Passive Control of Silane Diffusion for Gradient Application of Surface Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
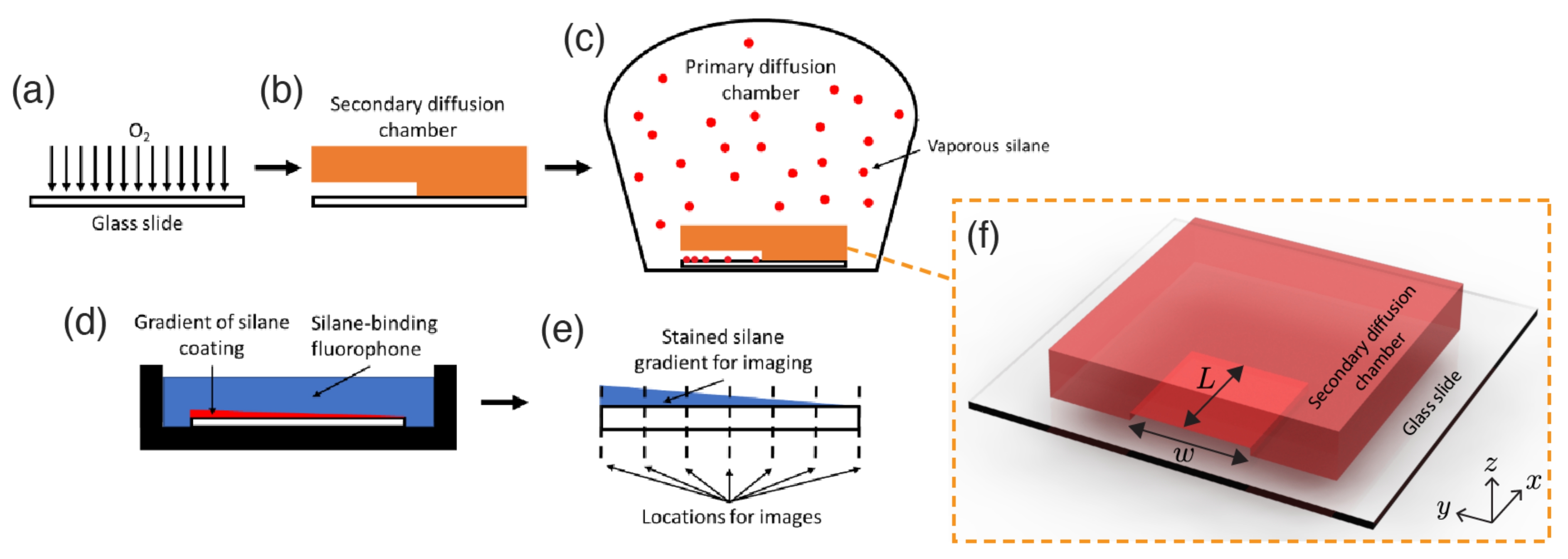
2.1. Experiments
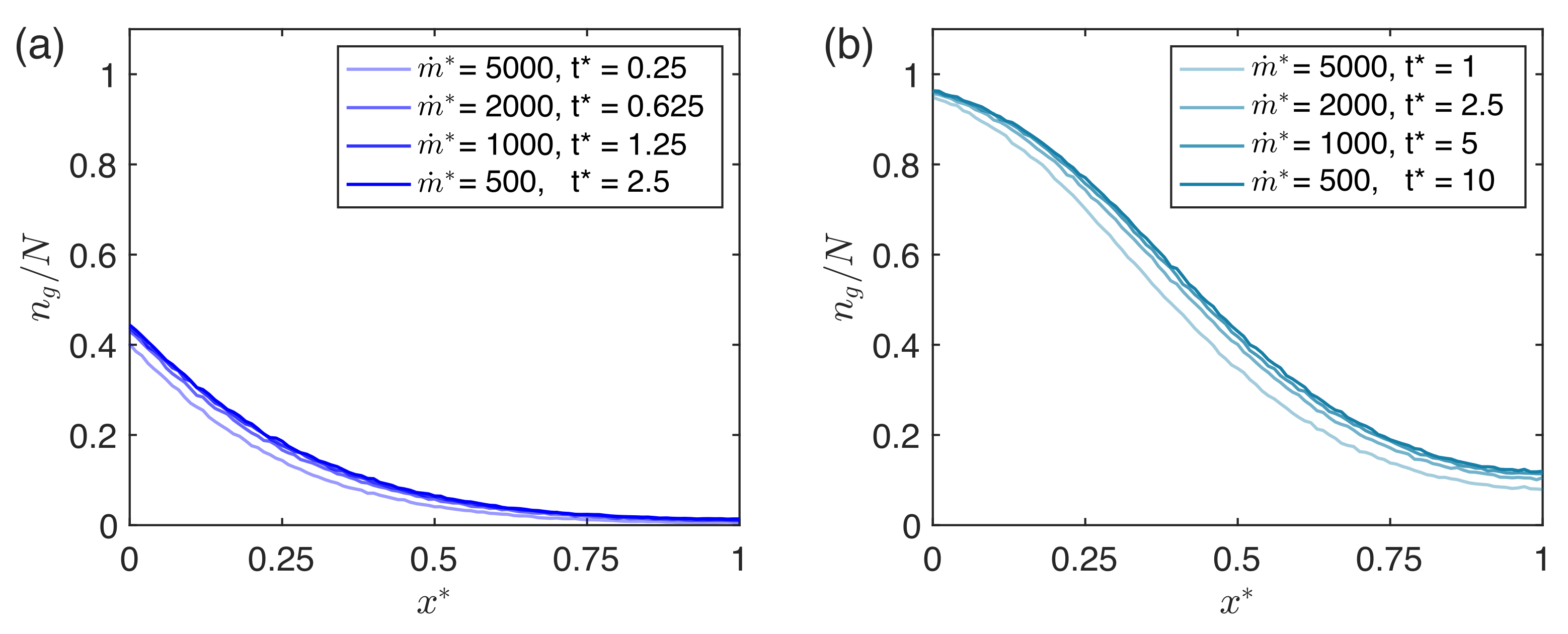
2.2. Mathematical Model and Numerical Simulations
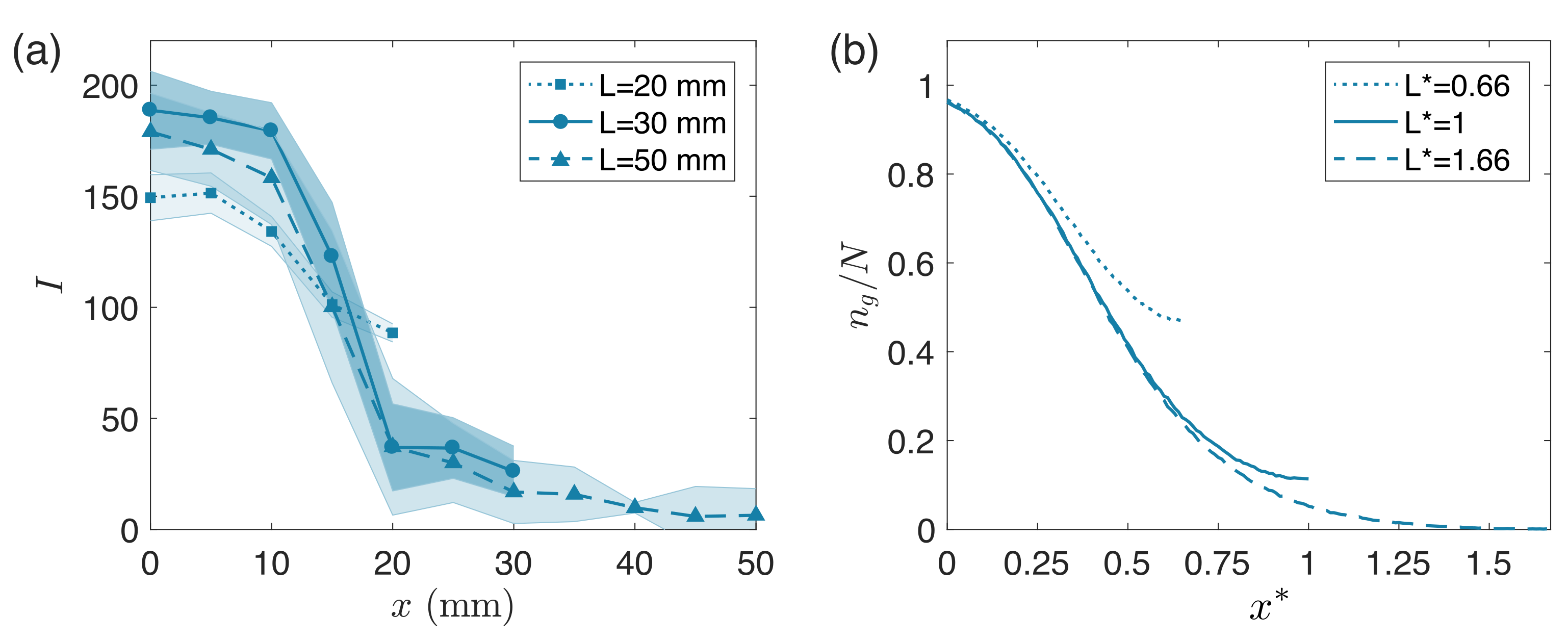
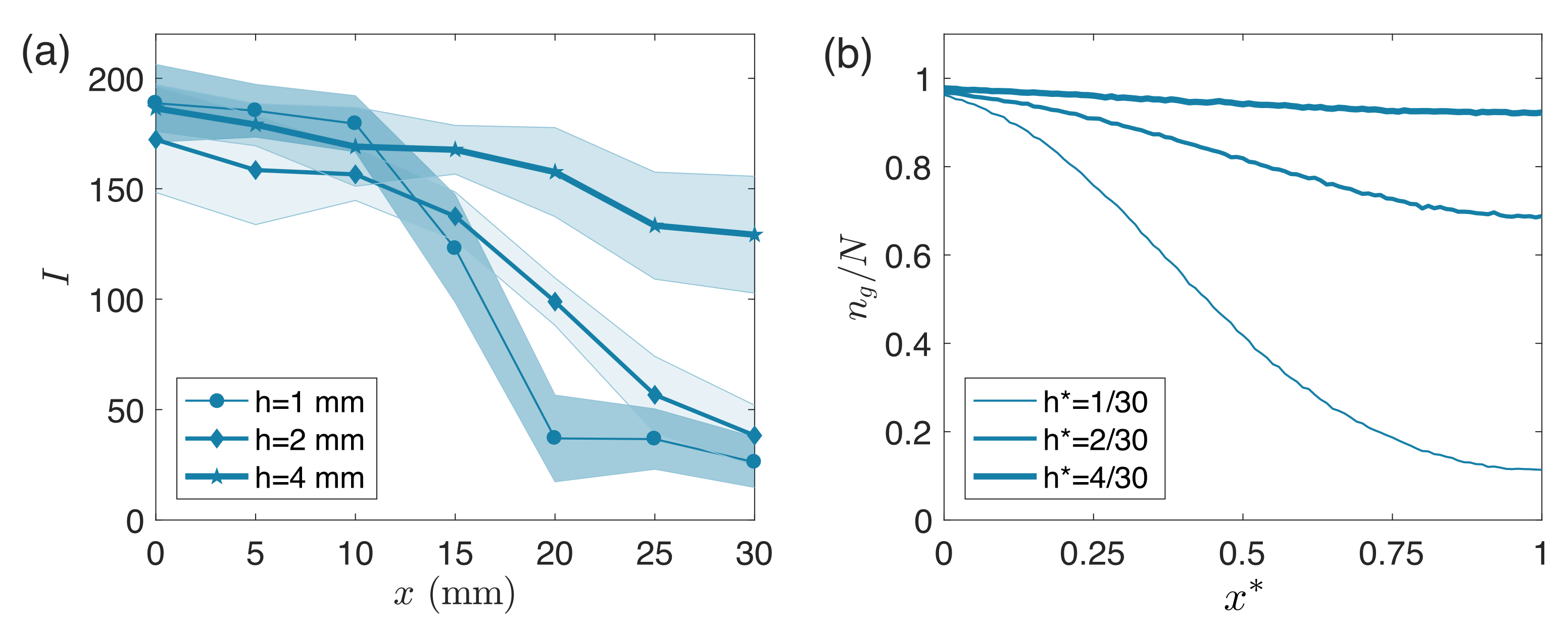
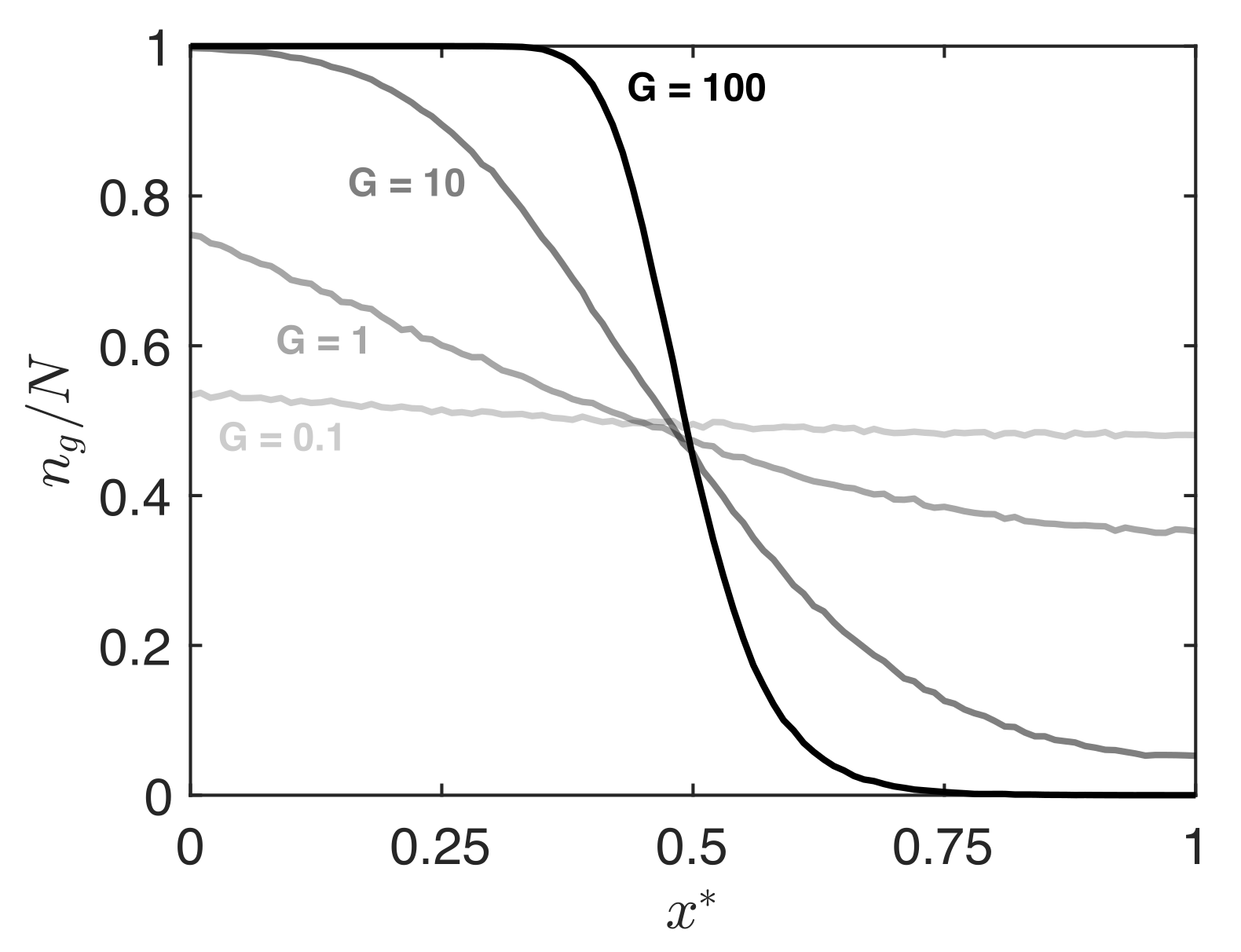
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, K.; Eom, T.J.; Lee, C. Comparison of the removal efficiency for organic contaminants on silicon wafers stored in plastic boxes between UV/O3 and ECR oxygen plasma cleaning methods. Thin Solid Films 2003, 435, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, J.; Azouz, I.B.; Rondelez, F. Silanization of solid substrates: A step toward reproducibility. Langmuir 1994, 10, 4367–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccafoschi, F.; Fusaro, L.; Cannas, M. Immobilization of peptides on cardiovascular stent. In Functionalised Cardiovascular Stents; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.; Blanch, H. Covalent immobilization of protein monolayers for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1994, 9, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of silanization on chitosan porous scaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, R.; Csáki, A.; Köhler, J.M.; Fritzsche, W. DNA probes on chip surfaces studied by scanning force microscopy using specific binding of colloidal gold. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, Y.J.; Kuddannaya, S.; Lee, M.H.A.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y. The effects of poly (dimethylsiloxane) surface silanization on the mesenchymal stem cell fate. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinatier, C.; Magne, D.; Weiss, P.; Trojani, C.; Rochet, N.; Carle, G.; Vignes-Colombeix, C.; Chadjichristos, C.; Galera, P.; Daculsi, G.; et al. A silanized hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel for the three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6643–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, G.H.; Park, J.Y. Microwell fabrication methods and applications for cellular studies. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2013, 3, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balowski, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Allbritton, N.L. Fabrication of 3d microstructures from interactions of immiscible liquids with a structured surface. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, P.F.; Shea, K.A.; Ferguson, S.J. Simulated tissue growth for 3D printed scaffolds. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2018, 17, 1481–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Jin, Y.; Luo, M. Micro-Curvature Environment Is a Determinant of airway Smooth Muscle Cell Orientation and Stiffness During Early Pattern Formation in Culture. In B30. Mechanisms of Airway Smooth Muscle Contractility and Relazation: Potential Therapeutic Targets; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2017; p. A3154. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Lam, R.H. Influence of micro-scale substrate curvature on subcellular behaviors of vascular cells. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Sendai, Japan, 22–25 August 2016; pp. 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Chrastina, A.; Massey, K.; Schnitzer, J. Overcoming in vivo barriers to targeted nanodeliver. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, A.; Ramalingam, M.; Elloumi-Hannachi, I.; Ostrovidov, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Gradient biomaterials for soft-to-hard interface tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mao, Z.; Tan, H.; Han, L.; Ren, T.; Gao, C. Gradient biomaterials and their influences on cell migration. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.M.; Folch, A. Biomolecular gradients in cell culture systems. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant, S.; Hancock, M.J.; Donnelly, J.P.; Iyer, D.; Khademhosseini, A. Biomimetic gradient hydrogels for tissue engineering. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genzer, J. Surface-bound gradients for studies of soft materials behavior. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2012, 42, 435–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, K.S.; Ram, R.J. Plastic–PDMS bonding for high pressure hydrolytically stable active microfluidics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, A.R.; Krummel, A.T.; Lee, D.; Marquez, M.; Holtze, C.; Weitz, D.A. Photoreactive coating for high-contrast spatial patterning of microfluidic device wettability. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2157–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Allbritton, N.L. Use of liquid lithography to form in vitro intestinal crypts with varying microcurvature surrounding the stem cell niche. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Y.; Tsai, W.B.; Voelcker, N.H. Screening of rat mesenchymal stem cell behaviour on polydimethylsiloxane stiffness gradients. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaghavan, H.G.; Monteiro, G.A.; Firestein, B.L.; Shreiber, D.I. Neurite growth in 3D collagen gels with gradients of mechanical properties. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppälä, J.; Korhonen, H.; Hakala, R.; Malin, M. Photocrosslinkable polyesters and poly (ester anhydride) s for biomedical applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, B.; Dong, D.; Higgins, D.A.; Collinson, M.M. Profile control in surface amine gradients prepared by controlled-rate infusion. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrum, C.; Hennink, W. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, N. Introduction to the Principles of Vacuum Physics; CERN: Meyrin, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Burdick, J.A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Fabrication of gradient hydrogels using a microfluidics/photopolymerization process. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5153–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Velasco, A.; Rajagopalan, P.; Pham, Q. Directed movement of vascular smooth muscle cells on gradient-compliant hydrogels. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; DiSalvo, M.; Gunasekara, D.B.; Dutton, J.; Proctor, A.; Lebhar, M.S.; Williamson, I.A.; Speer, J.; Howard, R.L.; Smiddy, N.M.; et al. Self-renewing monolayer of primary colonic or rectal epithelial cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, M.K.; Whitesides, G.M. How to make water run uphill. Science 1992, 256, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genzer, J. Templating surfaces with gradient assemblies. J. Adhes. 2005, 81, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, M.M.; Higgins, D.A. Organosilane Chemical Gradients: Progress, Properties, and Promise. Langmuir 2017, 33, 13719–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimenko, K.; Genzer, J. How to prepare tunable planar molecular chemical gradients. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.R.; Sriram, R.; Carter, J.A.; Miller, B.L. Comparative study of solution–phase and vapor–phase deposition of aminosilanes on silicon dioxide surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 35, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Chemical vapor deposition of coatings on glass. J. -Non-Cryst. Solids 1997, 218, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Chun, C.; Hickman, J.J.; Molnar, P. Growth and electrophysiological properties of rat embryonic cardiomyocytes on hydroxyl-and carboxyl-modified surfaces. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zargar, R.