Advancements in Neuroimaging to Unravel Biological and Molecular Features of Brain Tumors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
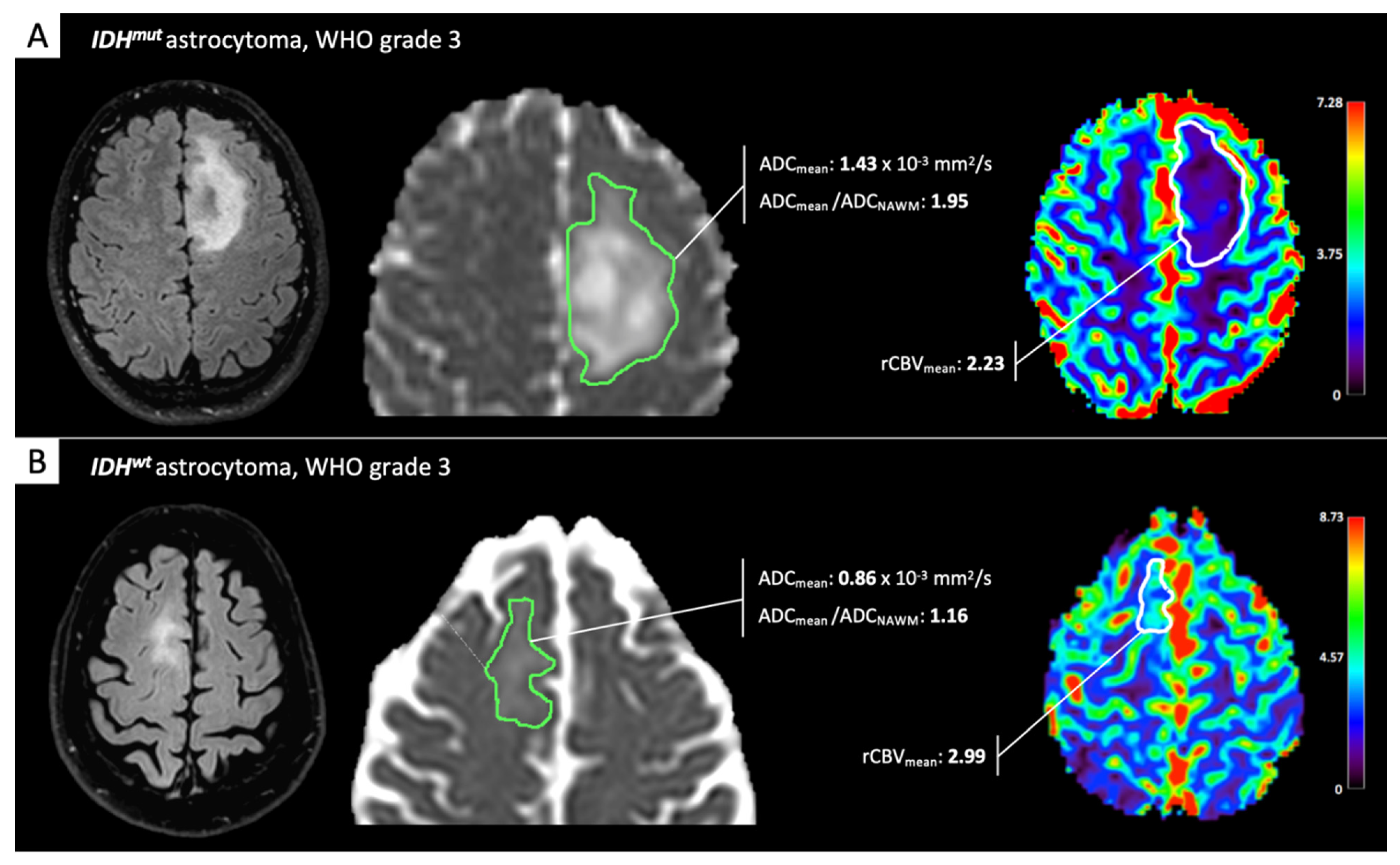
2. IDH-Status Prediction in Gliomas through Perfusion and Diffusion Assessment
3. Spectroscopy Advancements: 2-Hydroxyglutarate Direct Detection to Demonstrate IDH-Mutation
4. 1p/19q Codeletion Determination for Oligodendrogliomas
5. Additional Molecular Markers in GBM: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Modifications and O6-Methylguanine DNA Methyltransferase (MGMT) Methylation
6. Novel GBM-Defining Genotypes: EGFR Amplification and Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) Mutation in IDHwt-Gliomas
7. Diffuse Midline Gliomas H3K27M-Mutated
8. Medulloblastomas
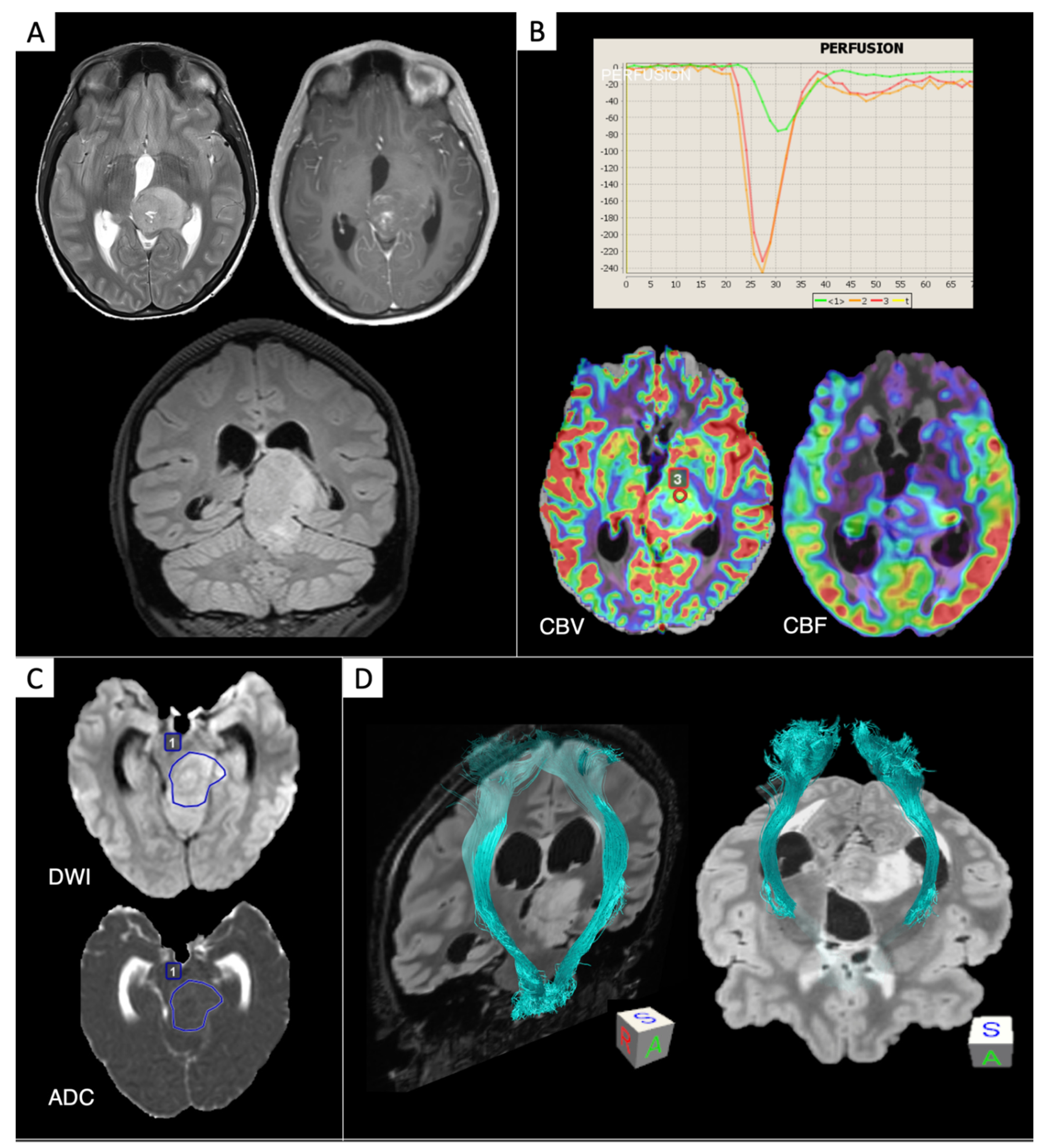
9. DTI and DKI for Glioma Assessment
10. Biophysical Models: Toward Microstructural dMRI
11. BOLD Imaging to Evaluate Tumor Microvascularization and Oxygen Metabolism
12. Frontiers of Ultra-High-Field Imaging
13. Contributions from Artificial Intelligence
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabouret, E.; Network, F.P.; Nguyen, A.T.; Dehais, C.; Carpentier, C.; Ducray, F.; Idbaih, A.; Mokhtari, K.; Jouvet, A.; Uro-Coste, E.; et al. Prognostic impact of the 2016 WHO classification of diffuse gliomas in the French POLA cohort. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.-J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Buczkowicz, P.; Rakopoulos, P.; Liu, X.-Y.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; Albrecht, S.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Letourneau, L.; et al. K27M mutation in histone H3.3 defines clinically and biologically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gu, Y.; Basu, S.; Berglund, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Forster, K.; Aerts, H.J.; Dekker, A.; Fenstermacher, D.; et al. Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; Van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Origgi, D.; Fanciullo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Bellomi, M. Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.; Priya, S.; Bathla, G. Texture analysis in cerebral gliomas: A review of the literature. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulakbaşı, N.; Paksoy, Y. Advanced imaging in adult diffusely infiltrating low-grade gliomas. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, K.; Ott, G.A.; Lai, A.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Pope, W.B.; Yong, W.H.; Liau, L.M.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M. Perfusion and diffusion MRI signatures in histologic and genetic subtypes of WHO grade II–III diffuse gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 134, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Jain, R.; Radmanesh, A.; Poisson, L.; Guo, W.Y.; Zagzag, D.; Snuderl, M.; Placantonakis, D.G.; Golfinos, J.; Chi, A. predicting genotype and survival in glioma using standard clinical MR imaging apparent diffusion coefficient images: A pilot study from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahm, V.; Boxheimer, L.; Bruehlmeier, M.; Berberat, J.; Nitzsche, E.U.; Remonda, L.; Roelcke, U. Focal changes in diffusivity on apparent diffusion coefficient MR imaging and amino acid uptake on PET do not colocalize in nonenhancing Low-grade gliomas. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Tong, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.-G. Clinical Applications of contrast-enhanced perfusion MRI Techniques in Gliomas: Recent advances and current challenges. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2017, 2017, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D. Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.H.; Helpern, J.A.; Ramani, A.; Lu, H.; Kaczynski, K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelescu, I.O.; Palombo, M.; Bagnato, F.; Schilling, K.G. Challenges for biophysical modeling of microstructure. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 344, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Zaharchuk, G.; Thomas, D.L.; Lövblad, K.-O.; Barkhof, F.; Golay, X. Arterial spin labeling perfusion of the brain: Emerging clinical applications. Radiology 2016, 281, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Ganji, S.K.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Rakheja, D.; Kovacs, Z.; Yang, X.-L.; Mashimo, T.; Raisanen, J.M.; Marin-Valencia, I.; et al. 2-hydroxyglutarate detection by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in IDH-mutated patients with gliomas. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lang, F.; Chou, F.-J.; Zaghloul, K.A.; Yang, C. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in glioma: Genetics, biochemistry, and clinical indications. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Barresi, V.; Castellano, A.; Tabouret, E.; Pasqualetti, F.; Salvalaggio, A.; Cerretti, G.; Caccese, M.; Padovan, M.; Zagonel, V.; et al. Clinical management of diffuse low-grade gliomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Shang, E.; Siegelin, M.D. Novel IDH1-targeted glioma therapies. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. Imaging prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation in patients with glioma: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kickingereder, P.; Sahm, F.; Radbruch, A.; Wick, W.; Heiland, S.; Von Deimling, A.; Bendszus, M.; Wiestler, B. IDH mutation status is associated with a distinct hypoxia/angiogenesis transcriptome signature which is non-invasively predictable with rCBV imaging in human glioma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Park, J.E.; Jo, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Advanced imaging parameters improve the prediction of diffuse lower-grade gliomas subtype, IDH mutant with no 1p19q codeletion: Added value to the T2/FLAIR mismatch sign. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Yang, X.; She, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D. Noninvasive assessment of IDH mutational status in World Health Organization grade II and III astrocytomas using DWI and DSC-PWI combined with conventional MR imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, J.; Okuchi, S.; Wastling, S.; Al Busaidi, A.; Almossawi, O.; Mbatha, W.; Brandner, S.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Koç, A.M.; Mancini, L.; et al. World Health Organization grade II/III glioma molecular status: Prediction by MRI morphologic features and apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 2020, 296, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thust, S.; Hassanein, S.; Bisdas, S.; Rees, J.H.; Hyare, H.; Maynard, J.A.; Brandner, S.; Tur, C.; Jäger, H.R.; Yousry, T.A.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient for molecular subtyping of non-gadolinium-enhancing WHO grade II/III glioma: Volumetric segmentation versus two-dimensional region of interest analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, E.; Dutta, S.W.; Feng, X.; Tustison, N.J.; Batchala, P.P.; Schiff, D.; Lopes, M.B.; Jain, R.; Druzgal, T.J.; Mukherjee, S.; et al. Automated apparent diffusion coefficient analysis for genotype prediction in lower grade glioma: Association with the T2-FLAIR mismatch sign. J. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-W.; Lyu, G.-W.; He, W.-J.; Lei, Y.; Lin, F.; Wang, M.-Z.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.-H.; Feng, Y.-N.; Yang, J.-H. DSC and DCE histogram analyses of glioma biomarkers, including IDH, MGMT, and TERT, on differentiation and survival. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, e263–e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.-E.; Yun, T.; Hwang, I.; Hong, E.K.; Kang, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.-K.; Won, J.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Sohn, C.-H. Arterial spin labeling perfusion-weighted imaging aids in prediction of molecular biomarkers and survival in glioblastomas. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendle, C.; Hempel, J.-M.; Schittenhelm, J.; Skardelly, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Bender, B.; Ernemann, U.; Klose, U. Glioma grading and determination of IDH mutation status and ATRX loss by DCE and ASL perfusion. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2017, 28, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Zhang, H.; She, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, Z.; Cao, D. IDH genotypes differentiation in glioblastomas using DWI and DSC-PWI in the enhancing and peri-enhancing region. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Alger, J.; Kim, H.; Brown, M.; Okada, K.; Pope, W.; Goldin, J. Between-scanner and between-visit variation in normal white matter apparent diffusion coefficient values in the setting of a multi-center clinical trial. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2015, 26, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merhemic, Z.; Imširović, B.; Bilalovic, N.; Stojanov, D.; Boban, J.; Thurnher, M.M. Apparent diffusion coefficient reproducibility in brain tumors measured on 1.5 and 3 T clinical scanners: A pilot study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 108, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, K.M.; Boxerman, J.; Kalnin, A.; Kaufmann, T.; Shiroishi, M.; Wintermark, M. ASFNR recommendations for clinical performance of MR dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion imaging of the brain. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, e41–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxerman, J.L.; Quarles, C.C.; Hu, L.S.; Erickson, B.J.; Gerstner, E.R.; Smits, M.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Barboriak, D.P.; Huang, R.H.; Wick, W.; et al. Consensus recommendations for a dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI protocol for use in high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thust, S.C.; Heiland, S.; Falini, A.; Jäger, H.R.; Waldman, A.D.; Sundgren, P.C.; Godi, C.; Katsaros, V.K.; Ramos, A.; Bargallo, N.; et al. Glioma imaging in Europe: A survey of 220 centres and recommendations for best clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3306–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Macdonald, D.R.; Reardon, D.A.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Sorensen, A.G.; Galanis, E.; DeGroot, J.; Wick, W.; Gilbert, M.R.; Lassman, A.B.; et al. Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: Response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, D.; Craig, P.; Godoy, L.F.; Leite, C.D.C.; Policeni, B. Response assessment in neuro-oncology criteria for gliomas: Practical approach using conventional and advanced techniques. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 41, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. 2-Hydroxyglutarate MR spectroscopy for prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant glioma: A systemic review and meta-analysis using individual patient data. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Raisanen, J.M.; Ganji, S.K.; Zhang, S.; McNeil, S.S.; An, Z.; Madan, A.