Association of Vitamins and Minerals with Type 1 Diabetes Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
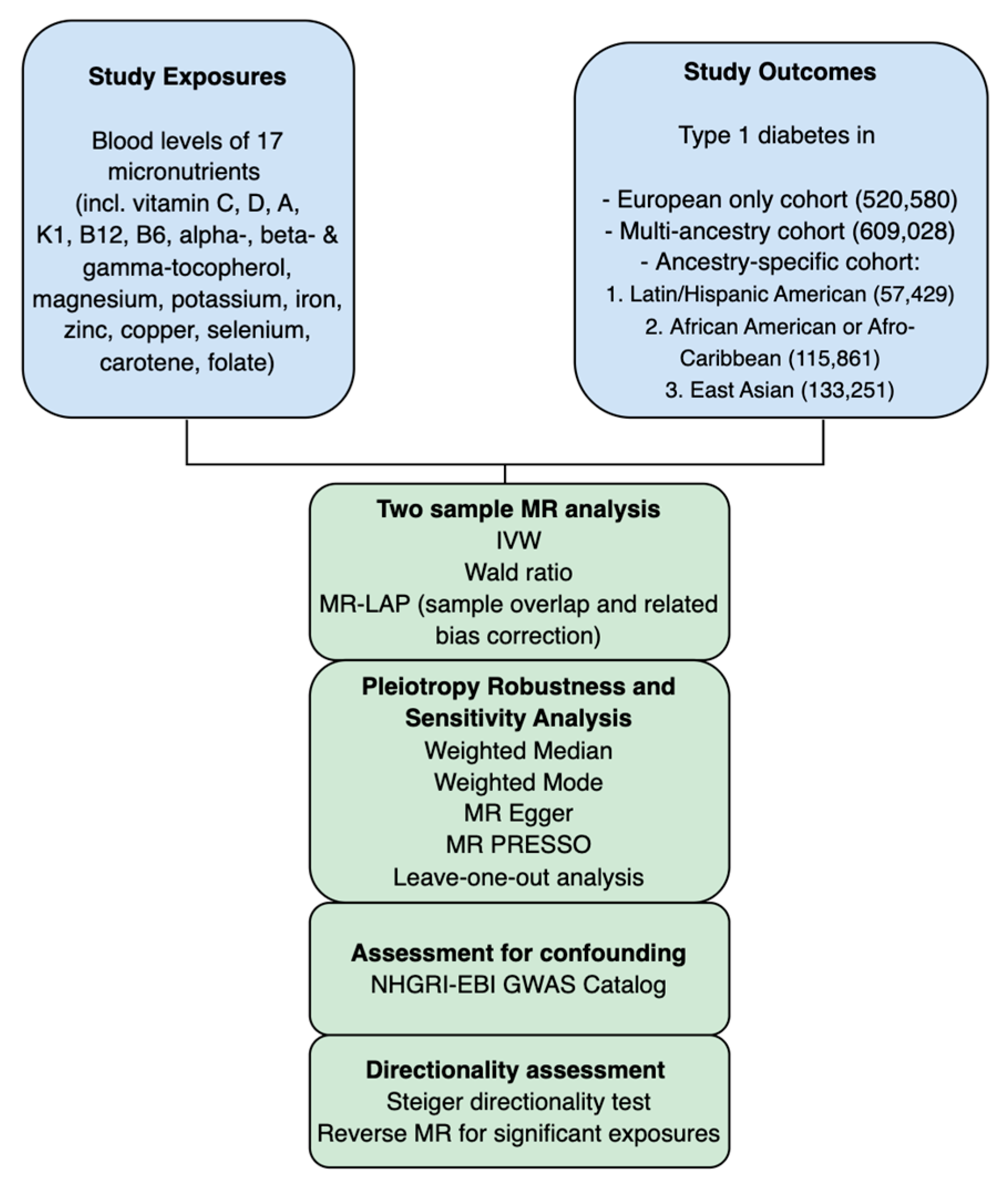
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MR Study Design
- Relevance Assumption: SNPs must demonstrate a strong association with the exposure variable.
- Independence Assumption: SNPs are not correlated with any confounding factors.
- Exclusion Restriction Assumption: SNPs influence the outcome exclusively via the exposure.
