Application of Community Detection Algorithm to Investigate the Correlation between Imaging Biomarkers of Tumor Metabolism, Hypoxia, Cellularity, and Perfusion for Precision Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. PET Data Acquisition
2.3. PET/CTData Analysis
2.4. MRI Data Acquisition
2.5. MRI Data Analysis
2.5.1. DWI Analysis
2.5.2. Fast Exchange Regime DCE-MRI Analysis
2.6. MRI Tumor Regions of Interests Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
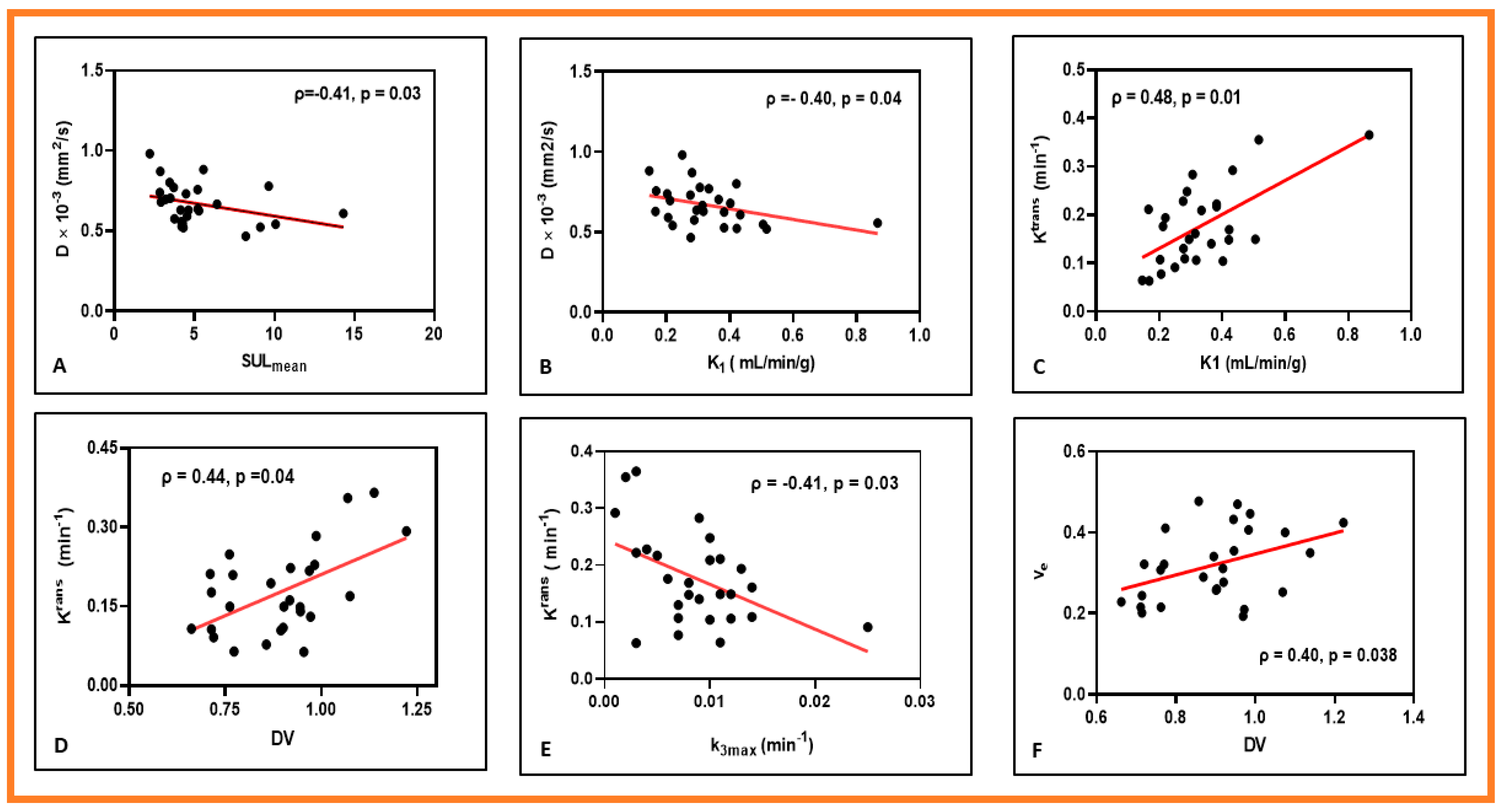
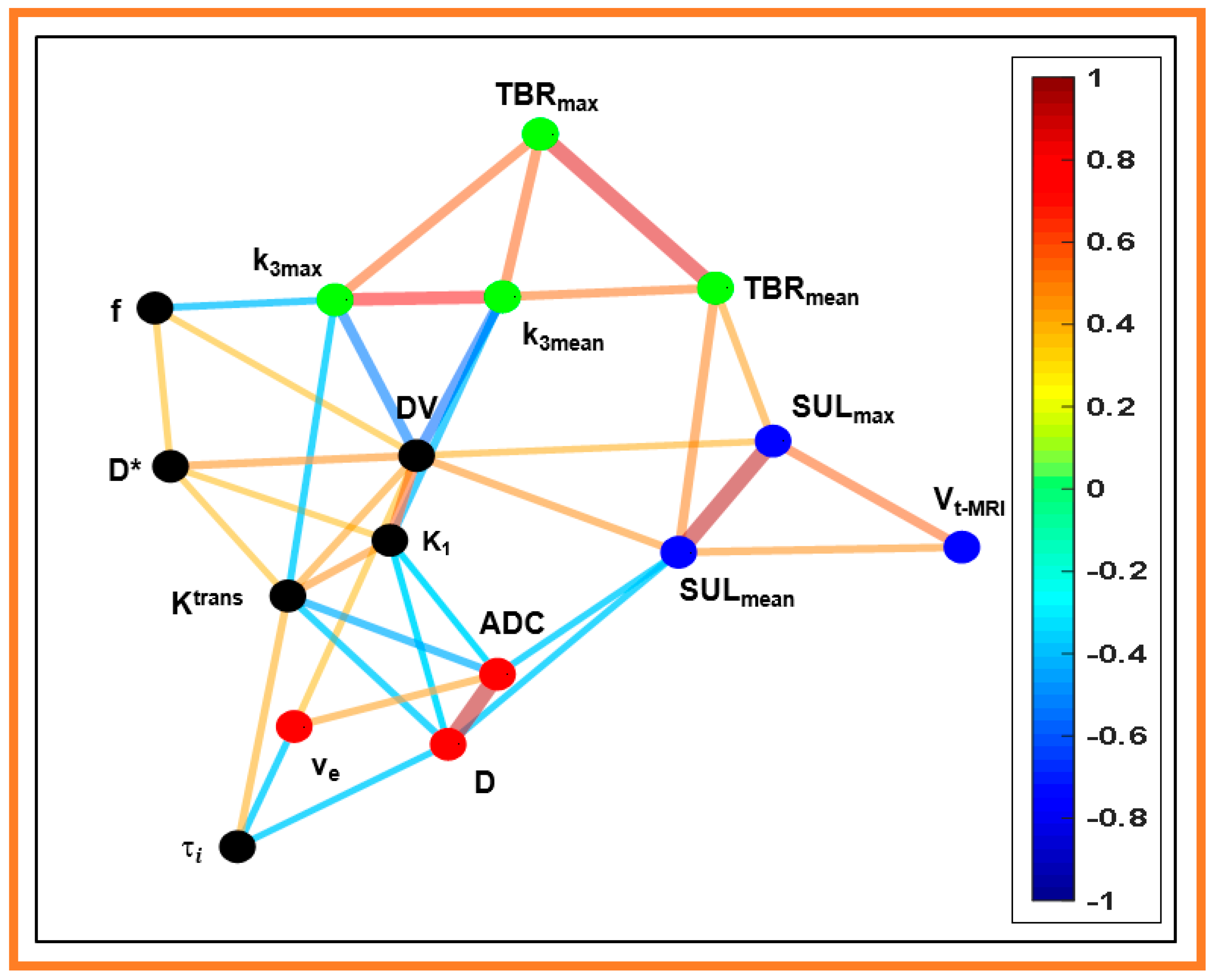
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lo Nigro, C.; Denaro, N.; Merlotti, A.; Merlano, M. Head and neck cancer: Improving outcomes with a multidisciplinary approach. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M. HPV and its effect on head and neck cancer prognosis. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 8, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Psyrri, A.; Cohen, E. Oropharyngeal cancer: Clinical implications of the HPV connection. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. ESMO 2011, 22, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D. Multimodality imaging of head and neck cancer. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, J.G.; Krohn, K.A. F-18 Fluoromisonidazole for Imaging Tumor Hypoxia: Imaging the Microenvironment for Personalized Cancer Therapy. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 45, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibfarth, S.; Simoncic, U.; Monnich, D.; Welz, S.; Schmidt, H.; Schwenzer, N.; Zips, D.; Thorwarth, D. Analysis of pairwise correlations in multi-parametric PET/MR data for biological tumor characterization and treatment individualization strategies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Moore, W.; Sumer, B.; Khan, S.; Sher, D.; Subramaniam, R.M. Clinical Practice in PET/CT for the Management of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidiri, A.; Gangemi, E.; Ruberto, E.; Pasqualoni, R.; Sciuto, R.; Sanguineti, G.; Farneti, A.; Benevolo, M.; Rollo, F.; Sperati, F. Correlation between histogram-based DCE-MRI parameters and 18F-FDG PET values in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Evaluation in primary tumors and metastatic nodes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, M.; Yamane, T.; Shinohara, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Hori, S.Y.; Tona, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Naito, Y.; Senda, M. 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography before treatment is a predictor of radiotherapy outcome and survival prognosis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2011, 25, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovski, M.; Lee, N.Y.; Schoder, H.; Carlin, S.D.; Beattie, B.J.; Riaz, N.; Leeman, J.E.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Humm, J.L. Monitoring early response to chemoradiotherapy with (18)F-FMISO dynamic PET in head and neck cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.; Leifels, L.; Meyer, H.J.; Winter, K.; Sabri, O.; Purz, S. Associations Between Histogram Analysis DCE MRI Parameters and Complex F-18-FDG-PET Values in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncic, U.; Leibfarth, S.; Welz, S.; Schwenzer, N.; Schmidt, H.; Reischl, G.; Pfannenberg, C.; la Fougere, C.; Nikolaou, K.; Zips, D.; et al. Comparison of DCE-MRI kinetic parameters and FMISO-PET uptake parameters in head and neck cancer patients. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 2358–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minosse, S.; Marzi, S.; Piludu, F.; Boellis, A.; Terrenato, I.; Pellini, R.; Covello, R.; Vidiri, A. Diffusion kurtosis imaging in head and neck cancer: A correlation study with dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Phys. Med. 2020, 73, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, J.G.; Schwartz, D.L.; O’Sullivan, J.; Peterson, L.M.; Ng, P.; Scharnhorst, J.; Grierson, J.R.; Krohn, K.A. Tumor hypoxia imaging with [F-18] fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5435–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandurska-Luque, A.; Lock, S.; Haase, R.; Richter, C.; Zophel, K.; Abolmaali, N.; Seidlitz, A.; Appolda, S.; Krause, M.; Steinbach, J.; et al. FMISO-PET-based lymph node hypoxia adds to the prognostic value of tumor only hypoxia in HNSCC patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, N.; Sherman, E.; Pei, X.; Schoder, H.; Grkovski, M.; Paudyal, R.; Katabi, N.; Selenica, P.; Yamaguchi, T.N.; Ma, D.; et al. Precision Radiotherapy: Reduction in Radiation for Oropharyngeal Cancer in the 30 ROC Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Grenier, P.; Cabanis, E.; Laval-Jeantet, M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecaveye, V.; Dirix, P.; De Keyzer, F.; Op de Beeck, K.; Poorten, V.V.; Delaere, P.; Verbeken, E.; Hermans, R.; Nuyts, S. Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted Mri for Nodal Staging and Radiotherapy Planning of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 88, S152–S153. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Loevner, L.; Quon, H.; Sherman, E.; Weinstein, G.; Kilger, A.; Poptani, H. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for predicting and detecting early response to chemoradiation therapy of squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using steady-state free precession. Magn. Reson. Med. 1988, 7, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.; Essig, M.; Jensen, A.; Laun, F.B.; Munter, M.; Maier-Hein, K.H.; Stieltjes, B. Prediction of treatment response in head and neck carcinomas using IVIM-DWI: Evaluation of lymph node metastasis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hazle, J.D.; Mohamed, A.S.; Frank, S.J.; Hobbs, B.P.; Colen, R.R.; Gunn, G.B.; Wang, J.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Garden, A.S.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging kinetics during chemoradiotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx: Preliminary results from a prospective pilot study. NMR Biomed. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, R.; Oh, J.H.; Riaz, N.; Venigalla, P.; Li, J.; Hatzoglou, V.; Leeman, J.; Nunez, D.A.; Lu, Y.; Deasy, J.O.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI during chemoradiation therapy to characterize and monitor treatment response in human papillomavirus head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.L.; Hu, J. MRI and MRS of human brain tumors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 520, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Chow, S.K.; Yu, K.H.; Mo, F.K.; Yeung, D.K.; Yuan, J.; Law, B.K.; Bhatia, K.S.; Vlantis, A.C.; Ahuja, A.T. DCE-MRI for Pre-Treatment Prediction and Post-Treatment Assessment of Treatment Response in Sites of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Head and Neck. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Kim, S.; Dougherty, L.; Wang, S.; Loevner, L.A.; Quon, H.; Poptani, H. Pretreatment diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for prediction of local treatment response in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Lee, N.Y.; Jansen, J.F.; Thaler, H.T.; Stambuk, H.E.; Fury, M.G.; Patel, S.G.; Moreira, A.L.; Sherman, E.; Karimi, S.; et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of outcome in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma patients with nodal metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Loevner, L.A.; Quon, H.; Kilger, A.; Sherman, E.; Weinstein, G.; Chalian, A.; Poptani, H. Prediction of response to chemoradiation therapy in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quon, H.; Kim, S.; Loevner, L.; Rosen, M.; Sherman, E.; Kilger, A.; Poptani, H. DCE-MRI perfusion imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma nodal metastasis: Identifying radioresistance and the distant metastatic phenotyp. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.; Paudyal, R.; Nelson, D.; Pickup, S.; Zhou, R.; Leeper, D.; Heitjan, D.; Poptani, H.; Glickson, J. Acute changes in cellular-interstitial water exchange rate in DB-1 melanoma xenografts after lonidamine administration as a marker of tumor energetics and ion transport. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 2014, 22, 2757. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, C.S., Jr.; Li, X.; Tudorica, L.A.; Oh, K.Y.; Roy, N.; Chui, S.Y.; Naik, A.M.; Holtorf, M.L.; Afzal, A.; Rooney, W.D.; et al. Intratumor mapping of intracellular water lifetime: Metabolic images of breast cancer? NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Loevner, L.A.; Kim, S.G.; Hwang, W.T.; Wang, S.; Verma, G.; Mohan, S.; LiVolsi, V.; Quon, H.; Poptani, H. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI-Derived Intracellular Water Lifetime (tau i): A Prognostic Marker for Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Paeng, J.C.; Sohn, C.H.; Pagsisihan, J.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.G.; Jang, J.Y.; Yun, T.J.; Kim, J.H.; Han, M.H.; et al. Correlation of 18F-FDG uptake with apparent diffusion coefficient ratio measured on standard and high b value diffusion MRI in head and neck cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamatsu, S.; Matsusue, E.; Miyoshi, H.; Kakite, S.; Kaminou, T.; Ogawa, T. Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficients measured by diffusion-weighted MR imaging and standardized uptake values from FDG PET/CT in metastatic neck lymph nodes of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zwirner, K.; Thorwarth, D.; Winter, R.M.; Welz, S.; Weiss, J.; Schwenzer, N.F.; Schmidt, H.; la Fougere, C.; Nikolaou, K.; Zips, D.; et al. Voxel-wise correlation of functional imaging parameters in HNSCC patients receiving PET/MRI in an irradiation setup. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2018, 194, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.F.; Schoder, H.; Lee, N.Y.; Wang, Y.; Pfister, D.G.; Fury, M.G.; Stambuk, H.E.; Humm, J.L.; Koutcher, J.A.; Shukla-Dave, A. Noninvasive assessment of tumor microenvironment using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography imaging in neck nodal metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenmann, N.; Grosu, A.L.; Buchert, M.; Rischke, H.C.; Ruf, J.; Bielak, L.; Majerus, L.; Ruhle, A.; Bamberg, F.; Baltas, D.; et al. The utility of multiparametric MRI to characterize hypoxic tumor subvolumes in comparison to FMISO PET/CT. Consequences for diagnosis and chemoradiation treatment planning in head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 150, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, J.; Bornholdt, S. Statistical mechanics of community detection. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 016110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovski, M.; Schoder, H.; Lee, N.Y.; Carlin, S.D.; Beattie, B.J.; Riaz, N.; Leeman, J.E.