Fatty Acid Profiling of Breast Milk at Different Gestational Ages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
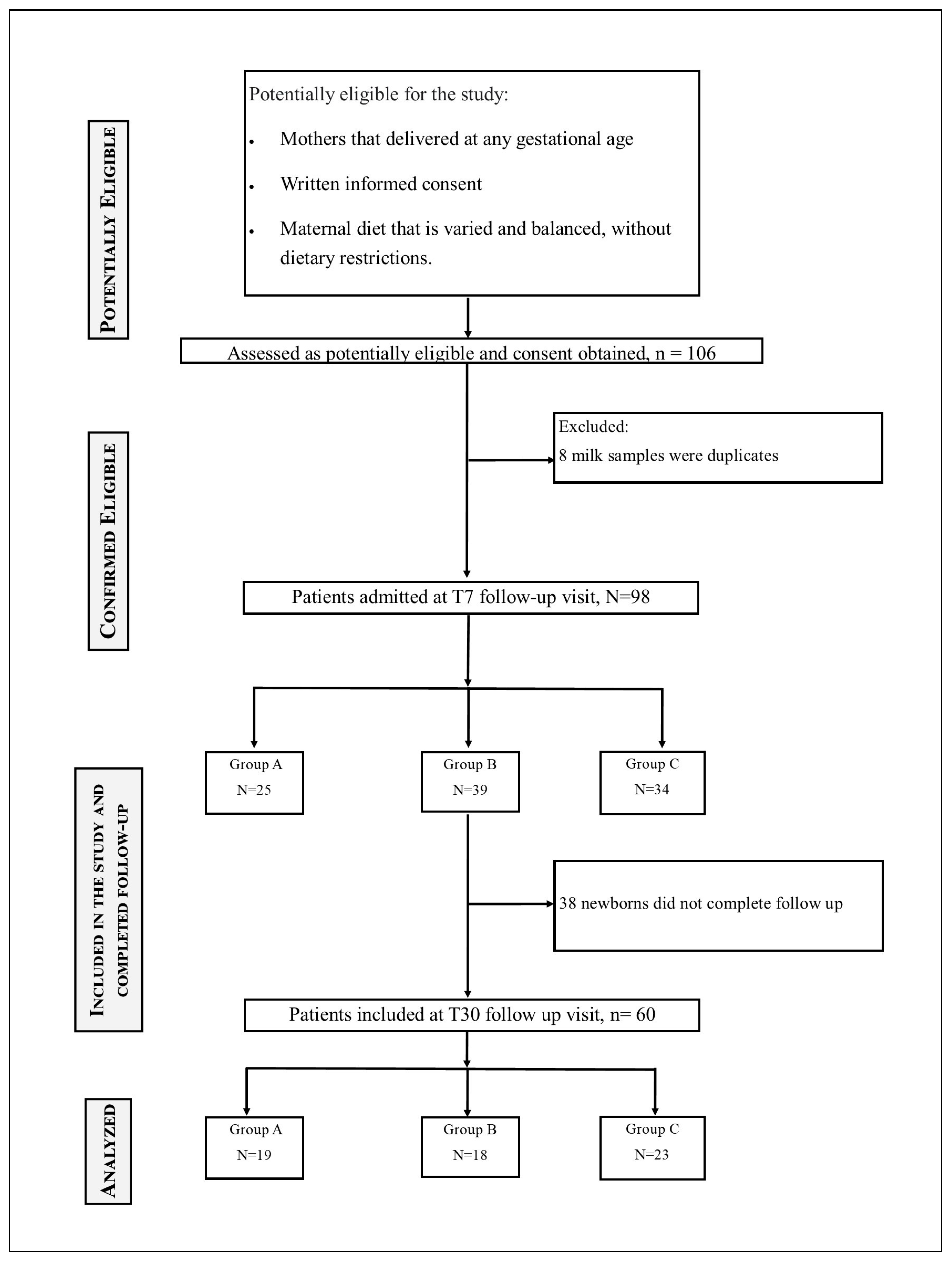
2.1. Study Design
- Group < 32 wks (A): women who delivered before 32 weeks of GA;
- Group 32–36.6 wks (B): women who delivered between 32 weeks and 36 + 6 weeks of GA’
- Group > 37 wks (C): women who delivered after 37 weeks of GA.
