Boron Neutron Capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade Meningiomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
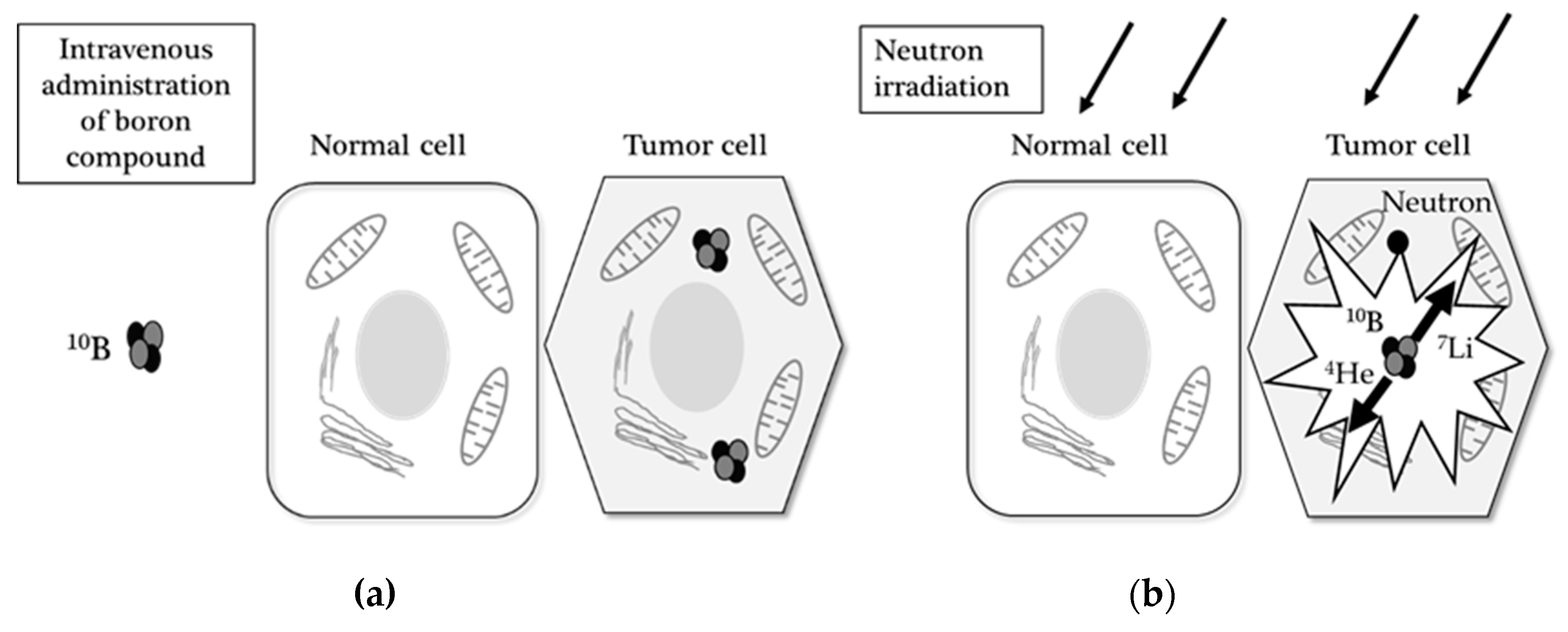
2.1. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
2.1.1. Background of BNCT
2.1.2. Boron Compounds
2.1.3. Boron Uptake Imaging with PET
2.1.4. BNCT for High-Grade Meningiomas
2.1.5. Adverse Events and Limitations of BNCT
2.1.6. Future Prospect of BNCT
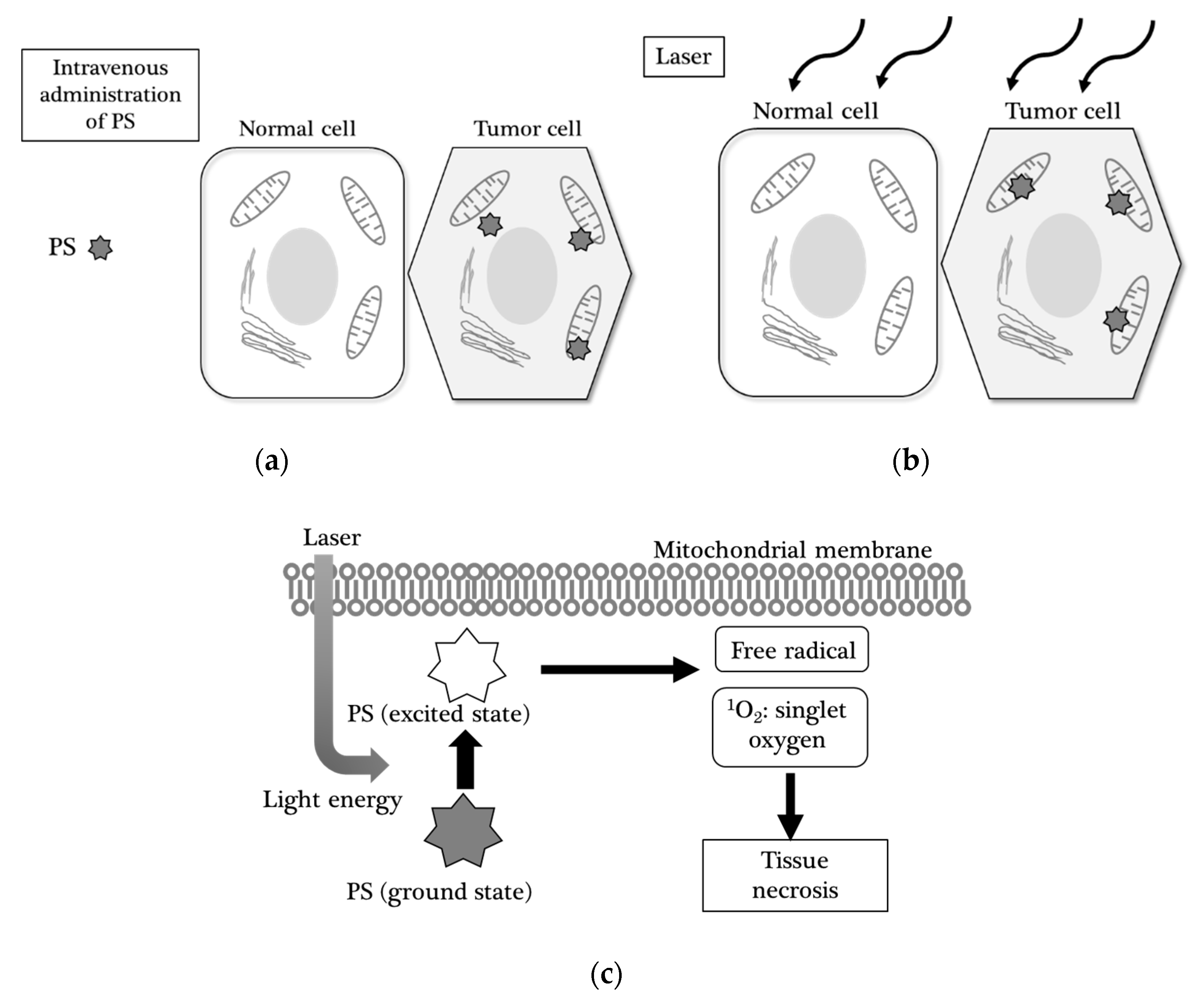
2.2. Photodynamic Therapy
2.2.1. Background on PDT
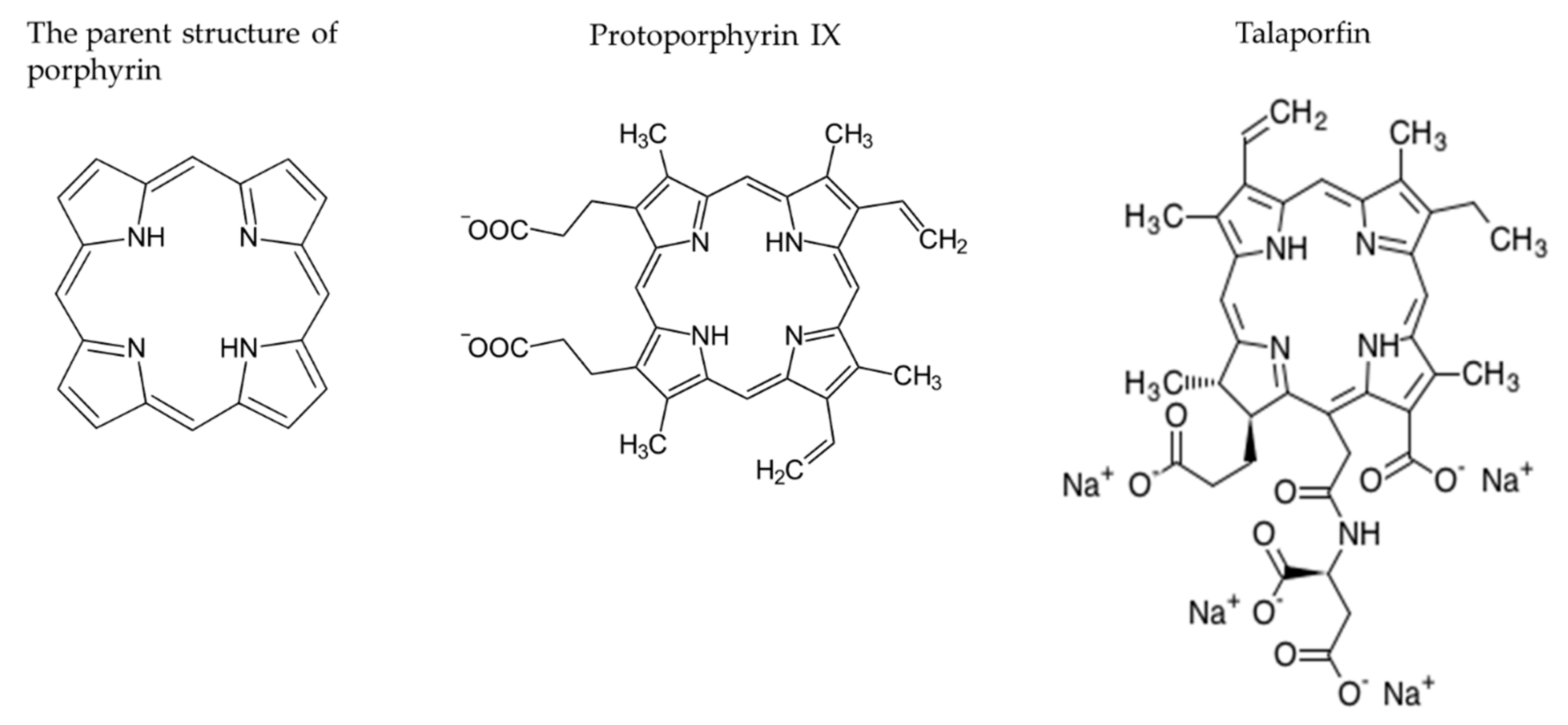
2.2.2. Photosensitizers (PSs)
2.2.3. 5-Aminolevulic Acid Based PDT (5-ALA-PDT)
Mechanism and Fluorescence of 5-ALA
Application of 5-ALA-PDT to Meningiomas
2.2.4. Talaporfin Sodium Based PDT (TS-PDT)
Development of Talaporfin Sodium as a Photosensitizer
Application of TS-PDT for Meningiomas
Adverse Events and Limitations of TS-PDT
2.2.5. Future Prospect of PDT
3. Literature Analysis Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bondy, M.; Lee Ligon, B. Epidemiology and etiology of intracranial meningiomas: A review. J. Neurooncol. 1996, 29, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemels, J.; Wrensch, M.; Claus, E.B. Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Park, C.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.G.; Chung, Y.S.; Jung, H.-W. Atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: Prognostic implications of clinicopathological features. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Galanis, E.; Butowski, N.; Chan, J.W.; Dunn, I.F.; Goldbrunner, R.; Herold-Mende, C.; Ippen, F.M.; Mawrin, C.; McDermott, M.W.; et al. Advances in multidisciplinary therapy for meningiomas. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, I18–I31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhood, B.; Samadian, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Zakariaee, S.S.; Knaup, C. Physical, dosimetric and clinical aspects and delivery systems in neutron capture therapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2018, 23, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.-I.; Kawabata, S.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kuroiwa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kondo, N.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for malignant brain tumors. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2016, 56, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.L. Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostron, H.; Plangger, C.; Fritsch, E.; Maier, H. Photodynamic treatment of malignant brain tumors. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1990, 102, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, P.J.; Wilson, B.C. Photodynamic therapy of brain tumors—A work in progress. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, D.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Pagnini, P.G.; Yu, C.; Wang, M.Y.; Apuzzo, M.L.J. Chained lightning, Part I: Exploitation of energy and radiobiological principles for therapeutic purposes. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, J.A.; Morris, G.M. The radiation biology of boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat. Res. 1999, 151, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensuu, H.; Tenhunen, M. Physical and biological targeting of radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. Suppl. 1999, 38, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pisarev, M.A.; Dagrosa, M.A.; Juvenal, G.J. Boron neutron capture therapy in cancer: Past, present and future. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2007, 51, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, S.L.; DeHaan, C.E.; Griebenow, M.L. Biodistribution of Boron in Dogs with Spontaneous Intracranial Tumors Following Borocaptate Sodium Administration. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Stragliotto, G.; Fankhauser, H. Biodistribution of boron sulfhydryl for boron neutron capture therapy in patients with intracranial tumors. Neurosurgery 1995, 36, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, T.L.; Kabalka, G.W.; Miller, L.F.; Khan, M.K.; Smith, G.T. Improved treatment planning for boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme using fluorine-18 labeled boronophenylalanine and positron emission tomography. Med. Phys. 2002, 29, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; Jori, G.; Martini, D.; Sotti, G. Boron neutron capture therapy and 18F-labelled borophenylalanine positron emission tomography: A critical and clinical overview of theliterature. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 74, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havu-Aurén, K.; Kiiski, J.; Lehtiö, K.; Eskola, O.; Kulvik, M.; Vuorinen, V.; Oikonen, V.; Vähätalo, J.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Minn, H. Uptake of 4-borono-2-[18F]fluoro-L-phenylalanine in sporadic and neurofibromatosis 2-related schwannoma and meningioma studied with PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariai, T.; Ishiwata, K.; Kimura, Y.; Inaji, M.; Momose, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsumura, A.; Ishii, K.; Ohno, K. PET pharmacokinetic analysis to estimate boron concentration in tumor and brain as a guide to plan BNCT for malignant cerebral glioma. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S348–S350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Kawabata, S.; Hiramatsu, R.; Matsushita, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, K.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Kuroiwa, T. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for High-Grade Skull-Base Meningioma. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2018, 79, S322–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshr, R.; Isohashi, K.; Watabe, T.; Naka, S.; Horitsugi, G.; Romanov, V.; Kato, H.; Miyatake, S.I.; Shimosegawa, E.; Hatazawa, J. Preliminary feasibility study on differential diagnosis between radiation-induced cerebral necrosis and recurrent brain tumor by means of [18 F]fluoro-borono-phenylalanine PET/CT. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulvik, M.; Kallio, M.; Laakso, J.; Vähätalo, J.; Hermans, R.; Järviluoma, E.; Paetau, A.; Rasilainen, M.; Ruokonen, I.; Seppälä, M.; et al. Biodistribution of boron after intravenous 4-dihydroxyborylphenylalanine-fructose (BPA-F) infusion in meningioma and schwannoma patients: A feasibility study for boron neutron capture therapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 106, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageji, T.; Sogabe, S.; Mizobichi, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Shinji, N.; Nakagawa, Y. Radiation-induced meningiomas after BNCT in patients with malignant glioma. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 106, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaji, H.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Shinmura, K.; Kawabata, S.; Tokuyama, T.; Namba, H. Effect of boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent anaplastic meningioma: An autopsy case report. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2014, 32, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, S.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kuroiwa, T.; Ono, K.; Miyatake, S.-I. Boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent high-grade meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyama, H.; Nakai, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Nariai, T.; Kumada, H.; Ishikawa, E.; Isobe, T.; Endo, K.; Takada, T.; Yoshida, F.; et al. A clinical trial protocol for second line treatment of malignant brain tumors with BNCT at University of Tsukuba. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.-I.; Kawabata, S.; Nonoguchi, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Matsui, H.; Ono, K. Pseudoprogression in boron neutron capture therapy for malignant gliomas and meningiomas. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.-I.; Tamura, Y.; Kawabata, S.; Iida, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for malignant tumors related to meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenstam, B.H.; Pellettieri, L.; Sorteberg, W.; Rezaei, A.; Sköld, K. BNCT for recurrent intracranial meningeal tumours—Case reports. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 115, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Nonoguchi, N.; Miyata, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Doi, A.; Kuroiwa, T.; Asada, M.; Tanabe, H.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent malignant meningioma: Case report. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.; Kawabata, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Doi, A.; Iida, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Maruhashi, A.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for malignant meningiomas using epithermal neutron and 2 kinds of boron compounds with different accumulation mechanism. KURRI Prog. Rep. 2006, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake, S.-I. Modern radiotherapy for malignant brain tumors including the role of surgery in radiotherapy. Japanese J. Neurosurg. 2010, 19, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miyashita, M.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Imahori, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Kawabata, S.; Kajimoto, Y.; Shibata, M.