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Humm, J.L. Multiparametric Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia and Perfusion with (18)F-Fluoromisonidazole Dynamic PET in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beichel, R.R.; Smith, B.J.; Bauer, C.; Ulrich, E.J.; Ahmadvand, P.; Budzevich, M.M.; Gillies, R.J.; Goldgof, D.; Grkovski, M.; Hamarneh, G. Multi-site quality and variability analysis of 3D FDG PET segmentations based on phantom and clinical image data. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, R.; Konar, A.S.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Hatzoglou, V.; Chenevert, T.L.; Malyarenko, D.I.; Swanson, S.D.; LoCastro, E.; Jambawalikar, S.; Liu, M.Z.; et al. Repeatability of Quantitative Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Metrics in Phantoms, Head-and-Neck and Thyroid Cancers: Preliminary Findings. Tomogr. A J. Imaging Res. 2019, 5, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankeelov, T.E.; Rooney, W.D.; Li, X.; Springer, C.S., Jr. Variation of the relaxographic "shutter-speed" for transcytolemmal water exchange affects the CR bolus-tracking curve shape. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, R.; Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Nagaraja, T.N.; Fenstermacher, J.D.; Ewing, J.R. Modeling of Look-Locker estimates of the magnetic resonance imaging estimate of longitudinal relaxation rate in tissue after contrast administration. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, H.M. Reaction Rates by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, R.; Poptani, H.; Cai, K.; Zhou, R.; Glickson, J.D. Impact of transvascular and cellular–interstitial water exchange on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging estimates of blood to tissue transfer constant and blood plasma volume. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Lee, N.; Stambuk, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Thaler, H.T.; Patel, S.G.; Shah, J.P.; Koutcher, J.A. Average arterial input function for quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of neck nodal metastases. BMC Med. Phys. 2009, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jansen, J.F.; Mazaheri, Y.; Stambuk, H.E.; Koutcher, J.A.; Shukla-Dave, A. Extension of the intravoxel incoherent motion model to non-gaussian diffusion in head and neck cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, R.; Chen, L.; Oh, J.; Zakeri, K.; Hatzoglou, V.; Tsai, C.; Lee, N.; Shukla-Dave, A. Nongaussian intravoxel Incoherent motion diffusion weighted and fast exchange regime dynamic contrast-enhanced-MRI of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Preliminary study for predicting locoregional failure. Cancers 2021, 15, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoCastro, E.; Paudyal, R.; Mazaheri, Y.; Hatzoglou, V.; Oh, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Konar, A.S.; Vom Eigen, K.; Ho, A.; Ewing, J.R.; et al. Computational Modeling of Interstitial Fluid Pressure and Velocity in Head and Neck Cancer Based on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Feasibility Analysis. Tomogr. A J. Imaging Res. 2020, 6, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Jain, R.; Nejad-Davarani, S.P.; Mikkelsen, T.; Lu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Scarpace, L.; Arbab, A.S.; Narang, J.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H.; et al. Model selection for DCE-T1 studies in glioblastoma. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. Detecting community structure in networks. Eur Phys. J. B 2004, 38, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: http://www.R-project.org.
