Association of Coffee and Energy Drink Intake with Suicide Attempts and Suicide Ideation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Risk of Bias
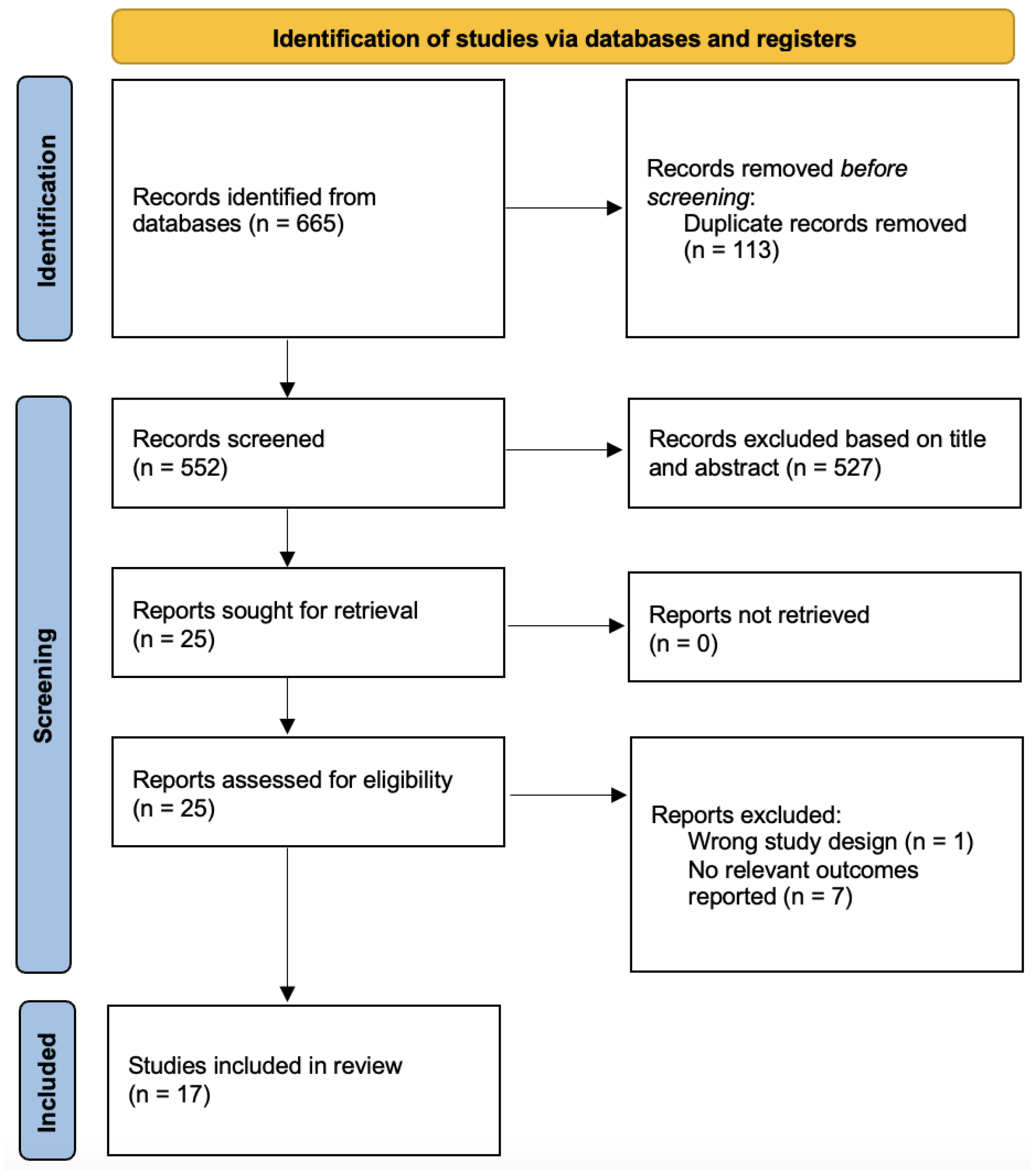
3. Results
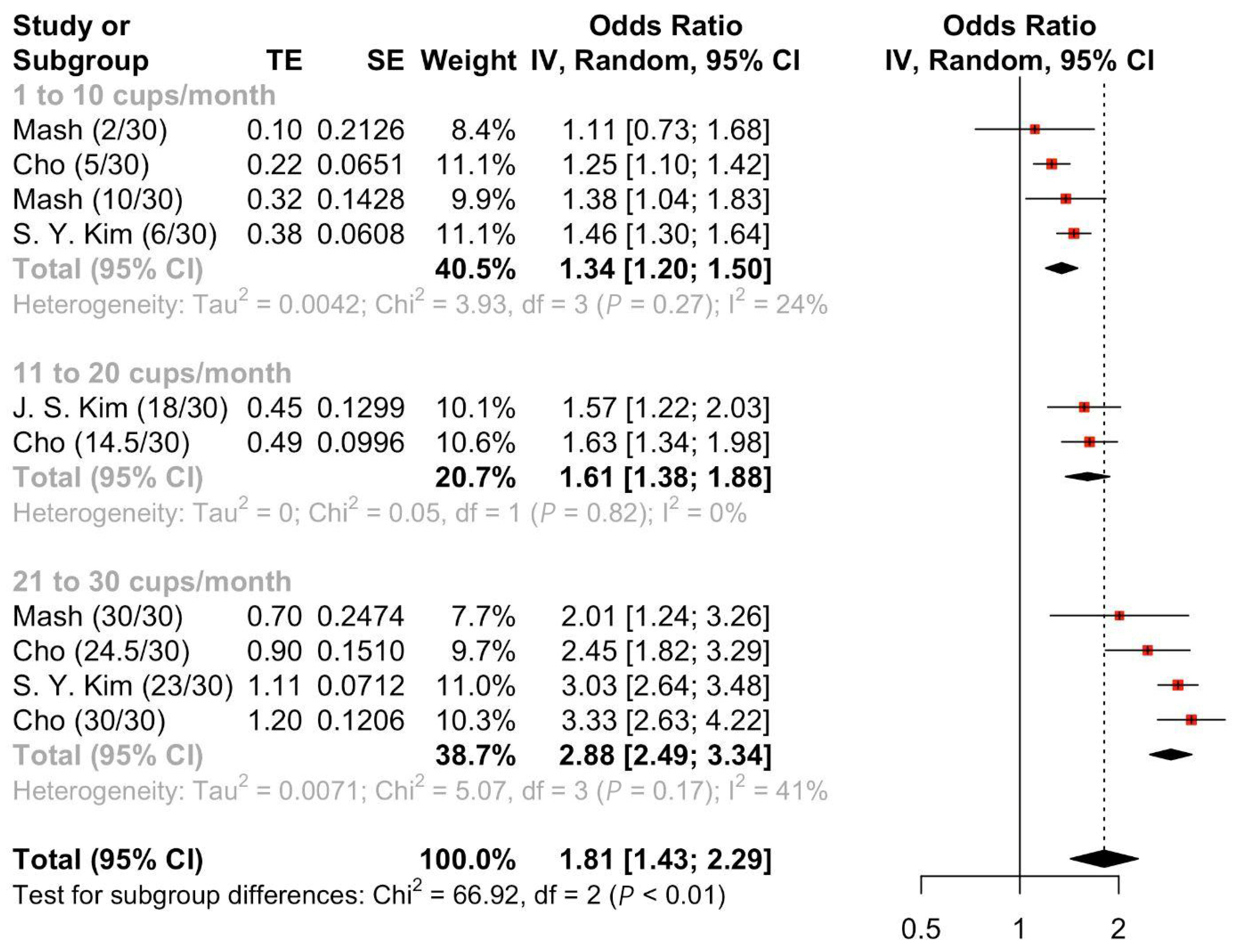
3.1. Energy Drink Consumption and Suicide Attempts
3.2. Energy Drink Consumption and Suicidal Ideation
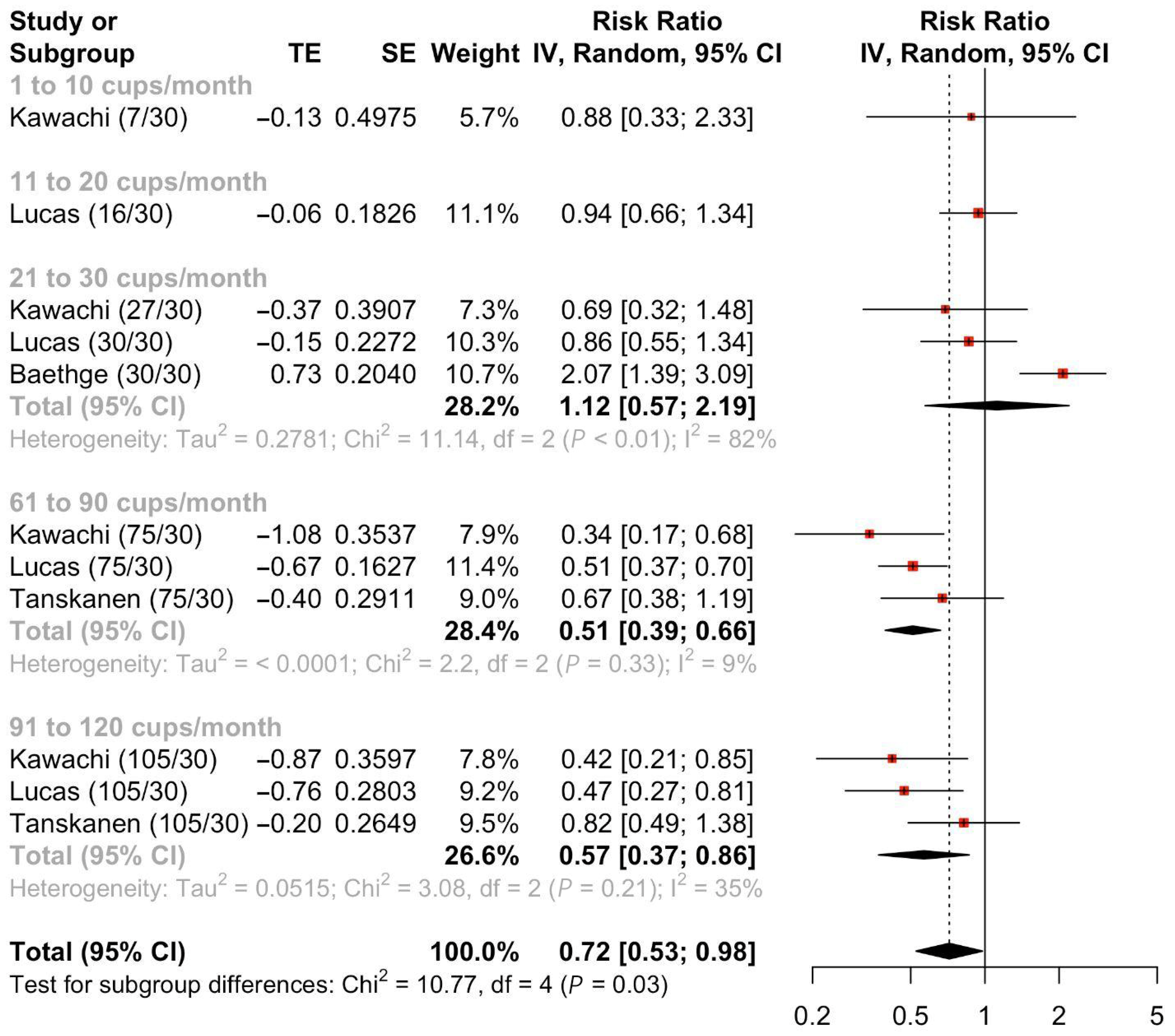
3.3. Coffee Consumption and Suicide Attempts
3.4. Systematic Review on the Factors Affecting Consumption
3.4.1. Substance Usage
3.4.2. Gender
3.4.3. Risk-of-Bias
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, J.; Richards, J.R.; Battisti, A.S. Caffeine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Samoggia, A.; Rezzaghi, T. The Consumption of Caffeine-Containing Products to Enhance Sports Performance: An Application of an Extended Model of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Nutrients 2021, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planning Committee for a Workshop on Potential Health Hazards Associated with Consumption of Caffeine in Food and Dietary Supplements; Food and Nutrition Board; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Institute of Medicine. Intake and Exposure to Caffeine. In Caffeine in Food and Dietary Supplements: Examining Safety: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alsunni, A.A. Energy Drink Consumption: Beneficial and Adverse Health Effects. Int. J. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA FoodData Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Wilson, P.W.F.; Bloom, H.L. Caffeine Consumption and Cardiovascular Risks: Little Cause for Concern. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, S.; Daria, P.; Sani, G.; Aromatario, M. Caffeine: Cognitive and Physical Performance Enhancer or Psychoactive Drug? Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodak, K.; Kokot, I.; Kratz, E.M. Caffeine as a Factor Influencing the Functioning of the Human Body—Friend or Foe? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Micek, A.; Castellano, S.; Pajak, A.; Galvano, F. Coffee, tea, caffeine and risk of depression: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.Y.; Ge, G.; Low, C.E.; Rana, S.; Tan, T.Y.Z.; Fang, N.B.J.; Teo, J.Y.Y.; Yap, Y.T.; Yau, C.E.; Lee, A.R.Y.B.; et al. Suicide and Suicidal Ideation Among Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2457544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, C.E.; Loke, S.; Rana, S.; Sim, B.; Ho, C.S.H. Prevalence and incidence of suicide, suicidal ideation and self-harm in caregivers of cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2024, 90, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, C.E.; Loke, S.; Pang, G.E.; Sim, B.; Yang, V.S. Psychological outcomes in patients with rare cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 72, 102631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.R.Y.B.; Low, C.E.; Yau, C.E.; Li, J.; Ho, R.; Ho, C.S.H. Lifetime Burden of Psychological Symptoms, Disorders, and Suicide Due to Cancer in Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2023, 177, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suicide. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/suicide (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Khan, A.P.; Asad, A.; Azam. WHO EMRO|Psychosocial Factors of Deliberate Self-Harm in Afghanistan: A Hospital Based, Matched Case-Control Study|Volume 25, Issue 11|EMHJ Volume 25. 2019. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/emhj-volume-25-2019/volume-25-issue-11/psychosocial-factors-of-deliberate-self-harm-in-afghanistan-a-hospital-based-matched-case-control-study.html (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Park, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.H. Association between energy drink intake, sleep, stress, and suicidality in Korean adolescents: Energy drink use in isolation or in combination with junk food consumption. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, I.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Speizer, F.E. A prospective study of coffee drinking and suicide in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996, 156, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Pan, A.; Mirzaei, F.; Willett, W.C.; Okereke, O.I.; Ascherio, A. Coffee, caffeine, and risk of completed suicide: Results from three prospective cohorts of American adults. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Odds Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Makowski, D.; Lüdecke, D.; Patil, I.; Wiernik, B.M.; Thériault, R.; Kelley, K.; Stanley, D.; Caldwell, A.; Burnett, J.; et al. effectsize: Indices of Effect Size. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/effectsize/effectsize.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Barker, T.H.; Moola, S.; Tufanaru, C.; Stern, C.; McArthur, A.; Stephenson, M.; Aromataris, E. Methodological quality of case series studies: An introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. GRADE Handbook. Available online: https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Baethge, C.; Tondo, L.; Lepri, B.; Baldessarini, R.J. Coffee and cigarette use: Association with suicidal acts in 352 Sardinian bipolar disorder patients. Bipolar Disord. 