- Section 1: Personal Information
- Section 2: Dietary Habits
- Section 3: Supplementation
- Section 4: Maternal Health
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.4. Calibration Curves and GC-MS Method Validation
2.5. Calculation of Lipid Quality Indices Formulas
- Index of atherogenicity (IA)= [C12:0 + (4 × C14:0) + C16:0]/∑unsaturated FA(UFA).
- Index of thrombogenicity (IT) = (C14:0 + C16:0 + C18:0)/[(0.5 × ∑MUFA) + (0.5 × ∑n-6 PUFA) + (3 × ∑n-3 PUFA) + (n-3/n-6)].
- Hypocholesterolemic/hypercholesterolemic ratio (HH) = (cis-C18:1 + ∑PUFA)/(C12:0 + C14:0 + C16:0).
- Health-promoting index (HPI) = ∑UFA/[C12:0 + (4 × C14:0) + C16:0].
- Unsaturation index (UI) = 1 × (% monoenoics) + 2 × (% dienoics) + 3 × (% trienoics) + 4 × (% tetraenoics) + 5 × (% pentaenoics) + 6 × (% hexaenoics).
- Fish lipid quality/flesh Lipid quality (FLQ) = 100 × (C22:6 n-3 + C20:5 n-3)/SFA.
- Linoleic acid/-linolenic acid ratio (LA/ALA) = C18:2 n-6/C18:3 n-3.
- Trans fatty acid (TFA) = ∑TFA.
- Index of Desirable Fatty Acids (DFA) = UFA + C18:0.
- Index of Hypercholesterolemic Fatty Acids (OFA)= C12:0 + C14:0 + C16:0.
- PUFA/SFA ratio = ∑PUFA/∑SFA.
- PUFA/MUFA ratio = ∑PUFA/∑MUFA.
- MUFA/SFA ratio = ∑MUFA/∑SFA.
- ω-6/ω-3 ratio = ∑n-6 PUFA/∑n-3 PUFA.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition of Breast Milk Across Different Gestational Ages
4.2. Characteristics of Transitional and Mature Milk
4.3. Diet and Mother Supplementation During Pregnancy
4.4. Lipid Quality Indices
4.5. Implications of the Study
4.6. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BM | Breast milk |
| TAGs | Triglycerides |
| FFA | Free fatty Acid |
| GA | Gestational age |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acid |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated fatty acid |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| EFA | Essential fatty acid |
| ALA | α-linolenic acid |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| FA | Fatty acids |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentanoic acid |
| FAME | Fatty Acid Methyl Esters |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| LOQ | Limits of quantification |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| IT | Index of thrombogenicity |
| HH | Hypocholesterolemic/Hypercholesterolemic ratio |
| UI | Unsaturation index |
| HPI | Health-promoting index |
| FLQ | Fish lipid quality/flesh lipid quality |
| LA/ALA | Linoleic acid/α-linolenic acid ratio |
| TFA | Trans fatty acid |
| DFAs | Desirable fatty acids |
| OFA | Hypercholesterolemic fatty acids |
| FAHFA | Fatty acid ester of hydroxyl fatty acid |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
References
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L.; Section on Breastfeeding. Policy Statement: Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak-Fiećko, R.; Kamelska-Sadowska, A.M. The Comparison of Nutritional Value of Human Milk with Other Mammals’ Milk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B. Interindividual variation of human milk metabolome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, A.; Marin, T.; Leo, G.; Stansfield, B.K. Review of Preterm Human-Milk Nutrient Composition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. Lipids in human milk. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith-Dennis, L.; Xu, G.; Goonatilleke, E.