Simple Summary
Non-surgical management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is used for selected patients. Of these management options, transarterial embolisation (TAE) and transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) are the two main locoregional treatment options. There was no difference in OS among patients treated with TACE/TAE, single versus repeat treatments. Post-procedural adverse effects were higher in the TACE group but were not statistically significant. TACE has a comparable long-term survival and complications profile to TAE for patients with HCC. However, the low-to-moderate quality of current RCTs warrants high-quality RCTs, which are necessary to provide enough evidence to give a definitive answer and inform treatment plans for the future.
Abstract
Although hepatocellular carcinoma is increasingly common, debate exists surrounding the management of patients with unresectable disease comparing transarterial embolisation (TAE) or transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE). This study aimed to compare the outcomes of patients receiving TAE and TACE. A systematic review was performed using PubMed, Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases to identify randomised controlled trials (RCTs) until August 2021. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS) and the secondary outcomes were progression-free survival (PFS) and adverse events. Five studies with 609 patients were included in the analysis. There was no statistically significant difference in the OS (p = 0.36) and PFS (p = 0.81). There was no difference in OS among patients treated with a single TACE/TAE versus repeat treatments. Post-procedural adverse effects were higher in the TACE group but were not statistically significant. TACE has comparable long-term survival and complications profile to TAE for patients with HCC. However, the low-to-moderate quality of current RCTs warrants high-quality RCTs are necessary to provide enough evidence to give a definitive answer and inform treatment plans for the future.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer worldwide, with a rising incidence and an increasing global health burden over the last decade [1,2]. For patients with HCC within Milan criteria, preferred curative options include either liver transplantation or resection, with a reported 5-year survival of 65–80% [3,4]. Liver transplantation is the curative option for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for patients with background liver disease and 20-25% of the LT performed in Western countries are for HCC. The selection criteria of HCC candidates reminas fairly rigid despite of some extended criteria applied to the well accepted Milan criteria. Surgical resection is not often possible in the presence of background liver disease and portal hypertension and the criteria for liver transplantation are rigid in order to obtain best oncological outcomes. For patients who are not suitable for surgical treatment, the management options are usually based on the degree of background liver disease, and the extent of tumour load, including portal venous involvement.
Transarterial embolisation (TAE) and transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) are the two main locoregional treatment options in the management of unresectable HCCs, to palliate or downstage or to bridge to transplantation. Liver embolization for HCC is commonly used in two main settings: (1) large unresectable HCCs unsuitable for surgery or ablation, and (2) prior to resection or to liver transplantation as a bridge therapy. The vascular supply to the HCC tissue is predominantly arterial and the selective blockade of arterial flow using superselective angiography is used as a strategy to cause necrosis of tumor tissue.
TAE aims to reduce tumour burden through the embolisation of the arteries that predominantly feed the tumour. In TAE, superselective vascular embolization using gelatin sponge, Lipiodol, or microparticles as small as 40μm in diameter with no drugs are injected. TACE involves the additional administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy to the tumour cells in addition to embolisation. Principally, both these treatment modalities lead to hypoxia-induced necrosis of the tumour [5,6]. A variety of materials are used for embolization to slow tumor progression. During TACE procedure, tumor is filled with a chemotherapeutic drug such as doxorubicin, epirubicin, cisplatin, or mitomycin C along with Lipiodol or drug-eluting beads. In general, the best candidates for these procedures are those patients with unresectable lesions without vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread and with well-preserved liver function.
The relative potential superiority of TACE and TAE for patients with the unresectable disease remains unclear. In particular, data in favour of the superiority of TACE over TAE are still lacking [7]. A RCT comparing conventional TACE, TAE, and best supportive care (BSC) was prematurely terminated because of the superiority of TACE over BSC, which prevented the ability to determine the efficacy of TAE relative to TACE, which could only be hypothesised based on the trend observed in overall survival (OS) [8]. In addition, other RCTs published more recently on this topic seem to provide discordant results [9,10]. These discrepancies may be due to a number of unsolved issues concerning TACE. For example, the optimal chemotherapeutic agent to inject, as well as the efficacy of drug-eluting embolic agents, are still a matter of debate [11,12]. The objective of the current study was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing RCT data on TAE and TACE among patients with unresectable HCC.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library databases was conducted up to August 2021 by four independent investigators (SKK, AP, AL, and KP). The search terms included ‘transarterial embolisation’ or ‘transarterial chemoembolisation’ or ‘chemoembolisation’ and ‘survival’ and ‘hepatocellular carcinoma,’ individually or in combination (Table 1). The ‘related articles’ function was used to broaden the search, and all citations were considered for relevance. A manual search of reference lists in recent reviews and eligible studies was also undertaken.