2009, 11, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Suh, B.S.; Lee, K. Relationship between daily coffee intake and suicidal ideation. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 256, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanskanen, A.; Tuomilehto, J.; Viinamäki, H.; Vartiainen, E.; Lehtonen, J.; Puska, P. Heavy coffee drinking and the risk of suicide. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 16, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatsky, A.L.; Armstrong, M.A.; Friedman, G.D. Coffee, tea, and mortality. Ann. Epidemiol. 1993, 3, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S. Use of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Caffeine and Suicide Attempts: Findings From a Nationally Representative Cross-sectional Study. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11, 2150132720913720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evren, C.; Evren, B. Energy-drink consumption and its relationship with substance use and sensation seeking among 10th grade students in Istanbul. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2015, 15, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.A.; Park, E.-C. Association between energy drink consumption, depression and suicide ideation in Korean adolescents. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2020, 66, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, K.; Seo, Y. Associations Between Korean Adolescents’ Energy Drink Consumption and Suicidal Ideation and Attempts. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2018, 32, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Sim, S.; Choi, H.G. High stress, lack of sleep, low school performance, and suicide attempts are associated with high energy drink intake in adolescents. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masengo, L.; Sampasa-Kanyinga, H.; Chaput, J.-P.; Hamilton, H.A.; Colman, I. Energy drink consumption, psychological distress, and suicidality among middle and high school students. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 268, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mash, H.B.H.; Fullerton, C.S.; Ramsawh, H.J.; Ng, T.H.H.; Wang, L.; Kessler, R.C.; Stein, M.B.; Ursano, R.J. Risk for suicidal behaviors associated with alcohol and energy drink use in the US Army. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2014, 49, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.-K.; Sa, J.; Choe, S.