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Underwood, M.A.; Smilowitz, J.T. Composition and Variation of Macronutrients, Immune Proteins, and Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Human Milk From Nonprofit and Commercial Milk Banks. J. Hum. Lact. 2018, 34, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvordsen Lindahl, I.E.; Artegoitia, V.M.; Downey, E.; O’Mahony, J.A.; O’Shea, C.A.; Ryan, C.A.; Kelly, A.L.; Bertram, H.C.; Sundekilde, U.K. Quantification of Human Milk Phospholipids: The Effect of Gestational and Lactational Age on Phospholipid Composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, A.; Funke, S.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Burus, I.; Decsi, T. Fatty acids in early human milk after preterm and full-term delivery. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Docosahexaenoic Acid. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69 (Suppl. 1), 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćwiek, D.; Zimny, M.; Szymoniak, K.; Czechowska, K.; Sipak-Szmigiel, O. Assessment of Fatty Acid Content in the Milk of Women from the West Pomeranian Region of Poland with Regard to Supplementation and the Amount of Adipose Tissue. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreynian, M.; Feizi, A.; Kelishadi, R. Is fatty acid composition of breast milk different in various populations? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amza, M.; Haj Hamoud, B.; Sima, R.M.; Dinu, M.D.; Gorecki, G.P.; Popescu, M.; Gică, N.; Poenaru, M.O.; Pleș, L. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) and Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)-Should They Be Mandatory Supplements in Pregnancy? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.A.; Pollard, R.D.; Ferguson, D.S. Nutriential Hazards: Macronutrients: Essential Fatty Acids. Encycl. Food Saf. 2014, 3, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alsubaie, A.M.; Hakami, F.M.; Hamithi, D.M.; Alshekh, M.M.; Khobrani, F.A.; Dalak, F.E.; Hakami, A.A.; Alsueaadi, E.H.; Alsaawi, L.S.; et al. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Hachem, M.; Ahmmed, F.; Rashidinejad, A.; Oz, F.; Bekhit, A.A.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.E.A. Marine Fish-Derived Lysophosphatidylcholine: Properties, Extraction, Quantification, and Brain Health Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidrewicz, D.A.; Fenton, T.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the nutrient content of preterm and term breast milk. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravi, F.; Wiens, F.; Decarli, A.; Dal Pont, A.; Agostoni, C.; Ferraroni, M. Impact of maternal nutrition on breast-milk composition: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Simultaneous Determination of C18 Fatty Acids in Milk by GC-MS. Separations 2021, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty Acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkiewicz, A.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Determination of the Fatty Acid Profile and Lipid Quality Indices in Selected Infant Formulas. Molecules 2024, 29, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkiewicz, A.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Changes in the Fatty Acid Profile of Lactating Women Living in Poland-A Comparison with the Fatty Acid Profile of Selected Infant Formulas. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers, R.S.; Luxwolda, M.F.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.; Muskiet, F.A. Differences in preterm and term milk fatty acid compositions may be caused by the different hormonal milieu of early parturition. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 2011, 85, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimouni, F.B.; Lubetzky, R.; Yochpaz, S.; Mandel, D. Preterm Human Milk Macronutrient and Energy Composition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, A.P.; Bains, H.S.; Kansal, S.; Singh, D. Serial composition of human milk in preterm and term mothers. Indian. J. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 21, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Ye, D.; Yu, R.; Yang, Q. Comprehensive lipidomic profiling of human milk from lactating women across varying lactation stages and gestational ages. Food Chem. 2025, 463 Pt. 2, 141242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.X.; Yan, D.Y.; Dong, P. Compositional Differences between Preterm Milk of Different Gestational Ages with the Term Milk: A Comparative Lipidomic Study by LC-MS/MS. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 2100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.K.; De Castro, C.A.; Beauport, L.; Tolsa, J.F.; Fischer Fumeaux, C.J.; Affolter, M.; Giuffrida, F. Temporal Progression of Fatty Acids in Preterm and Term Human Milk of Mothers from Switzerland. Nutrients 2019, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.H.; Heal, W.P.; Mann, D.J.; Tate, E.W. Protein myristoylation in health and disease. J. Chem. Biol. 2010, 3, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, B.; Jiang, X.; Sidhu, R.; Ory, D.S.; Warner, B.B.; Tarr, P.I. Gut Sphingolipid Composition as a Prelude to Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Freije, A.; Omran, A.; Rondanelli, M.; Marino, M.; Perna, S. Human Milk Fatty Acid Composition and Its Effect on Preterm Infants’ Growth Velocity. Children 2023, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Shin, J.A.; Lee, K.T. Quantitative Analysis of Nervonic and Erucic Acids in Human Milk: Comparison with Infant Formula with Different Fat Sources and Nutritional Stages. J. Oleo Sci. 2024, 73, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Cheesman, A.; Brown, J.; Makda, M.; Kutner, A.J.; DaSilva, D.; Zaman, M.; Freedman, S.D. Factors Determining Optimal Fatty Acid Absorption in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.T.; Martin, C.R. Fatty acid requirements for the preterm infant. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliku, K.; Duan, Q.L.; Moraes, T.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Sears, M.R.; Subbarao, P.; Field, C.J.; et al. Human milk fatty acid composition is associated with dietary, genetic, sociodemographic, and environmental factors in the CHILD Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B. Human Milk Lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69 (Suppl. 2), 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, M.; Andarwulan, N.; Wahyuningsih, U.; Kazimierczak, R.; Średnicka-Tober, D. Maternal Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Status in Pregnancy and Newborn Body Composition. Nutrients 2024, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. Palmitic Acid: Physiological Role, Metabolism and Nutritional Implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, L.M.; Stahl, B.; Abrahamse-Berkeveld, M.; Teller, I.C. Human milk fatty acid profile across lactational stages after term and preterm delivery: A pooled data analysis. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 2020, 156, 102023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Singh, P.; Liu, Y.; Medina-Morales, E.; Yakah, W.; Freedman, S.D.; Martin, C.R. Breast Milk Lipids and Fatty Acids in Regulating Neonatal Intestinal Development and Protecting against Intestinal Injury. Nutrients 2020, 12, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bernardo, G.; D’Urso, G.; Spadarella, S.; Giordano, M.; Leone, G.; Casapullo, A. Analysis of the Fecal Metabolomic Profile in Breast vs. Different Formula Milk Feeding in Late Preterm Infants. Metabolites 2024, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bernardo, G.; Vecchione, C.; Langella, C.; Ziello, C.; Parisi, G.; Giordano, M.; Buonocore, G.; Perrone, S. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Current Understanding and Challenges for the Future. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, F.; Gaeta, E.; Morlino, F.; Riccio, M.T.; Giordano, M.; De Bernardo, G. Long-term benefits of exclusive human milk diet in small for gestational age neonates: A systematic review of the literature. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 50, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, A.T.; Miller, E.R.; Butler, M.; Eden, C.; Kim, J.H.; Shah, S.I.; Patel, R.M. US state policies for Medicaid coverage of donor human milk. J. Perinatol. 2022, 42, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| <32 wks | 32–36.6 wks | >37 wks | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Q1–Q3) | ||||
| Number | 25 | 39 | 34 | |
| Mother age (years) | 33 (27–37) | 34 (30–37) | 32 (30–37) | 0.624 |
| BMI | 22.7 (20.7–30) | 24.6 (22.5–27) | 23 (21.8–25.2) | 0.667 |
| Number of Pregnancies | 1 (0–1) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (0–2) | 0.413 |
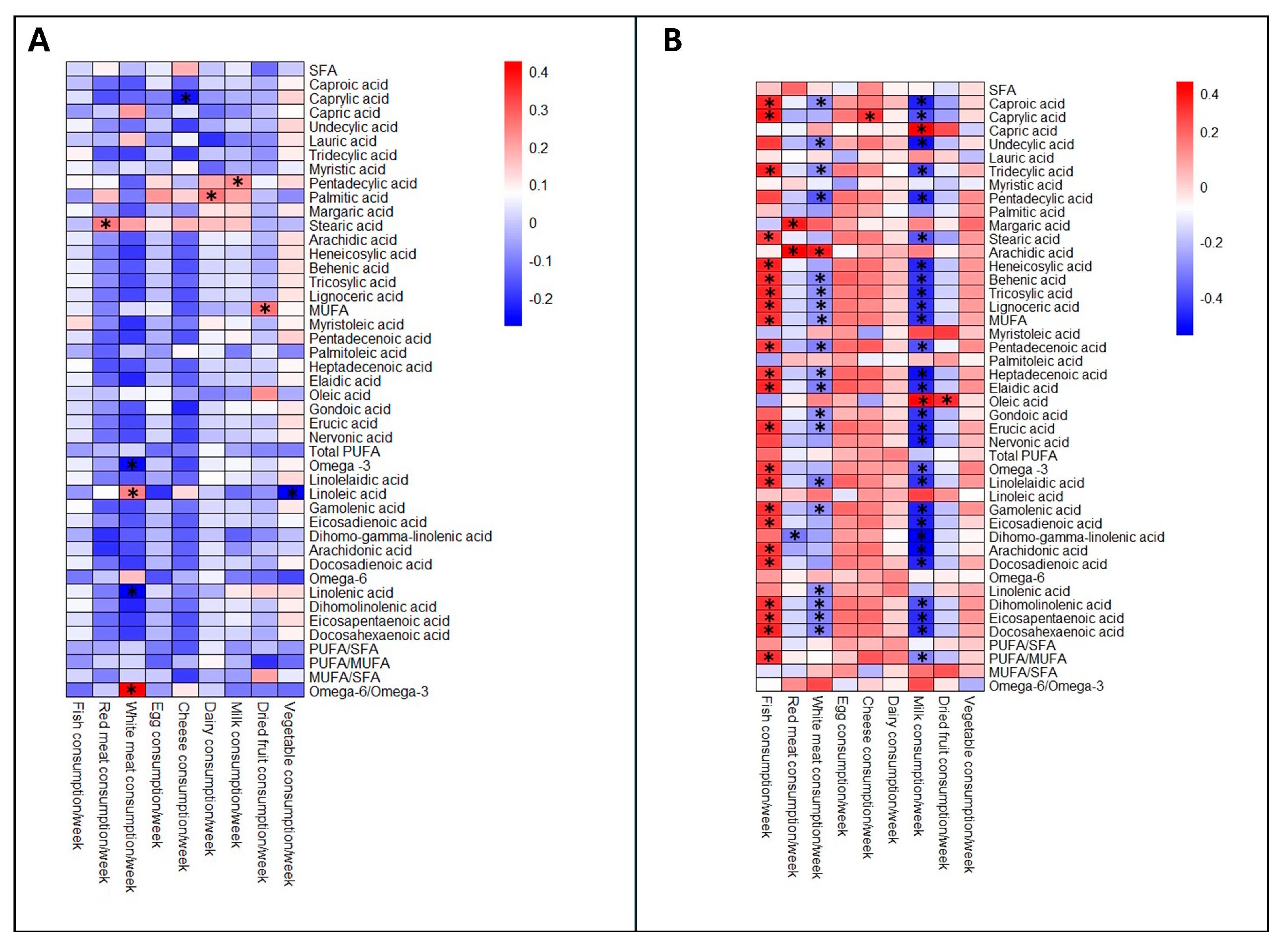
| Fish consumption/week | 2.0 (1–2) | 2.0 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.763 |
| Red meat consumption/week | 2.0 (1–2) | 1.8 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.449 |
| White consumption/week | 3.0 (2–3) | 2.0 (2–3) | 2 (2–3) | 0.152 |
| Eggs consumption/week | 1.3 (1–2) | 2.0 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.501 |
| Cheese consumption/week | 3.0 (1–5) | 2.0 (1–3.5) | 2 (1–4) | 0.519 |
| Dairy products consumption/week | 2.0 (1–3) | 1.0 (1–2.3) | 1.5 (1–2) | 0.513 |
| Dried fruit consumption/week | 1.0 (0–2) | 1.0 (0–4) | 2.8 (0–7) | 0.289 |
| Vegetables consumption/week | 7.0 (4–7) | 7.0 (6–7) | 7.0 (6–7) | 0.289 |
| DHA assumption (%) | 62 | 63 | 82 | 0.185 |
| T7 | T30 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acids | Chain Length | <32 wks | 32–36.6 wks | ≥37 wks | <32 wks | 32–36.6 wks | ≥37 wks |
| SFA | 51.371 (48.348–54.041) a | 48.18 (44.643–51.118) a | 49.596 (47.767–51.174) | 51.647 (49.05–54.919) c | 48.469 (47.082–50.795) | 48.751 (44.803–52.327) c | |
| Caproic acid (C6:0) | SCFA | 0.1 (0.1–0.1) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.15) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) |