Table 1.
Summary of search terms used for literature review.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria were (1) studies that compared TACE and TAE relative to overall survival in human subjects with HCC; (2) published in the English language; and (3) RCTs. Exclusion criteria were (1) conference abstracts, review articles, and case reports (<5 patients); (2) publications with mixed populations in which the outcomes of patients could not be separated by disease type (HCC) or patient population (i.e., resectable or unresectable); and (3) no reported survival data.
After excluding duplicates, four researchers (SKK, AP, AL, and KP) independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of studies identified by the literature search. Full copies of publications considered potentially relevant to the research question were obtained for further review. The reference lists of all included studies were hand-searched to identify other potentially relevant studies. Any areas of disagreement were resolved through discussion until consensus was achieved.
2.3. Study Outcomes
The primary outcome measures were OS defined as the interval between TAE or TACE and death or censoring of data. Secondary outcome measures were progression-free survival and adverse events (i.e., cholecystitis, liver abscess, liver failure, and leukopenia).
2.4. Data Extraction
Four researchers (SKK, AP, AL, and KP) extracted data on study characteristics (author, year of publication, country of origin, and patient numbers), patient demographics (age, sex, and TACE/TAE details), and OS. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion with other authors until consensus was achieved (SKK, AP, and BVMD). Where data were missing for some of the outcomes in the included studies, analyses were performed with the reported numbers for those outcomes.
2.5. Assessment of Methodological Quality
The methodological quality and quality of reported outcomes were assessed by four independent researchers (SKK, AP, AL, and KP). Methodological quality was formally assessed using the Cochrane tool for publication bias for randomised studies (SKK, AP, AL, and KP) [13,14]. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion amongst authors until consensus was achieved (SKK, AP, and BVMD).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the recommendations of the Cochrane Library and PRISMA guidelines [15]. For random effects, the DerSimonian–Laird method was used for the meta-analysis of RCTs. Reported Hazard Ratios (HR) were used directly in the quantitative meta-analysis. Standard errors for HRs were calculated from the 95% CI when provided in the article. Funnel plots were used to visually assess publication bias. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I2 value to determine the degree of variation not attributable to chance alone. I2 values were considered to represent low, moderate, and high degrees of heterogeneity where values were <25%, 25–75%, and >75%, respectively. Funnel plot asymmetry was assessed using the Egger test. Statistical significance was considered when p < 0.05. Data analysis was undertaken using R Foundation Statistical software (R 3.2.1), as previously described [16].
3. Results
Study Characteristics
Among the 5377 studies identified, 229 studies had full text reviewed; five studies [9,10,17] with 609 patients were included that reported on patients undergoing TACE or TAE for unresectable HCC. A summary of included studies is presented using the PRISMA diagram (Figure 1).
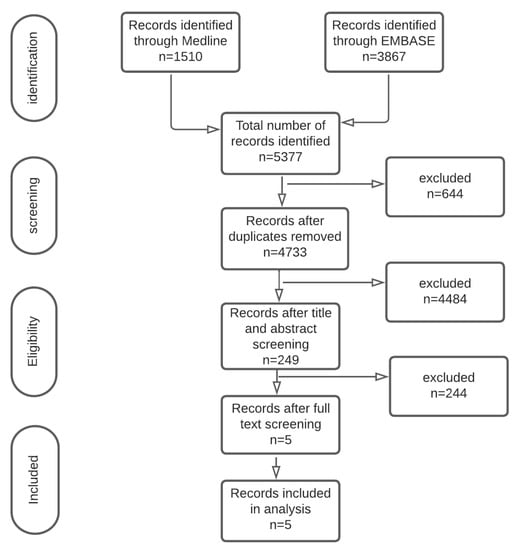
Figure 1.
PRISMA diagram.

Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of included studies.
Quality assessment of the included studies according to the Cochrane Risk of Bias is presented in Table 3 of publications published from 1992 to 2016. Studies were completed in different countries with all studies being completed in secondary/tertiary care (or local equivalents). Studies were published in a variety of high-impact journals.

