Cell-Free DNA as a Surveillance Tool for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Liver Transplant
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of Liquid Biopsy and Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) in Patients with HCC Undergoing Liver Transplantation
2.1. Liquid Biopsy
2.2. Quantitative
2.3. Qualitative
3. Other Components of Interest in Liquid Biopsy [89,90,91,92,93,94,95,99,100,101,102,103]
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valery, P.C.; Laversanne, M.; Clark, P.J.; Petrick, J.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Projections of primary liver cancer to 2030 in 30 countries worldwide. Hepatology 2018, 67, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Hallouch, O.; Chernyak, V.; Kamaya, A.; Sirlin, C.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Target population for surveillance and diagnosis. Abdom. Imaging 2018, 43, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Blissett, D.; Blissett, R.; Henry, L.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Racila, A.; Hunt, S.; Beckerman, R. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Harmsen, W.S.B.; Enders, F.; Gores, G.J.; Roberts, L.R.M. Recent Trends in the Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Olmsted County, Minnesota: A US population-based study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghouri, Y.A.; Mian, I.; Rowe, J.H. Review of hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, etiology, and carcinogenesis. J. Carcinog. 2017, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.-L.; Mak, L.-Y.; Cheung, K.-S.; Yuen, M.-F. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advances and emerging medical therapies. F1000Research 2020, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
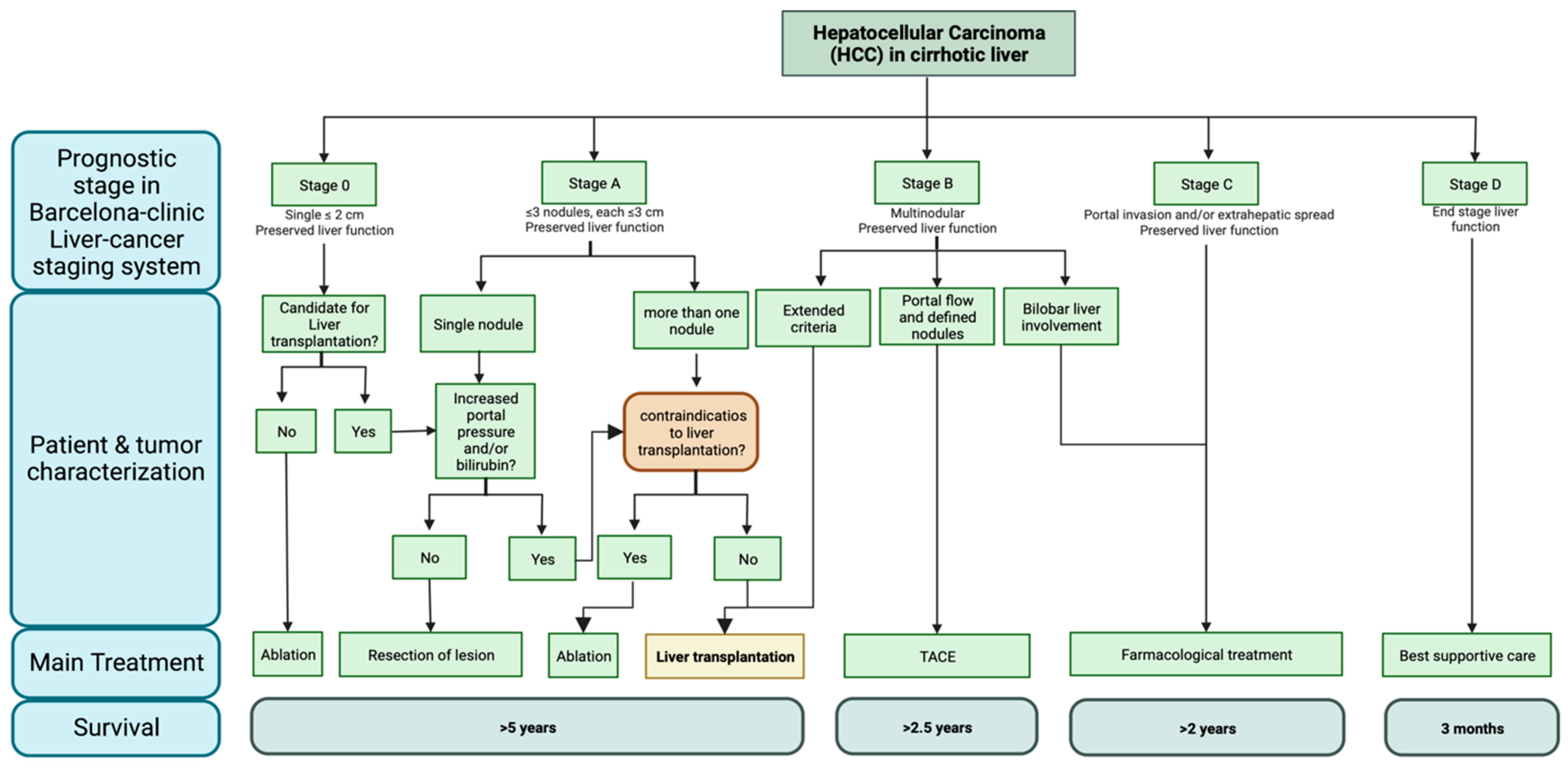
- Liu, P.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Hsia, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lee, F.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Huo, T.-I. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Assessment of eleven staging systems. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, H.; Hu, M.; Huang, T.; Hu, Y.; Sang, N.; Zhao, Y. Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2993–3036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-B.; Wu, T.-M.; Fu, D. New Therapeutic Options for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Control. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Bhangui, P.M.; Yao, F.Y.; Mazzaferro, V.; Toso, C.; Akamatsu, N.; Durand, F.; Ijzermans, J.; Polak, W.; Zheng, S.; et al. Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Working Group Report from the ILTS Transplant Oncology Consensus Conference. Transplantation 2020, 104, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.Y.; Ferrell, L.; Bass, N.M.; Watson, J.J.; Bacchetti, P.; Venook, A.; Ascher, N.L.; Roberts, J.P. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchetti, A.; Serenari, M.; Sposito, C.; Di Sandro, S.; Mosconi, C.; Vicentin, I.; Garanzini, E.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; De Carlis, L.; Golfieri, R.; et al. Including mRECIST in the Metroticket 2.0 criteria improves prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma-related death after liver transplant. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Singal, A.G. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Transplantation: Changing Patterns and Practices. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2017, 15, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.M.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver Transplantation for the Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Patients with Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.Y.; Xiao, L.; Bass, N.M.; Kerlan, R.; Ascher, N.L.; Roberts, J.P. Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Validation of the UCSF-Expanded Criteria Based on Preoperative Imaging. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.M.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaido, T.; Ogawa, K.; Mori, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ito, T.; Tomiyama, K.; Takada, Y.; Uemoto, S. Usefulness of the Kyoto criteria as expanded selection criteria for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery 2013, 154, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santopaolo, F.; Lenci, I.; Milana, M.; Manzia, T.M.; Baiocchi, L. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Where do we stand? World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2591–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Foley, K.; Movahedi, B.; Masciocchi, M.J.; Bledsoe, J.R.; Ding, L.; Rava, P.; Fitzgerald, T.J.; Sioshansi, S. Outcomes After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy as a Bridging Modality to Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.N.; Yu, Y.; Tan, Y.R.N.; Lim, B.L.K.; Iyer, S.G.; Madhavan, K.; Kow, A.W.C. Bridging therapies to liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A bridge to nowhere? Ann. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2018, 22, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.D.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Downstaging hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapisochin, G.; Goldaracena, N.; Laurence, J.M.; Dib, M.; Barbas, A.; Ghanekar, A.; Cleary, S.P.; Lilly, L.; Cattral, M.S.; Marquez, M.; et al. The extended Toronto criteria for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective validation study. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.F.; Sherman, M. Criteria for liver transplantation for HCC: What should the limits be? J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ameri, A.A.M.; Wei, X.; Wen, X.; Wei, Q.; Guo, H.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X. Systematic review: Risk prediction models for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De’angelis, N.; Landi, F.; Carra, M.C.; Azoulay, D. Managements of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11185–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodzin, A.S.; Lunsford, K.E.; Markovic, D.; Harlander-Locke, M.P.; Busuttil, R.W.; Agopian, V.G. Predicting Mortality in Patients Developing Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.D.; Sapisochin, G.; Mehta, N.; Gorgen, A.; Musto, K.R.; Hajda, H.; Yao, F.Y.; Hodge, D.O.; Carter, R.E.; Harnois, D.M. Surveillance for HCC after Liver Transplantation: Increased monitoring may yield aggressive treatment options and improved postrecurrence survival. Transplantation 2020, 104, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.; Esmail, A.; Chang, J.C.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Abdelrahim, M. Utility of Cell-Free DNA Detection in Transplant Oncology. Cancers 2022, 14, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, D.E.; Binder, D.; Bowlus, C.; Burgoyne, A.; Cloyd, J.; Glazer, E.S.; Jude, S.; Hawkins, W.G.; Jennings, L.; Kate Kelley, R.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Version 1.2023. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 2023. Available online: www.unos.org (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Yang, J.D.; Heimbach, J.K. New advances in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ 2020, 371, m3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnostic Performance of Multidetector CT and MR Imaging—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2015, 275, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Vilana, R.; Ayuso, C.; Bianchi, L.; Solé, M.; Ayuso, J.R.; Boix, L.; Sala, M.; Varela, M.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: Prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Pecorelli, A.; Brandi, N.; Brocchi, S.; Tovoli, F.; Granito, A.; Carrafiello, G.; Ierardi, A.M.; Golfieri, R. The Feasibility of Liver Biopsy for Undefined Nodules in Patients under Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is Biopsy Really a Useful Tool? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, R.; Garzillo, G.; Ascanio, S.; Renzulli, M. Focal Lesions in the Cirrhotic Liver: Their Pivotal Role in Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced MRI and Recognition by the Western Guidelines. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, F.; Baskiran, A. The Importance of AFP in Liver Transplantation for HCC. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2020, 51, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ling, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X. Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, R.-I.; Chen, K.; Usmani, A.; Chua, C.; Harris, P.K.; Binkley, M.S.; Azad, T.D.; Dudley, J.C.; Chaudhuri, A.A. Detection of Solid Tumor Molecular Residual Disease (MRD) Using Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA). Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P. METAISP Les acides nucléiques du plasma sanguin chez l’homme. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.M.; Schur, P.H.; Carr, R.I.; Kunkel, H.G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 1966, 45, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.A.; Shapiro, B.; Sklaroff, D.M.; Yaros, M.J. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Gahan, P.B.; Schwarzenbach, H.; Anker, P. The History and Future of Basic and Translational Cell-Free DNA Research at a Glance. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Liquid Biopsy: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (cfDNA) OR (ctDNA) OR (CTC)–Search Results–PubMed. Published 2023. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=%28cfDNA%29+OR+%28ctDNA%29+OR+%28CTC%29&filter=years.2013-2017&timeline=expanded (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Bardelli, A. Liquid Biopsies: Genotyping Circulating Tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Chabner, B.A. Application of Cell-free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Pantel, K. Liquid Biopsies, What We Do Not Know (Yet). Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.; Magenheim, J.; Neiman, D.; Zemmour, H.; Loyfer, N.; Korach, A.; Samet, Y.; Maoz, M.; Druid, H.; Arner, P.; et al. Comprehensive human cell-type methylation atlas reveals origins of circulating cell-free DNA in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselmann, V.; Ahmad-Nejad, P.; Geilenkeuser, W.J.; Duda, A.; Gabor, M.; Eichner, R.; Patton, S.; Neumaier, M. Results of the first external quality assessment scheme (EQA) for isolation and analysis of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 56, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
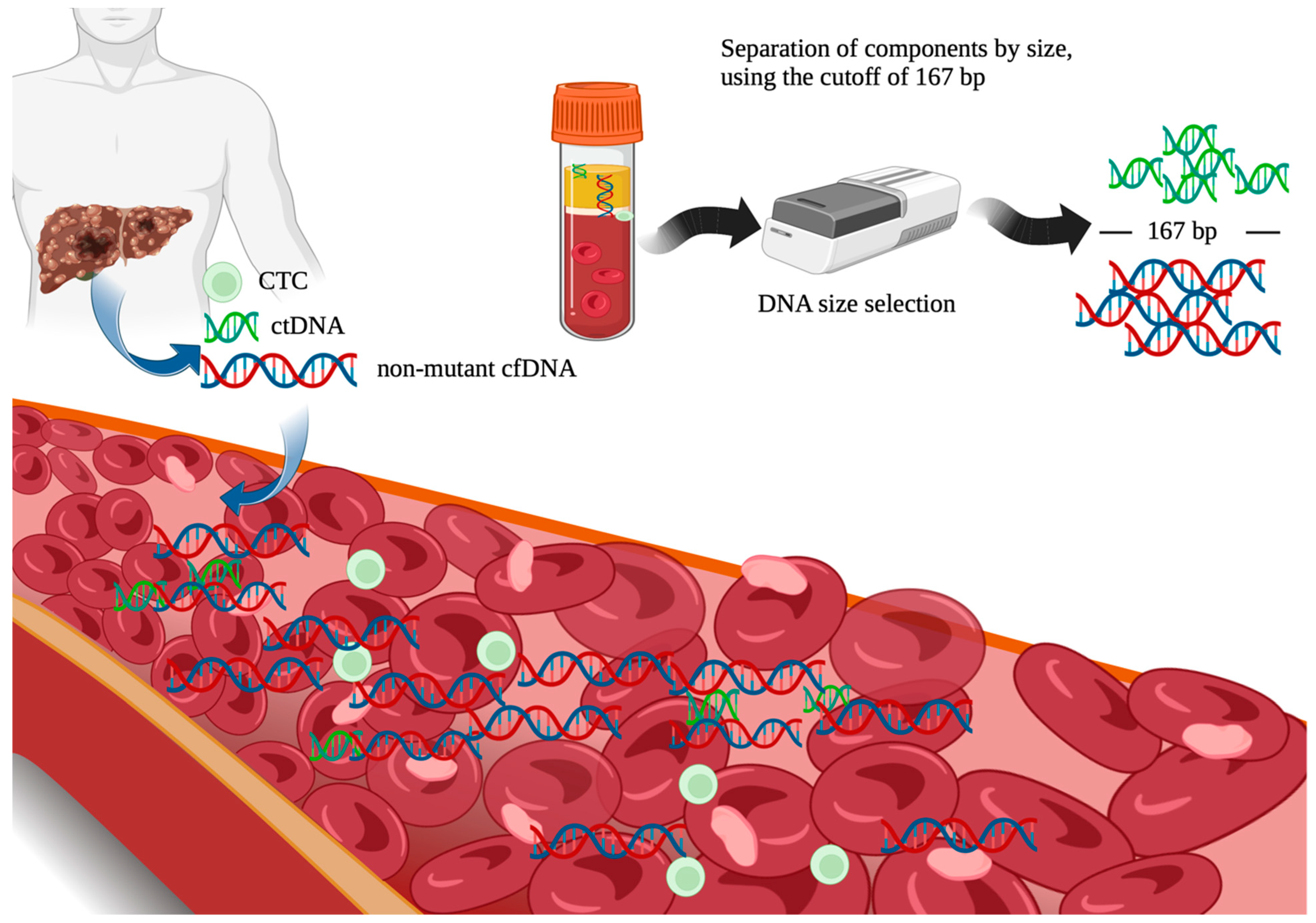
- Underhill, H.R.; Kitzman, J.O.; Hellwig, S.; Welker, N.C.; Daza, R.; Baker, D.N.; Gligorich, K.M.; Rostomily, R.C.; Bronner, M.P.; Shendure, J. Fragment Length of Circulating Tumor DNA. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliere, F.; Chandrananda, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Moore, E.K.; Morris, J.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Mair, R.; Goranova, T.; Marass, F.; Heider, K.; et al. Enhanced detection of circulating tumor DNA by fragment size analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidin, M.B.; Freydina, D.V.; Leung, M.; Fernandez, A.M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Lim, E. Circulating Tumor DNA Outperforms Circulating Tumor Cells for KRAS Mutation Detection in Thoracic Malignancies. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Hung, E.C.W.; Woo, J.K.S.; Chan, P.K.S.; Leung, S.-F.; Bn, F.P.T.L.; Cheng, A.S.M.; Yeung, S.W.; Chan, Y.W.; Tsui, T.K.C.; et al. Early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA analysis in a surveillance program. Cancer 2013, 119, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, F.; Xu, L.; Yin, R. Circulating Tumor DNA Is Effective for the Detection of EGFR Mutation in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.-H.; Wei, W.; Krawczyk, M.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Flagg, K.; Yi, S.; Shi, W.; Quan, Q.; Li, K.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA methylation markers for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, W.; Tang, Z.; Qu, W.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Tao, C.; Zhou, P.; et al. Serial circulating tumor DNA to predict early recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Letouzé, E.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Meiller, C.; Shinde, J.; Soysouvanh, F.; et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Malapelle, U.; André, F.; Paz-Ares, L.; Schuler, M.; Thomas, D.M.; Vainer, G.; Yoshino, T.; Rolfo, C. Practical Considerations for the Use of Circulating Tumor DNA in the Treatment of Patients With Cancer: A Narrative Review. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Chen, J.; Yu, M.; Liu, D. Using Circulating Tumor DNA as a Novel Biomarker to Screen and Diagnose Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.M.; Huelster, H.L.; Meeks, J.J.; Faltas, B.M.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Lerner, S.P.; Ross, J.S.; Spiess, P.E.; Grass, G.D.; Jain, R.K.; et al. Circulating and urinary tumour DNA in urothelial carcinoma—Upper tract, lower tract and metastatic disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, T.; Henriksen, T.V.; Christensen, E.; Sharma, S.; Salari, R.; Sethi, H.; Knudsen, M.; Nordentoft, I.K.; Wu, H.-T.; Tin, A.S.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA by Ultradeep Sequencing in Patients With Stages I to III Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; Chabon, J.J.