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Amoabediny, G. Preparation, characterization, and silanization of 3D microporous PDMS structure with properly sized pores for endothelial cell culture. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2016, 63, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huan, G.; Ma, Y. Computational Methods for Multiphase Flows in Porous Media; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Genzer, J.; Efimenko, K.; Fischer, D.A. Formation mechanisms and properties of semifluorinated molecular gradients on silica surfaces. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8532–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, R.; Hartmann, N.; Hasselbrink, E. Two-dimensional aggregation of species with weak and strong bonding interactions: Modeling the growth of self-assembled alkylsiloxane monolayers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6590–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, S.R.; Whitesides, G.M.; Tidswell, I.M.; Ocko, B.M.; Pershan, P.S.; Axe, J.D. The structure of self-assembled monolayers of alkylsiloxanes on silicon: A comparison of results from ellipsometry and low-angle x-ray reflectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 5852–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.C.; Stiff, C.M.; Fryxell, G.E. A simple determination of alkylsilane monolayer population density. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2006, 9, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibe, O.C. Elements of Random Walk and Diffusion Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ulman, A. Formation and structure of self-assembled monolayers. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1533–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeyre, B.; Pardoux, É.; Pardoux, E.; Sentis, R. Introduction to Monte Carlo Methods for Transport and Diffusion Equations; Oxford University Press on Demand: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, S.H.; Meldrum, D.R. Spontaneous, oscillatory liquid transport in surface tension-confined microfluidics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Khang, G.