Association Between Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status in Polish Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
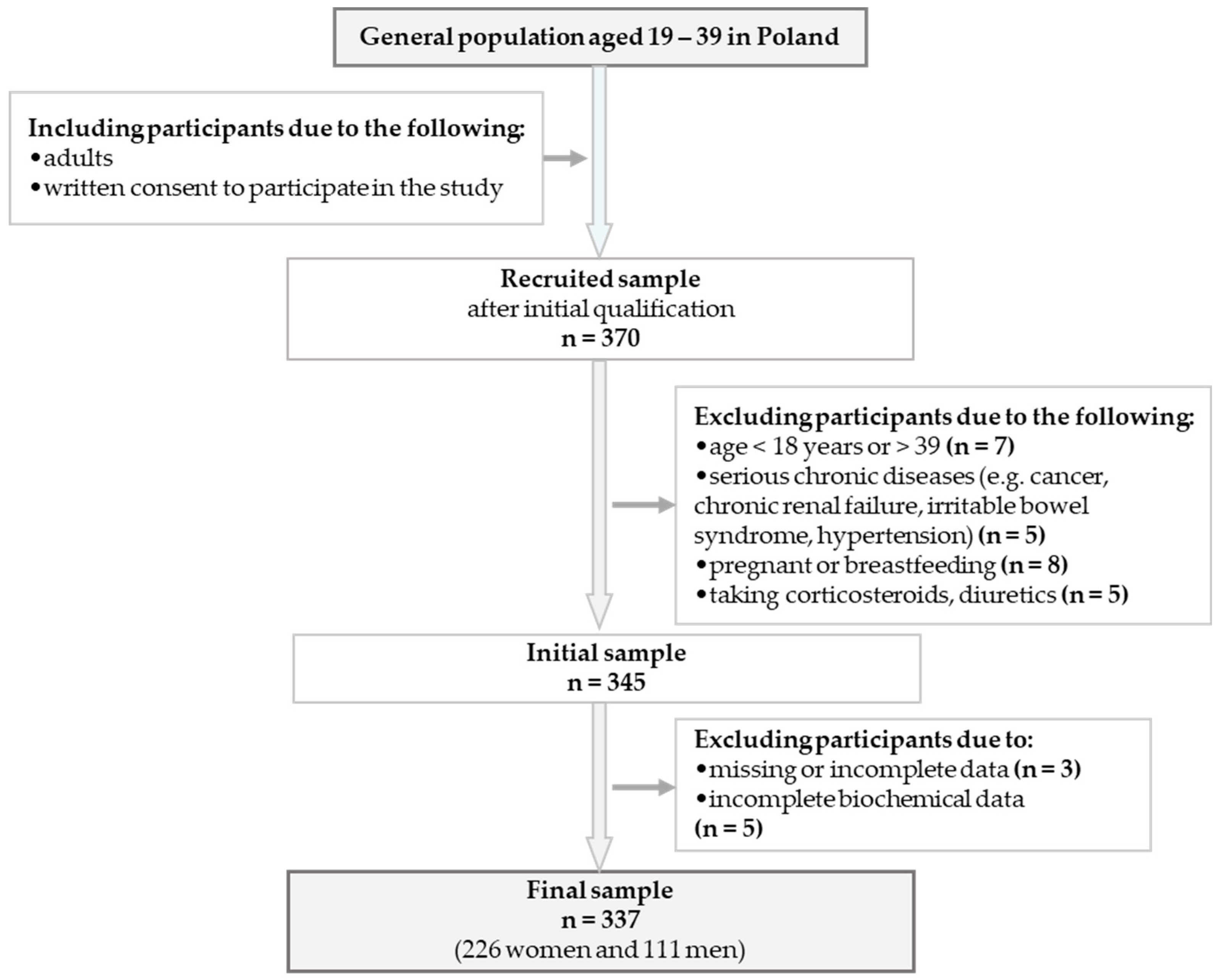
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Sociodemographic Data
2.3. Beverage Consumption Data
2.4. Health Status
2.4.1. Blood Pressure
2.4.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4.3. Body Composition
2.5. Hydration Status
Biochemical Analysis in Urine
2.6. Health-Related Behaviors and Health Index Scores (HISs)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Group
| Variables | 0–2 HIS (n = 115) | 3–5 HIS (n = 222) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Age (years) | 23.0 [22.0–25.0] * | 23.0 [21.0–25.0] * | 0.111 | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 64 | 55.6 | 162 | 72.9 | 0.001 |
| Male | 51 | 44.4 | 60 | 23.1 | |
| Education | |||||
| Secondary/‘I study’ | 80 | 69.6 | 153 | 68.9 | 0.903 |
| Higher | 35 | 30.4 | 69 | 31.1 | |
| Place of residence | |||||
| Village | 19 | 16.5 | 45 | 19.4 | 0.368 |
| Town | 30 | 26.1 | 44 | 20.6 | |
| City | 66 | 57.4 | 133 | 60.0 | |
| Economic status | |||||
| Very poor/poor | 35 | 30.4 | 57 | 25.7 | 0.352 |
| Average/very good | 80 | 69.6 | 165 | 74.3 | |
| Health status | |||||
| Very poor/poor | 27 | 23.5 | 50 | 22.5 | 0.843 |
| Average/very good | 88 | 76.5 | 172 | 77.5 | |
| Cigarette smoking | |||||
| Yes | 34 | 29.6 | 4 | 1.8 | 0.001 |
| No | 81 | 70.4 | 218 | 98.2 | |
| Physical activity | |||||
| No/low | 61 | 53.0 | 37 | 16.7 | 0.001 |
| Moderate | 34 | 29.6 | 121 | 54.5 | |
| High | 20 | 17.4 | 64 | 28.8 | |
| BMI | |||||
| <18.5 (kg/m2) | 3 | 2.6 | 19 | 8.5 | 0.001 |
| 18.5–24.9 (kg/m2) | 51 | 44.4 | 186 | 83.8 | |
| ≥25.0 (kg/m2) | 61 | 53.0 | 17 | 7.7 | |
| Sleeping status | |||||
| <6 h | 90 | 78.3 | 12 | 5.4 | 0.001 |
| >6 h | 25 | 21.7 | 210 | 94.6 | |
| Alcoholic drinking status | |||||
| <2 times/week | 24 | 20.9 | 207 | 93.2 | 0.001 |
| >2 times/week | 91 | 79.1 | 15 | 6.9 | |
3.2. Frequency of Beverage Consumption
| Variables | 0–2 HIS (n = 115) | 3–5 HIS (n = 222) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median [Q1–Q3] | |||
| Tea | 6.0 [4.0–7.0] | 6.0 [4.0–7.0] | 0.668 |
| Coffee | 5.0 [2.0–7.0] | 5.0 [2.0–6.0] | 0.232 |
| Herbal infusions | 2.0 [1.0–4.0] | 2.0 [1.0–4.0] | 0.548 |
| Milk | 3.0 [2.0–6.0] | 4.0 [2.0–6.0] | 0.878 |
| Natural fermented milk drinks | 2.0 [1.0–4.0] | 3.0 [2.0–4.0] | 0.048 |
| Flavored fermented milk drinks | 3.0 [1.0–4.0] | 2.0 [0.0–3.0] | 0.035 |
| Carbonated mineral water | 1.0 [0.0–4.0] | 1.0 [0.0–3.0] | 0.549 |
| Non-carbonated mineral water | 5.0 [3.0–6.0] | 7.0 [5.0–8.0] | 0.025 |
| Fruit juices | 3.0 [2.0–4.0] | 3.0 [2.0–3.0] | 0.077 |
| Vegetable juices | 1.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.426 |
| Fruit and vegetable juice | 1.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–3.0] | 0.592 |
| Non-carbonated fruit drinks | 2.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.042 |
| Sweetened carbonated drinks | 2.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.046 |
| Tea drinks | 2.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.026 |
| Cola drinks | 2.0 [1.0–3.0] | 2.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.801 |
| Energy drinks | 2.0 [0.0–3.0] | 1.0 [0.0–1.0] | 0.013 |
| Isotonic drinks | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 1.0 [0.0–1.0] | 0.204 |
| Non-alcoholic beer | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.885 |
