EGCG and Taurine Synergistically Ameliorate Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modulating Gut Microbiota and PPARα/FAS Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
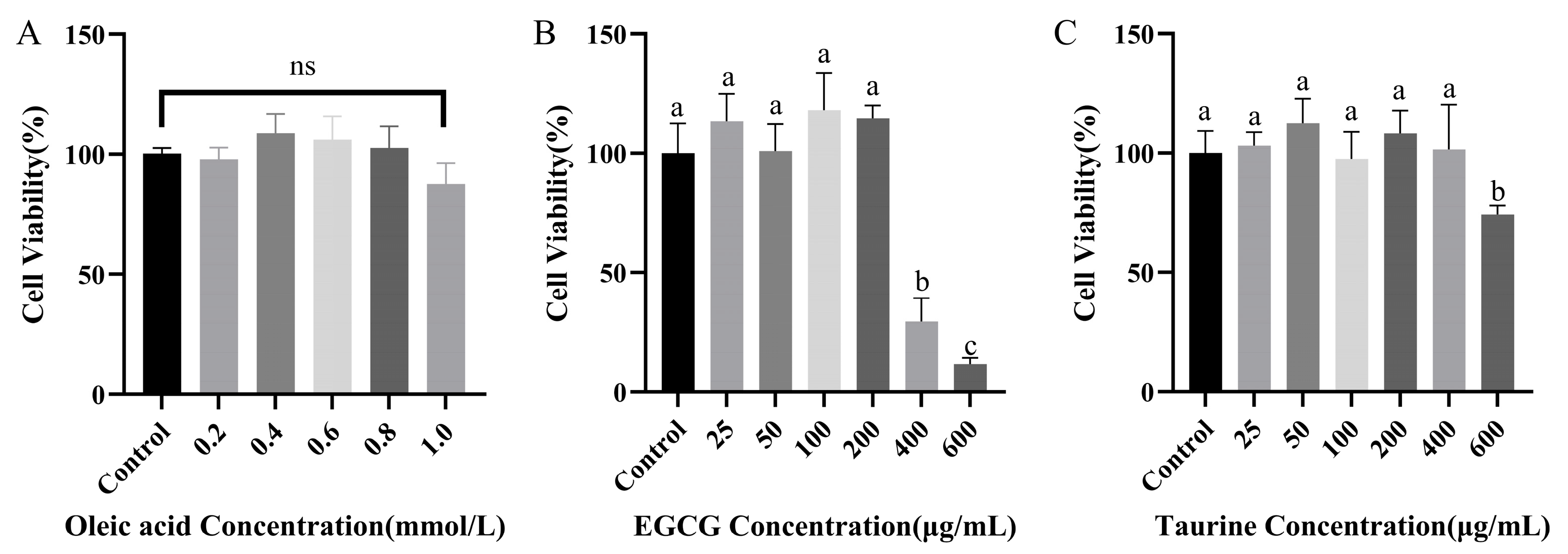
2.1.1. Cell Viability Assay
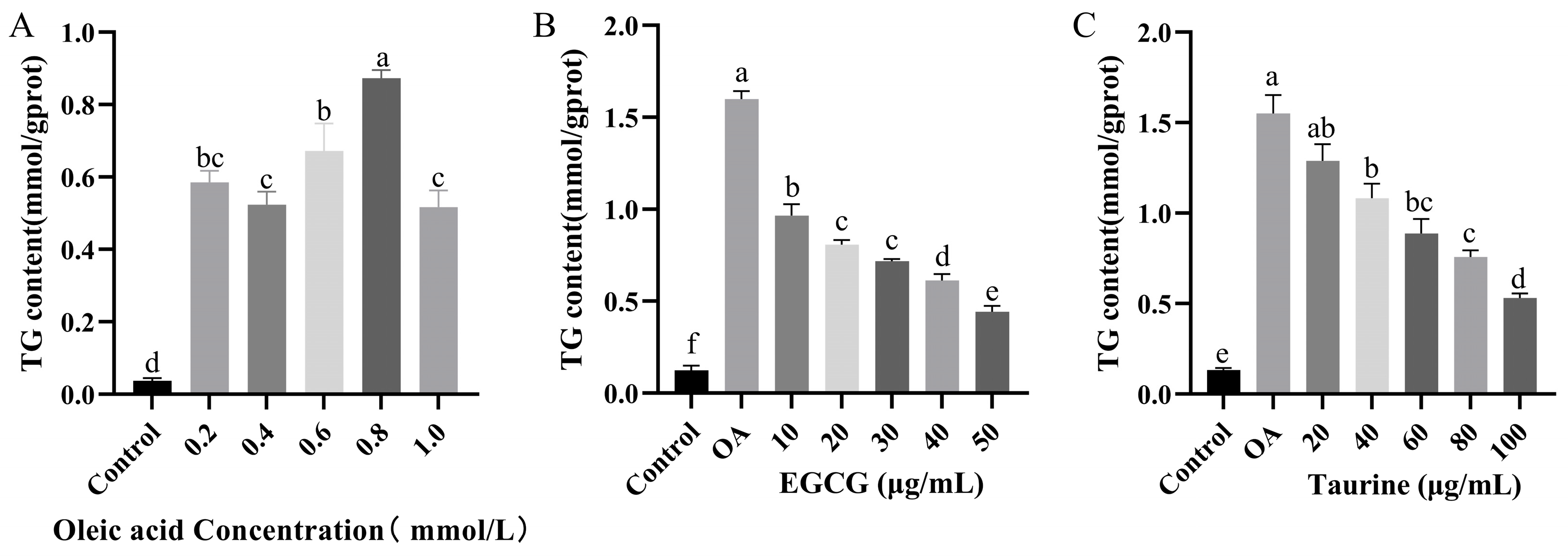
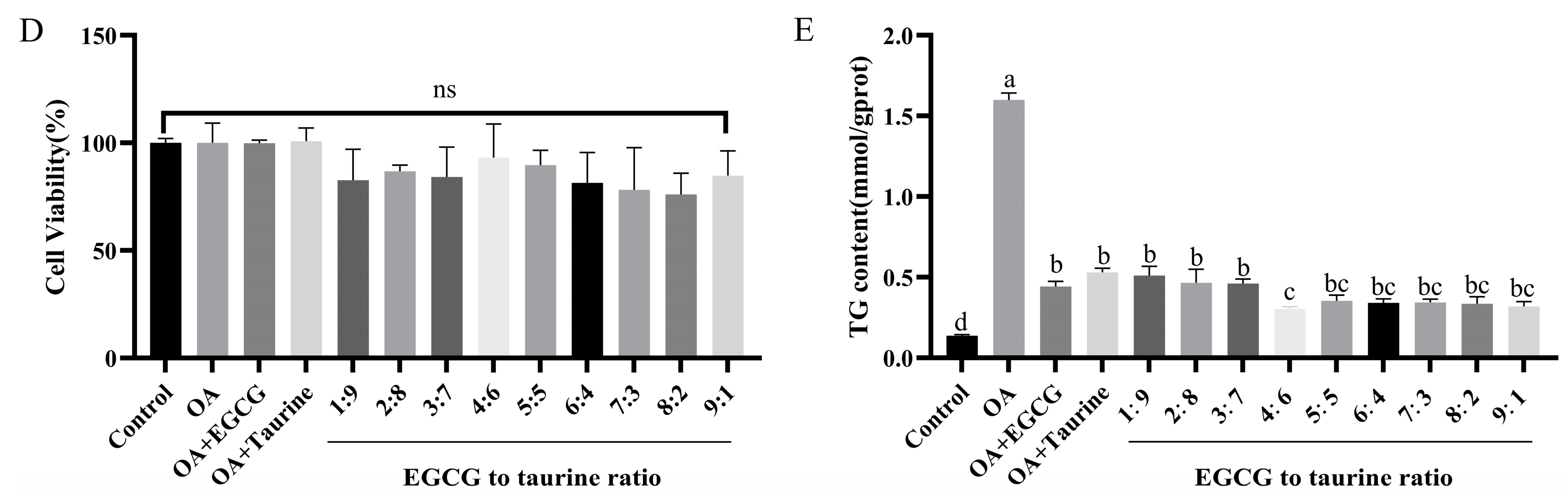
2.1.2. Determination of Cellular TG Level
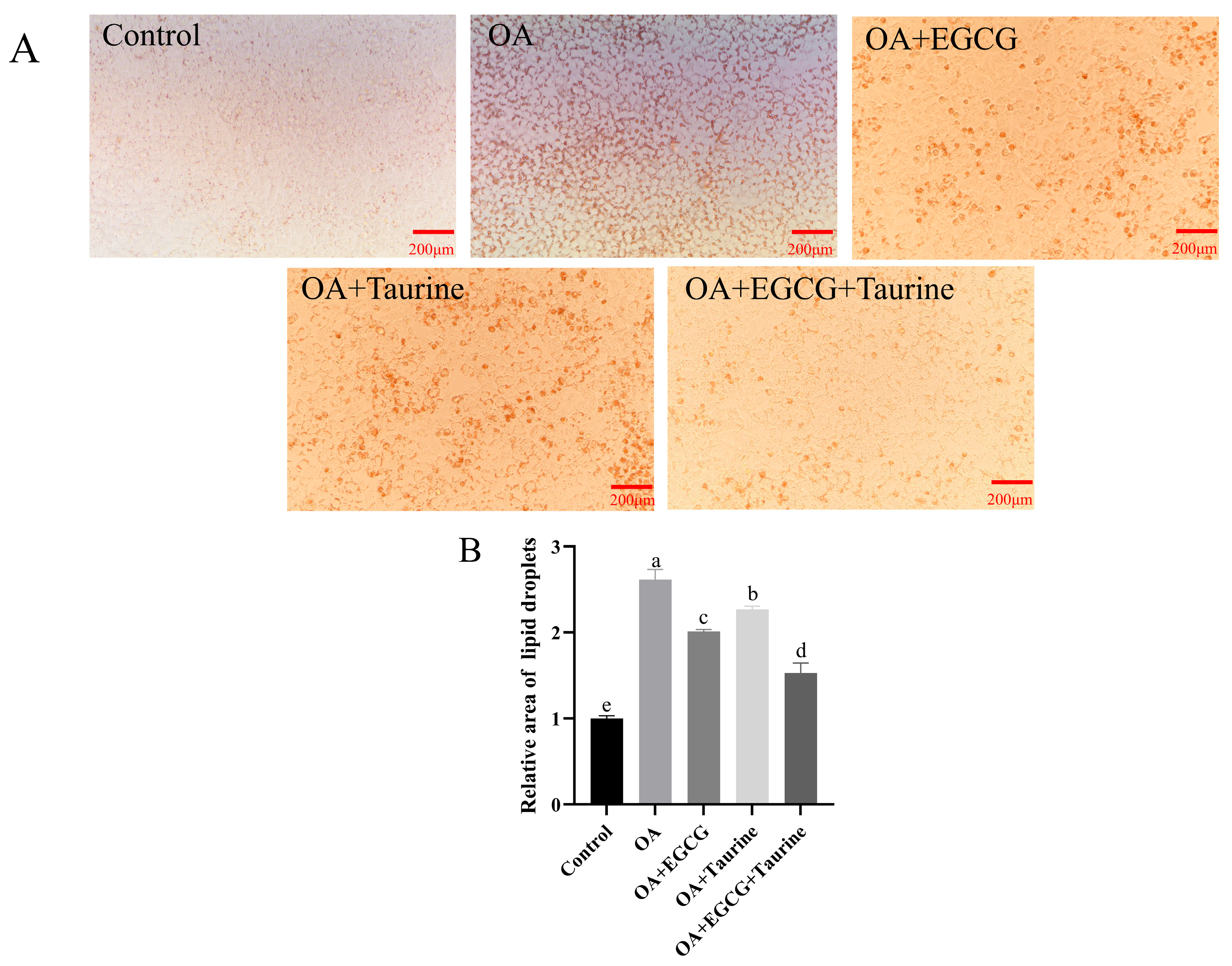
2.1.3. Oil Red O Staining
2.2. Animals and Treatments
2.2.1. Serum Lipids
2.2.2. Lipid Metabolism-Related Enzyme Activities and Free Fatty Acids
2.2.3. Liver Function Parameters
2.2.4. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Malondialdehyde Content
2.2.5. Histopathological Examination
2.2.6. Fecal Microbiota
2.2.7. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Determination
2.2.8. Metabolomics Analysis
2.2.9. Western Blot
2.2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Cellular Viability
3.2. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Triglyceride Levels in HepG2 Cells
3.3. Oil Red O Staining Analysis
3.4. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on the Body Weight of Rats Subjected to Long-Term HFD
3.5. Analysis of the Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Rat Blood Lipids, Lipid Synthesis and Metabolism-Related Enzymes, Key Hepatic Function Enzymes, and Antioxidant Enzymes
3.5.1. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Blood Lipid Levels in Rats
3.5.2. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Lipid Metabolism-Related Enzyme Activities and FFA Levels in Rats
3.5.3. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Liver Function-Related Enzyme Activities in Rats
3.5.4. Effects of EGCG and Taurine on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA Levels in Rats
3.6. H&E Staining of Liver and Small Intestine Tissues
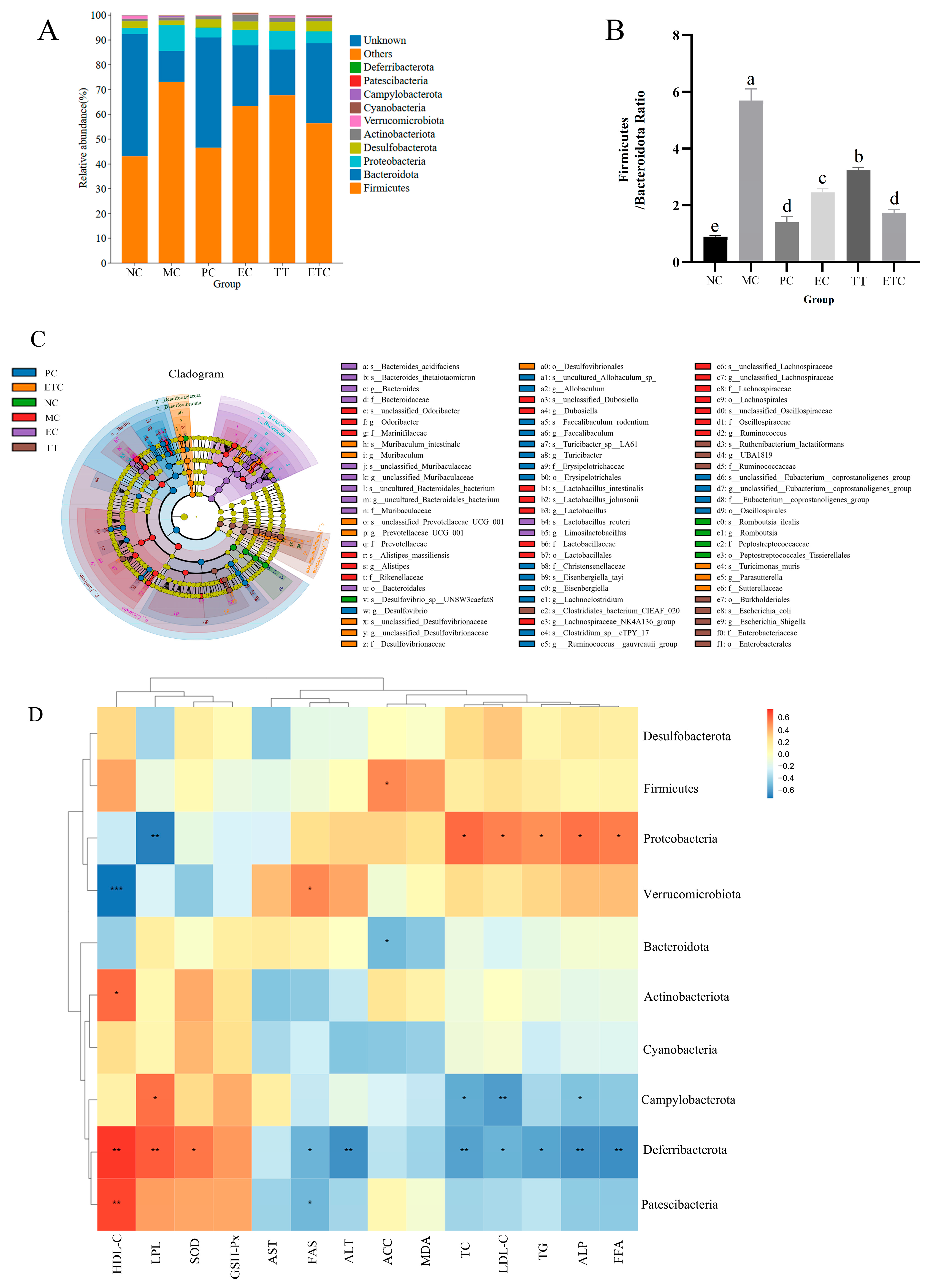
3.7. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
3.8. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Analysis
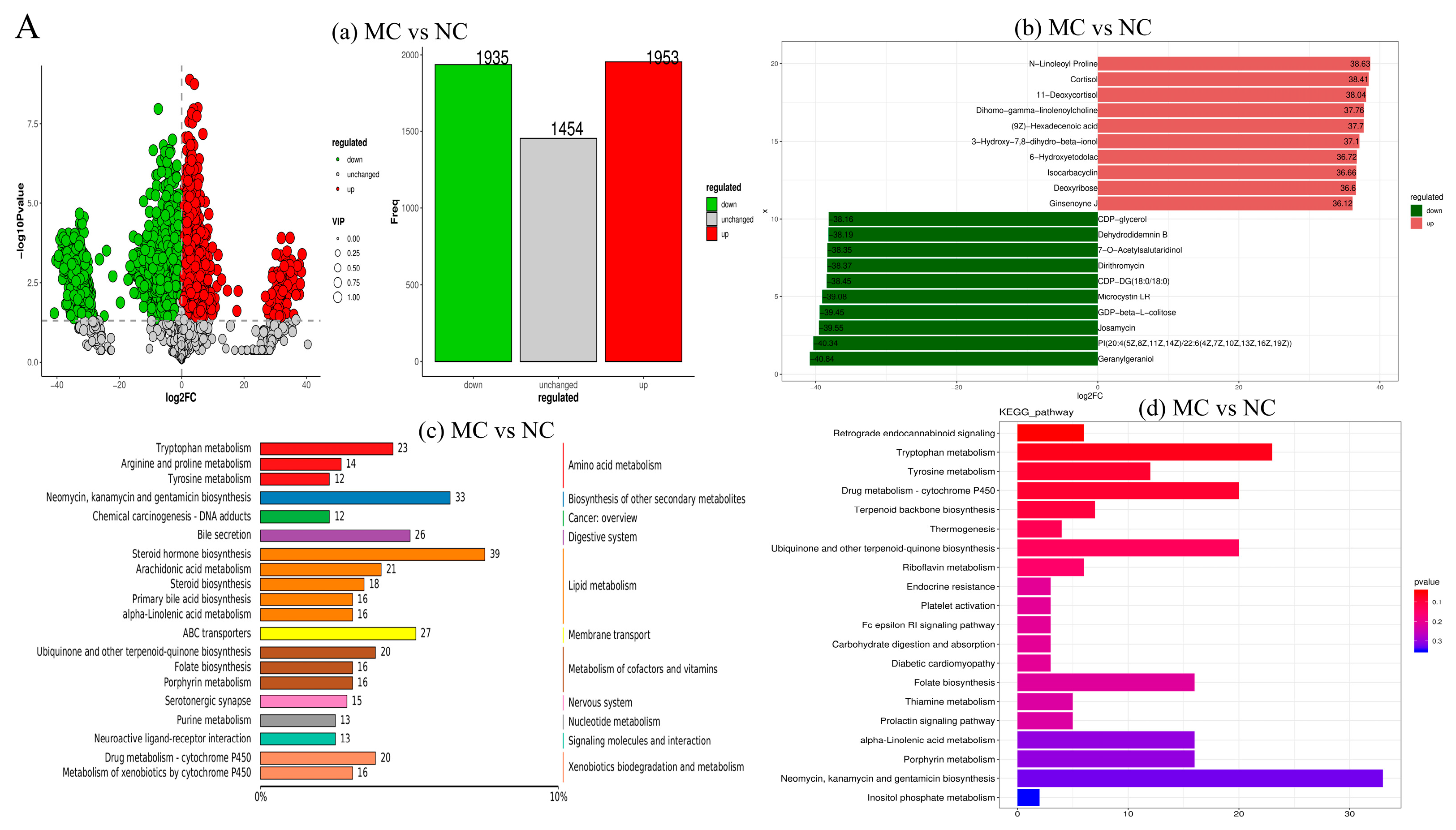
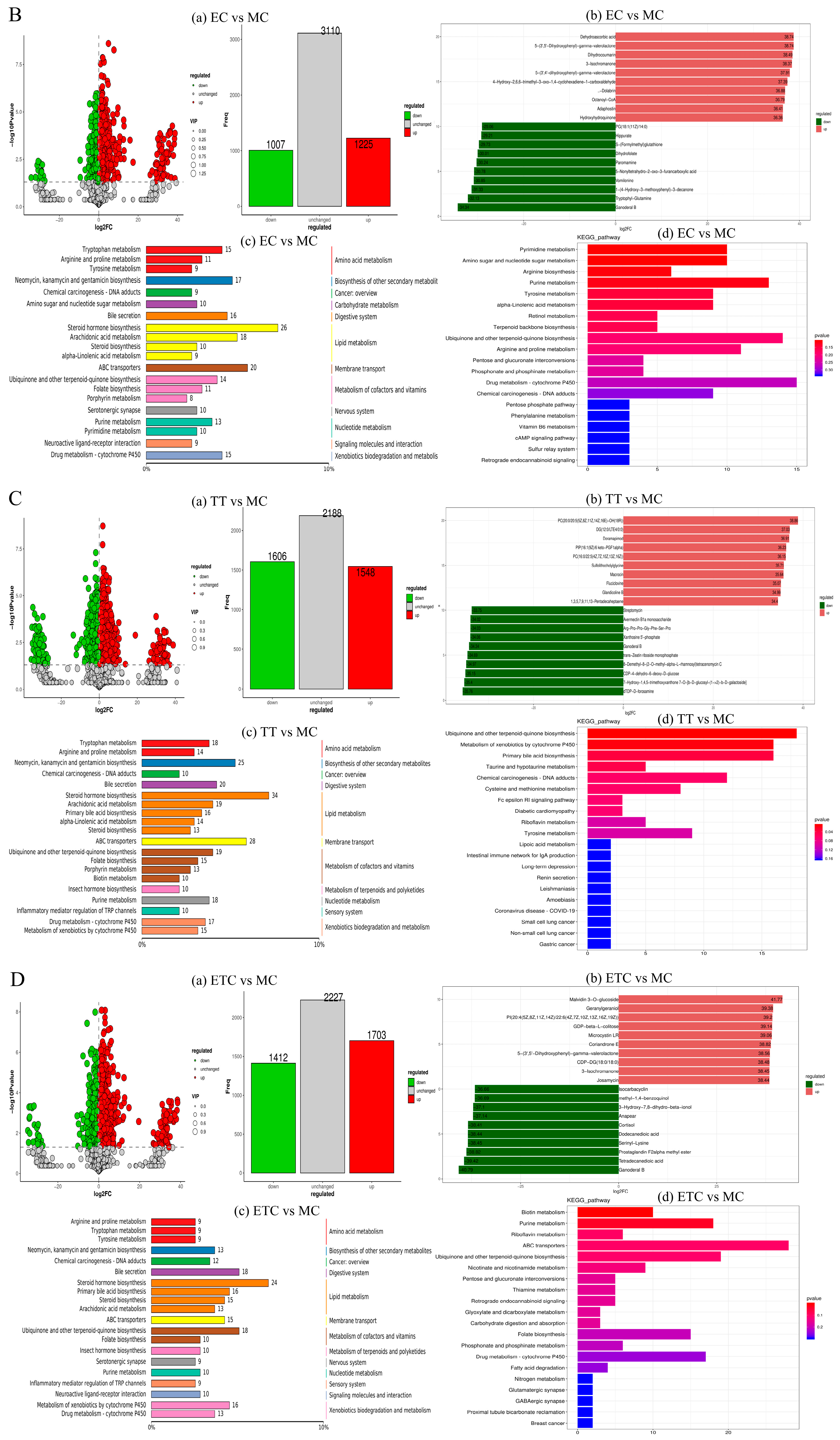
3.9. Metabolomics Result
3.10. EGCG and Taurine Regulate Glucose and Lipid Metabolism via PPARα/FAS Axis in Fatty Acid Synthesis/Catabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin gallate |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acid |
| PPARα | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| PEPCK | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-Enhancer of activated B cells |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| Fox-o1 | Forkhead box protein o1 |
| HepG2 | Human hepatoblastoma G2 cell line |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| OA | Oleic acid |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| PMSF | Phenyl methyl sulfonyl fluoride |
| SPF | Specific pathogen-free |
| SD | Sprague Dawley |
| SDS-PAGE | Sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
