Genome-Wide Interaction Study of Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Health in the Framingham Heart Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Fatty Acids
2.3. Biomarkers of Inflammation
2.4. Genotype Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
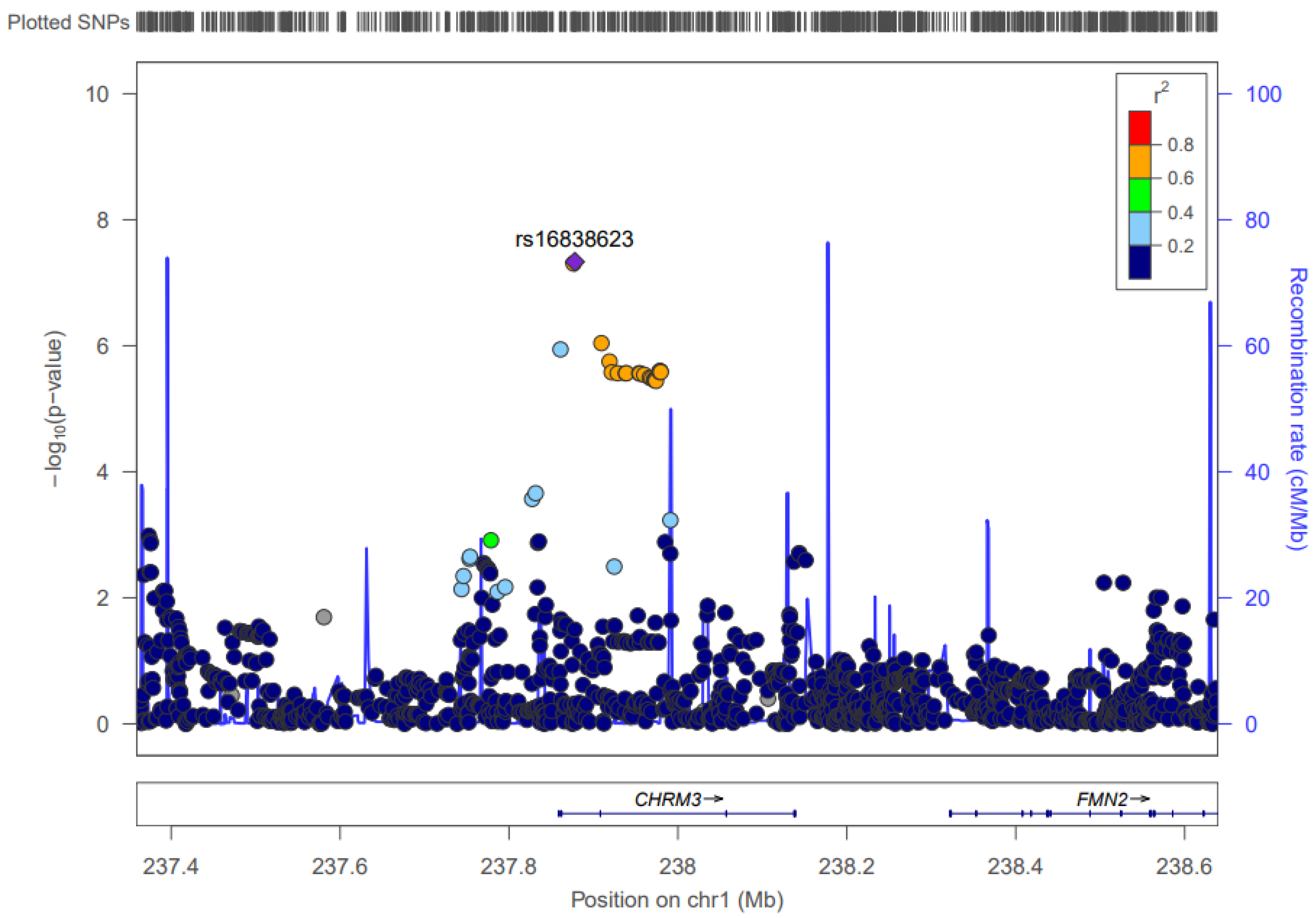
3.1. Chromosome 1: CHRM3
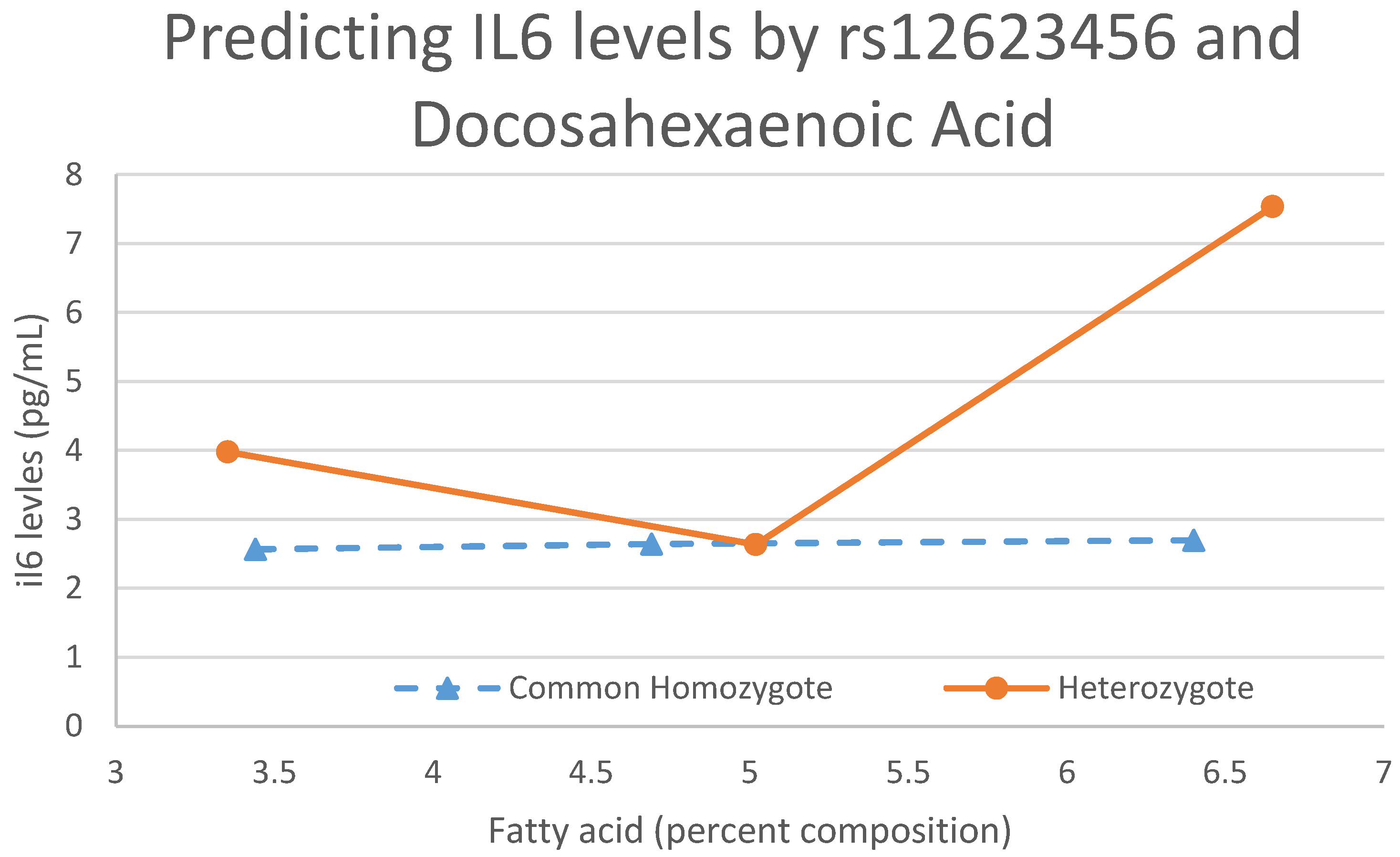
3.2. Chromosome 2: RPL7P61
3.3. Chromosome 3: RP11-373E16.1
3.4. Chromosome 7: CHCHD3
3.5. Chromosome 13: LOC105370115
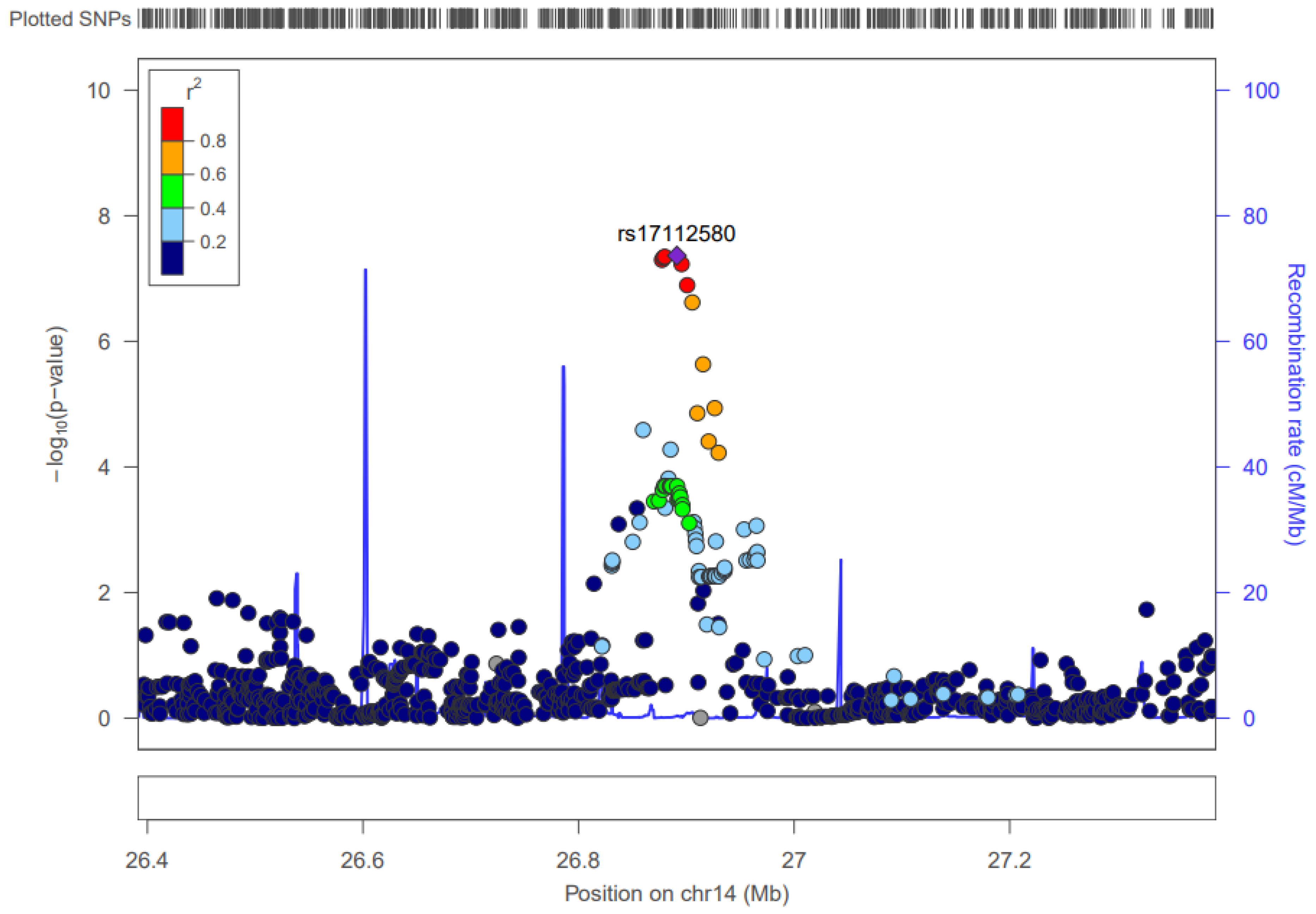
3.6. Chromosome 14
3.6.1. LOC105378178
3.6.2. CTD-3006G17.2
3.7. Chromosome 20: LINC00652
4. Discussion
4.1. Docosapentaenoic Acid (Omega-6)
4.2. Eicosadienoic Acid
4.3. Oleic Acid
4.3.1. Chromosome 3
4.3.2. Chromosome 13
4.3.3. Chromosome 14
4.3.4. Chromosome 20
4.4. Alpha Linoleic Acid
4.5. Docosahexaenoic Acid
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemaitre, R.N.; Tanaka, T.; Tang, W.; Manichaikul, A.; Foy, M.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Nettleton, J.A.; King, I.B.; Weng, L.C.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Genetic loci associated with plasma phospholipid n-3 fatty acids: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies from the CHARGE Consortium. PLoS Genetics 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tintle, N.L.; Pottala, J.V.; Lacey, S.; Ramachandran, V.; Westra, J.; Rogers, A.; Clark, J.; Olthoff, B.; Larson, M.; Harris, W.; et al. A genome-wide association study of saturated, mono-and polyunsaturated red blood cell fatty acids in the Framingham Heart Offspring Study. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 94, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottala, J.V.; Garg, S.; Cohen, B.E.; Whooley, M.A.; Harris, W.S. Blood eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids predict all-cause mortality in patients with stable coronary heart disease: The heart and soul study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2010, 3, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, G.C.; Pottala, J.V.; Spertus, J.A.; Harris, W.S. Red blood cell fatty acid patterns and acute coronary syndrome. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, R.C.; Harris, W.S.; Reid, K.J.; Spertus, J.A. Omega-6 and trans fatty acids in blood cell membranes: A risk factor for acute coronary syndromes? Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.S.; Pottala, J.V.; Lacey, S.M.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Robins, S.J. Clinical correlates and heritability of erythrocyte eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid content in the Framingham Heart Study. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, D.; Deuster, P.; Harris, W.; Macrae, H.; Dretsch, M. Red blood cell omega-3 fatty acid levels and neurocognitive performance in deployed US Servicemembers. Nutr. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottala, J.V.; Yaffe, K.; Robinson, J.; Espeland, M.; Wallace, R.; Harris, W.S. Higher RBC EPA+DHA corresponds with larger total brain and hippocampal volumes: WHIMS-MRI study. Neurology 2014, 82, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.S.; Harris, W.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Au, R.; Himali, J.J.; Debette, S.; Pikula, A.; Decarli, C.; Wolf, P.A.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Red blood cell omega-3 fatty acid levels and markers of accelerated brain aging. Neurology 2012, 78, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaneh-Far, R.; Harris, W.S.; Garg, S.; Na, B.; Whooley, M.A. Inverse association of erythrocyte n-3 fatty acid levels with inflammatory biomarkers in patients with stable coronary artery disease: The heart and soul study. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worns, M.A.; Victor, A.P.; Galle, R.; Hohler, T. Genetic and environmental contributions to plasma C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels–A study in twins. Genes Immun. 2006, 7, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraja, A.T.; Chasman, D.I.; North, K.E.; Reiner, A.P.; Yanek, L.R.; Kilpeläinen, T.O.; Smith, J.A.; Dehghan, A.; Dupuis, J.; Johnson, A.D.; et al. Pleiotropic genes for metabolic syndrome and inflammation. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 112, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, D.D.; Beaulieu, L.M.; Mick, E.; Tanriverdi, K.; Larson, M.G.; Keaney, J.F.; Benjamin, E.J.; Freedman, J.E. Relationship among circulating inflammatory proteins, platelet gene expression, and cardiovascular risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Lunetta, K.L.; Larson, M.G.; Dupuis, J.; Lipinska, I.; Rong, J.; Chen, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yamamoto, J.F.; Meigs, J.B.; et al. The relation of genetic and environmental factors to systemic inflammatory biomarker concentrations. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Wilson, P.W.; Lipinska, I.; Corey, D.; Vita, J.A.; Keaney, J.F.; Benjamin, E.J. Genome scan of systemic biomarkers of vascular inflammation in the Framingham Heart Study: Evidence for susceptibility loci on 1q. Atherosclerosis 2005, 182, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, J.D.; Rahman, F.; Lacey, S.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Harris, W.S.; Robins, S.J. Red blood cell fatty acids and biomarkers of in flammation : A cross-sectional study in a community-based cohort. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 240, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Arnett, D.K.; Peacock, J.M.; Parnell, L.D.; Kraja, A.; Hixson, J.E.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lai, C.Q.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Straka, R.J.; et al. Interleukin1beta genetic polymorphisms interact with polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate risk of the metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Psaty, B.M.; O’donnell, C.J.; Gudnason, V.; Lunetta, K.L.; Folsom, A.R.; Rotter, J.I.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Harris, T.B.; Witteman, J.C.; Boerwinkle, E. Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) Consortium: Design of prospective meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies from 5 cohorts. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, D.R.; Cupples, L.A.; Kannel, W.B.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Atwood, L.D.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Fox, C.S.; Larson, M.; Levy, D.; Murabito, J.; et al. Genetics of the Framingham Heart Study Population. Adv. Genet. 2008, 62, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupples, L.A.; Arruda, H.T.; Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Demissie, S.; DeStefano, A.L.; Dupuis, J.; Falls, K.M.; Fox, C.S.; Gottlieb, D.J.; et al. The Framingham Heart Study 100K SNP genome-wide association study resource: Overview of 17 phenotype working group reports. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Flock, M.R.; Richter, C.K.; Harris, W.S.; West, S.G.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Red blood cell docosapentaenoic acid (DPA n-3) is inversely associated with triglycerides and c-reactive protein (CRP) in healthy adults and dose-dependently increases following n-3 fatty acid supplementation. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6390–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Goede, J.W.; Verschuren, M.M.; Boer, J.M.A.; Verberne, L.D.M.; Kromhout, D.; Geleijnse, J.M. n-6 and n-3 fatty acid cholesteryl esters in relation to fatal CHD in a Dutch adult population: A nested case-control study and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Folsom, A.R.; Eckfeldt, J.H. Plasma fatty acid composition and incidence of coronary heart disease in middle aged adults: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2003, 13, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids: Partners in prevention. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorgeril, M.; Salen, P. New insights into the health effects of dietary saturated and omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, G.E.; Kramer, B.K.; Lorkowski, S.; Marz, W.; von Schacky, C.; Kleber, M.E. Individual omega-9 monounsaturated fatty acids and mortality-The Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health Study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Framingham Heart Study. Available online: http://www.framinghamheartstudy.org/ (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- Wang, J.; Tan, G.J.; Han, L.N.; Bai, Y.Y.; He, M.; Liu, H.B. Novel biomarkers for cardiovascular risk prediction. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, T.; Zabaneh, D.; Gaunt, T.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Shah, S.; Talmud, P.J.; Day, I.N.; Whittaker, J.; Holmes, M.V.; Sofat, R.; et al. Gene-centric analysis identifies variants associated with interleukin-6 levels and shared pathways with other inflammation markers. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.A. review about biomarkers for the investigation of vascular function and impairment in diabetes mellitus. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rifai, N.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hennekens, C.H. Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 2000, 101, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Su, D.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Xia, M.; et al. Serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez de Ciriza, C.; Lawrie, A.; Varo, N. Osteoprotegerin in Cardiometabolic Disorders. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 564934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Schon, M.P.; Boehncke, W.H. P-Selectin: A common therapeutic target for cardiovascular disorders, inflammation and tumour metastasis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, C.N.; Khan, H.; Mann, D.L.; Georgiopoulou, V.V.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Harris, T.; Koster, A.; Newman, A.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; et al. Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors and heart failure risk in older adults: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michigan Imputation Server. Available online: https://imputationserver.sph.umich.edu/index.html (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- Loh, P.R.; Danecek, P.; Palamara, P.F.; Fuchsberger, C.; Schoenherr, S.; Forer, L.; McCarthy, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Durbin, R. Reference-based phasing using the Haplotype Reference Consortium panel. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensembl. Available online: http://www.ensembl.org/index.html (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- Panagiotou, O.A.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. What should the genome-wide significance threshold be? Empirical replication of borderline genetic associations. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruim, R.J.; Welch, R.P.; Sanna, S.; Teslovich, T.M.; Chines, P.S.; Gliedt, T.P.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Willer, C.J. LocusZoom Regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2336–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bakker, P.I.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Jia, X.; Neale, B.M.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Voight, B.F. Practical aspects of imputation-driven meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, R122–R128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würtz, P.; Havulinna, A.S.; Soininen, P.; Tynkkynen, T.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Tillin, T.; Ghorbani, A.; Artati, A.; Wang, Q.; Tiainen, M.; et al. Metabolite profiling and cardiovascular event risk: A prospective study of 3 population-based cohorts. Circulation. 