Table 3.
Risk of bias assessment of included randomised controlled trials.
4. Survival Outcomes
4.1. Overall Survival
There were no data to support the superiority of either TACE or TAE among patients with HCC. Overall survival was reported in all five studies [9,10,17,18,19]. Hazard ratios ranged from 0.91 to 1.56 with no single study reporting a statistically significant difference in OS. A random effects model meta-analysis (Figure 2) demonstrated a non-significant pooled effect measure of HR 1.14 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.87–1.46 p = 0.36). There was low heterogeneity in this analysis with I2 = 0%.
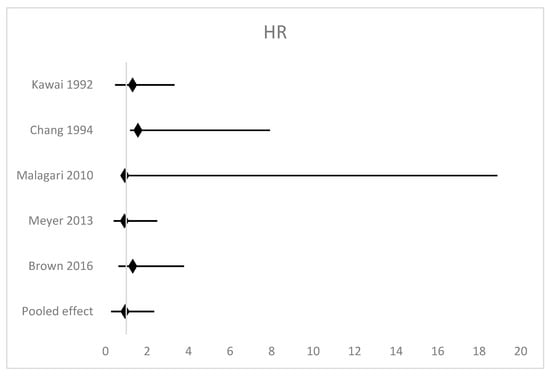
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the meta-analysis of overall survival [9,10,17,18,19].
4.2. Comparison by Number of Sessions
Sub-group analysis was performed based on whether patients received a single intervention or multiple repeat interventions. A single TACE/TAE session was used in two studies (328 patients). In these studies, a non-significant HR 1.32 (95% CI 0.87–2.01 p = 0.19) was observed. Similarly, for patients who underwent repeat TACE/TAE (271 patients), TAE was associated with a non-significant HR 1.06 (95% CI 0.70–1.61 p = 0.77); there was no difference in overall survival among patients treated with a single TACE/TAE versus repeat treatments.
4.3. Progression-Free Survival
Progression-free survival was reported by two studies [9,17]. These studies carried similar weights within the analysis. HR for the two studies ranged from 0.87 to 1.36, although neither study demonstrated a statistically significant result. Hazard ratios were used to calculate the pooled effect which was statistically non-significant [HR = 1.05 (95% CI 0.68–1.62 p = 0.81)]. Moderate levels of heterogeneity were observed in this analysis (I2 = 29%).
4.4. Comparison by Chemotherapeutic Agent
Subgroup analysis by chemotherapeutic agent used (Table 1) in TACE was performed. Doxorubicin was the chemotherapeutic agent in two [10,17] of the included studies. The pooled effect measure of these produced a result more in favour of TAE; however, it was not statistically significant, with HR 1.30 (95% CI 0.91–1.86 p = 0.16). This result also had no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). For studies [9,18] using Cisplatin as the chemotherapeutic agent (228 patients), the pooled effect favoured TACE with HR 0.97 (95% CI 0.67–1.41 p = 0.87). Again, this result was not statistically significant.
4.5. Adverse Events
Ten common adverse events were included in this review. A summary of the results of the meta-analyses is detailed in Table 4. The severity of grading of complications was only presented by two studies [9,17] using different grading measures. The analysis was therefore performed without differentiating the grades of adverse events.

Table 4.
Summary of meta-analysis of adverse events.
4.6. Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis was reported in three studies [10,17,18] including 231 patients. The Peto odds ratios ranged from 0.14 to 7.95. The pooled effect of this analysis was a non-significant Peto odds ratio = 0.70 (95% CI 0.12–4.06) associated with high levels of heterogeneity (I2 = 59%).
4.7. Liver Abscess
The incidence of the liver abscess was reported in three studies [9,10,17] including 271 patients. No study reported a statistically significant result. Two studies favoured TACE, whereas one favoured TAE. All studies had high degrees of uncertainty with large confidence intervals. Peto odds ratios ranged from 0.13 to 2.08 with a non-significant pooled effect of 0.51 (95% CI 0.10–2.58 p = 0.42) and moderate heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 30%).