References
- Chew, N.W.S.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Kong, G.; Lin, C.X.; Chin, Y.H.; Lim, W.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Quek, J.; Fu, C.E.; et al. The global burden of metabolic disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 414–428.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hroob, A.M.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Hussein, O.E.; Mahmoud, A.M. Pathophysiological mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the therapeutic potential of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 409, 2155–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, X.Z.; Bian, Y.X.; Meng, L.; Wu, Y.T.; Ma, Y.D.; Li, C.; Wang, J.J.; Fu, Z.Z.; Dai, J.Y.; et al. Taurine reduces apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress in islet 13-cells induced by high-fat and-glucose diets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 175, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellia, A.; Rizza, S.; Galli, A.; Fabiano, R.; Rossi, R.; Federici, M.; Sbraccia, P.; Lauro, D. 12 Vascular and metabolic acute effects of rosuvastatin compared to simvastatin in untreated dyslipidemic diabetic patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, S37–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursel, R.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Green tea catechin plus caffeine supplementation to a high-protein diet has no additional effect on body weight maintenance after weight loss. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Min, S.G.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, G.H.; Yun, Y.R. Anti-obesity effects of kimchi with red yeast rice in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 106, 105594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.F.; Xiao, J.B.; Weng, Z.B.; Lu, X.Y.; Shen, X.C.; Wang, F. A phenolic glycoside from Moringa oleifera Lam. improves the carbohydrate and lipid metabolisms through AMPK in db/db mice. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Ussher, J.R.; Folmes, C.D.L.; Jaswal, J.S.; Stanley, W.C. Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 207–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiot, M.J.; Riva, C.; Vinet, A. Effects of dietary polyphenols on metabolic syndrome features in humans: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Z.; Yu, Y.J.; Adeli, K. Role of gut microbiota in neuroendocrine regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism via the microbiota-gut-brain-liver axis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, S.M.; Wichienchot, S.; Tsao, R.