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Vemireddy, V.; Sheppard, C.A.; et al. Prospective longitudinal analysis of 2-Hydroxyglutarate magnetic resonance spectroscopy identifies broad clinical utility for the management of patients with IDH-mutant glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4030–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, A.; Choi, C.; Mickey, B.; Maher, E.A.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Sangill, R.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.; Lukacova, S.; Østergaard, L.; Von Oettingen, G. Noninvasive assessment of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation status in cerebral gliomas by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a clinical setting. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronesi, O.C.; Loebel, F.; Bogner, W.; Marjańska, M.; Heiden, M.G.V.; Iafrate, A.J.; Dietrich, J.; Batchelor, T.T.; Gerstner, E.R.; Kaelin, W.G.; et al. Treatment response assessment in IDH-mutant glioma patients by noninvasive 3D functional spectroscopic mapping of 2-Hydroxyglutarate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronesi, O.C.; Arrillaga-Romany, I.C.; Ly, K.I.; Bogner, W.; Ratai, E.M.; Reitz, K.; Iafrate, A.J.; Dietrich, J.; Gerstner, E.R.; Chi, A.S.; et al. Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, M.I.; Young, R.J.; Rubel, J.; Rosenblum, M.; Tisnado, J.; Briggs, S.; Arevalo-Perez, J.; Cross, J.R.; Campos, C.; Straley, K.; et al. Integration of 2-hydroxyglutarate-proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy into clinical practice for disease monitoring in isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Varghese, J.; Jain, R. Adult glioma WHO classification update, genomics, and imaging:What the radiologists need to know. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 29, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzoli, F.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Capelle, L.; Ottolenghi, C.; Valabrègue, R.; Deelchand, D.; Bielle, F.; Villa, C.; Baussart, B.; Lehéricy, S.; et al. Highly specific determination of IDH status using edited in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Melkus, G.; Taccone, M.; Moldovan, I.D.; Ghinda, D.; Gotfrit, R.; Torres, C.H.; Zakhari, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Woulfe, J.; et al. Preoperative determination of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation in gliomas using spectral editing MRS: A Prospective study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir, U.E.; Larkin, S.J.; De Pennington, N.; Voets, N.L.; Plaha, P.; Stacey, R.; Al-Qahtani, K.; McCullagh, O.J.S.; Schofield, C.J.; Clare, S.; et al. Noninvasive quantification of 2-hydroxyglutarate in human gliomas with IDH1 and IDH2 mutations. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, B.; Priesterbach-Ackley, L.; Petersen, J.; Wesseling, P. Molecular pathology of tumors of the central nervous system. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, M. Imaging of oligodendroglioma. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latysheva, A.; Emblem, K.E.; Brandal, P.; Vik-Mo, E.O.; Pahnke, J.; Røysland, K.; Hald, J.K.; Server, A. Dynamic susceptibility contrast and diffusion MR imaging identify oligodendroglioma as defined by the 2016 WHO classification for brain tumors: Histogram analysis approach. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branzoli, F.; Pontoizeau, C.; Tchara, L.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Kamoun, A.; Deelchand, D.K.; Valabrègue, R.; Lehéricy, S.; Sanson, M.; Ottolenghi, C.; et al. Cystathionine as a marker for 1p/19q codeleted gliomas by in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazerooni, A.F.; Bakas, S.; Rad, H.S.; Davatzikos, C. Imaging signatures of glioblastoma molecular characteristics: A radiogenomics review. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Pisapia, J.; Martinez-lage, M.; Rathore, S.; Dahmane, N.; Rourke, D.M.O. In Vivo detection of EG-FRvIII in glioblastoma via perfusion magnetic resonance imaging signature consistent with deep peritumoral infiltration: The Φ index. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 23, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkó, Z.; Nagy, B.; Klekner, Á.; Virga, J. Novel molecular markers in glioblastoma—Benefits of liquid biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimberger, A.B.; Hlatky, R.; Suki, D.; Yang, D.; Weinberg, J.; Gilbert, M.; Sawaya, R.; Aldape, K. Prognostic effect of epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1462–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegal, T. Clinical impact of molecular biomarkers in gliomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J.; Gupta, A.; Shah, A.; Graber, J.; Schweitzer, A.; Prager, A.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huse, J.; Omuro, A. Potential role of preoperative conventional MRI including diffusion measurements in assessing epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification status in patients with glioblastoma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 13, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Young, R.J.; Shah, A.D.; Schweitzer, A.D.; Graber, J.J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huse, J.; Omuro, A.M.P. Pretreatment dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI perfusion in glioblastoma: Prediction of EGFR gene amplification. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2015, 25, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Perez, J.; Thomas, A.A.; Kaley, T.J.; Lyo, J.K.; Peck, K.K.; Holodny, A.