2015, 131, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Huang, W.C.; Li, C.W.; Chuang, L.T. Eicosadienoic acid differentially modulates production of pro-inflammatory modulators in murine macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 358, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, L.; Beneit, N.; Otero, Y.F.; Escribano, Ó.; Díaz-Castroverde, S.; Gómez-Hernández, A.; Benito, M. Protective role of oleic acid against cardiovascular insulin resistance and in the early and late cellular atherosclerotic process. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, K.A.; Walker, C.L.; Xu, Z.; Whitley, P.; Pavlina, T.M.; Hise, M.; Zaloga, G.P.; Siddiqui, R.A. Oleic acid inhibits stearic acid-induced inhibition of cell growth and pro-inflammatory responses in human aortic endothelial cells. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.H.; Crawford, M.A.; Reifen, R. Update on alpha-linolenic acid. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Leyva, D.; Weighell, W.; Edel, A.L.; LaVallee, R.; Dibrov, E.; Pinneker, R.; Maddaford, T.G.; Ramjiawan, B.; Aliani, M.; Guzman, R.; et al. Potent antihypertensive action of dietary flaxseed in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2013, 62, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.A.; Woodman, R.J. The independent effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on cardiovascular risk factors in humans. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darshi, M.; Mendiola, V.L.; Mackey, M.R.; Murphy, A.N.; Koller, A.; Perkins, G.A.; Ellisman, M.H.; Taylor, S.S. ChChd3, an inner mitochondrial membrane protein, is essential for maintaining crista integrity and mitochondrial function. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 2918–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevik, E.J.; van Donkelaar, M.M.; Weber, H.; Sánchez-Mora, C.; Jacob, C.; Rivero, O.; Kittel-Schneider, S.; Garcia-Martínez, I.; Aebi, M.; van Hulzen, K.; et al. Genome-wide analyses of aggressiveness in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Kranzler, H.R.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Farrer, L.A.; Gelernter, J. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y. High glucose decreases claudins-5 and-11 in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells: Antagonistic effects of tongxinluo. Endocr. Res. 2017, 42, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.C.; Aliev, F.; Bierut, L.J.; Bucholz, K.K.; Edenberg, H.; Hesselbrock, V.; Kramer, J.; Kuperman, S.; Nurnberger, J.J.; Schuckit, M.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study of comorbid depressive syndrome and alcohol dependence. Psychiatr. Genet. 2012, 22, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.K.; Emil, J.; Sandholt, C.H.; Grarup, N. Identification of Novel Genetic Determinants of Erythrocyte Membrane Fatty Acid Composition among Greenlanders. PLoS Genet. 2016, 193, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasaje, C.F.; Bae, J.S.; PARk, B.L.; Jang, A.S.; Uh, S.T.; Kim, M.K.; Koh, I.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Association analysis of DTD1 gene variations with aspirin-intolerance in asthmatics. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del-Aguila, J.L.