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chung, J.; Cummings, G.; Lee, J. Prevalence and correlates of highly caffeinated beverage consumption among Korean adolescents. Osong Public. Health Res. Perspect. 2021, 12, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanni, O.O. A Survey on Caffeine Consumption and Risky Behaviors Among a Sample of Secondary School Students in Nigeria. J. Caffeine Res. 2017, 7, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, G.A.; Johnson, A.R.; Crouch, B.I.; Valento, M.; Horowitz, B.Z.; Hendrickson, R.G. A Retrospective Study of Clinical Effects of Powdered Caffeine Exposures Reported to Three US Poison Control Centers. J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Sultan, M.T. Coffee and its consumption: Benefits and risks. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Coffee and caffeine consumption and depression: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2016, 50, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasmari, F. Caffeine induces neurobehavioral effects through modulating neurotransmitters. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlig, A. Effects of coffee/caffeine on brain health and disease: What should I tell my patients? Pract. Neurol. 2016, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y. Consumption of coffee and tea with all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, A.; Maiese, A.; Lazzari, J.; Casula, C.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. The Dark Side of Energy Drinks: A Comprehensive Review of Their Impact on the Human Body. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, C.J.; Strain, E.C.; Griffiths, R.R. Caffeinated Energy Drinks—A Growing Problem. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 99, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, A.; Chaaya, N.; Beecher, K.; Ali, S.A.; Belmer, A.; Bartlett, S. The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 103, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, J.; Wiciński, M.; Wódkiewicz, E.; Nowaczewska, M.; Słupski, M.; Otto, S.W.; Kubiak, K.; Huk-Wieliczuk, E.; Malinowski, B. Effects of Energy Drink Consumption on Physical Performance and Potential Danger of Inordinate Usage. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Mergl, R.; Kohls, E.; Székely, A.; Gusmao, R.; Arensman, E.; Koburger, N.; Hegerl, U.; Rummel-Kluge, C. A cross-national study on gender differences in suicide intent. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Feigelman, W.; Rosen, Z. Association of High Traditional Masculinity and Risk of Suicide Death: Secondary Analysis of the Add Health Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller-Leimkühler, A.M. The gender gap in suicide and premature death or: Why are men so vulnerable? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 253, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killeen, T.K.; Wolf, B.; Greer, T.L.; Carmody, T.; Rethorst, C.D.; Trivedi, M.H. Gender and racial/ethnic differences in physiologic responses in the Stimulant Reduction Intervention using Dosed Exercise Study. Addict. Behav. 2020, 110, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, J.; Miller, D.; Schafer, W. Gender Differences in Risk Taking: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Bull. 1999, 125, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, J.M.; Fergusson, D.M. Alcohol and depression. Addiction 2011, 106, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xie, X.-M.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, X.; Lin, J.-X.; Sim, K.; Ungvari, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.-T. Prevalence of Suicidality in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 690130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Tervo-Clemmens, B.; Liu, R.T.; Gersten, M.B.; Jung, J.-Y.; Janes, A.C.; Gilman, J. Use of Tobacco Products and Suicide Attempts Among Elementary School–Aged Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e240376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.R. Smoking and Suicide: A Brief Overview. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 98, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, T.A.; Paulino, S.; Almeida, C.; Gomes, H.S.; Santos, N.; Gouveia-Pereira, M. Self-harm as a predisposition for suicide attempts: A study of adolescents’ deliberate self-harm, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempts. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 287, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Publication Year | Region of Study | Gender (Male) % | Age at Study (Mean ± SD) | Total Number of Participants | Characteristics of Exposed Group | Characteristics of Controls | Reported Amount Consumed per Month (Mean Cups) | Outcomes Investigated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coffee | |||||||||
| Baethge [24] | 2009 | Germany | 49.1 | 44.5 ± 14.7 | 352 | Bipolar | Non-user | 30 | Suicide |
| Kawachi [17] | 1996 | USA | 0 | NA | 86,626 | Women | Almost never | 7, 27, 75, 105 | Suicide |
| Lucas [18] | 2014 | USA | 21 | 48.3 ± 11.7 | 134,604 | General population | <1 cup a day | 16, 30, 75, 105 | Suicide |
| H. Park [25] | 2019 | Korea | 58 | 40.2 ± 6.8 | 80,173 | General population | <1 cup a day | 30, 75, 105 | suicidal ideation |