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Young, R.J. T1-weighted dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI as a noninvasive biomarker of epidermal growth factor receptor VIII status. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, H.; Bakas, S.; Pisapia, J.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Rozycki, M.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Dahmane, N.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Davatzikos, C. In vivoevaluation of EGFRvIII mutation in primary glioblastoma patients via complex multiparametric MRI signature. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; De Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Roh, H.G.; Lim, S.D.; Koh, Y.-C. Imaging parameters of high grade gliomas in relation to the MGMT promoter methylation status: The CT, diffusion tensor imaging, and perfusion MR imaging. Neuroradiology 2012, 54, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Calabria, L.F.; Tavanti, F.; Minniti, G.; Rossi-Espagnet, M.C.; Coppola, V.; Pugliese, S.; Guida, D.; Francione, G.; Colonnese, C.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient obtained by magnetic resonance imaging as a prognostic marker in glioblastomas: Correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, L.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, J.W.; Yi, K.S.; Lee, W.J.; Yoon, T.J.; Song, S.W.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient values measured by diffusion MRI and MGMT promoter methylation semiquantitatively analyzed with MS-MLPA in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, W.; Lai, A.; Mehta, R.; Kim, H.J.; Qiao, J.; Young, J.; Xue, X.; Goldin, J.; Brown, M.S.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; et al. Apparent Diffusion coefficient histogram analysis stratifies progression-free survival in newly diagnosed bevacizumab-treated glioblastoma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.S.; Shin, N.-Y.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S.-K. Prediction of methylguanine methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance and diffusion tensor imaging. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle-Thiele, D.; Day, B.W.; Stringer, B.W.; Fay, M.; Martin, J.; Jeffree, R.L.; Thomas, P.; Bell, C.; Salvado, O.; Gal, Y.; et al. Using the apparent diffusion coefficient to identifying MGMT promoter methylation status early in glioblastoma: Importance of analytical method. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2015, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.J.; Patankar, T.A.; Haroon, H.A.; Balériaux, D.; Swindell, R.; Jackson, A. Do cerebral blood volume and contrast transfer coefficient predict prognosis in human glioma? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brandes, A.A.; Tosoni, A.; Franceschi, E.; Sotti, G.; Frezza, G.; Amistà, P.; Morandi, L.; Spagnolli, F.; Ermani, M. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: Correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Kästner, B.; Felsberg, J.; Steinbach, J.P.; Wick, A.; Schnell, O.; Hau, P.; Herrlinger, U.; Sabel, M.C.; et al. MGMT promoter methylation is a strong prognostic biomarker for benefit from dose-intensified temozolomide rechallenge in progressive glioblastoma: The DIRECTOR Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronk, J.K.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Allen, P.K.; Mahajan, A.; Grosshans, D.R.; McGovern, S.L. Analysis of pseudoprogression after proton or photon therapy of 99 patients with low grade and anaplastic glioma. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 9, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, M.; Mehan, W.; Niemierko, A.; Kamran, S.C.; Lamba, N.; Dietrich, J.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Oh, K.S.; Batchelor, T.T.; Wen, P.Y.; et al. Increase of pseudoprogression and other treatment related effects in low-grade glioma patients treated with proton radiation and temozolomide. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 142, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, S.B.; Meng, A.; Ebani, E.J.; Chiang, G.C. Imaging glioblastoma posttreatment: Progression, pseudoprogression, pseudoresponse, radiation necrosis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 57, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Wesseling, P.; Aldape, K.; Brat, D.J.; Capper, D.; Cree, I.A.; Eberhart, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Fouladi, M.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. CIMPACT-NOW update 6: New entity and diagnostic principle recommendations of the CIMPACT-Utrecht meeting on future CNS tumor classification and grading. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, A.T.; Jordan, J.T.; Rapalino, O.; Ramamurthy, N.; Jessop, N.; DeWitt, J.C.; Nardi, V.; Alvarez, M.M.-L.; Frosch, M.; Batchelor, T.T.; et al. Financially effective test algorithm to identify an aggressive, EGFR-amplified variant of IDH-wildtype, lower-grade diffuse glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Ahn, S.; Park, C.J.; Han, K.; Kim, E.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.-K. Diffusion and perfusion MRI may predict EGFR amplification and the TERT promoter mutation status of IDH-wildtype lower-grade gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Miki, S.; Fukuoka, K.; Yasukawa, M.; Hayashi, M.; Hamada, A.; Mukasa, A.; Nishikawa, R.; Tamura, K.; Narita, Y.; et al. OS01.5 development of TERT-targeting therapy using eribulin mesylate in mouse glioblastoma model. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnari, F.B.; Cavenee, W.K. Targeting EGFR for treatment of glioblastoma: Molecular basis to overcome resistance. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2012, 12, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Chanchotisatien, A.; Qin, Z.; Wu, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, F.; Yao, Z.; Chu, S. Imaging characteristics of adult H3 K27M-mutant gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboian, M.S.; Solomon, D.A.; Felton, E.; Mabray, M.C.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Mueller, S.; Cha, S. Imaging characteristics of pediatric diffuse midline gliomas with histone H3 K27M mutation. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, A.; Tortora, D.; Mascelli, S.; Severino, M.; Piatelli, G.; Consales, A.; Pescetto, M.; Biassoni, V.; Schiavello, E.; Massollo, M.; et al. Advanced MR imaging and 18F-DOPA PET characteristics of H3K27M-mutant and wild-type pediatric diffuse midline gliomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, W.; He, H.; Yang, Y.; Wen, G.; Lv, X. Noninvasive assessment of H3 K27M mutational status in diffuse midline gliomas by using apparent diffusion coefficient measurements. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, C.; Vajapeyam, S.; Brown, D.; Kao, P.-C.; Ma, C.; Greenspan, L.; Gupta, N.; Goumnerova, L.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Dubois, F.; et al. MR Imaging correlates for molecular and mutational analyses in children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, P.W.; D’Arco, F.; Cooper, J.; Pfeuffer, J.; Hargrave, D.; Mankad, K.; Clark, C. Arterial spin labelling and diffusion-weighted imaging in paediatric brain tumours. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashi, E.; Cordero, F.J.; Halvorson, K.G.; Qi, Y.; Nouls, J.C.; Becher, O.J.; Johnson, G.A. Tumor location, but not H3.3K27M, significantly influences the blood–brain-barrier permeability in a genetic mouse model of pediatric high-grade glioma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 126, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poussaint, T.Y.; Vajapeyam, S.; Ricci, K.I.; Panigrahy, A.; Kocak, M.; Kun, L.E.; Boyett, J.M.; Pollack, I.F.; Fouladi, M. Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram metrics correlate with survival in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: A report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lober, R.M.; Cho, Y.J.; Tang, Y.; Barnes, P.D.; Edwards, M.S.; Vogel, H.; Fisher, P.G.; Monje, M.; Yeom, K.W. Diffusion-weighted MRI derived apparent diffusion coefficient identifies prognostically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 117, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettermann, F.J.; Felsberg, J.; Reifenberger, G.; Hasselblatt, M.; Forbrig, R.; Berding, G.; La Fougère, C.; Galldiks, N.; Schittenhelm, J.; Weis, J.; et al. Characterization of diffuse gliomas with histone H3-G34 mutation by MRI and dynamic 18F-FET PET. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Hatae, R.; Sangatsuda, Y.; Suzuki, S.O.; Hata, N.; Akagi, Y.; Kuga, D.; Hideki, M.; Yamashita, K.; Togao, O.; et al. Prevalence and clinicopathological features of H3.3 G34-mutant high-grade gliomas: A retrospective study of 411 consecutive glioma cases in a single institution. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2017, 34, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangouloff-Ros, V.; Varlet, P.; Levy, R.; Beccaria, K.; Puget, S.; Dufour, C.; Boddaert, N. Imaging features of medulloblastoma: Conventional imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging, perfusion-weighted imaging, and spectroscopy: From general features to subtypes and characteristics. Neurochirurgie 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüml, S.; Margol, A.S.; Sposto, R.; Kennedy, R.J.; Robison, N.J.; Vali, M.; Hung, L.T.; Muthugounder, S.; Finlay, J.L.; Erdreich-Epstein, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma identification using noninvasive magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.; Ellison, D.W.; Soares, B.P.; Carson, K.A.; Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Patay, Z. Pediatric Posterior Fossa Medulloblastoma: The role of diffusion imaging in identifying molecular groups. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, S.; Beeskow, A.; Dieckow, J.; Meyer, H.J.; Krause, M.; Frydrychowicz, C.; Hirsch, F.-W.; Meyer, H.J. Diffusion profiling of tumor volumes using a histogram approach can predict proliferation and further microarchitectural features in medulloblastoma. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Use of apparent diffusion coefficient histogram in differentiating between medulloblastoma and pilocytic astrocytoma in children. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 6107–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payabvash, S.; Tihan, T.; Cha, S. Differentiation of cerebellar hemisphere tumors: Combining apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis and structural MRI features. J. Neuroimaging 2018, 28, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitouni, S.; Koc, G.; Doganay, S.; Saracoglu, S.; Gumus, K.Z.; Ciraci, S.; Coskun, A.; Unal, E.; Per, H.; Kurtsoy, A.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient in differentiation of pediatric posterior fossa tumors. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2017, 35, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.W.; Narayan, A.K.; Bosemani, T.; Huisman, T.A.; Poretti, A. histogram analysis of diffusion tensor imaging parameters in pediatric cerebellar tumors. J. Neuroimaging 2015, 26, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, A.; Bello, L.; Michelozzi, C.; Gallucci, M.; Fava, E.; Iadanza, A.; Riva, M.; Casaceli, G.; Falini, A. Role of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance tractography in predicting the extent of resection in glioma surgery. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 14, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, L.; Gambini, A.; Castellano, A.; Carrabba, G.; Acerbi, F.; Fava, E.; Giussani, C.; Cadioli, M.; Blasi, V.; Casarotti, A.; et al. Motor and language DTI fiber tracking combined with intraoperative subcortical mapping for surgical removal of gliomas. NeuroImage 2008, 39, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, E.; Batchala, P.P.; Schiff, D.; Lopes, B.M.; Druzgal, J.T.; Mukherjee, S.; Patel, S.H. Increased intratumoral infiltration in IDH wild-type lower-grade gliomas observed with diffusion tensor imaging. J. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 145, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonm, A.V.; Ritterbusch, R.; Throckmorton, P.; Graber, J.J. Clinical imaging for diagnostic challenges in the management of gliomas: A review. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.L.; Huang, W.-Y.; Yin, B.; Xiong, J.; Wu, J.S.; Geng, D.Y. Can diffusion tensor imaging noninvasively detect IDH1 gene mutations in astrogliomas? A retrospective study of 112 cases. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, E.; Nourzadeh, H.; Batchala, P.; Schiff, D.; Lopes, M.B.S.; Druzgal, T.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Patel, S.H. Molecular subtype classification in lower-grade glioma with accelerated DTI. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Tan, W.-L.; Pan, J.-W.; Wang, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhang, J.; Geng, D. Detecting isocitrate dehydrogenase gene mutations in oligodendroglial tumors using diffusion tensor imaging metrics and their correlations with proliferation and microvascular density. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, G.; Dixon, L.; Sanverdi, E.; Machado, P.M.; Kwong, J.S.W.; Panovska-Griffiths, J.; Rojas-Garcia, A.; Yoneoka, D.; Veraart, J.; Van Cauter, S.; et al. The diagnostic role of diffusional kurtosis imaging in glioma grading and differentiation of gliomas from other intra-axial brain tumours: A systematic review with critical appraisal and meta-analysis. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.X.; Cheung, M.M. MR diffusion kurtosis imaging for neural tissue characterization. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.-P.; Song, Y.-K.; Tian, Y.-S.; Qiu, H.-S.; Huang, X.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, J. Diffusion kurtosis imaging in evaluating gliomas: Different region of interest selection methods on time efficiency, measurement repeatability, and diagnostic ability. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Li, X.-B.; Hu, M.-S.; Li, Z.-H.; Song, Y.-K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Tian, Y.-S.; Liu, D.-W.; Yan, X.; et al. Comparative analysis of the diffusion kurtosis imaging and diffusion tensor imaging in grading gliomas, predicting tumour cell proliferation and IDH-1 gene mutation status. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 141, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, M.; Schneider, T.; Alexander, D.C.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.G.; Zhang, H. Bingham–NODDI: Mapping anisotropic orientation dispersion of neurites using diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 2016, 133, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Schneider, T.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Alexander, D.C. NODDI: Practical In Vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figini, M.; Riva, M.; Graham, M.S.; Castelli, G.M.; Fernandes, B.; Grimaldi, M.; Baselli, G.; Pessina, F.; Bello, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase genotype in brain gliomas with MRI: Single-shell versus multishell diffusion models. Radiology 2018, 289, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Kelley, D.A.; Banerjee, S.; Lupo, J.M.; Chang, S.M.; Xu, D.; Hess, C.P.; Nelson, S.J. Clinically feasible NODDI characterization of glioma using multiband EPI at 7 T. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 9, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, V.; Sanvito, F.; Riva, M.; Petrini, A.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Cirillo, S.; Iadanza, A.; Bello, L.; Castellano, A.; Falini, A. Along-tract statistics of neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging diffusion metrics to enhance MR tractography quantitative analysis in healthy controls and in patients with brain tumors. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caverzasi, E.; Papinutto, N.; Castellano, A.; Zhu, A.H.; Scifo, P.; Riva, M.; Bello, L.; Falini, A.; Bharatha, A.; Henry, R. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging color maps to characterize brain diffusion in neurologic disorders. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, Y.; Hirai, T.; Azuma, M.; Hattori, Y.; Khant, Z.A.; Hori, M.; Saito, K.; Yokogami, K.; Takeshima, H.; Hirai, T.; et al. Differentiation between glioblastoma and solitary brain metastasis using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 47, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotaki, E.; Walker-Samuel, S.; Siow, B.; Johnson, S.P.; Rajkumar, V.; Pedley, R.B.