Individual Microparticle Manipulation Using Combined Electroosmosis and Dielectrophoresis through a Si3N4 Film with a Single Micropore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
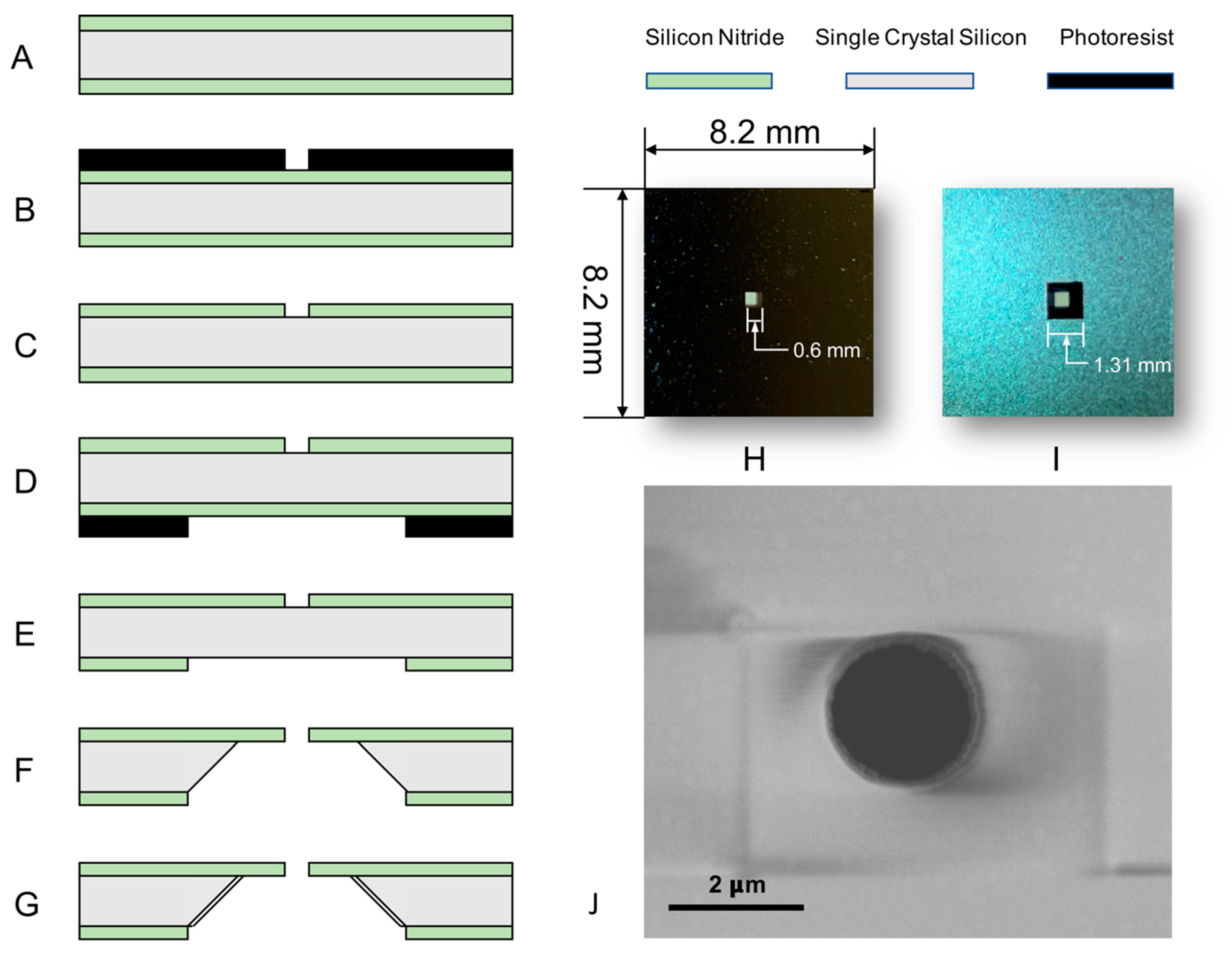
2.1. Micro-Pore Chip Fabrication
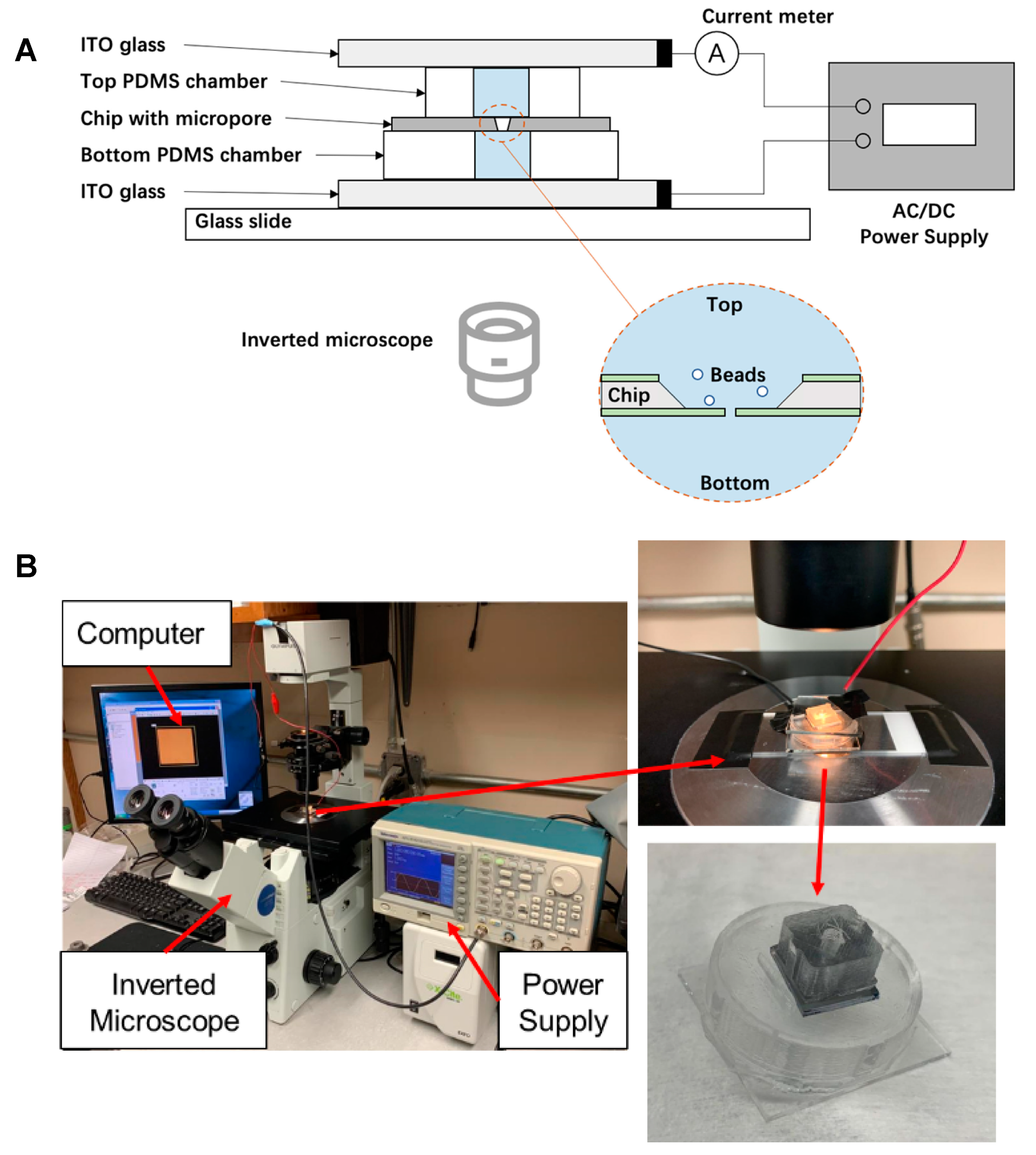
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Theoretical Estimation for the Movement of the Beads
2.3.1. Electrical Field Distribution
2.3.2. The Fluid Flow Model
2.3.3. Particle Trajectories
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical Estimations
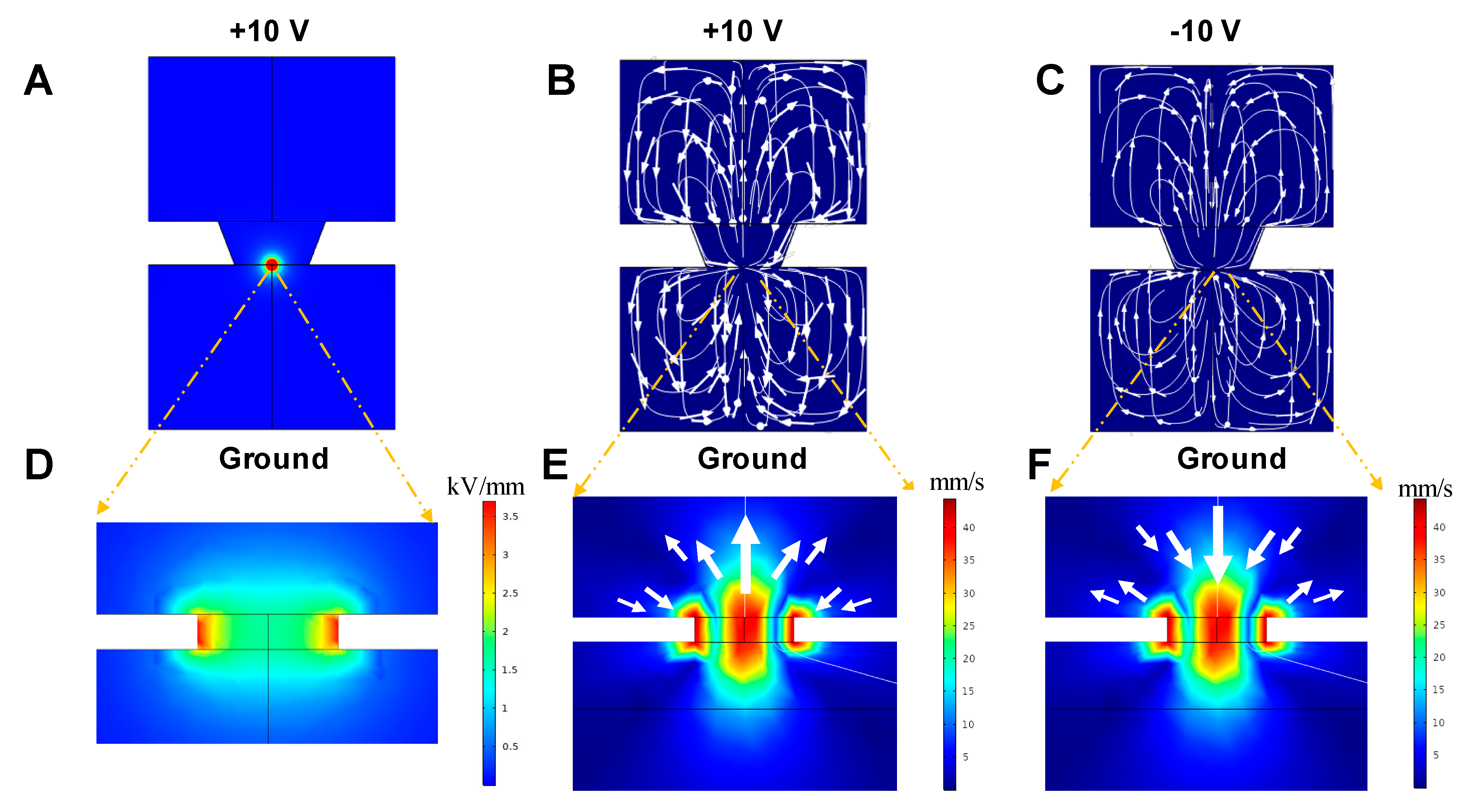
3.1.1. Electrical Field Distribution
3.1.2. Motion of the Fluid
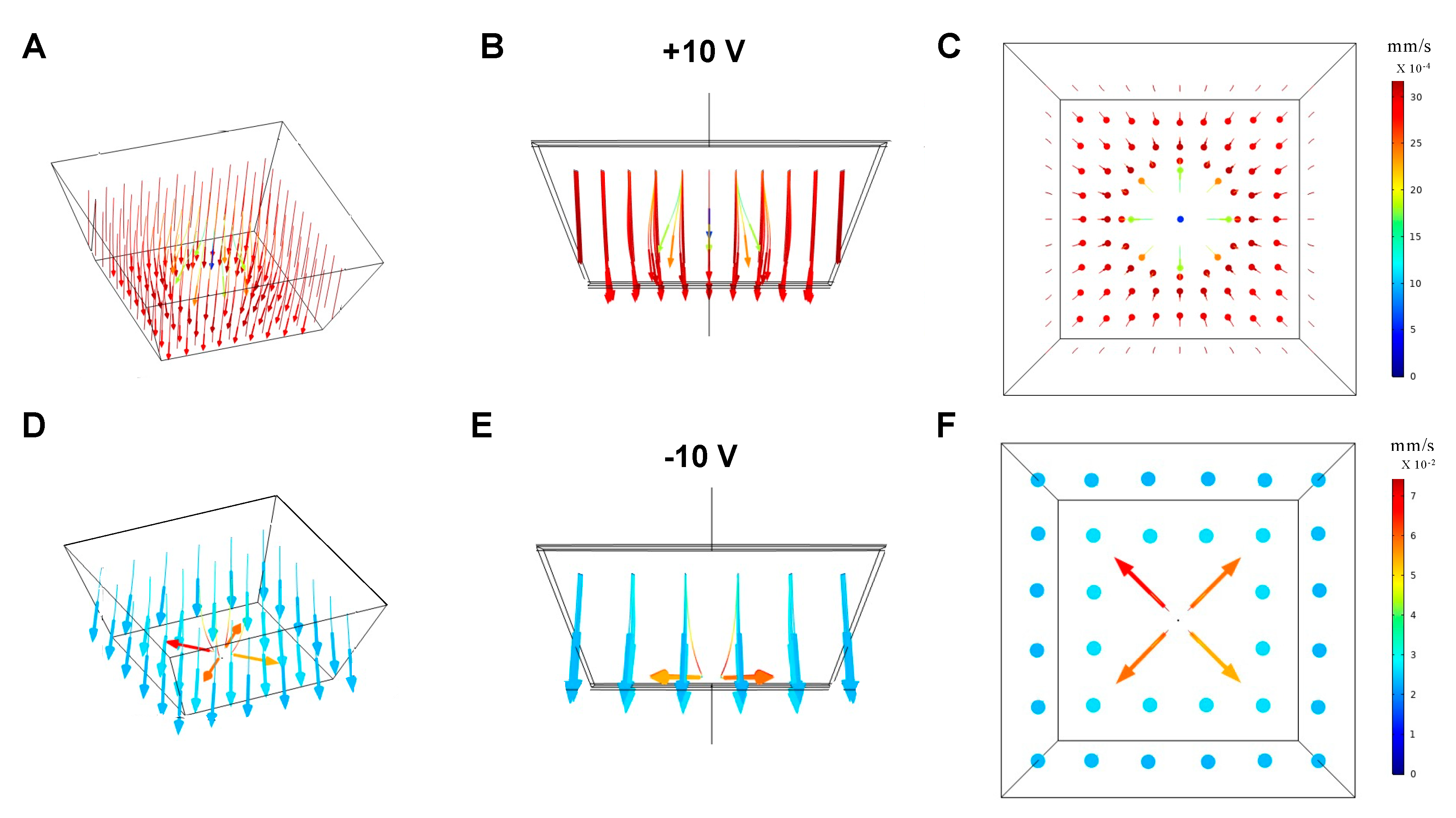
3.1.3. Particle Trajectories
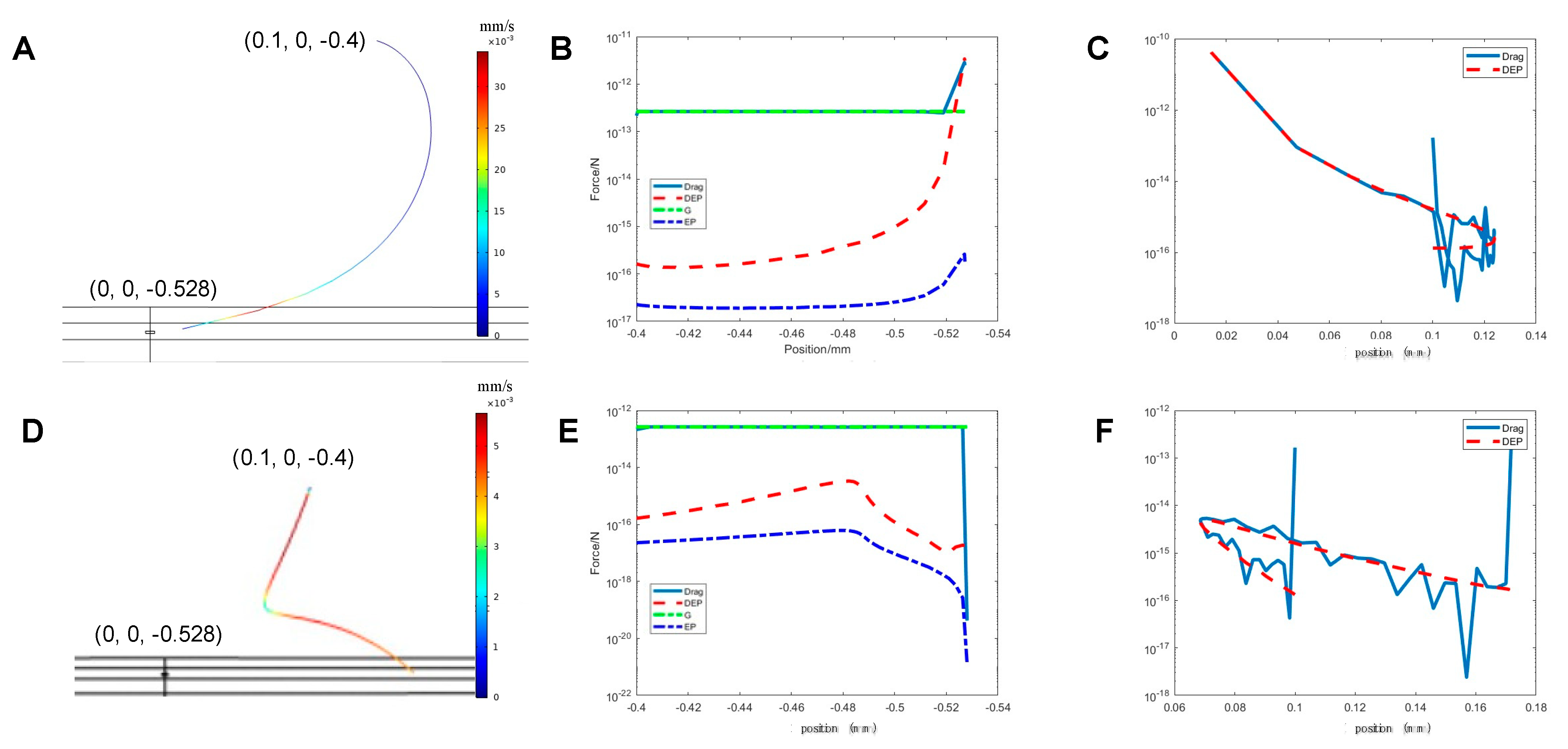
3.1.4. The Forces Applied on the Particles
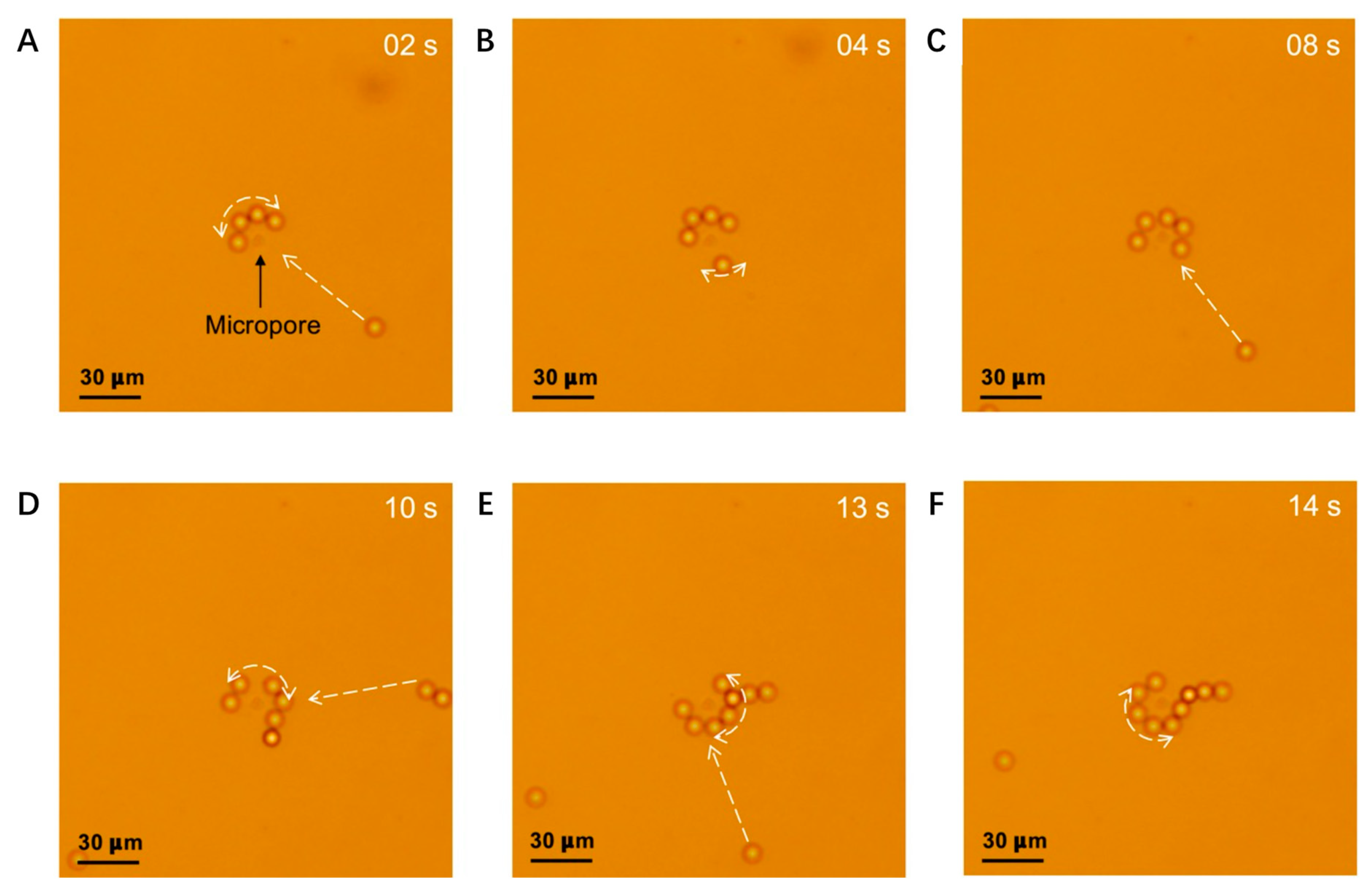
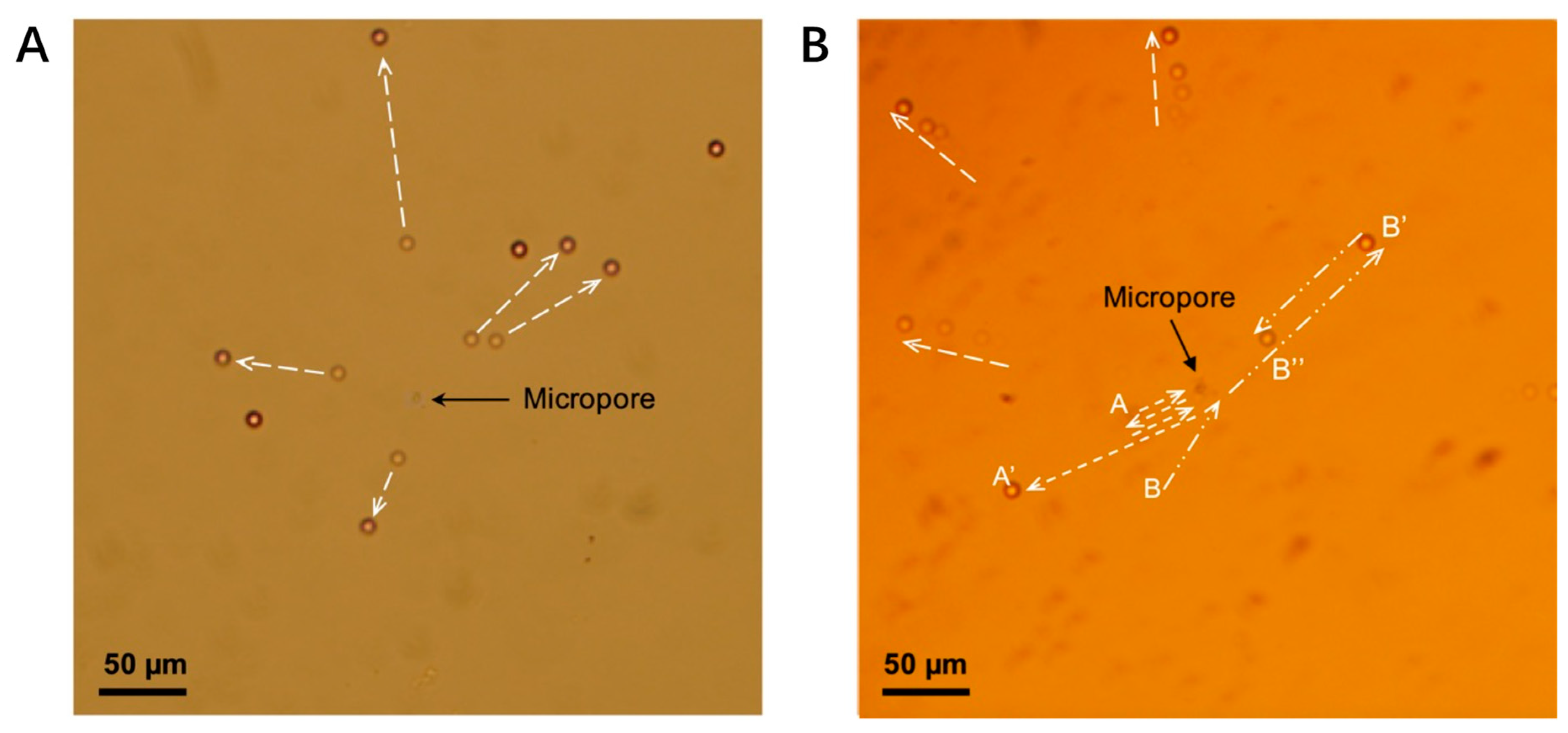