| Tanskanen [26] | 2000 | Finland | NR | NR | 43,166 | General population | 0–1 cups a day | 75, 105, 180, 240, >300 | Suicide |
| Klatsky [27] | 1993 | USA | 0.6 | NR | 128,934 | General population | Non-user | 30, 60, 150, >180 | Suicide |
| Energy Drinks | |||||||||
| Cho [28] | 2020 | Korea | 51 | 15 ± 0.3 | 62,276 | Students | Non-user | 5, 14.5, 24.5, 30 | Suicide |
| Evren [29] | 2015 | Turkey | 52.7 | 10th grade | 4957 | Students | Non-user | 0, 2, 12, 30 | suicidal ideation, Self-harm |
| H. Kim [30] | 2020 | Korea | 49.2 | NA | 53,312 | Adolescents | NA | 6, 23 | suicidal ideation |
| J. S. Kim [31] | 2018 | Korea | 56.5 | 15 ± 1.7 | 8961 | Adolescents | NA | 18, >30 | Suicide, suicidal ideation |
| S. Y. Kim [32] | 2017 | Korea | 50.1 | 15 (NR) | 121,106 | Adolescents | NA | 6, 23 | Suicide |
| Masengo [33] | 2020 | Canada | 42 | 15.3 ± 1.8 | 5538 | Students | Non-user | NR | Suicide, suicidal ideation |
| Mash [34] | 2014 | USA | 86 | NA | 508,088 | Soldiers | Non-user | 2, 10, 30 | Suicide |
| S. Park [16] | 2016 | Korea | 52 | 15 ± 1.7 | 68,043 | Adolescents | Non-user | 10, 27 | Suicide, suicidal ideation |
| Kwak [35] | 2021 | Korea | 51 | 15 ± 1.7 | 267,907 | Adolescents | Non-user | NR | Suicide, suicidal ideation |
| Caffeine | |||||||||
| Akanni [36] | 2017 | Nigeria | 54.8 | 16.9 ± 0.9 | 465 | Students | Non-user | NR | Suicide |
| Beauchamp [37] | 2016 | USA | 70 | NR | 40 | Poison-control centre patients | NR | NR | Self-harm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Low, C.E.; Chew, N.S.M.; Loke, S.; Tan, J.Y.; Phee, S.; Lee, A.R.Y.B.; Ho, C.S.H. Association of Coffee and Energy Drink Intake with Suicide Attempts and Suicide Ideation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111911
Low CE, Chew NSM, Loke S, Tan JY, Phee S, Lee ARYB, Ho CSH. Association of Coffee and Energy Drink Intake with Suicide Attempts and Suicide Ideation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111911
Chicago/Turabian StyleLow, Chen Ee, Nicole Shi Min Chew, Sean Loke, Jia Yang Tan, Shayne Phee, Ainsley Ryan Yan Bin Lee, and Cyrus Su Hui Ho. 2025. "Association of Coffee and Energy Drink Intake with Suicide Attempts and Suicide Ideation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111911
APA StyleLow, C. E., Chew, N. S. M., Loke, S., Tan, J. Y., Phee, S., Lee, A. R. Y. B., & Ho, C. S. H. (2025). Association of Coffee and Energy Drink Intake with Suicide Attempts and Suicide Ideation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 17(11), 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111911