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Alexander, D.C. Noninvasive quantification of solid tumor microstructure using VERDICT MRI. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccagna, F.; Riemer, F.; Priest, A.N.; McLean, M.A.; Allinson, K.; Grist, J.T.; Dragos, C.; Matys, T.; Gillard, J.H.; Watts, C.; et al. Non-invasive assessment of glioma microstructure using VERDICT MRI: Correlation with histology. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5559–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.A.; Hyare, H.; Agliardi, G.; Hipwell, B.; D’Esposito, A.; Ianus, A.; Breen-Norris, J.O.; Ramasawmy, R.; Taylor, V.; Atkinson, D.; et al. Noninvasive diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of brain tumour cell size for the early detection of therapeutic response. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Lätt, J.; Westen, D.; Brockstedt, S.; Lasič, S.; Ståhlberg, F.; Topgaard, D. Noninvasive mapping of water diffusional exchange in the human brain using filter-exchange imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 69, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Liang, H.; Basser, P. Feasibility of filter-exchange imaging (FEXI) in measuring different exchange processes in human brain. NeuroImage 2020, 219, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampinen, B.; Szczepankiewicz, F.; van Westen, D.; Englund, E.M.; Sundgren, P.C.; Latt, J.; Ståhlberg, F.; Nilsson, M. Optimal experimental design for filter exchange imaging: Apparent exchange rate measurements in the healthy brain and in intracranial tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, O.J.; Boniface, S. How well do we understand the neural origins of the FMRI BOLD signal? Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzi, A. Presurgical mapping of verbal language in brain tumors with functional MR imaging and MR tractography. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2009, 19, 573–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, A.; Cirillo, S.; Bello, L.; Riva, M.; Falini, A. Functional MRI for surgery of gliomas. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2017, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvito, F.; Caverzasi, E.; Riva, M.; Jordan, K.M.; Blasi, V.; Scifo, P.; Iadanza, A.; Crespi, S.A.; Cirillo, S.; Casarotti, A.; et al. FMRI-targeted high-angular resolution diffusion MR tractography to identify functional language tracts in healthy controls and glioma patients. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, J.J.; Zacà, D. Comparison of BOLD cerebrovascular reactivity mapping and DSC MR perfusion imaging for prediction of neurovascular uncoupling potential in brain tumors. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 11, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englander, Z.; Horenstein, C.I.; Bowden, S.G.; Chow, D.; Otten, M.L.; Lignelli, A.; Bruce, J.N.; Canoll, P.; Grinband, J. Extent of BOLD vascular dysregulation is greater in diffuse gliomas without isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 R132H mutation. Radiology 2018, 287, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Kitzwögerer, M.; Oberndorfer, S.; Rössler, K.; Dörfler, A.; Buchfelder, M.; Heinz, G. MR imaging–derived oxygen metabolism and neovascularization characterization for grading and IDH gene mutation detection of gliomas. Radiology 2017, 283, 161422–161809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Doerfler, A.; Oberndorfer, S.; Buchfelder, M.; Coras, R.; Kitzwögerer, M.; Roessler, K. Intratumoral heterogeneity of oxygen metabolism and neovascularization uncovers 2 survival-relevant subgroups of IDH1 wild-type glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Mouridsen, K.; Doerfler, A.; Hansen, M.B.; Oberndorfer, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Buchfelder, M.; Heinz, G.; Roessler, K. Recurrence of glioblastoma is associated with elevated microvascular transit time heterogeneity and increased hypoxia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 38, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatekawa, H.; Hagiwara, A.; Yao, J.; Oughourlian, T.C.; Ueda, I.; Uetani, H.; Raymond, C.; Lai, A.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; et al. Voxel-wise and patient-wise correlation of 18F-FDOPA PET, rCBV, and ADC in treatment-naïve diffuse gliomas with different molecular subtypes. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 120, 247411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladd, M.E.; Bachert, P.; Meyerspeer, M.; Moser, E.; Nagel, A.M.; Norris, D.G.; Schmitter, S.; Speck, O.; Nagel, A.M.; Zaiss, M. Pros and cons of ultra-high-field MRI/MRS for human application. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2018, 109, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barisano, G.; Sepehrband, F.; Ma, S.; Jann, K.; Cabeen, R.P.; Wang, D.J.; Toga, A.W.; Law, M. Clinical 7 T MRI: Are we there yet? A review about magnetic resonance imaging at ultra-high field. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balchandani, P.; Naidich, T.P. Ultra-high-field MR neuroimaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 36, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paech, D.; Windschuh, J.; Oberhollenzer, J.; Dreher, C.; Sahm, F.; Meissner, J.-E.; Goerke, S.; Schuenke, P.; Zaiss, M.; Regnery, S.; et al. Assessing the predictability of IDH mutation and MGMT methylation status in glioma patients using relaxation-compensated multipool CEST MRI at 7.0 T. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuenke, P.; Koehler, C.; Korzowski, A.; Windschuh, J.; Bachert, P.; Ladd, M.E.; Mundiyanapurath, S.; Paech, D.