-A.; Otsuki, Y.; Kirihata, M.; Ono, K.; et al. Evaluation of fluoride-labeled boronophenylalanine-PET imaging for the study of radiation effects in patients with glioblastomas. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 89, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, S.; Miyatake, S.-I. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Malignant Meningiomas; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 9783642313, ISBN 9783642313349. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, K.; Konno, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ono, K.; Otsuki, N.; Hatazawa, J.; Hiratsuka, J.; Takai, Y. Updated results of a phase II study evaluating accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy (AB-BNCT) with borofalan(10B) (SPM-011) in recurrent squamous cell carcinoma (R-SCC-HN) and recurrent and locally advanced non-SCC (R/LA-nSCC-HN) of the head an. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman, A.; Wile, A.G.; Burns, R.G.; Mason, G.R.; Berns, M.W.; Johnson, F.M. Laser Photoradiation Therapy of Cancer. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostron, H.; Fritsch, E.; Grunert, V. Photodynamic therapy of malignant brain tumours: A phase III trial. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 2, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plattner, M.; Bernwick, W.; Kostron, H. Hematoporphyrin-Derivative Photodynamic In vitro Sensitivity testing for Braintumors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Photodynamic Therapy and Laser Medicine, Beijing, China, 5 March 1991; Volume 1616, pp. 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhu, S. Adjuvant photodynamic therapy in surgical management of cerebral tumors. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Beijing, China, 15 October 1991; Volume 1616, pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, S.K. Current status of lasers in neurosurgical oncology. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1992, 8, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.V.; Furneaux, C.; Shivvakumar, R. An in vitro study of the effect of photodynamic therapy on human meningiomas. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 6, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Powers, S.K. Lasers in neurosurgery. Lasers Surg. Med. 1994, 15, 126–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostron, H.; Hochleitner, B.W.; Obwegeser, A.; Seiwald, M. Clinical and experimental results of photodynamic therapy in neurosurgery. In Proceedings of the 5th International Photodynamic Association Biennial Meeting, Amelia Island, FL, USA, 1 March 1995; Volume 2371, pp. 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Origitano, T.C.; Karesh, S.M.; Henkin, R.E.; Halama, J.R.; Reichman, O.H. Pal neoplasms: Investigations of photosensitizer uptake and distribution using indium-111 photofrin-ii single photon emission computed tomography scans in humans with intracranial neoplasms. Neurosurgery 1993, 32, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-C.; Hsiao, Y.-Y.; Teng, L.-J.; Chen, C.-T.; Kao, M.