Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Audible Acoustic Fundamentals
2.1. Sound Propagation in Air
2.2. Sound Pressure Level and Sound Power
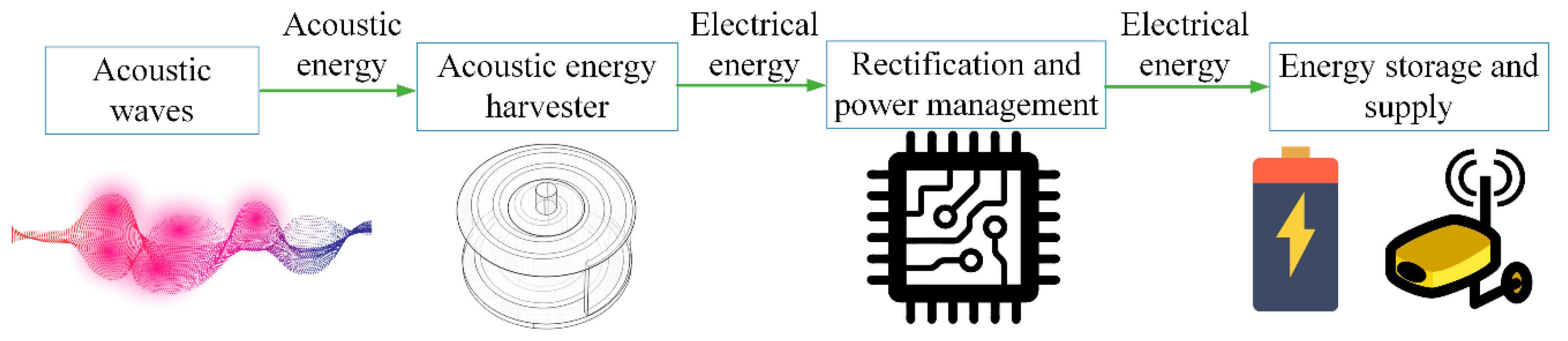
3. Acoustic Energy Harvesting (AEH) Mechanism
3.1. Acoustic-Wave Manipulation
3.2. Energy Conversion
3.2.1. Piezoelectric Conversion
3.2.2. Electromagnetic Conversion
4. Established AEH Approaches
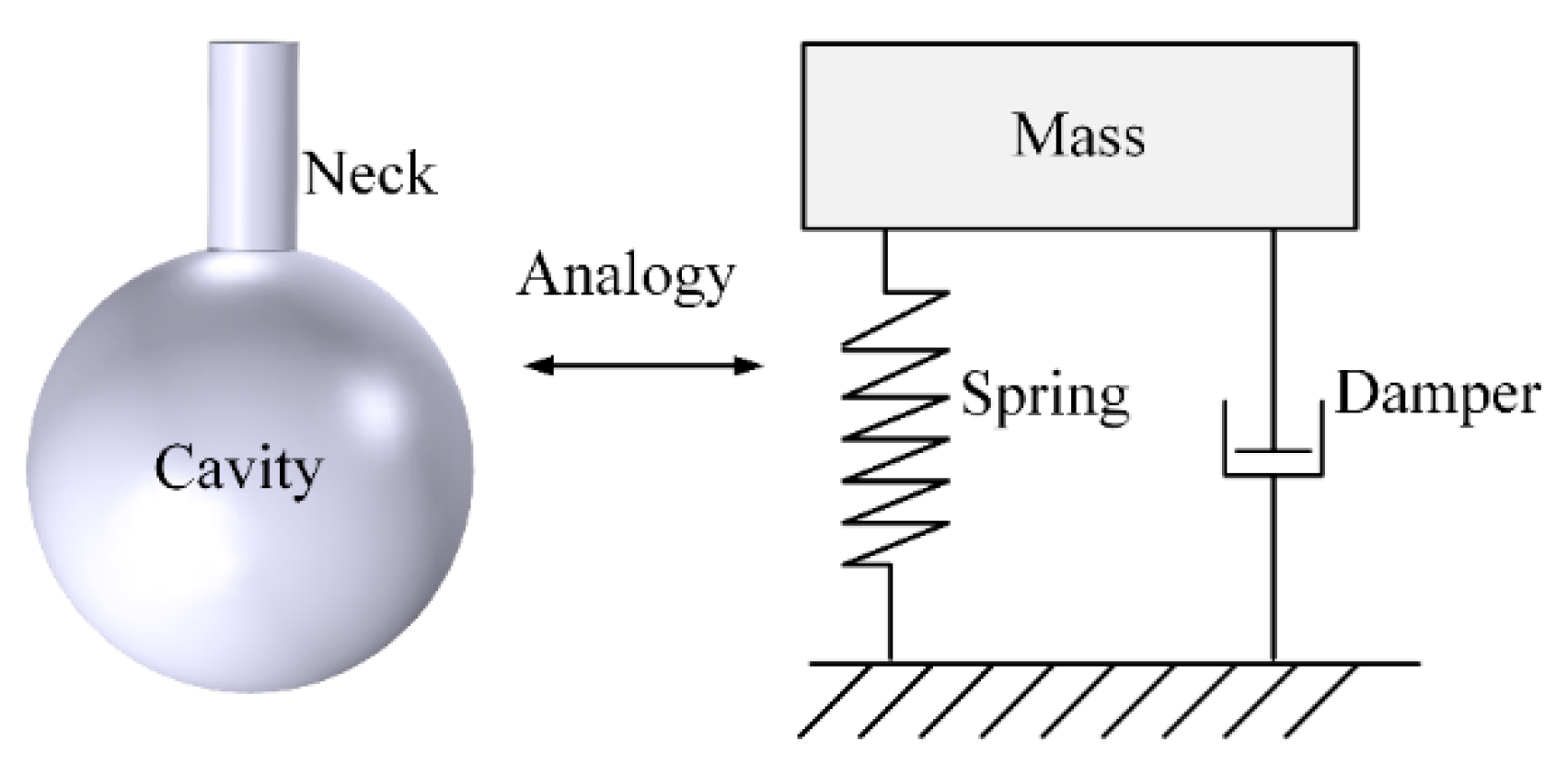
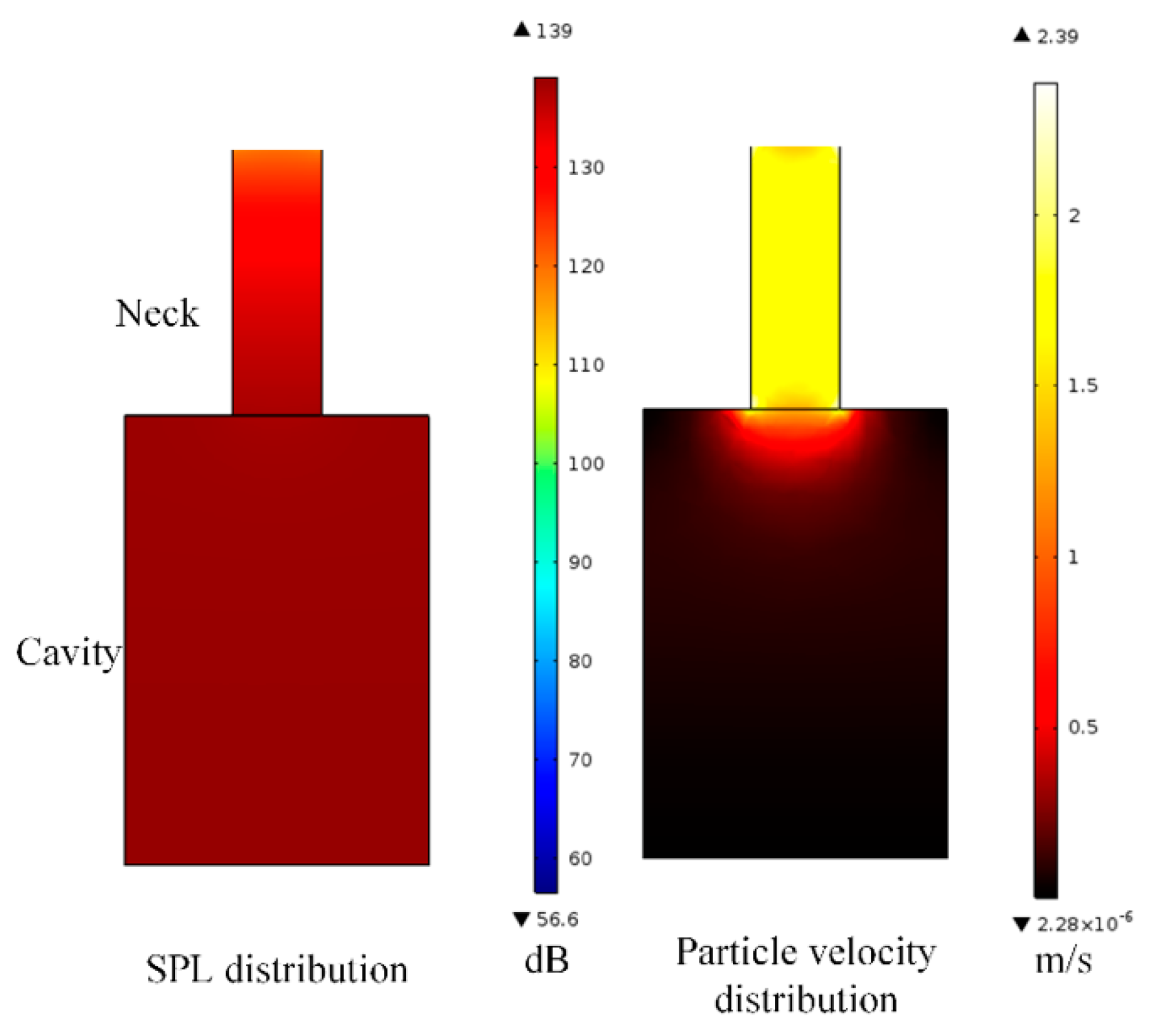
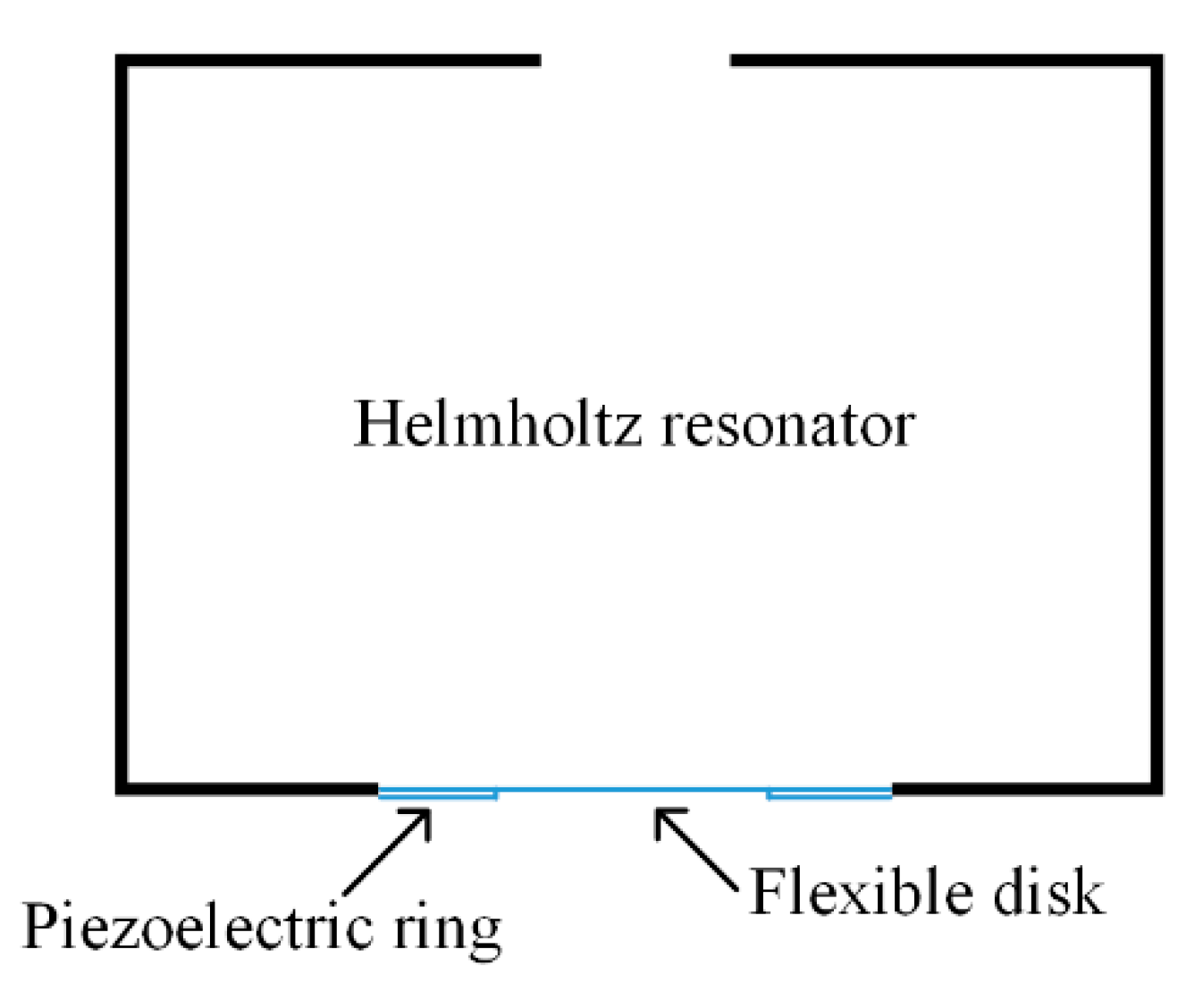
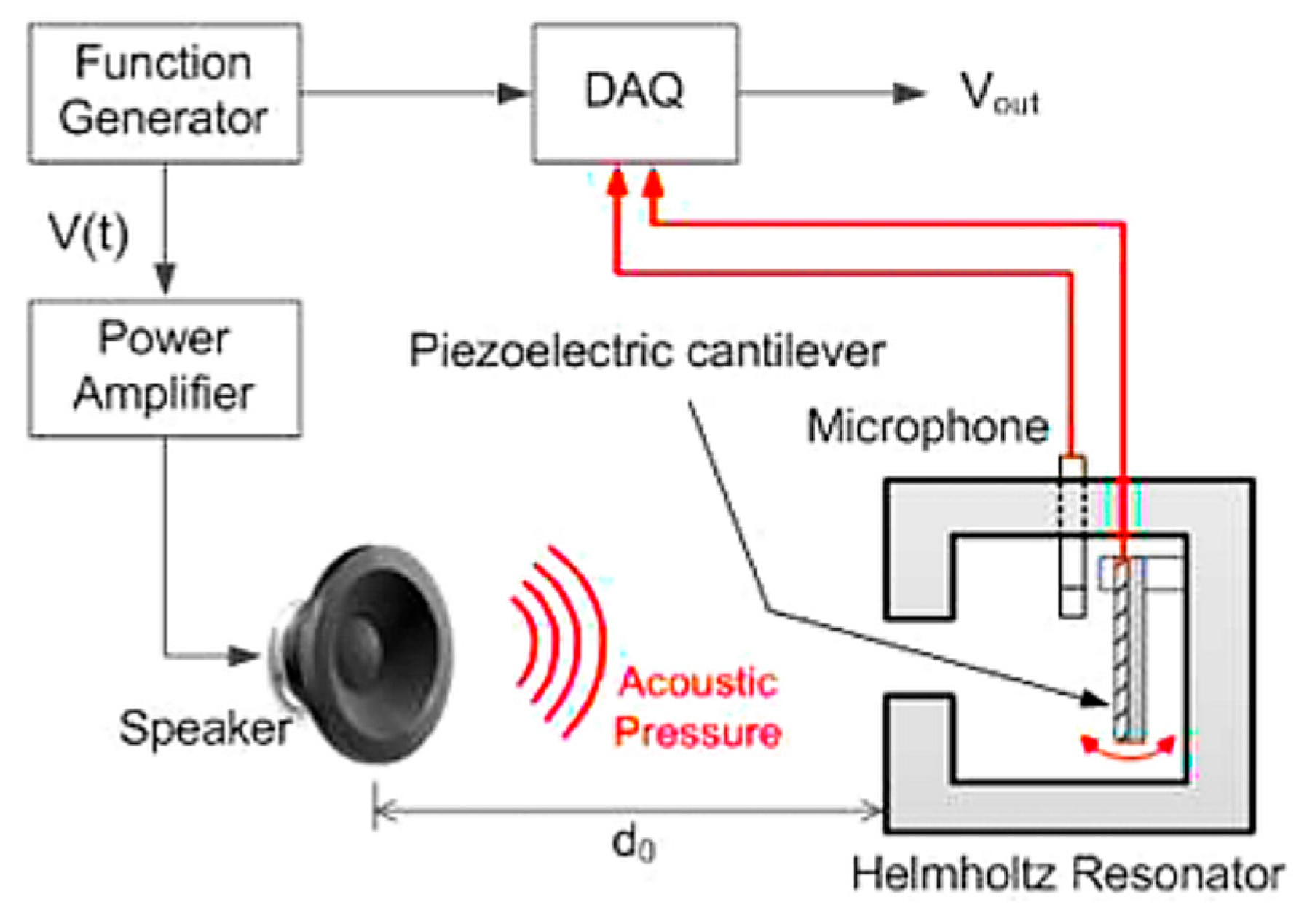
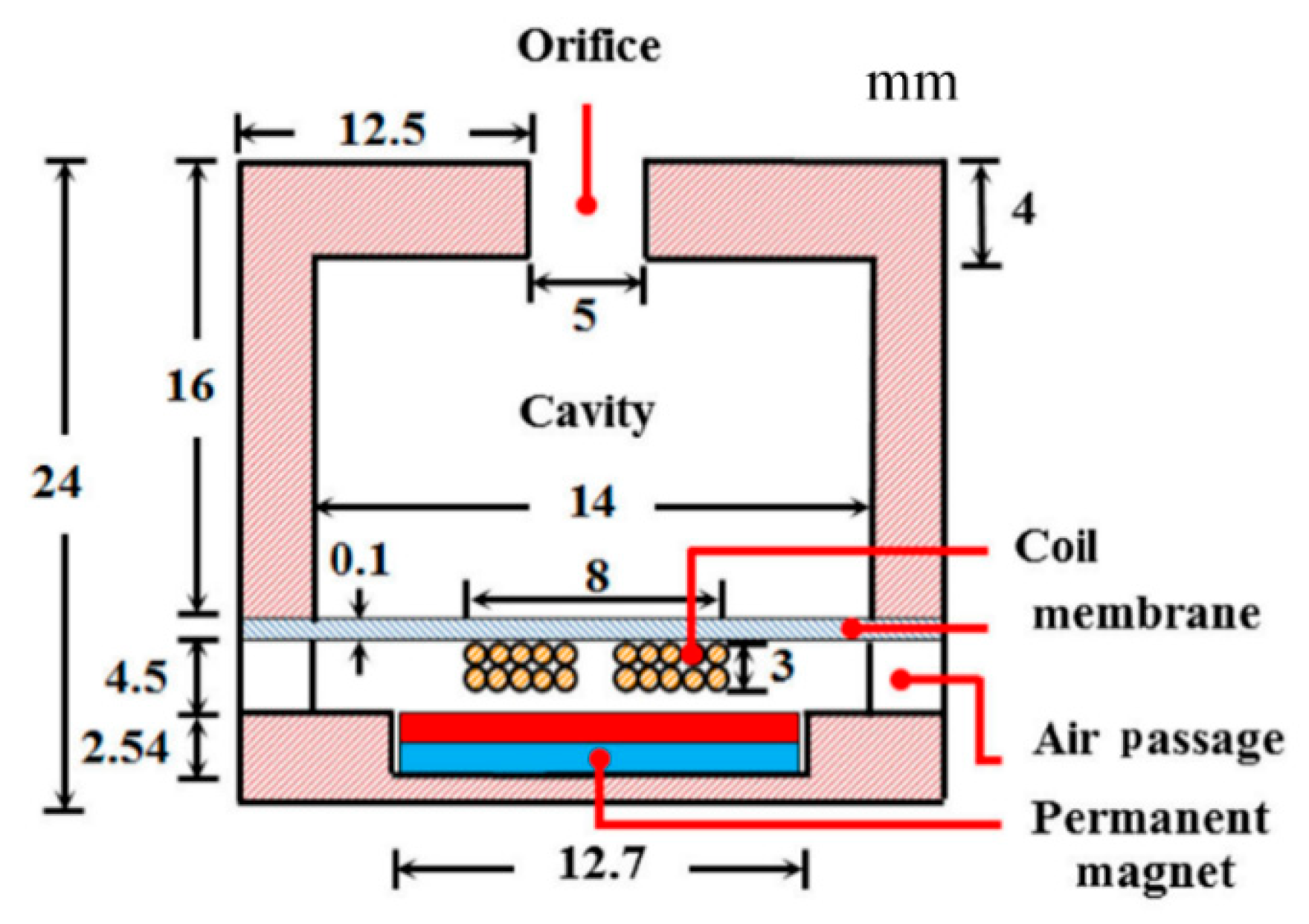
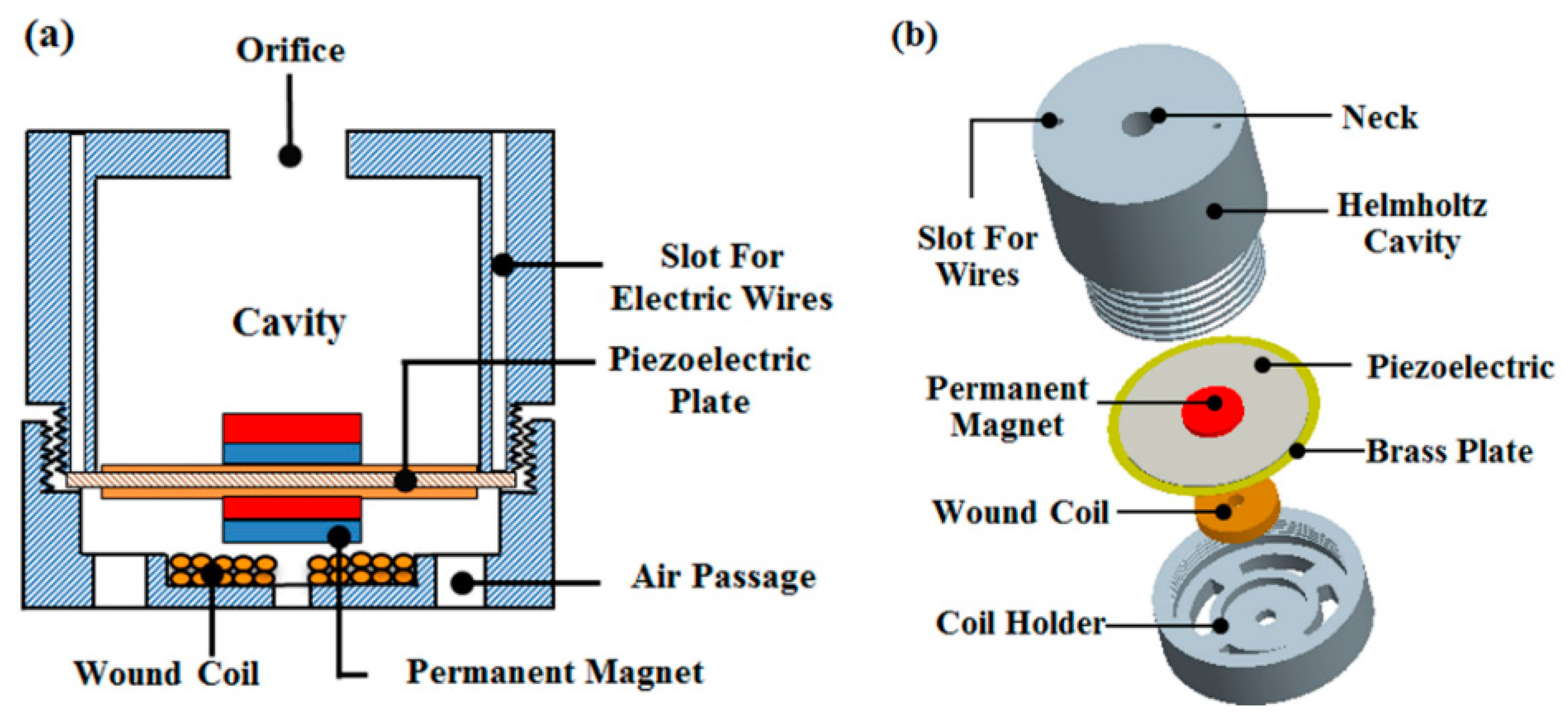
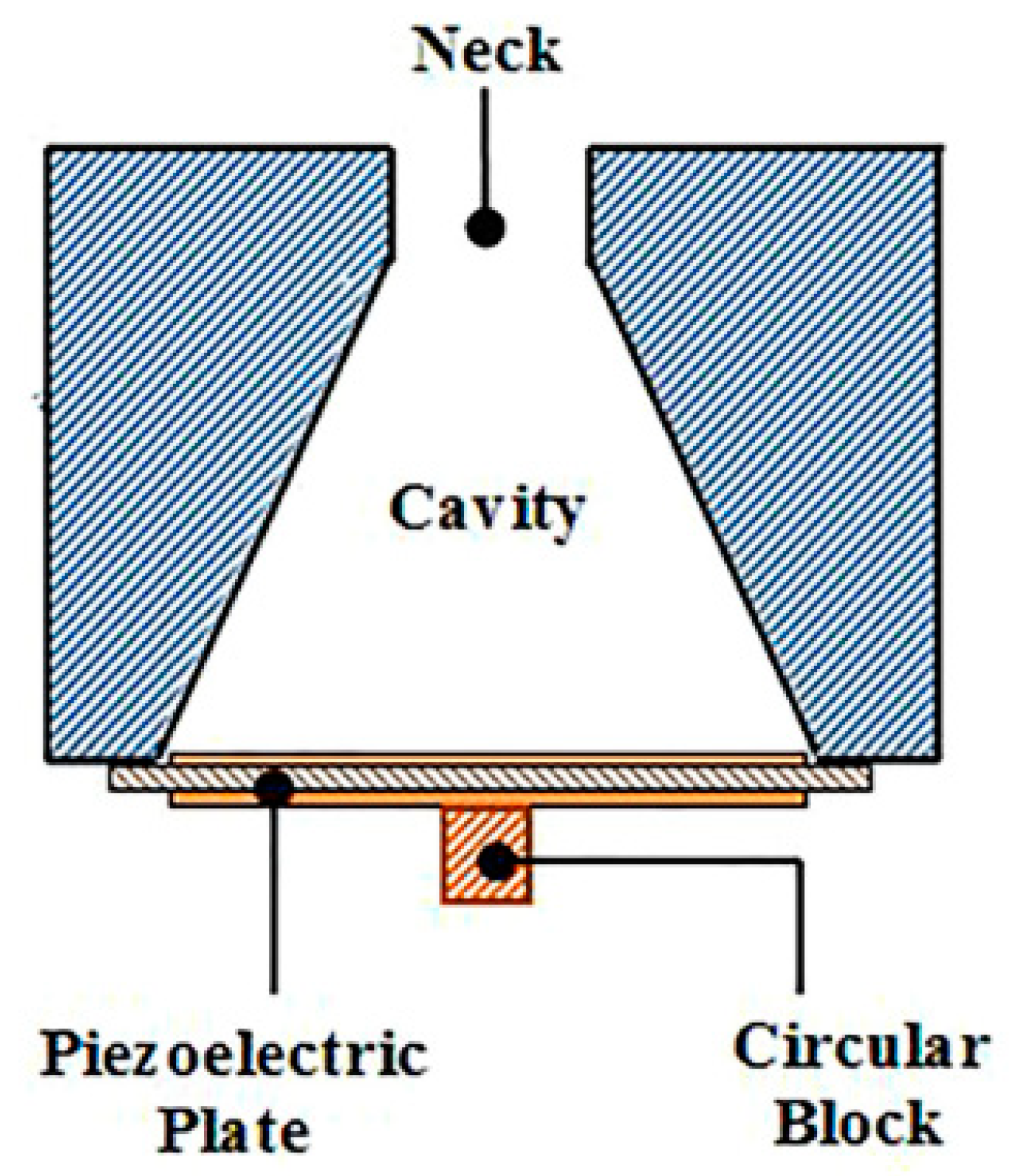
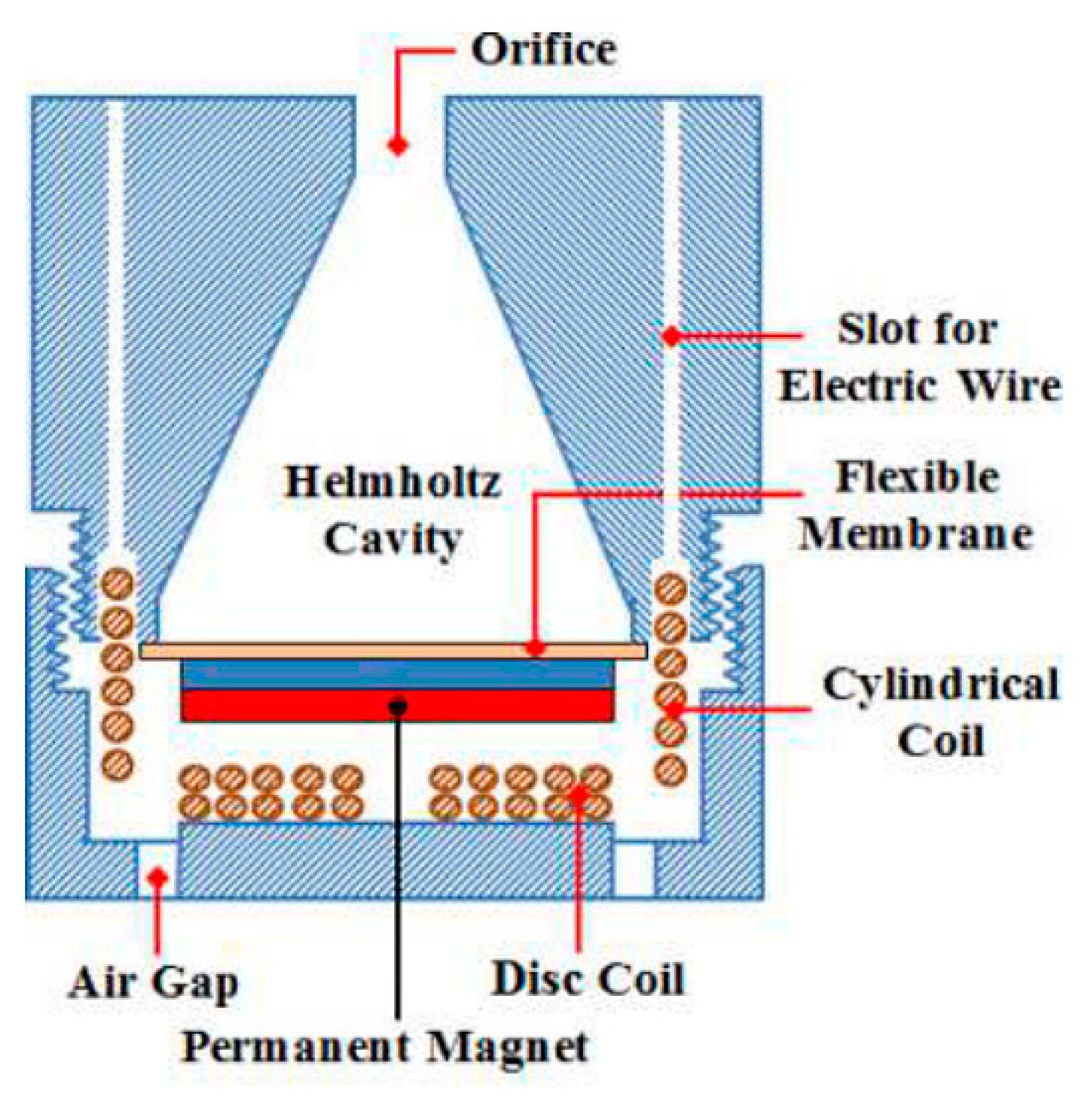
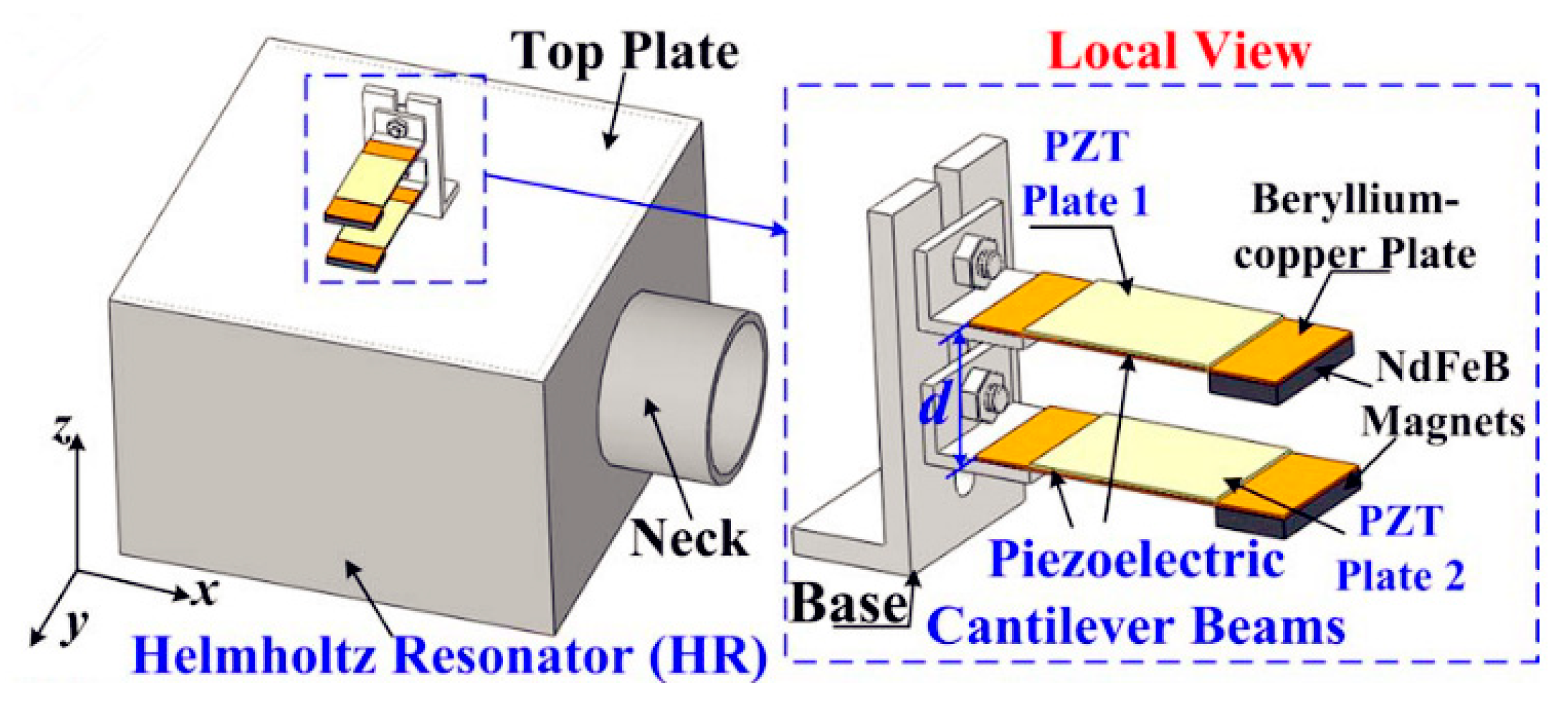
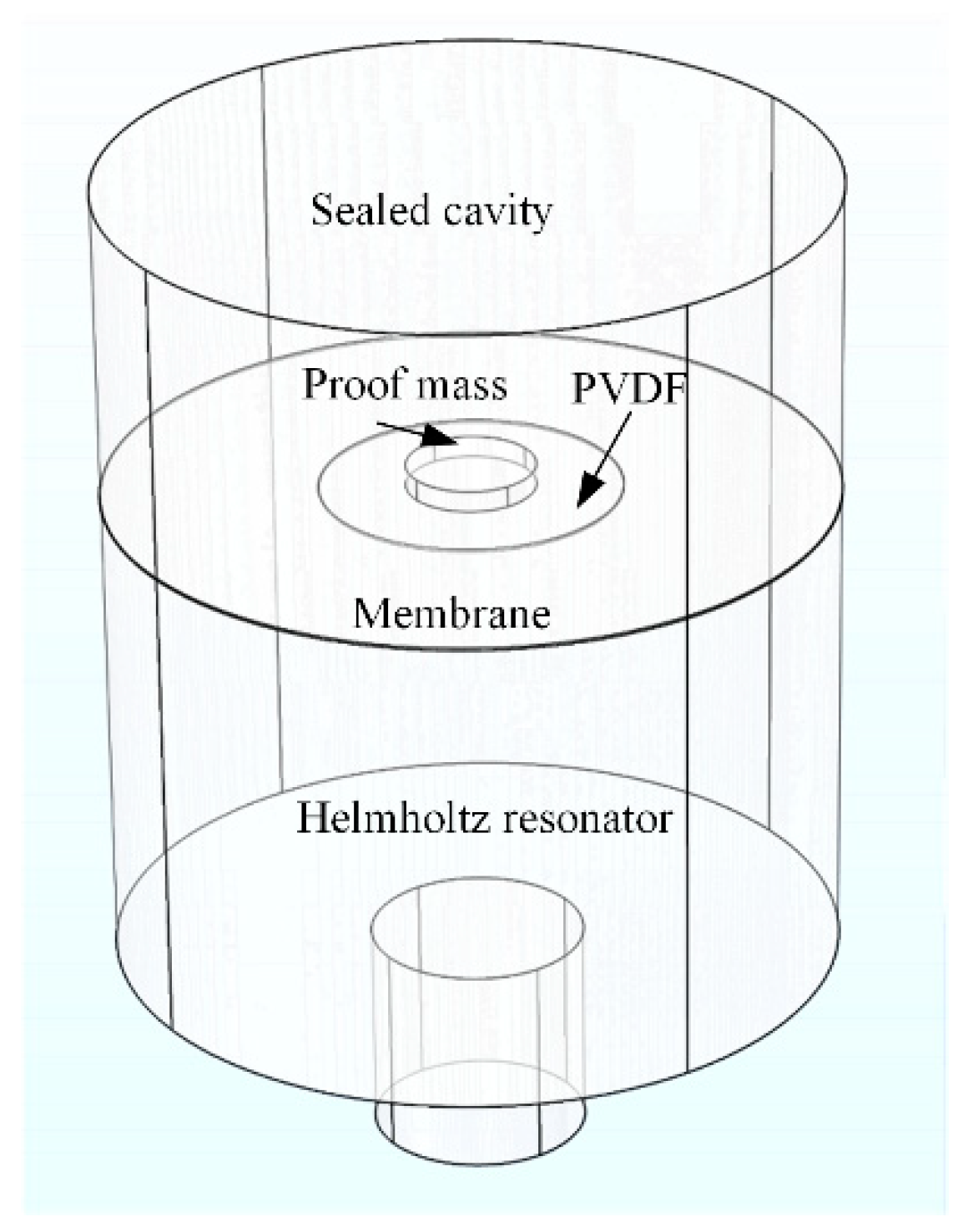
4.1. Helmholtz Resonator-Based Approaches
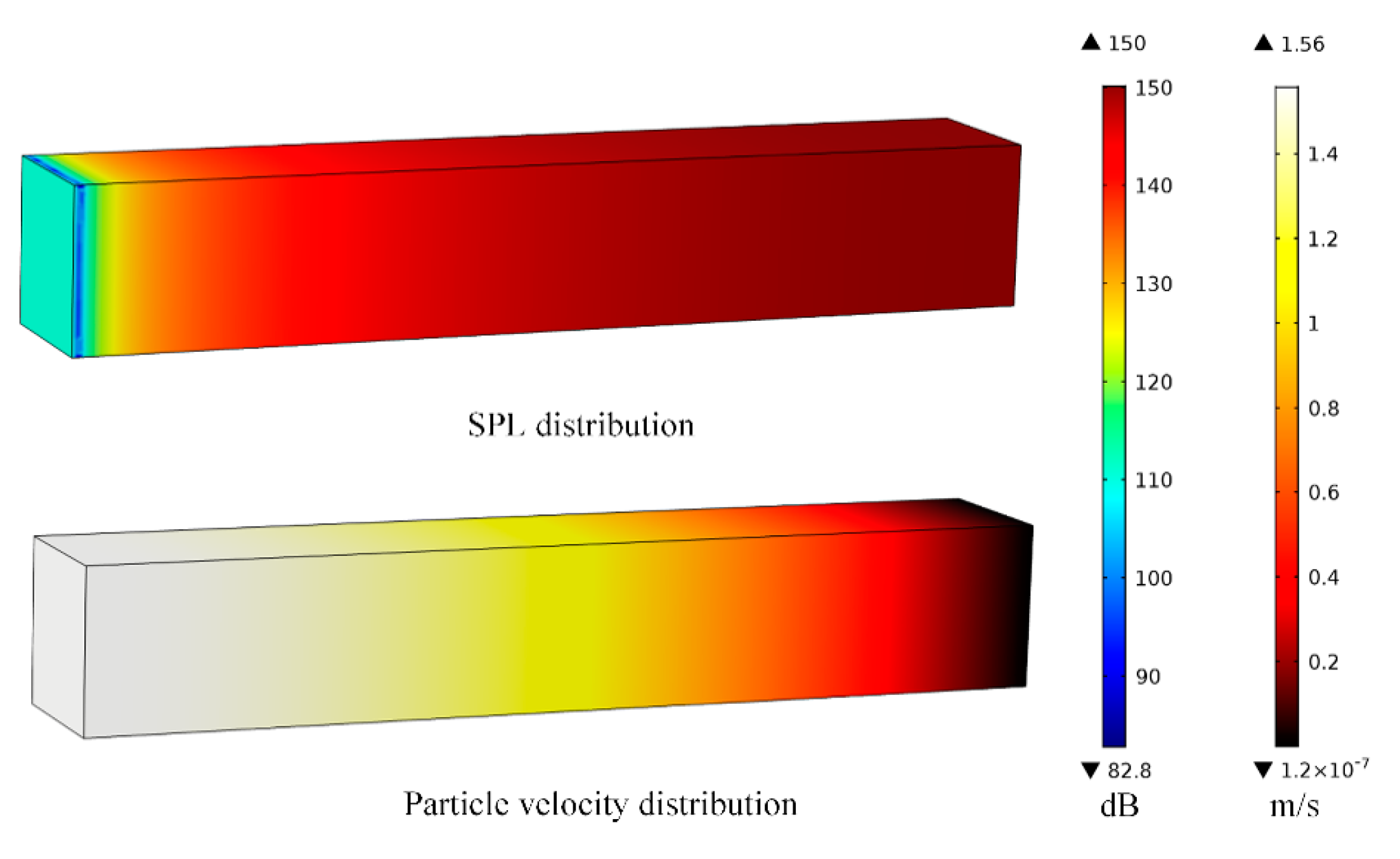
4.2. Quarter-Wavelength Resonator-Based Approaches
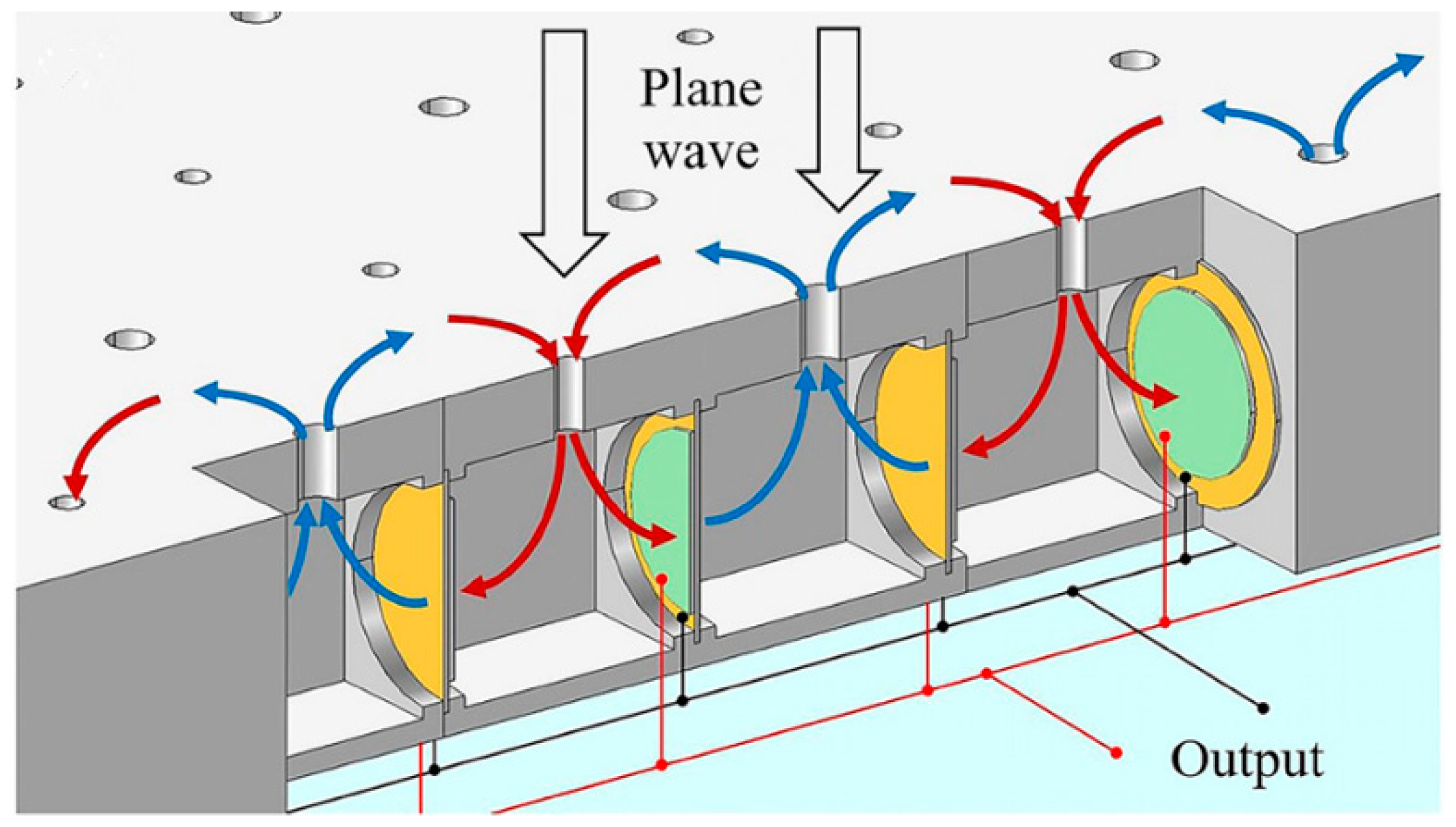
4.3. Acoustic Metamaterial Based-Approaches
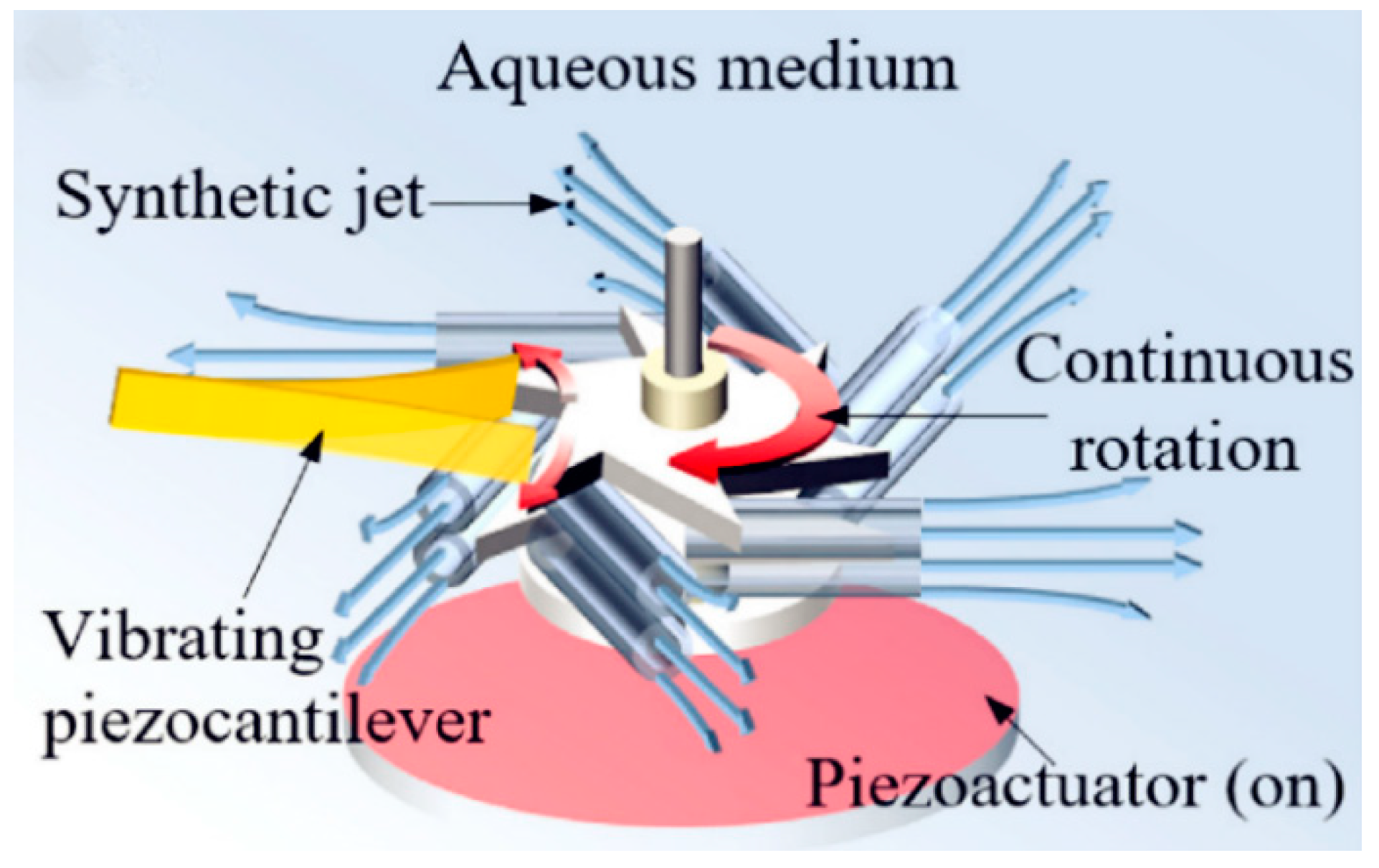
4.4. Other Approaches
5. Performance Comparison
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noh, H.-M. Acoustic energy harvesting using piezoelectric generator for railway environmental noise. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazzam, M.R.; A Zakerian, S.; Kazemi, Z.; Ebrahimi, M.H.; Ghaljahi, M.; Mehri, A.; Afkhaminia, F.; Abbasi, M. Investigation of occupational noise annoyance in a wind turbine power plant. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, J.L.; Pérez, J.; Barrio, R.; González, J. A simple acoustic model to characterize the internal low frequency sound field in centrifugal pumps. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Leclercq, L.; Lelong, J.; Botteldooren, D. Traffic noise spectrum analysis: Dynamic modeling vs. experimental observations. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, J. Aircraft interior noise. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 190, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yang, F.; Luo, J.; Cao, Z. Planar acoustic notch filter for low frequency sound wave suppression. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.H. Ultrathin lightweight plate-type acoustic metamaterials with positive lumped coupling resonant. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Guo, Q.; Hu, G.; Yang, J. Ultrathin low-frequency sound absorbing panels based on coplanar spiral tubes or coplanar Helmholtz resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 121901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Assouar, B.M. Acoustic metasurface-based perfect absorber with deep subwavelength thickness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 063502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cheng, L.; Hu, Z. Reducing interior noise in a cylinder using micro-perforated panels. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 95, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wen, J.; Wen, X. Sound transmission loss of metamaterial-based thin plates with multiple subwavelength arrays of attached resonators. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 5408–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, W. Development of a sweeping Helmholtz resonator for noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 141, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Ohayon, R.; Qiu, J. Decentralized active control of turbulent boundary induced noise and vibration: a numerical investigation. J. Vib. Control 2016, 22, 3821–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Inman, D.J.; Neild, D.S. A survey of control strategies for simultaneous vibration suppression and energy harvesting via piezoceramics. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, K.; Mokrý, P.; Václavík, J. Application of piezoelectric macro-fiber-composite actuators to the suppression of noise transmission through curved glass plates. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2012, 59, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, L. Mechanisms of active control of sound transmission through a linked double-wall system into an acoustic cavity. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H. Active Control of Noise and Vibration, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.U.; Khattak, M.U. Contributed Review: Recent developments in acoustic energy harvesting for autonomous wireless sensor nodes applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 21501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Mir, F.; Banerjee, S. A review on energy harvesting approaches for renewable energies from ambient vibrations and acoustic waves using piezoelectricity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 085031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J. Characterization the influences of diodes to piezoelectric energy harvester. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2018, 9, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.Y.L.; Koh, Y.K.; Lee, H.P. A note on the viscous boundary layer in plate-type acoustic metamaterials with an internal tonraum resonator. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 140, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsler, L.E.; Frey, A.R. Fundamentals of Acoustics, 4th ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, A.D. Acoustics: An Introduction to Its Physical Principles and Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Sheng, P. Acoustic metamaterials: From local resonances to broad horizons. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummer, S.A.; Christensen, J.; Alù, A. Controlling sound with acoustic metamaterials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Nguyen, D.M.; Rho, J. Acoustic wave science realized by metamaterials. Nano Converg. 2017, 4, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Yang, M.; Ma, C.; Lu, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Fang, N.; Sheng, P. Breaking the barriers: Advances in acoustic functional materials. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 5, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, B.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, C. Metamaterials-based enhanced energy harvesting: A review. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2014, 438, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, H.J.