4.8. Liver Failure
The incidence of liver failure was reported in three studies [9,10,17] (271 patients). Two studies favoured TAE and one study favoured TACE, with no significant difference in the overall analysis. There was a notable degree of uncertainty in the results from the studies with a wide 95% CI calculated. The Peto odds ratio ranged from 0.14 to 1.89 and the pooled effect of these studies is 1.01 (95% CI 0.25–4.11 p = 0.99). No heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0%) at two degrees of freedom (Chi2 = 1.28)
4.9. Abdominal Pain
Incidence of abdominal pain was reported in two studies [9,19] (335 patients). Both studies favoured TAE with the Peto odds ratio ranging from 1.03 to 1.58. Both results were not statistically significant. The meta-analysis gave a pooled effect Peto odds ratio of 1.12 (95% CI 0.71–1.78 p = 0.62). No heterogeneity was observed in this study (I2 = 0%) with one degree of freedom (Chi2 = 0.56)
4.10. Fever
Incidence of fever is reported by two studies [9,19] (335 patients). One study favours TACE, whereas the other favours TAE. Peto odds ratios for this outcome range from 0.29 to 1.04. The pooled effect of this meta-analysis gave a non-significant Peto odds ratio of 0.68 (95% CI 0.41–1.13 p = 0.13). Very high levels of heterogeneity were observed (I2 = 81%) with one degree of freedom (Chi2 = 5.29)
5. Discussion
Although TACE is considered the standard of care for BCLC intermediate-stage HCC patients, robust data in favour of a clear superiority of TACE (with chemotherapy) over TAE (bland embolisation) are still lacking. The well-known hypervascularisation of HCC nodules provides the rationale for the occlusion by embolic particles, which results in tumour hypoxia and necrosis. However, whether the addition of local chemotherapy has an additive anti-tumour effect is still a matter of debate [20,21,22]. The current study demonstrated TAE to have a comparable survival and morbidity profile compared with TACE.
Side effects of liver embolization include pain, nausea, fatigue, fever, and transient elevations of asparate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and bilirubin levels. Symptoms are usually self-limiting. There was, however, a decreased odds of emesis in the TAE group and increased odds of experiencing anaemia in the TACE group, which are expected adverse effects of chemotherapy. Serious complications such as hepatic failure, gastroduodenal ulceration, kidney failure, and death (2–3%) have been reported.
Trials comparing TAE versus TACE included different size cohorts, patient populations, and tumour stages. For instance, some studies included patients with vascular involvement by the tumour, where the benefit of TACE or TAE is debatable and the survival can be influenced by the extent of tumour irrespective of the endovascular embolising comparators that are evaluated [23]. The embolising agent varied over time in recent decades, hence the different sizes and the different embolising techniques may have led to a lack of demonstration of efficacy due to dilution bias and high heterogeneity in the meta-analysis of data [23,24]. This is particularly relevant considering that the time range in which the included studies were retrieved spanned from 1988–1989 to 2007–2012 for the rest of the study period to 2021. Including the studies over this period would have accounted for the variability. It will be interesting to know the outcomes of the ongoing trials that assess the role of combined immunotherapy and TACE. Technical aspects of the procedures have evolved with more selective embolisation in recent times, as is the selection of patients for repeat procedures to those only with residual tumour activity. Hence, the strength of the conclusion from this study is limited by such intrinsic shortcomings. At the same time, a more restricted selection of the literature would lead to a too-limited amount of data to be analysed. Hence, at present, there is no better way to provide data on the comparison of survival outcomes between TACE and TAE and some of these results need further validation in future studies.
Understanding tumour response to both TAE and TACE will allow a better understanding of patient selection for either treatment arm. However, the studies included in the present review lack a standardised approach to reporting this, precluding a reliable assessment. The well-established tools to assess tumour response are the RECIST and mRECIST systems. Many of the included studies pre-date the use of RECIST tool and hence a variety of regional or radiological cut-offs to define patient response to treatment. With the global challenge of increasing HCC incidence, the need for internationally translatable research is necessary, and hence more randomised studies using consistent measures. Furthermore, identifying non-responders helps choose alternative treatment options.
It will need further research regarding the ability to predict the candidates who would respond to the embolization procedures and who could have complete tumor ne crosis on the initial or repeat procedures. The prognostic indices that are currently in use are based on clinical and laboratory parameters. These are useful in assessing the safety of the procedure but there is a need for further discrimination based on the tumor morphological characteristics and molecular markers to assess response to TACE or TAE. Early work demonstrated that transcriptome profiling to identify unique gene signatures of naïve HCC cells can be a predictor of response to treatment [25]. The adaptive mech anisms resulting from embolization procedure induced hypoxia have been investigated – hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) for neoangiogenesis, CD34 for microvessel density, CA9 for antiapoptotic activity, CD133 and nestin for stem cell features, and vimentin and E-cadherin for the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. However, on multivariate analysis it is found that only CD34 and VEGF retained a significant association with TACE response. A typical pattern of expression (VEGF–, CD34+) was associated with resistance to TACE, suggesting that HCCs with this expression pattern are more resistant to hypoxia because they have developed a complete vascular network (increased CD34) without requiring further neoangiogenesis (decreased VEGF). These include HIF 1-alpha, which is upregulated in non-responders and contributes to neovascularisation, making TACE or TAE ineffective.