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, H.B. Interaction of different types of cells on polymer surfaces with wettability gradient. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 205, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Xiao, K.; Yao, X.; Bai, H.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired conical copper wire with gradient wettability for continuous and efficient fog collection. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5937–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| G [Equation (4)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 2.18 | |||||
| Reference case | 1000 | 5.00 | ||||
| 1000 | 13.8 | |||||
| 2000 | 1.25 | |||||
| 4000 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Howard, R.L.; Bernardi, F.; Leff, M.; Abele, E.; Allbritton, N.L.; Harris, D.M. Passive Control of Silane Diffusion for Gradient Application of Surface Properties. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111360
Howard RL, Bernardi F, Leff M, Abele E, Allbritton NL, Harris DM. Passive Control of Silane Diffusion for Gradient Application of Surface Properties. Micromachines. 2021; 12(11):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111360
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoward, Riley L., Francesca Bernardi, Matthew Leff, Emma Abele, Nancy L. Allbritton, and Daniel M. Harris. 2021. "Passive Control of Silane Diffusion for Gradient Application of Surface Properties" Micromachines 12, no. 11: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111360
APA StyleHoward, R. L., Bernardi, F., Leff, M., Abele, E., Allbritton, N. L., & Harris, D. M. (2021). Passive Control of Silane Diffusion for Gradient Application of Surface Properties. Micromachines, 12(11), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111360