-C. Comparative study on the ALA photodynamic effects of human glioma and meningioma cells. Lasers Surg. Med. 1999, 24, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljamel, M.S. Which intracranial lesions would be suitable for fluoresce guided resection? A prospective review of 110 consecutive lesions. In Proceedings of the Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging—Proceedings of SPIE, Seattle, WA, USA, 13 July 2009; Volume 7380. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kajimoto, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Ikegami, Y.; Kuroiwa, T. Critical Role of ABCG2 in ALA-Photodynamic Diagnosis and Therapy of Human Brain Tumor. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 125, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Khatib, M.; Tepe, C.; Senger, B.; Dibué-Adjei, M.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Stummer, W.; Steiger, H.J.; Cornelius, J.F. Aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy of human meningioma: An in vitro study on primary cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9936–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez Valle, R.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Stummer, W. Established and emerging uses of 5-ALA in the brain: An overview. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefti, M.; Holenstein, F.; Albert, I.; Looser, H.; Luginbuehl, V. Susceptibility to 5-Aminolevulinic acid based photodynamic therapy in WHO i meningioma cells corresponds to ferrochelatase activity. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefti, M.; Von Campe, G. Fluorescence guided resection and photodynamic therapy in meningiomas. J. Anal. Oncol. 2012, 1, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, M.J.; Leyen, K.V.; Jeffree, R.L. Aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-protoporphyrin IX fluorescence guided tumour resection. Part 2: Theoretical, biochemical and practical aspects. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Kajimoto, Y.; Inoue, H.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuroiwa, T. Gefitinib enhances the efficacy of photodynamic therapy using 5-aminolevulinic acid in malignant brain tumor cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2013, 10, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahaninia, M.; Martirosyan, N.L.; Georges, J.; Udovich, J.A.; Kalani, M.Y.S.; Feuerstein, B.G.; Nakaji, P.; Spetzler, R.F.; Preul, M.C. Intraoperative fluorescent imaging of intracranial tumors: A review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokes, B.; Apel, M.; Jones, C.; Brown, G.; Lang, J.E. Aminolevulinic acid (ALA): Photodynamic detection and potential therapeutic applications. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 181, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, J.F.; Slotty, P.J.; El Khatib, M.; Giannakis, A.; Senger, B.; Steiger, H.J. Enhancing the effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid based photodynamic therapy in human meningioma cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2014, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechet, D.; Mordon, S.R.; Guillemin, F.; Barberi-Heyob, M.A. Photodynamic therapy of malignant brain tumours: A complementary