Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
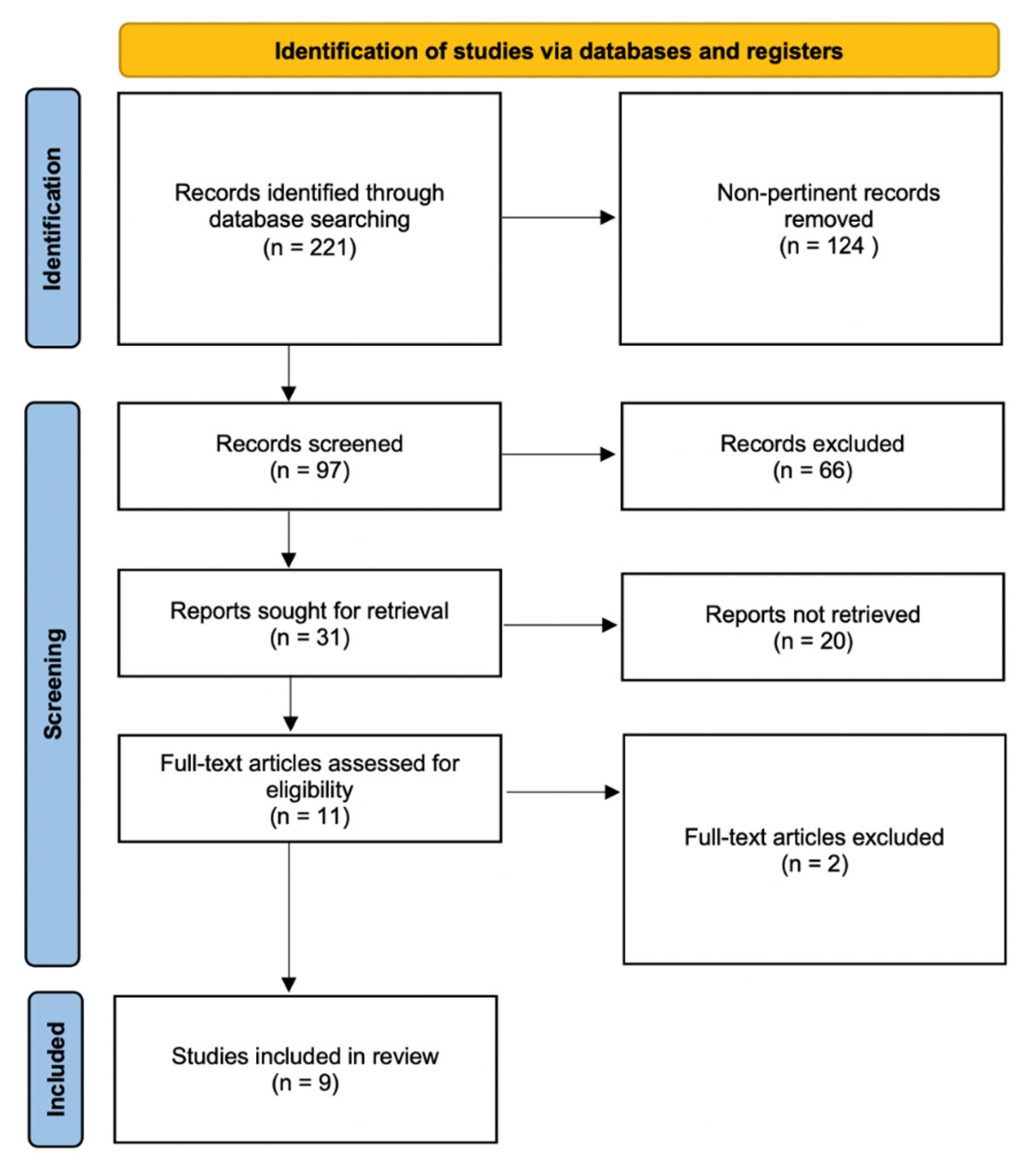
2.1. Literature Search Methodology
2.2. Selection Process
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Outcome Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
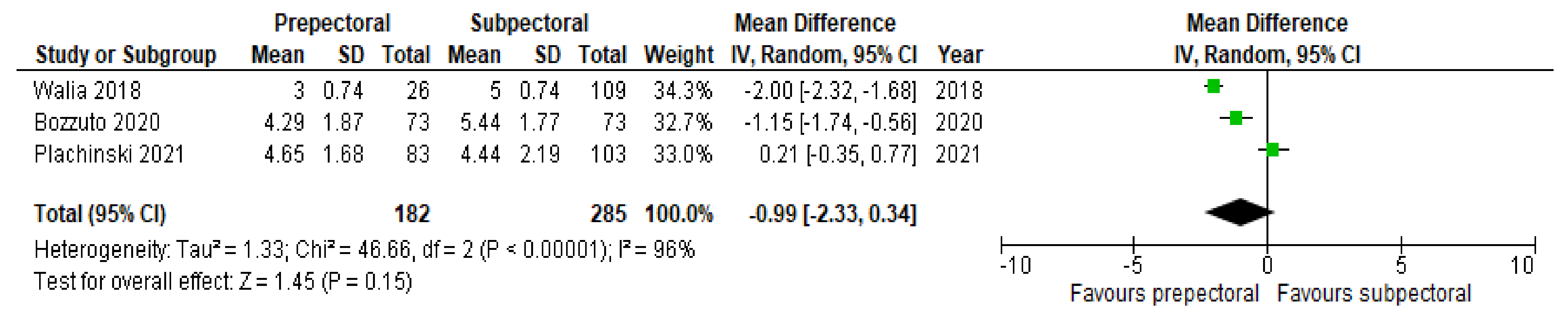
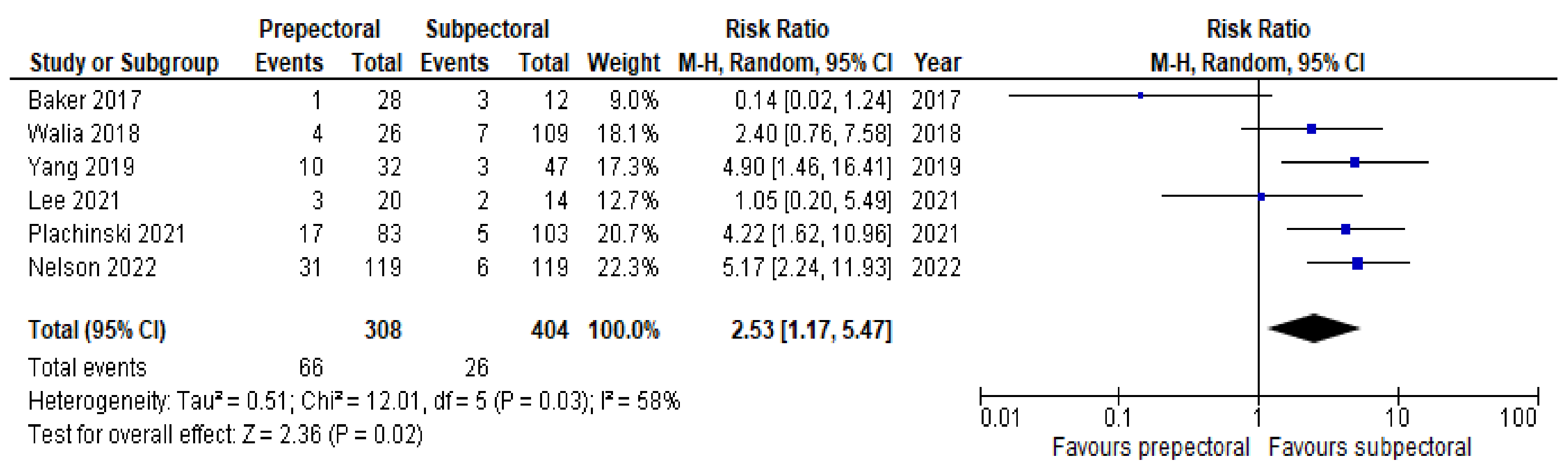
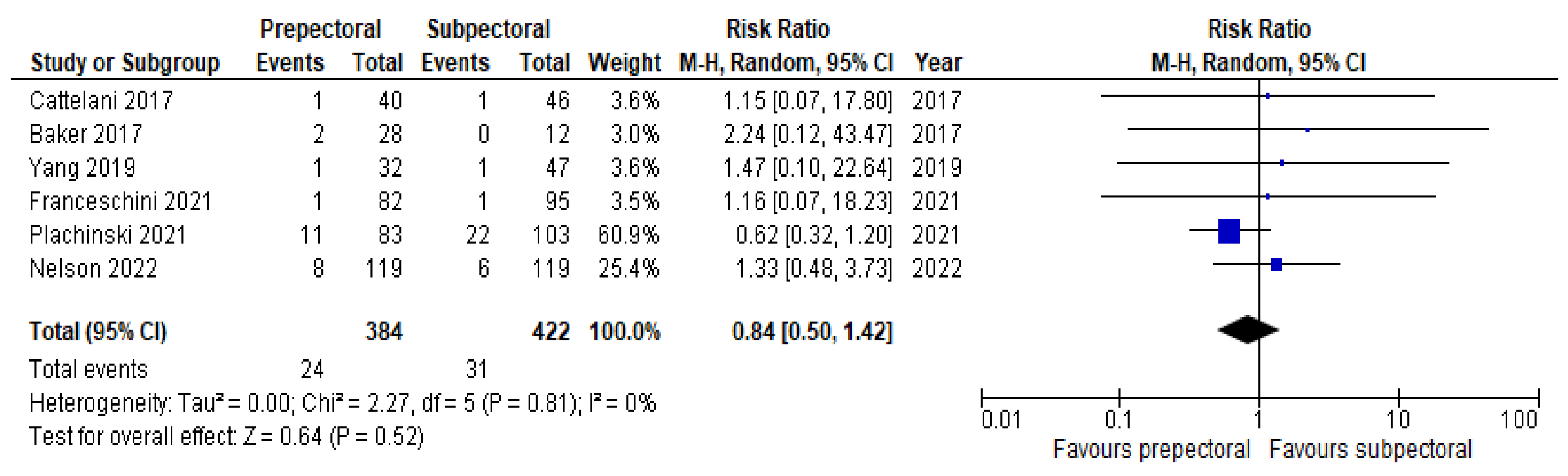
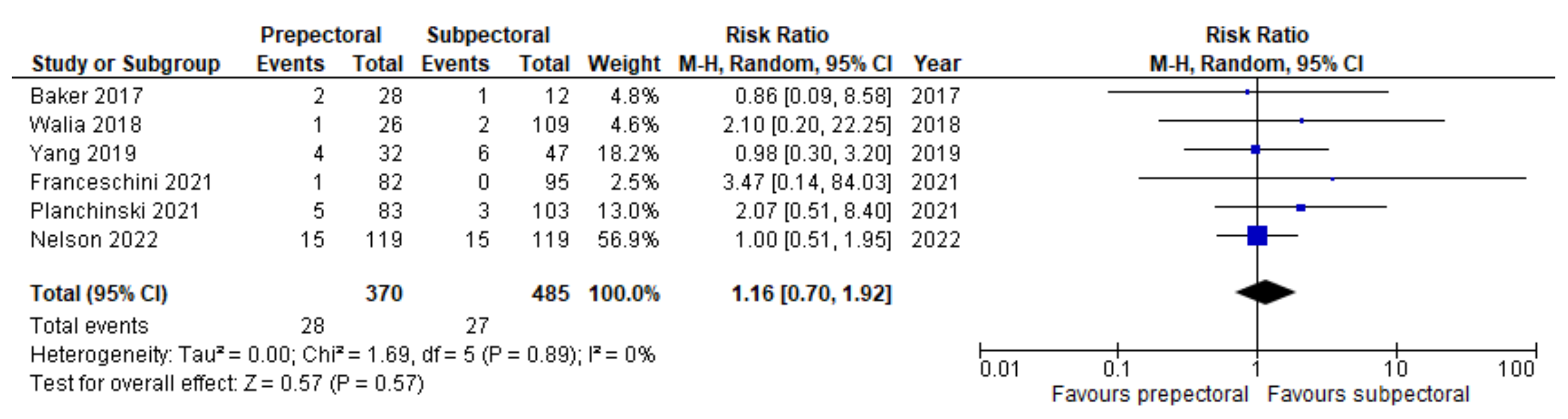
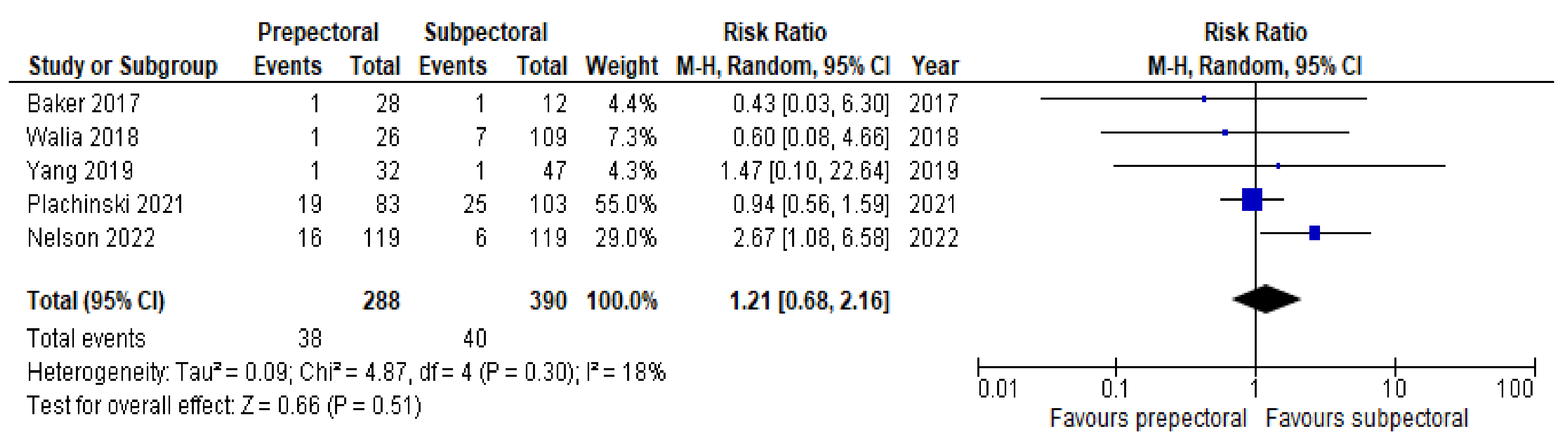
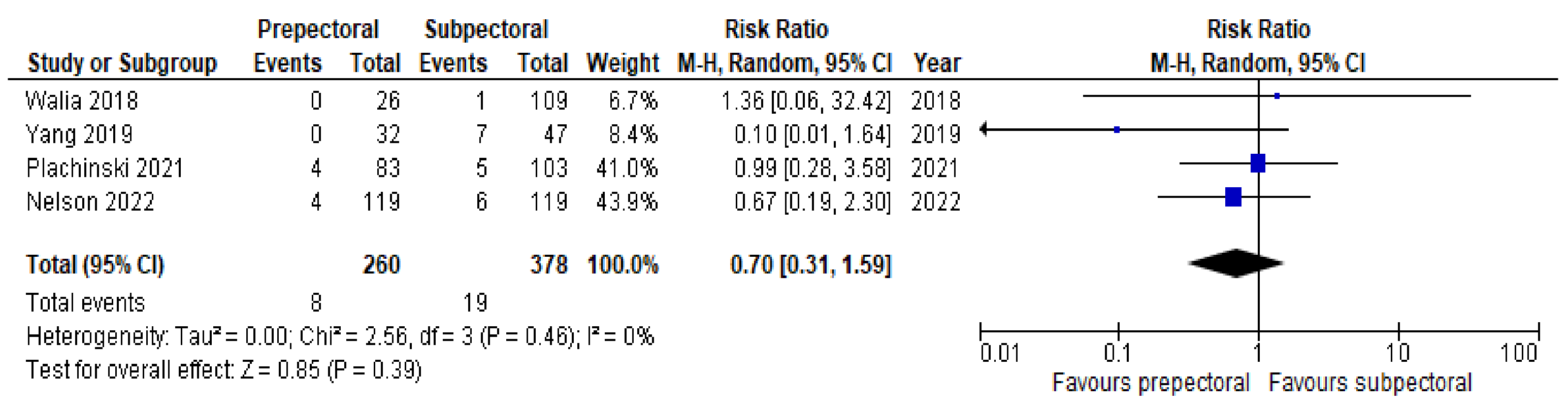
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2021 WHO Statistics Report—Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Pusic, A.L.; Matros, E.; Fine, N.; Buchel, E.; Gordillo, G.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Kim, H.L.; Qi, J.; Albornoz, C.; Klassen, A.F.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes 1 year after immediate breast reconstruction: Results of the Mastectomy Reconstruction Outcomes Consortium Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Li, S. A retrospective study of primary breast augmentation: Recovery period, complications and patient satisfaction. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18737–18743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leff, D.R.; Bottle, A.; Mayer, E.; Patten, D.K.; Rao, C.; Aylin, P.; Hadjiminas, D.J.; Athanasiou, T.; Darzi, A.; Gui, G. Trends in immediate post- mastectomy breast reconstruction in the United Kingdom. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyserkani, N.M.; Jorgensen, M.G.; Tabatabaeifar, S.; Damsgaard, T.; Sorensen, J.A. Autologous versus implant-based breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Breast-Q patient-reported outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2020, 73, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.E.; Irons, G.B., Jr.; Arnold, P.G. The case for submuscular implantation of prostheses in reconstructive breast surgery. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1980, 5, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Mohan, A.T.; Abdelsattar, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Vijayasekaran, A.; Hwang, S.M.; Tran, N.V.; Saint-Cyr, M. Comparison of subcutaneous versus submuscular expander placement in the first stage of immediate breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 69, e77–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, R.P.; Kahn, R.A.; Lash, H.; Maser, M.R.; Apfelberg, D.B.; Laub, D.R. Breast reconstruction following mastectomy: A comparison of submuscular and subcutaneous techniques. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1981, 67, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenker, J.D.; Bueno, R.A.; Ricketson, G.; Lynch, J.B. Loss of silicone implants after subcutaneous mastectomy and reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1978, 62, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical Aspects of the Analysis of Data from Retrospective Studies of Disease. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.G.; Irri, R.; McCallum, V.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Murphy, J.; Harvey, J.R. A Prospective Comparison of Short-Term Outcomes of Subpectoral and Prepectoral Strattice-Based Immediate Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattelani, L.; Polotto, S.; Arcuri, M.F.; Pedrazzi, G.; Linguadoca, C.; Bonati, E. One-step prepectoral breast reconstruction with dermal matrix-covered implant compared to submuscular implantation: Functional and cost evaluation. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e703–e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, G.S.; Aston, J.; Bello, R.; Mackert, G.A.; Pedreira, R.A.; Cho, B.H.; Carl, H.M.; Rada, E.M.; Rosson, G.D.; Sacks, J.M. Prepectoral versus subpectoral tissue expander placement: A clinical and quality of life outcomes study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Global. Open. 2018, 6, e1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.A.; Hwang, E. Considerations for patient selection: Prepectoral versus subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2019, 46, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, L.M.; Bartholomew, A.; Tung, S.; Sosin, M.; Tambar, S.; Cox, S.; Perez-Alvarez, I.M.; King, C.A.; Chan, M.C.; Pittman, T.A.; et al. Decreased postoperative pain and opioid use following prepectoral versus subpectoral breast reconstruction after mastectomy: A retrospective cohort study: Pain after pre- versus subpectoral reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2021, 74, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, G.; Scardina, L.; Di Leone, A.; Terribile, D.A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Magno, S.; D’Archi, S.; Franco, A.; Mason, E.J.; Carnassale, B.; et al. Immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction after nipple-sparing mastectomy: Traditional subpectoral technique versus direct-to-implant prepectoral reconstruction without acellular dermal matrix. J. Pers Med. 2021, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, E.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Park, H.Y.; Yang, J.D.; Jung, T.-D. A prospective comparison study of early functional outcomes after implant-based breast reconstruction: Subpectoral versus prepectoral technique. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 2520–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachinski, S.J.; Boehm, L.M.; Adamson, K.A.; LoGiudice, J.A.; Doren, E.L. Comparative analysis of prepectoral versus subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 27, e3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.A.; Shamsunder, M.G.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Polanco, T.O.; Matros, E.; Corridi, M.R.; Mehrara, B.J.; Allen, R.J., Jr.; Dayan, J.H.; Disa, J.J. Prepectoral and subpectoral tissue expander-based breast reconstruction: A propensity-matched analysis of 90-day clinical and health-related quality-of-life outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 607e–616e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.S.; Wallace, A.M.; Lee, J.; Dobke, M.K. Pain after breast surgery: A survey of 282 women. Pain 1996, 66, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelu, N.; Schreck, M.; Lopez, J.; Kodumudi, G.; Narayan, D. Pain after mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland-Halperin, L.R.; Yemc, L.; Emery, E.; Collins, C.; Liu, C.; Mesbahi, A.N.; Venturi, M.L. Evaluating postoperative narcotic use in prepectoral versus dual-plane breast reconstruction following mastectomy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, C.V.; Dassoulas, K.R.; Thuman, J.; Campbell, C.A. Early functional outcomes after prepectoral breast reconstruction: A case-matched cohort Study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2019, 82, S399–S403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.C.; Darnall, B.D.; Baker, L.C.; Mackey, S. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Chronic Opioid Use Among Opioid-Naive Patients in the Postoperative Period. JAMA Intern Med. 2016, 176, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.; Sigalove, S.; Sigalove, N.M.; Storm-Dickerson, T.L.; Rice, J.; Pope, N.; Maxwell, G.P. Prepectoral Revision Breast Reconstruction for Treatment of Implant-Associated Animation Deformity: A Review of 102 Reconstructions. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salibian, A.A.; Frey, J.D.; Choi, M.; Karp, N.S. Subcutaneous implant-based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix/mesh: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Global. Open 2016, 4, e1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, F.; Dravet, F.; Classe, J.M.; Campion, L.; François, T.; Labbe, D.; Robard, S.; Theard, J.L.; Pioud, R. Postoperative care and patient satisfaction after ambulatory surgery for breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 31, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breast-Q user’s Manual, Version 2.0. 2015. Available online: www.breast-Q.org (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Nahabedian, M. Current approaches to prepectoral breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Yu, N.; Huang, J.; Long, X. Prepectoral Versus Subpectoral Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Meta-analysis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 85, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion | Exclusion | |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Adult patients who underwent IBR following mastectomy for treatment or prevention of breast cancer | Non-oncologic-related breast augmentations |
| Intervention | Prepectoral reconstruction with or without ADM | Non-implant-based breast augmentations |
| Comparator | Subpectoral reconstruction | Dual-plane reconstruction |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: pain Secondary outcomes: patient satisfaction, seroma, implant loss, skin necrosis, wound infection, hematoma | Primary outcome not assessed in study |
| Study design | Prospective and retrospective comparative studies | Non-English articles, meta-analyses, reviews, case reports, letters to the editor, isolated abstracts |
| Author | Year | Total Patients | PP | SP | Mean Age PP (y) | Mean Age SP (y) | Mean BMI PP | Mean BMI SP | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baker et al. [14] | 2018 | 40 | 28 | 12 | 47.5 | 48 | 26.0 | 23.4 | *** |
| Cattelani et al. [15] | 2018 | 84 | 39 | 45 | 52.9 | 52.3 | 24.9 | 26.1 | 12 mo |
| Walia et al. [16] | 2018 | 135 | 26 | 109 | 51.4 | 48.6 | 24.3 | 26.1 | 30–60 d |
| Yang et al. [17] | 2019 | 79 | 32 | 47 | 48.9 | 46.4 | 23.5 | 21.3 | 52 mo |
| Bozzuto et al. [18] | 2020 | 146 | 73 | 73 | 49 | 49 | 23.7 | 23.2 | *** |
| Franceschini et al. [19] | 2021 | 177 | 82 | 95 | 47 | 44 | 23.9 | 24.8 | 18 mo |
| Lee et al. [20] | 2021 | 34 | 20 | 14 | 46.2 | 46.8 | 20.9 | 21.3 | *** |
| Plachinski et al. [21] | 2021 | 186 | 83 | 103 | 47.9 | 49.9 | 28.1 | 26.1 | 19 +/− 11 mo |
| Nelson et al. [22] | 2022 | 238 | 119 | 119 | 50.3 | 48 | 26.4 | 26.2 | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mégevand, V.; Scampa, M.; McEvoy, H.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174223
Mégevand V, Scampa M, McEvoy H, Kalbermatten DF, Oranges CM. Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174223
Chicago/Turabian StyleMégevand, Vladimir, Matteo Scampa, Helen McEvoy, Daniel F. Kalbermatten, and Carlo M. Oranges. 2022. "Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174223
APA StyleMégevand, V., Scampa, M., McEvoy, H., Kalbermatten, D. F., & Oranges, C. M. (2022). Comparison of Outcomes Following Prepectoral and Subpectoral Implants for Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 14(17), 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174223