3.2. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Z.; Lin, J.M. Recent development of cell analysis on microfludics. In Cell Analysis on Microfluidics; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 43–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics based point-of-care diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.; Loganathan, M.; Dey, K.; Shinde, P.; Chang, H.Y.; Nagai, M.; Santra, T.S. Single-cell electroporation: Current trends, applications and future prospects. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipoor, M.; Vafaie, R.H.; Pourmand, A.; Poorreza, E.; Ghavifekr, H.B. A novel four phase AC electroosmotic micropump for lab-on-a-chip applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Symposium on Mechatronics and its Applications, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 10–12 April 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, S. AC dielectrophoresis lab-on-chip devices. In Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Electroosmotic pumps and their applications in microfluidic systems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 6, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walid Rezanoor, M.; Dutta, P. Combined AC electroosmosis and dielectrophoresis for controlled rotation of microparticles. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, I.J.; Benguigui, L. Dielectrophoretic filtration and separation: General outlook. Sep. Purif. Methods 1981, 10, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.H.; Yang, S. Continuous dielectrophoretic bacterial separation and concentration from physiological media of high conductivity. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.B.; Caldwell, J.L.; Davalos, R.V. Modeling and development of a low frequency contactless dielectrophoresis (cDEP) platform to sort cancer cells from dilute whole blood samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Chao, T.C.; Ariyasinghe, N.; Ruiz, Y.; Lake, D.; Ros, R.; Ros, A. Selective trapping of single mammalian breast cancer cells by insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. On the recent developments of insulator-based dielectrophoresis: A review. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, P.Y.; Ohta, A.T.; Wu, M.C. Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images. Nature 2005, 436, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethig, R.; Talary, M.S.; Lee, R.S. Enhancing traveling-wave dielectrophoresis with signal superposition. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Juvert, J.; Tian, P.; Navarro, J.C.; Cooper, J.M.; Neale, S.L. Use of optoelectronic tweezers in manufacturing—Accurate solder bead positioning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 221110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovarik, M.L.; Jacobson, S.C. Integrated nanopore/microchannel devices for ac electrokinetic trapping of particles. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Park, C.; Lee, J.G.; Ko, C. Bacteria concentration using a membrane type insulator-based dielectrophoresis in a plastic chip. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rivera, R.E.; Rubinsky, B. Electrical and thermal characterization of nanochannels between a cell and a silicon based micro-pore. Biomed. Microdevices 2006, 8, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Rubinsky, B. Micro-electroporation: Improving the efficiency and understanding of electrical permeabilization of cells. Biomed. Microdevices 1999, 2, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Chen, W.H.; Waypa, J.J. Measuring the zeta (electrokinetic) potential of reverse osmosis membranes by a streaming potential analyzer. Desalination 1994, 95, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Mirzakhanloo, M.; Dabirzadeh, M.R. Numerical simulation for efficient mixing of newtonian and non-newtonian fluids in an electro-osmotic micro-mixer. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2016, 107, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mezic, I.; Meinhart, C.; Petzold, L. Numerical simulation of an electroosmotic micromixer. In Proceedings of the ASME 2003 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Washington, DC, USA, 15–21 November 2003; ASME: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin, M.N.; Edwards IV, J.M.; Lee, M.L.; Woolley, A.T.; Hawkins, A.R. Electroosmotic flow in vapor deposited silicon dioxide and nitride microchannels. Biomicrofluidics 2007, 1, 034101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Gencoglu, A.; Minerick, A.R. DC insulator dielectrophoretic applications in microdevice technology: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkersma, R.; van Diemen, A.J.; Stein, H.N. Electrophoretic properties of polystyrene spheres. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5973–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Wang, J.; Rubinsky, B. Non-electrolytic microelectroporation. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Wang, J.; Powell-Palm, M.; Rubinsky, B. Simultaneous electroporation and dielectrophoresis in non-electrolytic micro/nano-electroporation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attard, P.; Antelmi, D.; Larson, I. Comparison of the zeta potential with the diffuse layer potential from charge titration. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, C.; Lou, L.; Powell-Palm, M.J.; Ukpai, G.; Li, X.; Rubinsky, B. Individual Microparticle Manipulation Using Combined Electroosmosis and Dielectrophoresis through a Si3N4 Film with a Single Micropore. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121578
Lyu C, Lou L, Powell-Palm MJ, Ukpai G, Li X, Rubinsky B. Individual Microparticle Manipulation Using Combined Electroosmosis and Dielectrophoresis through a Si3N4 Film with a Single Micropore. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121578
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Chenang, Leo Lou, Matthew J. Powell-Palm, Gideon Ukpai, Xing Li, and Boris Rubinsky. 2021. "Individual Microparticle Manipulation Using Combined Electroosmosis and Dielectrophoresis through a Si3N4 Film with a Single Micropore" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121578
APA StyleLyu, C., Lou, L., Powell-Palm, M. J., Ukpai, G., Li, X., & Rubinsky, B. (2021). Individual Microparticle Manipulation Using Combined Electroosmosis and Dielectrophoresis through a Si3N4 Film with a Single Micropore. Micromachines, 12(12), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121578