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Newman, A.M.; Stehr, H.; Azad, T.D.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Esfahani, M.S.; Liu, C.L.; Zhou, L.; et al. Early Detection of Molecular Residual Disease in Localized Lung Cancer by Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, D.C.; Sahin, T.K.; Yildirim, H.C.; Aktepe, O.H.; Dizdar, O.; Yalcin, S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 168, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Davarpanah, N.; Banchereau, R.; Szabados, B.E.; Yuen, K.C.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature 2021, 595, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Kawakubo, H.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Hisaoka, K.; Okui, J.; Takeuchi, M.; Aimono, E.; Fukuda, K.; et al. Tumor Burden Monitoring with Circulating Tumor DNA During Treatment in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.Y.; Di Costanzo, G.G.; Terracciano, L.M.; Piscuoglio, S. Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Insights and Outlook. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Chen, H.; Huang, P.; Li, C.-H.; Dong, Z.-H.; Hou, Y.-L. Quantification of plasma hTERT DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma patients by quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction. Clin. Investig. Med. 2011, 34, E238–E244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hua, D.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Du, X.; Zeng, Y. Quantitation of Plasma Circulating DNA Using Quantitative PCR for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2012, 18, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhisa, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Sakaida, I.; Moribe, T.; Fujita, N.; Miura, T.; Tamatsukuri, S.; Ishitsuka, H.; Uchida, K.; Terai, S.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA as a predictive marker for distant metastasis of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, N.; Sakaida, I.; Moribe, T.; Fujita, N.; Miura, T.; Stark, M.; Tamatsukuri, S.; Ishitsuka, H.; Uchida, K.; Terai, S.; et al. Elevated levels of circulating cell-free DNA in the blood of patients with hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 4713–4719. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.K.Y.; Di Costanzo, G.; Tosti, N.; Paradiso, V.; Coto-Llerena, M.; Roscigno, G.; Perrina, V.; Quintavalle, C.; Boldanova, T.; Wieland, S.; et al. Genetic profiling using plasma-derived cell-free DNA in therapy-naïve hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A pilot study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Qin, L.-X.; Tu, H.; Liu, Y.-K.; Zhang, B.-H.; Tang, Z.-Y. The prognostic value of circulating plasma DNA level and its allelic imbalance on chromosome 8p in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 132, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Guo, D.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Sun, Q.; He, Y.; et al. Publication Only Application of Circulating Tumor DNA for Prediction and Surveillance of Tumor Recurrence after Liver Transplantation: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Akamatsu, S.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Kawaoka, T.; Tsuge, M.; Abe, H.; Hayes, C.N.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis for Liver Cancers and Its Usefulness as a Liquid Biopsy. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Esmail, A.; Umoru, G.; Westhart, K.; Abudayyeh, A.; Saharia, A.; Ghobrial, R.M. Immunotherapy as a Neoadjuvant Therapy for a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Pretransplant Setting: A Case Report. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4267–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Zeng, X.; Tang, J.; Liang, Z.; Qi, X.; Huang, L. E16196 Publication Only Circulating Tumor DNA Is a Potential Prognostic Risk Factor of Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated by Liver Transplantation. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Long, G.; Fang, T.; Su, W.; Mi, X.; Zhou, L. The prognostic value of postoperative circulating cell-free DNA in operable hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, A.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yin, Y.; Fu, P.