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Instrumental Variable (IV) Selection
2.4. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
3. Results
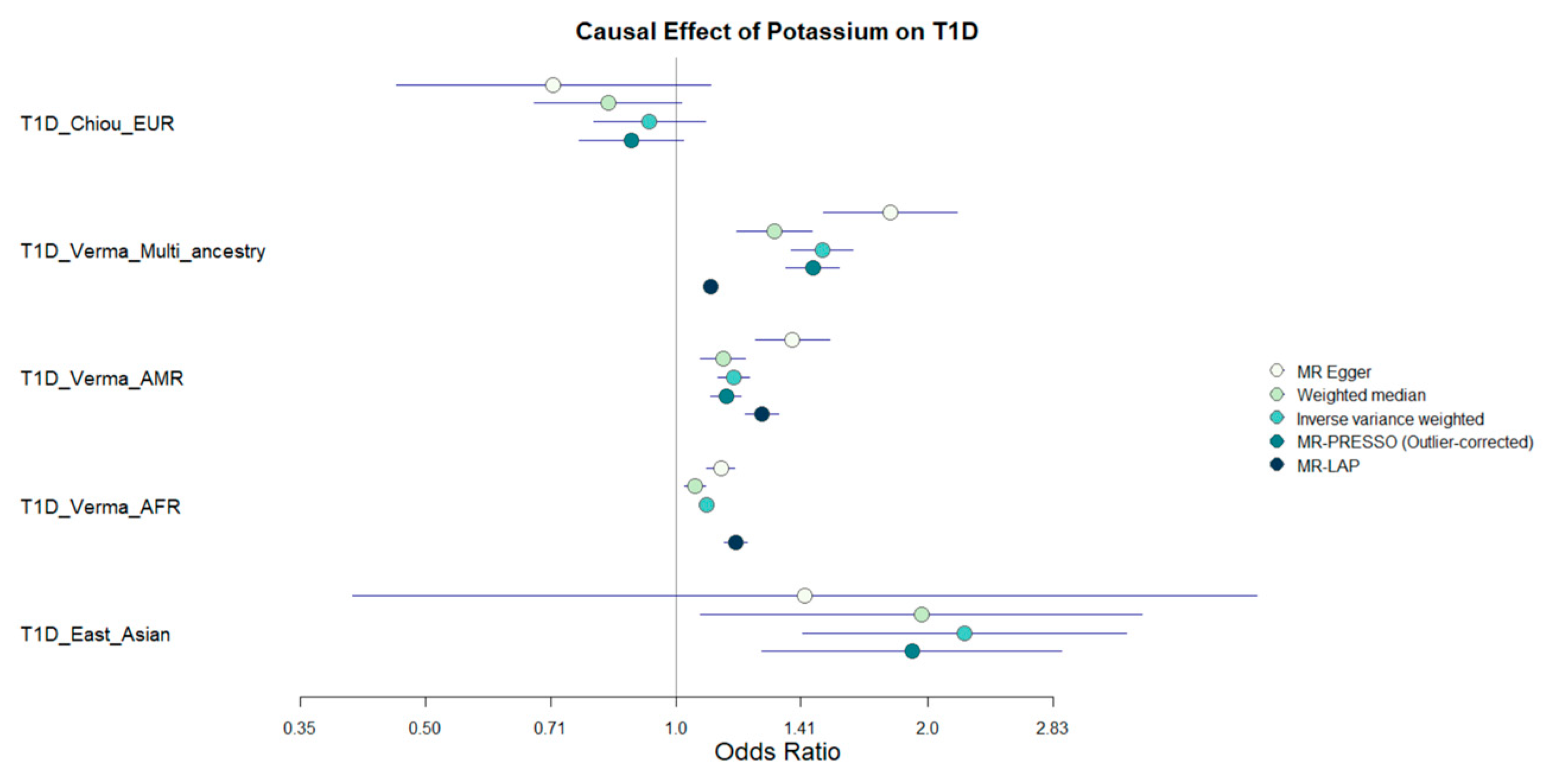
3.1. MR Results
3.2. Suggestive MR Associations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maahs, D.M.; West, N.A.; Lawrence, J.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampousi, A.-M.; Carlsson, S.; Löfvenborg, J.E. Dietary factors and risk of islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eBioMedicine 2021, 72, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.A.; Fernandes, G.; Yunis, E.J.; Cooper, W.C.; Jose, D.C.; Kramer, T.R.; Hansen, M.A. Nutritional deficiency, immunologic function, and disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 84, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Younes, S. The role of micronutrients on the treatment of diabetes. Hum. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 35, 200238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkin, A. The key role of micronutrients. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qin, L.; Zheng, J.; Tong, L.; Lu, W.; Lu, C.; Sun, J.; Fan, B.; Wang, F. Research Progress on the Relationship between Vitamins and Diabetes: Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.T.; Rodrigues, D.; Guimarães, J.; Lemos, M.C. Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Type 1 Diabetes: A Case–Control Association Study. Genes 2020, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurhuus, M.S.; Klitgaard, N.A.H.; Pedersen, K.K.; Blaabjerg, O.; Altura, B.M.; Altura, B.T.; Henriksen, J.E. Magnesium reduces insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and serum lipid concentrations in type 1 diabetes. Metabolism 2001, 50, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghobashy, A.A.; Alkholy, U.M.; Talat, M.A.; Abdalmonem, N.; Zaki, A.; Ahmed, I.A.; Mohamed, R.H. Trace elements and oxidative stress in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkholy, U.M.; Abdalmonem, N.; Zaki, A.; Elkoumi, M.A.; Hashim, M.I.A.; Basset, M.A.A.; Salah, H.E. The antioxidant status of coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E in children with type 1 diabetes. J. De Pediatr. 2019, 95, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyvsgaard, J.N.; Overgaard, A.J.; Jacobsen, L.D.; Thorsen, S.U.; Pipper, C.B.; Hansen, T.H.; Husted, S.; Mortensen, H.B.; Pociot, F.; Svensson, J. Low perinatal zinc status is not associated with the risk of type 1 diabetes in children. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, S.U.; Mortensen, H.B.; Carstensen, B.; Fenger, M.; Thuesen, B.H.; Husemoen, L.L.; Bergholdt, R.; Brorsson, C.; Pociot, F.; Linneberg, A.; et al. No Difference in Vitamin D Levels Between Children Newly Diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Healthy Siblings: A 13-Year Nationwide Danish Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, e157–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, P.R.; Waanders, F.; Qiu, J.; de Boer, H.H.R.; van Goor, H.; Bilo, H.J.G. Hypomagnesemia in persons with type 1 diabetes: Associations with clinical parameters and oxidative stress. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 11, 2042018820980240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasino, S.E.; Benoit, Y.D.; Gudas, L.J. Vitamin A Deficiency Causes Hyperglycemia and Loss of Pancreatic β-Cell Mass*. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1456–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsha, M.K.N.S.; Thiagarajan, R.; Manikandan, R.; Dhanasekaran, G. Vitamin K1 alleviates streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes by mitigating free radical stress, as well as inhibiting NF-κB activation and iNOS expression in rat pancreas. Nutrition 2015, 31, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Varsha, M.K.N.; Raman, T.; Manikandan, R.; Dhanasekaran, G. Hypoglycemic action of vitamin K1 protects against early-onset diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced rats. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, J.C.; Permutt, M.A.; Nichols, C.G. Diabetes and insulin secretion: The ATP-sensitive K+ channel (K ATP) connection. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Bocca, B.; Peruzzu, A.; Tolu, F.; Asara, Y.; Farace, C.; Oggiano, R.; Madeddu, R. Blood Metals Concentration in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetics. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Dimou, N.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomisation (STROBE-MR): Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2021, 375, n2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Zhu, G.; Dy, V.; Heath, A.C.; Madden, P.A.F.; Kemp, J.P.; McMahon, G.; St Pourcain, B.; Timpson, N.J.; Golding, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies loci affecting blood copper, selenium and zinc. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3998–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Huffman, J.E.; Rodriguez, A.; Conery, M.; Liu, M.; Ho, Y.-L.; Kim, Y.; Heise, D.A.; Guare, L.; Panickan, V.A.; et al. Diversity and scale: Genetic architecture of 2068 traits in the VA Million Veteran Program. Science 2024, 385, eadj1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaziano, J.M.; Concato, J.; Brophy, M.; Fiore, L.; Pyarajan, S.; Breeling, J.; Whitbourne, S.; Deen, J.; Shannon, C.; Humphries, D.; et al. Million Veteran Program: A mega-biobank to study genetic influences on health and disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 70, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-S.; Luan, J.; Sofianopoulou, E.; Imamura, F.; Stewart, I.D.; Day, F.R.; Pietzner, M.; Wheeler, E.; Lotta, L.A.; Gundersen, T.E.; et al. Plasma Vitamin C and Type 2 Diabetes: Genome-Wide Association Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis in European Populations. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, T.; Pettersson-Kymmer, U.; Stewart, I.D.; Butler-Laporte, G.; Nakanishi, T.; Cerani, A.; Liang, K.Y.H.; Yoshiji, S.; Willett, J.D.S.; et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grarup, N.; Sulem, P.; Sandholt, C.H.; Thorleifsson, G.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Bjarnason, H.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Magnusson, O.T.; Sparsø, T.; et al. Genetic Architecture of Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels Uncovered Applying Deeply Sequenced Large Datasets. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Scheet, P.; Giusti, B.; Bandinelli, S.; Piras, M.G.; Usala, G.; Lai, S.; Mulas, A.; Corsi, A.M.; Vestrini, A.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study of Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Folate, and Homocysteine Blood Concentrations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H.S.; Shea, M.K.; Smith, C.E.; Tanaka, T.; Hruby, A.; Richardson, K.; Wang, T.J.; Nalls, M.A.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for circulating phylloquinone concentrations12345. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.M.; Yu, K.; Wheeler, W.; Zhang, H.; Cornelis, M.C.; Wright, M.E.; Yeager, M.; Snyder, K.; Weinstein, S.J.; Mondul, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants associated with circulating vitamin E levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3876–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, P.; Stewart, I.D.; Au Yeung, V.P.W.; Pietzner, M.; Raffler, J.; Wörheide, M.A.; Li, C.; Smith, R.F.; Wittemans, L.B.L.; Bomba, L.; et al. Rare and common genetic determinants of metabolic individuality and their effects on human health. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, J.; Geusz, R.J.; Okino, M.