-P.P.; Ohayon, R. Fluid Structure Interaction; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, R.; Soize, C. Advanced Computational Vibroacoustics: Reduced-Order Models and Uncertainty Quantification; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, R.; Soize, C. Computational Vibroacoustics in Low- and Medium- Frequency Bands: Damping, ROM, and UQ Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APC International. Piezoelectric Ceramics: Principles and Applications; APC International: Mackeyville, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zu, J. Comparison of PZN-PT, PMN-PT single crystals and PZT ceramic for vibration energy harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 122, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, M.; Cao, Z. Low-frequency energy harvesters made from double-layer PZT thick films on titanium plate. Phys. Status Solidi A 2016, 214, 1600444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-L.; Lin, S.-C.; Wu, W.-J. Fabrication and performance evaluation of a metal-based bimorph piezoelectric MEMS generator for vibration energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, S.B.; Sheplak, M.; Cattafesta, L.N.; Nishida, T. A MEMS acoustic energy harvester. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, B. A study on the acoustic energy harvesting with Helmholtz resonator and piezoelectric cantilevers. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.U. Electromagnetic energy harvester for harvesting acoustic energy. Sadhana 2016, 41, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.U. Izhar Hybrid acoustic energy harvesting using combined electromagnetic and piezoelectric conversion. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 25003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izhar; Khan, F. Piezoelectric type acoustic energy harvester with a tapered Helmholtz cavity for improved performance. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 54701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar; Khan, F.U. Electromagnetic based acoustic energy harvester for low power wireless autonomous sensor applications. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, A.; Bai, X. Enhanced acoustoelectric coupling in acoustic energy harvester using dual helmholtz resonators. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, A.; Bai, X. A wideband acoustic energy harvester using a three degree-of-freedom architecture. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 164106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Li, P.; Wen, Y.; Lu, C.; Peng, X.; He, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, F. Note: High-efficiency broadband acoustic energy harvesting using Helmholtz resonator and dual piezoelectric cantilever beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar; Khan, F.U. Three degree of freedom acoustic energy harvester using improved Helmholtz resonator. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Chang, C. An efficient low-frequency acoustic energy harvester. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 264, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Pang, Z. Low frequency acoustic energy harvester based on a planar Helmholtz resonator. AIP Adv. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, T.; Bano, S.; Pan, H.; Qi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y. A renewable low-frequency acoustic energy harvesting noise barrier for high-speed railways using a Helmholtz resonator and a PVDF film. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-Based Organic Film Nanogenerator for Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Active Acoustic Sensing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, N.; Gu, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, S.; Qiu, J.; Fu, J.; Kou, X.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. High performance sound driven triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting noise energy. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Laviage, A.J.; You, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Harvesting low-frequency acoustic energy using multiple PVDF beam arrays in quarter-wavelength acoustic resonator. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; You, J.H.; Kim, Y.-J. Low frequency acoustic energy harvesting using PZT piezoelectric plates in a straight tube resonator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 55013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.H.; Li, B. Experimental study on self-powered synchronized switch harvesting on inductor circuits for multiple piezoelectric plates in acoustic energy harvesting. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.-Y.; Chen, L.-W.; Liu, C.-M. Acoustic energy harvesting using resonant cavity of a sonic crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
