
| In-field failure-free survival rates | |||
| Prognostic factors | HR | 95% CI | p |
| Tumor size ≥ 10 cm | 1.57 | 1.05–2.36 | 0.028 |
| Multiple tumors | 1.58 | 1.08–2.31 | 0.019 |
| BED ≥ 62.5 Gy | 0.51 | 0.35–0.76 | 0.001 |
| Models | Radiomics Model AUC | Clinical Model AUC | CCR Model AUC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Validation | Training | Validation | Training | Validation | |
| Objective Rate | ||||||
| OR−AP−Tumor | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.622 | 0.729 | 0.622 | 0.729 |
| OR−AP−Peri−1cm | 0.615 | 0.614 | 0.668 | 0.743 | ||
| OR−AP−Peri−2cm | 0.608 | 0.600 | 0.665 | 0.742 | ||
| OR−PVP−Tumor | 0.748 | 0.495 | 0.761 | 0.710 | ||
| OR−PVP−Peri−1cm | 0.684 | 0.647 | 0.704 | 0.759 | ||
| OR−PVP−Peri−2cm | 0.653 | 0.610 | 0.686 | 0.739 | ||
| In-field failure-free survival rate | ||||||
| IFFR−AP−Tumor | 0.581 | 0.625 | 0.626 | 0.687 | 0.643 | 0.659 |
| IFFR−AP−Peri−1cm | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.626 | 0.687 | ||
| IFFR−AP−Peri−2cm | 0.601 | 0.506 | 0.666 | 0.681 | ||
| IFFR−PVP−Tumor | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.626 | 0.687 | ||
| IFFR−PVP−Peri−1cm | 0.691 | 0.673 | 0.718 | 0.736 | ||
| IFFR−PVP−Peri−2cm | 0.613 | 0.560 | 0.671 | 0.714 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.W.; Lee, H.; Hong, H.; Seong, J. Efficacy of Radiomics in Predicting Oncologic Outcome of Liver-Directed Combined Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225405
Park JW, Lee H, Hong H, Seong J. Efficacy of Radiomics in Predicting Oncologic Outcome of Liver-Directed Combined Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225405
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jong Won, Hansang Lee, Helen Hong, and Jinsil Seong. 2023. "Efficacy of Radiomics in Predicting Oncologic Outcome of Liver-Directed Combined Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225405
APA StylePark, J. W., Lee, H., Hong, H., & Seong, J. (2023). Efficacy of Radiomics in Predicting Oncologic Outcome of Liver-Directed Combined Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 15(22), 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225405