- Nakajo, M.; Nakajo, M.; Kajiya, Y.; Tani, A.; Kamiyama, T.; Yonekura, R.; Fukukura, Y.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nishimoto, K.; Nomoto, M.; et al. FDG PET/CT and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Comparison of Prognostic Significance Between Primary Tumor Standardized Uptake Value and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, D.N.; Medina, A.L.; Iglesias, M.M.; Gomez, F.S.; Dave, A.; Hatzoglou, V.; Paudyal, R.; Calzado, A.; Deasy, J.O.; Shukla-Dave, A.; et al. Multimodality functional imaging using DW-MRI and F-18-FDG-PET/CT during radiation therapy for human papillomavirus negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Meixoeiro Hospital of Vigo Experience. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglese, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Monti, S.; Forte, E.; Incoronato, M.; Nicolai, E.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. A multi-parametric PET/MRI study of breast cancer: Evaluation of DCE-MRI pharmacokinetic models and correlation with diffusion and functional parameters. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hectors, S.J.; Wagner, M.; Besa, C.; Huang, W.; Taouli, B. Multiparametric FDG-PET/MRI of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Initial Experience. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 5638283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Wu, C.T.; Ko, J.Y.; Yang, T.L.; Lou, P.J.; Wang, C.P.; Chang, Y.L. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in an endemic betel quid region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, B.; Huang, S.H.; Siu, L.L.; Waldron, J.; Zhao, H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Kim, J.; Ringash, J.; Bayley, A.; et al. Deintensification candidate subgroups in human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal cancer according to minimal risk of distant metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.J.; Jenkins, W.T.; Jenkins, K.