| Beer | 3.0 [1.0–4.0] | 1.0 [1.0–3.0] | 0.017 |
| Wine | 2.0 [1.0–2.0] | 2.0 [1.0–2.0] | 0.903 |
| Vodka | 2.0 [1.0–2.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.006 |
| Alcoholic drinks | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 0.894 |
3.3. Anthropometric Measurements, Biochemical Analysis, and HIS Groups
| Variables | 0–2 HIS (n = 115) | 3–5 HIS (n = 222) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median [Q1–Q3] | |||
| Blood pressure | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | 125 [114.0–134.0] | 118 [109.0–128.0] | 0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.0 [75.0–79.0] | 77.0 [71.0–78.0] | 0.002 |
| Anthropometric measurements | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.1 [22.5–26.9] | 21.8 [20.0–23.3] | 0.001 |
| HC (cm) | 103 [97.0–109.0] | 97.7 [91.5–100.0] | 0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 82.0 [74.4–88.0] | 72.0 [67.0–77.0] | 0.001 |
| HGS (kg) | 38.0 [34.0–72.0] | 37.0 [32.0–65.0] | 0.736 |
| Body composition—BIA | |||
| MM (kg) | 23.5 [20.0–31.2] | 21.4 [19.3–25.4] | 0.001 |
| MM (%) | 9.45 [9.0–15.7] | 35.5 [13.0–21.5] | 0.003 |
| FFM (kg) | 51.0 [45.1–65.9] | 47.1 [42.9–56.2] | 0.001 |
| FFM (%) | 75.7 [66.5–81.1] | 78.0 [73.6–83.3] | 0.002 |
| TBW (kg) | 38.4 [33.5–47.9] | 34.2 [30.7–40.9] | 0.001 |
| TBW (%) | 54.9 [50.2–58.8] | 56.8 [52.7–60.3] | 0.002 |
| ECW (kg) | 17.2 [15.5–19.9] | 15.80 [14.1–17.7] | 0.001 |
| ECW (%) | 45.1 [42.5–46.3] | 44.3 [43.2–45.9] | 0.321 |
| ICW (kg) | 20.2 [18.2–25.9] | 18.9 [17.5–22.3] | 0.001 |
| ICW (%) | 54.9 [53.7–57.5] | 55.6 [54.0–56.8] | 0.322 |
| FM (kg) | 17.6 [13.3–24.4] | 13.5 [9.9–17.3] | 0.001 |
| FM (%) | 24.3 [18.0–33.5] | 21.9 [16.7–26.4] | 0.005 |
| Biochemical analysis—urine | |||
| USG (g/mL) | 1.024 [1.016–1.025] | 1.019 [1.011–1.020] | 0.038 |
| Uosm (mOsm/kg) | 572 [416.0–650.0] | 516 [390.0–550] | 0.027 |
| pH | 6.00 [5.9–6.5] | 6.00 [5.9–6.5] | 0.821 |
| HIS | SBP | DBP | BW | WC | HC | HGS | TBW | ICW | ECW | USG | Uosm | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIS | 1.000 | −0.139 * | −0.121 * | −0.411 *** | −0.398 ** | −0.330 ** | −0.068 | 0.315 ** | 0.139 * | −0.130 * | −0.103 * | −0.085 | −0.007 |
| SBP | −0.134 * | 1.000 | 0.549 *** | 0.293 * | 0.258 * | 0.258 * | −0.015 | −0.206 * | 0.010 | −0.001 | 0.084 | 0.094 | −0.078 |
| DBP | −0.121 * | 0.546 *** | 1.000 | 0.147 * | 0.177 * | 0.146 * | 0.017 | −0.180 * | −0.016 | 0.017 | 0.097 | 0.076 | −0.147 * |
| BW | −0.411 ** | 0.299 * | 0.147 * | 1.000 | 0.817 *** | 0.779 *** | 0.116 * | −0.658 *** | −0.258 * | 0.259 * | 0.025 | 0.046 | 0.034 |
| WC | −0.398 ** | 0.259 * | 0.177 * | 0.817 *** | 1.000 | 0.654 *** | 0.127 * | −0.714 *** | −0.202 * | 0.203 * | 0.019 | 0.037 | 0.010 |
| HC | −0.330 ** | 0.258 * | 0.146 * | 0.779 *** | 0.654 *** | 1.000 | 0.038 | −0.587 *** | −0.187 * | 0.186 * | 0.017 | 0.048 | 0.026 |
| HGS | −0.068 | −0.010 | 0.017 | 0.116 * | 0.127* | 0.038 | 1.000 | −0.216 * | −0.104 | 0.100 | −0.106 | −0.097 | −0.099 |
| TBW | 0.315 ** | −0.200 * | −0.180 * | −0.658 *** | −0.714 *** | −0.587 *** | −0.216 * | 1.000 | 0.099 | −0.090 | −0.040 | −0.074 | 0.072 |
| ICW | 0.139 * | 0.001 | −0.016 | −0.258 * | −0.202 * | −0.187 * | −0.104 | 0.099 | 1.000 | −0.993 *** | −0.046 | −0.068 | 0.050 |
| ECW | −0.130 * | −0.001 | 0.017 | 0.259 * | 0.203 * | 0.186 * | 0.100 | −0.090 | −0.993 *** | 1.000 | 0.049 | 0.087 | −0.057 |
