A Cantilever-Based Piezoelectric MEMS for Arbitrary XY Path Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Model
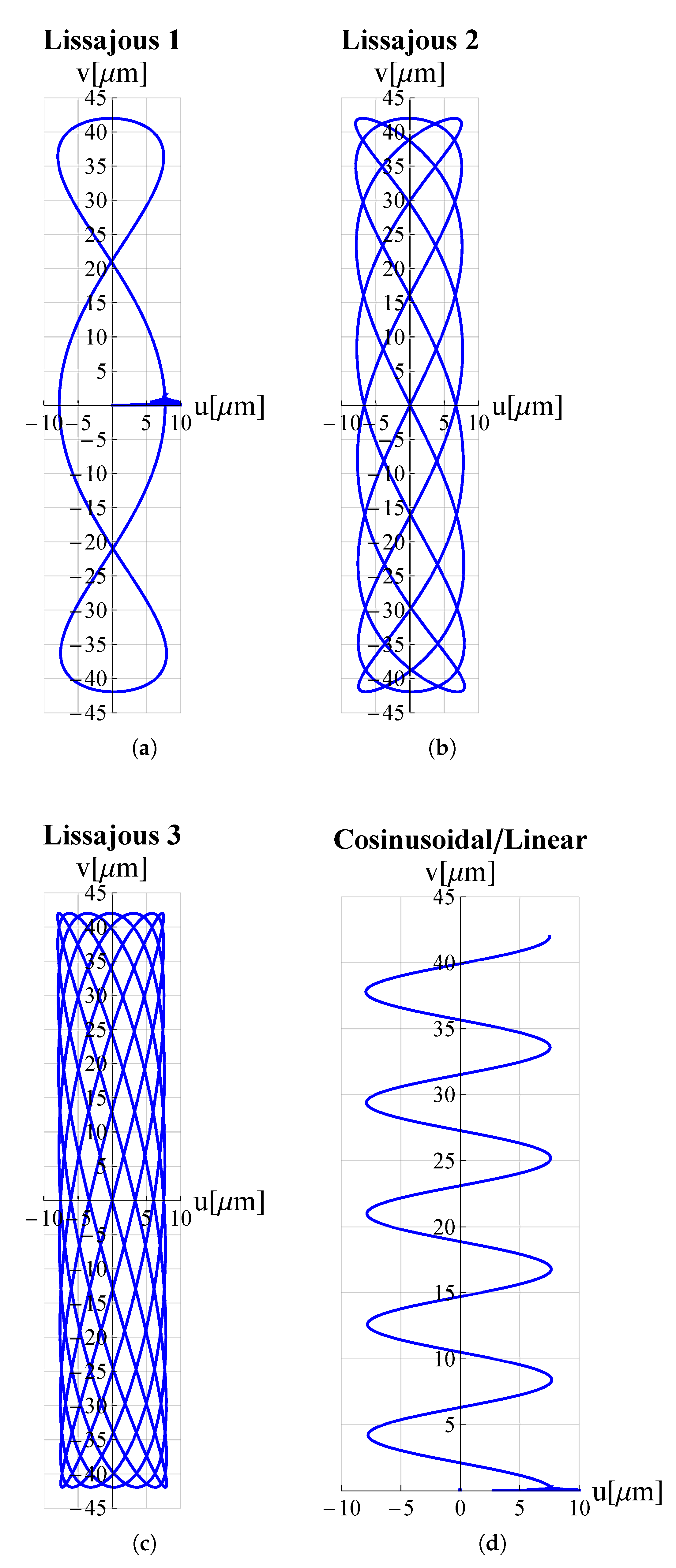
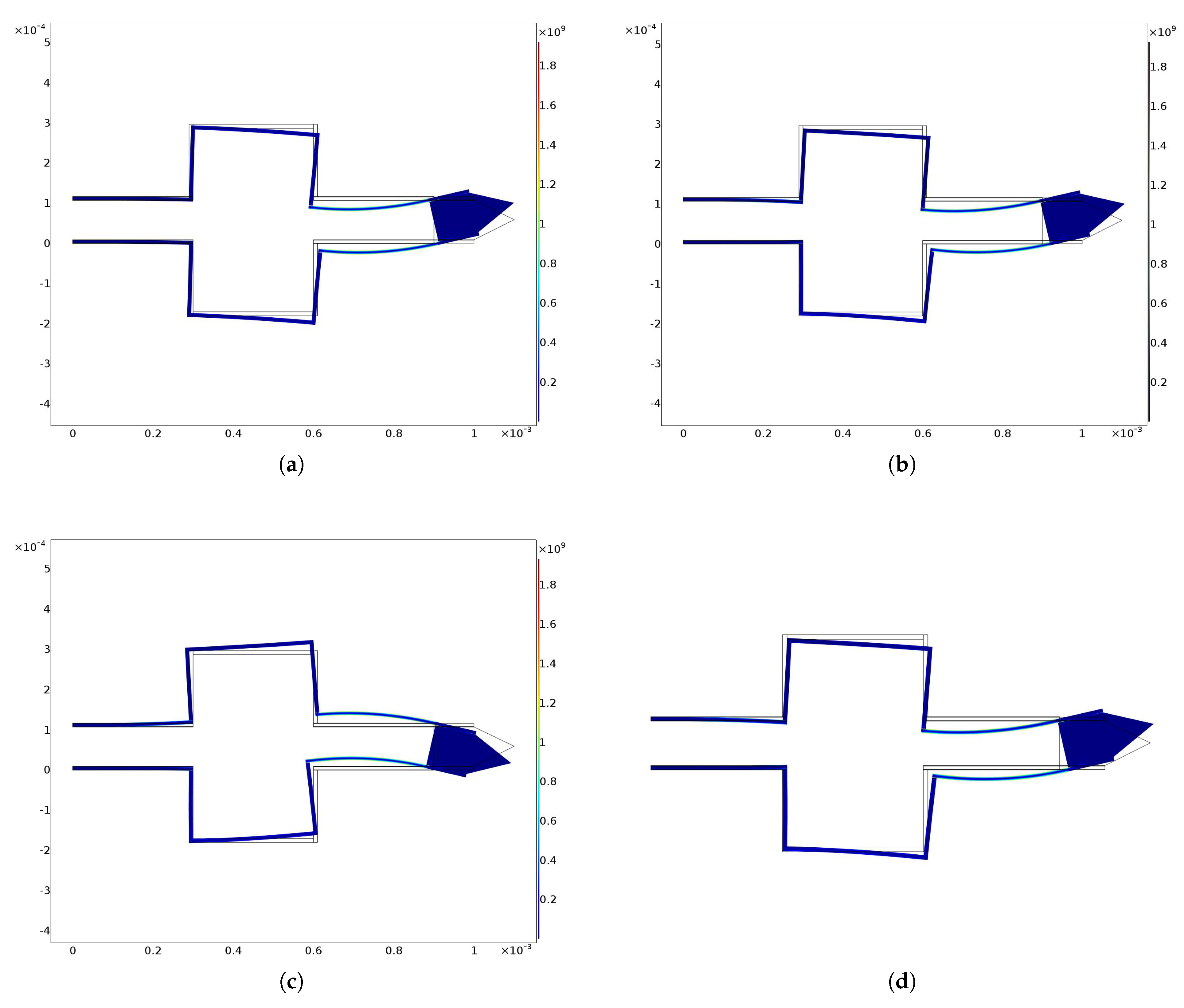
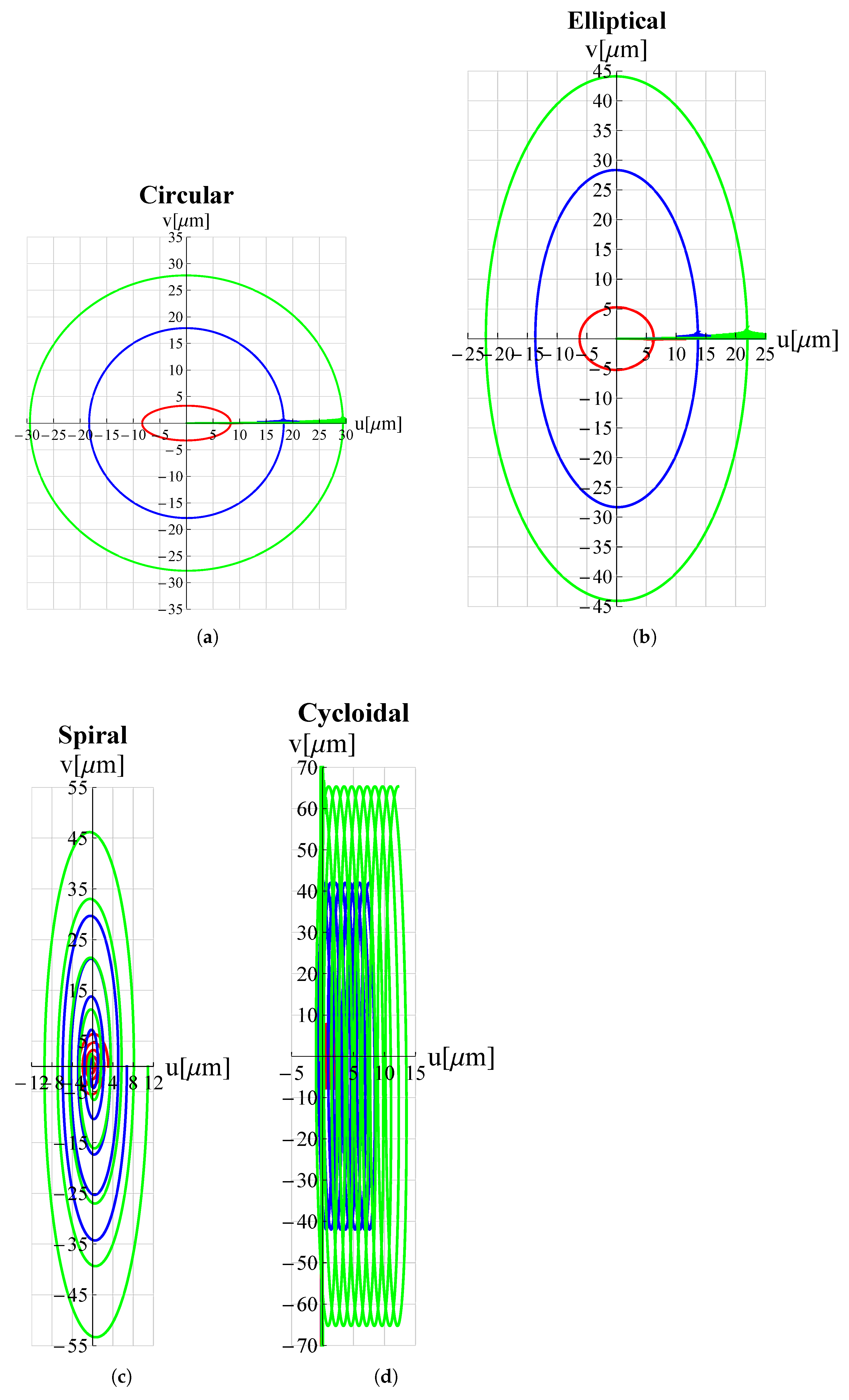
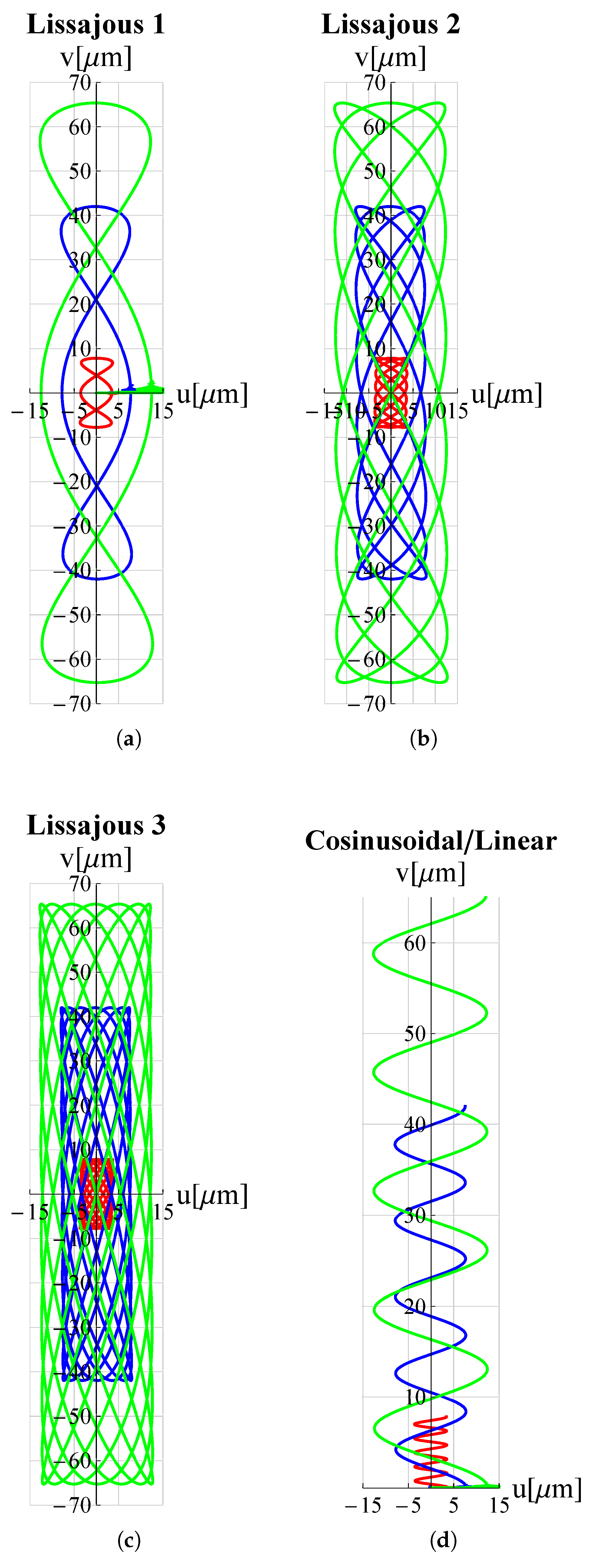
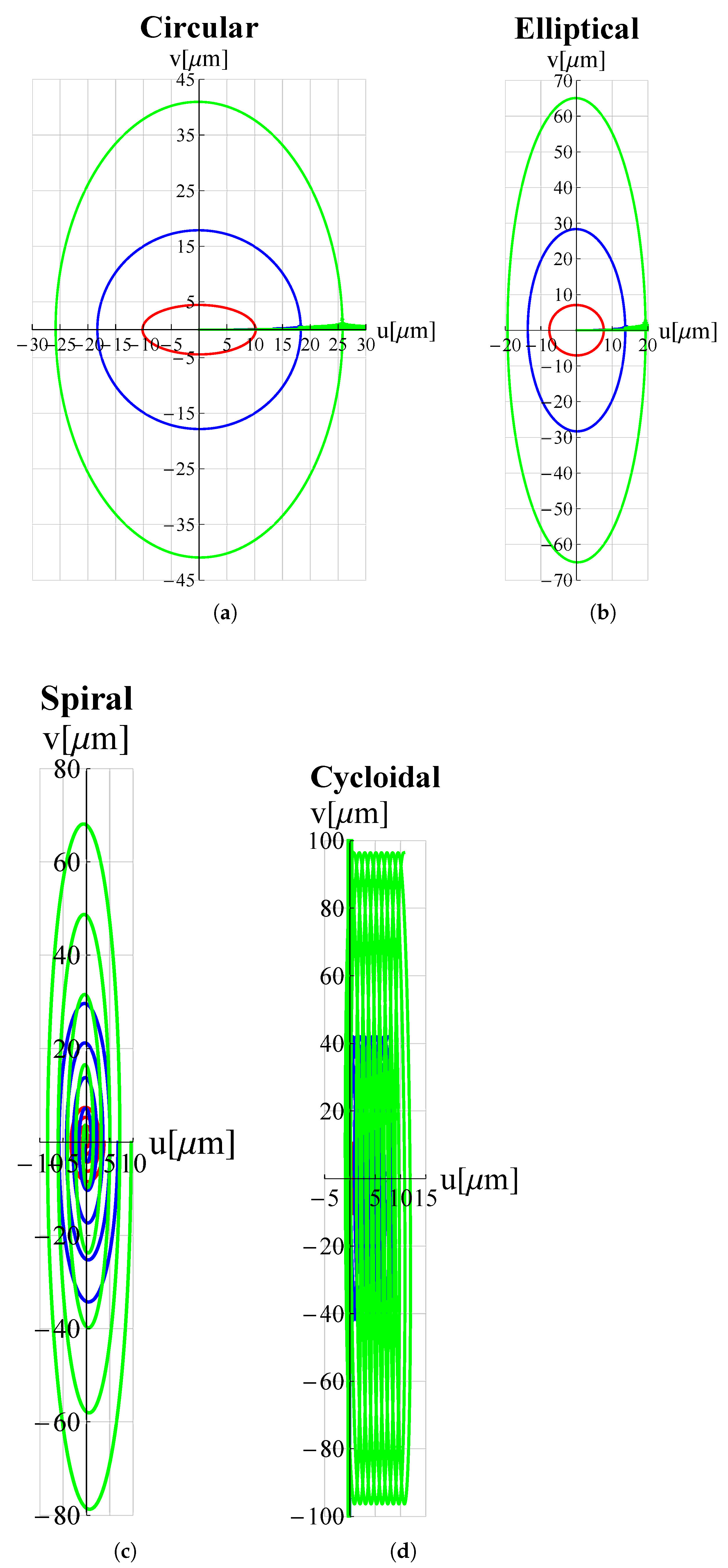
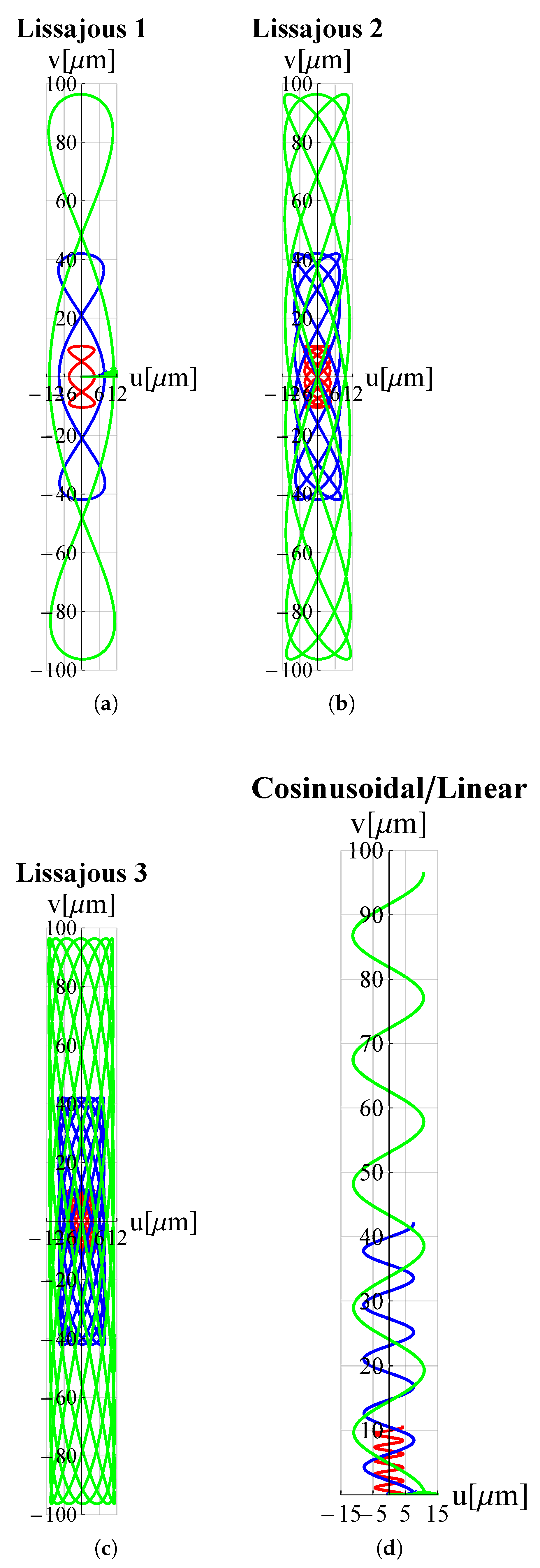
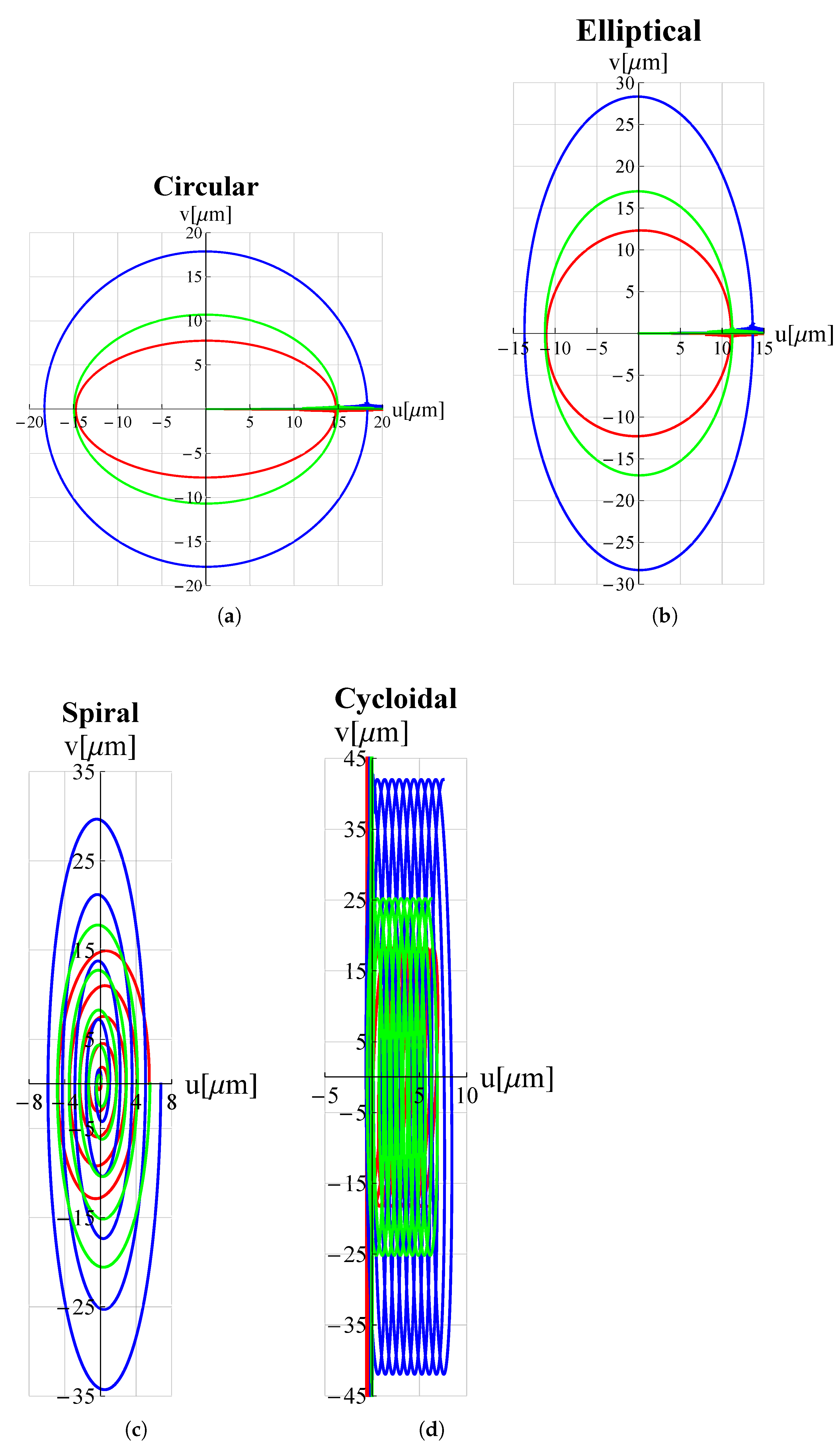
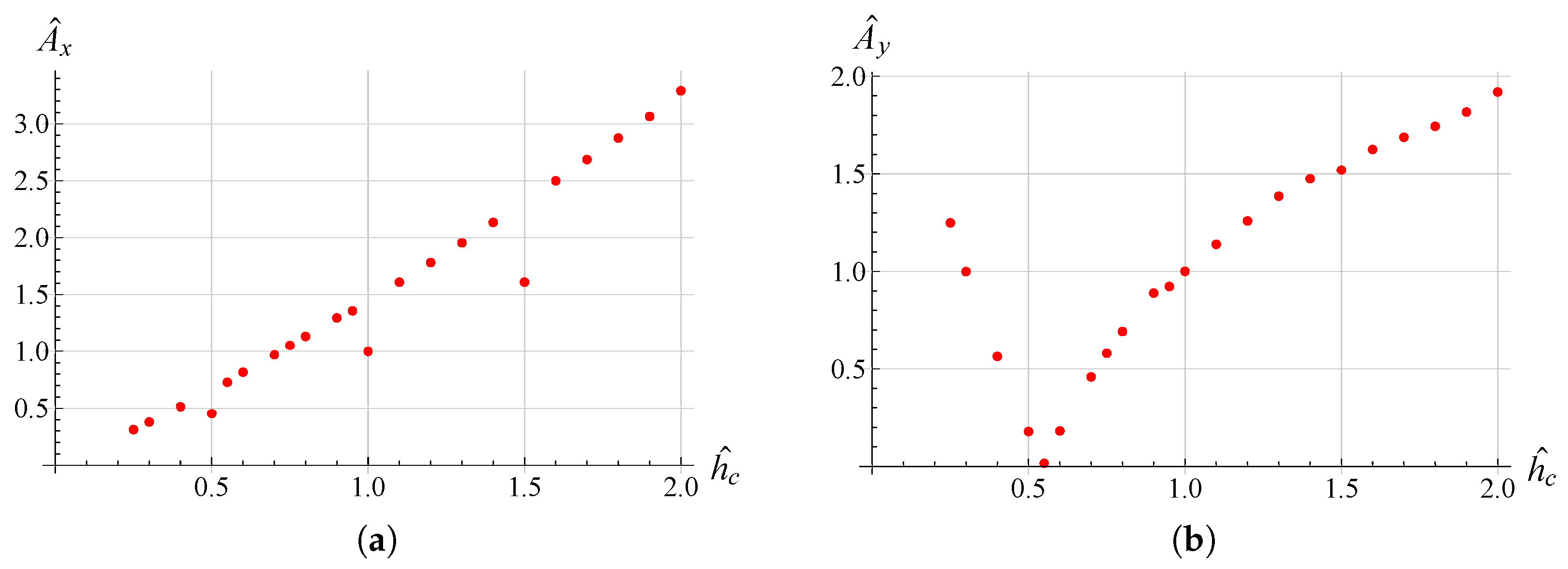
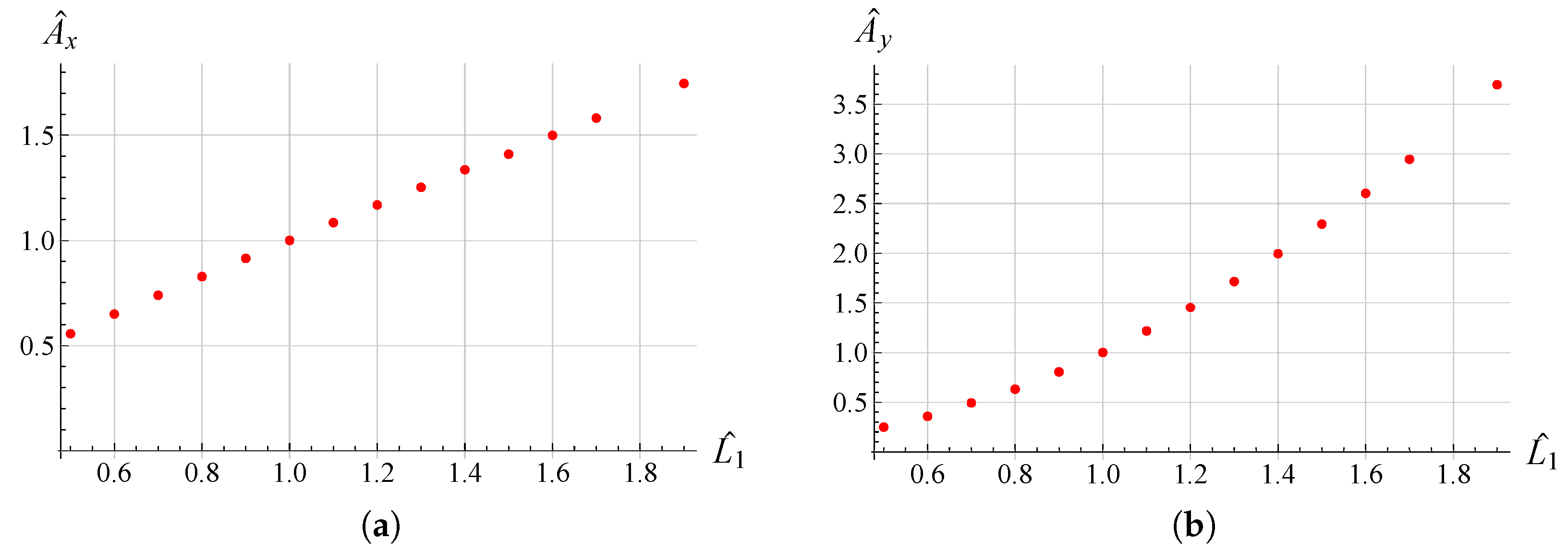
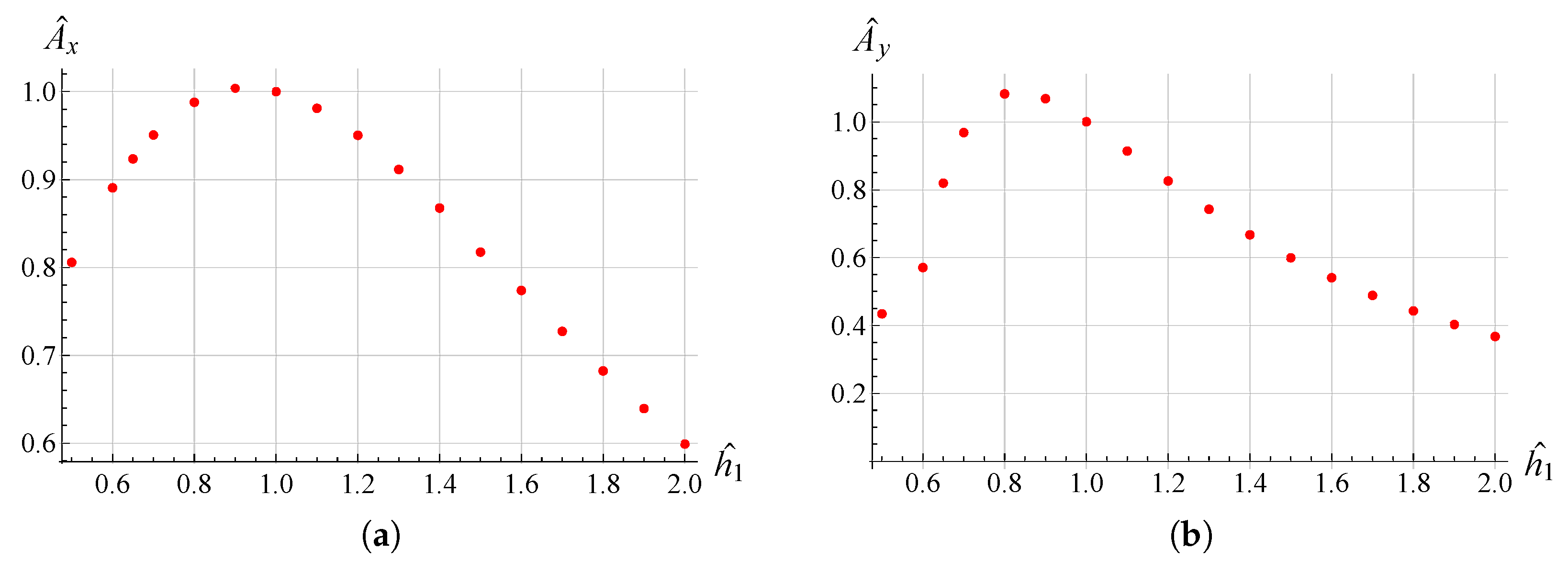
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otic, C.J.C.; Yonemura, S. Thermally Induced Knudsen Forces for Contactless Manipulation of a Micro-Object. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Hong, K. Design and Control of a Piezoelectric-Driven Microgripper Perceiving Displacement and Gripping Force. Micromachines 2020, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Ferreira, P.M. Design, fabrication and testing of a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) MEMS parallel kinematics XY stage. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Ling, Z.; Yu, W.; Shi, J. A Review of MEMS Scale Piezoelectric Energy Harvester. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, F.; Leng, H.; Zhang, C.; Luo, K.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X. Simplified Method of Microcontact Force Measurement by Using Micropressure Sensor. Micromachines 2021, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, H.; Elias, J.; Etienne, P.; Calas-Etienne, S. The Rise of the OM-LoC: Opto-Microfluidic Enabled Lab-on-Chip. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verotti, M.; Dochshanov, A.; Belfiore, N.P. Compliance Synthesis of CSFH MEMS-Based Microgrippers. J. Mech. Des. Trans. ASME 2017, 139, 022301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Verotti, M.; Bagolini, A.; Bellutti, P.; Belfiore, N.P. Mechanical response of four-bar linkage microgrippers with bidirectional electrostatic actuation. Actuators 2018, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, G.A. Modern Kinematics: Developments in the Last Forty Years; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kempe, A.B. On a General Method of describing Plane Curves of the nth degree by Linkwork. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1875, s1-7, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, H. Zur Synthese der ebenen Mechanismen. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech./Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1921, 1, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, A. Zur Theorie der ebenen ähnlich veränderlichen Systeme. Jahresber. Dtsch. Math.-Ver. 1914, 19, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Sanò, P.; Verotti, M.; Bosetti, P.; Belfiore, N.P. Kinematic Synthesis of a D-Drive MEMS Device With Rigid-Body Replacement Method. J. Mech. Des. Trans. ASME 2018, 140, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, W.; Xu, Q. New Structural Design of a Compliant Gripper Based on the Scott-Russell Mechanism. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2014, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Du, B.C. A precision piezodriven micropositioner mechanism with large travel range. Rev. Sci. Instrum 1998, 69, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hwang, D.; Byun, J.; Jeong, J.; Lee, M.G. Robust Design and Performance Verification of an In-Plane XYθ Micropositioning Stage. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2011, 10, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.L.; Kung, Y.S.; Hu, S.C.; Fung, R.F. Optimal design of a micro-positioning Scott-Russell mechanism by Taguchi method. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 2006, 125, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursi, P.; Rossi, A.; Botta, F.; Belfiore, N.P. Analytical Modeling of a New Compliant Microsystem for Atherectomy Operations. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verotti, M.; Dochshanov, A.; Belfiore, N.P. A Comprehensive Survey on Microgrippers Design: Mechanical Structure. J. Mech. Des. Trans. ASME 2017, 139, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, N.P. Micromanipulation: A challenge for actuation. Actuators 2018, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzin, A.; Rossi, A.; Giovine, E.; de Cesare, G.; Belfiore, N.P. Downsizing Effects on Micro and Nano Comb Drives. Actuators 2022, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovic, B.; Liu, A.Q.; Popa, D.; Cai, H.; Lewis, F.L. Open-loop versus closed-loop control of MEMS devices: Choices and issues. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, Y.; Chapuis, Y.A.; Mita, Y.; Fujita, H. Design, fabrication, and control of MEMS-based actuator arrays for air-flow distributed micromanipulation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennestrì, E.; Belfiore, N.P. On the numerical computation of Generalized Burmester Points. Meccanica 1995, 30, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennestrí, E.; Belfiore, N.P. On Crossley’s contribution to the development of graph based algorithms for the analysis of mechanisms and gear trains. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 89, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Rossi, A.; Belfiore, N.P. A novel method to fully suppress single and bi-modal excitations due to the support vibration by means of piezoelectric actuators. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 510, 116260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Marx, N.; Gentili, S.; Schwingshackl, C.; Di Mare, L.; Cerri, G.; Dini, D. Optimal placement of piezoelectric plates for active vibration control of gas turbine blades: Experimental results. In Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems 2012; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 8345, pp. 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, F.; Scorza, A.; Rossi, A. Optimal Piezoelectric Potential Distribution for Controlling Multimode Vibrations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Toccaceli, F. Piezoelectric plates distribution for active control of torsional vibrations. Actuators 2018, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, K.; Hirai, S.; Fujita, T.; Maenaka, K. Piezoelectric MEMS with multilayered Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 thin films for energy harvesting. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 281, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, H.; Hui, X.; Mu, X. Theoretical and Experimental Studies on MEMS Variable Cross-Section Cantilever Beam Based Piezoelectric Vibration Energy Harvester. Micromachines 2021, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naono, T.; Fujii, T.; Esashi, M.; Tanaka, S. Non-resonant 2-D piezoelectric MEMS optical scanner actuated by Nb doped PZT thin film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfusterschmied, G.; Kucera, M.; Wistrela, E.; Manzaneque, T.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L.; Bittner, A.; Schmid, U. Temperature dependent performance of piezoelectric MEMS resonators for viscosity and density determination of liquids. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellasivalingam, M.; Imran, H.; Pandit, M.; Boies, A.M.; Seshia, A.A. Weakly Coupled Piezoelectric MEMS Resonators for Aerosol Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, P.C.; Duan, H.; Chung, T.K. A Novel Three-Axial Magnetic-Piezoelectric MEMS AC Magnetic Field Sensor. Micromachines 2019, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, A.; Ishfaque, A.; Kim, B. Effect of Torsional Beam Length on Acoustic Functionalities of Bio-Inspired Piezoelectric MEMS Directional Microphone. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6046–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ruan, T.; Xu, Q.; Yang, B.; Liu, J. Wearable multifunctional piezoelectric MEMS device for motion monitoring, health warning, and earphone. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, M.; Ivan, I.A. Development and Force/Position Control of a New Hybrid Thermo-Piezoelectric MicroGripper Dedicated to Micromanipulation Tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Abo-Ismail, A.; El-Melegy, M.; Hamzaid, N.; Osman, N. Development of a Micro-Gripper Using Piezoelectric Bimorphs. Sensors 2013, 13, 5826–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Han, M.L.; Yu, M.Y.; Shee, C.Y.; Ang, W.T. Automatic Hysteresis Modeling of Piezoelectric Micromanipulator in Vision-Guided Micromanipulation Systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Majumder, S.; Ghosh, B.; Saha, S. Design and manufacturing of mobile micro manipulation system with a compliant piezoelectric actuator based micro gripper. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 35, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. A piezo-driven 2-DOF compliant micropositioning stage with remote center of motion. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 239, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q. Design and control of a novel piezo-driven XY parallel nanopositioning stage. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gan, J.; Ding, H.; Li, H. Design of a pure rotation micropositioning stage with dual-range. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 169, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Rossi, A.; Belfiore, N.P. A feasibility study of a novel piezo MEMS tweezer for soft materials characterization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, E.F.; de Luis, J. Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 1987, 25, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomi, Y.; Shlofmitz, R.A.; Colombo, A.; Serruys, P.W.; Onuma, Y. Patient Selection and Procedural Considerations for Coronary Orbital Atherectomy System. Interv Cardiol. 2016, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Badal, F.R.; Rahman, A.; Islam, A.; Sarker, S.K.; Paul, N. Improvement of Alternative Non-Raster Scanning Methods for High Speed Atomic Force Microscopy: A Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115603–115624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marauska, S.; Hrkac, V.; Dankwort, T.; Jahns, R.; Quenzer, H.J.; Knöchel, R.; Kienle, L.; Wagner, B. Sputtered thin film piezoelectric aluminum nitride as a functional MEMS material. Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 18, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Marx, N.; Schwingshackl, C.; Cerri, G.; Dini, D. A wireless vibration control technique for gas turbine blades using piezoelectric plates and contactless energy transfer. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 55263, p. V07AT32A006. [Google Scholar]

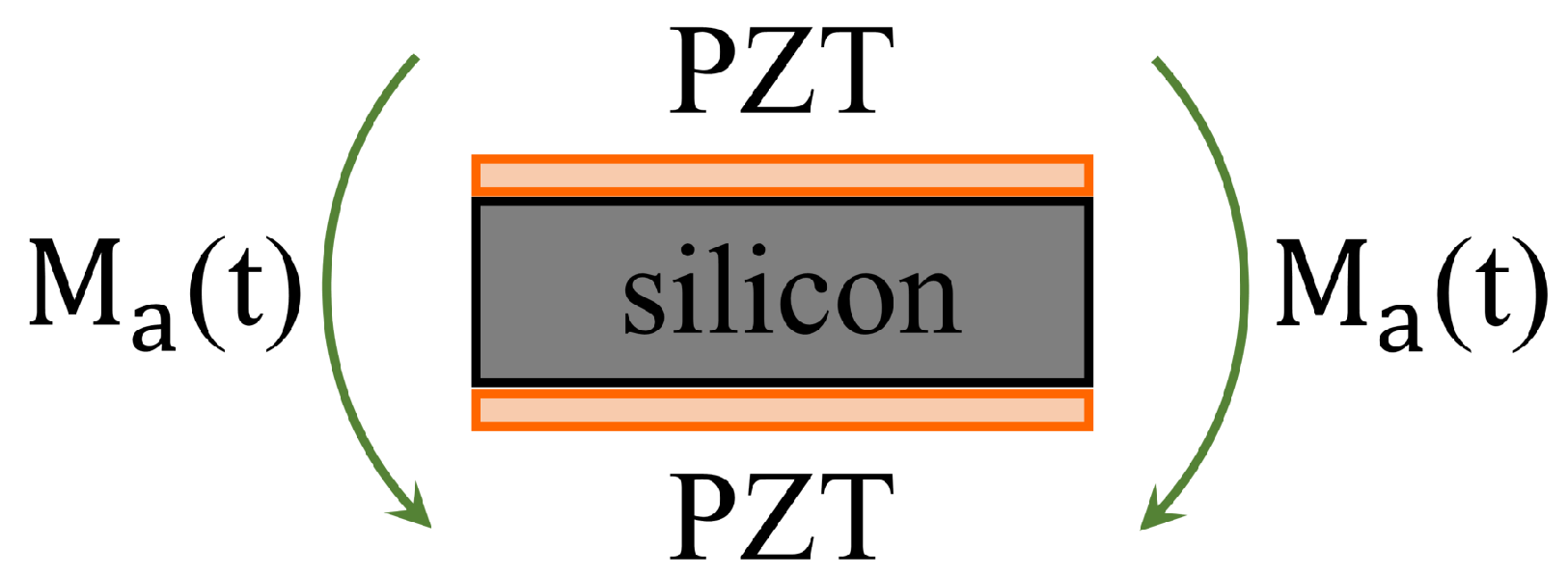




| Label | Value (m) | Label | Value (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 100 | ||