| Caprylic acid (C8:0) | MCFA | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.2 (0.2–0.2) | 0.2 (0.2–0.3) | 0.2 (0.2–0.3) | 0.2 (0.2–0.3) |
| Capric acid (C10:0) | MCFA | 1.1 (0.8–1.5) | 0.95 (0.4–1.4) | 1.2 (0.8–1.4) | 1.1 (0.9–1.6) | 1.55 (1.05–1.8) | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) |
| Undecylic acid (C11:0) | MCFA | 0.1 (0.1–0.1) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.1) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) |
| Lauric acid (C12:0) | MCFA | 6.5 (5.4–7.9) | 5.75 (3.5–7.8) | 5.8 (4.8–7.2) | 7 (5.6–8.6) | 6.8 (5.35–8.3) | 5.8 (4.8–7.2) |
| Tridecylic acid (C13:0) | LCFA | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.15) | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | LCFA | 8.4 (6.5–9.2) a | 6.6 (5.2–8.8) a | 6.7 (5.5–8.2) | 8.2 (6–9) c | 7.15 (6.15–8.8) | 7.1 (5.4–7.5) c |
| Pentadecylic acid (C15:0) | LCFA | 0.5 (0.4–0.5) | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.4 (0.4–0.5) | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.45 (0.4–0.5) | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | LCFA | 24.2 (23.3–25.6) | 22.5 (21–24.3) | 24.5 (22.2–25.5) | 22.9 (21.6–25.2) | 21.7 (20.55–22.9) | 22.9 (21–23.6) |
| Margaric acid (C17:0) | LCFA | 0.5 (0.5–0.6) | 0.5 (0.5–0.6) | 0.5 (0.5–0.6) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.5 (0.45–0.6) | 0.5 (0.5–0.7) |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | LCFA | 7 (6.2–7.9) | 5.85 (5.1–7.1) | 6.8 (6.1–7.6) | 7.5 (5.7–9.1) | 7 (6.45–7.3) | 7.3 (5.5–8.5) |
| Arachidic acid (C20:0) | VLCFA | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.7 (0.5–1) | 0.7 (0.5–0.9) | 0.8 (0.6–1.1) | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 0.7 (0.6–1) |
| Heneicosylic acid (C21:0) | VLCFA | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.7) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.3 (0.2–0.45) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) |
| Behenic acid (C22:0) | VLCFA | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.6 (0.4–0.9) | 0.6 (0.4–0.7) | 0.6 (0.4–0.9) | 0.45 (0.3–0.6) | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) |
| Tricosylic acid (C23:0) | VLCFA | 0.4 (0.3–0.4) | 0.5 (0.3–0.7) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.7) | 0.35 (0.2–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.7) |
| Lignoceric acid (C24:0) | VLCFA | 0.7 (0.5–0.9) | 0.9 (0.6–1.3) | 0.8 (0.6–1) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 0.65 (0.4–0.85) | 0.8 (0.5–1.2) |
| MUFA | 33.631 (32.489–36.498) a | 36.585 (33.679–38.899) a | 35.946 (34.542–37.2) | 33.501 (30.92–35.584) c | 35.133 (33.518–36.941) | 36.23 (34.492–38.621) c | |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1, n-5) | LCFA | 0.3 (0.3–0.3) | 0.3 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.3–0.3) | 0.3 (0.3–0.4) | 0.3 (0.25–0.4) | 0.3 (0.3–0.5) |
| Pentadecenoic acid (C15:1, n-5) | LCFA | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1, n-7) | LCFA | 1.5 (1.3–2.3) | 1.65 (1.4–1.9) | 1.5 (1.3–1.8) | 1.7 (1.1–1.8) | 1.5 (1.35–1.95) | 1.5 (1.3–2) |
| Heptadecenoic acid (C17:1, n-7) | LCFA | 0.4 (0.3–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.45) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) |
| Elaidic acid (C18:1, n-9) | LCFA | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 0.2 (0.2–0.3) | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 0.2 (0.1–0.25) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