| USG | −0.103 * | 0.083 | 0.097 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.017 | −0.106 | −0.040 | −0.046 | 0.049 | 1.000 | 0.967 *** | −0.095 |
| Uosm | −0.085 | 0.094 | 0.076 | 0.046 | 0.037 | 0.048 | −0.097 | −0.074 | −0.068 | 0.087 | 0.967 *** | 1.000 | −0.160 |
| pH | −0.007 | −0.078 | −0.147 * | 0.034 | 0.010 | 0.026 | −0.099 | 0.072 | 0.050 | −0.057 | −0.095 | −0.160 | 1.000 |
| Variables | 0–2 HIS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Β a | Eβ b | 95% CI c | p-Value d | ||
| Model 1 | |||||
| Health status | |||||
| Fatigue during the day | 0.470 | 1.60 | 1.05 | 3.63 | 0.039 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 0.378 | 1.46 | 1.02 | 1.68 | 0.042 |
| WC (cm) | 0.257 | 1.29 | 1.07 | 1.43 | 0.001 |
| FM (%) | 0.699 | 2.01 | 1.21 | 2.67 | 0.024 |
| Hydration status | |||||
| Non-carbonated mineral water e | −0.198 | 0.82 | 0.11 | 0.94 | 0.014 |
| Uosm | 0.475 | 1.61 | 1.27 | 2.48 | 0.017 |
| Model 2 | |||||
| Health status | |||||
| Fatigue during the day | 0.580 | 1.45 | 1.11 | 1.78 | 0.025 |
| WC (cm) | 0.347 | 1.35 | 1.15 | 1.57 | 0.031 |
| Hydration status | |||||
| Non-carbonated mineral water e | −0.217 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0.86 | 0.019 |
| Uosm | 0.511 | 1.87 | 1.33 | 2.37 | 0.024 |
4. Discussion
4.1. The Relationship Between Sociodemographic Factors and Health-Related Behaviors
4.2. Health Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status
4.3. Strength and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIA | Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| BW | Body Weight |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| FFM | Fat-free Mass |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| FM | Fat Mass |
| H | Height |
| HC | Hip Circumference |
| HGS | Handgrip Strength |
| HIS | Health Index Score |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| MET | Metabolic Equivalent of Work |
| MM | Muscle Mass |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| Q | Quartile |
| pH | Potential Hydrogen Value |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| TBW | Total Body Water |
| Uosm | Urine Osmolality |
| USG | Urine Specific Gravity |
| WC | Waist Circumference |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Li, Y.; Pan, A.; Wang, D.D.; Liu, X.; Dhana, K.; Franco, O.H.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Stampfer, M.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the Us Population. Circulation 2018, 138, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, E.; Ciesla, E.; Lelonek, M.; Piechowska, A.; Gluszek, S. Lifestyle Elements and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alorayf, A.E.A.; Alhamamah, M.A.M.; Alhamamah, S.A.M.; Alhamamah, H.A.M.; Almasabi, F.M.; Al Jamish, Y.A.A.; Al-Aorif, F.M.A.; Allajam, M.M.M.; Alsoma, M.A.H.; Al Abbas, A.M.H. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Lifestyle Interventions in Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Ecohumanism 2024, 3, 4651–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killick, R.; Stranks, L.; Hoyos, C.M. Sleep Deficiency and Cardiometabolic Disease. Sleep Med. Clin. 2024, 19, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ba, M.; Chen, P.