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Shuman, A.L.; Pickup, S.; Riehl, C.R.; Paudyal, R.; Poptani, H.; Evans, S.M. Mechanisms of blood flow and hypoxia production in rat 9L-epigastric tumors. Tumor Microenviron. Ther. 2013, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asgari, H.; Soltani, M.; Sefidgar, M. Modeling of FMISO [F(18)] nanoparticle PET tracer in normal-cancerous tissue based on real clinical image. Microvasc. Res. 2018, 118, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertsenshteyn, I.; Epel, B.; Barth, E.; Leoni, L.; Markiewicz, E.; Tsai, H.M.; Fan, X.; Giurcanu, M.; Bodero, D.; Zamora, M.; et al. Improving Tumor Hypoxia Location in (18)F-Misonidazole PET with Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI Using Quantitative Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Partial Oxygen Pressure Images. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e200104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

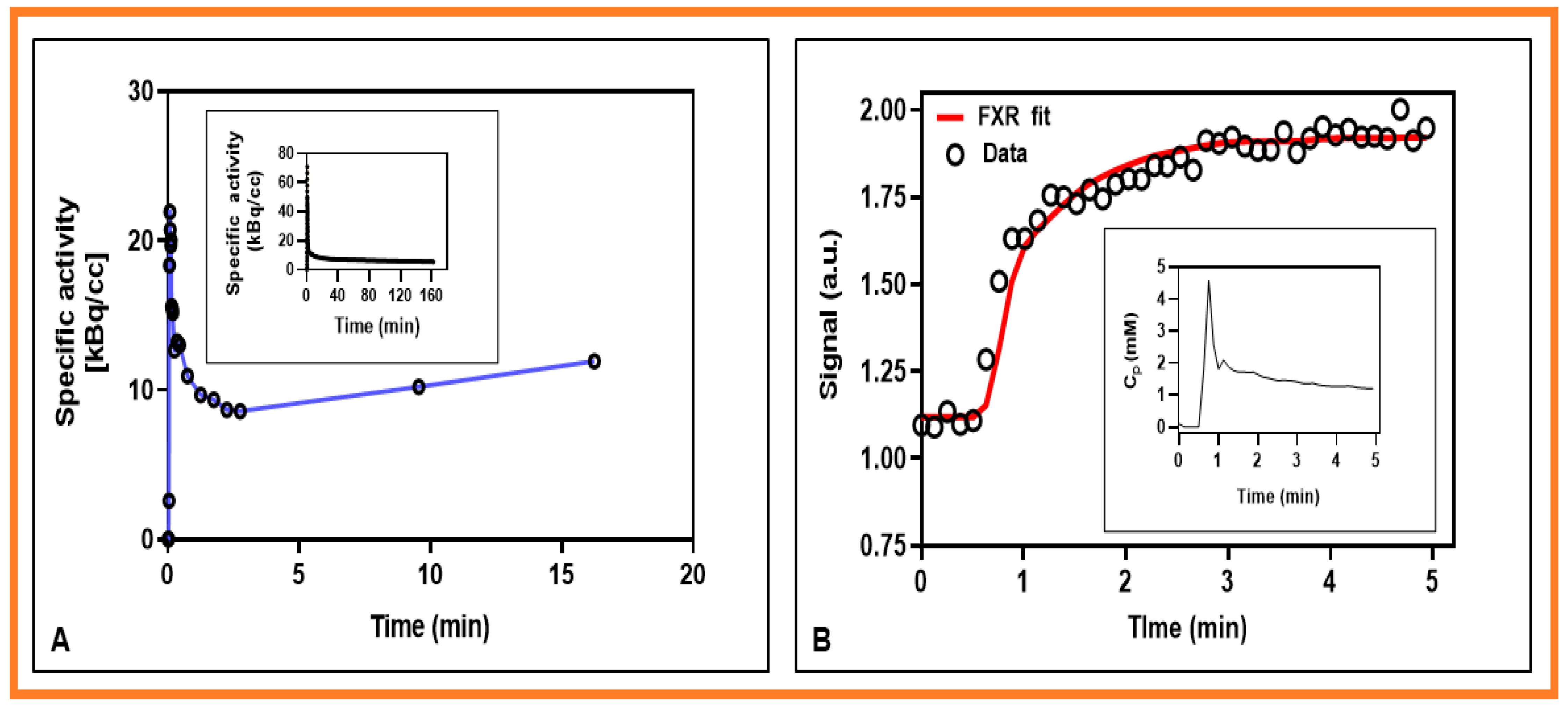
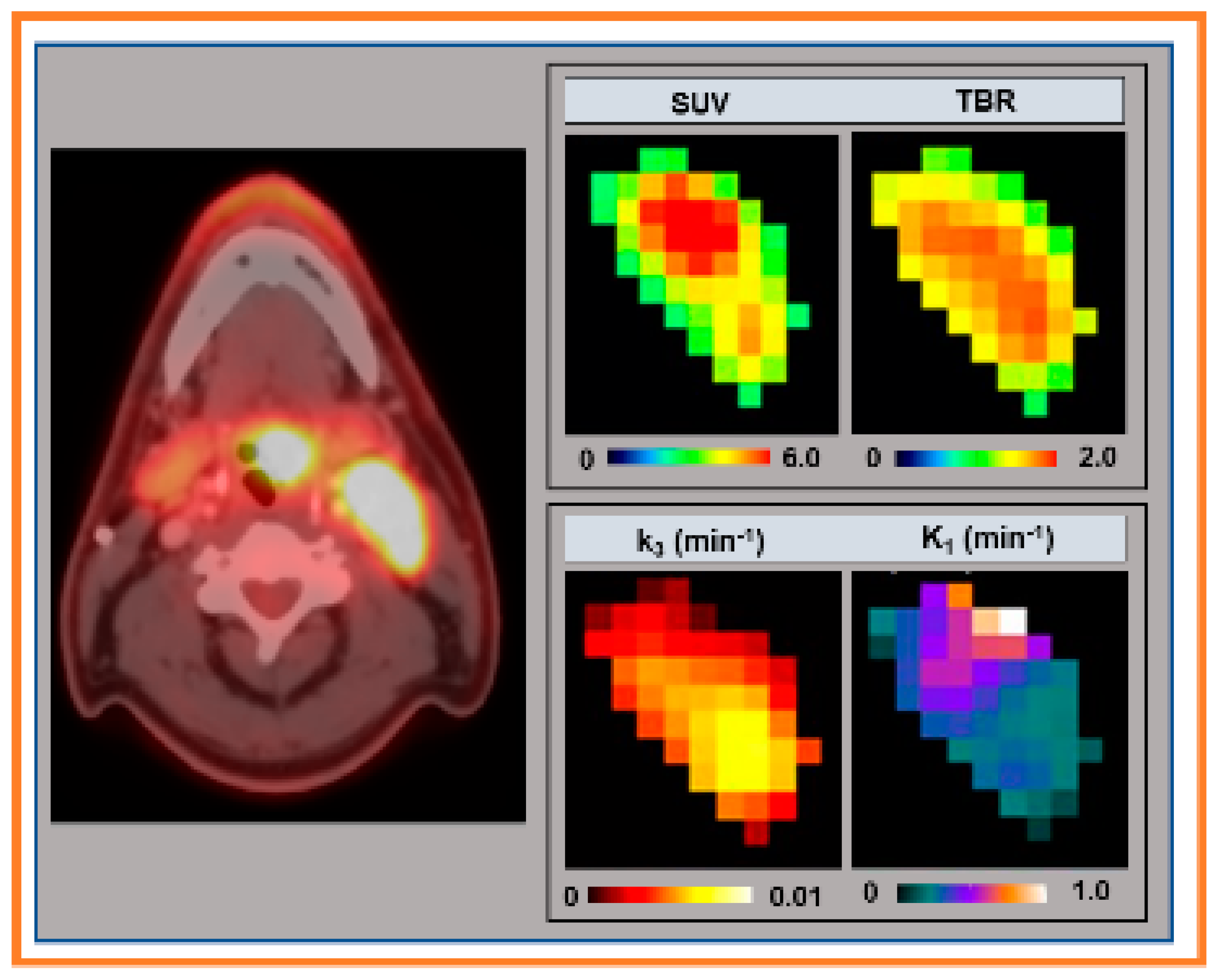
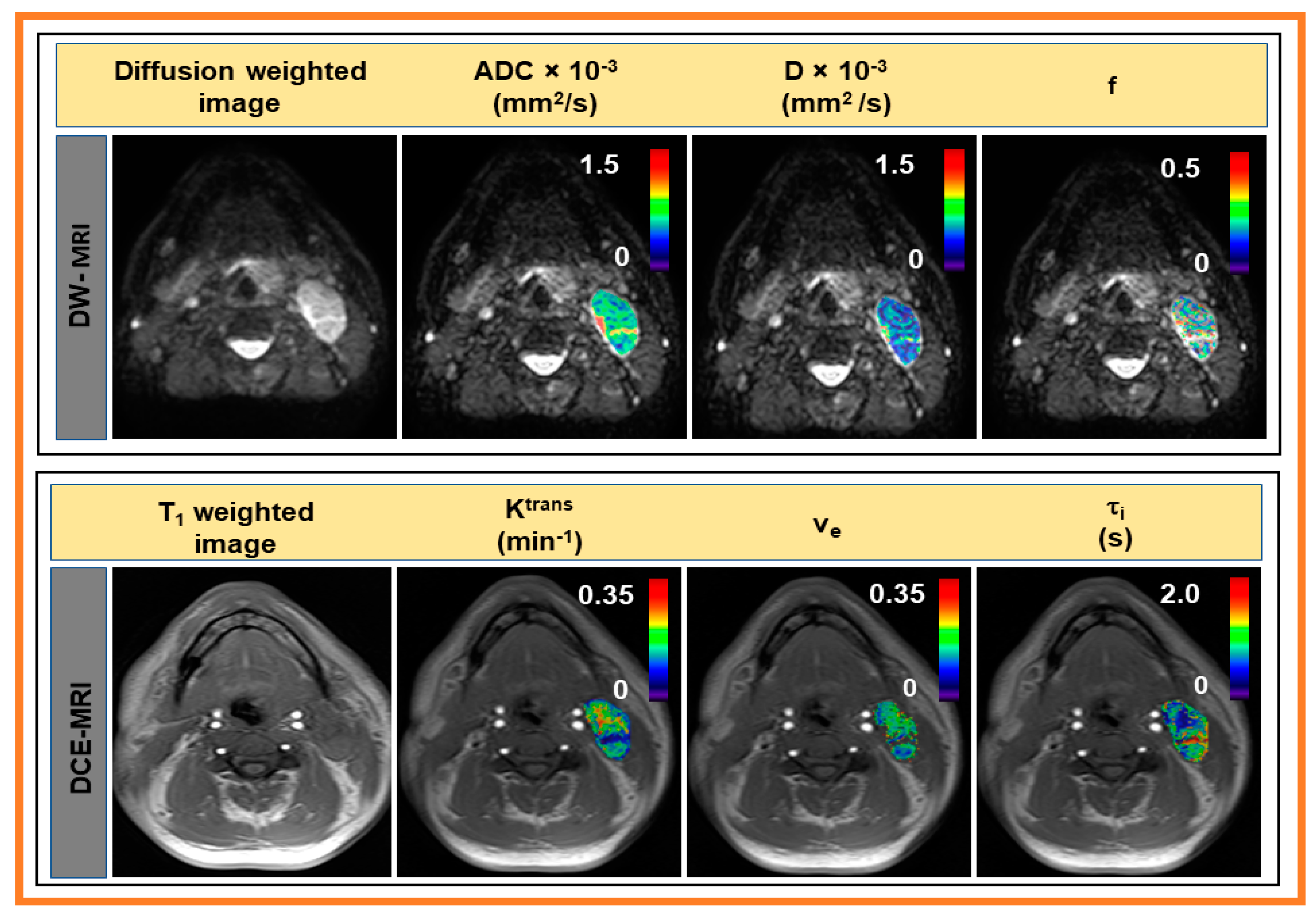

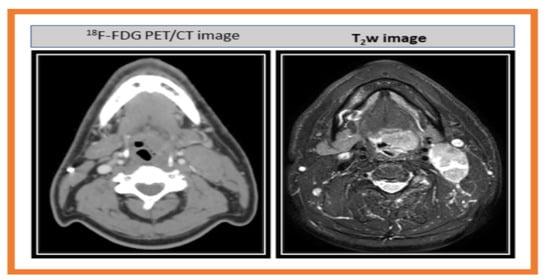
| Method | Model Parameter | Value 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 18F-FDG-PET/CT | SULmax | 8.91 ± 3.94 |
| SULmean | 5.26 ± 2.76 | |
| 18F-FMISO-PET/CT | K1 (min−1) | 0.33 ± 0.15 |
| k3 max (min−1) | 0.0087 ± 0.0049 | |
| k3 mean (min−1) | 0.0034 ± 0.0021 | |
| TBRmax | 1.76 ± 0.53 | |
| TBRmean | 1.29 ± 0.27 | |
| DV | 0.89 ± 0.14 | |
| DW | ADC × 10−3 (mm2/s) | 0.93 ± 0.14 |
| D × 10−3 (mm2/s) | 0.67 ± 0.13 | |
| D* × 1 0−3 (mm2/s) | 9.02 ± 1.80 | |
| f | 0.16 ± 0.06 | |
| DCE | Ktrans (min−1) | 0.18 ± 0.06 |
| ve | 0.32 ± 0.09 | |
| τi (s) | 0.670 ± 0.15 | |
| FDG-PET tumor volume | Vt-PET (cm3) | 13.59 ± 7.65 |
| T2w MRI tumor volume | Vt-MRI (cm3) | 11.41 ± 10.09 |