| Oleic acid (C18:1, n-9) | LCFA | 28.8 (27.5–31.1) | 31.25 (28.2–33.4) | 30.8 (29.4–31.5) | 29.1 (24.1–30.6) | 30.65 (29.05–32.15) | 30.6 (28.6–32.4) |
| Gondoic acid (C20:1, n-9) | VLCFA | 1 (0.8–1.1) | 1.1 (1–1.3) | 1 (0.9–1.1) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) | 0.8 (0.75–0.95) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) |
| Erucic acid (C22:1, n-9) | VLCFA | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) a | 0.85 (0.6–1.1) a | 0.7 (0.6–1) | 0.7 (0.5–1.1) | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 0.7 (0.5–1) |
| Nervonic acid (C24:1, n-9) | VLCFA | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) a | 0.6 (0.4–0.8) a | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.5 (0.3–0.8) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) |
| PUFA | 14.384 (12.724–15.683) | 15.571 (13.779–17.408) | 13.985 (13.133–16.227) | 14.861 (13.047–17.019) | 15.439 (13.114–18.368) | 14.1 (12.635–18.056) | |
| ω-6 | 12.17 (10.982–13.449) | 13.297 (11.51–14.2) | 12.313 (10.251–13.575) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.25–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | |
| Linolelaidic acid (C18:2, n-6) | LCFA | 0.3 (0.3–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.25–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2, n-6) | LCFA | 8.4 (6.4–9.6) | 8.1 (6.4–10.1) | 8.3 (6.6–9.7) | 7.7 (6.7–9) | 9.2 (7.15–11.45) | 7.8 (6.7–11.1) |
| Gamolenic acid (C18:3, n-6) | LCFA | 0.3 (0.2–0.3) | 0.35 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.3–0.4) | 0.3 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.25–0.4) | 0.3 (0.3–0.6) |
| Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2, n-6) | VLCFA | 1 (0.9–1.2) | 1.25 (0.9–1.6) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1 (0.8–1.4) | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 1 (0.9–1.3) |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (C20:3, n-6) | VLCFA | 0.8 (0.8–1) | 0.9 (0.8–1.2) b | 0.8 (0.7–0.8) b | 0.7 (0.6–1) | 0.7 (0.6–1) | 0.8 (0.7–1) |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4, n-6) | VLCFA | 0.9 (0.6–1.1) | 0.95 (0.7–1.4) b | 0.8 (0.7–0.9) b | 0.8 (0.6–1.2) | 0.85 (0.7–1.1) | 0.8 (0.7–1.2) |
| Docosadienoic acid (C22:2, n-6) | VLCFA | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.65 (0.4–1) | 0.6 (0.4–0.7) | 0.6 (0.4–0.9) | 0.45 (0.3–0.6) | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) |
| ω-3 | 2.153 (1.571–2.388) | 2.44 (1.834–3.518) | 2.172 (1.908–2.64) | 2.519 (2.045–3.263) | 2.076 (1.866–2.7) | 2.604 (1.863–3.827) | |
| Linolenic acid (C18:3, n-3) | LCFA | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.65 (0.5–0.9) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.7 (0.6–0.8) | 0.7 (0.5–0.85) | 0.8 (0.6–0.9) |
| Dihomolinolenic acid (C20:3, n-3) | VLCFA | 0.3 (0.3–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.3 (0.2–0.5) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5, n-3) | VLCFA | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6, n-3) | VLCFA | 0.9 (0.7–1) | 1.1 (0.8–1.6) | 1 (0.8–1.2) | 1 (0.7–1.4) | 0.85 (0.7–1.1) | 1 (0.7–1.5) |
| T7 | T30 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <32 wks | 32–36.6 wks | >37 wks | <32 wks | 32–36.6 wks | >37 wks | |