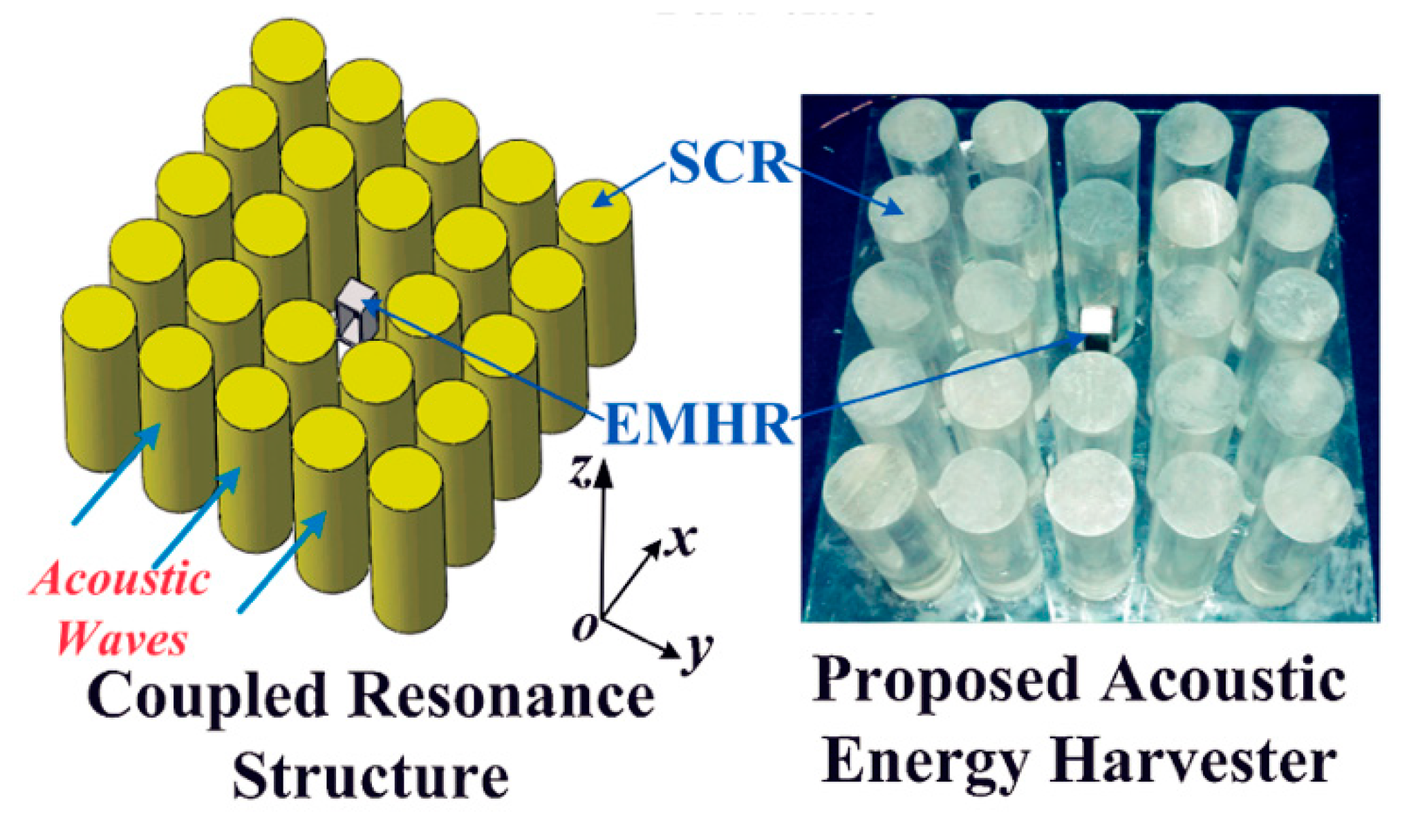
- Yang, A.; Li, P.; Wen, Y.; Lu, C.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J.; He, W. Enhanced Acoustic Energy Harvesting Using Coupled Resonance Structure of Sonic Crystal and Helmholtz Resonator. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6, 127101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
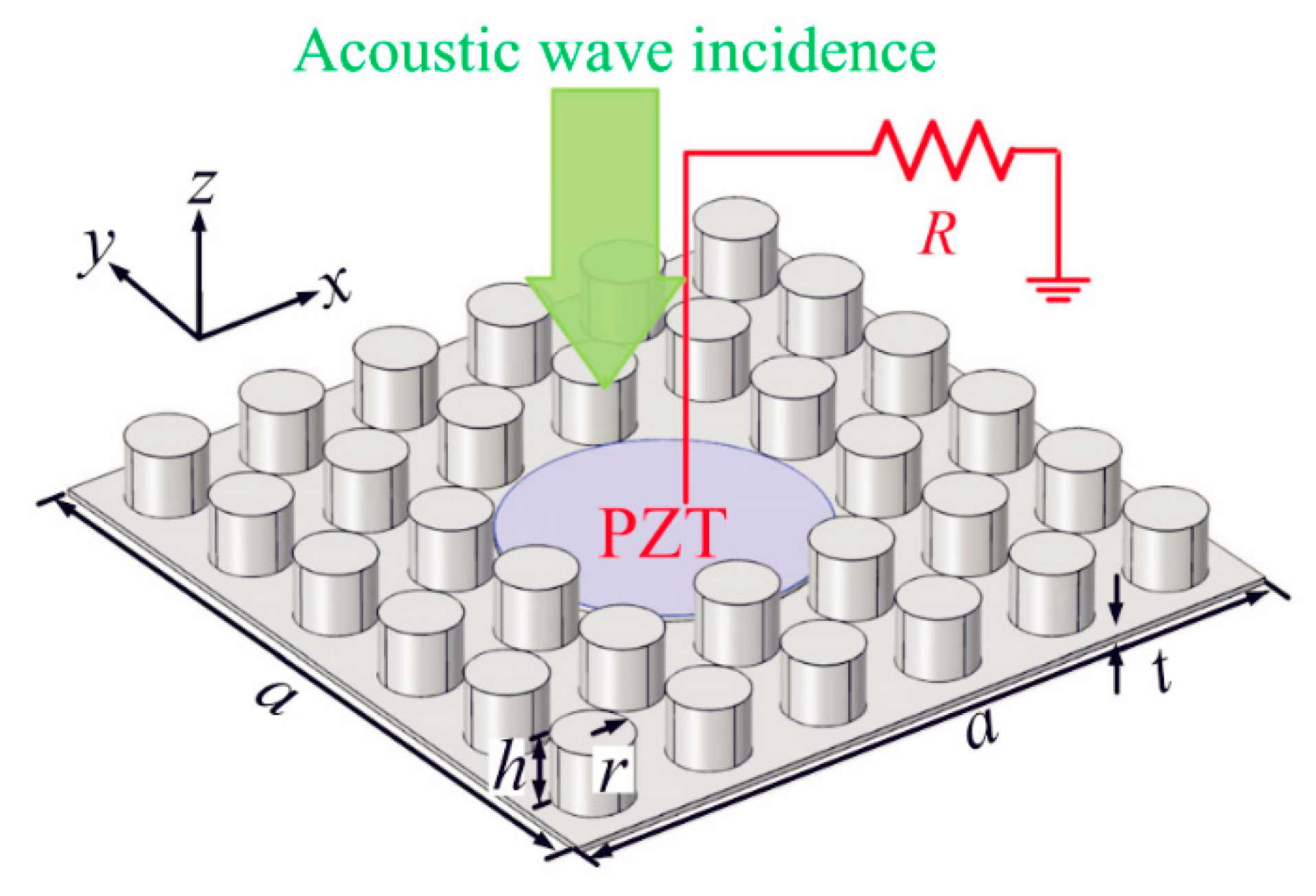
- Qi, S.; Oudich, M.; Li, Y.; Assouar, B. Acoustic energy harvesting based on a planar acoustic metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 263501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudich, M.; Li, Y. Tunable sub-wavelength acoustic energy harvesting with a metamaterial plate. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 315104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
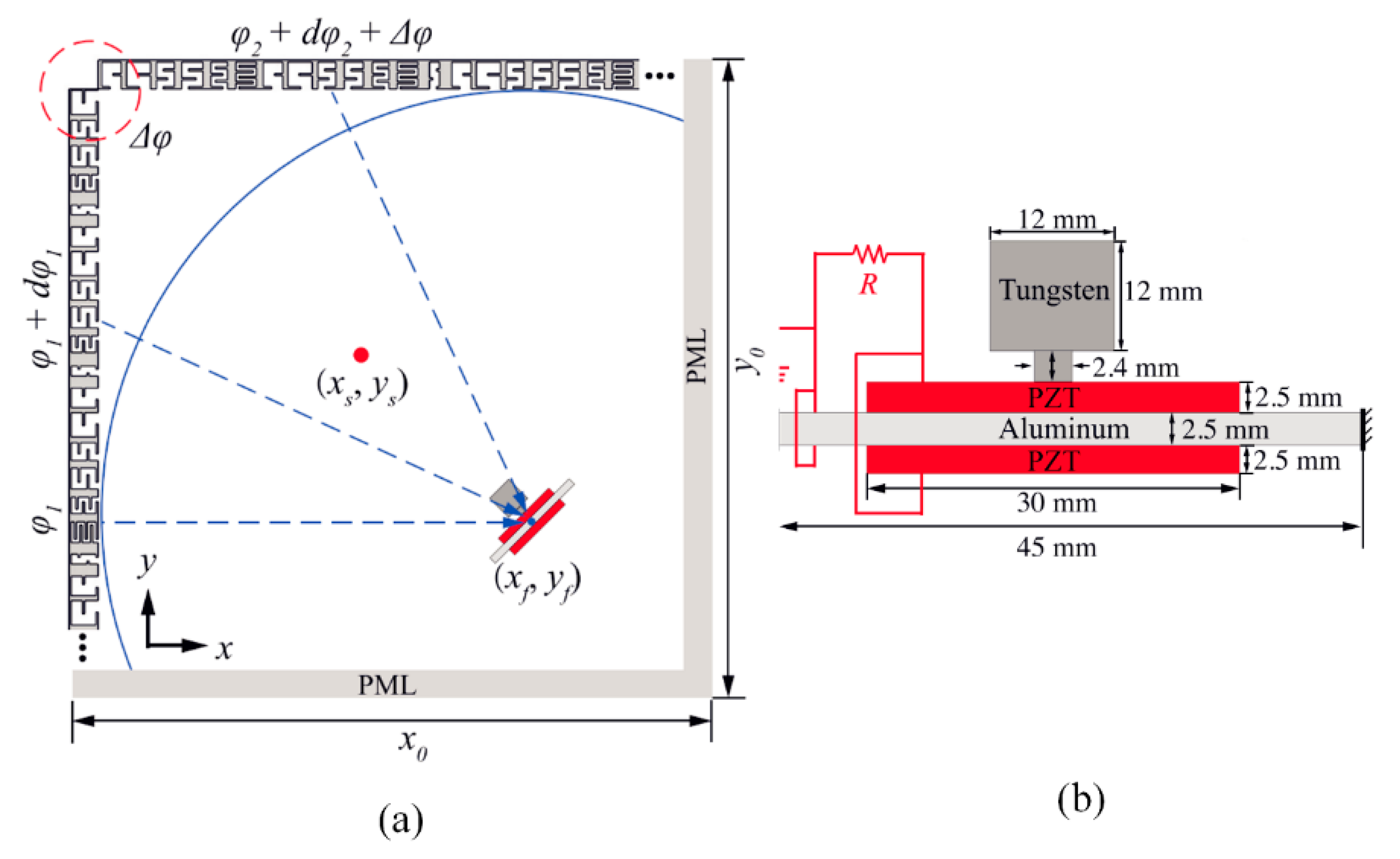
- Qi, S.; Assouar, B. Acoustic energy harvesting based on multilateral metasurfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 243506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
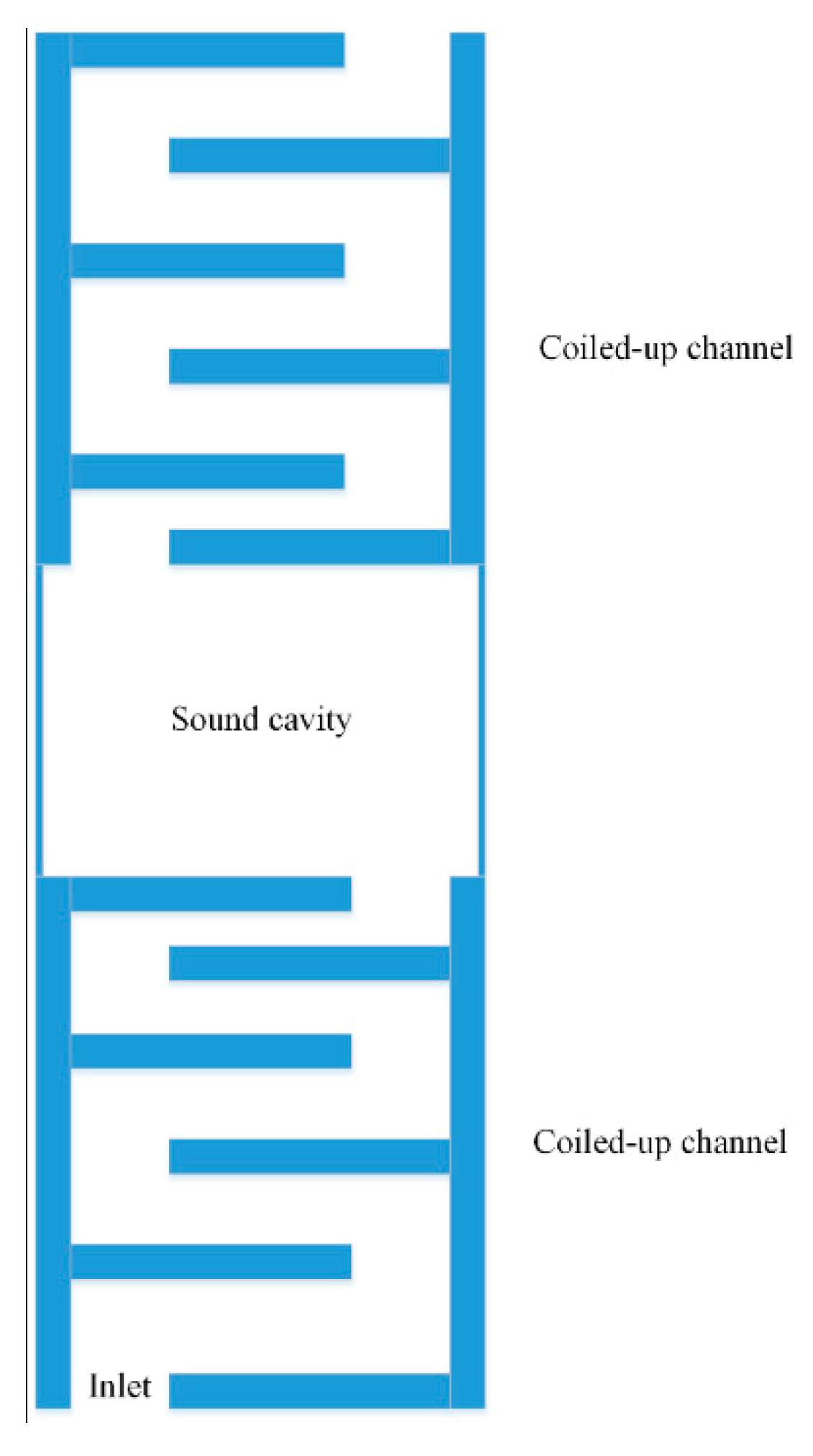
- Sun, K.H.; Kim, J.E.; Song, K. Sound energy harvesting using a doubly coiled-up acoustic metamaterial cavity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 75011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Pang, Z. Helix structure for low frequency acoustic energy harvesting. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 55002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.; Fu, G.; Bai, C. Cochlear bionic acoustic metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 213702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Yang, M.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Z.Y.; Sheng, P. Acoustic metasurface with hybrid resonances. Nature Mater 2014, 13, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, G.; Hu, G. Acoustic metamaterials capable of both sound insulation and energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 45013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Ohayon, R. Acoustic metastructure for effective low-frequency acoustic energy harvesting. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018, 37, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.U.; Banerjee, S. Low frequency energy scavenging using sub-wave length scale acousto-elastic metamaterial. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Madisetti, D.; Banerjee, S. A sub-wavelength scale acoustoelastic sonic crystal for harvesting energies at very low frequencies (<~1 kHz) using controlled geometric configurations. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.; Saadatzi, M.; Ahmed, R.U.; Banerjee, S. Acoustoelastic MetaWall noise barriers for industrial application with simultaneous energy harvesting capability. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 139, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G. Simultaneous realization of large sound insulation and efficient energy harvesting with acoustic metamaterial. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-S.; Peng, Y.-Y.; Liu, M.-H.; Zou, X.-Y.; Cheng, J.-C. Broadband acoustic energy harvesting metasurface with coupled Helmholtz resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 153503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.-B.; Huang, C.-P.; Hu, J.-H. Sound energy harvesting using an acoustic grating. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhu, P. Harvesting acoustic energy by coherence resonance of a bi-stable piezoelectric harvester. Energy 2017, 126, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Jeon, J.; Chung, S.K. Acoustic bubble-powered miniature rotor for wireless energy harvesting in a liquid medium. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 276, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
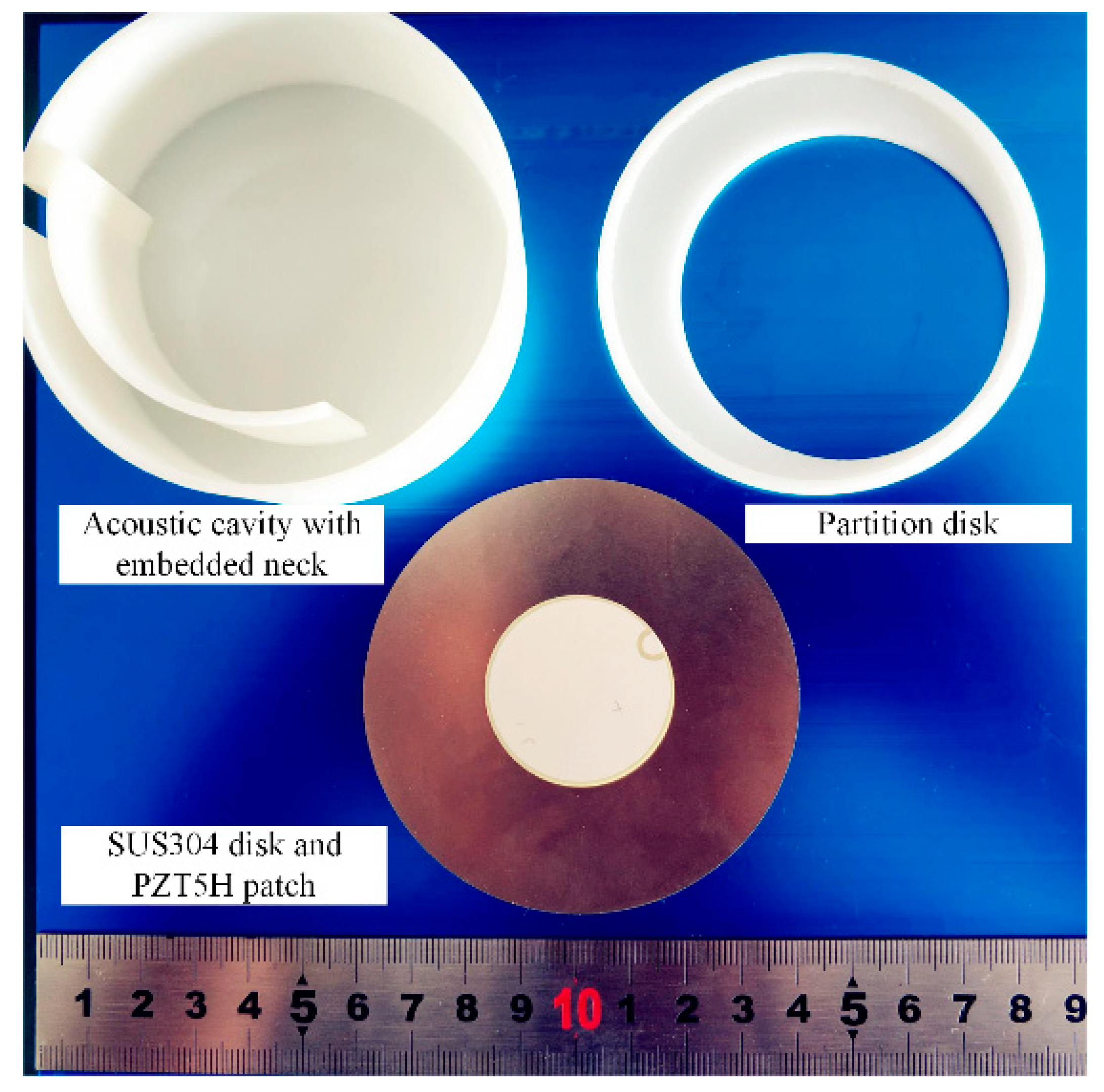
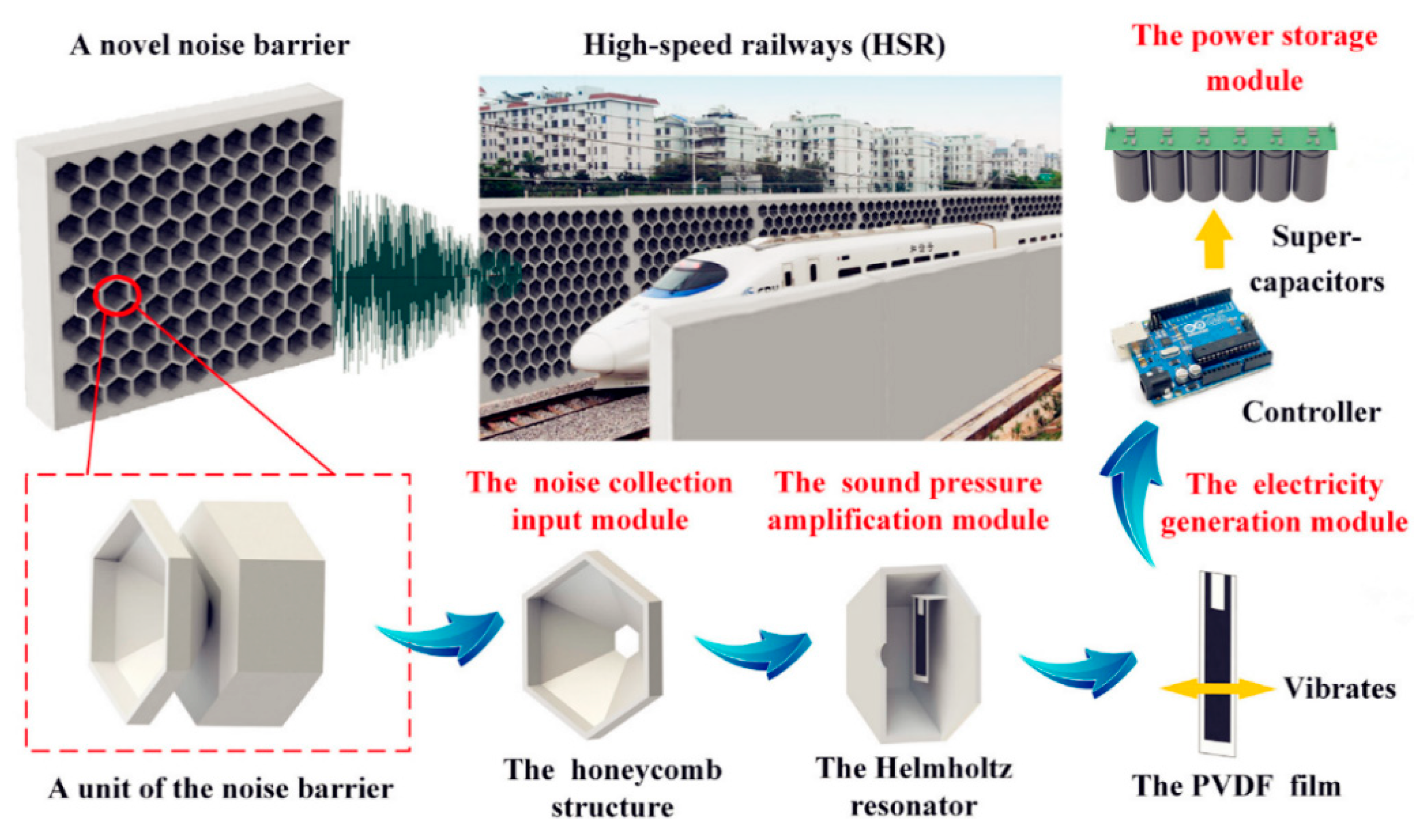
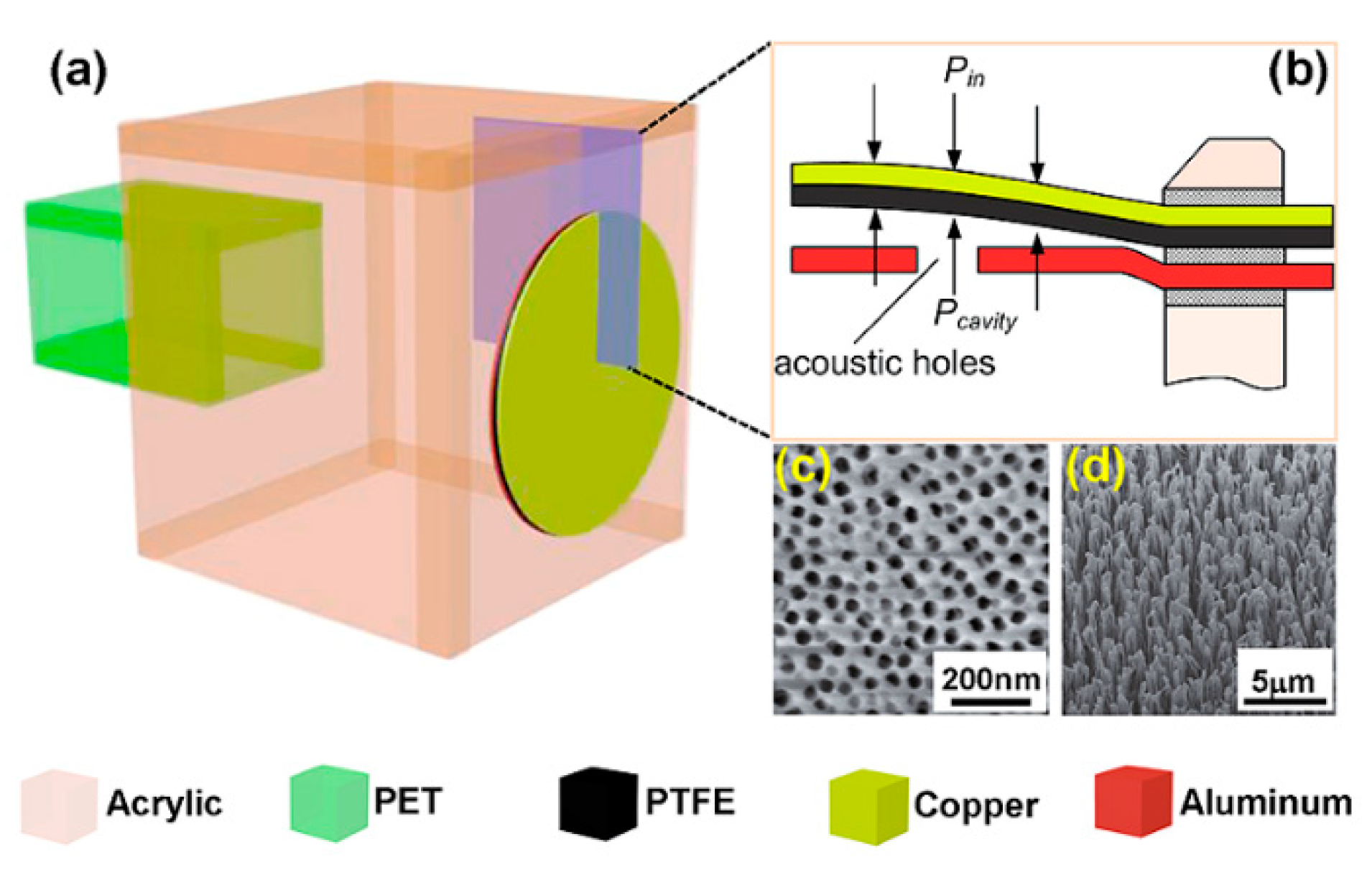
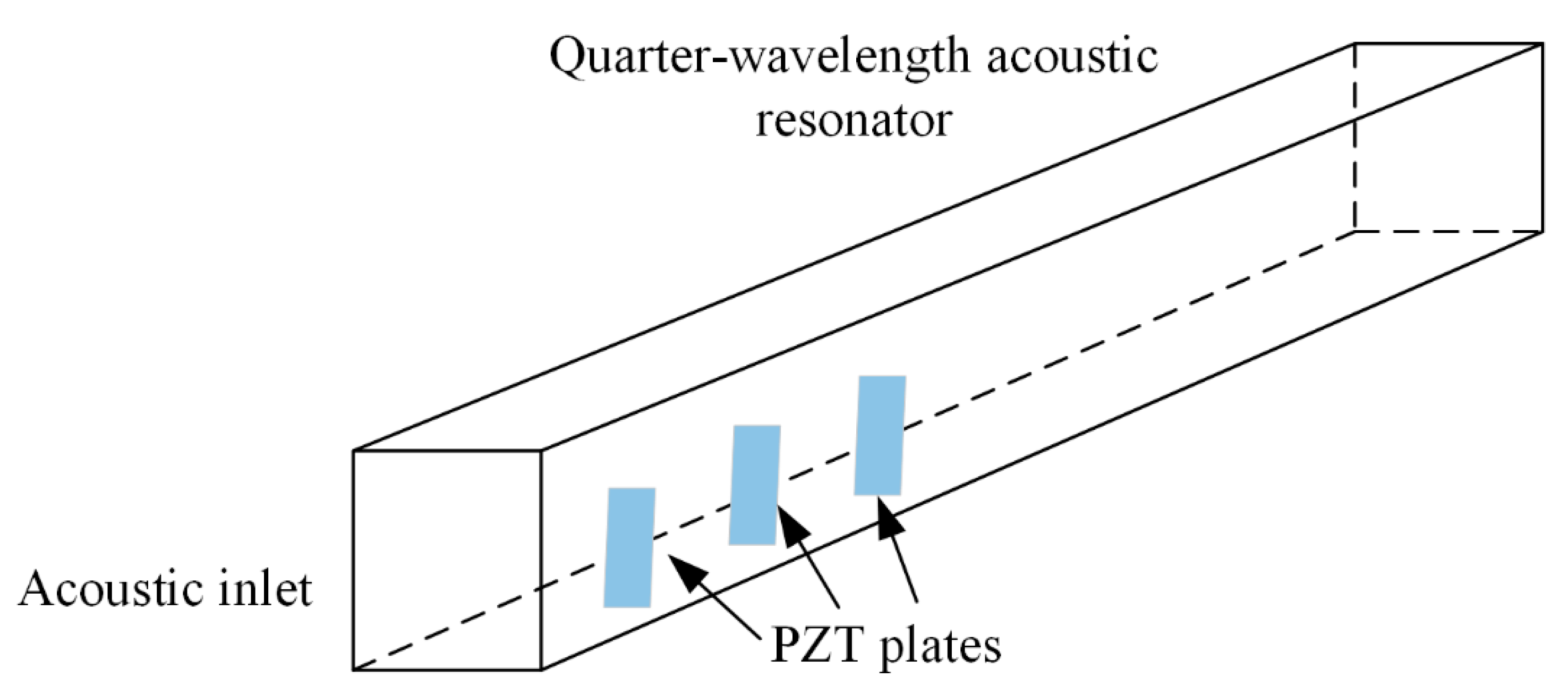
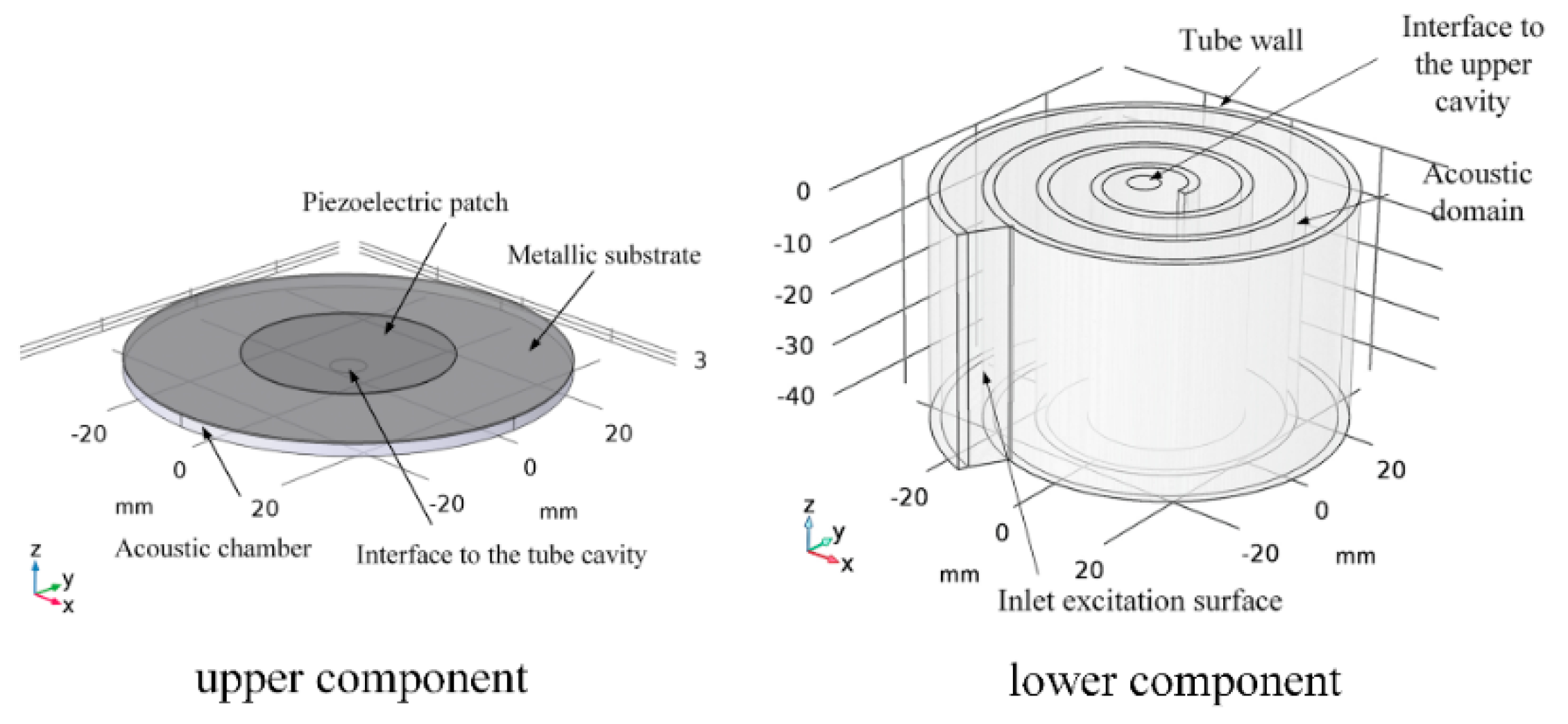
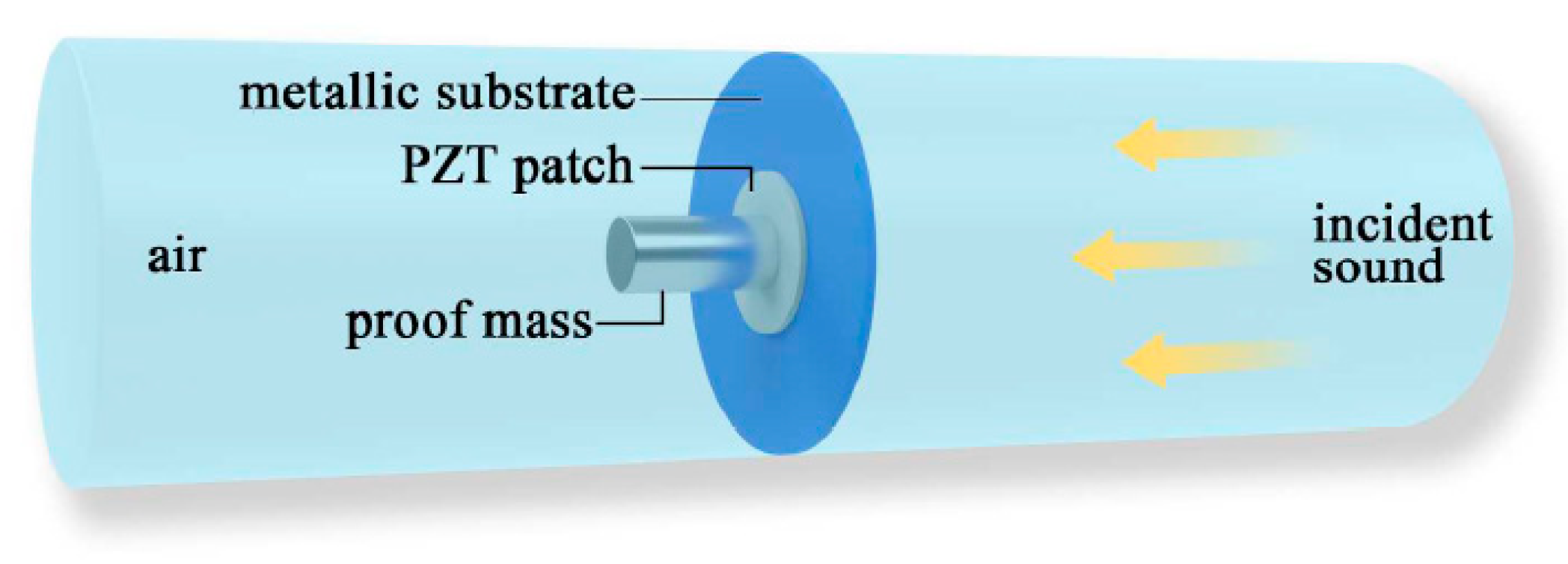
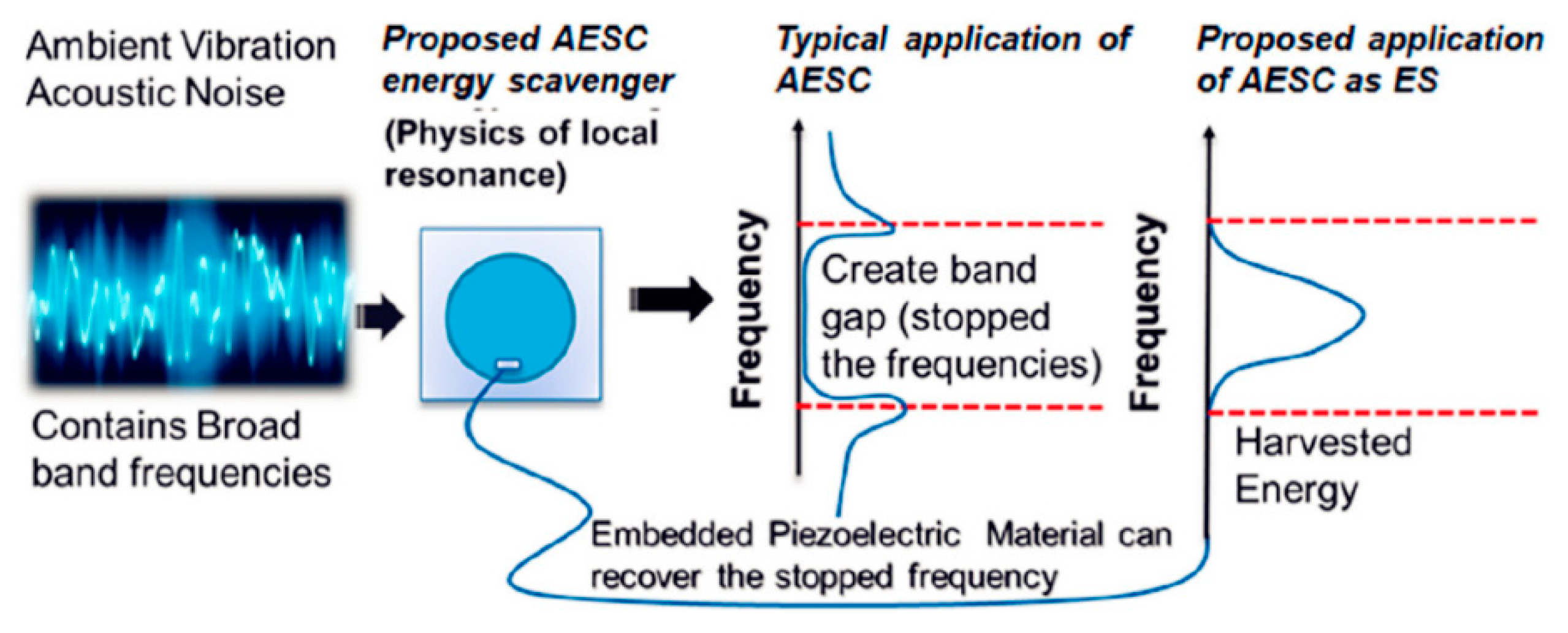
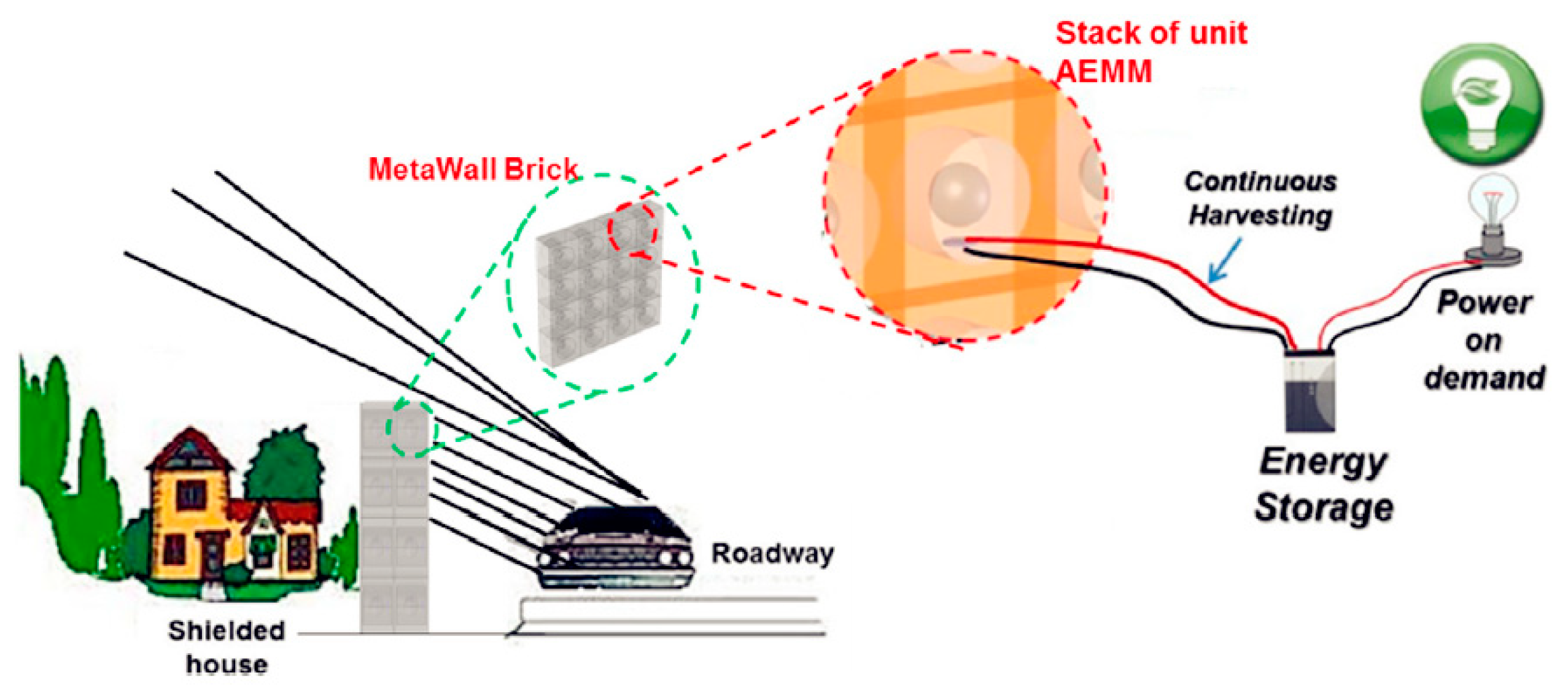
| Sound Pressure (Pa) | SPL (dB) | Sound Intensity (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 80 | 0.0001 |
| 1 | 94 | 0.0025 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.01 |
