Investigation of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on the Bandwidth of an Accelerometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
2.1. Vibration Model and Bandwidth of Accelerometer
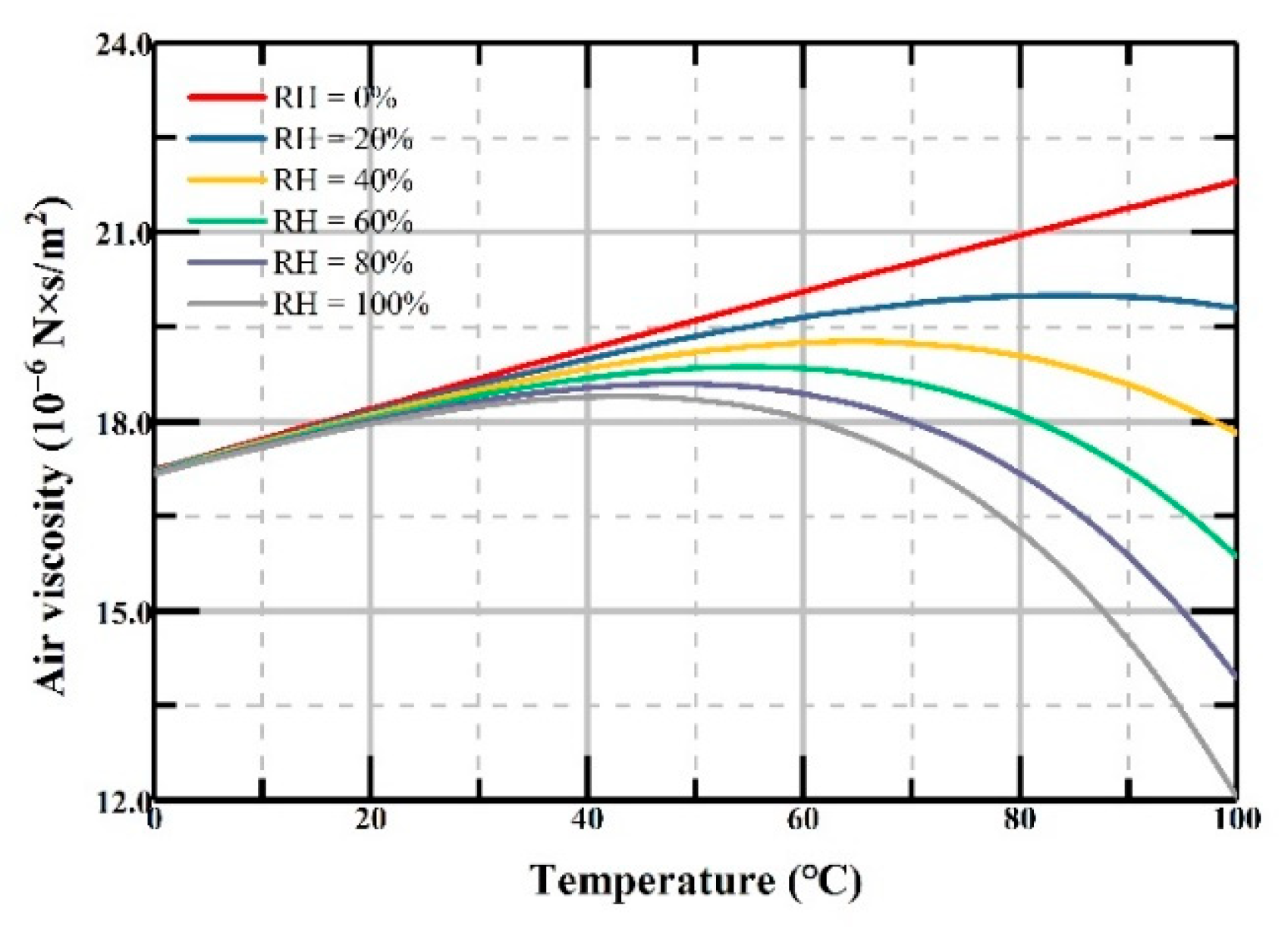
2.2. Environment Effect on Bandwidth of Accelerometer
3. Simulation Verification
3.1. Simulation Model
3.2. Benchmark between the Simulation and Theoretical Results
3.2.1. Damping Coefficient
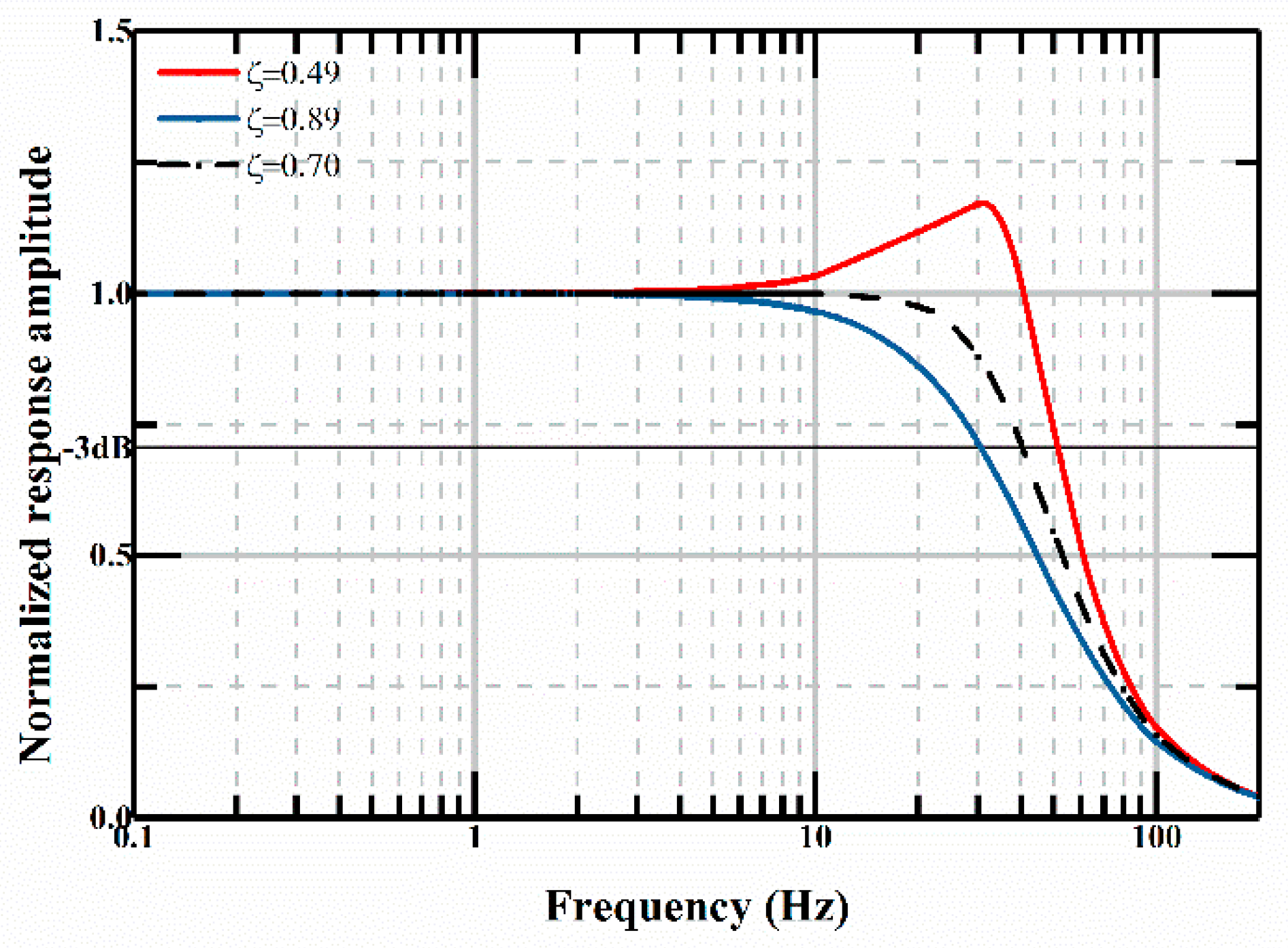
3.2.2. Vibration Response
3.2.3. Compensation Guide for Bandwidth under Environment Effect
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Q.B.; Wang, Y.A.; Wang, X.X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.W.; Huang, W. Review of micromachined optical accelerometers: From mg to sub-mu g. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2021, 4, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Liu, C.Y. A novel estimation scheme for six-accelerometer inertial navigation system. JSME Int. J. Ser. C Mech. Syst. Mach. Elem. Manuf. 1999, 42, 369–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, A.; Beverini, N.; Cella, G.; DeSalvo, R.; Fidecaro, F.; Francesconi, M.; Simonetti, D. Geometric anti-spring vertical accelerometers for seismic monitoring. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2004, 518, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ghosh, S.; Barat, A.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Chowdhury, D. Real-time Implementation of Electromyography for Hand Gesture Detection Using Micro Accelerometer. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2016, 394, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, S.; Coupland, J. The new laser Doppler accelerometer for shock and vibration measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 1996, 25, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, J.J.; Zucker, P.A.; Martin, L.P. Precision Accelerometers for Gravity Gradient Measurements. J. Hopkins APL Tech. D 1994, 15, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Utz, A.; Walk, C.; Stanitzki, A.; Mokhtari, M.; Kraft, M.; Kokozinski, R. A High-Precision and High-Bandwidth MEMS-Based Capacitive Accelerometer. LEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6533–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corigliano, A. Mechanics of Microsystems.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 168–192. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.G.; Winger, M.; Blasius, T.D.; Lin, Q.; Painter, O. A high-resolution microchip optomechanical accelerometer. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, M. Analysis and Design Principles of MEMS Devices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 84–96. [Google Scholar]
- Veijola, T.; Kuisma, H.; Lahdenpera, J. The influence of gas-surface interaction on gas-film damping in a silicon accelerometer. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 1998, 66, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creath, K. V Phase-Measurement Interferometry Techniques. Prog. Opt. 1988, 26, 349–393. [Google Scholar]
- Blech, J.J. On Isothermal Squeeze Films. J. Lubr. Technol. 1983, 105, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, H.; Chatterjee, A.N.; Elfadel, I.M.; Ocak, I.E.; Zhang, T.J. A novel approach to the analysis of squeezed-film air damping in microelectromechanical systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 27, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharipov, F.; Seleznev, V. Data on internal rarefied gas flows. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1998, 27, 657–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsilingiris, P.T. Thermophysical and transport properties of humid air at temperature range between 0 and 100°C. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Wang, K.; Jiao, X.; Han, D.; Chen, P.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G. Determination of thermally induced effects and design guidelines of optomechanical accelerometers. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravve, A. Principles of Polymer Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]