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. Circulating tumor DNA correlates with microvascular invasion and predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, N.; Hüsing-Kabar, A.; Schmidt, H.H.; Cicinnati, V.R.; Beckebaum, S.; Kabar, I. Acute allograft rejection in liver transplant recipients: Incidence, risk factors, treatment success, and impact on graft failure. J. Int. Med Res. 2018, 46, 3979–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitsky, J.; Goldberg, D.; Smith, A.R.; Mansfield, S.A.; Gillespie, B.W.; Merion, R.M.; Lok, A.S.; Levy, G.; Kulik, L.; Abecassis, M.; et al. Acute Rejection Increases Risk of Graft Failure and Death in Recent Liver Transplant Recipients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 584–593.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, M.; Levitsky, J.; Aqel, B.; O’Grady, J.; Hemibach, J.; Rinella, M.; Fung, J.; Ghabril, M.; Thomason, R.; Burra, P.; et al. International Liver Transplantation Society Consensus Statement on Immunosuppression in Liver Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2018, 102, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitsky, J.; O’Leary, J.G.; Asrani, S.; Sharma, P.; Fung, J.; Wiseman, A.; Niemann, C.U. Protecting the Kidney in Liver Transplant Recipients: Practicee-Based Recommendations From the American Society of Transplantation Liver and Intestine Community of Practice. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2532–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestaneh, L.; Alvarez, P.J.; Reaven, N.L.; Funk, S.E.; McGaughey, K.J.; Romero, A.; Brenner, M.S.; Onuigbo, M. All-cause costs increase exponentially with increased chronic kidney disease stage. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, S163–S172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- VanWagner, L.B.; Serper, M.; Kang, R.; Levitsky, J.; Hohmann, S.; Abecassis, M.; Skaro, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Factors Associated With Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Liver Transplantation Among a National Sample. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitsky, J.; Kandpal, M.; Guo, K.; Kleiboeker, S.; Sinha, R.; Abecassis, M. Donor-derived cell-free DNA levels predict graft injury in liver transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 22, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, A.; Kumar, D.; Gupta, G. Donor-derived Cell-free DNA in Solid-organ Transplant Diagnostics: Indications, Limitations, and Future Directions. Transplantation 2021, 105, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielis, E.M.; Ledeganck, K.J.; De Winter, B.Y.; Del Favero, J.; Bosmans, J.-L.; Claas, F.H.J.; Abramowicz, D.; Eikmans, M. Cell-Free DNA: An Upcoming Biomarker in Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, J.S.; Brennan, D.C.; Poggio, E.; Bunnapradist, S.; Langone, A.; Sood, P.; Matas, A.J.; Mannon, R.B.; Mehta, S.; Sharfuddin, A.; et al. Biological Variation of Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA in Renal Transplant Recipients: Clinical Implications. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2017, 2, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Bierau, S.; Balzer, S.; Andag, R.; Kanzow, P.; Schmitz, J.; Gaedcke, J.; Moerer, O.; Slotta, J.E.; Walson, P.; et al. Digital Droplet PCR for Rapid Quantification of Donor DNA in the Circulation of Transplant Recipients as a Potential Universal Biomarker of Graft Injury. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vlaminck, I.; Valantine, H.A.; Snyder, T.M.; Strehl, C.; Cohen, G.; Luikart, H.; Neff, N.F.; Okamoto, J.; Bernstein, D.; Weisshaar, D.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Enables Noninvasive Diagnosis of Heart Transplant Rejection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 241ra77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Oellerich, M.; Schütz, E. A Universal Droplet Digital PCR Approach for Monitoring of Graft Health After Transplantation Using a Preselected SNP Set. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1768, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-I.; Sun, L.-Y.; Zhu, Z.-J. Application of graft-derived cell-free DNA in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency patient after living donor liver transplantation. Medicine 2018, 97, e13843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.I.; Zhu, X.; Xuan, L.; Long, Y.; Mao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, L.; Liang, B.; Scaglia, F.; Choy, K.W.; et al. Analysis of fragment size distribution of cell-free DNA: A potential non-invasive marker to monitor graft damage in living-related liver transplantation for inborn errors of metabolism. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 127, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and Integrative Genomic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 1327–1341.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Furuta, M.; Totoki, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Kato, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Ueno, M.; et al. Whole-genome mutational landscape and characterization of noncoding and structural mutations in liver cancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.R.; Kong, S.-Y.; Im, H.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Yoon, K.-A.; Cho, E.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; et al. Genome-wide copy number alteration and VEGFA amplification of circulating cell-free DNA as a biomarker in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with Sorafenib. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Q.; Ren, W.; Liu, C.; Peng, B.; et al. TP53 R249S mutation detected in circulating tumour DNA is associated with Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with or without hepatectomy. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2834–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Watt, G.P.; Stevenson, H.L.; Calderone, T.L.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; Ye, Y.; Wu, X.; Vierling, J.M.; Beretta, L. Telomerase reverse transcriptase mutations in plasma DNA in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis: Prevalence and risk factors. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Chen, G.; Zeng, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xin, F.; Qiu, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Comprehensive Liquid Profiling of Circulating Tumor DNA and Protein Biomarkers in Long-Term Follow-Up Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5284–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Felden, J.; Craig, A.J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Labgaa, I.; Haber, P.K.; D’avola, D.; Asgharpour, A.; Dieterich, D.; Bonaccorso, A.; Torres-Martin, M.; et al. Mutations in circulating tumor DNA predict primary resistance to systemic therapies in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oversoe, S.K.; Clement, M.S.; Pedersen, M.H.; Weber, B.; Aagaard, N.K.; Villadsen, G.E.; Grønbæk, H.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.J.; Sorensen, B.S.; Kelsen, J. TERT promoter mutated circulating tumor DNA as a biomarker for prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Na, G.-H.; You, Y.-K.; Kim, D.-G. Immunohistochemical markers for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis after liver resection and liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N.; Nishimura, T.; Kaido, T.; Minaga, K.; Yamao, K.; Kamata, K.; Takenaka, M.; Ida, H.; Hagiwara, S.; Minami, Y.; et al. Molecular Scoring of Hepatocellular Carcinoma for Predicting Metastatic Recurrence and Requirements of Systemic Chemotherapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Gassa, A.; Buchner, D.; Alakus, H.; Dong, Q.; Ren, N.; Liu, M.; Odenthal, M.; Stippel, D.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA as an emerging liquid biopsy biomarker for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, N.; Macher, H.C.; Rubio, A.; Jiménez-Arriscado, P.; Bernal-Bellido, C.; Bellido-Díaz, M.L.; Suárez-Artacho, G.; Guerrero, J.M.; Gómez-Bravo, M.A.; Molinero, P. Detection of p53 Mutations in Circulating DNA of Transplanted Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients as a Biomarker of Tumor Recurrence. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 924, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.-Q.; Yuan, C.-H.; Qu, Z.; Guan, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.-B. Liquid Biopsy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Circulating Tumor-Derived Biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 1427849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-B.; Zhong, L.; Teng, M.-J.; Fan, J.-W.; Tang, H.-M.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Qiu, G.-Q.; Peng, Z.-H. Identification of recurrence-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following liver transplantation. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Chen, I.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-J.; Tseng, H.-P.; Huang, K.-T.; Hu, T.-H.; Li, L.-C.; Goto, S.; Cheng, Y.-F.; et al. Circulating exosomal miR-92b: Its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 3250–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Eun, J.W.; Choi, J.