approach to conventional therapies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, M.; Akimoto, J.; Miki, Y.; Maeda, J.; Takahashi, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kohno, M. Photodynamic therapy with talaporfin sodium induces dose- and time-dependent apoptotic cell death in malignant meningioma HKBMM cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 25, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, S.; Misawa, S.; Akimoto, J.; Shinoda, Y.; Fujiwara, Y. Photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in rat malignant meningioma KMY-J cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woehlck, H.; Herrmann, D.; Kaslow, O. Safe use of pulse oximetry during verteporphin therapy. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Devaux, B.C.; Roux, F.X. Experimental and clinical standards, and evolution of lasers in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir. (Wien.) 1996, 138, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malham, G.M.; Thomsen, R.J.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C. Subcellular distribution and photocytotoxicity of aluminium phthalocyanines and haematoporphyrin derivative in cultured human meningioma cells. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 10, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.C.; Malham, G.M.; Thomsen, R.J.; Harvey, J.D.; Baguley, B.C. Determination of the activation spectrum of aluminium phthalocyanine chloride against cultured meningioma cells using a tunable laser. J. Clin. Neurosci. 1996, 3, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, J.D.; Weiss, M.J.; Elmaleh, D.R.; Martuza, R.L. Enhanced in vitro uptake and retention of 3H-tetraphenylphosphonium by nervous system tumor cells. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 74, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; Stepp, H.; Möller, G.; Ehrhardt, A.; Leonhard, M.; Reulen, H.J. Technical principles for protoporphyrin-IX-fluorescence guided microsurgical resection of malignant glioma tissue. Acta Neurochir. (Wien.) 1998, 140, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; Pichlmeier, U.; Meinel, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Zanella, F.; Reulen, H.-J. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebeiz, N.; Rebeiz, C.C.; Arkins, S.; Kelley, K.W.; Rebeiz, C.A. Photodestruction of tumor cells by induction of endogenouw accumulation of protoporphyrin IX: Enhancement by 1,10-phenanthroline. Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 55, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.S.; Roberts, W.G.; Berns, M.W. In Vivo Studies on the Utilization of Mono-L-aspartyl Chlorin (NPe6) for Photodynamic Therapy. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 4681–4685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, J.; Haraoka, J.; Aizawa, K. Preliminary clinical report on safety and efficacy of photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium for malignant gliomas. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muragaki, Y.; Akimoto, J.; Maruyama, T.; Iseki, H.; Ikuta, S.; Nitta, M.; Maebayashi, K.; Saito, T.; Okada, Y.