| 100 | 1 | ||
| 7.5 | 180 | ||
| 10 | |||
| Lg | |||
| out-of-plane thickness | 7.5 | ||
| Property | Silicon | PZT-5A | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 2329 | 7750 | kg/m |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.28 | – | – |
| Young’s modulus | 170 | 65 | GPa |
| – | −1.71 | C/N | |
| – | 3.74 | C/N | |
| – | 5.84 | C/N |
| Trajectory | Voltage Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | ||||
| Circular | ||||
| Elliptical | ||||
| Spiral | ||||
| Cycloidal | ||||
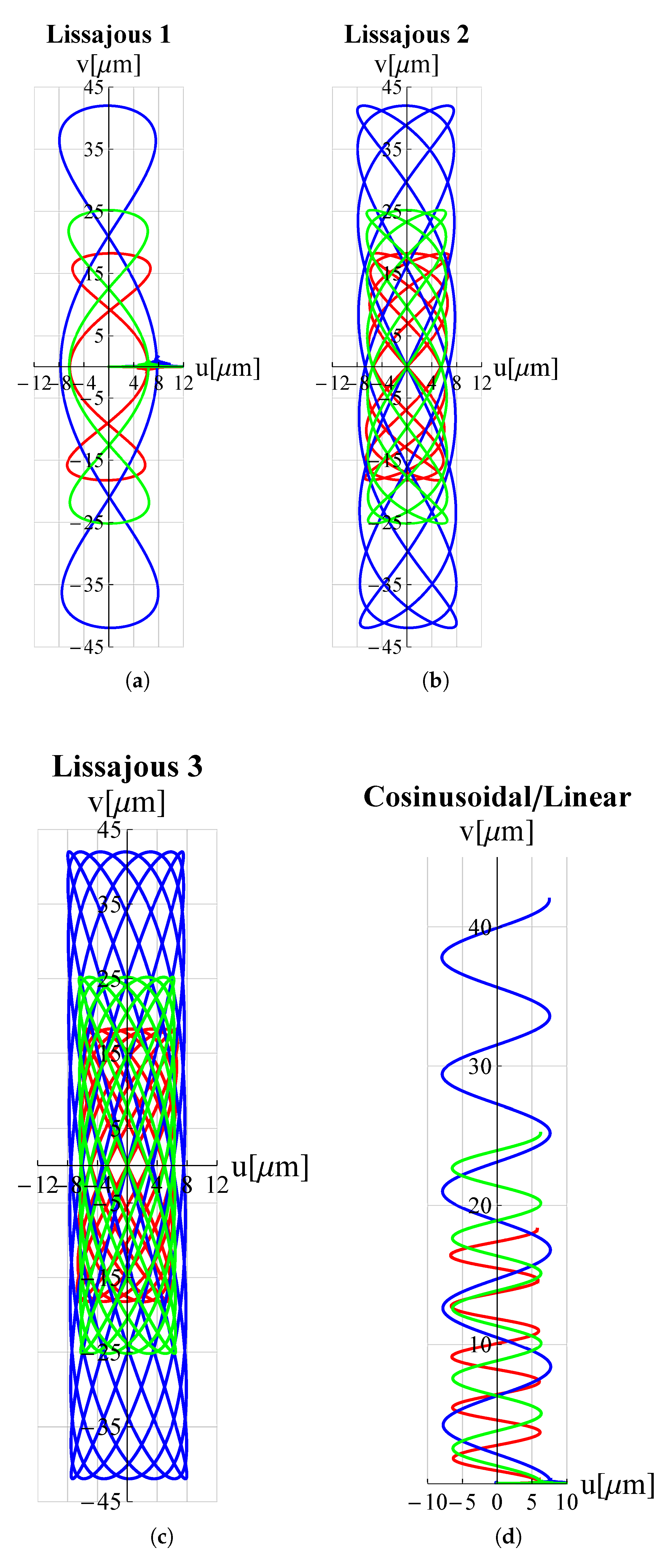
| Lissajous 1 | ||||
| Lissajous 2 | ||||
| Lissajous 3 | ||||
| Cosinusoidal/Linear | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botta, F.; Rossi, A.; Belfiore, N.P. A Cantilever-Based Piezoelectric MEMS for Arbitrary XY Path Generation. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091514
Botta F, Rossi A, Belfiore NP. A Cantilever-Based Piezoelectric MEMS for Arbitrary XY Path Generation. Micromachines. 2022; 13(9):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091514
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotta, Fabio, Andrea Rossi, and Nicola Pio Belfiore. 2022. "A Cantilever-Based Piezoelectric MEMS for Arbitrary XY Path Generation" Micromachines 13, no. 9: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091514
APA StyleBotta, F., Rossi, A., & Belfiore, N. P. (2022). A Cantilever-Based Piezoelectric MEMS for Arbitrary XY Path Generation. Micromachines, 13(9), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091514