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Bonekamp, D.; et al. Adiabatically prepared spin-lock approach for T1ρ-based dynamic glucose enhanced MRI at ultrahigh fields. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, K.; Lindig, T.; Deshmane, A.; Schittenhelm, J.; Skardelly, M.; Bender, B.; Ernemann, U.; Scheffler, K.; Zaiss, M. T1ρ-based dynamic glucose-enhanced (DGEρ) MRI at 3 T: Method development and early clinical experience in the human brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1832–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trattnig, S.; Springer, E.; Bogner, W.; Hangel, G.; Strasser, B.; Dymerska, B.; Lima Cardoso, P.; Robinson, S.D. Key clinical benefits of neuroimaging at 7 T Europe PMC Funders Group. Neuroimage 2018, 168, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, A.M.; Bock, M.; Hartmann, C.; Gerigk, L.; Neumann, J.-O.; Weber, M.-A.; Bendszus, M.; Radbruch, A.; Wick, W.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; et al. The potential of relaxation-weighted sodium magnetic resonance imaging as demonstrated on brain tumors. Investig. Radiol. 2011, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, A.M.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Weber, M.-A.; Jurkat-Rott, K.; Wolf, M.B.; Radbruch, A.; Umathum, R.; Semmler, W. In Vivo 35 Cl MR Imaging in Humans: A Feasibility Study. Radiology 2014, 271, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umathum, R.; Rösler, M.B.; Nagel, A.M. In Vivo 39 K MR imaging of human muscle and brain. Radiology 2013, 269, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.H.; Radbruch, A.; Bock, M.; Semmler, W.; Nagel, A.M. Direct 17O MRI with partial volume correction: First experiences in a glioblastoma patient. Magma Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2014, 27, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, L.P.N.; Madelin, G.; Sood, T.P.; Wu, C.-C.; Kondziolka, D.; Placantonakis, D.; Golfinos, J.G.; Chi, A.; Jain, R. Quantitative sodium imaging and gliomas: A feasibility study. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltens, C.; Menten, J.; Feron, M.; Bellon, E.; Demaerel, P.; Maes, F.; Bogaert, W.V.D.; van den Schueren, E. Interobserver variations in gross tumor volume delineation of brain tumors on computed tomography and impact of magnetic resonance imaging. Radiother. Oncol. 2001, 60, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, E.; Jain, R.; Razavian, N.; Fatterpekar, G.; Lui, Y.W. State of the art: Machine learning applications in glioma imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, M.M.; Kohanteb, P.A.; Chiou, C.; Bardis, M.; Chantaduly, C.; Bota, A.D.; Filippi, C.; Weinberg, B.D.; Grinband, J.; Chow, D.S.; et al. Optimizing neuro-oncology imaging: A review of deep learning approaches for glioma imaging. Cancers 2019, 11, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalepa, J.; Marcinkiewicz, M.; Kawulok, M. Data augmentation for brain-tumor segmentation: A review. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isensee, F.; Jäger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Automated design of deep learning methods for biomedical image segmentation. 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.08128 (accessed on 31 December 2020).
- Kickingereder, P.; Isensee, F.; Tursunova, I.; Petersen, J.; Neuberger, U.; Bonekamp, D.; Brugnara, G.; Schell, M.; Kessler, T.; Foltyn, M.; et al. Automated quantitative tumour response assessment of MRI in neuro-oncology with artificial neural networks: A multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlochower, A.; Chow, D.S.; Chang, P.; Khatri, D.; Boockvar, J.A.; Filippi, C. Deep learning AI applications in the imaging of glioma. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 29, 115-00. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.; Grinband, J.; Weinberg, B.D.; Bardis, M.; Khy, M.; Cadena, G.; Su, M.-Y.; Cha, S.; Filippi, C.G.; Bota, D.; et al. Deep-learning convolutional neural networks accurately classify genetic mutations in gliomas. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.-C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhai, G. A deep learning-based radiomics model for prediction of survival in glioblastoma multiforme. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Correa, R.; Hill, V.B.; Statsevych, V.; Bera, K.; Beig, N.; Mahammedi, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Ahluwalia, M.; Tiwari, P. Tumor habitat–derived radiomic features at pretreatment MRI that are prognostic for progression-free survival in glioblastoma are associated with key morphologic attributes at histopathologic examination: A feasibility study. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanvito, F.; Castellano, A.; Falini, A. Advancements in Neuroimaging to Unravel Biological and Molecular Features of Brain Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030424
Sanvito F, Castellano A, Falini A. Advancements in Neuroimaging to Unravel Biological and Molecular Features of Brain Tumors. Cancers. 2021; 13(3):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanvito, Francesco, Antonella Castellano, and Andrea Falini. 2021. "Advancements in Neuroimaging to Unravel Biological and Molecular Features of Brain Tumors" Cancers 13, no. 3: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030424
APA StyleSanvito, F., Castellano, A., & Falini, A. (2021). Advancements in Neuroimaging to Unravel Biological and Molecular Features of Brain Tumors. Cancers, 13(3), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030424