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Phase II clinical study on intraoperative photodynamic therapy with talaporfin sodium and semiconductor laser in patients with malignant brain tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shibuya, H.; Okunaka, T.; Aizawa, K.; Kato, H. Fibrin plugging as a cause of microcirculatory occlusion during photodynamic therapy. Lasers Med. Sci. 1999, 14, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors | Country | Published Year | No. of Patient with a Meningioma (WHO Grade) | Boron Compound | Research Target or Content | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Takeuchi, et al. | Japan | 2018 | 33 (12 grade II, 21 grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Patients with skull base HGMs | [20] |
| Beshr, et al. | Japan | 2018 | 1 (ND) | 18F-BPA | 18F-BPA -PET | [21] |
| Kulvik, et al. | Finland | 2015 | 3 (3 grade I) | BPA | Biodistribution of boron | [22] |
| Kageji, et al. | Japan | 2015 | 1 (ND) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Radiation-induced meningioma after BNCT | [23] |
| Kawaji, et al. | Japan | 2014 | 1 (grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | An autopsy case after BNT | [24] |
| Kawabata, et al. | Japan | 2013 | 20 (4 grade II, 16 grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Patients with recurrent HGMs | [25] |
| Aiyama, et al. | Japan | 2011 | 1 (grade III) | BPA, 18F-BPA | A case of MM | [26] |
| Miyatake, et al. | Japan | 2009 | 13 (MM) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Pseudoprogression in patients after BNCT | [27] |
| Miyatake, et al. | Japan | 2007 | 7 (1 grade II, 6 grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Patients with HGMs | [28] |
| Stenstam, et al. | Sweden | 2007 | 3 (1 grade II, 2 grade III) | BPA | Accumulation of boron | [29] |
| Havu-Aurén, et al. | Finland | 2007 | 4 (ND) | 18F-BPA | 18F-BPA -PET | [18] |
| Tamura, et al. | Japan | 2006 | 1 (1 grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | The first case of MM treated by BNCT | [30] |
| Miyatake, et al. | Japan | 2006 | 11 (11 grade III) | BPA, BSH, 18F-BPA | Patients with MM | [31] |
| Stragliotto, et al. | Switzerland | 1995 | 14 (ND) | BSH | Biodistribution of boron | [15] |
| Kraft, et al. | USA | 1994 | 8 animal models (ND) | BSH | Biodistribution of boron | [14] |
| PS | 1st Generation | 2nd Generation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porfimer Sodium | 5-Aminolevulinic Acid | Talaporfin Sodium | |
| Structure | Porphyrin | Porphyrin precursor | Chlorin |
| Laser Device | Excimer dye laser | Semiconductor laser | Semiconductor laser |
| Wavelength (nm) | 630 | 635 | 664 |
| Target Cancers | Lung, esophagus, bile duct, bladder, ovarian, brain | Skin, bladder, esophagus, brain | Lung, esophagus, brain |
| References of Studies for Meningiomas | [9,44] | [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] | [20,58] |
| Type of Study | Authors | Published Year | PS | No. of Patients with a Meningioma (WHO Grade) | Cell Lines | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro | Ichikawa, et al. | 2019 | talaporfin | HKBMM (human MM), KMY-J (rat MM) | [58] | |