| Quantitative metric | PET volume | MR T2 weighted volume | ADC | D | D* | f | Ktrans | ve | τi | kep | SULmax | SULmean | K1 | k3.max | k3.mean | DV | TBR Max | TBR Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET volume | 0.84 * | −0.09 | −0.10 | 0.28 | −0.06 | 0.19 | −0.09 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.58 * | 0.42 * | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.20 | |
| MRI T2 weighted volume | −0.17 | −0.18 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.14 | −0.14 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.57 * | 0.48 * | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.27 | ||
| ADC | 0.95 * | −0.34 | −0.18 | −0.48 * | 0.46 * | −0.36 | 0.18 | −0.29 | −0.42 * | −0.40 * | 0.26 | 0.15 | −0.31 | 0.07 | −0.14 | |||
| D | −0.26 | −0.18 | −0.43 * | 0.32 | −0.41 * | 0.23 | −0.31 | −0.41 * | −0.40 * | 0.32 | 0.23 | −0.32 | 0.14 | −0.08 | ||||
| D* | 0.39 * | 0.39 * | −0.11 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.40 * | −0.25 | −0.35 | 0.49 * | 0.09 | 0.13 | |||||
| f | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.14 | −0.14 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.20 | −0.45 * | −0.30 | 0.40 * | −0.18 | 0.12 | ||||||
| Ktrans | −0.10 | 0.43 * | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.48 * | −0.41 * | −0.27 | 0.44 * | −0.17 | −0.03 | |||||||
| ve | −0.41 * | −0.15 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.02 | −0.20 | −0.26 | 0.40 * | 0.14 | 0.13 | ||||||||
| τi | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.08 | −0.17 | 0.05 | −0.04 | −0.23 | −0.12 | |||||||||
| kep | −0.11 | −0.16 | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.20 | −0.23 | −0.09 | −0.20 | ||||||||||
| SULmax | 0.94 * | −0.01 | −0.09 | −0.02 | 0.42 * | 0.36 | 0.44 * | |||||||||||
| SULmean | 0.003 | −0.15 | −0.02 | 0.48 * | 0.38 | 0.53* | ||||||||||||
| K1 | −0.26 | −0.46 * | 0.59 * | −0.18 | −0.19 | |||||||||||||