-H.; Woo, H.G.; Cho, H.J.; Ahn, H.R.; Suh, C.W.; Baek, G.O.; Cho, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y. MLH1 single-nucleotide variant in circulating tumor DNA predicts overall survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erstad, D.J.; Fuchs, B.C.; Tanabe, K.K. Molecular signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma: A step toward rationally designed cancer therapy. Cancer 2018, 124, 3084–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galun, D.; Mijac, D.; Filipovic, A.; Bogdanovic, A.; Zivanovic, M.; Masulovic, D. Precision Medicine for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical Perspective. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Atyah, M.; Zhou, C.; Ren, N. Prospects and challenges of circulating tumor DNA in precision medicine of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-X.; Zhu, Q.-G.; Zhang, S.-M.; Guan, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.-Y.; Ren, W.-L.; Chen, X.-M.; Zhao, J.; et al. Precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma: Driver mutations and targeted therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55715–55730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Shinagare, A.B.; Rennke, H.G.; Ghai, S.; Lorch, J.H.; Ott, P.A.; Rahma, O.E. The Safety and Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Transplant Recipients: A Case Series and Systematic Review of Literature. Oncologist 2020, 25, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, N.; Renzulli, M. The Synergistic Effect of Interventional Locoregional Treatments and Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondetti, P.; Saggiante, L.; Ierardi, A.M.; Iavarone, M.; Sangiovanni, A.; Pesapane, F.; Fumarola, E.M.; Lampertico, P.; Carrafiello, G. Interventional Radiology Image-Guided Locoregional Therapies (LRTs) and Immunotherapy for the Treatment of HCC. Cancers 2021, 13, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, A.S.; McCall, J.L.; Ameratunga, R.; Howden, B.; Yeong, M.; Benjamin, C.D.; Hess, D.; Peach, R.; Munn, S.R. Costimulatory blockade prevents early rejection, promotes lymphocyte apoptosis, and inhibits the upregulation of intragraft interleukin-6 in an orthotopic liver transplant model in the rat. Liver Transplant. 2002, 8, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labgaa, I.; Villanueva, A.; Dormond, O.; Demartines, N.; Melloul, E. The Role of Liquid Biopsy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognostication. Cancers 2021, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilic, B.; Offermanns, S. Intravascular Survival and Extravasation of Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocan, T.; Simão, A.L.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Słomka, A.; Wang, B.; Strassburg, C.; Wöhler, A.; Willms, A.G.; Kornek, M. Liquid Biopsies in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Are We Winning? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Ou, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Z. Clinical value of circulating tumor cells for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e22242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, F.; Qi, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q. Circulating Tumor Cells for Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 607150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, C.M.; Hou, S.; Winograd, P.; Segel, N.H.; Li, Q.W.; Zhu, Y.; Sadeghi, S.; Finn, R.S.; Ganapathy, E.; Song, M.; et al. A novel multimarker assay for the phenotypic profiling of circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2018, 24, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Krech, T.; Ewald, F.; Nashan, B.; Pantel, K.; Lohse, A.W.; Riethdorf, S.; Wege, H. Circulating tumor cells as liquid biomarker for high HCC recurrence risk after curative liver resection. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89978–89987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, W.-S.; Zhu, X.-L.; Ni, C.-F. High Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule–Positive Circulating Tumor Cell Count Predicts Poor Survival of Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimir, M.; Ma, Y.; Jeffreys, S.A.; Opperman, T.; Young, F.; Khan, T.; Ding, P.; Chua, W.; Balakrishnar, B.; Cooper, A.; et al. Detection of AR-V7 in Liquid Biopsies of Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients: A Comparison of AR-V7 Analysis in Circulating Tumor Cells, Circulating Tumor RNA and Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Iinuma, H.; Wada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Minezaki, S.; Kainuma, M.; Shibuya, M.; Miura, F.; Sano, K. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-4525, microRNA-451a and microRNA-21 in portal vein blood is a high-sensitive liquid biomarker for the selection of high-risk pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2019, 26, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, H.; Mi, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, H.; Rong, P.; Liu, D. Nanozyme-assisted sensitive profiling of exosomal proteins for rapid cancer diagnosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9303–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.-Q.; Yang, X.-W.; Chen, Y.-B.; Zhang, D.-W.; Jiang, X.-F.; Xue, P. Correction to: Exosomal miR-21 regulates the TETs/PTENp1/PTEN pathway to promote hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Lee, Y.-T.; Zhang, R.Y.; Kao, R.; Teng, P.-C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.J.; Smalley, M.; Chen, P.-J.; et al. Purification of HCC-specific extracellular vesicles on nanosubstrates for early HCC detection by digital scoring. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Weigelt, B.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Going with the Flow: From Circulating Tumor Cells to DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 207ps14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczynski, G.T.; Laus, A.C.; dos Reis, M.B.; Reis, R.M.; Vazquez, V.D.L. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) detection is associated with shorter progression-free survival in advanced melanoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, J.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Paweletz, C.P.; Camidge, D.R.; Heymach, J.V.; Solit, D.B.; Johnson, B.E. Realizing the Potential of Plasma Genotyping in an Age of Genotype-Directed Therapies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 106, dju214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelizzaro, F.; Cardin, R.; Penzo, B.; Pinto, E.; Vitale, A.; Cillo, U.; Russo, F.P.; Farinati, F. Liquid Biopsy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Where Are We Now? Cancers 2021, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikanjam, M.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. Liquid biopsy: Current technology and clinical applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.N.; Nisar, S.; Masoodi, T.; Singh, M.; Rizwan, A.; Hashem, S.; El-Rifai, W.; Bedognetti, D.; Batra, S.K.; Haris, M.; et al. Liquid biopsy: A step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Venesio, T.; Marsoni, S.; Seoane, J.; Dive, C.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kopetz, S.; Corcoran, R.; Siu, L.; et al. How liquid biopsies can change clinical practice in oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, I.; Ribeiro, I.P.; Jorge, J.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Melo, J.B.; Carreira, I.M. Liquid Biopsies: Applications for Cancer Diagnosis and Monitoring. Genes 2021, 12, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzi, J.; Hoff, C.O.; Ferreira, R.; Glehn-Ponsirenas, R.; Selvaggi, G.; Tekin, A.; O’Brien, C.B.; Feun, L.; Vianna, R.; Abreu, P. Cell-Free DNA as a Surveillance Tool for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Liver Transplant. Cancers 2023, 15, 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123165
Manzi J, Hoff CO, Ferreira R, Glehn-Ponsirenas R, Selvaggi G, Tekin A, O’Brien CB, Feun L, Vianna R, Abreu P. Cell-Free DNA as a Surveillance Tool for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Liver Transplant. Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123165
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzi, Joao, Camilla O. Hoff, Raphaella Ferreira, Renata Glehn-Ponsirenas, Gennaro Selvaggi, Akin Tekin, Christopher B. O’Brien, Lynn Feun, Rodrigo Vianna, and Phillipe Abreu. 2023. "Cell-Free DNA as a Surveillance Tool for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Liver Transplant" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123165
APA StyleManzi, J., Hoff, C. O., Ferreira, R., Glehn-Ponsirenas, R., Selvaggi, G., Tekin, A., O’Brien, C. B., Feun, L., Vianna, R., & Abreu, P. (2023). Cell-Free DNA as a Surveillance Tool for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Liver Transplant. Cancers, 15(12), 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123165