| 10 | 114 | 0.25 |
| 100 | 134 | 25 |
| 2000 | 160 | 10000 |
| Property | Units | PVDF | BaTiO3 | PZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative dielectric constant | – | 12 | 600–1200 | 1000–4000 |
| Piezo charge constant | pC/N | 20 | −60–−30 | −600–−100 |
| Electromechanical coupling factor | % | 11 | 21 | 30–75 |
| Young’s modulus | 1010N/m2 | 0.3 | 11–12 | 6–9 |
| Density | kg/m3 | 1780 | 5300–5700 | 7500–770 |
| Incident SPL (dB) | Sound Pressure (Pa) | Volume of Harvester (cm3) | Harvested Power (µW) | Metric µW/(Pa2·cm3) | Frequency (Hz) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149 | 563.7 | 2.445 | 6 × 10−6 | 7.7228 × 10−12 | 13570 | [36] |
| 145.5 | 376 | 55.5 | 0.094 | 1.198 × 10−8 | 834 | [37] |
| 100 | 2 | 13.57 | 789.65 | 14.536 | 319 | [38] |
| 130 | 63.2 | 21.2 | 49 | 0.0005787 | 2100 | [39] |
| 100 | 2 | 735 | 7.5 | 0.0026 | 1324 | [43] |
| 100 | 2 | 3970 | 1430 | 0.09 | 170 | [44] |
| 130 | 63.2 | 13.12 | 214.23 | 0.0041 | 1501 | [45] |
| 100 | 2 | 160 | 3.49 | 0.0054 | 332 | [46] |
| 100 | 2 | 200 | 27.2 | 0.034 | 217 | [47] |
| 113 | 9 | 1160 | 2.2 | 0.0000234 | 146 | [51] |
| 113 | 9 | 840 | 12700 | 0.187 | 199 | [52] |
| 100 | 2 | 19.44 | 8.8 | 0.1132 | 2257.5 | [56] |
| 110 | 6.3 | 3027.6 | 429 | 0.0036 | 5545 | [55] |
| 100 | 2 | 251 | 7.3 | 0.0072 | 183 | [60] |
| 100 | 2 | 676 | 0.345 | 0.0001276 | 600 | [59] |
| 114 | 10 | 11.14 | 210 | 0.1885 | 155 | [64] |
| 94 | 1 | 154.96 | 3.22 | 0.021 | ~360,450 | [68] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Chou, X. Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review. Micromachines 2019, 10, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010048
Yuan M, Cao Z, Luo J, Chou X. Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review. Micromachines. 2019; 10(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ming, Ziping Cao, Jun Luo, and Xiujian Chou. 2019. "Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review" Micromachines 10, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010048
APA StyleYuan, M., Cao, Z., Luo, J., & Chou, X. (2019). Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review. Micromachines, 10(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010048