| k3.max | 0.79 * | −0.57 * | 0.57 * | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||
| k3.mean | −0.60 * | 0.57 * | 0.54 * | |||||||||||||||
| DV | 0.13 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||
| TBRmax | 0.88 * | |||||||||||||||||
| TBRmean |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paudyal, R.; Grkovski, M.; Oh, J.H.; Schöder, H.; Nunez, D.A.; Hatzoglou, V.; Deasy, J.O.; Humm, J.L.; Lee, N.Y.; Shukla-Dave, A. Application of Community Detection Algorithm to Investigate the Correlation between Imaging Biomarkers of Tumor Metabolism, Hypoxia, Cellularity, and Perfusion for Precision Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 3908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153908
Paudyal R, Grkovski M, Oh JH, Schöder H, Nunez DA, Hatzoglou V, Deasy JO, Humm JL, Lee NY, Shukla-Dave A. Application of Community Detection Algorithm to Investigate the Correlation between Imaging Biomarkers of Tumor Metabolism, Hypoxia, Cellularity, and Perfusion for Precision Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153908
Chicago/Turabian StylePaudyal, Ramesh, Milan Grkovski, Jung Hun Oh, Heiko Schöder, David Aramburu Nunez, Vaios Hatzoglou, Joseph O. Deasy, John L. Humm, Nancy Y. Lee, and Amita Shukla-Dave. 2021. "Application of Community Detection Algorithm to Investigate the Correlation between Imaging Biomarkers of Tumor Metabolism, Hypoxia, Cellularity, and Perfusion for Precision Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153908
APA StylePaudyal, R., Grkovski, M., Oh, J. H., Schöder, H., Nunez, D. A., Hatzoglou, V., Deasy, J. O., Humm, J. L., Lee, N. Y., & Shukla-Dave, A. (2021). Application of Community Detection Algorithm to Investigate the Correlation between Imaging Biomarkers of Tumor Metabolism, Hypoxia, Cellularity, and Perfusion for Precision Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers, 13(15), 3908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153908