| Name | Unit | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density of silicon | Kg/m3 | 2330 |
| Young’s modulus of silicon | GPa | Refer to Figure 4 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion of silicon | -- | Refer to Figure 4 |
| Length of the proof mass | m | 4.29 × 10−3 |
| Width of the proof mass | m | 4.29 × 10−3 |
| Height of the proof mass | m | 0.49 × 10−3 |
| Length of the cantilever | m | 2.50 × 10−3 |
| Width of the cantilever | m | 240 × 10−6 |
| Height of the cantilever | m | 10 × 10−6 |
| Weight of the proof mass | kg | 2.10 × 10−5 |
| Elastic coefficient | N/m | 10.20 |
| First-order resonant frequency | Hz | 110.88 |
| Air film thickness | m | 50 × 10−6 |
| Air viscosity | -- | Refer to Equation (11) |
| Designed damping coefficient | 0.0204 | |
| Designated damping ratio | -- | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Fang, W.; Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, Q. Investigation of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on the Bandwidth of an Accelerometer. Micromachines 2021, 12, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080860
Huang H, Fang W, Wang C, Bai J, Wang K, Lu Q. Investigation of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on the Bandwidth of an Accelerometer. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080860
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Haoyu, Weidong Fang, Chen Wang, Jian Bai, Kaiwei Wang, and Qianbo Lu. 2021. "Investigation of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on the Bandwidth of an Accelerometer" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080860
APA StyleHuang, H., Fang, W., Wang, C., Bai, J., Wang, K., & Lu, Q. (2021). Investigation of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on the Bandwidth of an Accelerometer. Micromachines, 12(8), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080860