| AI | 1.354 (1.061–1.511) a | 1.069 (0.863–1.296) a | 1.137 (1.013–1.321) | 1.404 (1.082–1.486) b | 1.134 (1.036–1.264) | 1.103 (0.893–1.255) b |
| IT | 1.286 (1.18–1.539) a | 1.141 (0.91–1.271) a | 1.229 (1.093–1.286) | 1.248 (1.074–1.405) | 1.168 (1.039–1.241) | 1.128 (0.906–1.308) |
| HH | 1.129 (1–1.264) a | 1.306 (1.172–1.59) a | 1.25 (1.126–1.333) | 1.13 (0.956–1.309) b | 1.302 (1.181–1.399) | 1.262 (1.158–1.571) b |
| UI | 57.866 (52.989–62.928) a | 60.41 (57.758–70.632) a | 60.562 (57.571–62.3) | 72.056 (65.908–79.058) | 75.412 (70.521–79.129) | 76.377 (69.096–84.633) |
| HPI | 0.739 (0.662–0.943) a | 0.936 (0.772–1.159) a | 0.88 (0.757–0.987) | 0.712 (0.673–0.924) b | 0.885 (0.791–0.965) | 0.907 (0.797–1.12) b |
| FLQ (%) | 1.228 (0.887–1.354) | 1.485 (1.082–2.108) | 1.228 (1.086–1.56) | 1.46 (1.072–1.991) | 1.171 (0.997–1.473) | 1.447 (1.033–2.195) |
| LA/ALA | 15.825 (11.563–19.359) | 12.305 (7.909–18.074) | 12.482 (9.534–18.355) | 9.474 (7.309–12.571) | 13.905 (10.481–18.882) | 9.3 (7.458–13.433) |
| TFA (%) | 0.477 (0.395–0.56) | 0.608 (0.441–0.957) | 0.521 (0.417–0.671) | 0.635 (0.426–0.847) | 0.525 (0.373–0.625) | 0.616 (0.472–0.99) |
| DFAs (%) | 55.793 (52.866–57.885) a | 59.04 (56.249–61.306) a | 57.498 (55.917–59.364) | 55.54 (52.315–58.698) b | 58.2455 (56.439–59.986) | 58.451 (56.243–60.593) b |
| OFA (%) | 39.144 (36.255–41.699) a | 35.453 (32.224–38.459) a | 36.498 (35.374–38.426) | 38.953 (35.524–40.62) b | 35.9435 (34.659–38.226) | 35.072 (31.743–37.794) b |
| PUFA/SFA | 0.289 (0.234–0.308)a | 0.328 (0.277–0.389)a | 0.284 (0.259–0.341) | 0.28 (0.228–0.343) | 0.324 (0.268–0.373) | 0.3 (0.242–0.397) |
| PUFA/MUFA | 0.418 (0.364–0.48) | 0.415 (0.387–0.487) | 0.38 (0.358–0.469) | 0.443 (0.372–0.509) | 0.417 (0.385–0.512) | 0.371 (0.358–0.508) |
| MUFA/SFA | 0.657 (0.602–0.739) a | 0.755 (0.655–0.892) a | 0.722 (0.692–0.765) | 0.641 (0.55–0.758) b | 0.733 (0.666–0.804) | 0.709 (0.657–0.856) b |
| ω-6/ω-3 | 6.147 (4.803–7.49) | 5.244 (3.375–6.748) | 5.055 (4.214–6.98) | 4.523 (3.258–6.014) | 5.519 (4.736–7.582) | 4.229 (3.751–6.077) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Bernardo, G.; Leone, G.; Izzo, F.; Giovengo, M.; Basilicata, M.G.; Centanni, F.; Morlino, F.; Salviati, E.; Giordano, M.; Perrone, S.; et al. Fatty Acid Profiling of Breast Milk at Different Gestational Ages. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162672
De Bernardo G, Leone G, Izzo F, Giovengo M, Basilicata MG, Centanni F, Morlino F, Salviati E, Giordano M, Perrone S, et al. Fatty Acid Profiling of Breast Milk at Different Gestational Ages. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162672
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Bernardo, Giuseppe, Giuseppina Leone, Federica Izzo, Marta Giovengo, Manuela Giovanna Basilicata, Fabio Centanni, Francesca Morlino, Emanuela Salviati, Maurizio Giordano, Serafina Perrone, and et al. 2025. "Fatty Acid Profiling of Breast Milk at Different Gestational Ages" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162672
APA StyleDe Bernardo, G., Leone, G., Izzo, F., Giovengo, M., Basilicata, M. G., Centanni, F., Morlino, F., Salviati, E., Giordano, M., Perrone, S., Buonocore, G., Delli Carri, M., Pepe, G., & Campiglia, P. (2025). Fatty Acid Profiling of Breast Milk at Different Gestational Ages. Nutrients, 17(16), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162672