-L.; Han, J.Y.; Miller, M.; Melton, R.; Beebe, E.; Benaglio, P.; Huang, S.; Korgaonkar, K.; et al. Interpreting type 1 diabetes risk with genetics and single cell epigenomics. Nature 2021, 594, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Spiller, W.; Bowden, J. Testing and correcting for weak and pleiotropic instruments in two-sample multivariable Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5434–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Inoko, H.; Kulski, J.K. The HLA genomic loci map: Expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 54, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, N.; Kutalik, Z. Bias correction for inverse variance weighting Mendelian randomization. Genet. Epidemiol. 2023, 47, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.E. The role of ion channels in insulin secretion. J. Cell. Biochem. 1992, 48, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Pérez, M.; Capera, J.; Benavente-Garcia, A.; Cassinelli, S.; Colomer-Molera, M.; Felipe, A. Kv1.3 in the spotlight for treating immune diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2024, 28, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, C. Imbalance in Th Cell Polarization and its Relevance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2005, 2, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, J.P.; Racine, J.J.; Ye, C.; Lamont, D.J.; Newby, B.N.; Leeth, C.M.; Chapman, H.D.; Brusko, T.M.; Chen, Y.-G.; Mathews, C.E.; et al. Interferon-γ Limits Diabetogenic CD8+ T-Cell Effector Responses in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2017, 66, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.W.; Tobin, J.D.; Rosa, R.M.; Andres, R. Effect of experimental potassium deficiency on glucose and insulin metabolism. Metabolism 1980, 29, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.; Martínez-Muñoz, L.; Cascio, G.; Lucas, P.; Pablos, J.L.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M. T Cell Migration in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, S.; Bobak, N.; Feuchtenberger, M.; Herrmann, A.M.; Göbel, K.; Kinne, R.W.; Hansen, A.J.; Budde, T.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Frey, O.; et al. Expression of K2P5.1 potassium channels on CD4+ T lymphocytes correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Terhorst, C.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells as therapeutic targets in SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Yeh, H.-C.; Edelman, D.; Brancati, F. Potassium and risk of Type 2 diabetes. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C. Vitamin A and retinoic acid in T cell–related immunity1234. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1166S–1172S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucock, M. Folic Acid: Nutritional Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Role in Disease Processes. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 71, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomization (STROBE-MR) Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.; Belbellaj, W.; Manousaki, D. Association of Vitamins and Minerals with Type 1 Diabetes Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203297
Shi L, Belbellaj W, Manousaki D. Association of Vitamins and Minerals with Type 1 Diabetes Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203297
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Lucia, Wiame Belbellaj, and Despoina Manousaki. 2025. "Association of Vitamins and Minerals with Type 1 Diabetes Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203297
APA StyleShi, L., Belbellaj, W., & Manousaki, D. (2025). Association of Vitamins and Minerals with Type 1 Diabetes Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients, 17(20), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203297