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Chakkaravarthi, S. Role of dietary polyphenols on gut microbiota, their metabolites and health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Ren, Z.P.; Zhang, J.; Chuang, C.C.; Kandaswamy, E.; Zhou, T.Y.; Zuo, L. Role of ROS and nutritional antioxidants in human diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, M.; Lambert, J.D.; Ju, J.; Reuhl, K.R.; Shapses, S.A.; Yang, C.S. The major green tea polyphenol, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, inhibits obesity, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease in high-fat-fed mice. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, C.; Artacho, R.; Giménez, R. Beneficial effects of green tea: A review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.B.; Jeong, H.W.; Cho, D.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Bae, I.H.; Lee, S.J. Fermented green tea extract alleviates obesity and related complications and alters gut microbiota composition in diet-induced obese mice. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.A.; Shin, K.O.; Choi, K.S. Studies on the function of Tturine: Review. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2015, 28, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spady, D.K.; Turley, S.D.; Dietschy, J.M. Rates of low density lipoprotein uptake and cholesterol synthesis are regulated independently in the liver. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Z.; Ou, T.; Yang, X.Y.; Song, Q.; Zhu, L.; Mi, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, W.; Guo, J.X. Untargeted metabolomics based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/MS reveals the lipid-lowering mechanism of taurine in hyperlipidemia mice. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1367589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.H.; Nagpal, R.; Wang, B.; Jain, S.; Razazan, A.; Mishra, S.P.; Zhu, X.W.; Wang, Z.; Kavanagh, K.; et al. A human-origin probiotic cocktail ameliorates aging-related leaky gut and inflammation via modulating the microbiota/taurine/tight junction axis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e132055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Choi, H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Yim, J.E. Taurine supplementation alters gene expression profiles in white adipose tissue of obese C57BL/6J mice: Inflammation and lipid synthesis perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.J.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, C.H.; Hong, T.; Yang, J.R.; Huang, X.J.; Geng, F.; Hu, J.L.; Nie, S.P. Tea polyphenol and epigallocatechin gallate ameliorate hyperlipidemia via regulating liver metabolism and remodeling gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2022, 404, 134591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.M.; Pang, Y.L.; Jiang, C.T. The role of the gut microbiome and its metabolites in metabolic diseases. Protein Cell. 2021, 12, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Chen, S.L.; Hu, K.-Q. Quantification and mechanisms of oleic acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 2, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinf. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Y.; Sun, N.; Huang, H.R.; Xie, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.B.; Hu, X.Y.; Dong, R.H.; Yu, Q. Catabolism of polyphenols released from mung bean coat and its effects on gut microbiota during in vitro simulated digestion and colonic fermentation. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisec, J.; Schauer, N.; Kopka, J.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling in plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X.T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.L.; Sun, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Gong, X.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; et al. Serum metabolomics for early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by UHPLC-QTOF/MS. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.Y.; Hu, F.C.; Gao, X.; Leng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; You, Y. Development of a simvastatin-loaded copolymer acid-sensitive nanocarrier and its experimental use in the treatment of keloids. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looft, T.; Johnson, T.A.; Allen, H.K.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Sul, W.J.; Stedtfeld, T.M.; Chai, B.L.; Cole, J.R.; et al. In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalia, R.; Pramono, A.; Afifah, D.N.; Noer, E.R.; Muniroh, M.; Kumoro, A.C. Mangrove fruit (Bruguiera gymnorhiza) increases circulating GLP-1 and PYY, modulates lipid profiles, and reduces systemic inflammation by improving SCFA levels in obese wistar rats. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.J.; Feng, Q.; Fan, L.L.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Y.Y. Serum and liver tissue metabonomic study on fatty liver in rats induced by high-fat diet and intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine Qushi Huayu decoction. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6242697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, X. The anti-obesity effects of green tea in human intervention and basic molecular studies. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.P.A.; Martin, A. Recent insights into the molecular regulators and mechanisms of taurine to modulate lipid metabolism: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 6005–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzang, C.C.; Chi, L.Y.; Lin, L.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Özcakar, L. Taurine reduces the risk for metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Diabetes 2024, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Li, H.B.; Feng, Y.B. Green tea and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD): Insights into the role of oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wei, M.L.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X.J. Targeting the alternative bile acid synthetic pathway for metabolic diseases. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.N.; Showalter, M.R.; Cajka, T.; Fan, S.L.; Pillai, V.V.; Fiehn, O.; Selvaraj, V. Metabolomic characteristics of cholesterol-induced non-obese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Dong, M.C.; Xu, C.X.; Jiang, N.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Pan, R.L. Effects of different chronic restraint stress periods on anxiety-and depression-like behaviors and tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism along the brain-gut axis in C57BL/6N mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 965, 176301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeriglio, A.; Marcoccia, D.; Denaro, M.; Trombetta, D. Nutraceuticals in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: How the panorama has changed in the last decade? Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 2165–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Cheng, C.; Cai, B.Y.; Li, H.S.; Tian, H.J.; Wang, X.; An, Z.M.; Sun, Q.M.; Hu, Y.Y.; Feng, Q. Caffeine and EGCG alleviate high-trans fatty acid and high-carbohydrate diet-induced NASH in mice: Commonality and specificity. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 784354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Kong, X.Q. Bixin ameliorates high fat diet-induced cardiac injury in mice through inflammation and oxidative stress suppression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delkhosh, A.; Shoorei, H.; Niazi, V.; Delashoub, M.; Gharamaleki, M.N.; Ahani-Nahayati, M.; Dehaghi, Y.K.; Raza, S.H.A.; Taheri, M.M.H.; Mohaqiq, M.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates inflammation, oxidative stress, and testicular histopathology in rats exposed to heat stress. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Baker, S.S.; Chapa-Rodriguez, A.; Liu, W.S.; Nugent, C.A.; Tsompana, M.; Mastrandrea, L.; Buck, M.; Baker, R.D.; Genco, R.J.; et al. Suppressed hepatic bile acid signalling despite elevated production of primary and secondary bile acids in NAFLD. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, S1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauchy, S.; Dutheil, F.; Weaver, R.J.; Chassoux, F.; Daumas-Duport, C.; Couraud, P.O.; Scherrmann, J.M.; De Waziers, I.; Declèves, X. ABC transporters, cytochromes P450 and their main transcription factors: Expression at the human blood-brain barrier. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Arellano, A.; Hernandez-Vazquez, A. Vitamins as cofactors for energy homeostasis and their genomic control, with special reference to biotin, thiamine, and pantothenic acid. Princ. Nutr. Nutr. 2020, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; White, M.F. Foxo1 in hepatic lipid metabolism. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, A.; Baes, M. Role of PPARα in hepatic carbohydrate metabolism. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 572405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszak, M.; Szulinska, M.; Bogdanski, P. You are what you eat-the relationship between diet, microbiota, and metabolic disorders-a review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, A.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.B.; Wang, T.Q.; Visentin, M.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Fu, X.J.; Wang, Z. Lipid accumulation and chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, A.; Gargouri, M.; Magné, C.; Ben-Nasr, H.; Kausar, M.A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Saeed, M.; Snoussi, M.; Adnan, M.; El-Feki, A.; et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) pharmacokinetics and molecular interactions towards amelioration of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia associated hepatorenal oxidative injury in alloxan induced diabetic mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Q.; Fu, X.J.; Chen, Q.F.; Patra, J.K.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, Z.G.; Gai, Z.B. Arachidonic acid metabolism and kidney inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.L.; Ferrell, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Boehme, S. Bile acid and cholesterol metabolism in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and therapy. Cardiol. Plus 2020, 5, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a nexus of metabolic and hepatic diseases. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.H.; Chen, S.W.; Chen, R.G.; Peng, Z.Q.; Wan, J.; Wu, B.Y. Taurine and tea polyphenols combination ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Louis, P. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and their role in human health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhao, K.; Jing, N.N.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.B. EGCG regulates fatty acid metabolism of high-fat diet-fed mice in association with enrichment of gut Akkermansia muciniphila. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.K.; Li, M.Y.; Yu, L.L.; Tian, F.W.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhai, Q.X. Effects of taurine on gut microbiota homeostasis: An evaluation based on two models of gut dysbiosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Molecular mechanism of PPARα action and its impact on lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.Y.; Feng, Y.F.; Yu, C.C.; Yao, Y.Y.; Chen, W.; Guo, J.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Mi, S.Q. Taurine supplementation decreases fat accumulation by suppressing FAS and enhancing ATGL through the ATGL pathway. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.M.; Li, W.; Hou, N.N.; Huang, N. A review of FoxO1-regulated metabolic diseases and related drug discoveries. Cells 2020, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein lipase: From gene to obesity. Am. J. Physiol. 2009, 297, E271–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.F.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Groups | Treatment Protocol | Treatment Time |