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Sha, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H. Association between High Blood Pressure and Long Term Cardiovascular Events in Young Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson-Pablo, P.; Nilsson, T.K.; Hurtig-Wennlöf, A. Relative Handgrip Strength Correlates Inversely with Increased Body Fat, Inflammatory Markers and Increased Serum Lipids in Young, Healthy Adults—The LBA Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 207, 111057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Fernández, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Torres-Costoso, A.; Cañete García-Prieto, J.; Franquelo-Morales, P.; Sánchez-López, M. Strength and Cardiometabolic Risk in Young Adults: The Mediator Role of Aerobic Fitness and Waist Circumference. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, S.; Rathored, J.; Barole, N. Exploring Multifactorial Relationships: Assessing the Correlation Between Cardiovascular Health Indicators and Metabolic Markers. Cureus 2024, 16, e59934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, D.; Mah, E.; Brisbois, T.; Barrios, P.L.; Baker, L.B.; Spriet, L.L. Narrative Review of Hydration and Selected Health Outcomes in the General Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, H.; von Andrian-Werburg, J.; Malisova, O.; Athanasatou, A.; Kapsokefalou, M.; Ortega, J.; Mora-Rodriguez, R.; Thevis, M. Differing Water Intake and Hydration Status in Three European Countries—A Day-to-Day Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; Courbebaisse, M.; Lepicard, E.M.; Friedlander, G. Assessment of Hydration Status in a Large Population. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frąckiewicz, J.; Szewczyk, K. Is There an Association Between Hydration Status, Beverage Consumption Frequency, Blood Pressure, Anthropometric Characteristics, and Urinary Biomarkers in Adults? Nutrients 2025, 17, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, B.P.; Zhao, X.; Veilleux, J.C. Association of Knowledge and Health Habits with Physiological Hydration Status. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, T.C.; Stuhlsatz, G.; Snyder, J.E. A Scoping Review and Assessment of the Area-Level Composite Measures That Estimate Social Determinants of Health Across the United States. Public Health Rep. 2025, 140, 67–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W. Personalized Hydration Requirements of Runners. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2022, 32, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, R.; Gan, Q.; Yang, T.; Pan, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Overweight and Obese Children Aged 6–17 Years in China Had Lower Level of Hydration Status: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachucka, P. Assessment of Beverage Consumption in a Selected Group of Adults—Comparison of Two Methods. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Human Nutrition Sciences, Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Palatini, P.; Parati, G.; O’Brien, E.; Januszewicz, A.; Lurbe, E.; Persu, A.; Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R. 2021 European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for Office and Out-of-Office Blood Pressure Measurement. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unda Villafuerte, F.; Llobera Cànaves, J.; Lorente Montalvo, P.; Moreno Sancho, M.L.; Oliver Oliver, B.; Bassante Flores, P.; Estela Mantolan, A.; Pou Bordoy, J.; Rodríguez Ruiz, T.; Requena Hernández, A.; et al. Effectiveness of a Multifactorial Intervention, Consisting of Self-Management of Antihypertensive Medication, Self-Measurement of Blood Pressure, Hypocaloric and Low Sodium Diet, and Physical Exercise, in Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension Taking 2 or More Antihypertensive Drugs. Medicine 2020, 99, e19769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.; Eston, R. Kinanthropometry and Exercise Physiology, 4th ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-315-38566-2. [Google Scholar]