In the East where Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the main etiology of HCC, it has been reported that Hepatitis B protein x (HBx) plays an important additional role in the promotion of the switch in the gene expression especially in hypoxic tumor microenvironment. The antigen enhances hypoxia signaling through HIF1α activation, enhamces EpCAM expression by activating β-catenin and regulates the EpCAM promoter methylation. [26]
Zhang et al. studied radiomics and demonstrated that lesions with arterial-hyper enhancement and well-circumscribed borders are more susceptible to TACE. Identification of responders may be even more important in patients receiving TACE/TAE as a bridging therapy to transplantation to allow the best use of available organs [27]. Post-embolisation transient hypertransaminesemia can also be an indicator of response to embolisation procedures [28]. Further evaluation of immunological responses of TACE is important and its influence on the higher incidence of metastatic disease following TACE [29,30], as well as the benefits of immunomodulation of TACE with immunotherapy [31], are being reported. Future studies should also consider evaluating other emerging locoregional therapies, such as hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) [32] and internal radiotherapy.
This study has limitations to note. Firstly, response rate and survival data were affected by moderate/high heterogeneity. Secondly, the low number of included studies requires caution in interpreting the findings. However, the study restricted the inclusion of RCTs only to provide robust and reliable outcome estimates. There are also several newer systemic treatment options and future studies should consider evaluating the benefit of invasive versus non-invasive options and create the tools to identify what will be the best option for the patient based on the radiomics and genomics. Future studies evaluating the impact of embolisation procedures on the liver function (Child–Pugh status) are also needed as a deterioration in the liver function might preclude the sequential and combined immunotherapy/tyrosine kinase inhibitors [32,33].
6. Conclusions
In summary, this study provides an update to the existing literature on this topic and broadens the spectrum of considered outcomes. It supports previous analyses showing a non-superiority of TACE over TAE and provides a starting point to consider more work in the future to improve the existing data and find deeper patterns and relationships in this treatment to best deploy its use for a growing global health burden of HCC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.V.M.D. and Y.T.M.; methodology, B.V.M.D., A.L., K.P. and S.K.K.; software, A.L. and K.P.; formal analysis, S.K., A.P., A.L. and B.V.M.D.; data curation, S.K.K., A.P. and B.V.M.D.; visualization, S.K. and B.V.M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L., S.K.K., B.V.M.D., A.P., S.K., T.S., Y.T.M., T.M.P., R.S. and K.P.; writing—review and editing, Y.T.M., S.K., S.K.K., T.M.P., R.S., B.V.M.D. and T.S.; supervision, B.V.M.D., Y.T.M., T.M.P., R.S., T.S. and S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Muralidharan, P.; Raj, J.P. Update in global trends and aetiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Contemp. Oncol. 2018, 22, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration; Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajah, S.K.; Frankel, T.L.; Sonnenday, C.; Cho, C.S.; Nathan, H. Critical evaluation of the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) 8th edition staging system for patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): A Surveillance, Epidemiology, End Results (SEER) analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajah, S.K.; Bundred, J.R.; Littler, P.; Reeves, H.; Manas, D.M.; White, S.A. Treatment strategies for early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. HPB 2021, 23, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Yan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qu, P.; Xu, X.; Yuan, P.; Huang, X.; Xing, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization aggravated peritumoral fibrosis via hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha dependent pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzao, C.; Lee, S.-C.; Tung, H.-J.; Hsu, H.-S.; Hsu, W.-H.; Sun, G.-H.; Yu, C.-P.; Jin, J.-S.; Cheng, Y.-L. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D as outcome predictors in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2008, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Fatourou, E.; O’Beirne, J.; Meyer, T.; Burroughs, A.K. Transarterial chemoembolization and bland embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Kirkwood, A.; Roughton, M.; Beare, S.; Tsochatzis, E.; Yu, D.; Davies, N.; Williams, E.; Pereira, S.; Hochhauser, D.; et al. A randomised phase II/III trial of 3-weekly cisplatin-based sequential transarterial chemoembolisation vs embolisation alone for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagari, K.; Pomoni, M.; Kelekis, A.; Pomoni, A.; Dourakis, S.; Spyridopoulos, T.; Moschouris, H.; Emmanouil, E.; Rizos, S.; Kelekis, D. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with BeadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Mariani, L.; Sposito, C.; Spreafico, C.; Bongini, M.; Morosi, C.; Cascella, T.; Marchianò, A.; Camerini, T.; Bhoori, S.; et al. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Di Maso, M.; Muscatiello, N. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.K.; Mertz, D.; Loeb, M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: Comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarajah, S.K.; Bundred, J.; Spence, G.; Kennedy, A.; Dasari, B.V.M.; Griffiths, E.A. Critical Appraisal of the Impact of Oesophageal Stents in the Management of Oesophageal Anastomotic Leaks and Benign Oesophageal Perforations: An Updated Systematic Review. World J. Surg. 2019, 44, 1173–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Do, R.K.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.M.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Jarnagin, W.R.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; et al. Randomized Trial of Hepatic Artery Embolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Doxorubicin-Eluting Microspheres Compared With Embolization With Microspheres Alone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.M.; Tzeng, W.S.; Pan, H.B.; Yang, C.F.; Lai, K.H. Transcatheter arterial embolization with or without cisplatin treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled study. Cancer 1994, 74, 2449–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Okamura, J.; Ogawa, M.; Ohashi, Y.; Tani, M.; Inoue, J.; Kawarada, Y.; Kusano, M.; Kubo, Y.; Kuroda, C.; et al. Prospective and randomized clinical trial for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma--a comparison of lipiodol-transcatheter arterial embolization with and without adriamycin (first cooperative study). The Cooperative Study Group for Liver Cancer Treatment of Japan. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1992, 31, S1–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Facciorusso, A.; Bellanti, F.; Villani, R.; Salvatore, V.; Muscatiello, N.; Piscaglia, F.; Vendemiale, G.; Serviddio, G. Transarterial chemoembolization vs bland embolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Kong, J. Comparison of initial tumor responses to transarterial bland embolization and drug-eluting beads-transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity-score matching analysis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Antonino, M.; Del Prete, V.; Neve, V.; Scavo, M.P.; Barone, M. Are hematopoietic stem cells involved in hepatocarcinogenesis? Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Salem, R. Transarterial chemoembolization and radioembolization. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.F. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fako, V.; Martin, S.P.; Pomyen, Y.; Budhu, A.; Chaisaingmongkol, J.; Franck, S.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Ng, I.O.-L.; Cheung, T.-T.; Wei, X.; et al. Gene signature predictive of hepatocellular carcinoma patient response to transarterial chemoembolization. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzumanyan, A.; Friedman, T.; Ng, I.O.; Clayton, M.M.; Lian, Z.; Feitelson, M.A. Does the hepatitis B antigen HBx promote the appearance of liver cancer stem cells? Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3701–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, A.H.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.H.; Sun, Q.L.; Shu, C. Radiological appearance of hepatocellular carcinoma predicts the response to trans-arterial chemoembolization in patients undergoing liver transplantation. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Facciorusso, A.; Sacco, R.; Bartalena, L.; Mosconi, C.; Cea, U.V.; Cappelli, A.; Antonino, M.; Modestino, F.; Brandi, N.; et al. TRANS-TACE: Prognostic Role of the Transient Hypertransaminasemia after Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.C.; Jia, Q.A.; Ge, N.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Ye, S.L. Imbalance in systemic inflammation and immune response following transarterial chemoembolization potentially increases metastatic risk in huge hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 8797–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viedma-Martinez, M.; Villegas Romero, I. Skin Necrosis after Transarterial Chemoembolization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidaway, P. HAIC-FO improves outcomes in HCC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granito, A.; Forgione, A.; Marinelli, S.; Renzulli, M.; Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Benevento, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Tovoli, F. Experience with regorafenib in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211016959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanini, B.; Ielasi, L.; Chen, R.; Abbati, C.; Tonnini, M.; Tovoli, F.; Granito, A. TKIs in combination with immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2023, 23, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).