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Cooper-Dehoff, R.M.; Chapman, A.B.; Gums, J.G.; Bailey, K.; Gong, Y.; Turner, S.T.; Johnson, J.A.; Boerwinkle, E. Genome-wide association analyses suggest NELL1 influences adverse metabolic response to HCTZ in African Americans. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comuzzie, A.G.; Cole, S.A.; Laston, S.L.; Voruganti, V.S.; Haack, K.; Gibbs, R.A.; Butte, N.F. Novel genetic loci identified for the pathophysiology of childhood obesity in the Hispanic population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsuran, V.; Kulkarni, H.; He, W.; Mlisana, K.; Wright, E.J.; Werner, L.; Castiblanco, J.; Dhanda, R.; Le, T.; Dolan, M.J.; et al. Duffy-null-associated low neutrophil counts influence HIV-1 susceptibility in high-risk South African black women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Silvertown, J.D. Inflammation, C-reactive protein, and atherothrombosis. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, A.; Chen, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Wu, J.H.; Sun, Q.; Campos, H.; Mozaffarian, D.; Hu, F.B. Alpha-Linolenic acid and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H. Critical roles of acetylcholine and the muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the regulation of immune function. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiuri, S.P.; Aukema, H.M.; Ravandi, A.; Guzman, R.; Dibrov, E.; Pierce, G.N. Flaxseed consumption reduces blood pressure in patients with hyper tension by altering circulating oxylipins via an α-linolenic acid-induced inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Hypertension 2014, 64, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkan, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; Ugocsai, P.; Isaacs, A.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Liebisch, G.; Wilson, J.F.; Johansson, A.; Rudan, I.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci associated with circulating phospho-and sphingolipid concentrations. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Schmidt, M.K.; Kraft, P.; Canisius, S.; Chen, C.; Khan, S.; Tyrer, J.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Dennis, J.; Michailidou, K. Identification of novel genetic markers of breast cancer survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Imamura, F.; Sharp, S.J.; Koulman, A.; Schulze, M.B.; Zheng, J.; Ye, Z.; Sluijs, I.; Guevara, M.; Huerta, J.M.; et al. Association of plasma phospholipid n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids with type 2 diabetes: The EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study. PLoS Medicine 2016, 13, e1002094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Fatty Acid | Mean (Percent Composition) | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Oleic acid (OA) | 13.900% | 1.030% |
| Eicosadienoic acid (EDA) | 0.278% | 0.046% |
| Gamma-linoleic acid (GLA) | 0.083% | 0.072% |
| Alpha-linoleic acid (ALA) | 0.184% | 0.098% |