- Batsis, J.A.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Bartels, S.J.; Sahakyan, K.R.; Somers, V.K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Diagnostic Accuracy of Body Mass Index to Identify Obesity in Older Adults: NHANES 1999–2004. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 40, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.J.; Racette, S.B. The Utility of Body Composition Assessment in Nutrition and Clinical Practice: An Overview of Current Methodology. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.D.; Edward, G.D.; Cumming, K.; Kafri, M.W.; Soiza, R.L.; Hooper, L.; Potter, J.F.; Myint, P.K. Bioelectrical Impedance Versus Biochemical Analysis of Hydration Status: Predictive Value for Prolonged Hospitalisation and Poor Discharge Destination for Older Patients. Healthcare 2021, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoutteten, M.K.; Lindeboom, L.; Brys, A.; Lanssens, D.; Smeets, C.J.P.; De Cannière, H.; De Moor, B.; Peeters, J.; Heylen, L.; Van Hoof, C.; et al. Comparison of Whole Body versus Thoracic Bioimpedance in Relation to Ultrafiltration Volume and Systolic Blood Pressure during Hemodialysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 135, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleymaet, R.; D’Hondt, M.; Scheinok, T.; Malbrain, L.; De Laet, I.; Schoonheydt, K.; Dits, H.; Van Regenmortel, N.; Mekeirele, M.; Cordemans, C.; et al. Comparison of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)-Derived Parameters in Healthy Volunteers and Critically Ill Patients. Life 2024, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Martinez-Abellán, A.; López-Gullón, J.M.; Morán-Navarro, R.; Pallarés, J.G.; De La Cruz-Sánchez, E.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Validity of Hydration Non-Invasive Indices during the Weightcutting and Official Weigh-in for Olympic Combat Sports. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelnik, S.B.; Davy, K.P.; Hedrick, V.E.; Thomas, D.T.; Davy, B.M. The Validity of Urine Color as a Hydration Biomarker within the General Adult Population and Athletes: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernat, E.; Stupnicki, R.; Gajewski, A. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—Polish Version. Phys. Educ. Sport 2007, 51, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Grzymisławska, M.; Puch, E.A.; Zawada, A.; Grzymisławski, M. Do Nutritional Behaviors Depend on Biological Sex and Cultural Gender? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Al-Othman, N.; Rabayaa, M.; Alqaraleh, M. Gender Differences in Health-Promoting Behaviors and Psychological Well-Being of Palestinian Medical Students Based on the HPLP II. Palest. Med. Pharm. J. 2022, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, T.; Whatnall, M.C.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Haslam, R.L.; Bezzina, A.; Collins, C.E.; Ashton, L.M. Effectiveness of Gender-Targeted versus Gender-Neutral Interventions Aimed at Improving Dietary Intake, Physical Activity and/or Overweight/Obesity in Young Adults (Aged 17–35 Years): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, T.R.; Tian, D.; Li, J.; Srivastava, P.; Zheng, Y. Cigarette Smoking, e-Cigarette Use, and Sociodemographic Correlates of Mental Health and Tobacco-Related Disease Risk in the All of Us Research Program. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2024, 31, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piercy, K.L.; Troiano, R.P.; Ballard, R.M.; Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Galuska, D.A.; George, S.M.; Olson, R.D. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 320, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.L.; Yiallourou, S.R.; Horne, R.S.C.; Wong, F.Y. Prone Sleeping Position in Infancy: Implications for Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Function. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 39, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosti, R.I.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sandeman, G.; Frittella, N.; Iasiello, B.; Teissedre, P.L.; Restani, P. Dietary and Lifestyle Habits of Drinkers with Preference for Alcoholic Beverage: Does It Really Matter for Public Health? A Review of the Evidence. OENO One 2021, 55, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, T.; Lehtoranta, L.; Palosaari, T.; Männistö, S.; Kaartinen, N.E.; Lundqvist, A.; Lahti, J. The interplay between healthy lifestyle and body mass index in metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Public Health 2024, 34, ckae144.1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, T.; Molla, G.M.; Ahamed, A. Association of Body Mass Index (BMI) with Diet, Physical Activity, and Lifestyle Among Undergraduate Dental Students in a Private Dental College in Bangladesh. Update Dent. Coll. J. 2024, 14, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, P.V. A Study on Lifestyle Pattern Associated with Diet, Physical activity, and Body Mass Index in a Case of GYM Goers. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag. 2023, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, L.A.; Kline, C.E.; Gunn, H.E.; Buysse, D.J.; Hall, M.H. The Role of Sleep Hygiene in Promoting Public Health: A Review of Empirical Evidence. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanshyam Patel, A.; Thakrar, G. Correlation of BMI with Physical Activity and Fatigue in College Going Students. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2023, 13, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global Burden of Alcohol Use Disorders and Alcohol Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Lima, M.d.O.; Pedrosa, A.K.P.; Serenini, R.; de Menezes, R.C.E.; Longo-Silva, G. Sleep and Circadian Hygiene Practices Association with Sleep Quality among Brazilian Adults. Sleep Med. X 2023, 6, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Chen, X.; Park, C.G.; Zhu, D.; Izci-Balserak, B. Fatigue and Sleep Quality Predict Eating Behavior among People with Type 2 Diabetes. Nurs. Res. 2020, 69, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ghazinour, G.; Tabaczynski, A.; Chong, S.Y.; Koperwas, I.; Trinh, L. Identifying Latent Profiles of Quality of Life and Lifestyle Behaviors in Cancer Survivors: The Interplay of Sedentary Behavior, Physical Activity, and Sleep. J. Cancer Surviv. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charchar, F.J.; Prestes, P.R.; Mills, C.; Ching, S.M.; Neupane, D.; Marques, F.Z.; Sharman, J.E.; Vogt, L.; Burrell, L.M.; Korostovtseva, L.; et al. Lifestyle Management of Hypertension: International Society of Hypertension Position Paper Endorsed by the World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2024, 42, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 22, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. Alcohol Consumption, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Health Across the Life Course: There Is No Such Thing as a One-Size-Fits-All Approach. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 7, e009698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasri, F.D.; Witjaksono, F.; Sudarsono, N.C. Correlation of Energy Intake and Physical Activity with Visceral Fat in Obese Office. World Nutr. J. 2023, 7, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Lesloom, F. Association of Cigarette Smoking with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2024, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Muley, A. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption Among College Students and Their Association with Body Composition, Bowel Movements and Menstrual Cycle. Int. J. Public Health 2025, 70, 1607712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, C.L.; da Silva, N.F.; Rodrigues, I.G.; Arcoverde, G.M.P.F.; Ferraz, V.D.; Sobral Filho, D.C.; Diniz, A.d.S.; Pinho, C.P.S.; Cabral, P.C.; de Arruda, I.K.G. Different Factors Modulate Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Accumulation in Adults: A Single-Center Study in Brazil. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1524389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, S.S.; Gupta, R.; Rastogi, A.; Agrawal, K.; Sachdeva, N.; Ram, S.; Dutta, P.; Bhadada, S.K.; Bhansali, A. Abdominal Obesity and Incident Cardio-Metabolic Disorders in Asian-Indians: A 10-Years Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2022, 16, 102418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczyk, E.; Walkiewicz, K.W.; Muc-Wierzgoń, M.; Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak, S. Estimation of Intake of Fat, Saturated Fatty Acids, and Trans Fatty Acids from Sweet and Salty Snacks Among Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vazquez, S.E.; Kammar-García, A.; Moctezuma-Velázquez, C.; Mancilla-Galindo, J.; García-Juárez, I.; Uscanga-Domínguez, L.F. The Impact of Dietary Sugars and Saturated Fats on Body and Liver Fat in a Healthcare Worker Population. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, S.; Xie, W.; Humińska-Lisowska, K.A.; Sawczyn, M.H.; Dzitkowska-Zabielska, M.; Qian, G.; Ossowski, Z. Relationship between Physical Activity and Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Markers in Postmenopausal Women. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlKalbani, S.R.; Murrin, C. The Association between Alcohol Intake and Obesity in a Sample of the Irish Adult Population, a Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.X.; Johnson, E.C.; Kunces, L.J.; McKenzie, A.L.; Wininger, M.; Butts, C.L.; Caldwell, A.; Seal, A.; McDermott, B.P.; Vingren, J.; et al. Impact of Nutrient Intake on Hydration Biomarkers Following Exercise and Rehydration Using a Clustering-Based Approach. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckiewicz, J.; Ciecierska, A.; Białkowska, A.; Drywień, M.; Hamulka, J. Hydration Status in Adults with Metabolic Disorders in Relation to Socioeconomic, Lifestyle and Health Factors. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaecke, T.; Dolci, A.