|---|---|---|
| Control | High-glucose DMEM with 10% FBS | 48 h total |
| OA | 0.8 mmol/L oleic acid | 48 h total |
| OA + EGCG | 0.8 mmol/L oleic acid → 50 μg/mL EGCG | 24 h + 24 h |
| OA + Taurine | 0.8 mmol/L oleic acid → 100 μg/mL taurine | 24 h + 24 h |
| OA + EGCG + Taurine | 0.8 mmol/L oleic acid → 50 μg/mL EGCG + 100 μg/mL taurine | 24 h + 24 h |
| Groups | Oral Gavage | Dosage | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | Saline | 2 mL/100 g | 8 weeks |
| MC | High-fat emulsion+ Saline | 2 mL/100 g + 2 mL/100 g | 8 weeks |
| PC | High-fat emulsion +Simvastatin | 2 mL/100 g + 10 mg/kg | 8 weeks |
| EC | High-fat emulsion + EGCG | 2 mL/100 g + 100 mg/kg | 8 weeks |
| TT | High-fat emulsion +Taurine | 2 mL/100 g + 300 mg/kg | 8 weeks |
| ETC | High-fat emulsion + (EGCG + Taurine) | 2 mL/100 g + (100 mg/kg + 300 mg/kg) | 8 weeks |
| NC | MC | PC | EC | TT | ETC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.301 ± 0.045 d | 1.242 ± 0.284 a | 0.380 ± 0.047 cd | 0.455 ± 0.107 bc | 0.569 ± 0.106 b | 0.350 ± 0.030 d |
| TC (mmol/L) | 1.444 ± 0.137 d | 20.607 ± 1.307 a | 7.540 ± 1.750 c | 11.403 ± 1.767 bc | 13.070 ± 3.010 b | 7.601 ± 0.571 c |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.151 ± 0.033 a | 0.567 ± 0.064 c | 0.526 ± 0.052 c | 0.789 ± 0.041 b | 0.601 ± 0.075 c | 0.904 ± 0.092 ab |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.546 ± 0.280 d | 16.416 ± 0.807 a | 6.162 ± 1.816 c | 10.154 ± 0.502 b | 9.721 ± 1.264 b | 6.879 ± 0.616 c |
| ALP (King/unit/100 mL) | 34.41 ± 7.63 e | 139.51 ± 15.15 a | 81.37 ± 14.32 c | 96.59 ± 4.49 bc | 110.12 ± 2.96 b | 68.19 ± 2.89 cd |
| ACC (μmol/h/g) | 370.43 ± 17.05 b | 500.90 ± 12.77 a | 332.23 ± 14.97 b | 418.69 ± 20.47 ab | 448.64 ± 12.37 ab | 322.30 ± 11.76 b |
| FAS (ng/mL) | 35.44 ± 0.74 c | 65.27 ± 3.61 a | 41.62 ± 1.92 c | 50.97 ± 1.37 b | 50.06 ± 1.67 b | 42.37 ± 1.09 c |
| LPL (μmol/min/mL) | 137.19 ± 18.45 a | 2.35 ± 0.74 e | 102.34 ± 6.24 b | 49.46 ± 8.18 c | 19.61 ± 7.89 d | 75.61 ± 12.08 b |
| FFA (μmol/mL) | 69.94 ± 1.51 d | 124.22 ± 3.55 a | 74.69 ± 1.70 d | 82.07 ± 2.23 c | 87.13 ± 1.25 b | 71.46 ± 1.70 d |
| ALT (nmol/min/mL) | 29.60 ± 4.71 c | 110.65 ± 28.07 a | 64.56 ± 3.76 b | 63.15 ± 7.95 b | 68.13 ± 3.02 b | 31.02 ± 3.62 c |
| AST (nmol/min/mL) | 38.22 ± 2.77 c | 58.75 ± 3.15 a | 47.48 ± 2.64 b | 46.86 ± 1.94 b | 50.07 ± 1.31 b | 38.34 ± 0.53 c |
| SOD (U/mL) | 42.01 ± 1.70 a | 20.38 ± 2.61 c | 24.54 ± 0.67 bc | 27.96 ± 4.88 b | 30.68 ± 2.26 b | 36.82 ± 2.27 ab |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 16.70 ± 3.30 c | 45.56 ± 5.75 a | 17.79 ± 3.42 c | 27.19 ± 1.62 b | 25.64 ± 2.67 b | 13.28 ± 0.85 c |
| GSH-Px (U/mL) | 5442.98 ± 260.47 a | 2673.26 ± 240.17 b | 4429.83 ± 219.90 ab | 3553.87 ± 307.67 b | 4665.75 ± 123.59 a | 5173.81 ± 185.46 a |