| Review | Diez, et al. | 2019 | 5-ALA | [49] | ||
| In vitro | Takahashi, et al. | 2018 | talaporfin | KMY-J (rat MM) | [59] | |
| In vitro | El-Khatib, et al. | 2015 | 5-ALA | 12 (grade I), 1 (grade II) and 1 (grade III) cultured from specimen | [48] | |
| Review | Ishikawa, et al. | 2015 | 5-ALA | [47] | ||
| Review | Bechet, et al. | 2014 | All established PSs before publish date | [57] | ||
| In vitro | Cornelius, et al. | 2014 | 5-ALA | KT21-MG (human MM) | [56] | |
| Review | Nokes, et al. | 2014 | 5-ALA | [55] | ||
| Review | Behbananinia, et al. | 2013 | All established PSs before publish date | [54] | ||
| In vitro | Sun, et al. | 2013 | 5-ALA | IOMM-Lee (human MM) | [53] | |
| Review | Colditz, et al. | 2012 | 5-ALA | [52] | ||
| Review | Hefti, et al. | 2012 | 5-ALA | [51] | ||
| In vitro | Hefti, et al. | 2011 | 5-ALA | HBL-52& BEN-MEN-1 (human benign meningioma) | [50] | |
| Clinical | Eljamel, et al. | 2009 | 5-ALA | 2 (ND) | [46] | |
| Clinical | Muller, et al. | 2006 | Profimer | 3 (MM) | [9] | |
| Clinical | Woehlck, et al. | 2003 | Verteporphin | 1 (MM) | [60] | |
| In vitro | Tsai, et al. | 1999 | 5-ALA | CH-157MN (benign meningioma) | [45] | |
| Review | Devaux, et al. | 1996 | All established PSs before publish date | [61] | ||
| In vitro | Malham, et al. | 1996 | HpD, AIPC | 5 cell lines cultured from specimen (WHO grade: ND) | [62] | |
| In vitro | Wilson, et al. | 1996 | AIPC | 2 cell lines cultured from specimen (WHO grade: ND) | [63] | |
| Clinical | Kostron, et al. | 1995 | HpD | 3(MM) | [43] | |
| Review | Krishnamurthy, et al. | 1994 | HpD | [42] | ||
| Clinical | Origitano, et al. | 1993 | Profimer | 1 (ND) | [44] | |
| In vitro | Marks, et al. | 1992 | HpD | 5 cell lines cultured from specimen (4: grade I, 1: grade II) | [41] | |
| Review | Powers, et al. | 1992 | HpD | [40] | ||
| Clinical | Chen, et al. | 1991 | HpD | 1 (MM) | [39] | |
| In vitro | Plattner, et al. | 1991 | HpD | 1 cell line cultured from specimen (WHO grade: ND) | [38] | |
| In vitro | Steichen, et al. | 1991 | Tritiated-TPP | 3 cell lines cultured from specimen (WHO grade: ND) | [64] | |
| Clinical | Kostron, et al. | 1990 | HpD | 1 (MM) | [8] | |
| Clinical | Kostron, et al. | 1988 | HpD | 1 (MM) | [37] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakahara, Y.; Ito, H.; Masuoka, J.; Abe, T. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade Meningiomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051334
Nakahara Y, Ito H, Masuoka J, Abe T. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade Meningiomas. Cancers. 2020; 12(5):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051334
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakahara, Yukiko, Hiroshi Ito, Jun Masuoka, and Tatsuya Abe. 2020. "Boron Neutron Capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade Meningiomas" Cancers 12, no. 5: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051334
APA StyleNakahara, Y., Ito, H., Masuoka, J., & Abe, T. (2020). Boron Neutron Capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade Meningiomas. Cancers, 12(5), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051334