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Lieberman, H.R. Associations between Urinary Hydration Markers and Metabolic Dysfunction: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of NHANES Data, 2008–2010. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4229–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; He, H.; Ma, G. The Comparison of Water Intake Patterns and Hydration Biomarkers among Young Adults with Different Hydration Statuses in Hebei, China. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinger, A.Y.; Chang, A.M.; Buxton, O.M.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Gao, X. Short Sleep Duration Is Associated with Inadequate Hydration: Cross-Cultural Evidence from US and Chinese Adults. Sleep 2019, 42, zsy210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J.D.; Kavouras, S.A.; Suh, H.; Lang, F. Underhydration Is Associated with Obesity, Chronic Diseases, and Death Within 3 to 6 Years in the U.S. Population Aged 51–70 Years. Nutrients 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Rogers, G.; Stookey, J.D.; Perrier, E.T. Water Intake and Markers of Hydration Are Related to Cardiometabolic Risk Biomarkers in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Du, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, S.; Cai, Y. Association between Urine Specific Gravity as a Measure of Hydration Status and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Kailuan Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, L.; McManus, T.; Harris, W.A.; Shanklin, S.L.; Flint, K.H.; Queen, B.; Lowry, R.; Chyen, D.; Whittle, L.; Thornton, J.; et al. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance—United States, 2017. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2019, 67, 1–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Chen, J.X.; Jiang, Y.W.; Xia, P.F.; Pan, A. Association of Sugar-Sweetened Beverage and Artificially Sweetened Beverage Intakes with Mortality: An Analysis of US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, A.D.; Bougatsas, D.; Arnaoutis, G.; Bottin, J.H.; Perrier, E.T.; Tsipouridi, S.; Kavouras, S. A First Morning Spot Sample Overestimates 24-Hour Urine Osmolality in Children and Adults. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2017, 49, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.X.; Acosta, A.M.; Farquhar, A.; Coleman, I.L.; Cook, J.C.; Chen-Ruan, K.; Mejia-Cornelio, S.; Bergeron, M.F. Utility of First Morning Urine Sampling To Indicate Previous 24 h And 5d Hydration Practices. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2021, 53, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frąckiewicz, J.; Szewczyk, K. Association Between Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status in Polish Adults. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162597
Frąckiewicz J, Szewczyk K. Association Between Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status in Polish Adults. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162597
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrąckiewicz, Joanna, and Kacper Szewczyk. 2025. "Association Between Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status in Polish Adults" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162597
APA StyleFrąckiewicz, J., & Szewczyk, K. (2025). Association Between Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status and Hydration Status in Polish Adults. Nutrients, 17(16), 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162597