| Groups | OUTs | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 759.33 ± 11.02 a | 763.35 ± 10.20 a | 759.85 ± 10.74 a | 0.97 ± 0.00097 a | 6.54 ± 0.027 a |
| MC | 419.67 ± 3.51 e | 426.95 ± 2.30 d | 422.80 ± 3.03 d | 0.96 ± 0.00050 c | 5.92 ± 0.017 c |
| PC | 610.33 ± 28.57 b | 614.23 ± 26.80 b | 610.71 ± 28.28 b | 0.98 ± 0.00040 a | 6.68 ± 0.030 a |
| EC | 547.33 ± 35.57 c | 539.10 ± 2.5 c | 548.11 ± 31.06 c | 0.97 ± 0.00061 b | 6.24 ± 0.011 b |
| TT | 510.67 ± 18.77 d | 513.23 ± 11.61 c | 512.45 ± 18.58 c | 0.97 ± 0.0006 b | 6.31 ± 0.028 b |
| ETC | 568.33 ± 25.42 bc | 589.65 ± 5.10 b | 568.82 ± 31.48 c | 0.98 ± 0.00045 a | 6.47 ± 0.035 ab |
| Group | Acetic Acid (μg/g) | Propionic Acid (μg/g) | Isobutyric Acid (μg/g) | Butyric Acid (μg/g) | Isovaleric Acid (μg/g) | Valeric Acid (μg/g) | Caproic Acid (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 2640.73 ± 71.90 a | 426.69 ± 21.19 a | 440.33 ± 11.00 a | 274.92 ± 5.31 a | 42.74 ± 1.75 a | 269.87 ± 21.12 a | 420.49 ± 4.43 a |
| MC | 1336.67 ± 51.51 f | 220.37 ± 9.94 e | 239.89 ± 18.33 c | 197.90 ± 6.53 d | 25.14 ± 3.11 c | 196.50 ± 8.36 c | 284.94 ± 5.71 d |
| PC | 2250.17 ± 100.24 b | 404.98 ± 10.54 a | 425.29 ± 16.64 a | 253.99 ± 5.25 ab | 42.15 ± 1.06 a | 234.30 ± 3.85 b | 415.00 ± 5.12 a |
| EC | 1777.66 ± 70.70 d | 355.46 ± 11.58 c | 367.88 ± 2.89 b | 226.59 ± 4.19 bc | 33.03 ± 0.87 b | 217.45 ± 3.70 b | 345.14 ± 6.53 bc |
| TT | 1557.83 ± 91.45 e | 305.28 ± 10.43 d | 361.07 ± 1.62 b | 212.92 ± 6.80 c | 30.90 ± 0.28 b | 217.89 ± 13.43 b | 328.61 ± 8.17 c |
| ETC | 2051.56 ± 106.84 c | 385.75 ± 8.03 b | 399.96 ± 6.11 ab | 240.57 ± 7.59 b | 37.47 ± 2.05 ab | 236.10 ± 1.91 b | 369.91 ± 12.52 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Yang, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, K.; Duan, Y. EGCG and Taurine Synergistically Ameliorate Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modulating Gut Microbiota and PPARα/FAS Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162595
Xiao Y, Yang M, Cai M, Zhang H, Hu K, Duan Y. EGCG and Taurine Synergistically Ameliorate Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modulating Gut Microbiota and PPARα/FAS Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162595
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yang, Mingyue Yang, Meihong Cai, Haihui Zhang, Kai Hu, and Yuqing Duan. 2025. "EGCG and Taurine Synergistically Ameliorate Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modulating Gut Microbiota and PPARα/FAS Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162595
APA StyleXiao, Y., Yang, M., Cai, M., Zhang, H., Hu, K., & Duan, Y. (2025). EGCG and Taurine Synergistically Ameliorate Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modulating Gut Microbiota and PPARα/FAS Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 17(16), 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162595