| Linoleic acid (LA) | 11.100% | 1.700% |
| Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid (DGLA) | 1.596% | 0.359% |
| Arachidonic acid (AA) | 16.800% | 1.600% |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | 0.732% | 0.447% |
| Docosatetranoic acid (DTA) | 3.790% | 0.826% |
| Docosapentaenoic acid-n-6 (DPA_N6) | 0.661% | 0.189% |
| Docosapentaenoic acid n-3 (DPA_N3) | 2.750% | 0.453% |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | 4.840% | 1.360% |
| Chr | Region | Sig SNPs | Biomarker | Location (bp) | Smallest Int. p-Value (rsid#:FA) | Genes Containing/Near SNPs | Previous Cardiometabolic Trait Evidence | EAF | Significant Without Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 239,809,739–239,811,390 | 2 | IL6 | 239,811,390 | 4.66 × 10–8 (rs16838623:ALA) | CHRM3, LOC105373225 | Hypertension [28] | 0.0222 | No |
| 2 | 163,855,536–164,056,447 | 4 | IL6 | 164,019,142 | 3.05 × 10–9 (rs12623456:DHA) | RPL7P61 | None | 0.0161 | No |
| 3 | 170,371,857–170,376,150 | 2 | MCP1 | 170,371,857 | 5.25 × 10–10 (rs7611820:OA) | RP11-373E16.1 CLDN11, LOC101928583, RPL28P1 | None | 0.0724 | No |
| 7 | 132,794,130–132,796,323 | 2 | ICAM | 132,796,323 | 1.00 × 10–8 (rs17424324:DPA_N6) | LOC105375512, CHCHD3 | None | 0.116 | No |
| 13 | 24,533,606 | 1 | TNF | 24,533,606 | 2.88 × 10–8 (rs17079653:OA) | LOC105370115, ANKRD20A19P, SPATA13 | None | 0.0233 | No |
| 14 | 49,803,164 | 1 | CRP | 49,803,164 | 2.93 × 10–8 (rs7160151:EDA) | LOC105378178 | None | 0.29 | No |
| 14 | 27,808,931–27,821,399 | 3 | CAM | 27,821,399 | 4.33 × 10–8 (rs17112580:OA) | CTD-3006G17.2, LOC728755 | None | 0.249 | No |
| 20 | 18,777,980–18,778,844 | 3 | CRP | 18,777,980 | 3.23 × 10–8 (rs3762220:OA) | LOC100270804, LINC00652, LOC107985399, EEF1A1P34, DTD1, C20orf78 | None | 0.0484 | No |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veenstra, J.; Kalsbeek, A.; Westra, J.; Disselkoen, C.; E. Smith, C.; Tintle, N. Genome-Wide Interaction Study of Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Health in the Framingham Heart Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080900
Veenstra J, Kalsbeek A, Westra J, Disselkoen C, E. Smith C, Tintle N. Genome-Wide Interaction Study of Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Health in the Framingham Heart Study. Nutrients. 2017; 9(8):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080900
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeenstra, Jenna, Anya Kalsbeek, Jason Westra, Craig Disselkoen, Caren E. Smith, and Nathan Tintle. 2017. "Genome-Wide Interaction Study of Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Health in the Framingham Heart Study" Nutrients 9, no. 8: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080900
APA StyleVeenstra, J., Kalsbeek, A., Westra, J., Disselkoen, C., E. Smith, C., & Tintle, N. (2017). Genome-Wide Interaction Study of Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Health in the Framingham Heart Study. Nutrients, 9(8), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080900





